6f76fb1ecde5758e7b5550fc6ac5e229.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 Status of WIMP search in KIMS experiment Kwak, Jungwon ( KIMS Collaboration ) The dark Side of the Universe KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop in KIAS May 26 th 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop
Status of WIMP search in KIMS experiment Kwak, Jungwon ( KIMS Collaboration ) The dark Side of the Universe KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop in KIAS May 26 th 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop
 KIMS Collaboration Korea Invisible Mass Search experiment since 2000 H. C. Bhang, J. H. Choi, S. C. Kim, S. K. Kim, S. Y. Kim, J. W. Kwak, J. H. Lee H. S. Lee, S. E. Lee, J. Lee, S. S. Myung, H. Y. Yang Seoul National University Y. D. Kim, J. I. Lee Sejong University H. J. Kim Kyungpook National University M. J. Hwang, Y. J. Kwon Yonsei University I. S. Hahn, I. H. Park Ewha Womans University M. H. Lee, E. S. Seo Univ. of Maryland J. Li Institute of High Energy Physics J. J. Zhu, D. He, Q. Yue, X. Lee Tsinghua University 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 2
KIMS Collaboration Korea Invisible Mass Search experiment since 2000 H. C. Bhang, J. H. Choi, S. C. Kim, S. K. Kim, S. Y. Kim, J. W. Kwak, J. H. Lee H. S. Lee, S. E. Lee, J. Lee, S. S. Myung, H. Y. Yang Seoul National University Y. D. Kim, J. I. Lee Sejong University H. J. Kim Kyungpook National University M. J. Hwang, Y. J. Kwon Yonsei University I. S. Hahn, I. H. Park Ewha Womans University M. H. Lee, E. S. Seo Univ. of Maryland J. Li Institute of High Energy Physics J. J. Zhu, D. He, Q. Yue, X. Lee Tsinghua University 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 2
 Yangyang Underground Laboratory, Y 2 L Korea Middleland Power Co. Yangyang Pumped Storage Power Plant Minimum depth : 700 m / Access to the lab by car (~2 km) Completion of the power plant(2006) Construction of the laboratory buildings done (2003) 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 3
Yangyang Underground Laboratory, Y 2 L Korea Middleland Power Co. Yangyang Pumped Storage Power Plant Minimum depth : 700 m / Access to the lab by car (~2 km) Completion of the power plant(2006) Construction of the laboratory buildings done (2003) 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 3
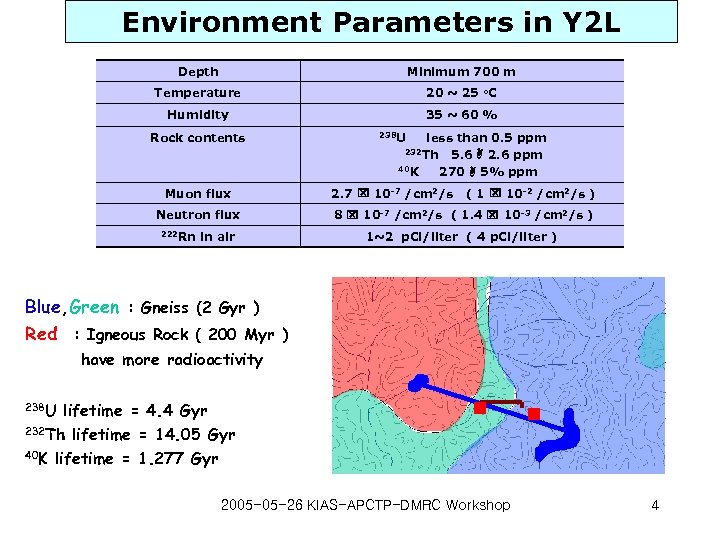 Environment Parameters in Y 2 L Depth Minimum 700 m Temperature 20 ~ 25 o. C Humidity 35 ~ 60 % Rock contents 238 U less than 0. 5 ppm 5. 6 A 2. 6 ppm 40 K 270 A 5% ppm 232 Th Muon flux Neutron flux 222 Rn in air 2. 7 x 10 -7 /cm 2/s ( 1 x 10 -2 /cm 2/s ) 8 x 10 -7 /cm 2/s ( 1. 4 x 10 -3 /cm 2/s ) 1~2 p. Ci/liter ( 4 p. Ci/liter ) Blue, Green : Gneiss (2 Gyr ) Red : Igneous Rock ( 200 Myr ) have more radioactivity 238 U lifetime = 4. 4 Gyr 232 Th lifetime = 14. 05 Gyr 40 K lifetime = 1. 277 Gyr 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 4
Environment Parameters in Y 2 L Depth Minimum 700 m Temperature 20 ~ 25 o. C Humidity 35 ~ 60 % Rock contents 238 U less than 0. 5 ppm 5. 6 A 2. 6 ppm 40 K 270 A 5% ppm 232 Th Muon flux Neutron flux 222 Rn in air 2. 7 x 10 -7 /cm 2/s ( 1 x 10 -2 /cm 2/s ) 8 x 10 -7 /cm 2/s ( 1. 4 x 10 -3 /cm 2/s ) 1~2 p. Ci/liter ( 4 p. Ci/liter ) Blue, Green : Gneiss (2 Gyr ) Red : Igneous Rock ( 200 Myr ) have more radioactivity 238 U lifetime = 4. 4 Gyr 232 Th lifetime = 14. 05 Gyr 40 K lifetime = 1. 277 Gyr 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 4
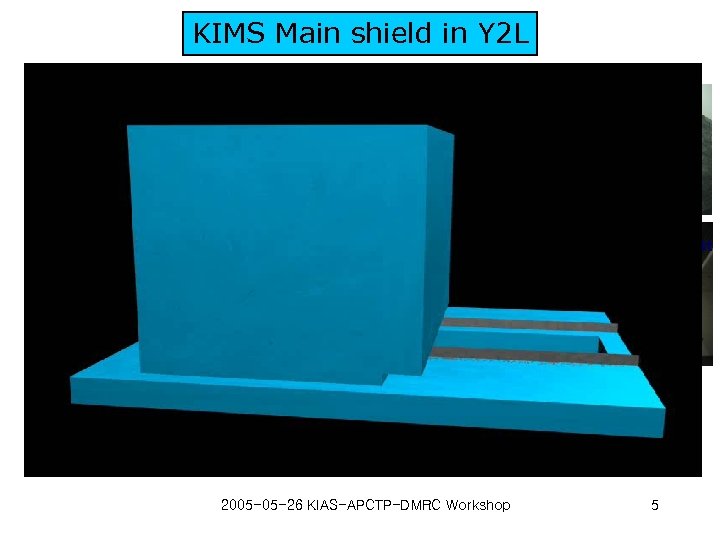 KIMS Main shield in Y 2 L HPGe detector measurement Mineral oil 30 cm PE 5 cm 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop Pb 15 cm : 30 t OFHC Cu 10 cm : 3 t 5
KIMS Main shield in Y 2 L HPGe detector measurement Mineral oil 30 cm PE 5 cm 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop Pb 15 cm : 30 t OFHC Cu 10 cm : 3 t 5
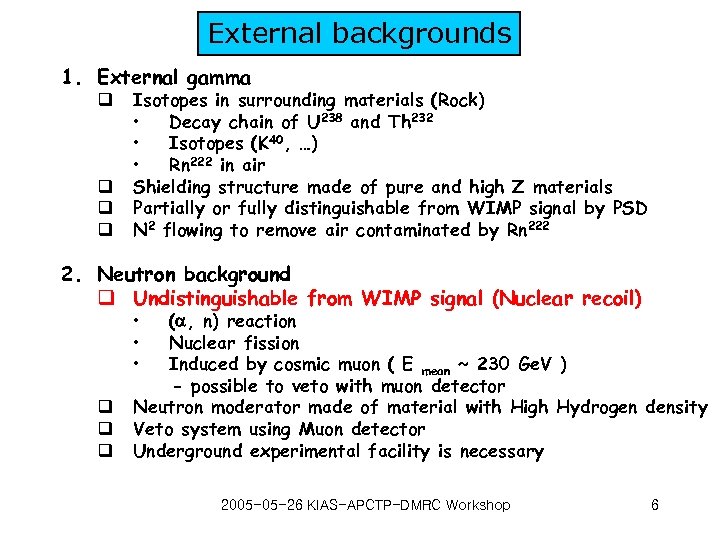 External backgrounds 1. External gamma q q Isotopes in surrounding materials (Rock) • Decay chain of U 238 and Th 232 • Isotopes (K 40, …) • Rn 222 in air Shielding structure made of pure and high Z materials Partially or fully distinguishable from WIMP signal by PSD N 2 flowing to remove air contaminated by Rn 222 2. Neutron background q Undistinguishable from WIMP signal (Nuclear recoil) • • • q q q ( , n) reaction Nuclear fission Induced by cosmic muon ( E mean ~ 230 Ge. V ) - possible to veto with muon detector Neutron moderator made of material with High Hydrogen density Veto system using Muon detector Underground experimental facility is necessary 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 6
External backgrounds 1. External gamma q q Isotopes in surrounding materials (Rock) • Decay chain of U 238 and Th 232 • Isotopes (K 40, …) • Rn 222 in air Shielding structure made of pure and high Z materials Partially or fully distinguishable from WIMP signal by PSD N 2 flowing to remove air contaminated by Rn 222 2. Neutron background q Undistinguishable from WIMP signal (Nuclear recoil) • • • q q q ( , n) reaction Nuclear fission Induced by cosmic muon ( E mean ~ 230 Ge. V ) - possible to veto with muon detector Neutron moderator made of material with High Hydrogen density Veto system using Muon detector Underground experimental facility is necessary 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 6
 Muon detector (MUD) q 2 x 2” PMT for each channel muon modules q 28 signal channels ( 6 + 4 x 4 + 3 x 2 ) q Liquid Scintillator 5 % • PC 1 liter + PPO 4 g + POPOP 15 mg q Mineral Oil 95 % - Neutron moderator q 10 -5 times of ground Muon rate at 700 m deep underground 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 7
Muon detector (MUD) q 2 x 2” PMT for each channel muon modules q 28 signal channels ( 6 + 4 x 4 + 3 x 2 ) q Liquid Scintillator 5 % • PC 1 liter + PPO 4 g + POPOP 15 mg q Mineral Oil 95 % - Neutron moderator q 10 -5 times of ground Muon rate at 700 m deep underground 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 7
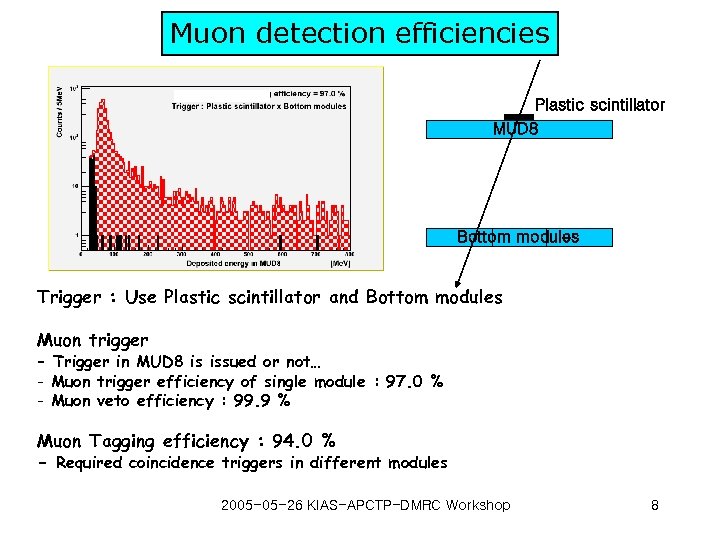 Muon detection efficiencies Plastic scintillator MUD 8 Bottom modules Trigger : Use Plastic scintillator and Bottom modules Muon trigger - Trigger in MUD 8 is issued or not… - Muon trigger efficiency of single module : 97. 0 % - Muon veto efficiency : 99. 9 % Muon Tagging efficiency : 94. 0 % - Required coincidence triggers in different modules 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 8
Muon detection efficiencies Plastic scintillator MUD 8 Bottom modules Trigger : Use Plastic scintillator and Bottom modules Muon trigger - Trigger in MUD 8 is issued or not… - Muon trigger efficiency of single module : 97. 0 % - Muon veto efficiency : 99. 9 % Muon Tagging efficiency : 94. 0 % - Required coincidence triggers in different modules 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 8
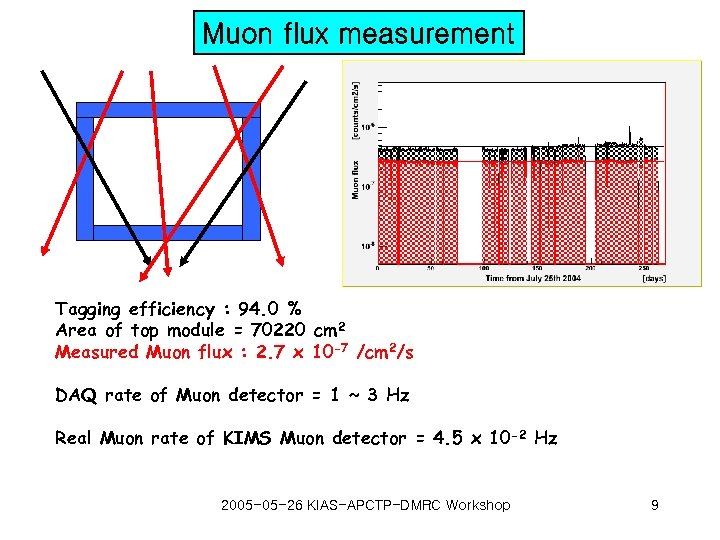 Muon flux measurement Tagging efficiency : 94. 0 % Area of top module = 70220 cm 2 Measured Muon flux : 2. 7 x 10 -7 /cm 2/s DAQ rate of Muon detector = 1 ~ 3 Hz Real Muon rate of KIMS Muon detector = 4. 5 x 10 -2 Hz 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 9
Muon flux measurement Tagging efficiency : 94. 0 % Area of top module = 70220 cm 2 Measured Muon flux : 2. 7 x 10 -7 /cm 2/s DAQ rate of Muon detector = 1 ~ 3 Hz Real Muon rate of KIMS Muon detector = 4. 5 x 10 -2 Hz 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 9
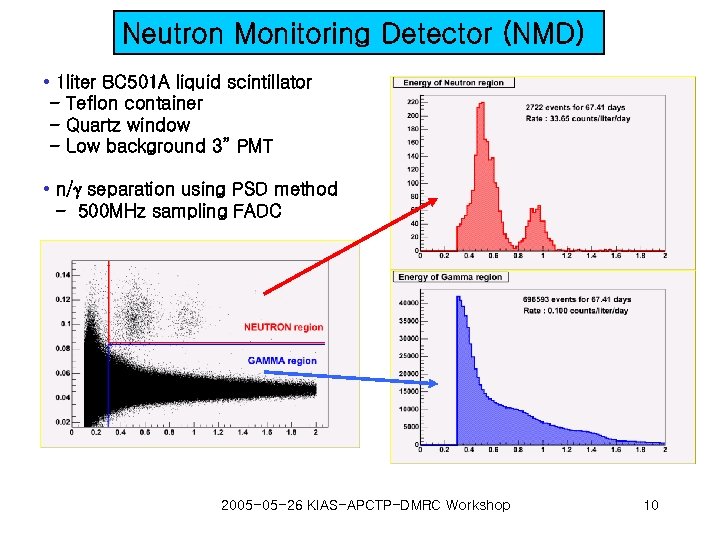 Neutron Monitoring Detector (NMD) • 1 liter BC 501 A liquid scintillator - Teflon container - Quartz window - Low background 3” PMT • n/g separation using PSD method - 500 MHz sampling FADC 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 10
Neutron Monitoring Detector (NMD) • 1 liter BC 501 A liquid scintillator - Teflon container - Quartz window - Low background 3” PMT • n/g separation using PSD method - 500 MHz sampling FADC 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 10
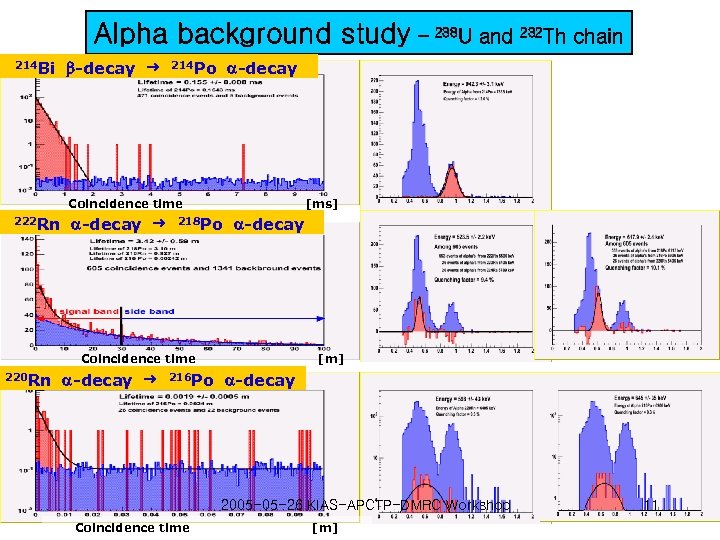 Alpha background study – 238 U and 232 Th chain 214 Bi -decay 214 Po -decay Coincidence time 222 Rn -decay [ms] 218 Po -decay Coincidence time 220 Rn -decay 216 Po [m] -decay 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop Coincidence time [m] 11
Alpha background study – 238 U and 232 Th chain 214 Bi -decay 214 Po -decay Coincidence time 222 Rn -decay [ms] 218 Po -decay Coincidence time 220 Rn -decay 216 Po [m] -decay 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop Coincidence time [m] 11
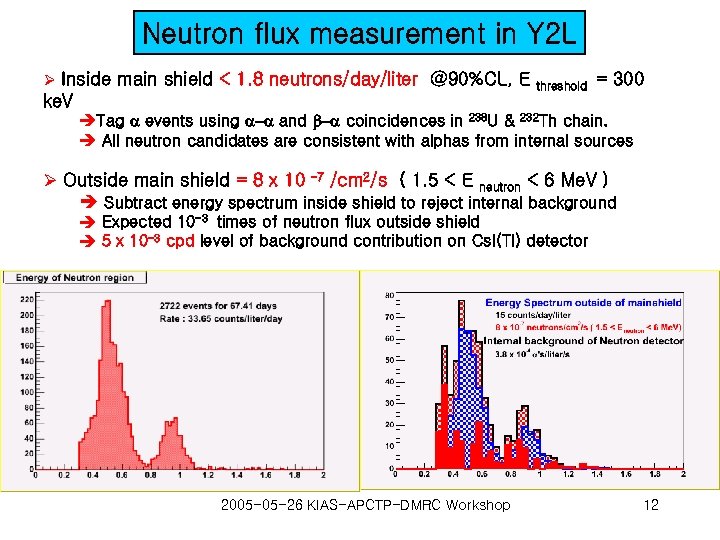 Neutron flux measurement in Y 2 L Ø Inside main shield < 1. 8 neutrons/day/liter @90%CL, E ke. V threshold = 300 èTag events using - and - coincidences in 238 U & 232 Th chain. è All neutron candidates are consistent with alphas from internal sources Ø Outside main shield = 8 x 10 – 7 /cm 2/s ( 1. 5 < E neutron < 6 Me. V ) è Subtract energy spectrum inside shield to reject internal background è Expected 10 -3 times of neutron flux outside shield è 5 x 10 -3 cpd level of background contribution on Cs. I(Tl) detector 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 12
Neutron flux measurement in Y 2 L Ø Inside main shield < 1. 8 neutrons/day/liter @90%CL, E ke. V threshold = 300 èTag events using - and - coincidences in 238 U & 232 Th chain. è All neutron candidates are consistent with alphas from internal sources Ø Outside main shield = 8 x 10 – 7 /cm 2/s ( 1. 5 < E neutron < 6 Me. V ) è Subtract energy spectrum inside shield to reject internal background è Expected 10 -3 times of neutron flux outside shield è 5 x 10 -3 cpd level of background contribution on Cs. I(Tl) detector 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 12
![Muon induced neutron Log 10(Dt) Energy [Me. V] Dt = min(Abs(t Muon event – Muon induced neutron Log 10(Dt) Energy [Me. V] Dt = min(Abs(t Muon event –](https://present5.com/presentation/6f76fb1ecde5758e7b5550fc6ac5e229/image-13.jpg) Muon induced neutron Log 10(Dt) Energy [Me. V] Dt = min(Abs(t Muon event – t Neutron event)) Require Dt < 1 ms for coincidence events Dtmean = 130 ns delay cable for muon and more electronics s. Dt = 32 ns 16 ns clock pulse used High energy events of neutron detector are mostly from muons. E mean ~ 230 Ge. V of muons at 2000 m w. e. underground 3. 5 muons /day in neutron detector ~ 2. 7 x 10– 7 /cm 2/s muon flux 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 13
Muon induced neutron Log 10(Dt) Energy [Me. V] Dt = min(Abs(t Muon event – t Neutron event)) Require Dt < 1 ms for coincidence events Dtmean = 130 ns delay cable for muon and more electronics s. Dt = 32 ns 16 ns clock pulse used High energy events of neutron detector are mostly from muons. E mean ~ 230 Ge. V of muons at 2000 m w. e. underground 3. 5 muons /day in neutron detector ~ 2. 7 x 10– 7 /cm 2/s muon flux 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 13
![Muon induced neutron Energy (cont’d) [Me. V] 2 events of Muon induced neutron during Muon induced neutron Energy (cont’d) [Me. V] 2 events of Muon induced neutron during](https://present5.com/presentation/6f76fb1ecde5758e7b5550fc6ac5e229/image-14.jpg) Muon induced neutron Energy (cont’d) [Me. V] 2 events of Muon induced neutron during 67. 4 days DAQ run ~ 0. 03 counts/day/liter Expected muon induced neutron rate = 0. 06 counts/days/liter 50% neutron detection efficiency - Lower efficiency for Higher Energy of neutron Neutron yield for muon = 2 x 10 -4 (m g/cm 2)-1 for 15 cm-thick lead Muon flux = 2. 7 x 10 -7 /cm 2/s Muon veto efficiency – 99. 9% Expected non-vetoed muon = 2. 7 x 10 -10 /cm 2/s non-vetoed Neutron rates = 1. 2 x 10 -4 counts/day/liter 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 14
Muon induced neutron Energy (cont’d) [Me. V] 2 events of Muon induced neutron during 67. 4 days DAQ run ~ 0. 03 counts/day/liter Expected muon induced neutron rate = 0. 06 counts/days/liter 50% neutron detection efficiency - Lower efficiency for Higher Energy of neutron Neutron yield for muon = 2 x 10 -4 (m g/cm 2)-1 for 15 cm-thick lead Muon flux = 2. 7 x 10 -7 /cm 2/s Muon veto efficiency – 99. 9% Expected non-vetoed muon = 2. 7 x 10 -10 /cm 2/s non-vetoed Neutron rates = 1. 2 x 10 -4 counts/day/liter 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 14
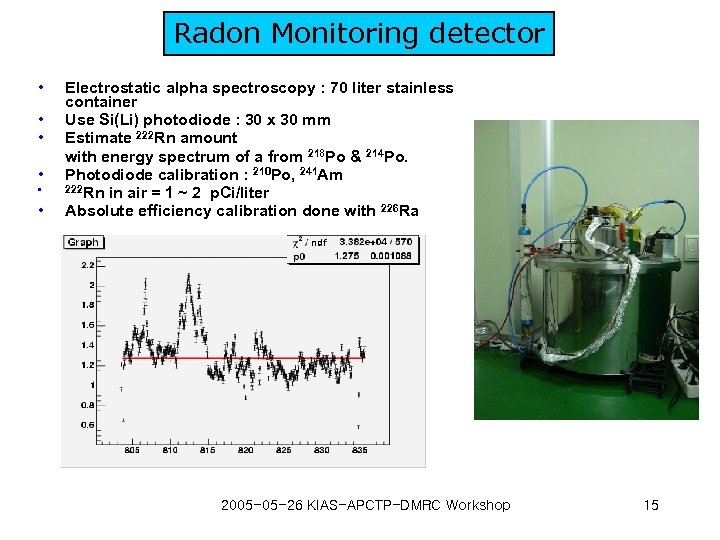 Radon Monitoring detector • • • Electrostatic alpha spectroscopy : 70 liter stainless container Use Si(Li) photodiode : 30 x 30 mm Estimate 222 Rn amount with energy spectrum of a from 218 Po & 214 Po. Photodiode calibration : 210 Po, 241 Am 222 Rn in air = 1 ~ 2 p. Ci/liter Absolute efficiency calibration done with 226 Ra 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 15
Radon Monitoring detector • • • Electrostatic alpha spectroscopy : 70 liter stainless container Use Si(Li) photodiode : 30 x 30 mm Estimate 222 Rn amount with energy spectrum of a from 218 Po & 214 Po. Photodiode calibration : 210 Po, 241 Am 222 Rn in air = 1 ~ 2 p. Ci/liter Absolute efficiency calibration done with 226 Ra 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 15
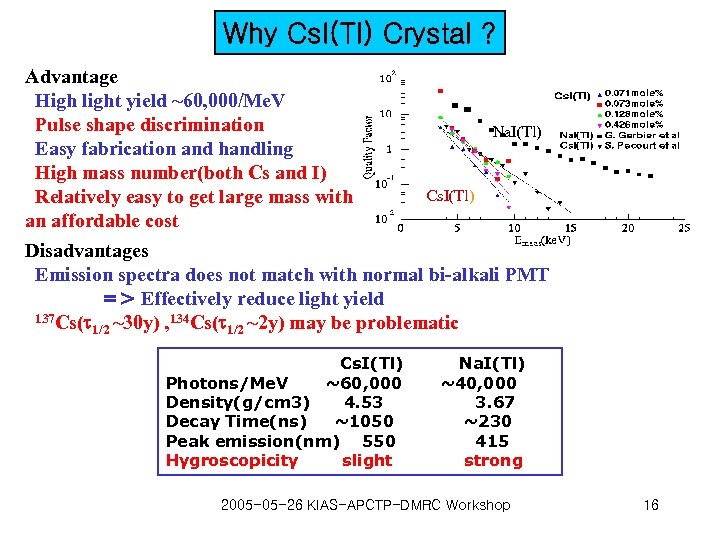 Why Cs. I(Tl) Crystal ? Advantage High light yield ~60, 000/Me. V Pulse shape discrimination Easy fabrication and handling High mass number(both Cs and I) Relatively easy to get large mass with an affordable cost Na. I(Tl) Cs. I(Tl) Disadvantages Emission spectra does not match with normal bi-alkali PMT => Effectively reduce light yield 137 Cs(t 134 Cs(t 1/2 ~30 y) , 1/2 ~2 y) may be problematic Cs. I(Tl) Photons/Me. V ~60, 000 Density(g/cm 3) 4. 53 Decay Time(ns) ~1050 Peak emission(nm) 550 Hygroscopicity slight Na. I(Tl) ~40, 000 3. 67 ~230 415 strong 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 16
Why Cs. I(Tl) Crystal ? Advantage High light yield ~60, 000/Me. V Pulse shape discrimination Easy fabrication and handling High mass number(both Cs and I) Relatively easy to get large mass with an affordable cost Na. I(Tl) Cs. I(Tl) Disadvantages Emission spectra does not match with normal bi-alkali PMT => Effectively reduce light yield 137 Cs(t 134 Cs(t 1/2 ~30 y) , 1/2 ~2 y) may be problematic Cs. I(Tl) Photons/Me. V ~60, 000 Density(g/cm 3) 4. 53 Decay Time(ns) ~1050 Peak emission(nm) 550 Hygroscopicity slight Na. I(Tl) ~40, 000 3. 67 ~230 415 strong 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 16
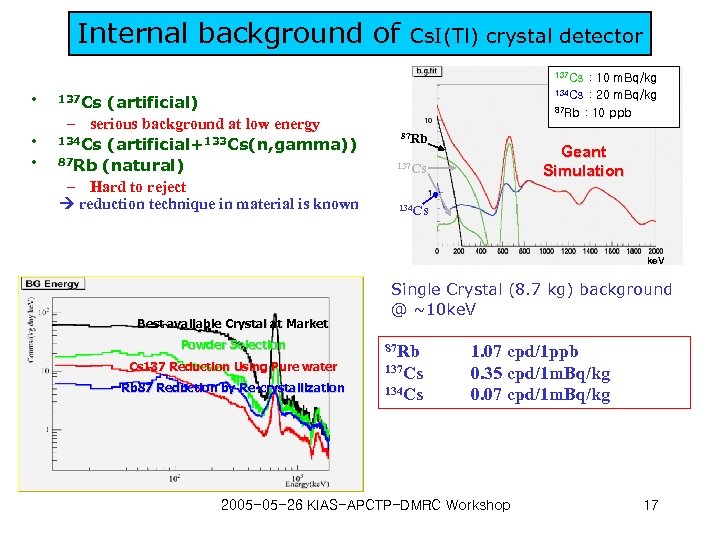 Internal background of Cs. I(Tl) crystal detector 137 Cs • • • (artificial) – serious background at low energy 134 Cs (artificial+133 Cs(n, gamma)) 87 Rb (natural) – Hard to reject reduction technique in material is known : 10 m. Bq/kg : 20 m. Bq/kg 87 Rb : 10 ppb 134 Cs 137 Cs 87 Rb Geant Simulation 137 Cs 134 Cs ke. V Best available Crystal at Market Powder Selection Cs 137 Reduction Using Pure water Rb 87 Reduction by Re-crystallization Single Crystal (8. 7 kg) background @ ~10 ke. V 87 Rb 137 Cs 134 Cs 1. 07 cpd/1 ppb 0. 35 cpd/1 m. Bq/kg 0. 07 cpd/1 m. Bq/kg 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 17
Internal background of Cs. I(Tl) crystal detector 137 Cs • • • (artificial) – serious background at low energy 134 Cs (artificial+133 Cs(n, gamma)) 87 Rb (natural) – Hard to reject reduction technique in material is known : 10 m. Bq/kg : 20 m. Bq/kg 87 Rb : 10 ppb 134 Cs 137 Cs 87 Rb Geant Simulation 137 Cs 134 Cs ke. V Best available Crystal at Market Powder Selection Cs 137 Reduction Using Pure water Rb 87 Reduction by Re-crystallization Single Crystal (8. 7 kg) background @ ~10 ke. V 87 Rb 137 Cs 134 Cs 1. 07 cpd/1 ppb 0. 35 cpd/1 m. Bq/kg 0. 07 cpd/1 m. Bq/kg 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 17
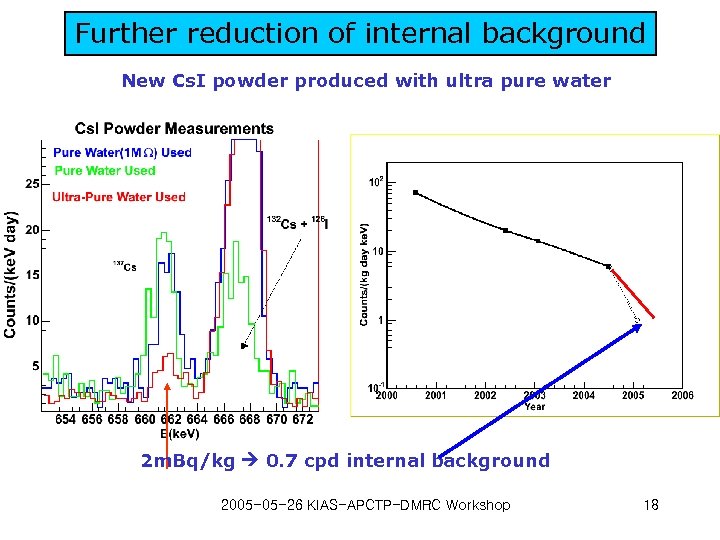 Further reduction of internal background New Cs. I powder produced with ultra pure water 2 m. Bq/kg 0. 7 cpd internal background 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 18
Further reduction of internal background New Cs. I powder produced with ultra pure water 2 m. Bq/kg 0. 7 cpd internal background 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 18
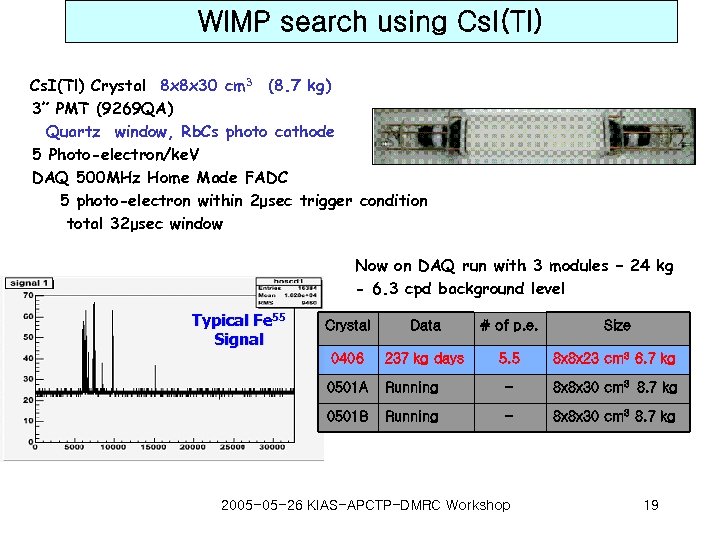 WIMP search using Cs. I(Tl) Crystal 8 x 8 x 30 cm 3 (8. 7 kg) 3” PMT (9269 QA) Quartz window, Rb. Cs photo cathode 5 Photo-electron/ke. V DAQ 500 MHz Home Made FADC 5 photo-electron within 2μsec trigger condition total 32μsec window Now on DAQ run with 3 modules – 24 kg - 6. 3 cpd background level Typical Fe 55 Signal Crystal Data # of p. e. Size 0406 237 kg days 5. 5 8 x 8 x 23 cm 3 6. 7 kg 0501 A Running - 8 x 8 x 30 cm 3 8. 7 kg 0501 B Running - 8 x 8 x 30 cm 3 8. 7 kg 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 19
WIMP search using Cs. I(Tl) Crystal 8 x 8 x 30 cm 3 (8. 7 kg) 3” PMT (9269 QA) Quartz window, Rb. Cs photo cathode 5 Photo-electron/ke. V DAQ 500 MHz Home Made FADC 5 photo-electron within 2μsec trigger condition total 32μsec window Now on DAQ run with 3 modules – 24 kg - 6. 3 cpd background level Typical Fe 55 Signal Crystal Data # of p. e. Size 0406 237 kg days 5. 5 8 x 8 x 23 cm 3 6. 7 kg 0501 A Running - 8 x 8 x 30 cm 3 8. 7 kg 0501 B Running - 8 x 8 x 30 cm 3 8. 7 kg 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 19
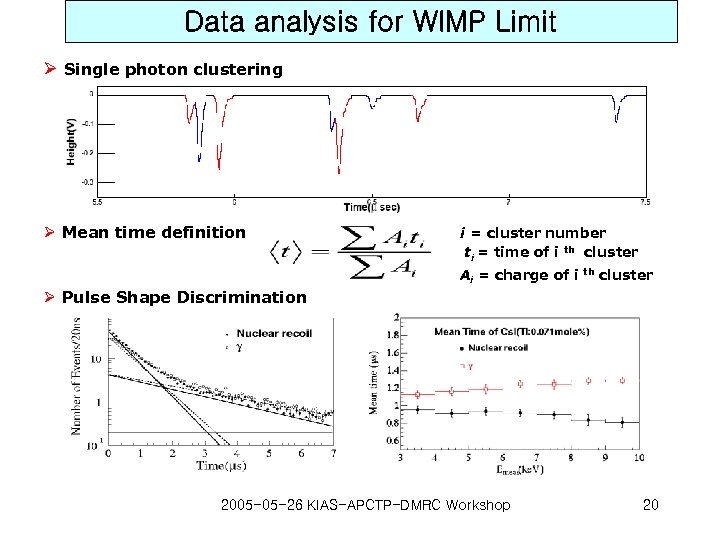 Data analysis for WIMP Limit Ø Single photon clustering Ø Mean time definition i = cluster number ti = time of i th cluster Ai = charge of i th cluster Ø Pulse Shape Discrimination 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 20
Data analysis for WIMP Limit Ø Single photon clustering Ø Mean time definition i = cluster number ti = time of i th cluster Ai = charge of i th cluster Ø Pulse Shape Discrimination 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 20
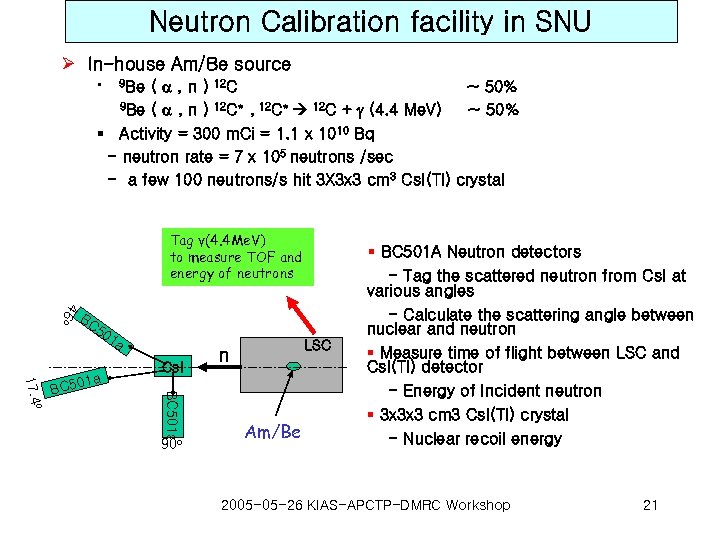 Neutron Calibration facility in SNU Ø In-house Am/Be source ( , n ) 12 C ~ 50% 9 Be ( , n ) 12 C* , 12 C* 12 C + g (4. 4 Me. V) ~ 50% § Activity = 300 m. Ci = 1. 1 x 1010 Bq - neutron rate = 7 x 105 neutrons /sec - a few 100 neutrons/s hit 3 X 3 x 3 cm 3 Cs. I(Tl) crystal § 9 Be Tag γ(4. 4 Me. V) to measure TOF and energy of neutrons § BC 501 A Neutron detectors 46 o BC 50 Cs. I BC 501 a o 17. 4 B a C 501 1 a 90 o LSC n Am/Be - Tag the scattered neutron from Cs. I at various angles - Calculate the scattering angle between nuclear and neutron § Measure time of flight between LSC and Cs. I(Tl) detector - Energy of Incident neutron § 3 x 3 x 3 cm 3 Cs. I(Tl) crystal - Nuclear recoil energy 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 21
Neutron Calibration facility in SNU Ø In-house Am/Be source ( , n ) 12 C ~ 50% 9 Be ( , n ) 12 C* , 12 C* 12 C + g (4. 4 Me. V) ~ 50% § Activity = 300 m. Ci = 1. 1 x 1010 Bq - neutron rate = 7 x 105 neutrons /sec - a few 100 neutrons/s hit 3 X 3 x 3 cm 3 Cs. I(Tl) crystal § 9 Be Tag γ(4. 4 Me. V) to measure TOF and energy of neutrons § BC 501 A Neutron detectors 46 o BC 50 Cs. I BC 501 a o 17. 4 B a C 501 1 a 90 o LSC n Am/Be - Tag the scattered neutron from Cs. I at various angles - Calculate the scattering angle between nuclear and neutron § Measure time of flight between LSC and Cs. I(Tl) detector - Energy of Incident neutron § 3 x 3 x 3 cm 3 Cs. I(Tl) crystal - Nuclear recoil energy 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 21
![Neutron Calibration facility in SNU Energy of neutrons from Am/Be source [Me. V] @Energy Neutron Calibration facility in SNU Energy of neutrons from Am/Be source [Me. V] @Energy](https://present5.com/presentation/6f76fb1ecde5758e7b5550fc6ac5e229/image-22.jpg) Neutron Calibration facility in SNU Energy of neutrons from Am/Be source [Me. V] @Energy = 4 ~ 5 ke. V a) Comparison between mean time distibutions of neutron data and compton data for test crystal b) Comparison between mean time distributions of compton data for test crystal and full sized crystal 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 22
Neutron Calibration facility in SNU Energy of neutrons from Am/Be source [Me. V] @Energy = 4 ~ 5 ke. V a) Comparison between mean time distibutions of neutron data and compton data for test crystal b) Comparison between mean time distributions of compton data for test crystal and full sized crystal 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 22
 Summary Cs. I(Tl) Data taking Ø Data for WIMP search Ø 430 kg days for 8 x 8 x 30 cm 3 crystal of 14 cpd background level 2004 spring Ø 237 kg days for 8 x 8 x 23 cm 3 crystal of 6. 3 cpd background level Ø MC data using Geant 4 simulation Ø Calibration data • Neutron data from Neutron calibration facility Reference distribution for nuclear recoil events • 57 Co ( 122. 06 ke. V g ), 241 Am (59. 54 ke. V) and 55 Fe(5. 899 ke. V) Compton data Check cut efficiency, Single photon calibration • 137 Cs ( 661. 657 ke. V g ) Compton data Reference distribution for electron recoil events 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 23
Summary Cs. I(Tl) Data taking Ø Data for WIMP search Ø 430 kg days for 8 x 8 x 30 cm 3 crystal of 14 cpd background level 2004 spring Ø 237 kg days for 8 x 8 x 23 cm 3 crystal of 6. 3 cpd background level Ø MC data using Geant 4 simulation Ø Calibration data • Neutron data from Neutron calibration facility Reference distribution for nuclear recoil events • 57 Co ( 122. 06 ke. V g ), 241 Am (59. 54 ke. V) and 55 Fe(5. 899 ke. V) Compton data Check cut efficiency, Single photon calibration • 137 Cs ( 661. 657 ke. V g ) Compton data Reference distribution for electron recoil events 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 23
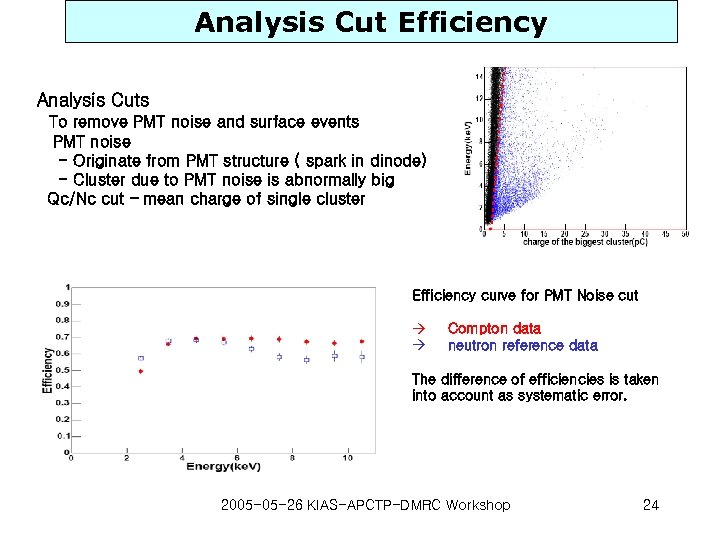 Analysis Cut Efficiency Analysis Cuts To remove PMT noise and surface events PMT noise - Originate from PMT structure ( spark in dinode) - Cluster due to PMT noise is abnormally big Qc/Nc cut – mean charge of single cluster Efficiency curve for PMT Noise cut à à Compton data neutron reference data The difference of efficiencies is taken into account as systematic error. 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 24
Analysis Cut Efficiency Analysis Cuts To remove PMT noise and surface events PMT noise - Originate from PMT structure ( spark in dinode) - Cluster due to PMT noise is abnormally big Qc/Nc cut – mean charge of single cluster Efficiency curve for PMT Noise cut à à Compton data neutron reference data The difference of efficiencies is taken into account as systematic error. 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 24
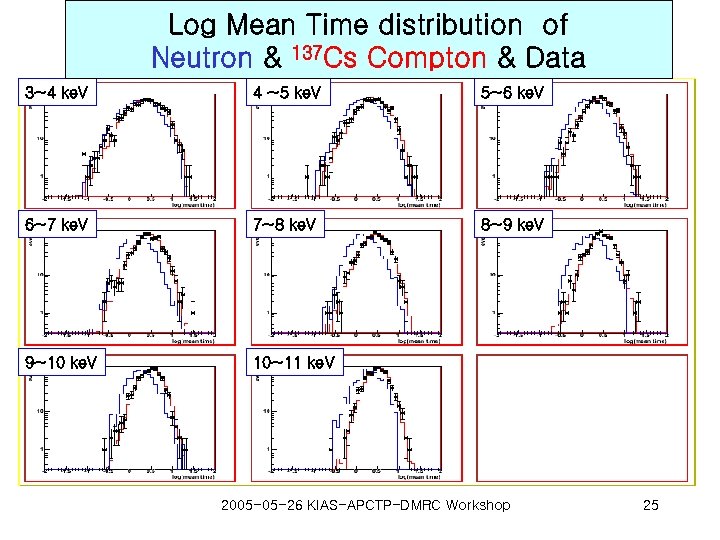 Log Mean Time distribution of Neutron & 137 Cs Compton & Data 3~4 ke. V 4 ~5 ke. V 5~6 ke. V 6~7 ke. V 7~8 ke. V 8~9 ke. V 9~10 ke. V 10~11 ke. V 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 25
Log Mean Time distribution of Neutron & 137 Cs Compton & Data 3~4 ke. V 4 ~5 ke. V 5~6 ke. V 6~7 ke. V 7~8 ke. V 8~9 ke. V 9~10 ke. V 10~11 ke. V 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 25
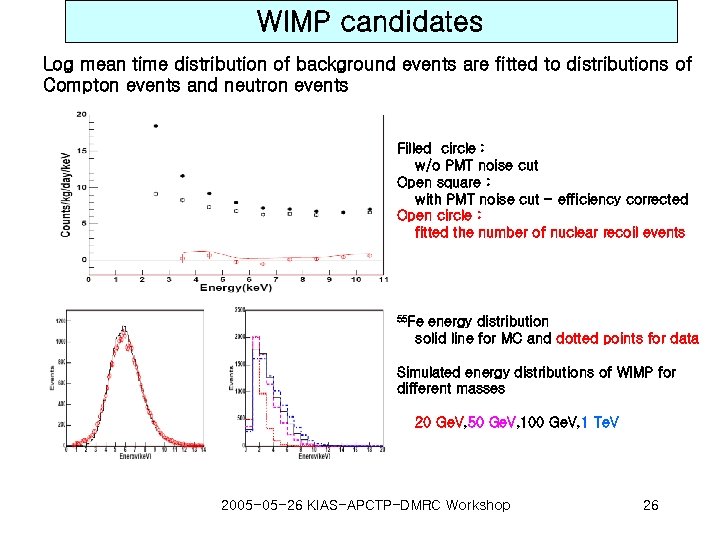 WIMP candidates Log mean time distribution of background events are fitted to distributions of Compton events and neutron events Filled circle : w/o PMT noise cut Open square : with PMT noise cut - efficiency corrected Open circle : fitted the number of nuclear recoil events 55 Fe energy distribution solid line for MC and dotted points for data Simulated energy distributions of WIMP for different masses 20 Ge. V, 50 Ge. V, 100 Ge. V, 1 Te. V 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 26
WIMP candidates Log mean time distribution of background events are fitted to distributions of Compton events and neutron events Filled circle : w/o PMT noise cut Open square : with PMT noise cut - efficiency corrected Open circle : fitted the number of nuclear recoil events 55 Fe energy distribution solid line for MC and dotted points for data Simulated energy distributions of WIMP for different masses 20 Ge. V, 50 Ge. V, 100 Ge. V, 1 Te. V 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 26
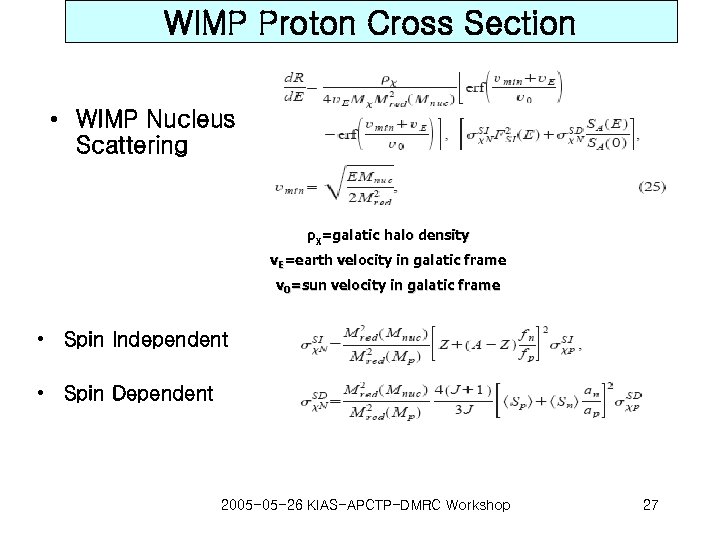 WIMP Proton Cross Section • WIMP Nucleus Scattering ρχ=galatic halo density v. E=earth velocity in galatic frame v 0=sun velocity in galatic frame • Spin Independent • Spin Dependent 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 27
WIMP Proton Cross Section • WIMP Nucleus Scattering ρχ=galatic halo density v. E=earth velocity in galatic frame v 0=sun velocity in galatic frame • Spin Independent • Spin Dependent 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 27
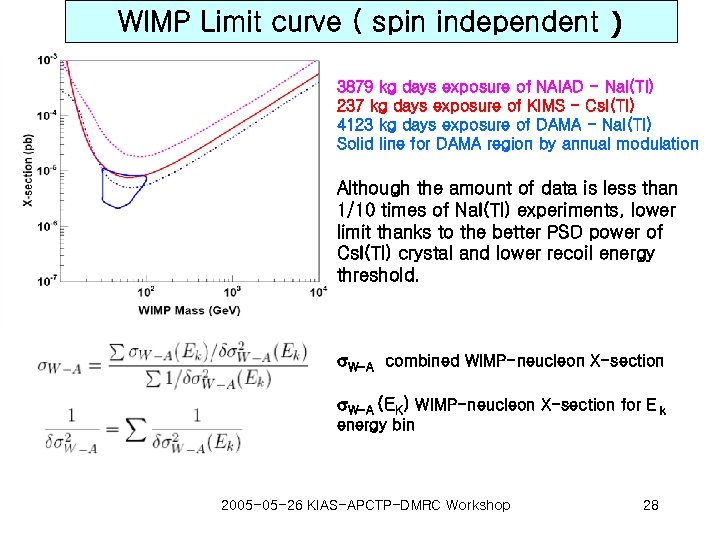 WIMP Limit curve ( spin independent ) 3879 kg days exposure of NAIAD - Na. I(Tl) 237 kg days exposure of KIMS - Cs. I(Tl) 4123 kg days exposure of DAMA - Na. I(Tl) Solid line for DAMA region by annual modulation Although the amount of data is less than 1/10 times of Na. I(Tl) experiments, lower limit thanks to the better PSD power of Cs. I(Tl) crystal and lower recoil energy threshold. s. W-A combined WIMP-neucleon X-section s. W-A (EK) WIMP-neucleon X-section for E k energy bin 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 28
WIMP Limit curve ( spin independent ) 3879 kg days exposure of NAIAD - Na. I(Tl) 237 kg days exposure of KIMS - Cs. I(Tl) 4123 kg days exposure of DAMA - Na. I(Tl) Solid line for DAMA region by annual modulation Although the amount of data is less than 1/10 times of Na. I(Tl) experiments, lower limit thanks to the better PSD power of Cs. I(Tl) crystal and lower recoil energy threshold. s. W-A combined WIMP-neucleon X-section s. W-A (EK) WIMP-neucleon X-section for E k energy bin 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 28
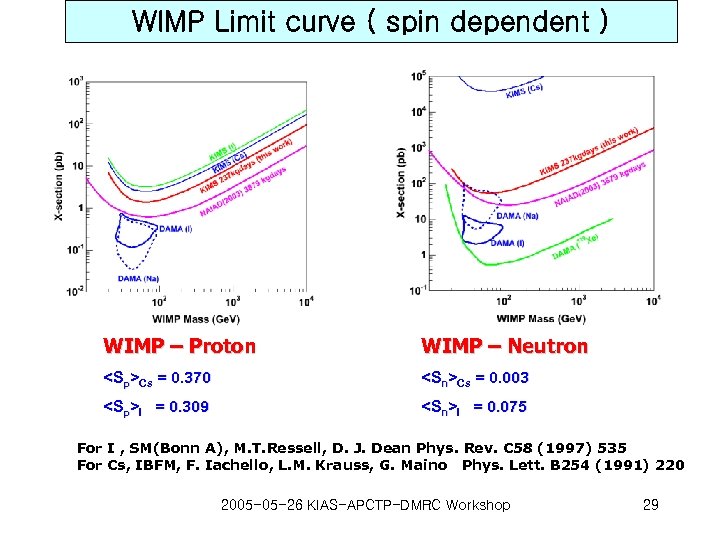 WIMP Limit curve ( spin dependent ) WIMP – Proton WIMP – Neutron
WIMP Limit curve ( spin dependent ) WIMP – Proton WIMP – Neutron
 Summary 1. External background - Gamma background ~ less than 10 -4 reduction rate by shield - Neutron background Neutron from environmental radioactive sources ~ neutron moderator = 30 cm of Mineral oil and 5 cm of PE ~ expected rate inside shield 10 -9 /cm 2/s ~ 5 x 10 -3 cpd on Cs. I(Tl) Neutron induced by cosmic muon ~ 700 m deep underground lab. in Y 2 L ~ muon flux in 700 m underground 2. 7 x 10 -7 /cm 2/s ~ 99. 9% of veto efficiency ~ expected rate inside shield 10 -8 /cm 2/s for 15 cm thick lead layer 2. Internal background - Achieve 6. 3 cpd level internal background level ~ 24 kg Cs. I(Tl) crystal detector is running - Successful powder R&D ~ Purification of process water and re-crystallization - PMT noise reduction with pulse shape analysis of signal photon cluster 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 30
Summary 1. External background - Gamma background ~ less than 10 -4 reduction rate by shield - Neutron background Neutron from environmental radioactive sources ~ neutron moderator = 30 cm of Mineral oil and 5 cm of PE ~ expected rate inside shield 10 -9 /cm 2/s ~ 5 x 10 -3 cpd on Cs. I(Tl) Neutron induced by cosmic muon ~ 700 m deep underground lab. in Y 2 L ~ muon flux in 700 m underground 2. 7 x 10 -7 /cm 2/s ~ 99. 9% of veto efficiency ~ expected rate inside shield 10 -8 /cm 2/s for 15 cm thick lead layer 2. Internal background - Achieve 6. 3 cpd level internal background level ~ 24 kg Cs. I(Tl) crystal detector is running - Successful powder R&D ~ Purification of process water and re-crystallization - PMT noise reduction with pulse shape analysis of signal photon cluster 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 30
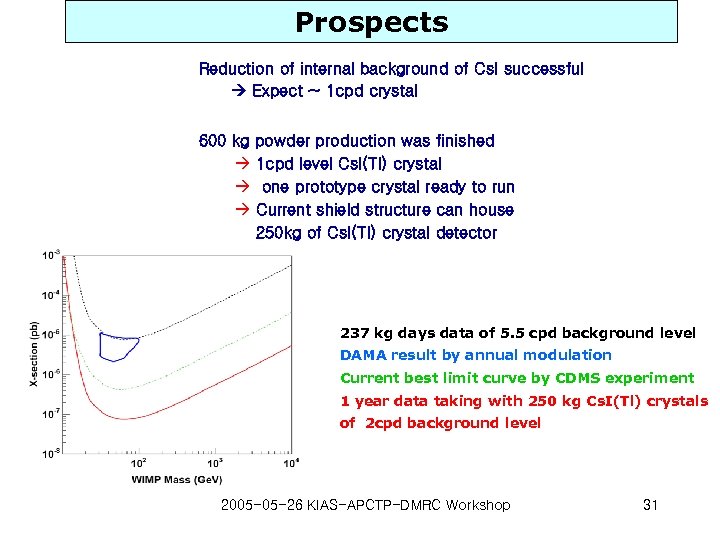 Prospects Reduction of internal background of Cs. I successful Expect ~ 1 cpd crystal 600 kg powder production was finished à 1 cpd level Cs. I(Tl) crystal à one prototype crystal ready to run à Current shield structure can house 250 kg of Cs. I(Tl) crystal detector 237 kg days data of 5. 5 cpd background level DAMA result by annual modulation Current best limit curve by CDMS experiment 1 year data taking with 250 kg Cs. I(Tl) crystals of 2 cpd background level 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 31
Prospects Reduction of internal background of Cs. I successful Expect ~ 1 cpd crystal 600 kg powder production was finished à 1 cpd level Cs. I(Tl) crystal à one prototype crystal ready to run à Current shield structure can house 250 kg of Cs. I(Tl) crystal detector 237 kg days data of 5. 5 cpd background level DAMA result by annual modulation Current best limit curve by CDMS experiment 1 year data taking with 250 kg Cs. I(Tl) crystals of 2 cpd background level 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 31
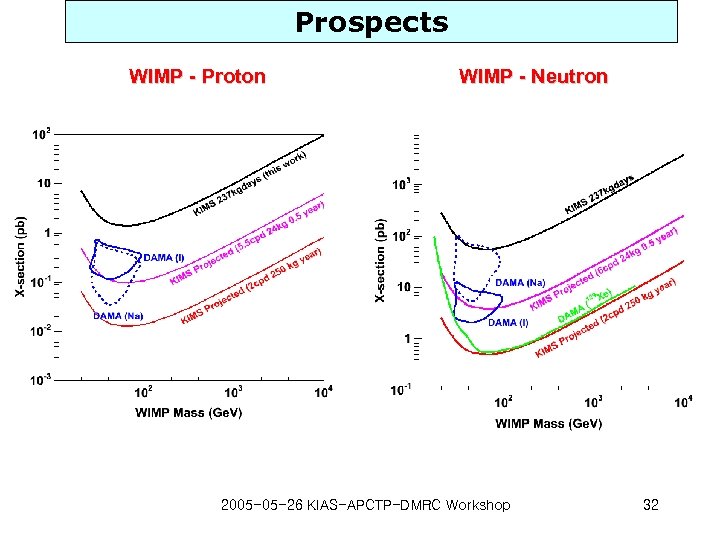 Prospects WIMP - Proton WIMP - Neutron 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 32
Prospects WIMP - Proton WIMP - Neutron 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 32
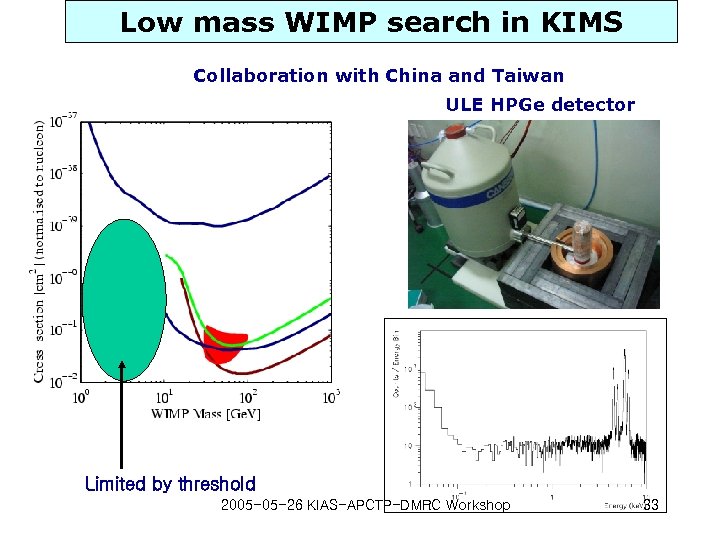 Low mass WIMP search in KIMS Collaboration with China and Taiwan ULE HPGe detector Limited by threshold 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 33
Low mass WIMP search in KIMS Collaboration with China and Taiwan ULE HPGe detector Limited by threshold 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 33
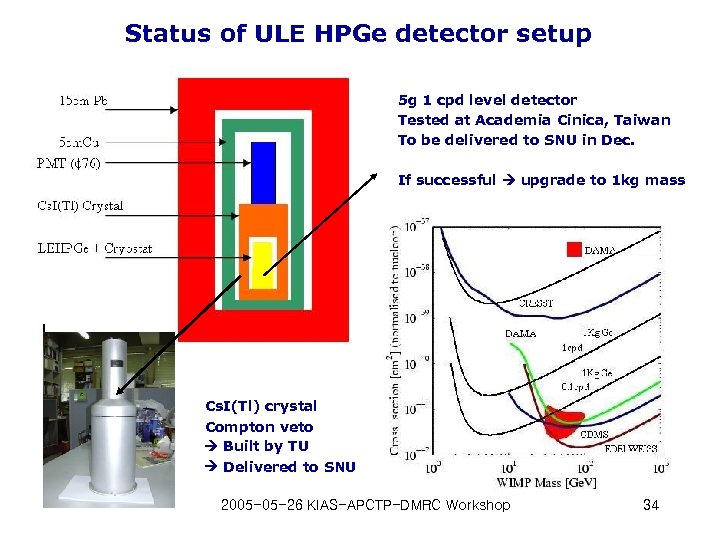 Status of ULE HPGe detector setup 5 g 1 cpd level detector Tested at Academia Cinica, Taiwan To be delivered to SNU in Dec. If successful upgrade to 1 kg mass Cs. I(Tl) crystal Compton veto Built by TU Delivered to SNU 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 34
Status of ULE HPGe detector setup 5 g 1 cpd level detector Tested at Academia Cinica, Taiwan To be delivered to SNU in Dec. If successful upgrade to 1 kg mass Cs. I(Tl) crystal Compton veto Built by TU Delivered to SNU 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 34
 Thanks !!! 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 35
Thanks !!! 2005 -05 -26 KIAS-APCTP-DMRC Workshop 35


