Lect9-10.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 16

Statistics toolbox
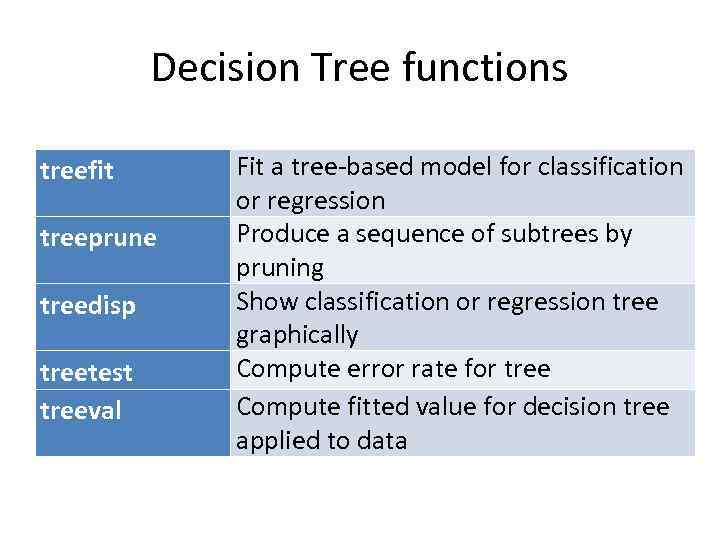
Decision Tree functions treefit treeprune treedisp treetest treeval Fit a tree-based model for classification or regression Produce a sequence of subtrees by pruning Show classification or regression tree graphically Compute error rate for tree Compute fitted value for decision tree applied to data
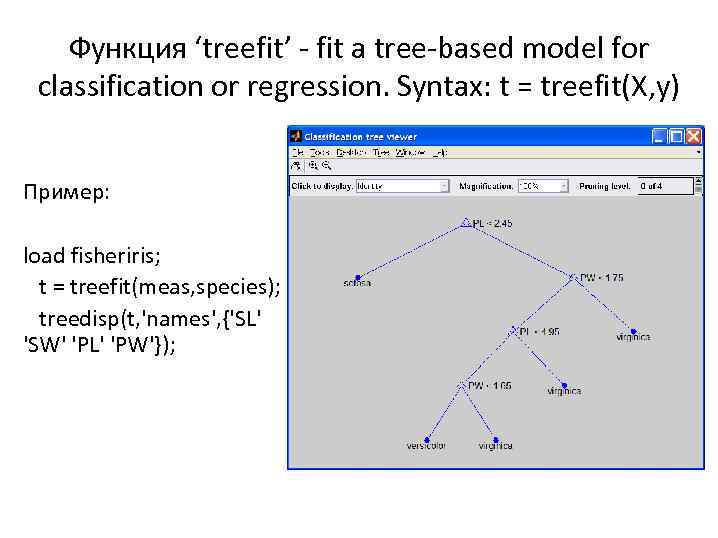
Функция ‘treefit’ - fit a tree-based model for classification or regression. Syntax: t = treefit(X, y) Пример: load fisheriris; t = treefit(meas, species); treedisp(t, 'names', {'SL' 'SW' 'PL' 'PW'});
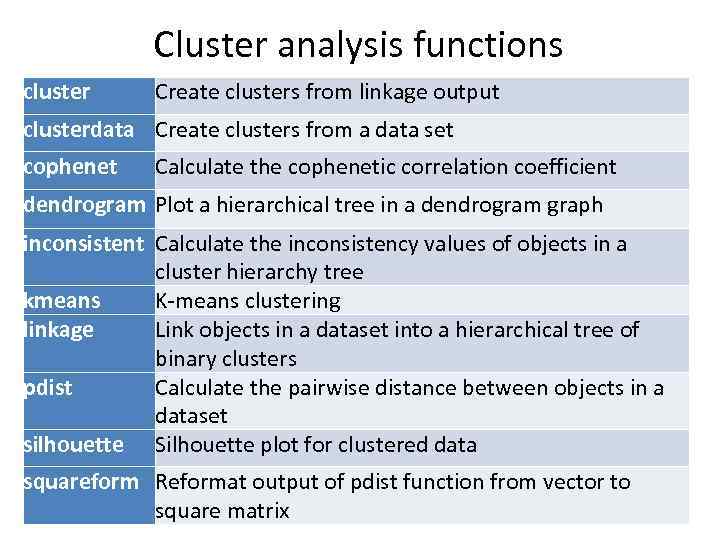
Cluster analysis functions cluster Create clusters from linkage output clusterdata Create clusters from a data set cophenet Calculate the cophenetic correlation coefficient dendrogram Plot a hierarchical tree in a dendrogram graph inconsistent Calculate the inconsistency values of objects in a cluster hierarchy tree kmeans K-means clustering linkage Link objects in a dataset into a hierarchical tree of binary clusters pdist Calculate the pairwise distance between objects in a dataset silhouette Silhouette plot for clustered data squareform Reformat output of pdist function from vector to square matrix
![Функция kmeans • • • IDX = kmeans(X, k) [IDX, C] = kmeans(X, k) Функция kmeans • • • IDX = kmeans(X, k) [IDX, C] = kmeans(X, k)](https://present5.com/presentation/187967559_443054254/image-5.jpg)
Функция kmeans • • • IDX = kmeans(X, k) [IDX, C] = kmeans(X, k) [IDX, C, sumd, D] = kmeans(X, k) [. . . ] = kmeans(. . . , 'param 1', val 1, 'param 2', val 2, . . . ) • IDX = kmeans(X, k) partitions the points in the n-by-p data matrix X into k clusters. This iterative partitioning minimizes the sum, over all clusters, of the within-cluster sums of point-to-cluster-centroid distances. Rows of X correspond to points, columns correspond to variables. By default, kmeans uses squared Euclidean distances. • IDX - n-by-1 vector containing the cluster indices of each point. • C - k-by-p matrix cluster centroid locations. • sumd - 1 -by-k vector within-cluster sums of point-to-centroid distances. • D - n-by-k matrix of distances from each point to every centroid.

Параметр ‘distance’ • 'sq. Euclidean‘ - Squared Euclidean distance (default). • 'cityblock‘ - Sum of absolute differences, i. e. , L 1. • 'cosine‘ - One minus the cosine of the included angle between points (treated as vectors). • 'correlation‘ - One minus the sample correlation between points (treated as sequences of values). • 'Hamming‘ - Percentage of bits that differ (only suitable for binary data).

Параметр ‘start’ • Method used to choose the initial cluster centroid positions, sometimes known as "seeds". Valid starting values are: • 'sample‘ - Select k observations from X at random (default). • 'uniform‘ - Select k points uniformly at random from the range of X. Not valid with Hamming distance. • 'cluster‘ - Perform a preliminary clustering phase on a random 10% subsample of X. This preliminary phase is itself initialized using 'sample'. • ‘Matrix’ - k-by-p matrix of centroid starting locations. In this case, you can pass in [] for k, and kmeans infers k from the first dimension of the matrix. You can also supply a 3 dimensional array, implying a value for the 'replicates' parameter from the array's third dimension.
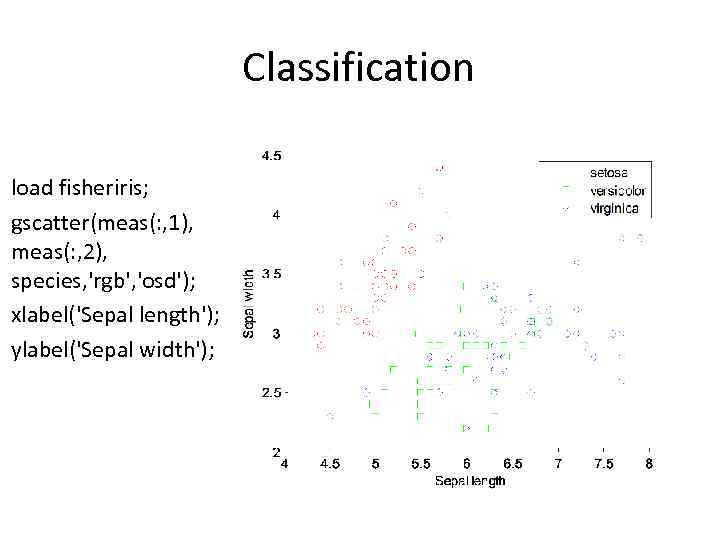
Classification load fisheriris; gscatter(meas(: , 1), meas(: , 2), species, 'rgb', 'osd'); xlabel('Sepal length'); ylabel('Sepal width');
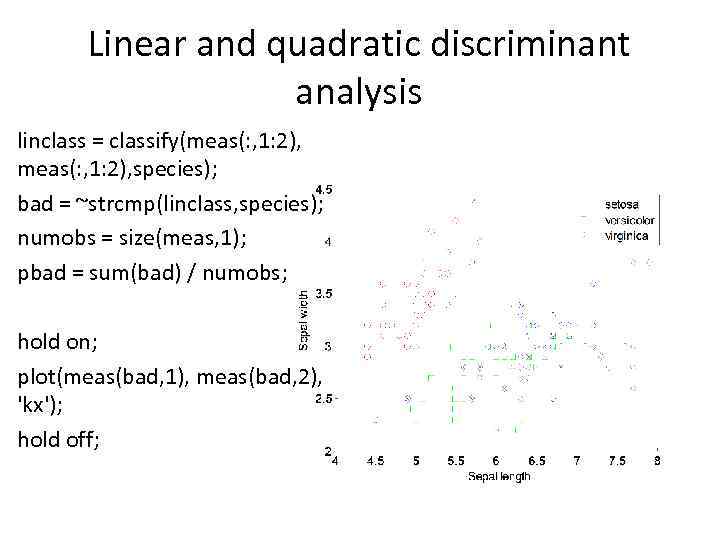
Linear and quadratic discriminant analysis linclass = classify(meas(: , 1: 2), species); bad = ~strcmp(linclass, species); numobs = size(meas, 1); pbad = sum(bad) / numobs; hold on; plot(meas(bad, 1), meas(bad, 2), 'kx'); hold off;
![Visualization regioning the plane [x, y] = meshgrid(4: . 1: 8, 2: . 1: Visualization regioning the plane [x, y] = meshgrid(4: . 1: 8, 2: . 1:](https://present5.com/presentation/187967559_443054254/image-10.jpg)
Visualization regioning the plane [x, y] = meshgrid(4: . 1: 8, 2: . 1: 4. 5); x = x(: ); y = y(: ); j = classify([x y], meas(: , 1: 2), species); gscatter(x, y, j, 'grb', 'sod')
![Decision trees tree = treefit(meas(: , 1: 2), species); [dtnum, dtnode, dtclass] = treeval(tree, Decision trees tree = treefit(meas(: , 1: 2), species); [dtnum, dtnode, dtclass] = treeval(tree,](https://present5.com/presentation/187967559_443054254/image-11.jpg)
Decision trees tree = treefit(meas(: , 1: 2), species); [dtnum, dtnode, dtclass] = treeval(tree, meas(: , 1: 2)); bad = ~strcmp(dtclass, species); sum(bad) / numobs
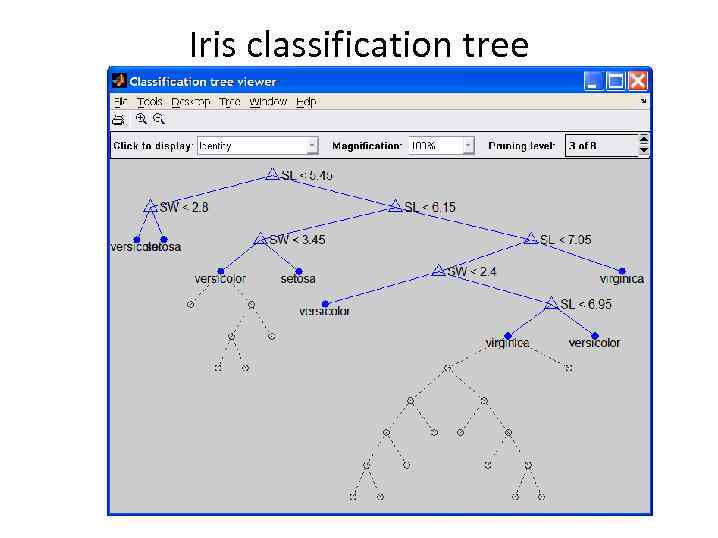
Iris classification tree
![Тестирование качества классификации resubcost = treetest(tree, 'resub'); [cost, secost, ntermnodes, bestlevel] = treetest(tree, 'cross', Тестирование качества классификации resubcost = treetest(tree, 'resub'); [cost, secost, ntermnodes, bestlevel] = treetest(tree, 'cross',](https://present5.com/presentation/187967559_443054254/image-13.jpg)
Тестирование качества классификации resubcost = treetest(tree, 'resub'); [cost, secost, ntermnodes, bestlevel] = treetest(tree, 'cross', meas(: , 1: 2), species); plot(ntermnodes, cost, 'b-', ntermnodes, resubcost, 'r--') figure(gcf); xlabel('Number of terminal nodes'); ylabel('Cost (misclassification error)') legend('Cross-validation', 'Resubstitution')
![Выбор уровня [mincost, minloc] = min(cost); cutoff = mincost + secost(minloc); hold on plot([0 Выбор уровня [mincost, minloc] = min(cost); cutoff = mincost + secost(minloc); hold on plot([0](https://present5.com/presentation/187967559_443054254/image-14.jpg)
Выбор уровня [mincost, minloc] = min(cost); cutoff = mincost + secost(minloc); hold on plot([0 20], [cutoff], 'k: ') plot(ntermnodes(bestlevel+1), cost(bestlevel+1), 'mo') legend('Cross-validation', 'Resubstitution', 'Min + 1 std. err. ', 'Best choice') hold off

Оптимальное дерево классификации prunedtree = treeprune(tree, bestlevel); treedisp(prunedtree) cost(bestlevel+1) >> ans = 0. 22
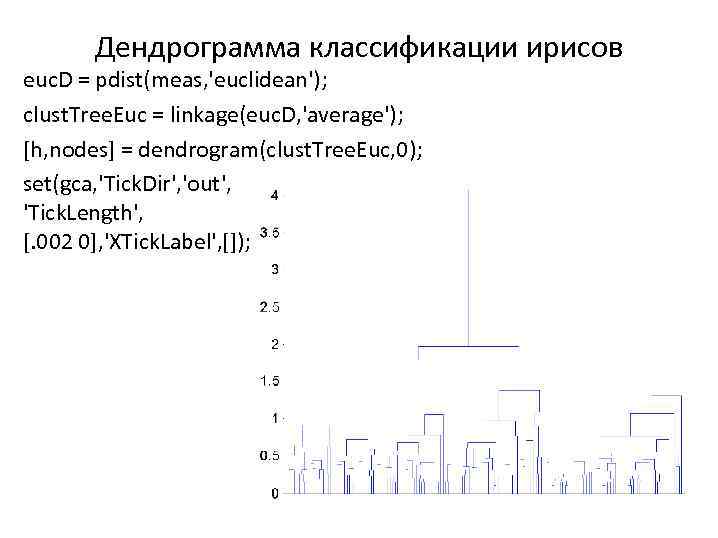
Дендрограмма классификации ирисов euc. D = pdist(meas, 'euclidean'); clust. Tree. Euc = linkage(euc. D, 'average'); [h, nodes] = dendrogram(clust. Tree. Euc, 0); set(gca, 'Tick. Dir', 'out', 'Tick. Length', [. 002 0], 'XTick. Label', []);
Lect9-10.pptx