a9c6187e1c23f547e47e6a72a8833008.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Statistical Reporting System OECD DAC Simon Scott Development Cooperation Directorate, OECD 28 October 2009 Bratislava, Slovak Republic
Statistical Reporting System OECD DAC Simon Scott Development Cooperation Directorate, OECD 28 October 2009 Bratislava, Slovak Republic
 What is the DAC? • • 22 Bilateral Donors, plus European Commission (EC). • Objective: improve development assistance through coordination and collaboration with major stakeholders. • 2 Development Assistance Committee (DAC) of the OECD. Collect and synthesize data on aid and foreign assistance and deliver the data to the public.
What is the DAC? • • 22 Bilateral Donors, plus European Commission (EC). • Objective: improve development assistance through coordination and collaboration with major stakeholders. • 2 Development Assistance Committee (DAC) of the OECD. Collect and synthesize data on aid and foreign assistance and deliver the data to the public.
 DAC Statistics • • 3 Measure resources for development (not just aid) including; üOfficial Development Assistance (ODA) üOther Official Flows (OOF) üPrivate Flows üNet Private Grants DAC statistics are the only reliable source of both total and comparative data on aid performance
DAC Statistics • • 3 Measure resources for development (not just aid) including; üOfficial Development Assistance (ODA) üOther Official Flows (OOF) üPrivate Flows üNet Private Grants DAC statistics are the only reliable source of both total and comparative data on aid performance
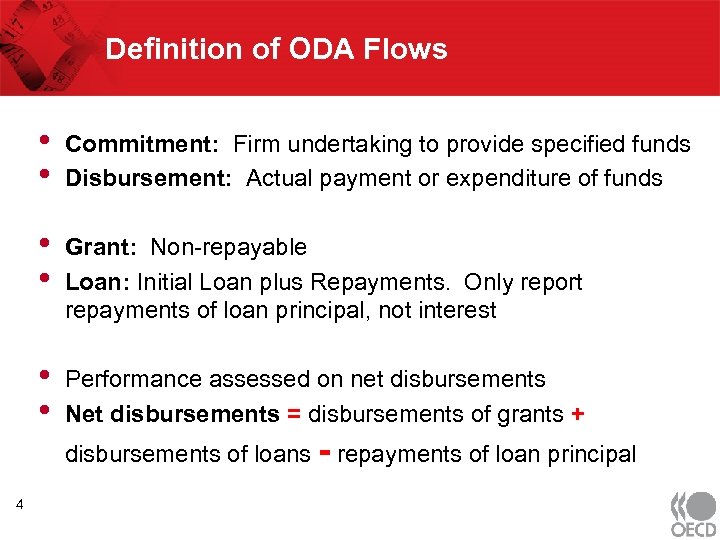 Definition of ODA Flows • • Commitment: Firm undertaking to provide specified funds Disbursement: Actual payment or expenditure of funds • • Grant: Non-repayable Loan: Initial Loan plus Repayments. Only report repayments of loan principal, not interest • • Performance assessed on net disbursements Net disbursements = disbursements of grants + disbursements of loans - repayments of loan principal 4
Definition of ODA Flows • • Commitment: Firm undertaking to provide specified funds Disbursement: Actual payment or expenditure of funds • • Grant: Non-repayable Loan: Initial Loan plus Repayments. Only report repayments of loan principal, not interest • • Performance assessed on net disbursements Net disbursements = disbursements of grants + disbursements of loans - repayments of loan principal 4
 DAC Reporters • • Limited data on aid only (ODA) from non-DAC members. • 5 Data are collected data from: üAll DAC Member Countries üNon DAC Donors (voluntary) üMultilateral Agencies (voluntary) In the future, we hope to improve reporting from non. DACs, multilaterals and foundations.
DAC Reporters • • Limited data on aid only (ODA) from non-DAC members. • 5 Data are collected data from: üAll DAC Member Countries üNon DAC Donors (voluntary) üMultilateral Agencies (voluntary) In the future, we hope to improve reporting from non. DACs, multilaterals and foundations.
 Collection Methods – DAC Members • • Both systems based on instructions agreed by members detailed in Statistical Reporting Directives • 6 DAC questionnaire – aggregate level data Creditor Reporting System (CRS) – activity level reports CRS++ Method Reports supplied by members and other reporters
Collection Methods – DAC Members • • Both systems based on instructions agreed by members detailed in Statistical Reporting Directives • 6 DAC questionnaire – aggregate level data Creditor Reporting System (CRS) – activity level reports CRS++ Method Reports supplied by members and other reporters
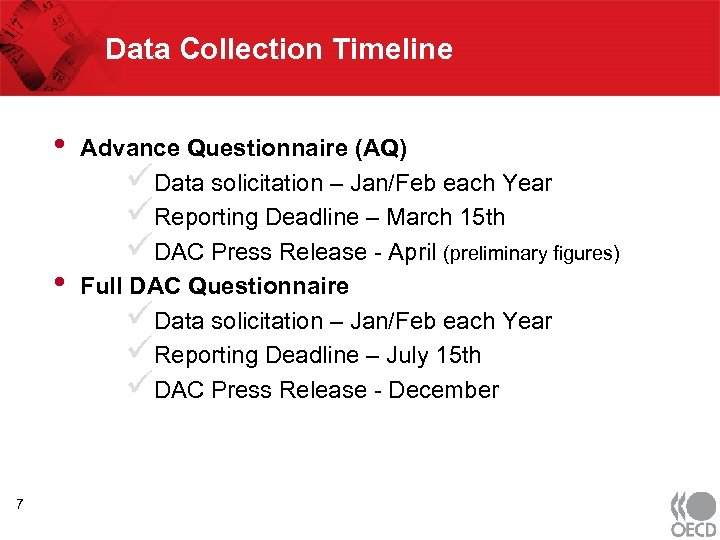 Data Collection Timeline • • 7 Advance Questionnaire (AQ) üData solicitation – Jan/Feb each Year üReporting Deadline – March 15 th üDAC Press Release - April (preliminary figures) Full DAC Questionnaire üData solicitation – Jan/Feb each Year üReporting Deadline – July 15 th üDAC Press Release - December
Data Collection Timeline • • 7 Advance Questionnaire (AQ) üData solicitation – Jan/Feb each Year üReporting Deadline – March 15 th üDAC Press Release - April (preliminary figures) Full DAC Questionnaire üData solicitation – Jan/Feb each Year üReporting Deadline – July 15 th üDAC Press Release - December
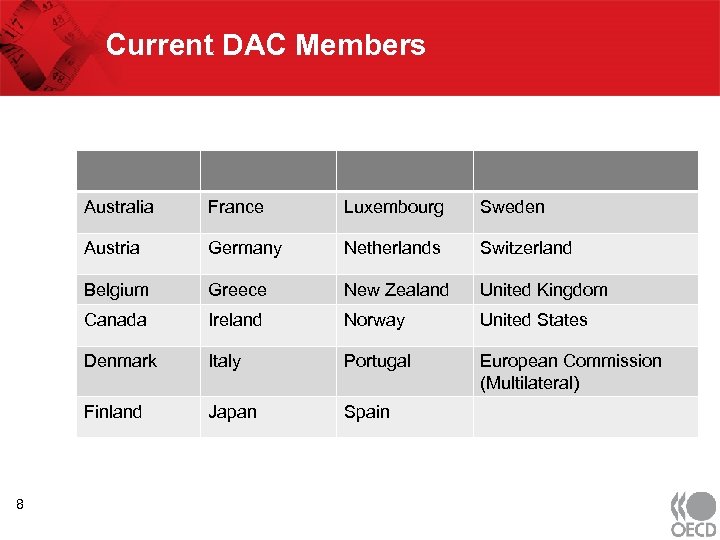 Current DAC Members Australia Luxembourg Sweden Austria Germany Netherlands Switzerland Belgium Greece New Zealand United Kingdom Canada Ireland Norway United States Denmark Italy Portugal European Commission (Multilateral) Finland 8 France Japan Spain
Current DAC Members Australia Luxembourg Sweden Austria Germany Netherlands Switzerland Belgium Greece New Zealand United Kingdom Canada Ireland Norway United States Denmark Italy Portugal European Commission (Multilateral) Finland 8 France Japan Spain
 DAC Questionnaire The full DAC Questionnaire consists of the following 7 Tables: • • 9 1 – Disbursements and Commitments of Official and Private Flows 2 a – Destination of Official Development Assistance – Disbursements 2 b – Destination of Other Official Flows – Disbursements 3 a – Destination of Official Development Assistance – Commitments 4 – Destination of Private Direct Investment and Other Private Capital 5 - Official Bilateral Commitments (or Gross Disb. ) by Sector of Destination 7 b – Tying Status of Bilateral Official Development Assistance – Commitments
DAC Questionnaire The full DAC Questionnaire consists of the following 7 Tables: • • 9 1 – Disbursements and Commitments of Official and Private Flows 2 a – Destination of Official Development Assistance – Disbursements 2 b – Destination of Other Official Flows – Disbursements 3 a – Destination of Official Development Assistance – Commitments 4 – Destination of Private Direct Investment and Other Private Capital 5 - Official Bilateral Commitments (or Gross Disb. ) by Sector of Destination 7 b – Tying Status of Bilateral Official Development Assistance – Commitments
 Creditor Reporting System CRS Form 1 reports on annual obligations, while CRS Form 2 reports on gross disbursements. Over 30+ variables per form including; • Recipient Countries (possibility of grouping by continent or by income group) • Donors (grouped into bilateral and multilateral) • Sectors and Sub-Sectors Codes • Activity/Project Titles and Descriptions • Flows: Grants, Loans, ODA, OOF • Channels of Delivery • Policy Markers (gender equality, environment, PD/GG) • RIO Markers (biodiversity, climate change, desertification) 10
Creditor Reporting System CRS Form 1 reports on annual obligations, while CRS Form 2 reports on gross disbursements. Over 30+ variables per form including; • Recipient Countries (possibility of grouping by continent or by income group) • Donors (grouped into bilateral and multilateral) • Sectors and Sub-Sectors Codes • Activity/Project Titles and Descriptions • Flows: Grants, Loans, ODA, OOF • Channels of Delivery • Policy Markers (gender equality, environment, PD/GG) • RIO Markers (biodiversity, climate change, desertification) 10
 Reporting for Non-DAC Donors • • Records disbursements of aid by recipient. • Limited presentation of data in DCR; but supplemented by textual information: draft supplied by donor. • 11 Abbreviated reporting form. Reporting is voluntary. Current reporters include all non-DAC OECD members (except Mexico), as well as Israel, Arab donors, Israel, Thailand Baltic states.
Reporting for Non-DAC Donors • • Records disbursements of aid by recipient. • Limited presentation of data in DCR; but supplemented by textual information: draft supplied by donor. • 11 Abbreviated reporting form. Reporting is voluntary. Current reporters include all non-DAC OECD members (except Mexico), as well as Israel, Arab donors, Israel, Thailand Baltic states.
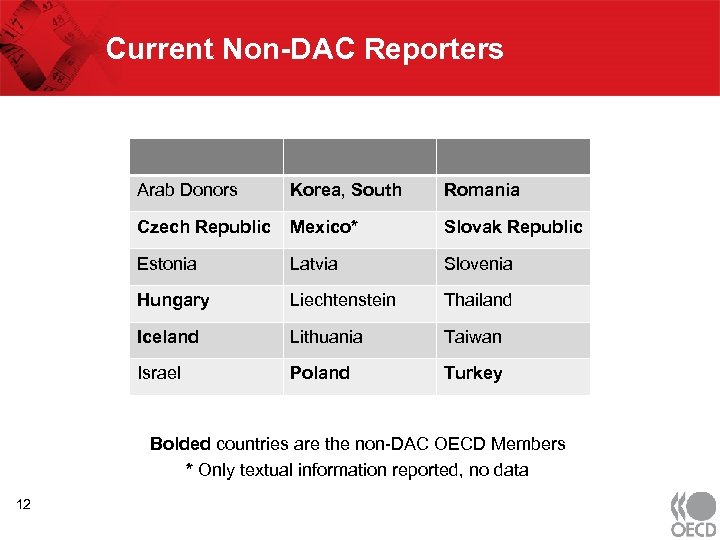 Current Non-DAC Reporters Arab Donors Korea, South Romania Czech Republic Mexico* Slovak Republic Estonia Latvia Slovenia Hungary Liechtenstein Thailand Iceland Lithuania Taiwan Israel Poland Turkey Bolded countries are the non-DAC OECD Members * Only textual information reported, no data 12
Current Non-DAC Reporters Arab Donors Korea, South Romania Czech Republic Mexico* Slovak Republic Estonia Latvia Slovenia Hungary Liechtenstein Thailand Iceland Lithuania Taiwan Israel Poland Turkey Bolded countries are the non-DAC OECD Members * Only textual information reported, no data 12
 Collection Method – Non DAC/Non OECD Members with annual ODA < USD 50 Million Abbreviated DAC Table 1 13
Collection Method – Non DAC/Non OECD Members with annual ODA < USD 50 Million Abbreviated DAC Table 1 13
 Collection Method – Non DAC, OECD Members and other donors with annual ODA > USD 50 Million Abbreviated DAC Table 2 a 14
Collection Method – Non DAC, OECD Members and other donors with annual ODA > USD 50 Million Abbreviated DAC Table 2 a 14
 Statistical Outputs • • • Annual Development Co-operation Report (DCR) Geographical Distribution of Financial Flows Statistical analysis in Peer Reviews of DAC member’s aid programme International Development Statistics Online • • 15 CD-ROM and on-line access External uses, including World Bank publications, Millennium Development Goals and other UN documents, databases and publications
Statistical Outputs • • • Annual Development Co-operation Report (DCR) Geographical Distribution of Financial Flows Statistical analysis in Peer Reviews of DAC member’s aid programme International Development Statistics Online • • 15 CD-ROM and on-line access External uses, including World Bank publications, Millennium Development Goals and other UN documents, databases and publications
 Importance of Data • • • 16 Domestic and Foreign Policy/Diplomacy Fosters Accountability Improves Transparency Provides a Platform for Dialogue üRecipient Countries üOther Donors Alignment with International Standard Drives Future Policy Decisions
Importance of Data • • • 16 Domestic and Foreign Policy/Diplomacy Fosters Accountability Improves Transparency Provides a Platform for Dialogue üRecipient Countries üOther Donors Alignment with International Standard Drives Future Policy Decisions
 Establishing a Database • Collection of facts, both financial and descriptive. • Living entity – flexible, updatable, everexpanding. • Requires a lot of up-front work. • ASSET. 17 Tool for answering questions and provides the basis for in-dept analysis, and future policy implications.
Establishing a Database • Collection of facts, both financial and descriptive. • Living entity – flexible, updatable, everexpanding. • Requires a lot of up-front work. • ASSET. 17 Tool for answering questions and provides the basis for in-dept analysis, and future policy implications.
 Data Collection • Who will collect the data? • What is the current mandate for data collection? ü Is this type of reporting mandated by law? ü Agreement between government and international organization? • How is the message of importance conveyed? 18
Data Collection • Who will collect the data? • What is the current mandate for data collection? ü Is this type of reporting mandated by law? ü Agreement between government and international organization? • How is the message of importance conveyed? 18
 Further Information & Resources • • Reporting Directives for the Creditor Reporting System (CRS): www. oecd. org/dac/stats/crs/directives • How to Report Debt Relief: http: //www. oecd. org/dataoecd/44/22/1894838. pdf • 19 DAC Statistical Reporting Directives: www. oecd. org/dac/stats/dac/directives Other Useful Links: www. oecd. org/dac/stats/statlinks www. oecd. org/dac
Further Information & Resources • • Reporting Directives for the Creditor Reporting System (CRS): www. oecd. org/dac/stats/crs/directives • How to Report Debt Relief: http: //www. oecd. org/dataoecd/44/22/1894838. pdf • 19 DAC Statistical Reporting Directives: www. oecd. org/dac/stats/dac/directives Other Useful Links: www. oecd. org/dac/stats/statlinks www. oecd. org/dac


