171b0e633b3ba4d240b29975eee245c4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 63
 Status of the NICA / MPD Project at Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (JINR) Dubna V. Kekelidze Ø Introduction Ø Physics Motivation – White Book Ø NICA Concept Ø Collaboration Ø MPD concept Ø Working Groups activity Ø Time Schedule & competitivenes Ø Conclusions 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 1
Status of the NICA / MPD Project at Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (JINR) Dubna V. Kekelidze Ø Introduction Ø Physics Motivation – White Book Ø NICA Concept Ø Collaboration Ø MPD concept Ø Working Groups activity Ø Time Schedule & competitivenes Ø Conclusions 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 1
 Introduction High Energy Machines at JINR, Dubna the Laboratory of High Energy Physics 10 Ge. V Synchrophasotron put in operation in 1957 the first superconducting accelerator for relativistic ions NUCLOTRON launched in 1993 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 2
Introduction High Energy Machines at JINR, Dubna the Laboratory of High Energy Physics 10 Ge. V Synchrophasotron put in operation in 1957 the first superconducting accelerator for relativistic ions NUCLOTRON launched in 1993 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 2
 Introduction Ø Project NICA (Nuclotron based Ion Collider f. Acility) MPD ((Multi Purpose Detector) is dedicated to study of hot & dense baryonic matter and development of the home accelerator facility providing relativistic heavy ions & polarized beams Ø all these allow to start a new strategic course of JINR towards the frontier research in the relevant fields of high energy physics Relativistic Heavy Ion Physics became a high priority task in many scientific centers (BNL, CERN, GSI, JINR, . . ) since last few decades 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 3
Introduction Ø Project NICA (Nuclotron based Ion Collider f. Acility) MPD ((Multi Purpose Detector) is dedicated to study of hot & dense baryonic matter and development of the home accelerator facility providing relativistic heavy ions & polarized beams Ø all these allow to start a new strategic course of JINR towards the frontier research in the relevant fields of high energy physics Relativistic Heavy Ion Physics became a high priority task in many scientific centers (BNL, CERN, GSI, JINR, . . ) since last few decades 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 3
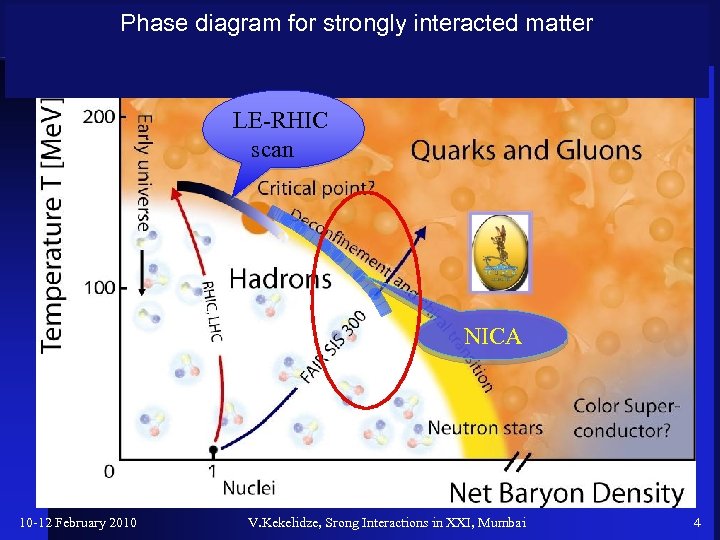 Phase diagram for strongly interacted matter LE-RHIC scan NICA 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 4
Phase diagram for strongly interacted matter LE-RHIC scan NICA 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 4
 Round Table IV & the NICA White Paper 86 authors from 39 scientific centers in Arizona State University, USA 15 Countries (8 JINR members) 9 September 2009 University of Oslo, Norway Kurchatov Institute, Russia Los Alamos National Laborator Lebedev Institute, Russia University of Illinois, USA JINR Dubna Wayne SU, USA St. Petersburg SU, Russia ITEP, Russia LBNL, USA INP MSU, Russia Ohio SU, USA MEPh. I, Russia BITP, Ukraine INR, Russia INFN, Italy Tel Aviv University, Israel SISSA, Italy Weizmann Institute, Israel University of Catania, Italy University of Trento, Italy GSI, Germany University of Florence, Italy University of Bielefeld, Germany University of Barselona, Spain University of Giessen, Germany University of Coimbra, Portugal University of Frankfurt, Germany Mateja Bela University, Slovakia Institute of Applied Science, Moldova Wroclav University, Poland Tsinghua University, Beijing, China Jan Kochanovski University, Poland Variable Energy Cyclotron Centre, India University of Cape Town, South Africa 10 -12 February 2010 Institute of High Energy Physics, China National Laboratory of Heavy Ion Accelerator, China V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 5
Round Table IV & the NICA White Paper 86 authors from 39 scientific centers in Arizona State University, USA 15 Countries (8 JINR members) 9 September 2009 University of Oslo, Norway Kurchatov Institute, Russia Los Alamos National Laborator Lebedev Institute, Russia University of Illinois, USA JINR Dubna Wayne SU, USA St. Petersburg SU, Russia ITEP, Russia LBNL, USA INP MSU, Russia Ohio SU, USA MEPh. I, Russia BITP, Ukraine INR, Russia INFN, Italy Tel Aviv University, Israel SISSA, Italy Weizmann Institute, Israel University of Catania, Italy University of Trento, Italy GSI, Germany University of Florence, Italy University of Bielefeld, Germany University of Barselona, Spain University of Giessen, Germany University of Coimbra, Portugal University of Frankfurt, Germany Mateja Bela University, Slovakia Institute of Applied Science, Moldova Wroclav University, Poland Tsinghua University, Beijing, China Jan Kochanovski University, Poland Variable Energy Cyclotron Centre, India University of Cape Town, South Africa 10 -12 February 2010 Institute of High Energy Physics, China National Laboratory of Heavy Ion Accelerator, China V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 5
 Physics tasks for Multi. Purpose Detector Ø event-by-event fluctuation in hadron productions (multiplicity, Pt etc. ) Ø HBT correlations indicating the space-time size of the systems involving π, K, p, Λ Ø directed & elliptic flows for various hadrons Ø multi-strange hyperon production: yield & spectra (the probes of nuclear media phases) Ø photon & electron probes Ø search for P- & CP violation as a charge asymmetry should be studied for different ions (from p to Au) by scanning in b & energy (in the range SNN = 4 - 11 Ge. V/u) 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 6
Physics tasks for Multi. Purpose Detector Ø event-by-event fluctuation in hadron productions (multiplicity, Pt etc. ) Ø HBT correlations indicating the space-time size of the systems involving π, K, p, Λ Ø directed & elliptic flows for various hadrons Ø multi-strange hyperon production: yield & spectra (the probes of nuclear media phases) Ø photon & electron probes Ø search for P- & CP violation as a charge asymmetry should be studied for different ions (from p to Au) by scanning in b & energy (in the range SNN = 4 - 11 Ge. V/u) 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 6
 Physics tasks for Spin Physics Detector Ø MMT-DY processes with L&T polarized p & D beams: - extraction of unknown (poor known) PDF - PDFs from J/y production processes Ø Spin effects in baryon, meson & photon productions Ø Spin effects in various exclusive reactions & diffractive processes Ø Cross sections, helicity amplitudes & double spin asymmetries (Krisch effect) in elastic reactions Ø Spectroscopy of quarkoniums Ø Polarimetry 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 7
Physics tasks for Spin Physics Detector Ø MMT-DY processes with L&T polarized p & D beams: - extraction of unknown (poor known) PDF - PDFs from J/y production processes Ø Spin effects in baryon, meson & photon productions Ø Spin effects in various exclusive reactions & diffractive processes Ø Cross sections, helicity amplitudes & double spin asymmetries (Krisch effect) in elastic reactions Ø Spectroscopy of quarkoniums Ø Polarimetry 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 7
 NICA working schema Injector: 2× 109 ions 197 Au 32+ energy 6. 2 Мe. V/u Booster acceleration 100 Мe. V/u 600 Мe. V/u striping (80%) IP-1 Two superconducting storage rings of the collider IP-2 197 Au 32+ 197 Au 79+ Nuclotron 1. 1× 109 ions 1 4. 5 Ge. V/u (max) 2 х17 injections per cycle 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 8
NICA working schema Injector: 2× 109 ions 197 Au 32+ energy 6. 2 Мe. V/u Booster acceleration 100 Мe. V/u 600 Мe. V/u striping (80%) IP-1 Two superconducting storage rings of the collider IP-2 197 Au 32+ 197 Au 79+ Nuclotron 1. 1× 109 ions 1 4. 5 Ge. V/u (max) 2 х17 injections per cycle 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 8
 NICA / MPD major milestones • Nuclotron-M - the 1 st stage of the NICA project 2010 an upgrade of existing SC accelerator Nuclotron • New Linac operational 2013 • Booster in operation 2013 • Nuclotron-M beam to NICA 2013 • NICA collider first beam 2014 • MPD min configuration ready for the beam 2015 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 9
NICA / MPD major milestones • Nuclotron-M - the 1 st stage of the NICA project 2010 an upgrade of existing SC accelerator Nuclotron • New Linac operational 2013 • Booster in operation 2013 • Nuclotron-M beam to NICA 2013 • NICA collider first beam 2014 • MPD min configuration ready for the beam 2015 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 9
 Nuclotron-М for NICA Ø The goal – Nuclotron parameters to be reached in 2010 necessary for the NICA complex: - accelerated heavy ions A~200, - beam intensity ~ 109 A/cycle (0. 2 -0. 4 Hz) - energy ~ 4. 5 Ge. V/u for 197 Au 79+ Ø Major tasks: • Development of new injection complex • Modernization of RF system • Upgrade of diagnostics & beam control systems • Modernization of the vacuum system • Modernization of the electric- and cryo- supply systems • Development of the minimum required infrastructure 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 10
Nuclotron-М for NICA Ø The goal – Nuclotron parameters to be reached in 2010 necessary for the NICA complex: - accelerated heavy ions A~200, - beam intensity ~ 109 A/cycle (0. 2 -0. 4 Hz) - energy ~ 4. 5 Ge. V/u for 197 Au 79+ Ø Major tasks: • Development of new injection complex • Modernization of RF system • Upgrade of diagnostics & beam control systems • Modernization of the vacuum system • Modernization of the electric- and cryo- supply systems • Development of the minimum required infrastructure 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 10
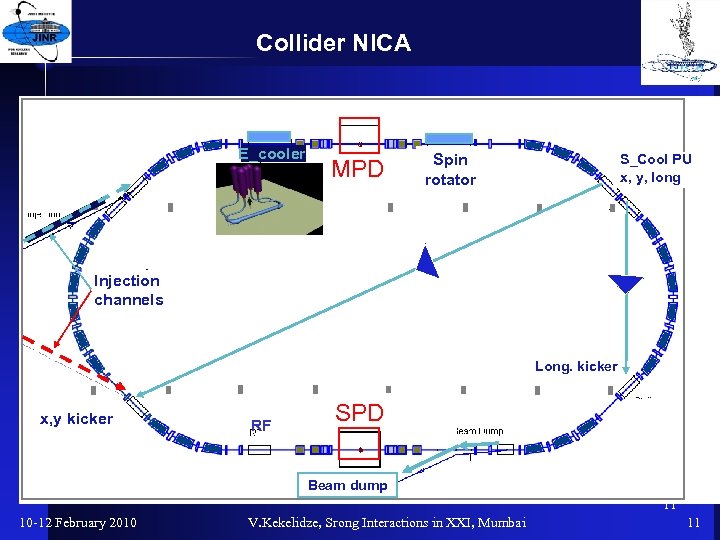 Collider NICA E_cooler MPD Spin rotator S_Cool PU x, y, long Injection channels 10 m x, y kicker RF Long. kicker SPD Beam dump 11 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 11
Collider NICA E_cooler MPD Spin rotator S_Cool PU x, y, long Injection channels 10 m x, y kicker RF Long. kicker SPD Beam dump 11 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 11
![Collider – general parameters Collider Ring circumference, [m] 251 (>) B max [ T Collider – general parameters Collider Ring circumference, [m] 251 (>) B max [ T](https://present5.com/presentation/171b0e633b3ba4d240b29975eee245c4/image-12.jpg) Collider – general parameters Collider Ring circumference, [m] 251 (>) B max [ T m ] 45. 0 Ion kinetic energy (Au 79+), [Ge. V/u] Dipole field (max), 1. 0 4. 56 [ T ] 4. 0 (2. 0) Free space at IP (for detector) 9 m Beam crossing angle at IP Vacuum, [ Torr ] 10 -11 Luminosity per one IP, cm-2∙s-1 10 -12 February 2010 0 0. 75÷ 11 ∙ 10^26 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 12
Collider – general parameters Collider Ring circumference, [m] 251 (>) B max [ T m ] 45. 0 Ion kinetic energy (Au 79+), [Ge. V/u] Dipole field (max), 1. 0 4. 56 [ T ] 4. 0 (2. 0) Free space at IP (for detector) 9 m Beam crossing angle at IP Vacuum, [ Torr ] 10 -11 Luminosity per one IP, cm-2∙s-1 10 -12 February 2010 0 0. 75÷ 11 ∙ 10^26 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 12
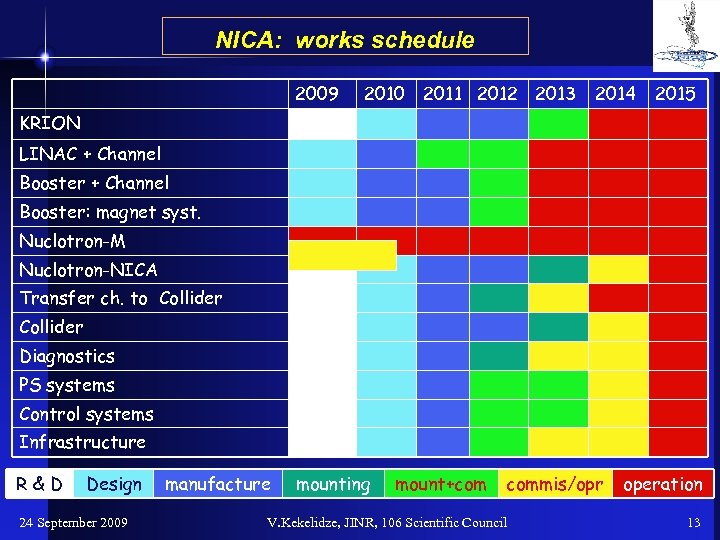 NICA: works schedule 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 KRION LINAC + Channel Booster: magnet syst. Nuclotron-M Nuclotron-NICA Transfer ch. to Collider Diagnostics PS systems Control systems Infrastructure R&D Design 24 September 2009 manufacture mounting mount+com commis/opr V. Kekelidze, JINR, 106 Scientific Council operation 13
NICA: works schedule 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 KRION LINAC + Channel Booster: magnet syst. Nuclotron-M Nuclotron-NICA Transfer ch. to Collider Diagnostics PS systems Control systems Infrastructure R&D Design 24 September 2009 manufacture mounting mount+com commis/opr V. Kekelidze, JINR, 106 Scientific Council operation 13
 NICA / MPD project documents • NICA CDR Jan 2008 • MPD Lo. I Feb 2008 • NICA TDR May 2009 • MPD CDR (first version) May 2009 • White book (first version) June 2009 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 14
NICA / MPD project documents • NICA CDR Jan 2008 • MPD Lo. I Feb 2008 • NICA TDR May 2009 • MPD CDR (first version) May 2009 • White book (first version) June 2009 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 14
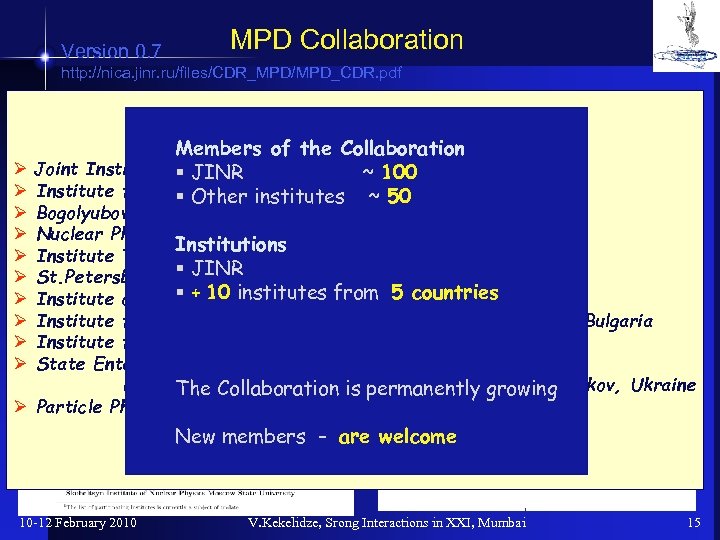 Version 0. 7 MPD Collaboration http: //nica. jinr. ru/files/CDR_MPD/MPD_CDR. pdf The MPD Collaboration Members of the Collaboration Ø Joint Institute for Nuclear Research ~ 100 § JINR Ø Institute for Nuclear Research, RAS, ~RF § Other institutes 50 Bogolyubov Institute for Theoretical Physics, NAS, Ukraine Nuclear Physics Institute of MSU, RF Institutions Institute Theoretical & Experimental Physics, RF § JINR St. Petersburg State University, RF § + 10 institutes Moldova Institute of Applied Physics, AS, from 5 countries Institute for Nuclear Reseach & Nuclear Energy BAS, Sofia, Bulgaria Institute for Scintillation Materials, Kharkov, Ukraine State Enterprise Scientific & Technology Research Institute for Apparatus construction, Kharkov, Ukraine The Collaboration is permanently growing Ø Particle Physics Center of Belarussia State University Ø Ø Ø Ø New members – are welcome 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 15
Version 0. 7 MPD Collaboration http: //nica. jinr. ru/files/CDR_MPD/MPD_CDR. pdf The MPD Collaboration Members of the Collaboration Ø Joint Institute for Nuclear Research ~ 100 § JINR Ø Institute for Nuclear Research, RAS, ~RF § Other institutes 50 Bogolyubov Institute for Theoretical Physics, NAS, Ukraine Nuclear Physics Institute of MSU, RF Institutions Institute Theoretical & Experimental Physics, RF § JINR St. Petersburg State University, RF § + 10 institutes Moldova Institute of Applied Physics, AS, from 5 countries Institute for Nuclear Reseach & Nuclear Energy BAS, Sofia, Bulgaria Institute for Scintillation Materials, Kharkov, Ukraine State Enterprise Scientific & Technology Research Institute for Apparatus construction, Kharkov, Ukraine The Collaboration is permanently growing Ø Particle Physics Center of Belarussia State University Ø Ø Ø Ø New members – are welcome 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 15
 Progress of the MPD project preparation • The first MPD concept was presented in Lo. I issued in February 2008 - it is now modified Version 0. 7 • The first version of MPD CDR was issued in June 2009 • Now the version 0. 7 is available • It will be developed in 2010 http: //nica. jinr. ru 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 16
Progress of the MPD project preparation • The first MPD concept was presented in Lo. I issued in February 2008 - it is now modified Version 0. 7 • The first version of MPD CDR was issued in June 2009 • Now the version 0. 7 is available • It will be developed in 2010 http: //nica. jinr. ru 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 16
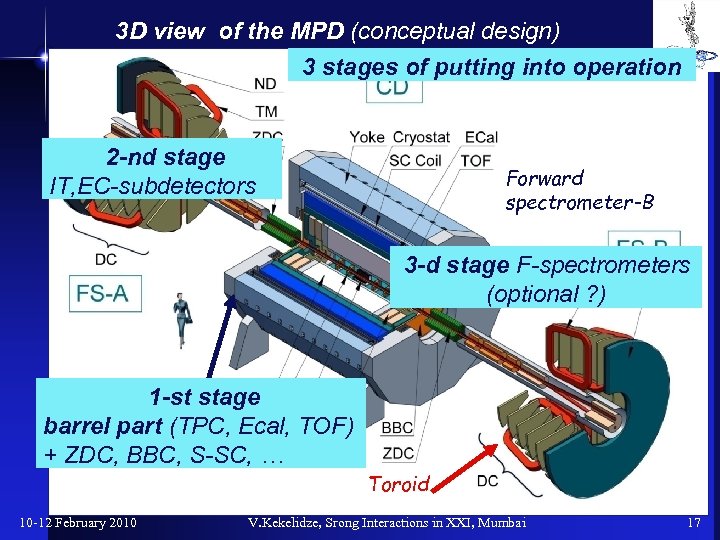 3 D view of the MPD (conceptual design) 3 stages of putting into operation 2 -nd stage IT, EC-subdetectors Forward spectrometer-B 3 -d stage F-spectrometers (optional ? ) 1 -st SC Solenoid stage barrel part (TPC, Ecal, TOF) + ZDC, BBC, S-SC, … Toroid 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 17
3 D view of the MPD (conceptual design) 3 stages of putting into operation 2 -nd stage IT, EC-subdetectors Forward spectrometer-B 3 -d stage F-spectrometers (optional ? ) 1 -st SC Solenoid stage barrel part (TPC, Ecal, TOF) + ZDC, BBC, S-SC, … Toroid 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 17
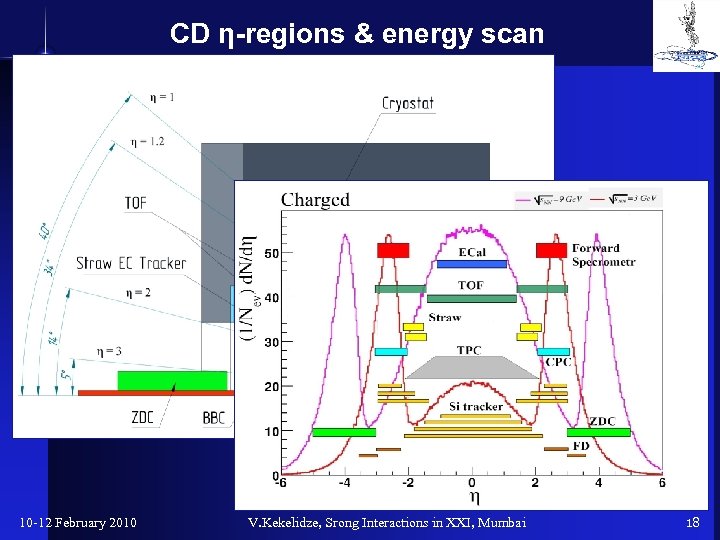 CD η-regions & energy scan 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 18
CD η-regions & energy scan 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 18
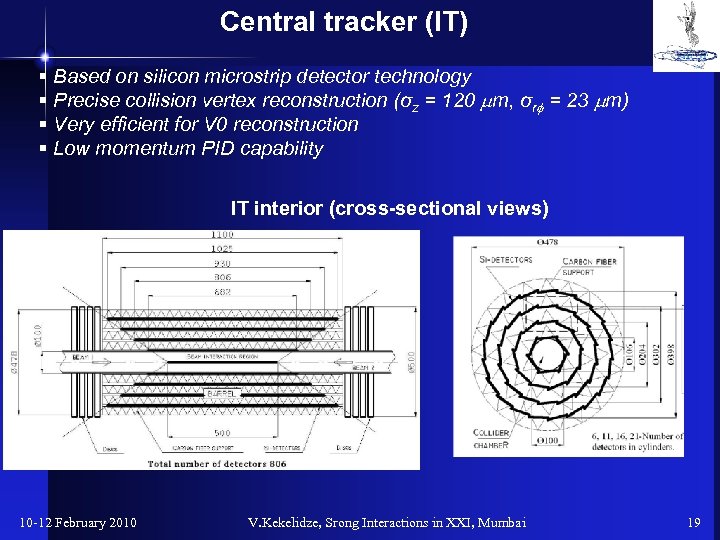 Central tracker (IT) § Based on silicon microstrip detector technology § Precise collision vertex reconstruction (σz = 120 mm, σrf = 23 mm) § Very efficient for V 0 reconstruction § Low momentum PID capability IT interior (cross-sectional views) 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 19
Central tracker (IT) § Based on silicon microstrip detector technology § Precise collision vertex reconstruction (σz = 120 mm, σrf = 23 mm) § Very efficient for V 0 reconstruction § Low momentum PID capability IT interior (cross-sectional views) 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 19
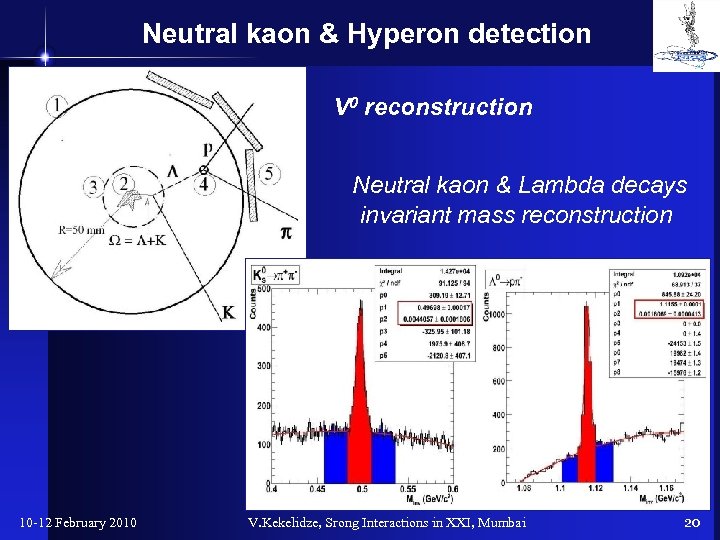 Neutral kaon & Hyperon detection V 0 reconstruction Neutral kaon & Lambda decays invariant mass reconstruction 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 20
Neutral kaon & Hyperon detection V 0 reconstruction Neutral kaon & Lambda decays invariant mass reconstruction 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 20
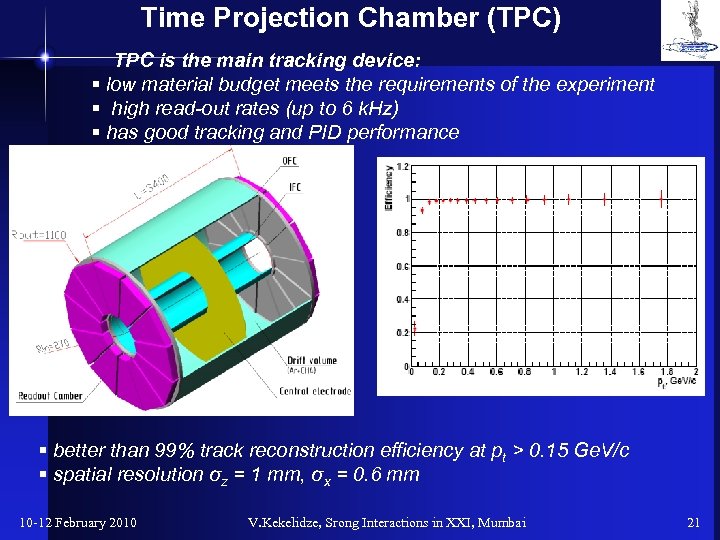 Time Projection Chamber (TPC) TPC is the main tracking device: § low material budget meets the requirements of the experiment § high read-out rates (up to 6 k. Hz) § has good tracking and PID performance § better than 99% track reconstruction efficiency at pt > 0. 15 Ge. V/c § spatial resolution σz = 1 mm, σx = 0. 6 mm 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 21
Time Projection Chamber (TPC) TPC is the main tracking device: § low material budget meets the requirements of the experiment § high read-out rates (up to 6 k. Hz) § has good tracking and PID performance § better than 99% track reconstruction efficiency at pt > 0. 15 Ge. V/c § spatial resolution σz = 1 mm, σx = 0. 6 mm 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 21
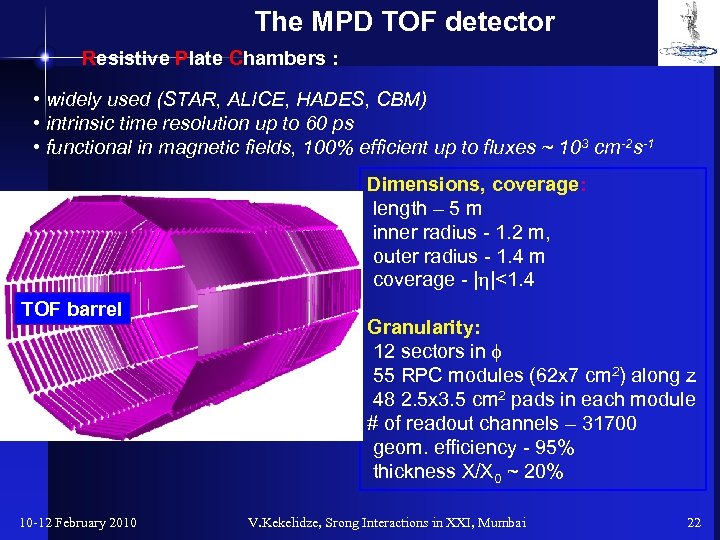 The MPD TOF detector Resistive Plate Chambers : • widely used (STAR, ALICE, HADES, CBM) • intrinsic time resolution up to 60 ps • functional in magnetic fields, 100% efficient up to fluxes ~ 103 cm-2 s-1 Dimensions, coverage: length – 5 m inner radius - 1. 2 m, outer radius - 1. 4 m coverage - |h|<1. 4 TOF barrel 10 -12 February 2010 Granularity: 12 sectors in f 55 RPC modules (62 x 7 cm 2) along z 48 2. 5 x 3. 5 cm 2 pads in each module # of readout channels – 31700 geom. efficiency - 95% thickness X/X 0 ~ 20% V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 22
The MPD TOF detector Resistive Plate Chambers : • widely used (STAR, ALICE, HADES, CBM) • intrinsic time resolution up to 60 ps • functional in magnetic fields, 100% efficient up to fluxes ~ 103 cm-2 s-1 Dimensions, coverage: length – 5 m inner radius - 1. 2 m, outer radius - 1. 4 m coverage - |h|<1. 4 TOF barrel 10 -12 February 2010 Granularity: 12 sectors in f 55 RPC modules (62 x 7 cm 2) along z 48 2. 5 x 3. 5 cm 2 pads in each module # of readout channels – 31700 geom. efficiency - 95% thickness X/X 0 ~ 20% V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 22
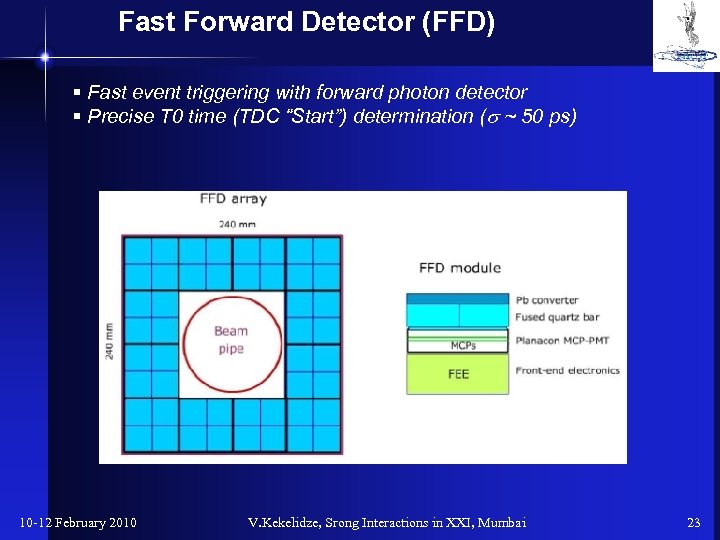 Fast Forward Detector (FFD) § Fast event triggering with forward photon detector § Precise T 0 time (TDC “Start”) determination (s ~ 50 ps) 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 23
Fast Forward Detector (FFD) § Fast event triggering with forward photon detector § Precise T 0 time (TDC “Start”) determination (s ~ 50 ps) 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 23
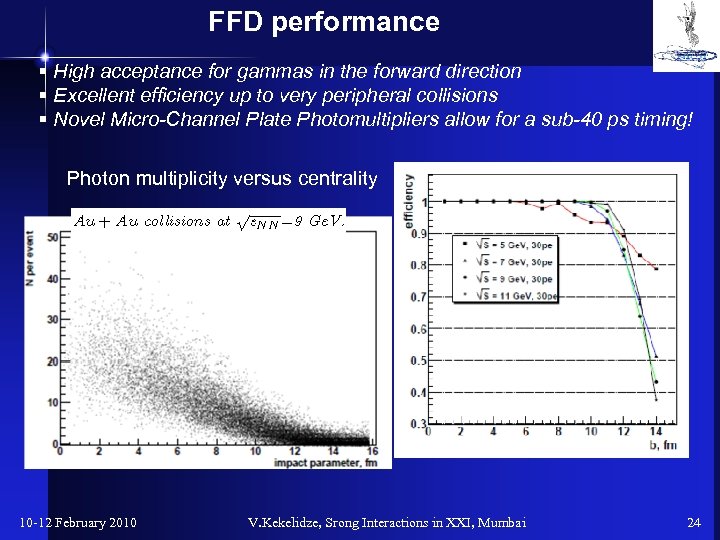 FFD performance § High acceptance for gammas in the forward direction § Excellent efficiency up to very peripheral collisions § Novel Micro-Channel Plate Photomultipliers allow for a sub-40 ps timing! Photon multiplicity versus centrality 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 24
FFD performance § High acceptance for gammas in the forward direction § Excellent efficiency up to very peripheral collisions § Novel Micro-Channel Plate Photomultipliers allow for a sub-40 ps timing! Photon multiplicity versus centrality 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 24
 EM calorimeter prototyping 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 25
EM calorimeter prototyping 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 25
 EM calorimeter (performance study) § High energy and time resolution § Good PID capabilities for photons, electrons and hadrons 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 26
EM calorimeter (performance study) § High energy and time resolution § Good PID capabilities for photons, electrons and hadrons 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 26
 Neutron / gamma separation with Ecal TOF + Energy E = 1 Ge. V Efficiency (Energy) 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 27
Neutron / gamma separation with Ecal TOF + Energy E = 1 Ge. V Efficiency (Energy) 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 27
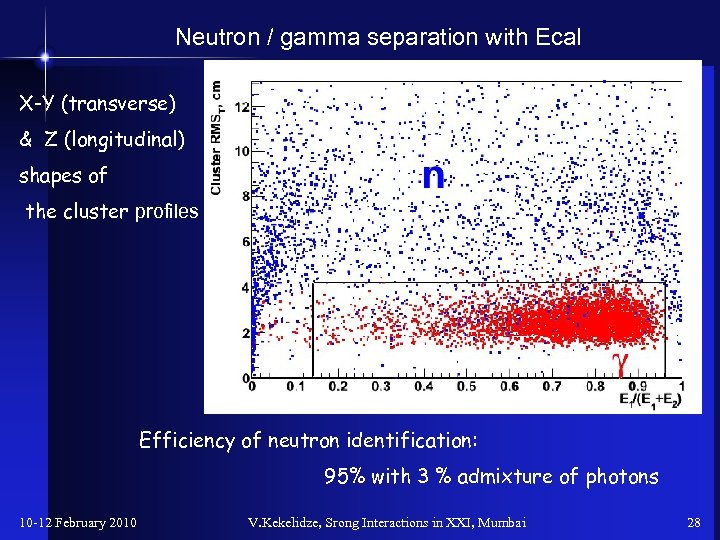 Neutron / gamma separation with Ecal X-Y (transverse) & Z (longitudinal) shapes of the cluster profiles Efficiency of neutron identification: 95% with 3 % admixture of photons 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 28
Neutron / gamma separation with Ecal X-Y (transverse) & Z (longitudinal) shapes of the cluster profiles Efficiency of neutron identification: 95% with 3 % admixture of photons 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 28
 Zero Degree Calorimeter (ZDC) § Event centrality determination § Event plane reconstruction capability 80 modules 5 x 5 cm 2 10 -12 February 2010 60 layers of lead-scintillator (4: 1), 6 l WLS-fibers for light readout MAPD as photodetectors V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 29
Zero Degree Calorimeter (ZDC) § Event centrality determination § Event plane reconstruction capability 80 modules 5 x 5 cm 2 10 -12 February 2010 60 layers of lead-scintillator (4: 1), 6 l WLS-fibers for light readout MAPD as photodetectors V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 29
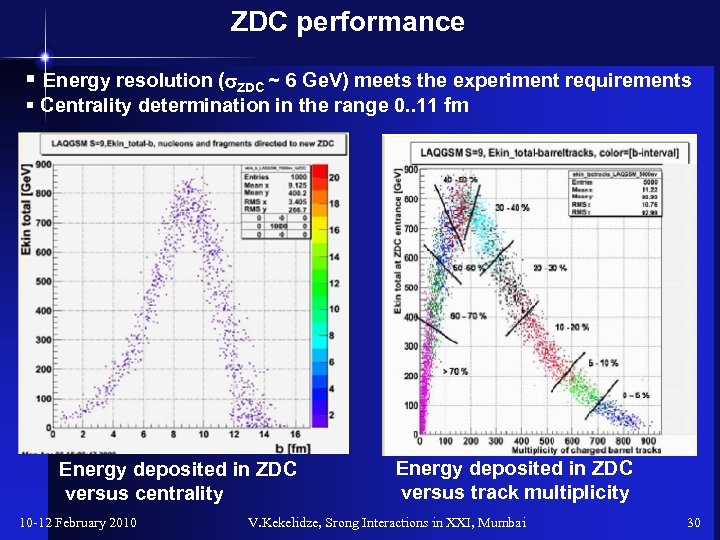 ZDC performance § Energy resolution (s. ZDC ~ 6 Ge. V) meets the experiment requirements § Centrality determination in the range 0. . 11 fm Energy deposited in ZDC versus centrality 10 -12 February 2010 Energy deposited in ZDC versus track multiplicity V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 30
ZDC performance § Energy resolution (s. ZDC ~ 6 Ge. V) meets the experiment requirements § Centrality determination in the range 0. . 11 fm Energy deposited in ZDC versus centrality 10 -12 February 2010 Energy deposited in ZDC versus track multiplicity V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 30
 Straw end-cap tracker (ECT) § Tracking in the forward direction § Complementary to TPC measurements 6 layers of straws 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 31
Straw end-cap tracker (ECT) § Tracking in the forward direction § Complementary to TPC measurements 6 layers of straws 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 31
 Working Groups q q q TPC prototyping Magnet ECal TOF Straw wheels ZCal CPC FFD BBC DAQ IT - Yu. Zanevski et. al. - A. Kovalenko, V. Borisov et. al. - I. Tyapkin, A. Olchevsky et. al. - V. Golovatyuk et. al. - V. Peshekhonov et. al. - A. Kurepin et. al. - Yu. Kiryushin et. al. - V. Yurevich et. al. - R. Zulkarneev et. al. - V. Slepnev, S. Bazylev et. al. - Yu. Murin, V. Nikitin et. al. The CBM-MPD SST consortium: GSI - JINR – IHEP - … in IT silicon module development is well progressing 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 32
Working Groups q q q TPC prototyping Magnet ECal TOF Straw wheels ZCal CPC FFD BBC DAQ IT - Yu. Zanevski et. al. - A. Kovalenko, V. Borisov et. al. - I. Tyapkin, A. Olchevsky et. al. - V. Golovatyuk et. al. - V. Peshekhonov et. al. - A. Kurepin et. al. - Yu. Kiryushin et. al. - V. Yurevich et. al. - R. Zulkarneev et. al. - V. Slepnev, S. Bazylev et. al. - Yu. Murin, V. Nikitin et. al. The CBM-MPD SST consortium: GSI - JINR – IHEP - … in IT silicon module development is well progressing 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 32
 Magnet - project development Discussion with the potential participators, contractors having an experience in large solenoid construction has started. A schedule and cost evaluation will be prepared a. s. a. p. for: • conceptual design + R&D • technical documentation reparation • production and tests 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 33
Magnet - project development Discussion with the potential participators, contractors having an experience in large solenoid construction has started. A schedule and cost evaluation will be prepared a. s. a. p. for: • conceptual design + R&D • technical documentation reparation • production and tests 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 33
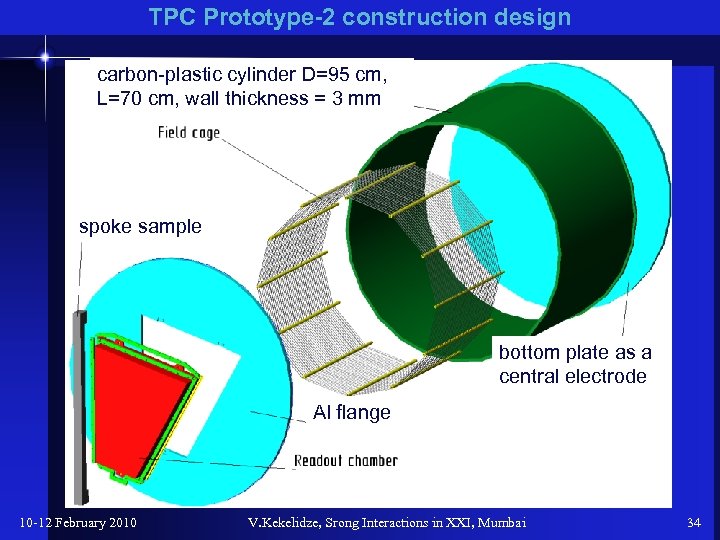 TPC Prototype-2 construction design carbon-plastic cylinder D=95 cm, L=70 cm, wall thickness = 3 mm spoke sample bottom plate as a central electrode Al flange 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 34
TPC Prototype-2 construction design carbon-plastic cylinder D=95 cm, L=70 cm, wall thickness = 3 mm spoke sample bottom plate as a central electrode Al flange 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 34
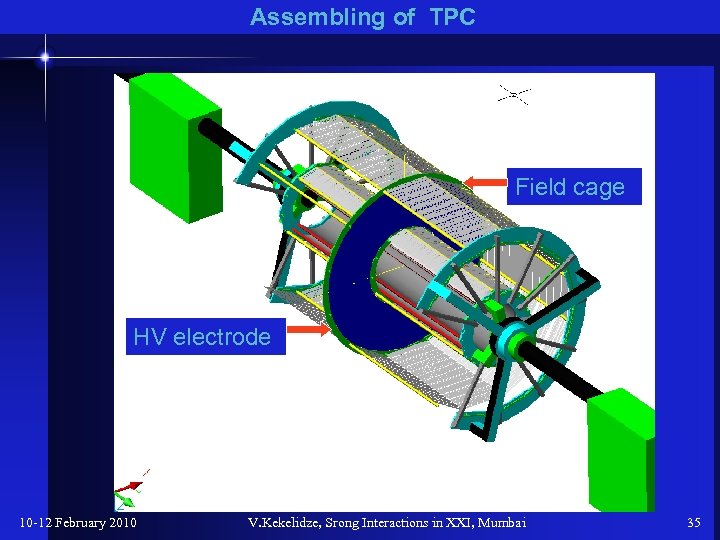 Assembling of ТРС Field cage HV electrode 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 35
Assembling of ТРС Field cage HV electrode 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 35
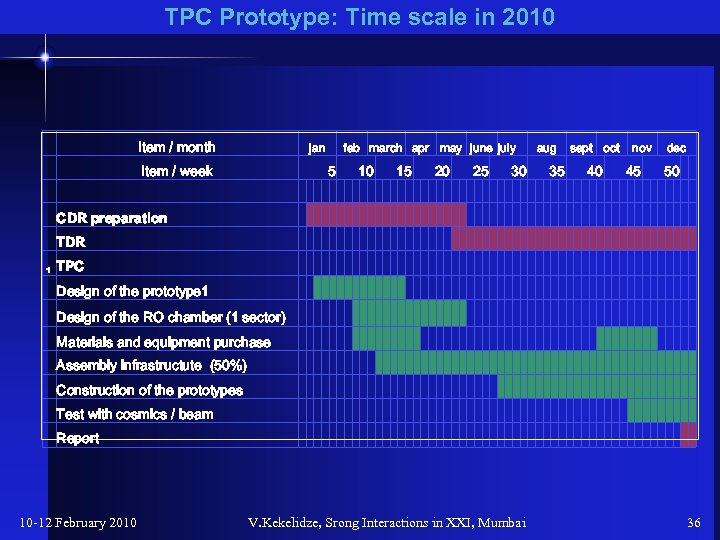 ТРС Prototype: Time scale in 2010 Item / month Item / week jan feb march apr may june july 5 10 15 20 25 aug 30 sept oct 35 40 nov 45 dec 50 CDR preparation TDR 1 TPC Design of the prototype 1 Design of the RO chamber (1 sector) Materials and equipment purchase Assembly infrastructute (50%) Construction of the prototypes Test with cosmics / beam Report 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 36
ТРС Prototype: Time scale in 2010 Item / month Item / week jan feb march apr may june july 5 10 15 20 25 aug 30 sept oct 35 40 nov 45 dec 50 CDR preparation TDR 1 TPC Design of the prototype 1 Design of the RO chamber (1 sector) Materials and equipment purchase Assembly infrastructute (50%) Construction of the prototypes Test with cosmics / beam Report 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 36
 TOF RPC prototyping Double stack (10 gaps) RPC, read-out pads 2. 5 х 3. 5 cm 2 An RPC prototype active area 7 x 14 cm 2 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 37
TOF RPC prototyping Double stack (10 gaps) RPC, read-out pads 2. 5 х 3. 5 cm 2 An RPC prototype active area 7 x 14 cm 2 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 37
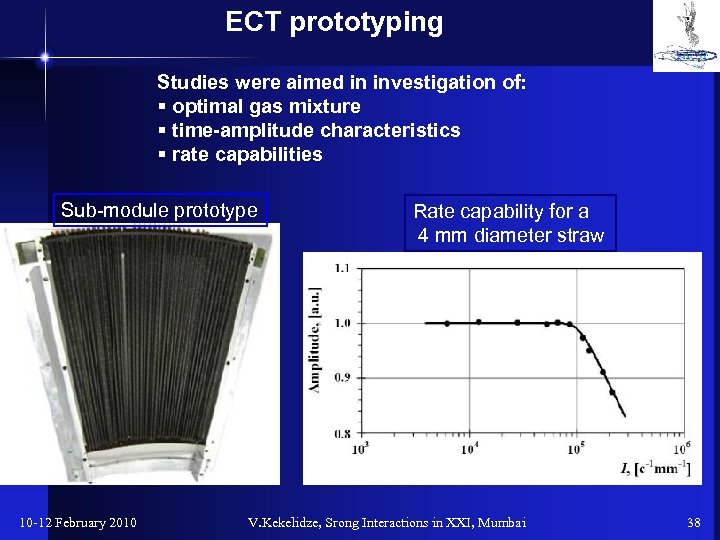 ECT prototyping Studies were aimed in investigation of: § optimal gas mixture § time-amplitude characteristics § rate capabilities Sub-module prototype 10 -12 February 2010 Rate capability for a 4 mm diameter straw V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 38
ECT prototyping Studies were aimed in investigation of: § optimal gas mixture § time-amplitude characteristics § rate capabilities Sub-module prototype 10 -12 February 2010 Rate capability for a 4 mm diameter straw V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 38
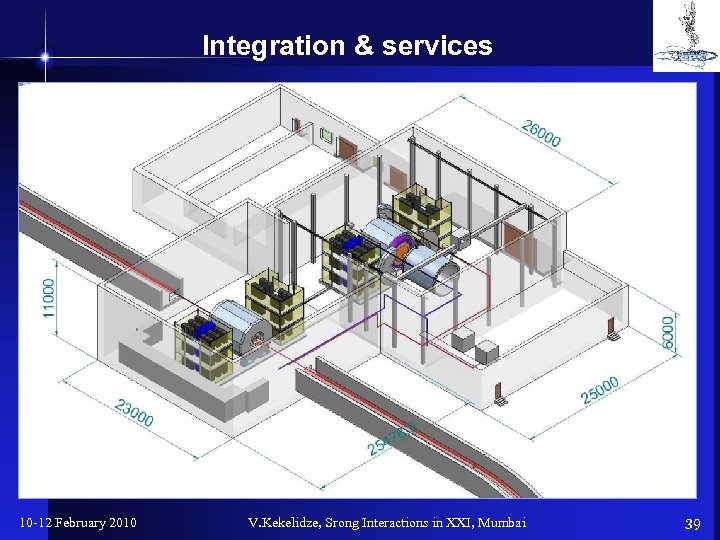 Integration & services 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 39
Integration & services 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 39
 Installation sequence & support structure Solenoid + ECal rails Solenoid + ECal +TOF 10 -12 February 2010 Solenoid + ECal +TOF+TPC V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 40
Installation sequence & support structure Solenoid + ECal rails Solenoid + ECal +TOF 10 -12 February 2010 Solenoid + ECal +TOF+TPC V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 40
 Analysis of hadron spectra & yields with the MPD detector Goals: § feasibility for extraction of hadronic yields with a proposed MPD design § estimation of sub-detector parameters crucial for good particle identification (PID) § § § Procedure: Full reconstruction chain implementing hit production, tracking, TPC-TOF matching, Particle identification procedure has been developed using TOF information All corrections are determined from MC simulation : reconstruction efficiency, acceptance, decays in flight, secondary interactions, etc. Invariant pt-distributions of p, K, p are obtained Analysis procedure and results are described in the CDR 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 41
Analysis of hadron spectra & yields with the MPD detector Goals: § feasibility for extraction of hadronic yields with a proposed MPD design § estimation of sub-detector parameters crucial for good particle identification (PID) § § § Procedure: Full reconstruction chain implementing hit production, tracking, TPC-TOF matching, Particle identification procedure has been developed using TOF information All corrections are determined from MC simulation : reconstruction efficiency, acceptance, decays in flight, secondary interactions, etc. Invariant pt-distributions of p, K, p are obtained Analysis procedure and results are described in the CDR 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 41
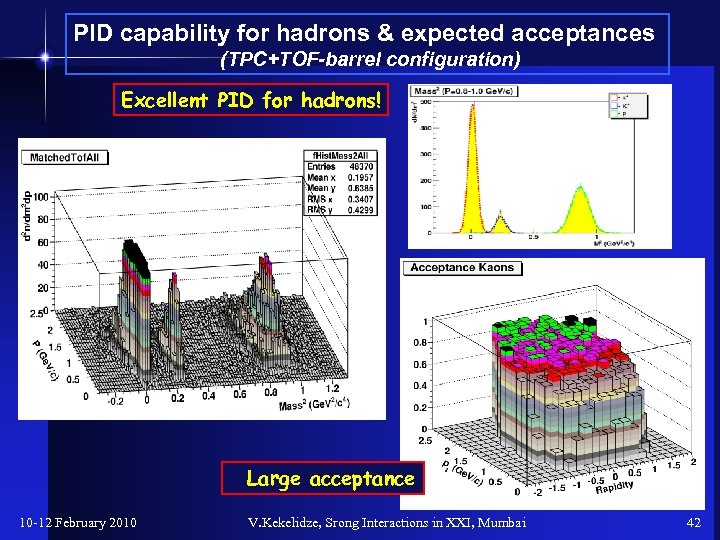 PID capability for hadrons & expected acceptances (TPC+TOF-barrel configuration) Excellent PID for hadrons! Large acceptance 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 42
PID capability for hadrons & expected acceptances (TPC+TOF-barrel configuration) Excellent PID for hadrons! Large acceptance 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 42
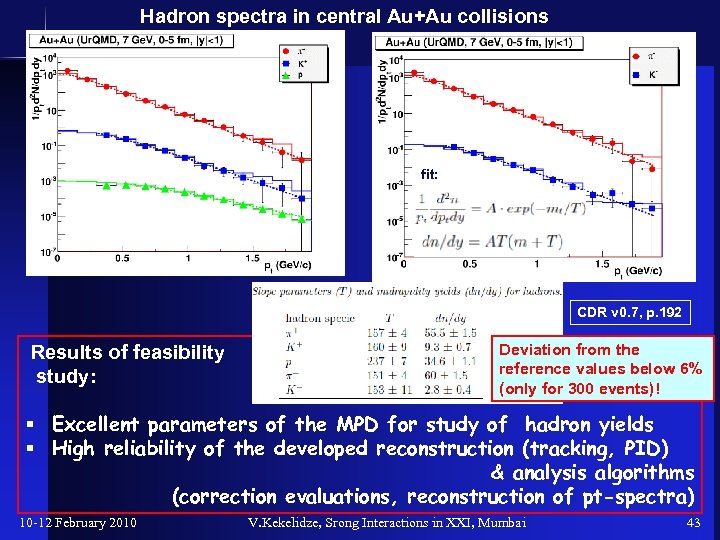 Hadron spectra in central Au+Au collisions 300 events fit: Fit: CDR v 0. 7, p. 192 Results of feasibility study: Deviation from the reference values below 6% (only for 300 events)! § Excellent parameters of the MPD for study of hadron yields § High reliability of the developed reconstruction (tracking, PID) & analysis algorithms (correction evaluations, reconstruction of pt-spectra) 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 43
Hadron spectra in central Au+Au collisions 300 events fit: Fit: CDR v 0. 7, p. 192 Results of feasibility study: Deviation from the reference values below 6% (only for 300 events)! § Excellent parameters of the MPD for study of hadron yields § High reliability of the developed reconstruction (tracking, PID) & analysis algorithms (correction evaluations, reconstruction of pt-spectra) 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 43
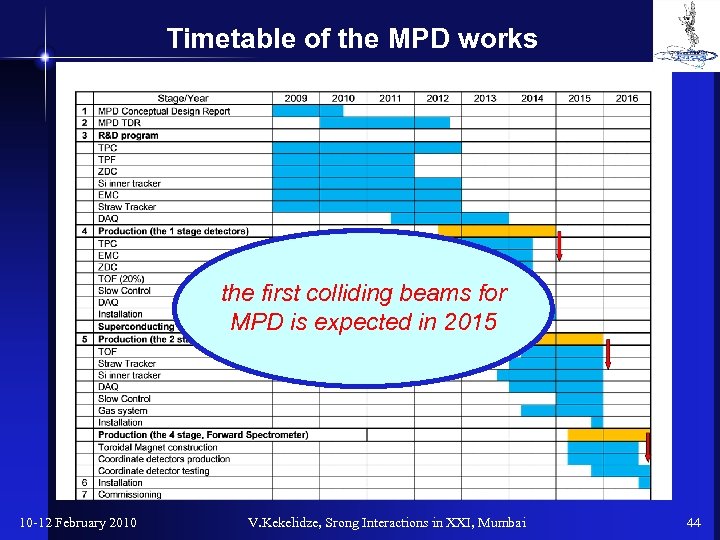 Timetable of the MPD works the first colliding beams for MPD is expected in 2015 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 44
Timetable of the MPD works the first colliding beams for MPD is expected in 2015 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 44
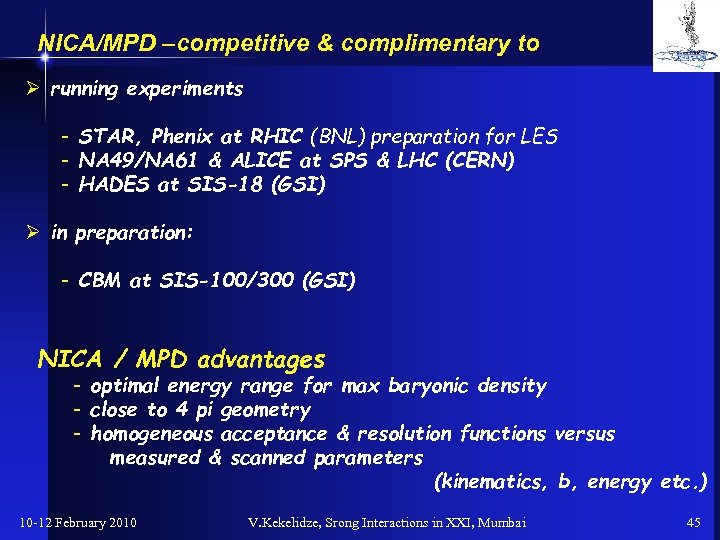 NICA/MPD –competitive & complimentary to Ø running experiments - STAR, Phenix at RHIC (BNL) preparation for LES - NA 49/NA 61 & ALICE at SPS & LHC (CERN) - HADES at SIS-18 (GSI) Ø in preparation: - CBM at SIS-100/300 (GSI) NICA / MPD advantages - optimal energy range for max baryonic density - close to 4 pi geometry - homogeneous acceptance & resolution functions versus measured & scanned parameters (kinematics, b, energy etc. ) 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 45
NICA/MPD –competitive & complimentary to Ø running experiments - STAR, Phenix at RHIC (BNL) preparation for LES - NA 49/NA 61 & ALICE at SPS & LHC (CERN) - HADES at SIS-18 (GSI) Ø in preparation: - CBM at SIS-100/300 (GSI) NICA / MPD advantages - optimal energy range for max baryonic density - close to 4 pi geometry - homogeneous acceptance & resolution functions versus measured & scanned parameters (kinematics, b, energy etc. ) 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 45
 Conclusions • Physics motivation & competitiveness are well proven by the White Book & Round Table -4 • Realization of the first stage - Nuclotron-M is going well - should be completed in 2010 • Other stages of the NICA complex are well defined & proposed for construction in the NICA TDR • The MPD design & R&D are progressing well - the CDR is available • The corresponding collaboration is growing New members are welcome 24 September 2009 V. Kekelidze, JINR, 106 Scientific Council 46
Conclusions • Physics motivation & competitiveness are well proven by the White Book & Round Table -4 • Realization of the first stage - Nuclotron-M is going well - should be completed in 2010 • Other stages of the NICA complex are well defined & proposed for construction in the NICA TDR • The MPD design & R&D are progressing well - the CDR is available • The corresponding collaboration is growing New members are welcome 24 September 2009 V. Kekelidze, JINR, 106 Scientific Council 46
 Thank you 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 47
Thank you 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 47
 Spare 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 48
Spare 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 48
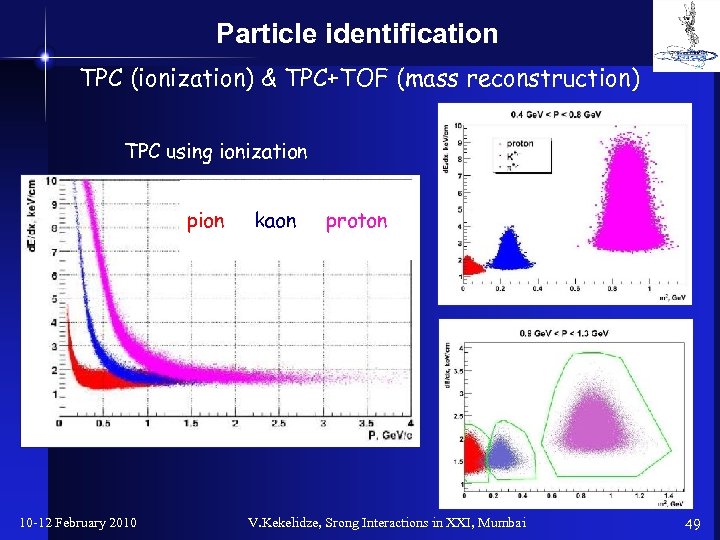 Particle identification TPC (ionization) & TPC+TOF (mass reconstruction) TPC using ionization pion 10 -12 February 2010 kaon proton V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 49
Particle identification TPC (ionization) & TPC+TOF (mass reconstruction) TPC using ionization pion 10 -12 February 2010 kaon proton V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 49
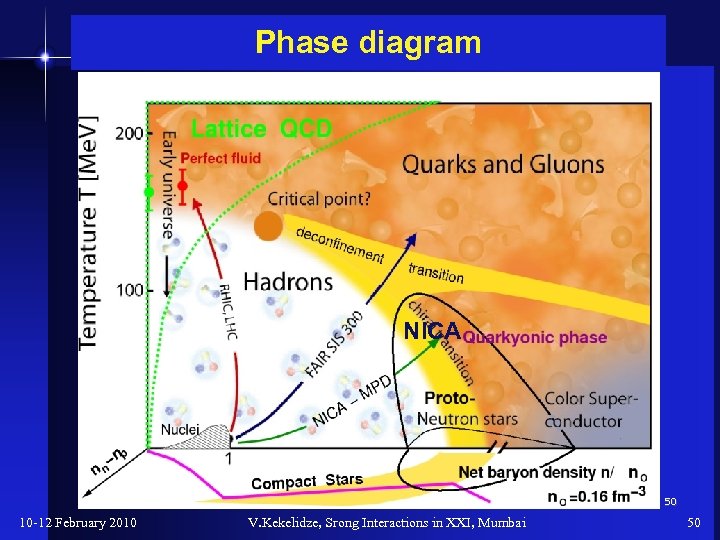 Phase diagram NICA 50 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 50
Phase diagram NICA 50 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 50
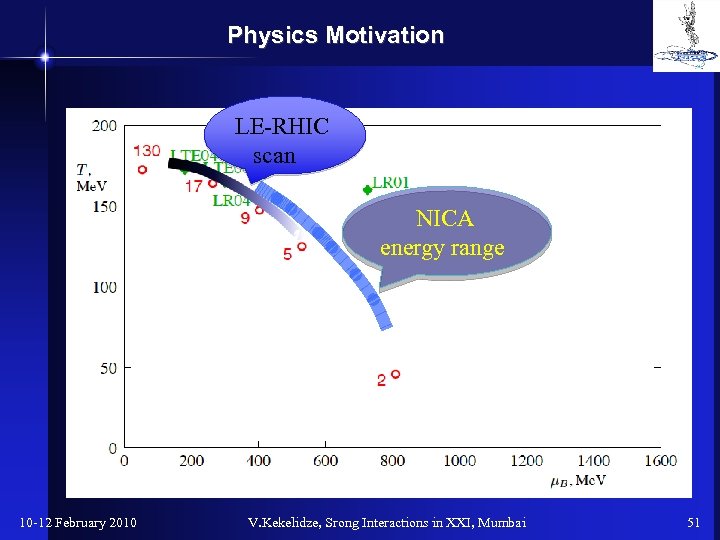 Physics Motivation LE-RHIC scan NICA energy range 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 51
Physics Motivation LE-RHIC scan NICA energy range 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 51
 CD assembly (without IT) completed ECal Rails TOF Solenoid 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 52
CD assembly (without IT) completed ECal Rails TOF Solenoid 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 52
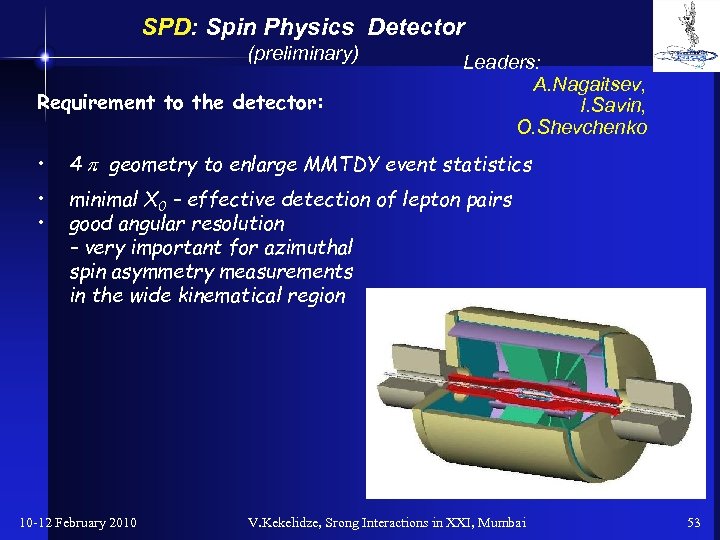 SPD: Spin Physics Detector (preliminary) Requirement to the detector: Leaders: A. Nagaitsev, I. Savin, O. Shevchenko • 4 p geometry to enlarge MMTDY event statistics • • minimal X 0 – effective detection of lepton pairs good angular resolution – very important for azimuthal spin asymmetry measurements in the wide kinematical region 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 53
SPD: Spin Physics Detector (preliminary) Requirement to the detector: Leaders: A. Nagaitsev, I. Savin, O. Shevchenko • 4 p geometry to enlarge MMTDY event statistics • • minimal X 0 – effective detection of lepton pairs good angular resolution – very important for azimuthal spin asymmetry measurements in the wide kinematical region 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 53
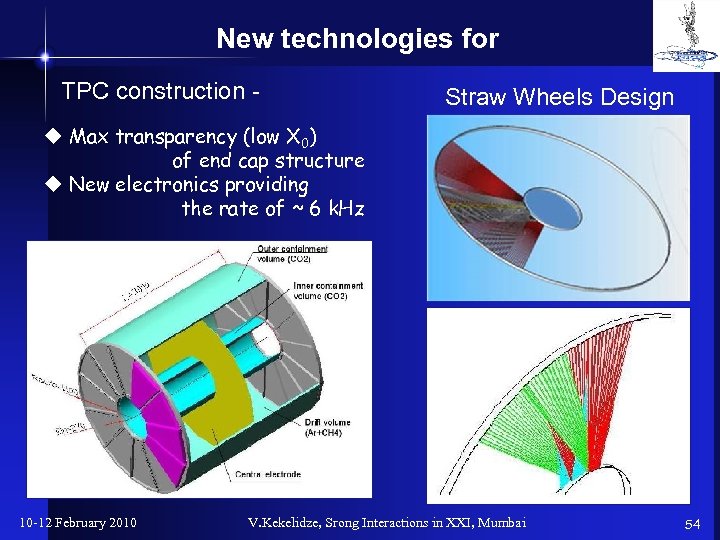 New technologies for TPC construction - Straw Wheels Design u Max transparency (low X 0) of end cap structure u New electronics providing the rate of ~ 6 k. Hz 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 54
New technologies for TPC construction - Straw Wheels Design u Max transparency (low X 0) of end cap structure u New electronics providing the rate of ~ 6 k. Hz 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 54
 Nuclotron-М - the first stage of NICA project The decision was taken to carry out the physical runs only in case of guaranteed stable & reliable work of accelerator main results of the runs #38 (2008) & #39 (2009): • essential improvement of accelerator performance • in addition, several shifts were provided for the physics experiments - Plans: - Run #40: Run #42: 10 -12 February 2010 November 2009 (400 -900 hours). February 2010 (400 -900 hours). V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 55
Nuclotron-М - the first stage of NICA project The decision was taken to carry out the physical runs only in case of guaranteed stable & reliable work of accelerator main results of the runs #38 (2008) & #39 (2009): • essential improvement of accelerator performance • in addition, several shifts were provided for the physics experiments - Plans: - Run #40: Run #42: 10 -12 February 2010 November 2009 (400 -900 hours). February 2010 (400 -900 hours). V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 55
 NICA/MPD –competitive & complimentary to Ø running experiments - STAR, Phenix at RHIC - NA 49/NA 61 at CERN - HADES at GSI Ø in preparation: - ALICE at CERN - CBM at GSI NICA / MPD advantages - optimal energy range for max baryonic density - close to 4 pi geometry - homogeneous acceptance & resolution functions versus measured & scanned parameters (kinematics, b, energy etc. ) 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 56
NICA/MPD –competitive & complimentary to Ø running experiments - STAR, Phenix at RHIC - NA 49/NA 61 at CERN - HADES at GSI Ø in preparation: - ALICE at CERN - CBM at GSI NICA / MPD advantages - optimal energy range for max baryonic density - close to 4 pi geometry - homogeneous acceptance & resolution functions versus measured & scanned parameters (kinematics, b, energy etc. ) 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 56
 Physics tasks for Multi. Purpose Detector Ø event-by-event fluctuation in hadron productions (multiplicity, Pt etc. ) Ø HBT correlations indicating the space-time size of the systems involving π, K, p, Λ Ø directed & elliptic flows for various hadrons Ø multi-strange hyperon production: yield & spectra (the probes of nuclear media phases) Ø photon & electron probes Ø search for P- & CP violation as a charge asymmetry should be studied for different ions (from p to Au) by scanning in b & energy (in the range SNN = 4 - 11 Ge. V/u) 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 57
Physics tasks for Multi. Purpose Detector Ø event-by-event fluctuation in hadron productions (multiplicity, Pt etc. ) Ø HBT correlations indicating the space-time size of the systems involving π, K, p, Λ Ø directed & elliptic flows for various hadrons Ø multi-strange hyperon production: yield & spectra (the probes of nuclear media phases) Ø photon & electron probes Ø search for P- & CP violation as a charge asymmetry should be studied for different ions (from p to Au) by scanning in b & energy (in the range SNN = 4 - 11 Ge. V/u) 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 57
 - successfully commissioned cryogenics after full-scale modernization (10 -15% less consumption of N & LHe) - ring vacuum – improvement for 2 order of magnitude (x 10 -9) -->x 10 -10 MODERNIZATION of: - 4 runs KRION-2: CН 4, N 2, O 2, Ar -> Xe 44+ - KRION 6 T; - SPD - Injector (fore-injector & LU-20): geodesy, new PS; -> for heavy ions; -RF system: trapping & bunching systems, controls & diagnostics; adiabatic capture (x 2 intensity) -automatic control system, diagnostics & beam orbit detection & correction system - slow extraction system for accelerated heavy ions at maximal energies (new HV PS for the electro-static septum) 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 58
- successfully commissioned cryogenics after full-scale modernization (10 -15% less consumption of N & LHe) - ring vacuum – improvement for 2 order of magnitude (x 10 -9) -->x 10 -10 MODERNIZATION of: - 4 runs KRION-2: CН 4, N 2, O 2, Ar -> Xe 44+ - KRION 6 T; - SPD - Injector (fore-injector & LU-20): geodesy, new PS; -> for heavy ions; -RF system: trapping & bunching systems, controls & diagnostics; adiabatic capture (x 2 intensity) -automatic control system, diagnostics & beam orbit detection & correction system - slow extraction system for accelerated heavy ions at maximal energies (new HV PS for the electro-static septum) 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 58
 Physics motivation Ø the study of hot & dense baryonic matter would provide us with relevant information on - in-medium properties of hadrons & nuclear matter equation of state - de-confinement and chiral symmetry restoration, - phase transition, mixed phase & critical end-point - possible strong P- & CP violation Ø It is indicated in series of theoretical works - A. Sissakian, A. Sorin, V. Toneev, G. Zinovjev et al. - M. Gazdzicki, M. Gorenstein, -. . that an optimal way to reach the highest possible baryon density in the lab is heavy ion collision at SNN = 4 - 11 Ge. V/u 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 59
Physics motivation Ø the study of hot & dense baryonic matter would provide us with relevant information on - in-medium properties of hadrons & nuclear matter equation of state - de-confinement and chiral symmetry restoration, - phase transition, mixed phase & critical end-point - possible strong P- & CP violation Ø It is indicated in series of theoretical works - A. Sissakian, A. Sorin, V. Toneev, G. Zinovjev et al. - M. Gazdzicki, M. Gorenstein, -. . that an optimal way to reach the highest possible baryon density in the lab is heavy ion collision at SNN = 4 - 11 Ge. V/u 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 59
 Nuclotron upgrade: achievements & open questions • Stable operation of beam intensity 2*1010 ppc at 1 Tesla = 2. 5 Ge. V/n • The magnetic field - reached 1. 5 T & the deutron beam up to 3. 8 Ge. V/n • Modern quench detection system & new energy evacuation systems - are under commissioning The goal for beam dynamics improvement: minimization of the beam losses at all stages from injection to acceleration & to extraction of the beams -not more then 15 -20% (it is now ~ 50 -80%) 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 60
Nuclotron upgrade: achievements & open questions • Stable operation of beam intensity 2*1010 ppc at 1 Tesla = 2. 5 Ge. V/n • The magnetic field - reached 1. 5 T & the deutron beam up to 3. 8 Ge. V/n • Modern quench detection system & new energy evacuation systems - are under commissioning The goal for beam dynamics improvement: minimization of the beam losses at all stages from injection to acceleration & to extraction of the beams -not more then 15 -20% (it is now ~ 50 -80%) 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 60
 Accelerator Facility Leaders: I. Meshkov, A. Kovalenko, G. Trubnikov, Ø Machine advisory committee (MAC) • Boris Sharkov, ITEP, chairman • Pavel Beloshitsky, CERN • Sergei Ivanov, IHEP • Thomas Roser, BNL • Markus Steck, GSI • Nicholas John Walker, Desy Ø 1 -st report on Nuclotron-M Ø 1 -st review on NICA Ø The next meeting is foreseen in Dubna 10 -12 February 2010 Jan 2009 June 2009 Jan 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 61
Accelerator Facility Leaders: I. Meshkov, A. Kovalenko, G. Trubnikov, Ø Machine advisory committee (MAC) • Boris Sharkov, ITEP, chairman • Pavel Beloshitsky, CERN • Sergei Ivanov, IHEP • Thomas Roser, BNL • Markus Steck, GSI • Nicholas John Walker, Desy Ø 1 -st report on Nuclotron-M Ø 1 -st review on NICA Ø The next meeting is foreseen in Dubna 10 -12 February 2010 Jan 2009 June 2009 Jan 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 61
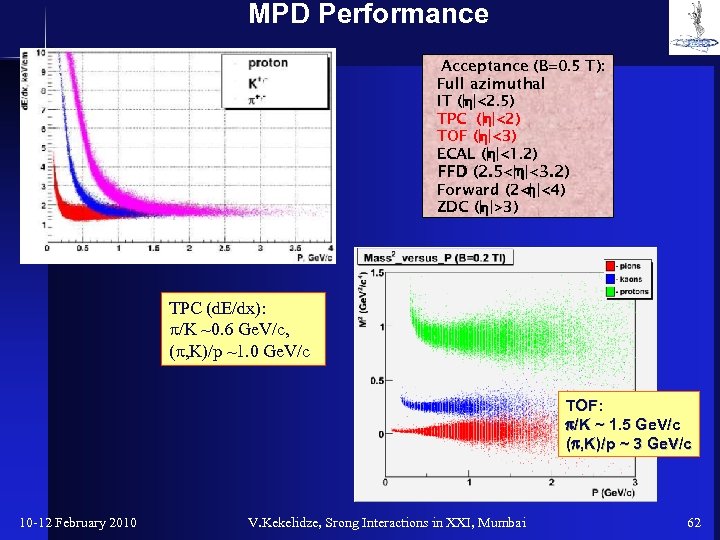 MPD Performance Acceptance (B=0. 5 T): Full azimuthal IT (|h|<2. 5) TPC (|h|<2) TOF (|h|<3) ECAL (|h|<1. 2) FFD (2. 5<|h|<3. 2) Forward (2<| |<4) h ZDC (|h|>3) TPC (d. E/dx): /K ~0. 6 Ge. V/c, ( , K)/p ~1. 0 Ge. V/c TOF: p/K ~ 1. 5 Ge. V/c (p, K)/p ~ 3 Ge. V/c 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 62
MPD Performance Acceptance (B=0. 5 T): Full azimuthal IT (|h|<2. 5) TPC (|h|<2) TOF (|h|<3) ECAL (|h|<1. 2) FFD (2. 5<|h|<3. 2) Forward (2<| |<4) h ZDC (|h|>3) TPC (d. E/dx): /K ~0. 6 Ge. V/c, ( , K)/p ~1. 0 Ge. V/c TOF: p/K ~ 1. 5 Ge. V/c (p, K)/p ~ 3 Ge. V/c 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 62
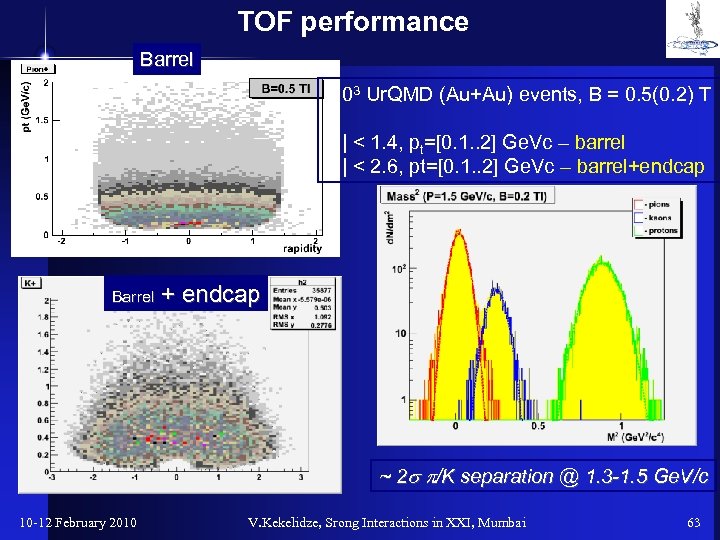 TOF performance Barrel 103 Ur. QMD (Au+Au) events, B = 0. 5(0. 2) T |h| < 1. 4, pt=[0. 1. . 2] Ge. Vc – barrel |h| < 2. 6, pt=[0. 1. . 2] Ge. Vc – barrel+endcap Barrel + endcap ~ 2 s p/K separation @ 1. 3 -1. 5 Ge. V/c 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 63
TOF performance Barrel 103 Ur. QMD (Au+Au) events, B = 0. 5(0. 2) T |h| < 1. 4, pt=[0. 1. . 2] Ge. Vc – barrel |h| < 2. 6, pt=[0. 1. . 2] Ge. Vc – barrel+endcap Barrel + endcap ~ 2 s p/K separation @ 1. 3 -1. 5 Ge. V/c 10 -12 February 2010 V. Kekelidze, Srong Interactions in XXI, Mumbai 63


