1fc8af3a54ab94c536e9b25ec37349f0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 86

Statistics 322 Object Oriented Data Analysis J. S. Marron Dept. of Statistics and Operations Research University of North Carolina

Administrative Info • Details on Course Web Page http: //www. unc. edu/~marron/ UNCstat 322 -2005/Home. Page. html • Go Through These

Who are we? • Varying Levels of Expertise – 2 nd Year Graduate Students –… – Senior Professors • Various Backgrounds – Statistics – Computer Science – Imaging – Bioinformatics – Other?
Object Oriented Data Analysis What is it? A personal view: What is the “atom of the statistical analysis”? • 1 st Course: Numbers • Multivariate Analysis Course : Vectors • Functional Data Analysis: Curves • More generally: Data Objects

Functional Data Analysis Active new field in statistics, see: Ramsay, J. O. & Silverman, B. W. (2005) Functional Data Analysis, 2 nd Edition, Springer, N. Y. ISBN 0 -387 -40080 -X (cited 8/30/05) Ramsay, J. O. & Silverman, B. W. (2002) Applied Functional Data Analysis, Springer, N. Y. ISBN 0 -38795414 -7 (cited 8/30/05) Ramsay, J. O. (2005) Functional Data Analysis Web Site, http: //ego. psych. mcgill. ca/misc/fda/ (cited 8/30/05)
Object Oriented Data Analysis Nomenclature Clash? Computer Science View: Object Oriented Programming: Programming that supports encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism (from Google: define object oriented programming, my favorite: www. innovatia. com/software/papers/com. htm)
Object Oriented Data Analysis Another View: J. O. Ramsay http: //www. psych. mcgill. ca/faculty/ramsay. html “Functional Data Objects” (closer to C. S. meaning) Personal Objection: “Functional” in mathematics is: “Function that operates on functions”
Object Oriented Data Analysis • Apologies for these cross – cultural distortions • But “OODA” has a nice sound • Hence will use it (Until somebody suggests a better name…)
Object Oriented Data Analysis Next time: comment from Randy Eubank: • About "Object Oriented data Analysis": • Name appeared in Florida FDA Meeting: • http: //www. stat. ufl. edu/symposium/2003/fu ndat/
Object Oriented Data Analysis Next time: list major statistical tasks: • Understanding population structure • Classification (i. e. Discrimination) • Time Series of Data Objects
Visualization • How do we look at data? • Start in Euclidean Space, • Will later study other spaces

Notation Note: many statisticians prefer “p”, not “d” (perhaps for “parameters” or “predictors”) I will use “d” for “dimension” (with idea that it is more broadly understandable)

Visualization How do we look at Euclidean data? • 1 -d: histograms, etc. • 2 -d: scatterplots • 3 -d: spinning point clouds

Visualization How do we look at Euclidean data? • Higher Dimensions? Workhorse Idea: Projections

Projection Important Point • There are many “directions of interest” on which projection is useful An important set of directions: Principal Components
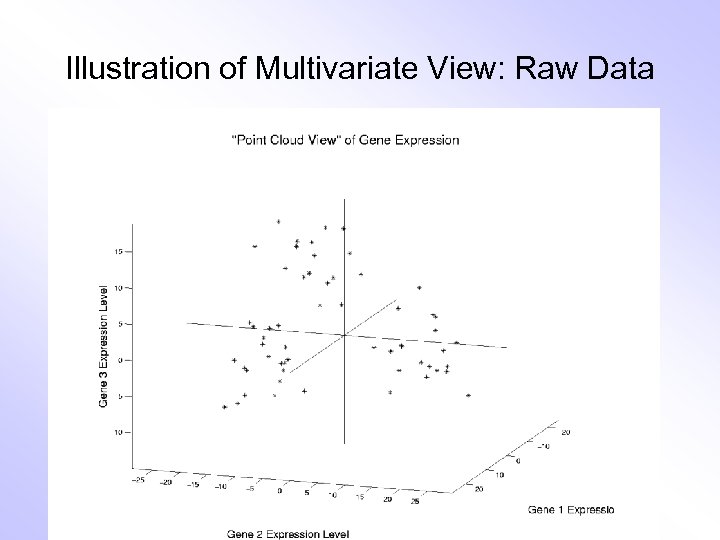
Illustration of Multivariate View: Raw Data
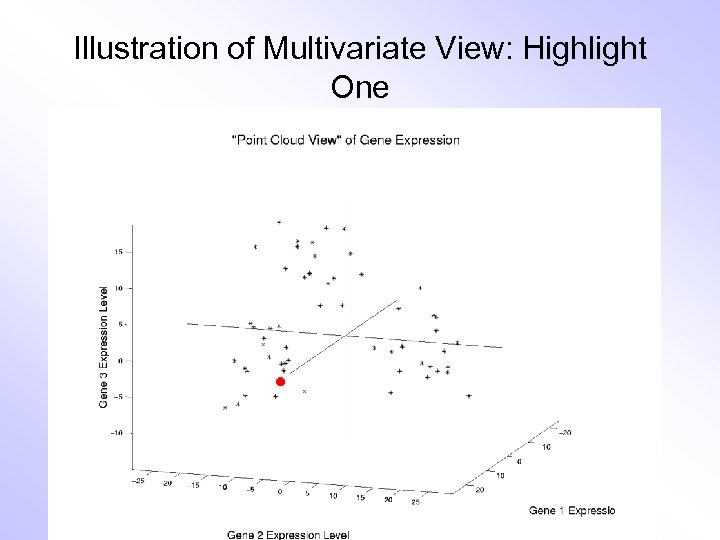
Illustration of Multivariate View: Highlight One
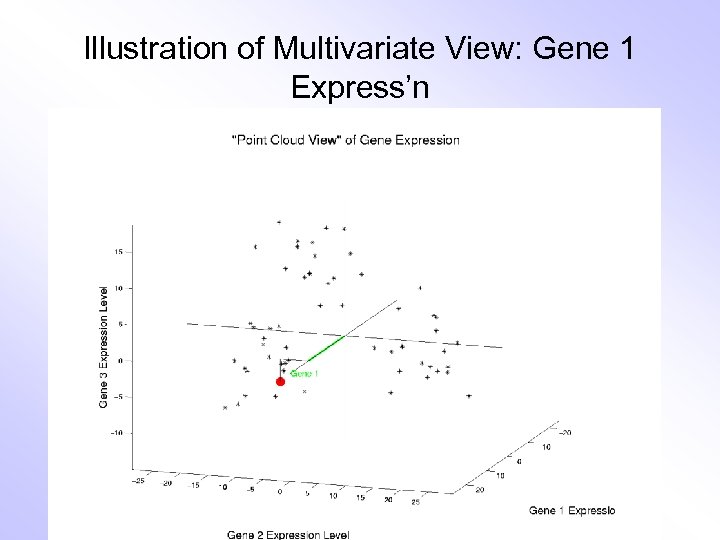
Illustration of Multivariate View: Gene 1 Express’n
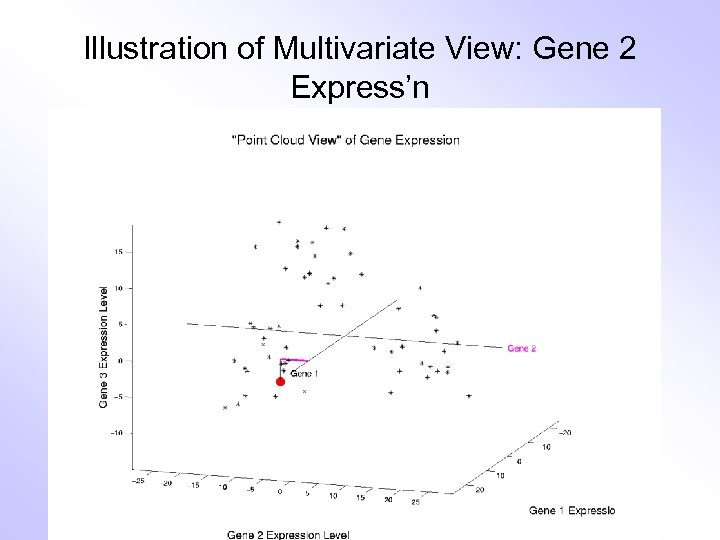
Illustration of Multivariate View: Gene 2 Express’n
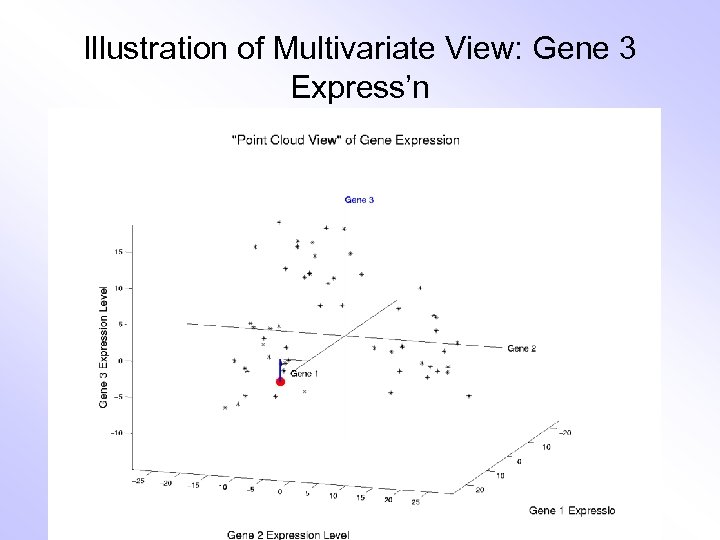
Illustration of Multivariate View: Gene 3 Express’n
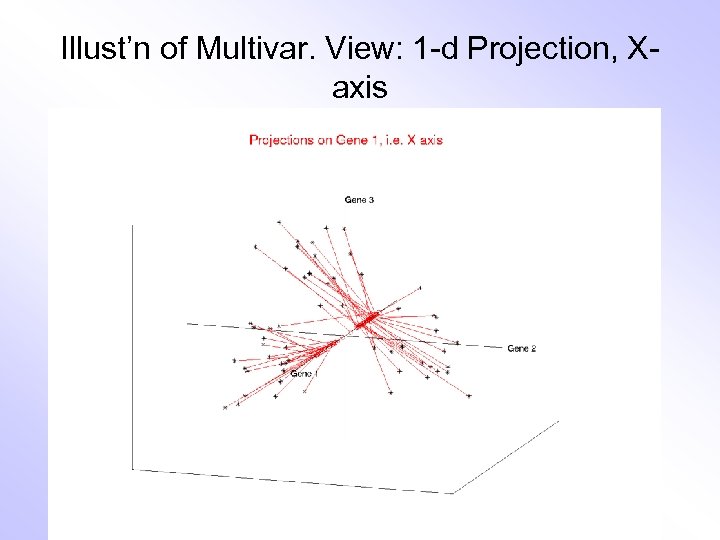
Illust’n of Multivar. View: 1 -d Projection, Xaxis
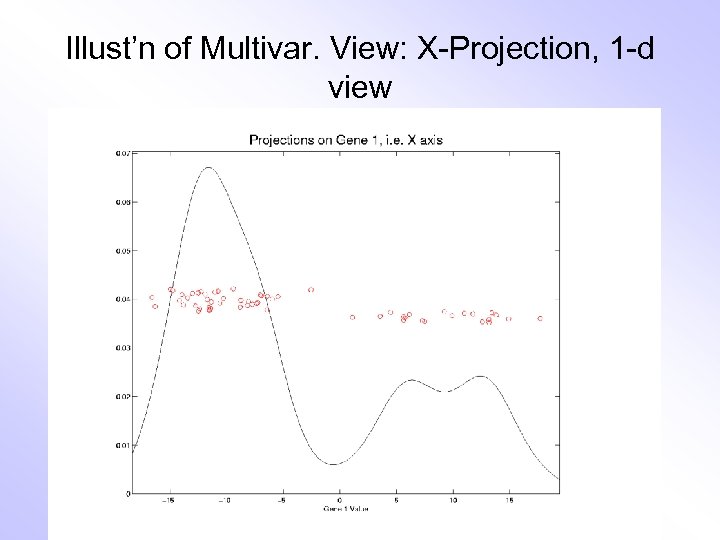
Illust’n of Multivar. View: X-Projection, 1 -d view
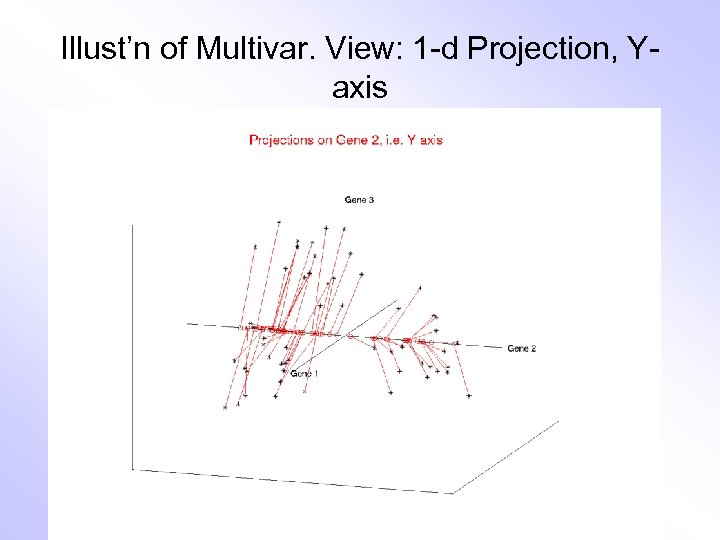
Illust’n of Multivar. View: 1 -d Projection, Yaxis
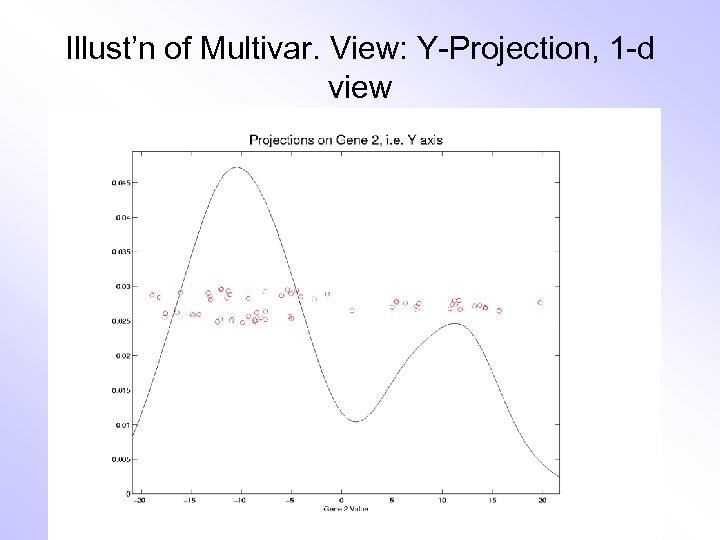
Illust’n of Multivar. View: Y-Projection, 1 -d view
Illust’n of Multivar. View: 1 -d Projection, Zaxis
Illust’n of Multivar. View: Z-Projection, 1 -d view

Illust’n of Multivar. View: 2 -d Proj’n, XYplane
Illust’n of Multivar. View: XY-Proj’n, 2 -d view
Illust’n of Multivar. View: 2 -d Proj’n, XZplane
Illust’n of Multivar. View: XZ-Proj’n, 2 -d view
Illust’n of Multivar. View: 2 -d Proj’n, YZplane
Illust’n of Multivar. View: YZ-Proj’n, 2 -d view
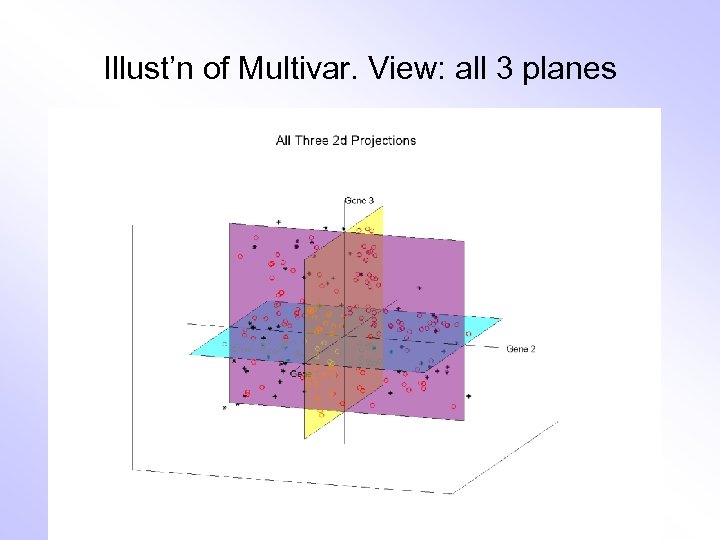
Illust’n of Multivar. View: all 3 planes

Illust’n of Multivar. View: Diagonal 1 -d proj’ns
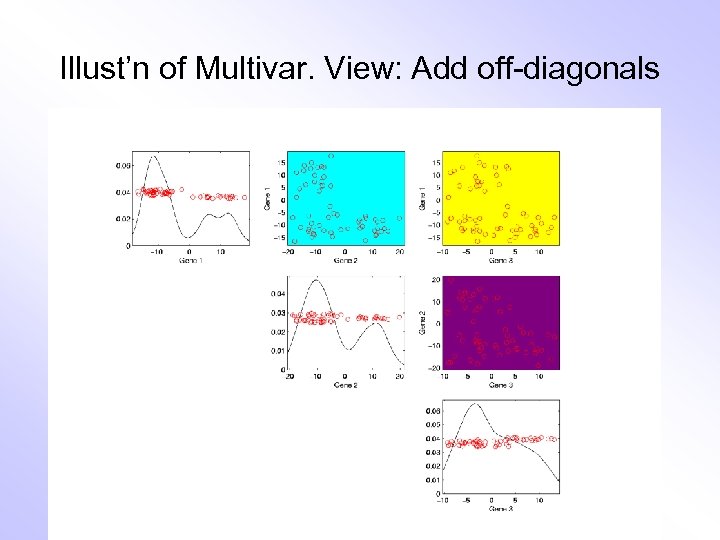
Illust’n of Multivar. View: Add off-diagonals
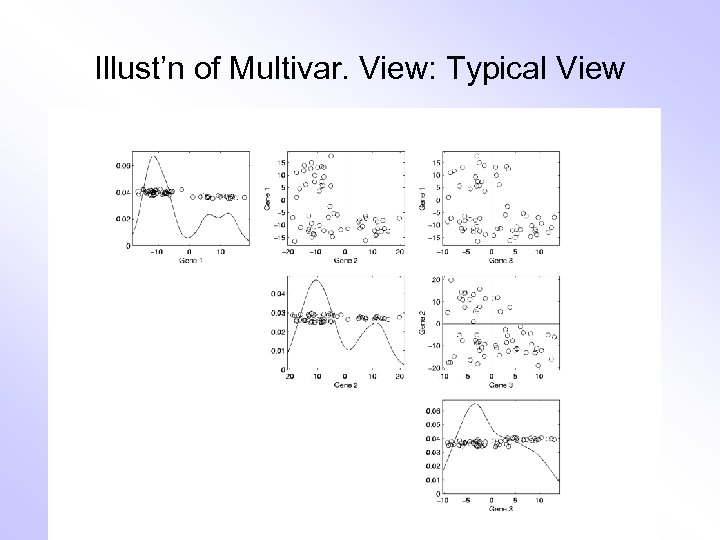
Illust’n of Multivar. View: Typical View

Projection Important Point • There are many “directions of interest” on which projection is useful An important set of directions: Principal Components

Principal Components Find Directions of: “Maximal (projected) Variation” • Compute Sequentially • On orthogonal subspaces Will take careful look at mathematics later
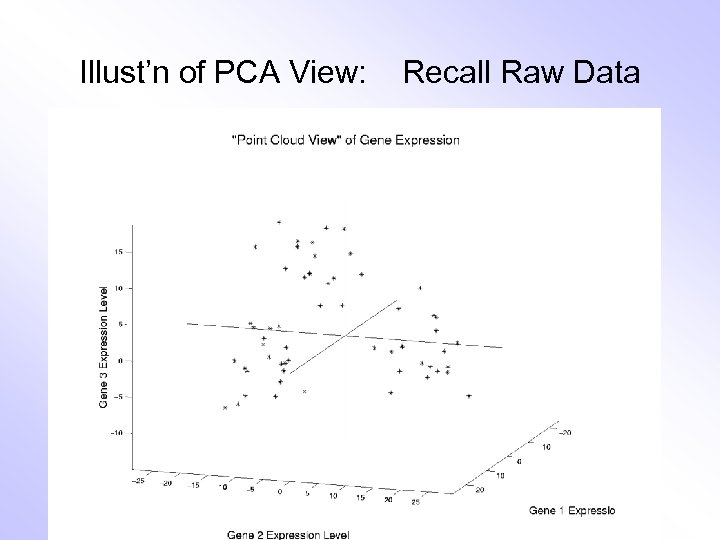
Illust’n of PCA View: Recall Raw Data
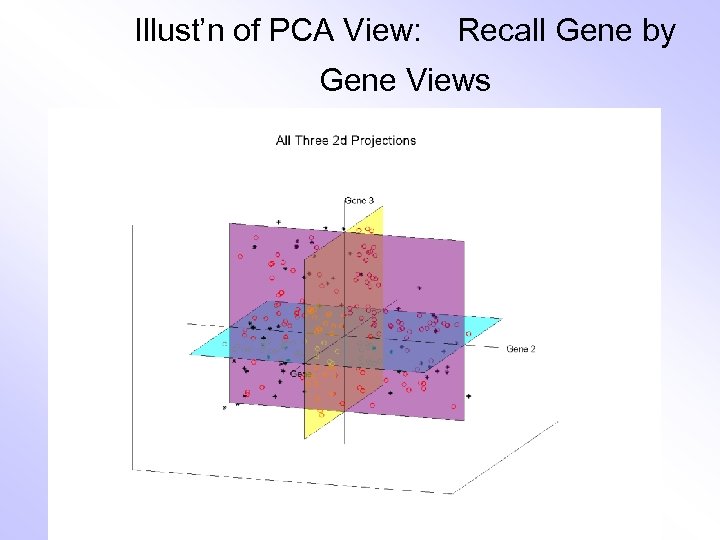
Illust’n of PCA View: Recall Gene by Gene Views
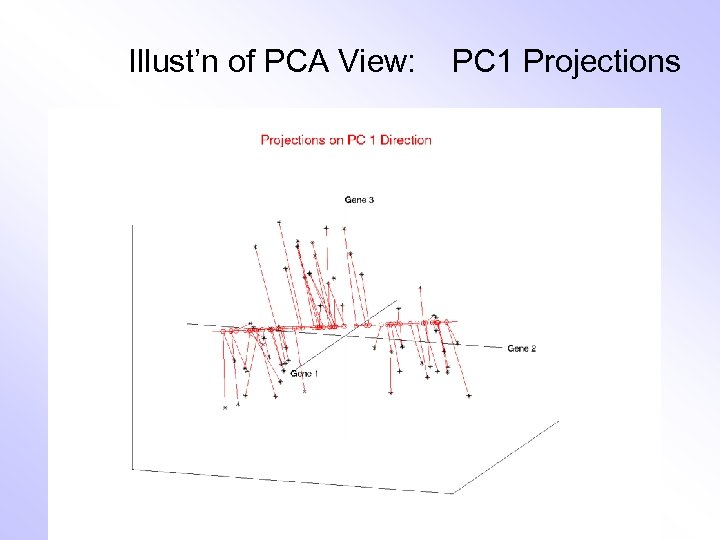
Illust’n of PCA View: PC 1 Projections
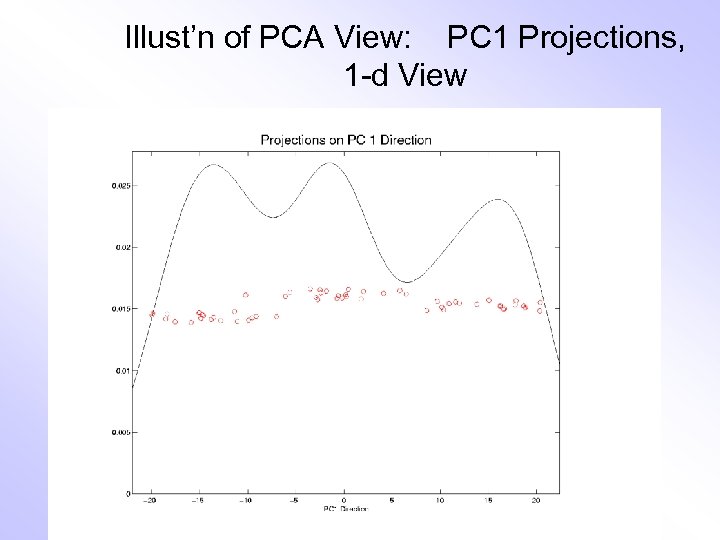
Illust’n of PCA View: PC 1 Projections, 1 -d View
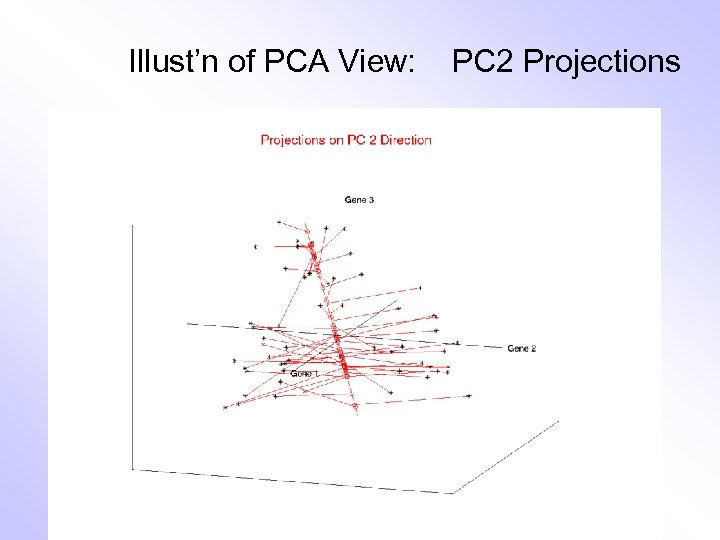
Illust’n of PCA View: PC 2 Projections
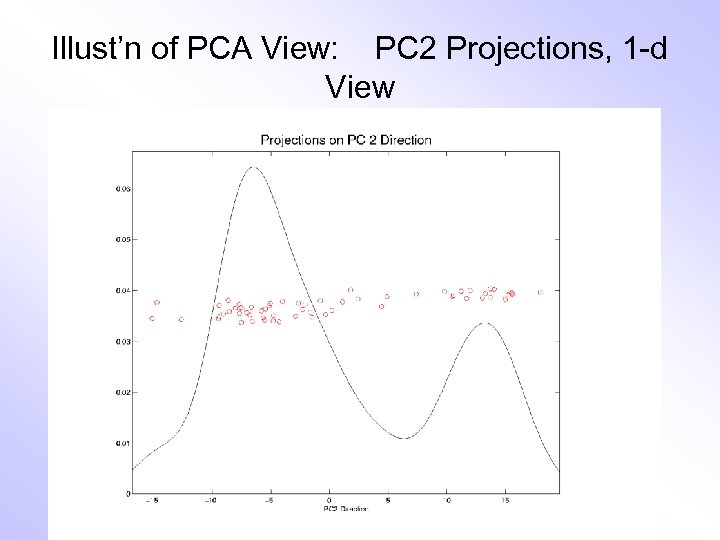
Illust’n of PCA View: PC 2 Projections, 1 -d View
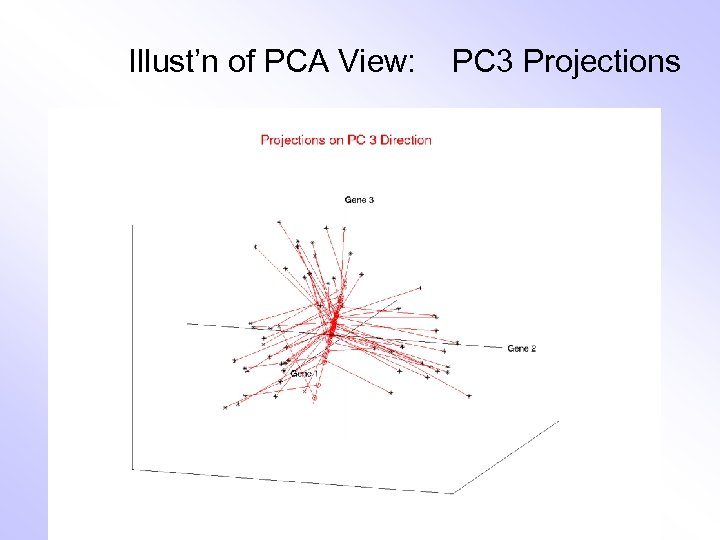
Illust’n of PCA View: PC 3 Projections
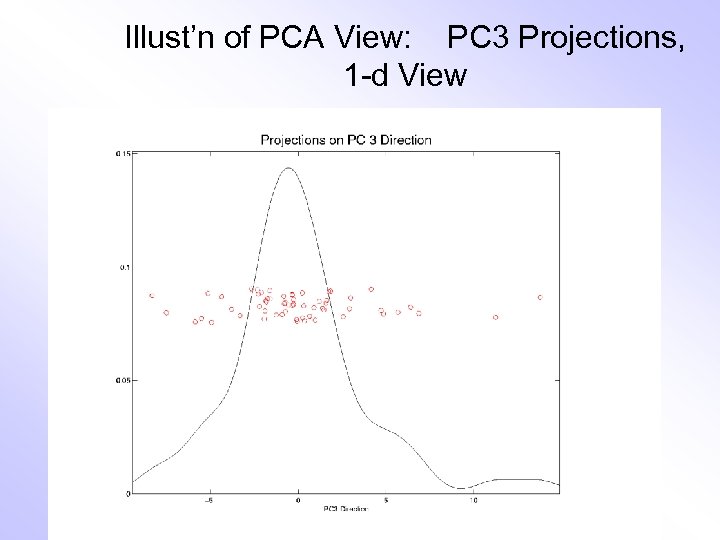
Illust’n of PCA View: PC 3 Projections, 1 -d View
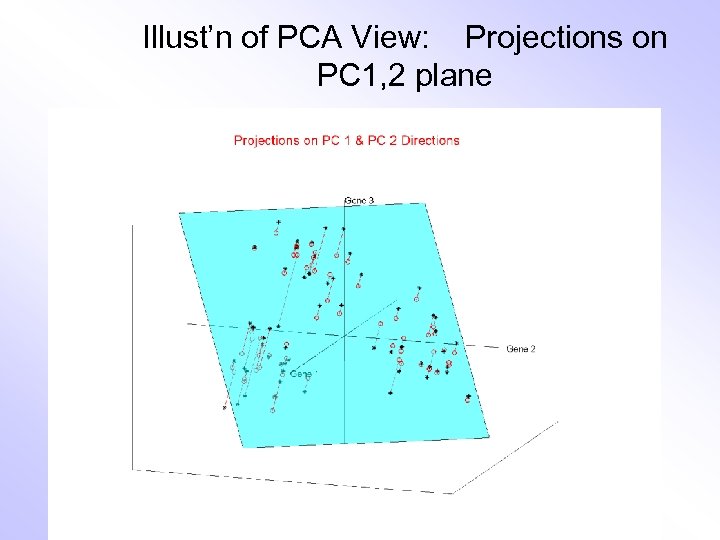
Illust’n of PCA View: Projections on PC 1, 2 plane
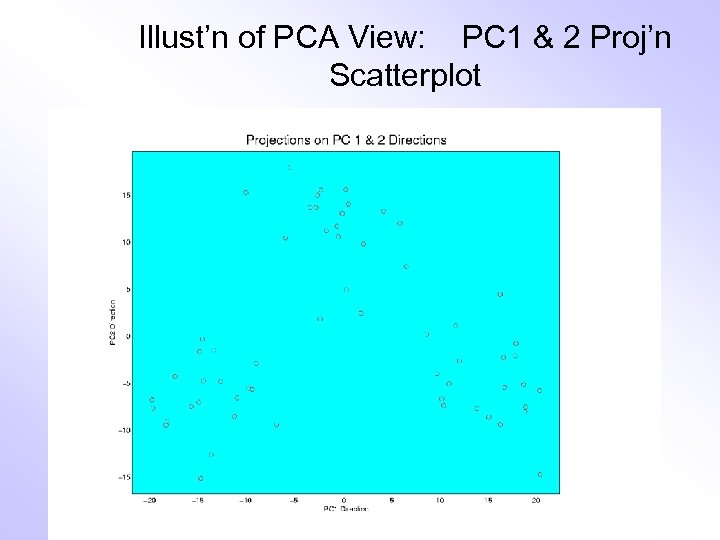
Illust’n of PCA View: PC 1 & 2 Proj’n Scatterplot
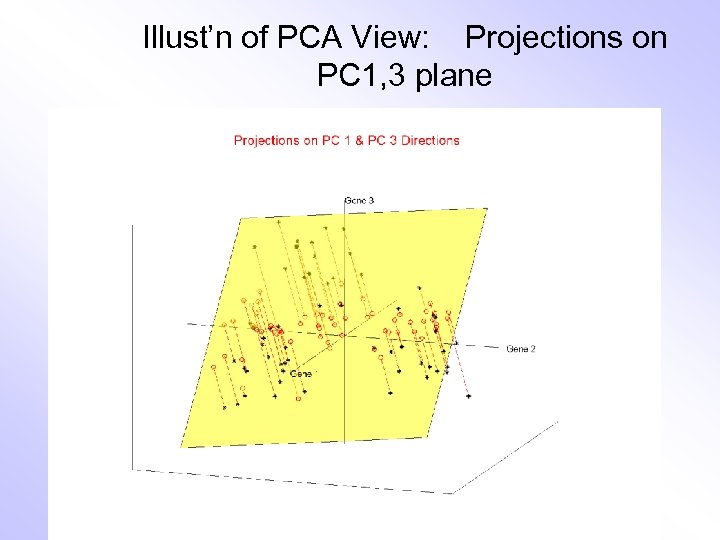
Illust’n of PCA View: Projections on PC 1, 3 plane
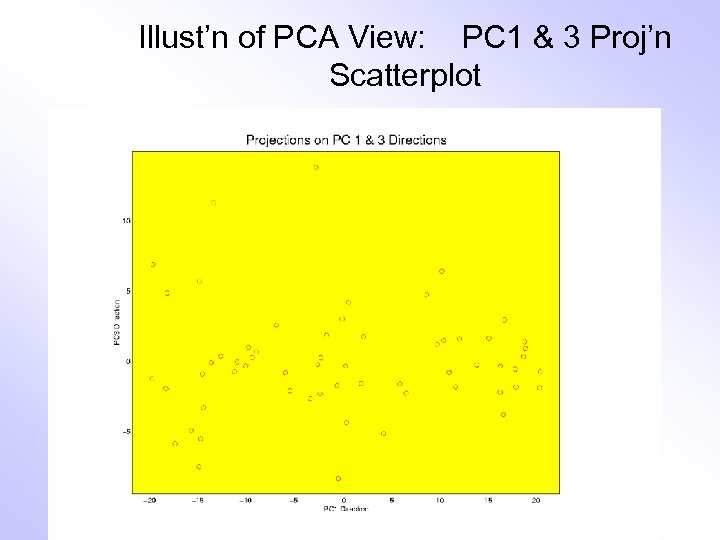
Illust’n of PCA View: PC 1 & 3 Proj’n Scatterplot
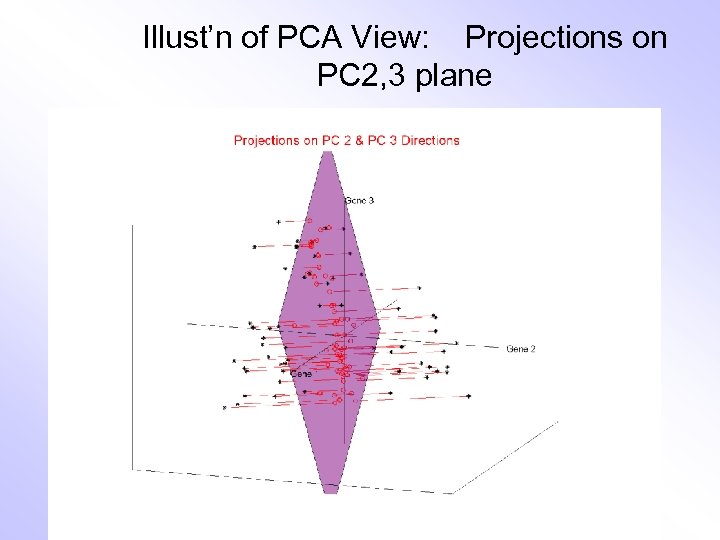
Illust’n of PCA View: Projections on PC 2, 3 plane
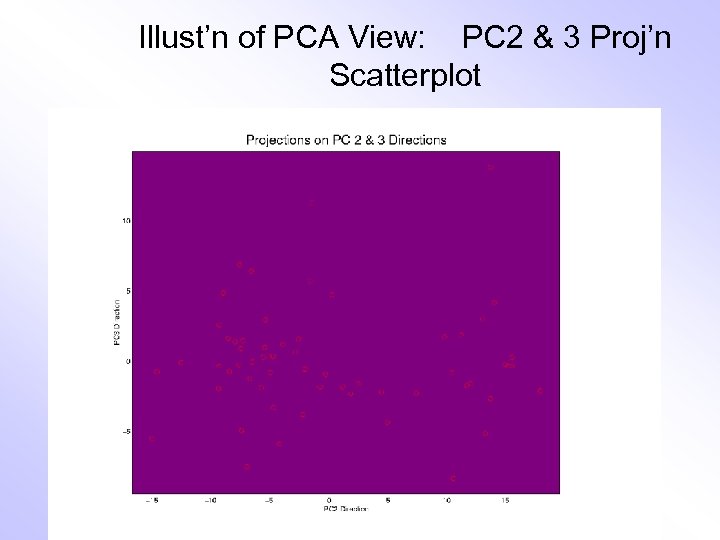
Illust’n of PCA View: PC 2 & 3 Proj’n Scatterplot
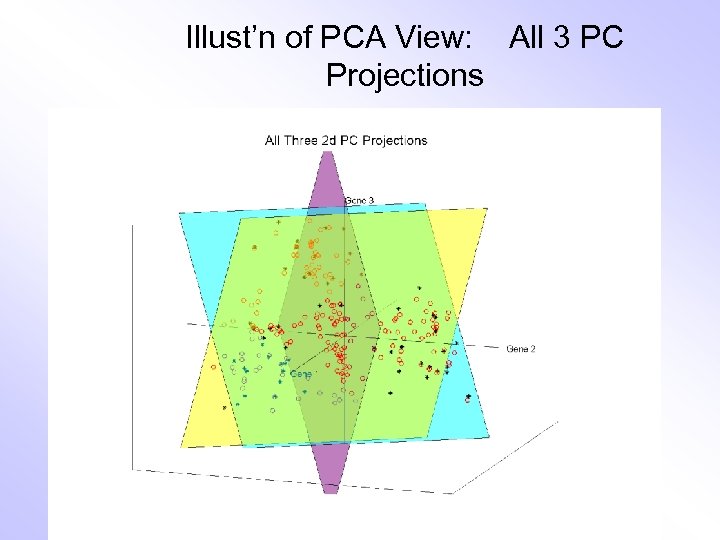
Illust’n of PCA View: All 3 PC Projections
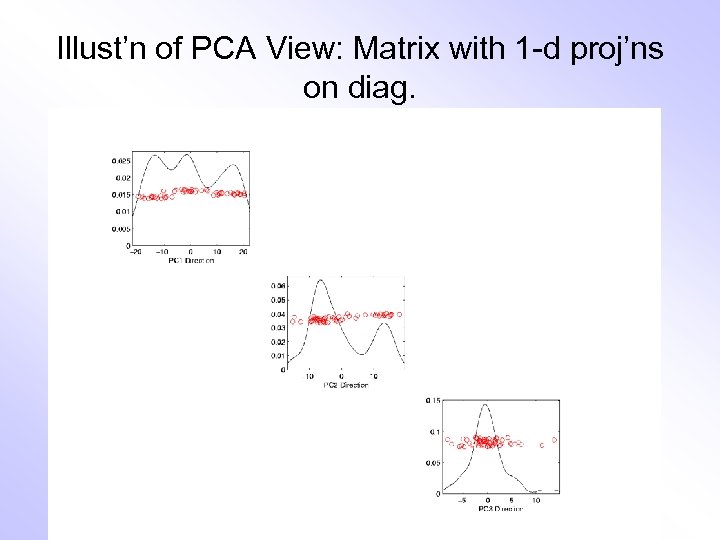
Illust’n of PCA View: Matrix with 1 -d proj’ns on diag.
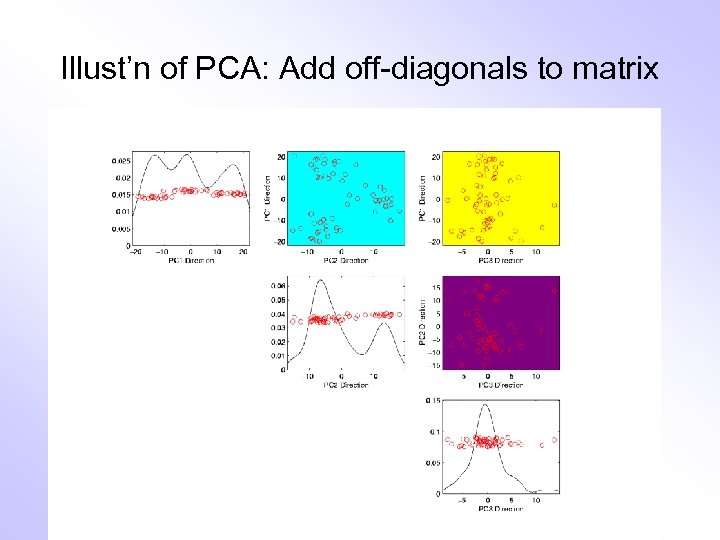
Illust’n of PCA: Add off-diagonals to matrix
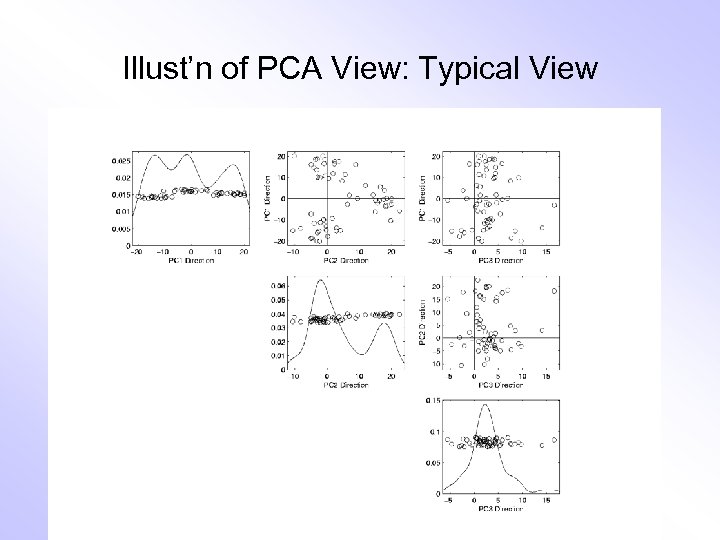
Illust’n of PCA View: Typical View

Comparison of Views • Highlight 3 clusters • Gene by Gene View – Clusters appear in all 3 scatterplots – But never very separated • PCA View – 1 st shows three distinct clusters – Better separated than in gene view – Clustering concentrated in 1 st scatterplot • Effect is small, since only 3 -d
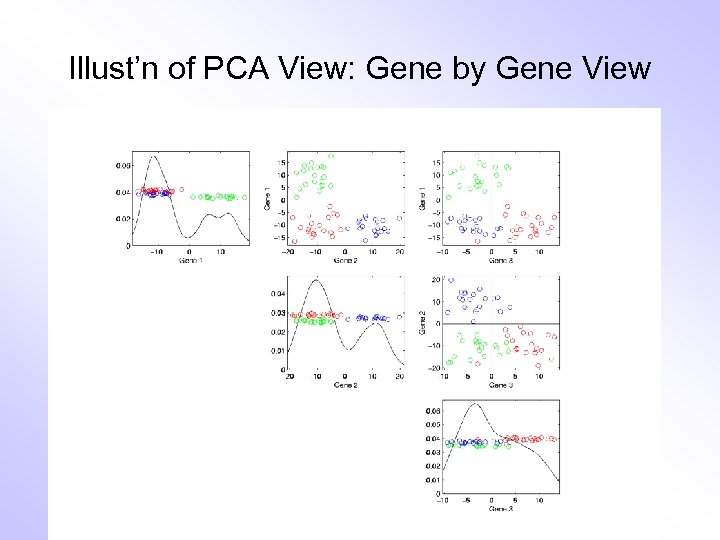
Illust’n of PCA View: Gene by Gene View
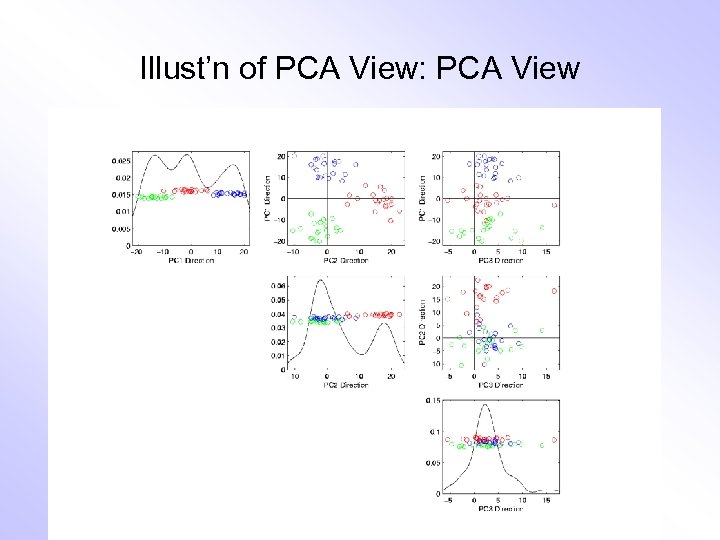
Illust’n of PCA View: PCA View
Another Comparison of Views • Much higher dimension, # genes = 4000 • Gene by Gene View – Clusters very nearly the same – Very slight difference in means • PCA View – Huge difference in 1 st PC Direction – Magnification of clustering – Lesson: Alternate views can show much more – (especially in high dimensions, i. e. for many genes) – Shows PC view is very useful
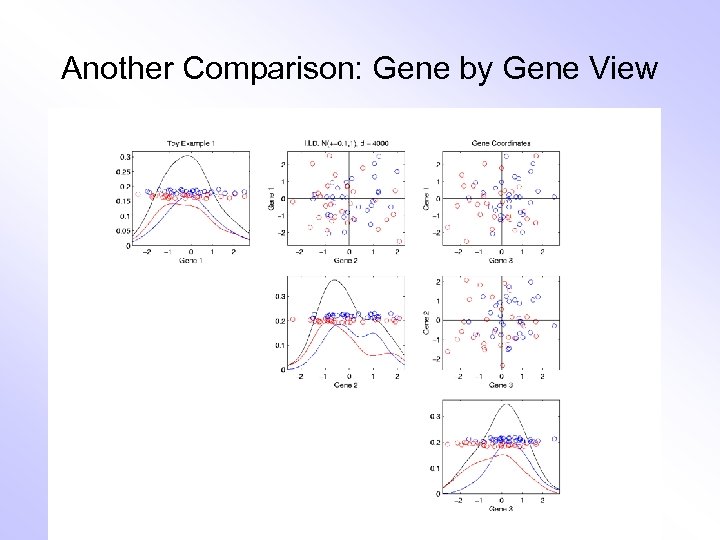
Another Comparison: Gene by Gene View
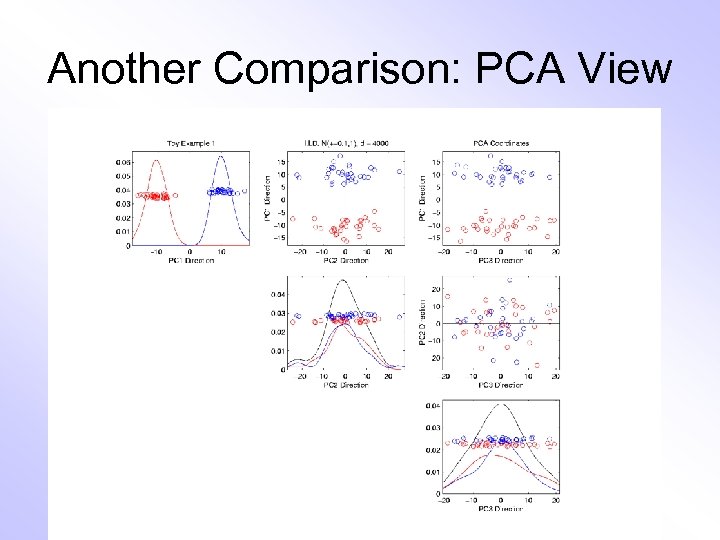
Another Comparison: PCA View
Data Object Conceptualization Object Space Feature Space Curves Images Manifolds Shapes Tree Space Trees

Data Object Conceptualization Next time: Terminology: “feature vector” from field of Statistical Pattern Recognition Famous reference (there are many): Devijver, P. A. and Kittler, J. (1982) Pattern Recognition: A Statistical Approach, Prentice Hall, London. Caution: “features” in that field are entries of vectors For me, “features” are “aspects of populations”
E. g. Curves As Data Object Space: Set of curves Feature Space(s): • Curves digitized to vectors (look at 1 st) • Basis Representations: • Fourier (sin & cos) • B-splines • Wavelets

E. g. Curves As Data, I Very simple example (Travis Gaydos) • “ 2 dimensional” family of (digitized) curves • Object space: piece-wise linear f’ns • Feature space = PCA: reveals “population structure”
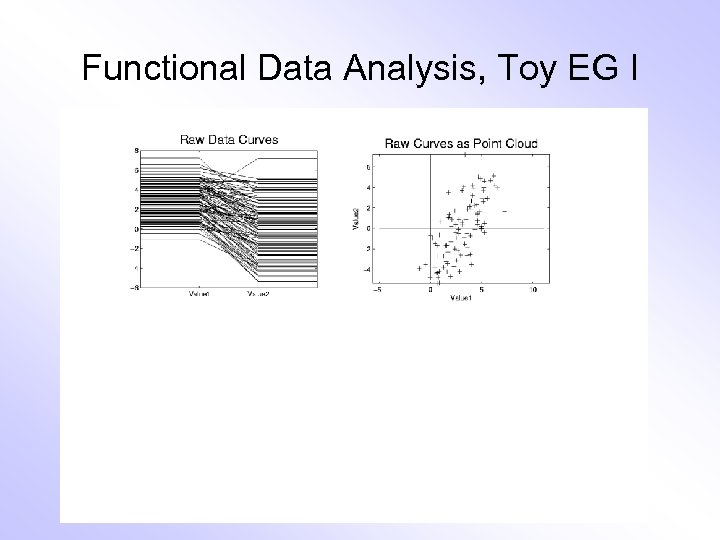
Functional Data Analysis, Toy EG I
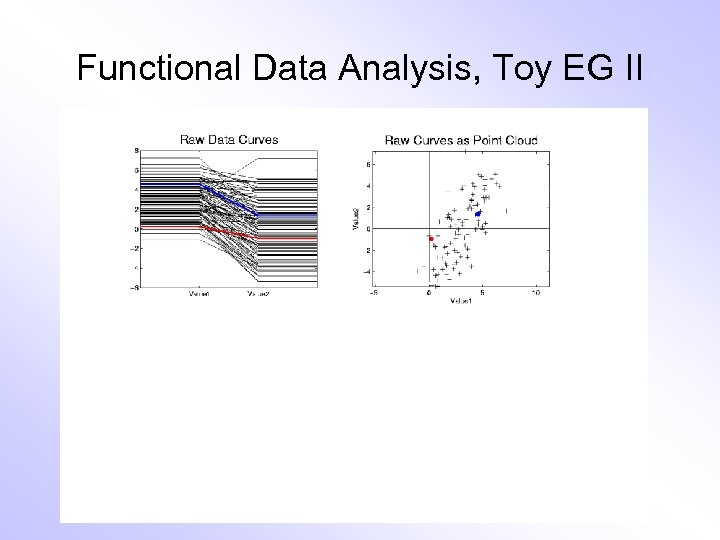
Functional Data Analysis, Toy EG II
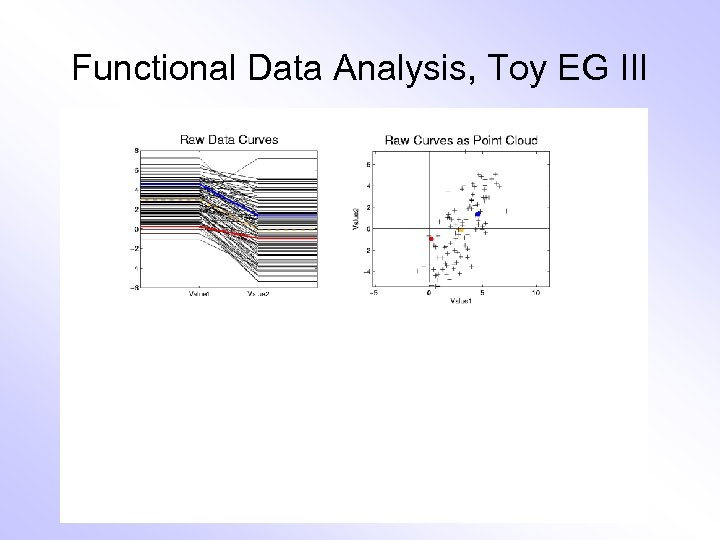
Functional Data Analysis, Toy EG III
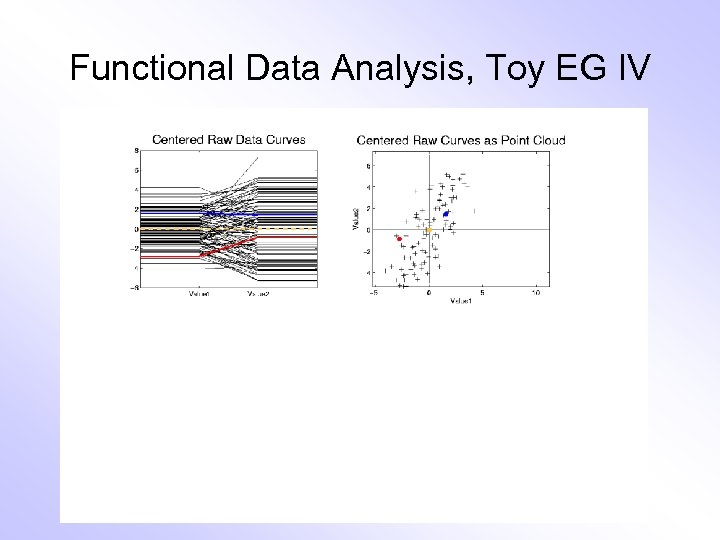
Functional Data Analysis, Toy EG IV
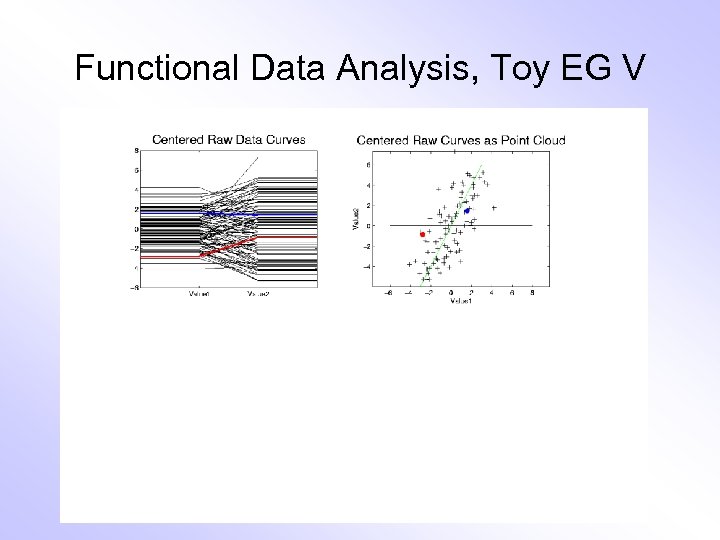
Functional Data Analysis, Toy EG V
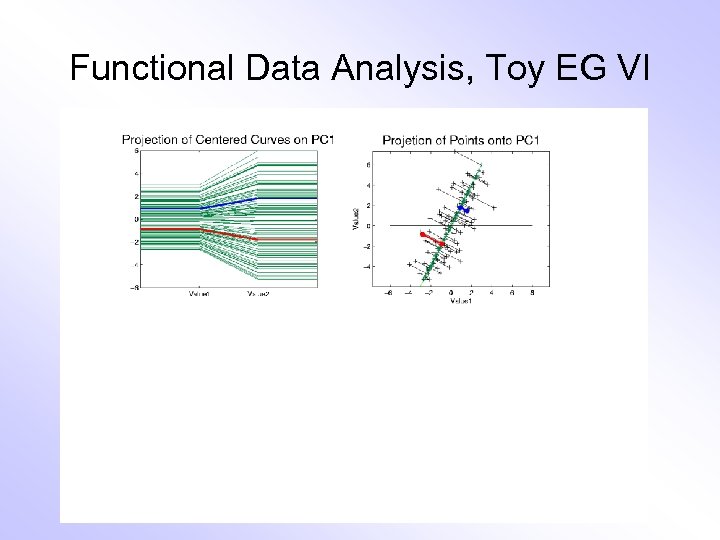
Functional Data Analysis, Toy EG VI
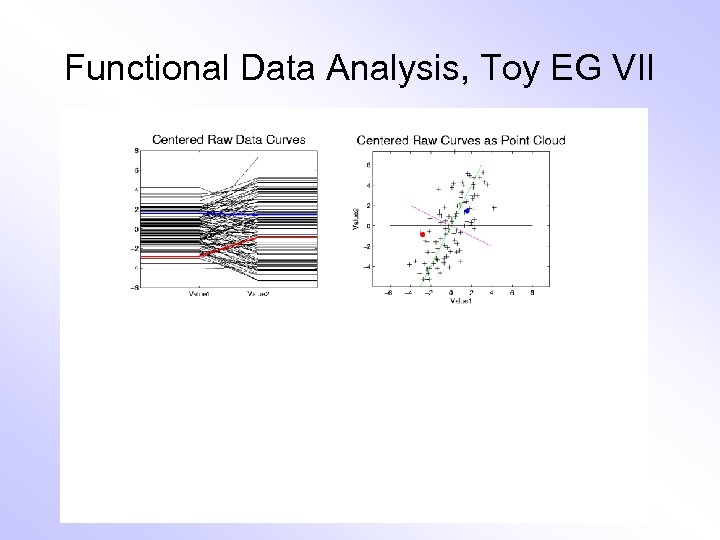
Functional Data Analysis, Toy EG VII
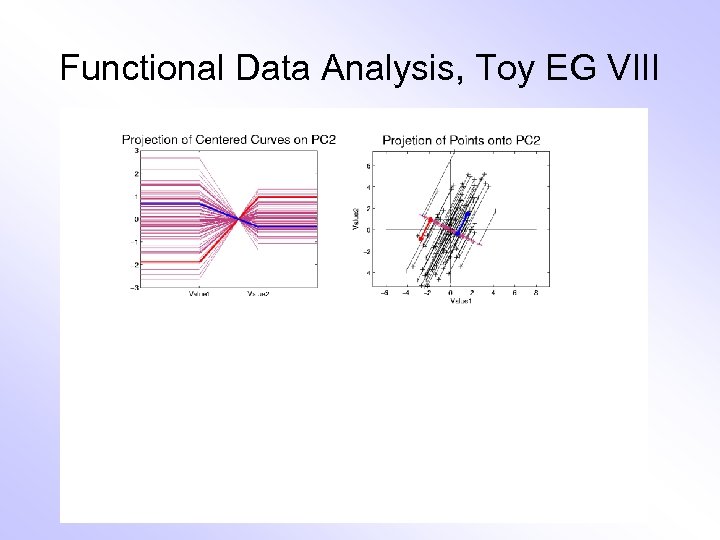
Functional Data Analysis, Toy EG VIII
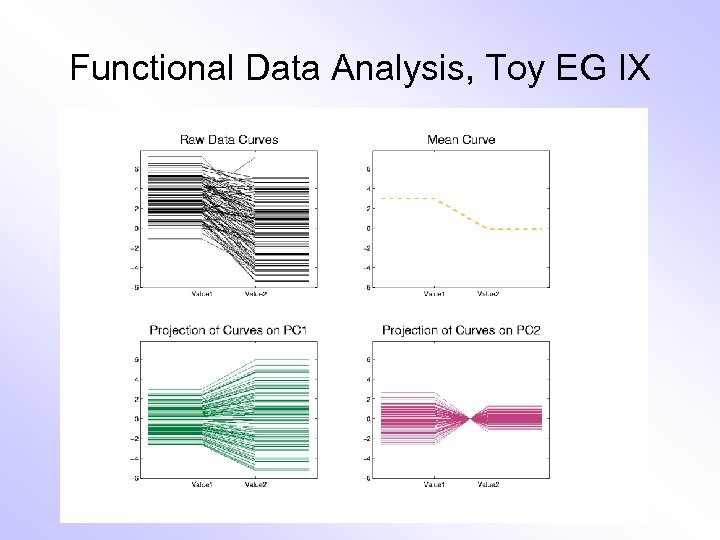
Functional Data Analysis, Toy EG IX
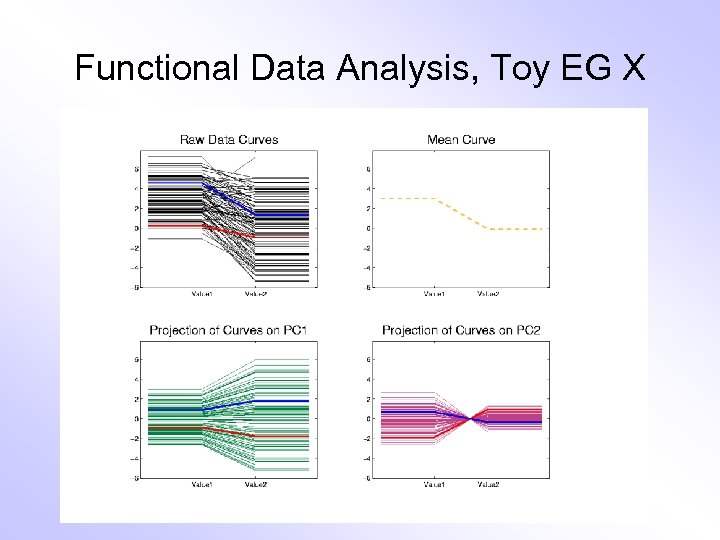
Functional Data Analysis, Toy EG X
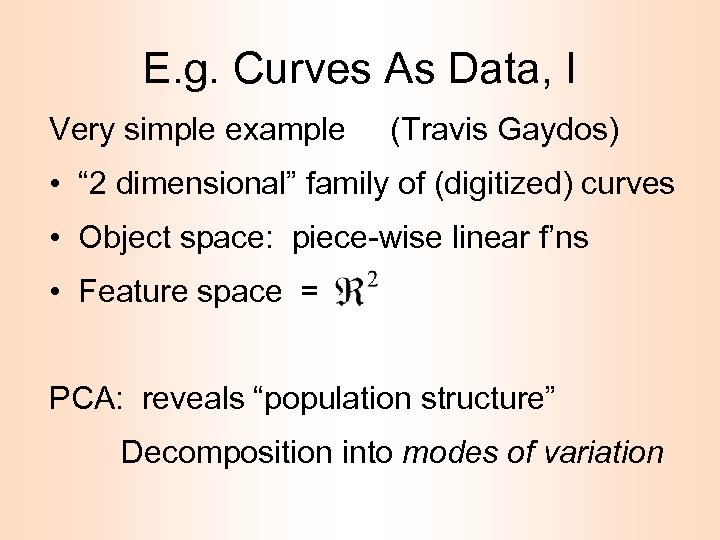
E. g. Curves As Data, I Very simple example (Travis Gaydos) • “ 2 dimensional” family of (digitized) curves • Object space: piece-wise linear f’ns • Feature space = PCA: reveals “population structure” Decomposition into modes of variation
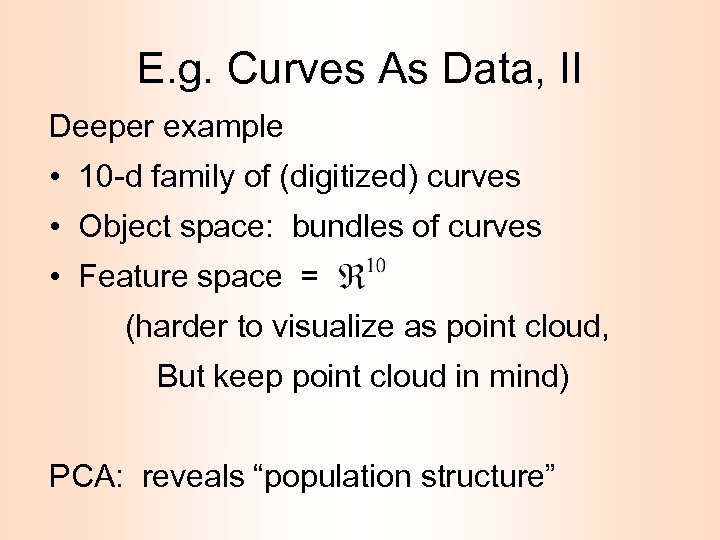
E. g. Curves As Data, II Deeper example • 10 -d family of (digitized) curves • Object space: bundles of curves • Feature space = (harder to visualize as point cloud, But keep point cloud in mind) PCA: reveals “population structure”
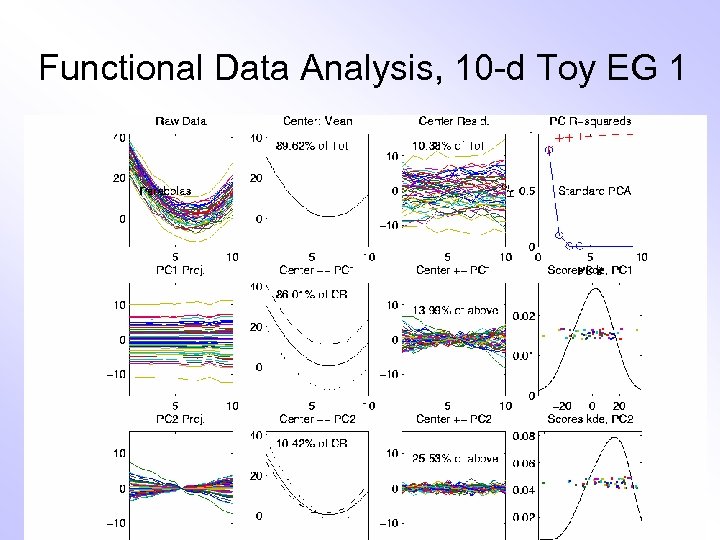
Functional Data Analysis, 10 -d Toy EG 1
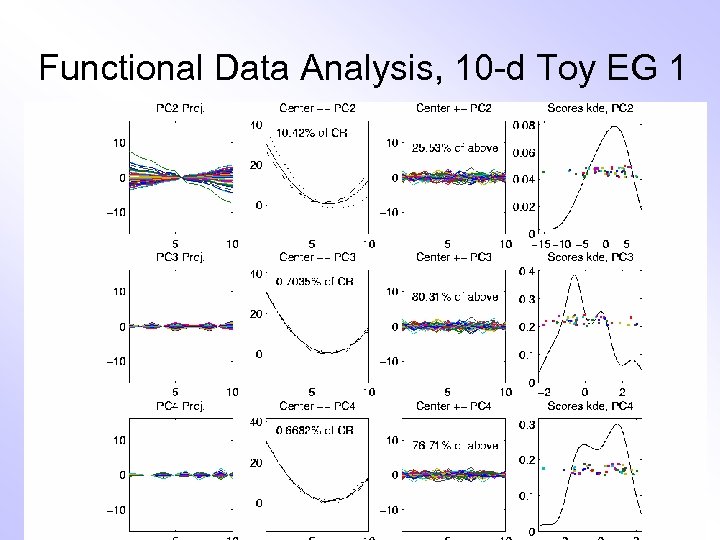
Functional Data Analysis, 10 -d Toy EG 1

E. g. Curves As Data, II PCA: reveals “population structure” • Mean Parabolic Structure • PC 1 Vertical Shift • PC 2 Tilt • higher PCs Gaussian (spherical) Decomposition into modes of variation
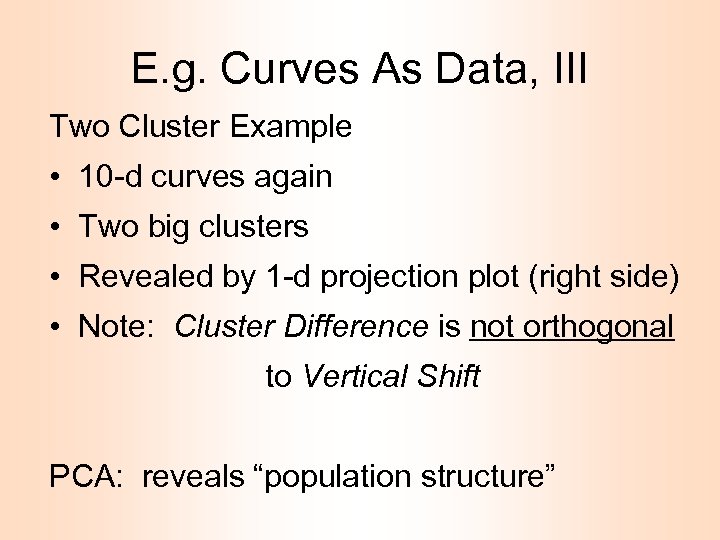
E. g. Curves As Data, III Two Cluster Example • 10 -d curves again • Two big clusters • Revealed by 1 -d projection plot (right side) • Note: Cluster Difference is not orthogonal to Vertical Shift PCA: reveals “population structure”
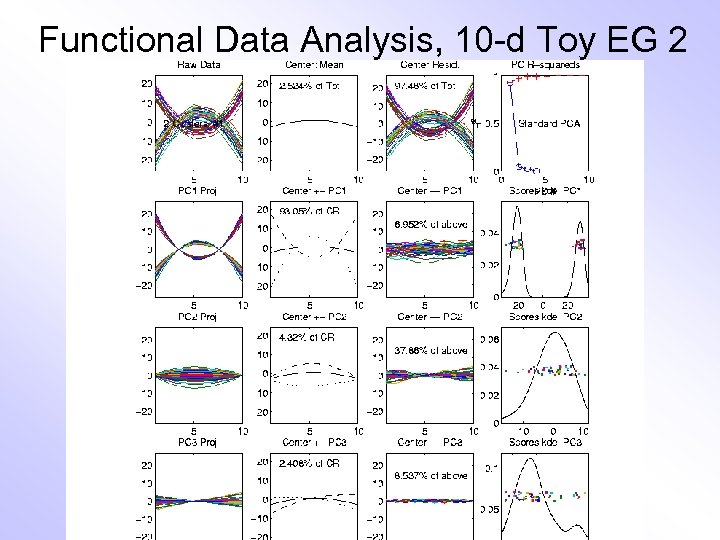
Functional Data Analysis, 10 -d Toy EG 2
E. g. Curves As Data, IV More Complicated Example • 10 -d curves again • Pop’n structure hard to see in 1 -d • 2 -d projections make structure clear PCA: reveals “population structure”
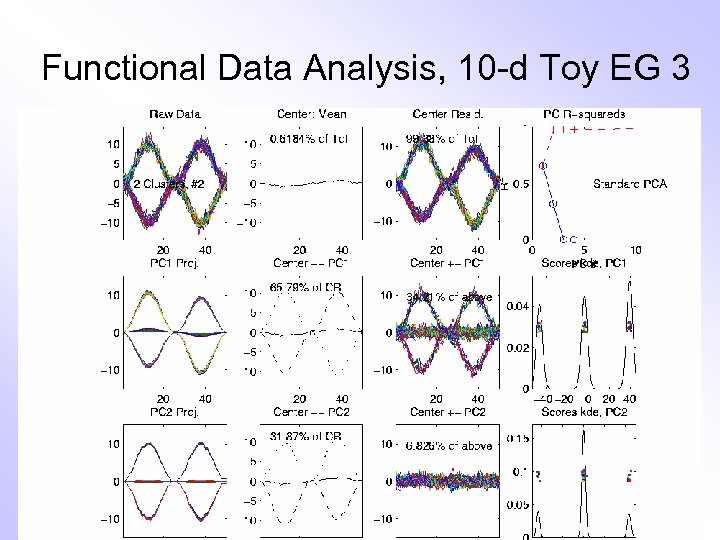
Functional Data Analysis, 10 -d Toy EG 3
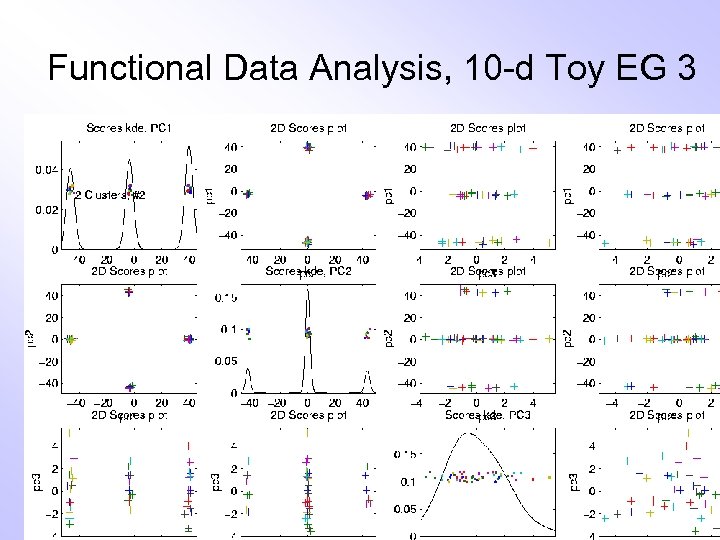
Functional Data Analysis, 10 -d Toy EG 3
1fc8af3a54ab94c536e9b25ec37349f0.ppt