5fcf6982be1ce23f415aef341e9b1dfb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42
 Statistical Process Control Hypothesis Tests
Statistical Process Control Hypothesis Tests
 Hypothesis Tests • An Hypothesis is a guess about a situation that can be tested, and the test outcome can be either true or false. – The Null Hypothesis has a symbol H 0, and is always the default situation that must be proven unlikely beyond a reasonable doubt. – The Alternative Hypothesis is denoted by the symbol HA and can be thought of as the opposite of the Null Hypothesis - it can also be either true or false, but it is always false when H 0 is true and vice-versa.
Hypothesis Tests • An Hypothesis is a guess about a situation that can be tested, and the test outcome can be either true or false. – The Null Hypothesis has a symbol H 0, and is always the default situation that must be proven unlikely beyond a reasonable doubt. – The Alternative Hypothesis is denoted by the symbol HA and can be thought of as the opposite of the Null Hypothesis - it can also be either true or false, but it is always false when H 0 is true and vice-versa.
 Hypothesis Testing Errors – Type I Errors occur when a test statistic leads us to reject the Null Hypothesis when the Null Hypothesis is true in reality. • The chance of making a Type I Error is estimated by the parameter (or level of significance), which quantifies the reasonable doubt. – Type II Errors occur when a test statistic leads us to fail to reject the Null Hypothesis when the Null Hypothesis is actually false in reality. • The probability of making a Type II Error is estimated by the parameter .
Hypothesis Testing Errors – Type I Errors occur when a test statistic leads us to reject the Null Hypothesis when the Null Hypothesis is true in reality. • The chance of making a Type I Error is estimated by the parameter (or level of significance), which quantifies the reasonable doubt. – Type II Errors occur when a test statistic leads us to fail to reject the Null Hypothesis when the Null Hypothesis is actually false in reality. • The probability of making a Type II Error is estimated by the parameter .
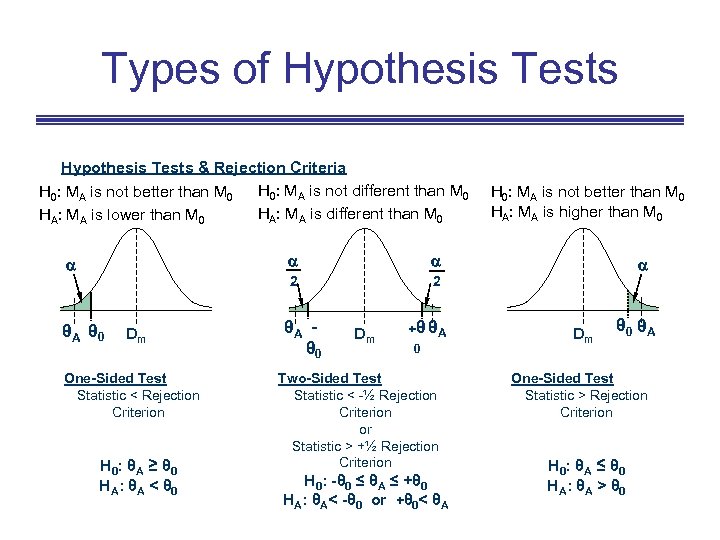 Types of Hypothesis Tests & Rejection Criteria H 0: MA is not different than M 0 H 0: MA is not better than M 0 HA: MA is different than M 0 HA: MA is lower than M 0 θA θ 0 Dm One-Sided Test Statistic < Rejection Criterion H 0 : θ A ≥ θ 0 H A: θ A < θ 0 2 H 0: MA is not better than M 0 HA: MA is higher than M 0 2 θA θ 0 Dm +θ θ A 0 Two-Sided Test Statistic < -½ Rejection Criterion or Statistic > +½ Rejection Criterion H 0: -θ 0 ≤ θA ≤ +θ 0 HA: θA< -θ 0 or +θ 0< θA Dm θ 0 θA One-Sided Test Statistic > Rejection Criterion H 0 : θ A ≤ θ 0 H A: θ A > θ 0
Types of Hypothesis Tests & Rejection Criteria H 0: MA is not different than M 0 H 0: MA is not better than M 0 HA: MA is different than M 0 HA: MA is lower than M 0 θA θ 0 Dm One-Sided Test Statistic < Rejection Criterion H 0 : θ A ≥ θ 0 H A: θ A < θ 0 2 H 0: MA is not better than M 0 HA: MA is higher than M 0 2 θA θ 0 Dm +θ θ A 0 Two-Sided Test Statistic < -½ Rejection Criterion or Statistic > +½ Rejection Criterion H 0: -θ 0 ≤ θA ≤ +θ 0 HA: θA< -θ 0 or +θ 0< θA Dm θ 0 θA One-Sided Test Statistic > Rejection Criterion H 0 : θ A ≤ θ 0 H A: θ A > θ 0
 Hypothesis Testing Steps 1. State the null hypothesis (H 0) from one of the alternatives: that the test statistic m. A = m 0 , m. A ≥ m 0 , or m. A ≤ m 0. 2. Choose the alternative hypothesis (HA) from the alternatives: m. A ¹ m 0 , m. A < m 0 , or m. A > m 0. (Respective to above!) • Choose a significance level of the test ( ). • Select the appropriate test statistic and establish a critical region. (If the decision is to be based on a P-value, it is not necessary to have a critical region) • Compute the value of the test statistic ( ) from the sample data. 2. Decision: Reject H 0 if the test statistic has a value in the critical region (or if the computed P-value is less than or equal to the desired significance level ); otherwise, do not reject H 0.
Hypothesis Testing Steps 1. State the null hypothesis (H 0) from one of the alternatives: that the test statistic m. A = m 0 , m. A ≥ m 0 , or m. A ≤ m 0. 2. Choose the alternative hypothesis (HA) from the alternatives: m. A ¹ m 0 , m. A < m 0 , or m. A > m 0. (Respective to above!) • Choose a significance level of the test ( ). • Select the appropriate test statistic and establish a critical region. (If the decision is to be based on a P-value, it is not necessary to have a critical region) • Compute the value of the test statistic ( ) from the sample data. 2. Decision: Reject H 0 if the test statistic has a value in the critical region (or if the computed P-value is less than or equal to the desired significance level ); otherwise, do not reject H 0.
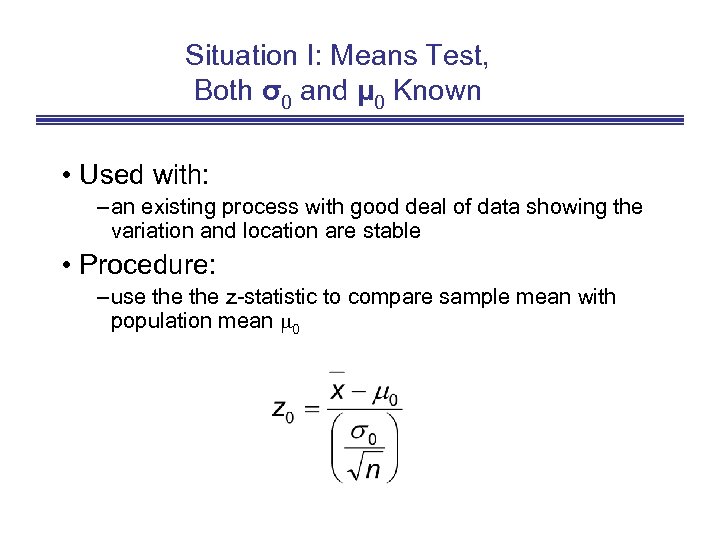 Situation I: Means Test, Both σ0 and μ 0 Known • Used with: – an existing process with good deal of data showing the variation and location are stable • Procedure: – use the z-statistic to compare sample mean with population mean 0
Situation I: Means Test, Both σ0 and μ 0 Known • Used with: – an existing process with good deal of data showing the variation and location are stable • Procedure: – use the z-statistic to compare sample mean with population mean 0
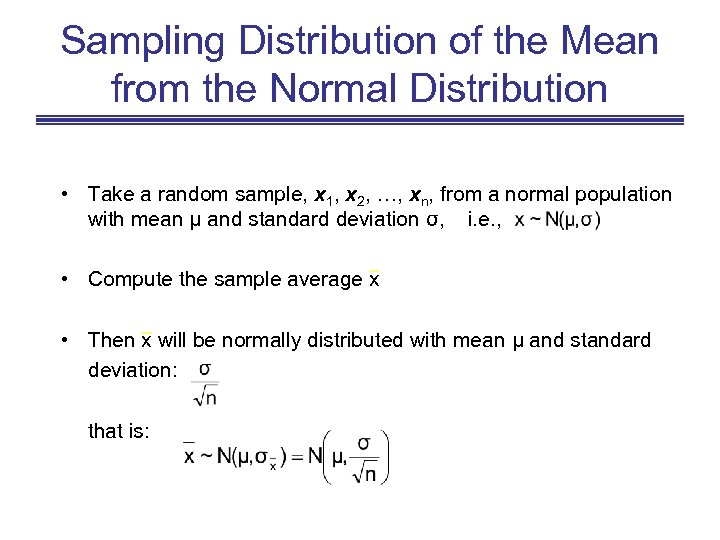 Sampling Distribution of the Mean from the Normal Distribution • Take a random sample, x 1, x 2, …, xn, from a normal population with mean μ and standard deviation σ, i. e. , • Compute the sample average x • Then x will be normally distributed with mean μ and standard deviation: that is:
Sampling Distribution of the Mean from the Normal Distribution • Take a random sample, x 1, x 2, …, xn, from a normal population with mean μ and standard deviation σ, i. e. , • Compute the sample average x • Then x will be normally distributed with mean μ and standard deviation: that is:
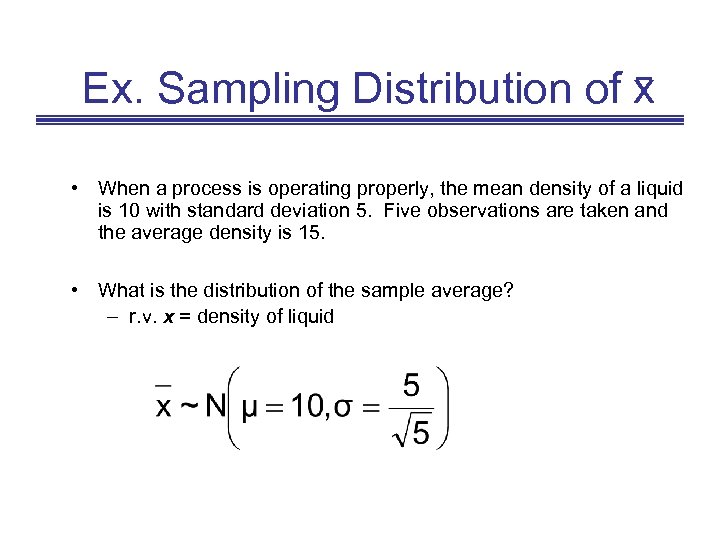 Ex. Sampling Distribution of x • When a process is operating properly, the mean density of a liquid is 10 with standard deviation 5. Five observations are taken and the average density is 15. • What is the distribution of the sample average? – r. v. x = density of liquid
Ex. Sampling Distribution of x • When a process is operating properly, the mean density of a liquid is 10 with standard deviation 5. Five observations are taken and the average density is 15. • What is the distribution of the sample average? – r. v. x = density of liquid
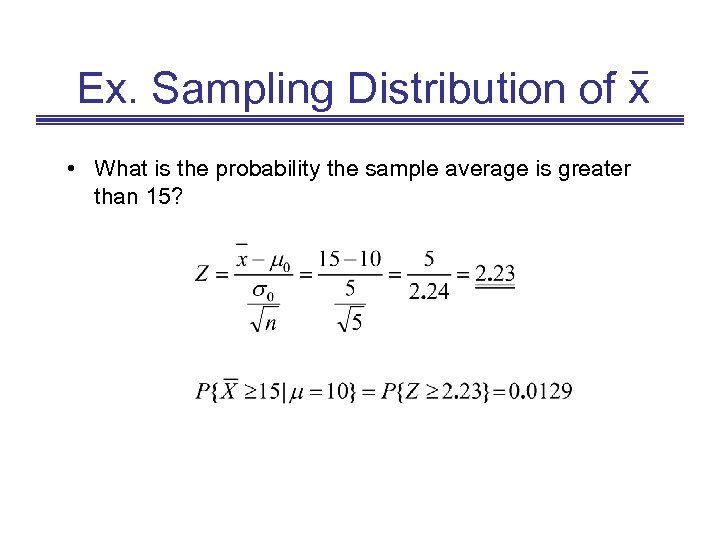 Ex. Sampling Distribution of x • What is the probability the sample average is greater than 15? • Would you conclude the process is operating properly?
Ex. Sampling Distribution of x • What is the probability the sample average is greater than 15? • Would you conclude the process is operating properly?

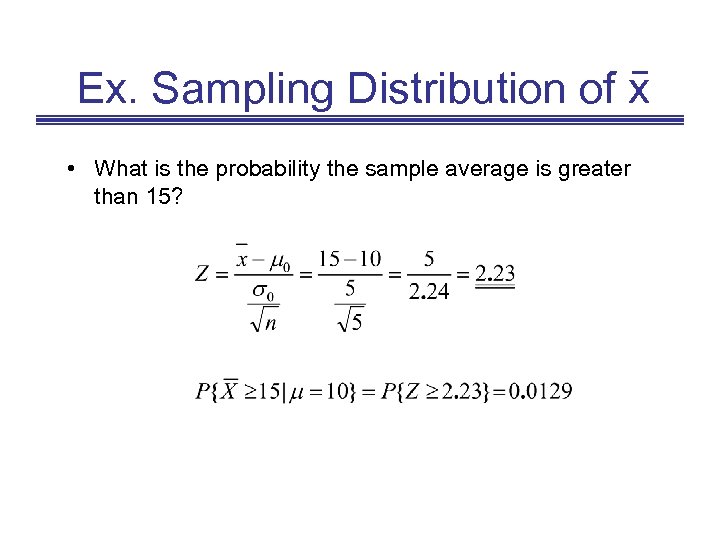 Ex. Sampling Distribution of x • What is the probability the sample average is greater than 15? • Would you conclude the process is operating properly?
Ex. Sampling Distribution of x • What is the probability the sample average is greater than 15? • Would you conclude the process is operating properly?
 Statistical Process Control Operating Characteristic Curves
Statistical Process Control Operating Characteristic Curves
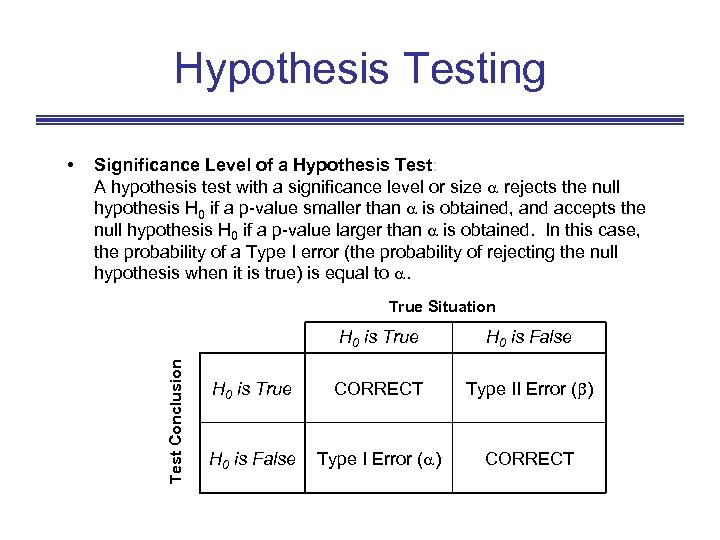 Hypothesis Testing Significance Level of a Hypothesis Test: A hypothesis test with a significance level or size rejects the null hypothesis H 0 if a p-value smaller than is obtained, and accepts the null hypothesis H 0 if a p-value larger than is obtained. In this case, the probability of a Type I error (the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true) is equal to . True Situation H 0 is True Test Conclusion • H 0 is False H 0 is True CORRECT Type II Error ( ) H 0 is False Type I Error ( ) CORRECT
Hypothesis Testing Significance Level of a Hypothesis Test: A hypothesis test with a significance level or size rejects the null hypothesis H 0 if a p-value smaller than is obtained, and accepts the null hypothesis H 0 if a p-value larger than is obtained. In this case, the probability of a Type I error (the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true) is equal to . True Situation H 0 is True Test Conclusion • H 0 is False H 0 is True CORRECT Type II Error ( ) H 0 is False Type I Error ( ) CORRECT
 error = 0. 0129 1 - 0 2. 23 In words: If the true mean is 10, the probably that we would see a sample mean of 15 or higher is only 1. 3%. If we say that the mean has shifted to something larger than 10, there is a 1. 3% chance we are wrong.
error = 0. 0129 1 - 0 2. 23 In words: If the true mean is 10, the probably that we would see a sample mean of 15 or higher is only 1. 3%. If we say that the mean has shifted to something larger than 10, there is a 1. 3% chance we are wrong.
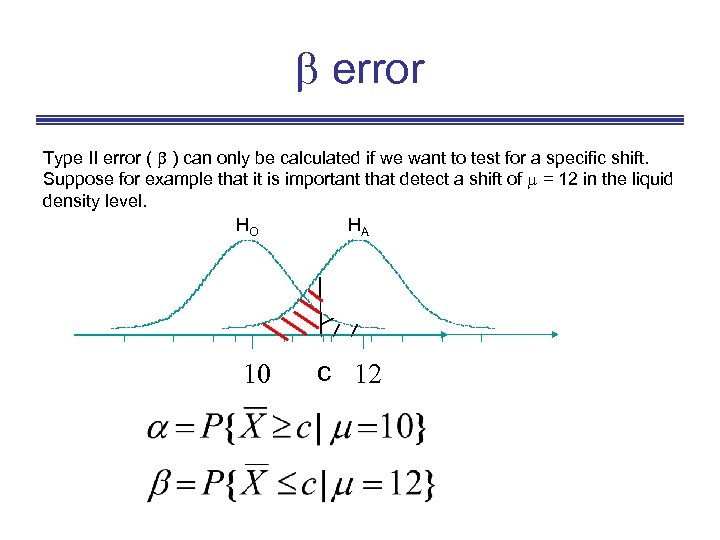 error Type II error ( ) can only be calculated if we want to test for a specific shift. Suppose for example that it is important that detect a shift of = 12 in the liquid density level. HO HA 10 c 12
error Type II error ( ) can only be calculated if we want to test for a specific shift. Suppose for example that it is important that detect a shift of = 12 in the liquid density level. HO HA 10 c 12
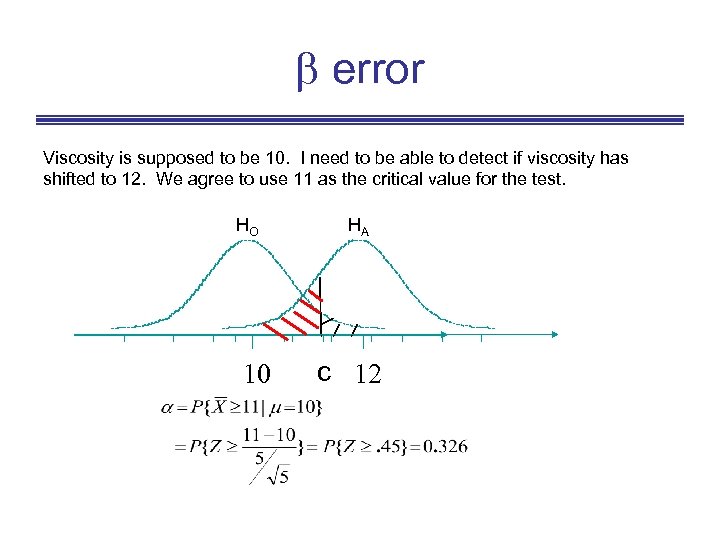 error Viscosity is supposed to be 10. I need to be able to detect if viscosity has shifted to 12. We agree to use 11 as the critical value for the test. HO 10 HA c 12
error Viscosity is supposed to be 10. I need to be able to detect if viscosity has shifted to 12. We agree to use 11 as the critical value for the test. HO 10 HA c 12
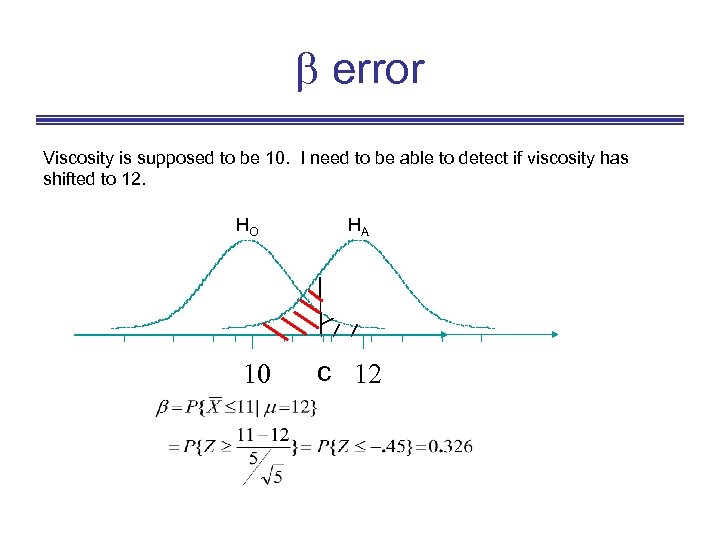 error Viscosity is supposed to be 10. I need to be able to detect if viscosity has shifted to 12. HO 10 HA c 12
error Viscosity is supposed to be 10. I need to be able to detect if viscosity has shifted to 12. HO 10 HA c 12
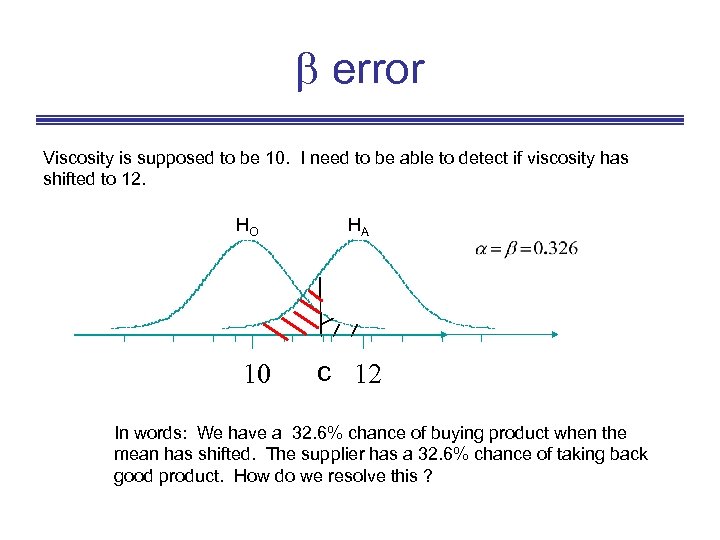 error Viscosity is supposed to be 10. I need to be able to detect if viscosity has shifted to 12. HO 10 HA c 12 In words: We have a 32. 6% chance of buying product when the mean has shifted. The supplier has a 32. 6% chance of taking back good product. How do we resolve this ?
error Viscosity is supposed to be 10. I need to be able to detect if viscosity has shifted to 12. HO 10 HA c 12 In words: We have a 32. 6% chance of buying product when the mean has shifted. The supplier has a 32. 6% chance of taking back good product. How do we resolve this ?
 Operating Characteristic Curve • We know that a small change in the mean is hard to detect. • For a given sample, we want to minimize our risk of accepting product where the mean has shifted ( error). • For a given sample, the vendor wants to minimize his/her risk of having to buy back product that is good ( error). • I can calculate risk for any given sample size and mean difference that is of interest.
Operating Characteristic Curve • We know that a small change in the mean is hard to detect. • For a given sample, we want to minimize our risk of accepting product where the mean has shifted ( error). • For a given sample, the vendor wants to minimize his/her risk of having to buy back product that is good ( error). • I can calculate risk for any given sample size and mean difference that is of interest.
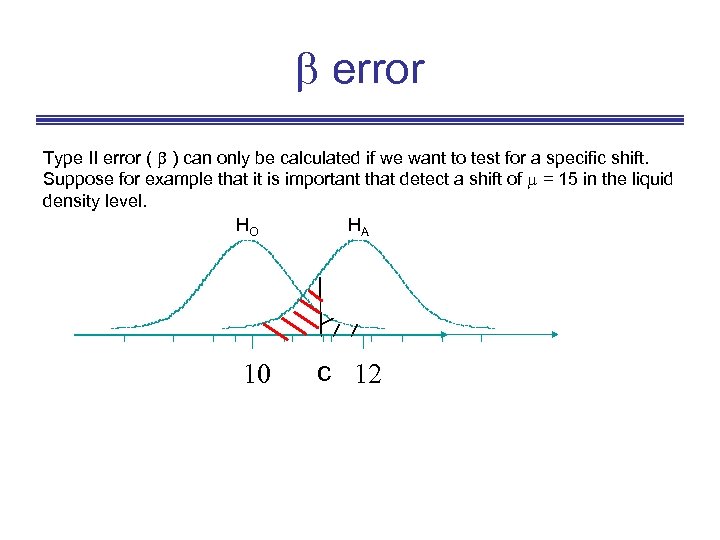 error Type II error ( ) can only be calculated if we want to test for a specific shift. Suppose for example that it is important that detect a shift of = 15 in the liquid density level. HO HA 10 c 12
error Type II error ( ) can only be calculated if we want to test for a specific shift. Suppose for example that it is important that detect a shift of = 15 in the liquid density level. HO HA 10 c 12
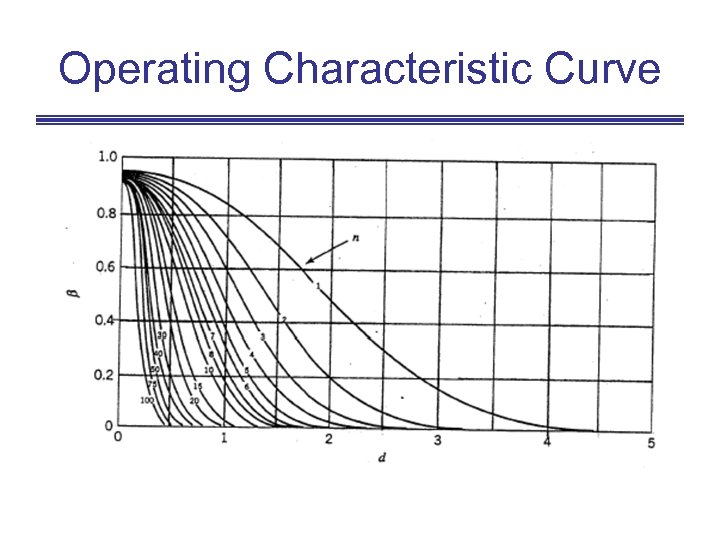 Operating Characteristic Curve
Operating Characteristic Curve
 OC Curve Example (uses Fig 3 -7, p. 111) • Assume our previous problem had a process std. dev. of 18 (instead of 5), and the same means (125 population & spec, 134 supplier sample). • Assume the boss wants = 0. 05 of exceeding either the high or low spec. for such a sample. – Probability of what (in English)? – Contracting an incapable supplier, based on a bad-luck test outcome • Assume supplier needs = 0. 2 – Probability of what (in English)? – Unfairly being the incapable supplier, based on a bad-luck test outcome • What sample size is needed to fit these constraints?
OC Curve Example (uses Fig 3 -7, p. 111) • Assume our previous problem had a process std. dev. of 18 (instead of 5), and the same means (125 population & spec, 134 supplier sample). • Assume the boss wants = 0. 05 of exceeding either the high or low spec. for such a sample. – Probability of what (in English)? – Contracting an incapable supplier, based on a bad-luck test outcome • Assume supplier needs = 0. 2 – Probability of what (in English)? – Unfairly being the incapable supplier, based on a bad-luck test outcome • What sample size is needed to fit these constraints?
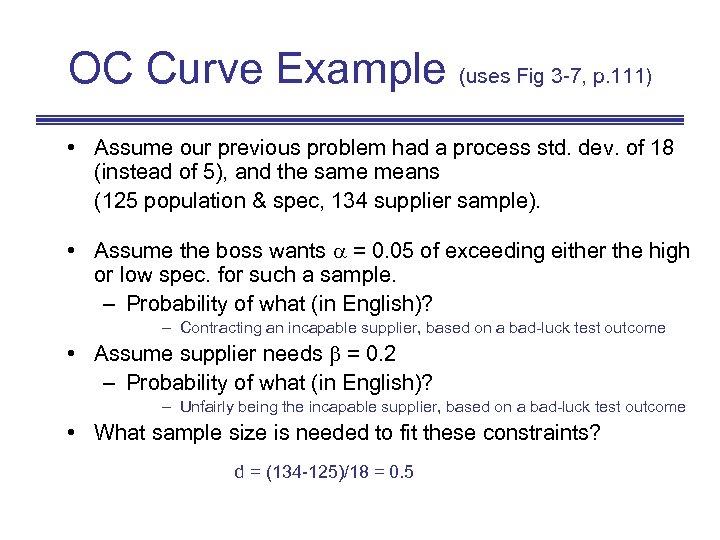 OC Curve Example (uses Fig 3 -7, p. 111) • Assume our previous problem had a process std. dev. of 18 (instead of 5), and the same means (125 population & spec, 134 supplier sample). • Assume the boss wants = 0. 05 of exceeding either the high or low spec. for such a sample. – Probability of what (in English)? – Contracting an incapable supplier, based on a bad-luck test outcome • Assume supplier needs = 0. 2 – Probability of what (in English)? – Unfairly being the incapable supplier, based on a bad-luck test outcome • What sample size is needed to fit these constraints? d = (134 -125)/18 = 0. 5
OC Curve Example (uses Fig 3 -7, p. 111) • Assume our previous problem had a process std. dev. of 18 (instead of 5), and the same means (125 population & spec, 134 supplier sample). • Assume the boss wants = 0. 05 of exceeding either the high or low spec. for such a sample. – Probability of what (in English)? – Contracting an incapable supplier, based on a bad-luck test outcome • Assume supplier needs = 0. 2 – Probability of what (in English)? – Unfairly being the incapable supplier, based on a bad-luck test outcome • What sample size is needed to fit these constraints? d = (134 -125)/18 = 0. 5
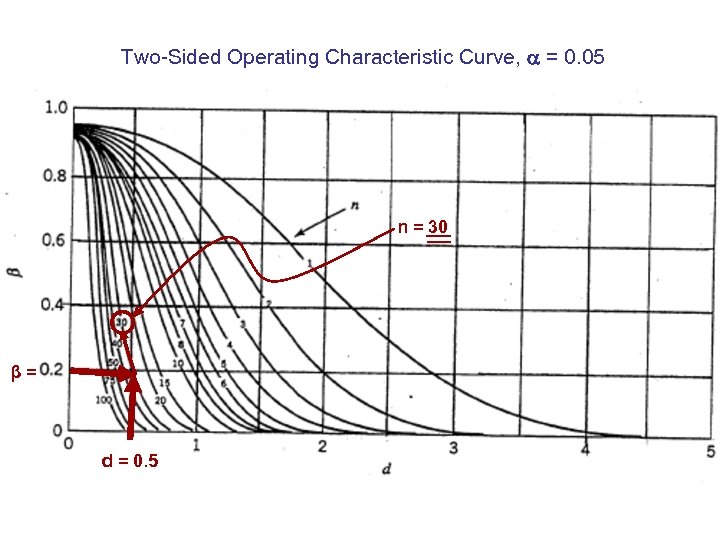 Two-Sided Operating Characteristic Curve, = 0. 05 n = 30 β= d = 0. 5
Two-Sided Operating Characteristic Curve, = 0. 05 n = 30 β= d = 0. 5
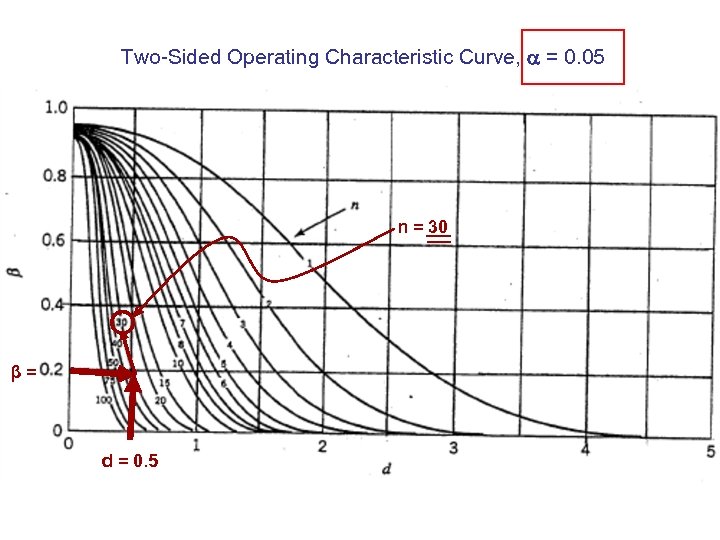 Two-Sided Operating Characteristic Curve, = 0. 05 n = 30 β= d = 0. 5
Two-Sided Operating Characteristic Curve, = 0. 05 n = 30 β= d = 0. 5
 Statistical Process Control Testing for Mean Differences
Statistical Process Control Testing for Mean Differences
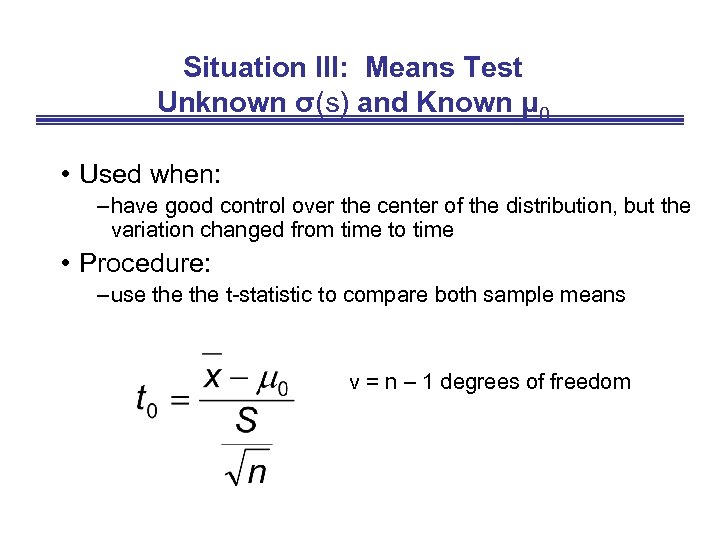 Situation III: Means Test Unknown σ(s) and Known μ 0 • Used when: – have good control over the center of the distribution, but the variation changed from time to time • Procedure: – use the t-statistic to compare both sample means v = n – 1 degrees of freedom
Situation III: Means Test Unknown σ(s) and Known μ 0 • Used when: – have good control over the center of the distribution, but the variation changed from time to time • Procedure: – use the t-statistic to compare both sample means v = n – 1 degrees of freedom
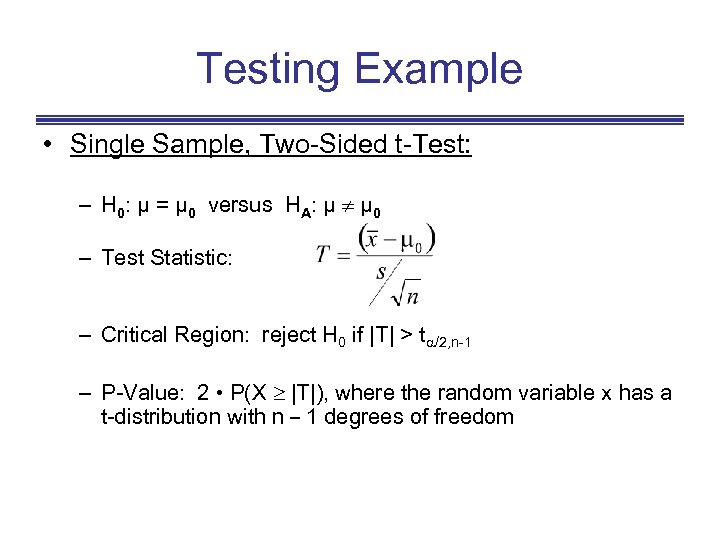 Testing Example • Single Sample, Two-Sided t-Test: – H 0: µ = µ 0 versus HA: µ µ 0 – Test Statistic: – Critical Region: reject H 0 if |T| > t /2, n-1 – P-Value: 2 • P(X ³ |T|), where the random variable x has a t-distribution with n _ 1 degrees of freedom
Testing Example • Single Sample, Two-Sided t-Test: – H 0: µ = µ 0 versus HA: µ µ 0 – Test Statistic: – Critical Region: reject H 0 if |T| > t /2, n-1 – P-Value: 2 • P(X ³ |T|), where the random variable x has a t-distribution with n _ 1 degrees of freedom
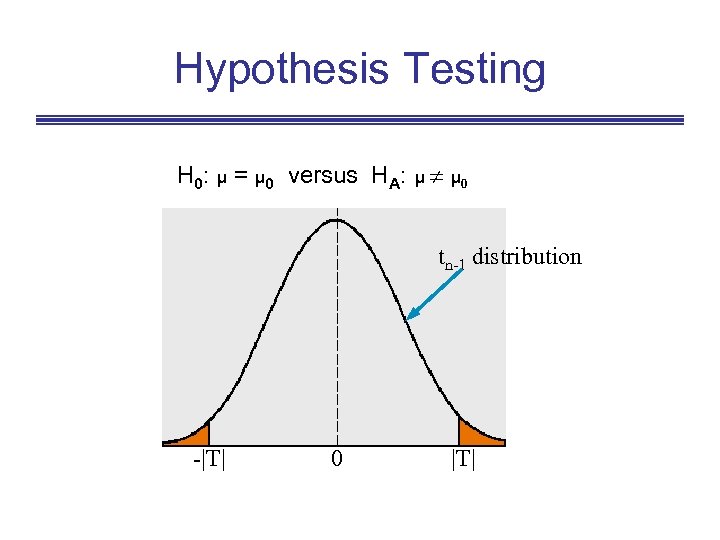 Hypothesis Testing H 0: μ = μ 0 versus HA: μ μ 0 tn-1 distribution -|T| 0 |T|
Hypothesis Testing H 0: μ = μ 0 versus HA: μ μ 0 tn-1 distribution -|T| 0 |T|
 Statistics and Sampling • Objective of statistical inference: – Draw conclusions/make decisions about a population based on a sample selected from the population • Random sample – a sample, x 1, x 2, …, xn , selected so that observations are independently and identically distributed (iid). • Statistic – function of the sample data – Quantities computed from observations in sample and used to make statistical inferences – e. g. measures central tendency
Statistics and Sampling • Objective of statistical inference: – Draw conclusions/make decisions about a population based on a sample selected from the population • Random sample – a sample, x 1, x 2, …, xn , selected so that observations are independently and identically distributed (iid). • Statistic – function of the sample data – Quantities computed from observations in sample and used to make statistical inferences – e. g. measures central tendency
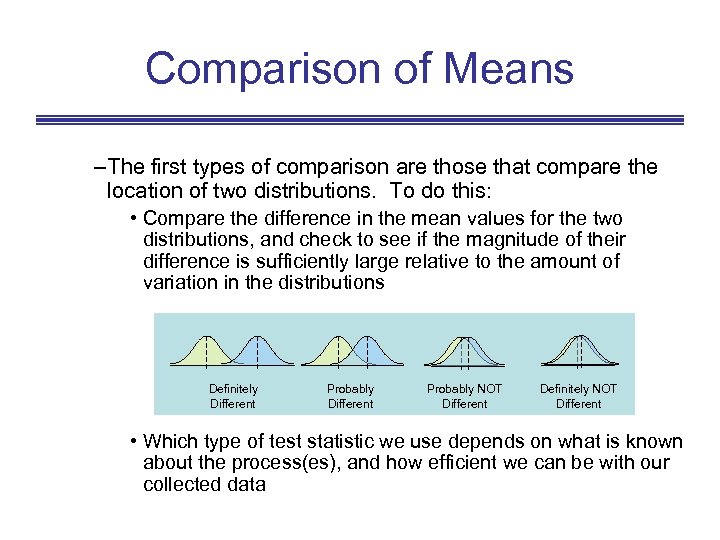 Comparison of Means – The first types of comparison are those that compare the location of two distributions. To do this: • Compare the difference in the mean values for the two distributions, and check to see if the magnitude of their difference is sufficiently large relative to the amount of variation in the distributions Definitely Different Probably NOT Different Definitely NOT Different • Which type of test statistic we use depends on what is known about the process(es), and how efficient we can be with our collected data
Comparison of Means – The first types of comparison are those that compare the location of two distributions. To do this: • Compare the difference in the mean values for the two distributions, and check to see if the magnitude of their difference is sufficiently large relative to the amount of variation in the distributions Definitely Different Probably NOT Different Definitely NOT Different • Which type of test statistic we use depends on what is known about the process(es), and how efficient we can be with our collected data
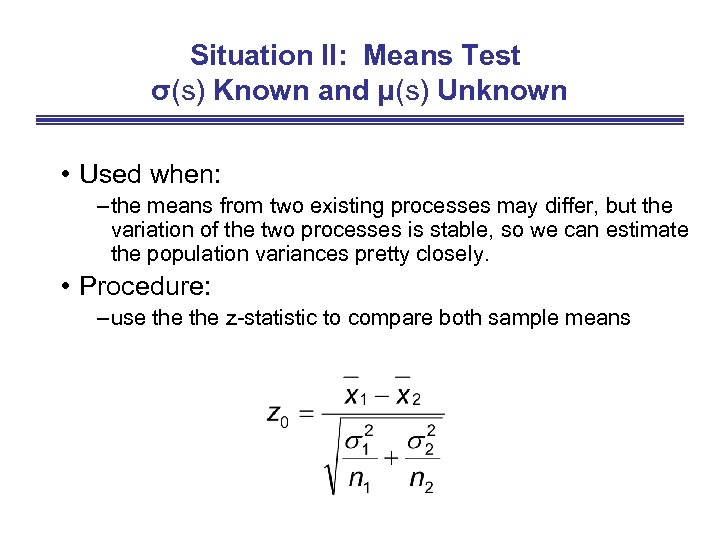 Situation II: Means Test σ(s) Known and μ(s) Unknown • Used when: – the means from two existing processes may differ, but the variation of the two processes is stable, so we can estimate the population variances pretty closely. • Procedure: – use the z-statistic to compare both sample means
Situation II: Means Test σ(s) Known and μ(s) Unknown • Used when: – the means from two existing processes may differ, but the variation of the two processes is stable, so we can estimate the population variances pretty closely. • Procedure: – use the z-statistic to compare both sample means
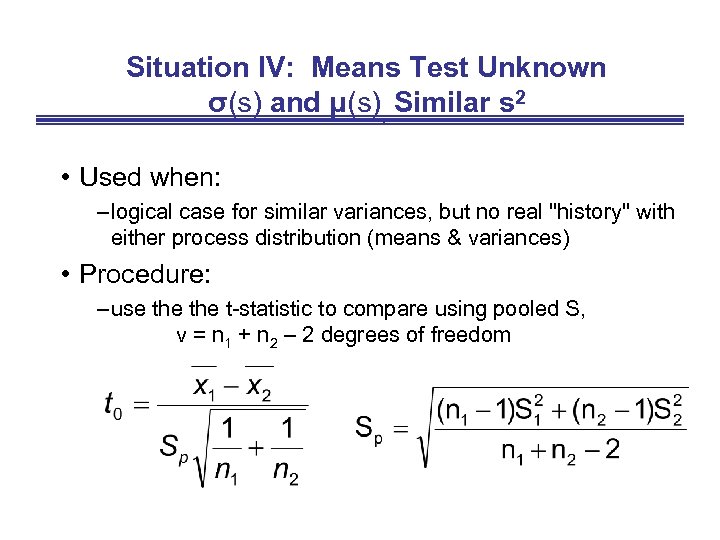 Situation IV: Means Test Unknown σ(s) and μ(s), Similar s 2 • Used when: – logical case for similar variances, but no real "history" with either process distribution (means & variances) • Procedure: – use the t-statistic to compare using pooled S, v = n 1 + n 2 – 2 degrees of freedom
Situation IV: Means Test Unknown σ(s) and μ(s), Similar s 2 • Used when: – logical case for similar variances, but no real "history" with either process distribution (means & variances) • Procedure: – use the t-statistic to compare using pooled S, v = n 1 + n 2 – 2 degrees of freedom
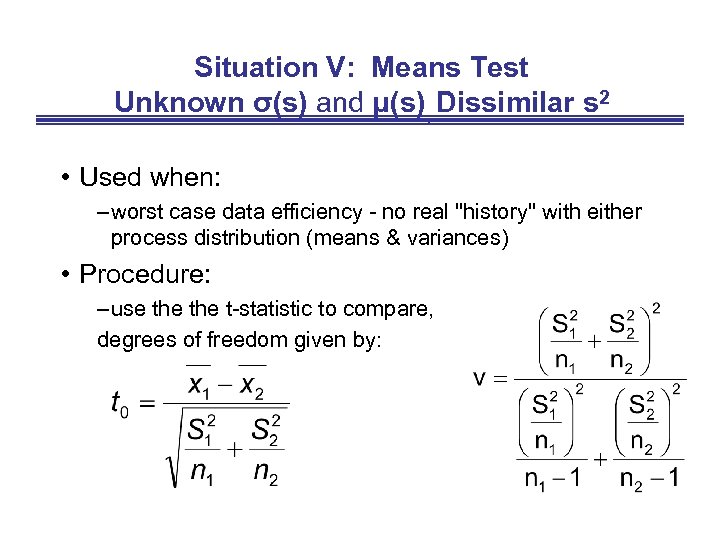 Situation V: Means Test Unknown σ(s) and μ(s), Dissimilar s 2 • Used when: – worst case data efficiency - no real "history" with either process distribution (means & variances) • Procedure: – use the t-statistic to compare, degrees of freedom given by:
Situation V: Means Test Unknown σ(s) and μ(s), Dissimilar s 2 • Used when: – worst case data efficiency - no real "history" with either process distribution (means & variances) • Procedure: – use the t-statistic to compare, degrees of freedom given by:
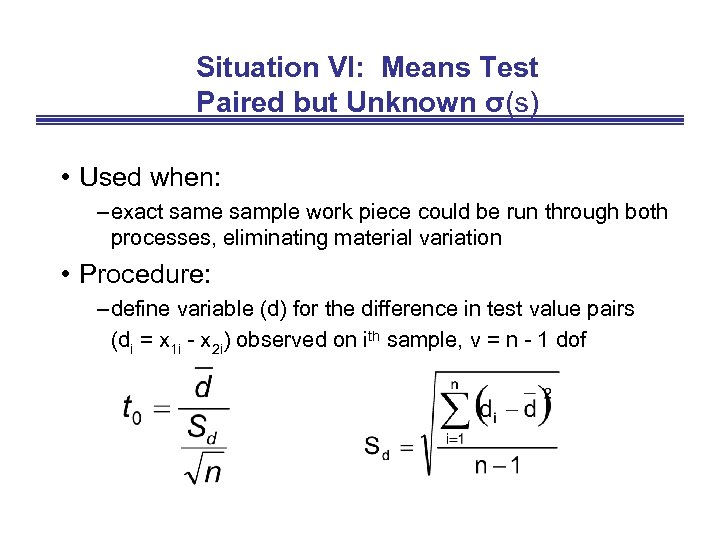 Situation VI: Means Test Paired but Unknown σ(s) • Used when: – exact same sample work piece could be run through both processes, eliminating material variation • Procedure: – define variable (d) for the difference in test value pairs (di = x 1 i - x 2 i) observed on ith sample, v = n - 1 dof
Situation VI: Means Test Paired but Unknown σ(s) • Used when: – exact same sample work piece could be run through both processes, eliminating material variation • Procedure: – define variable (d) for the difference in test value pairs (di = x 1 i - x 2 i) observed on ith sample, v = n - 1 dof
 Ex. Surface Roughness • Surface roughness is normally distributed with mean 125 and std dev of 5. The specification is 125 ± 11. 65 and we have calculated that 98% of parts are within specs during usual production. This has been the case for a long time. • My supplier of these parts has sent me a large shipment. I take a random sample of 10 parts. The sample average roughness is 134 which is within specifications. • Test the hypothesis that the lot roughness is higher than specifications at = 0. 05.
Ex. Surface Roughness • Surface roughness is normally distributed with mean 125 and std dev of 5. The specification is 125 ± 11. 65 and we have calculated that 98% of parts are within specs during usual production. This has been the case for a long time. • My supplier of these parts has sent me a large shipment. I take a random sample of 10 parts. The sample average roughness is 134 which is within specifications. • Test the hypothesis that the lot roughness is higher than specifications at = 0. 05.
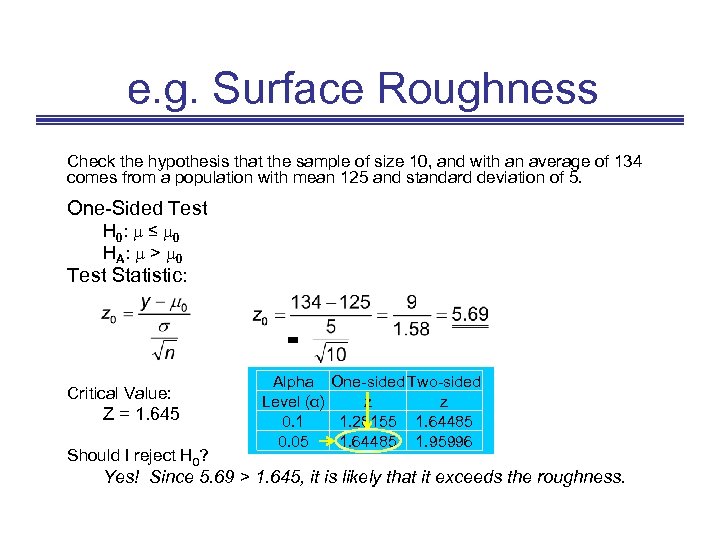 e. g. Surface Roughness Check the hypothesis that the sample of size 10, and with an average of 134 comes from a population with mean 125 and standard deviation of 5. One-Sided Test H 0 : ≤ 0 HA : > 0 Test Statistic: = Critical Value: Z = 1. 645 Should I reject H 0? Alpha One-sided Two-sided Level (α) z z 0. 1 1. 28155 1. 64485 0. 05 1. 64485 1. 95996 Yes! Since 5. 69 > 1. 645, it is likely that it exceeds the roughness.
e. g. Surface Roughness Check the hypothesis that the sample of size 10, and with an average of 134 comes from a population with mean 125 and standard deviation of 5. One-Sided Test H 0 : ≤ 0 HA : > 0 Test Statistic: = Critical Value: Z = 1. 645 Should I reject H 0? Alpha One-sided Two-sided Level (α) z z 0. 1 1. 28155 1. 64485 0. 05 1. 64485 1. 95996 Yes! Since 5. 69 > 1. 645, it is likely that it exceeds the roughness.
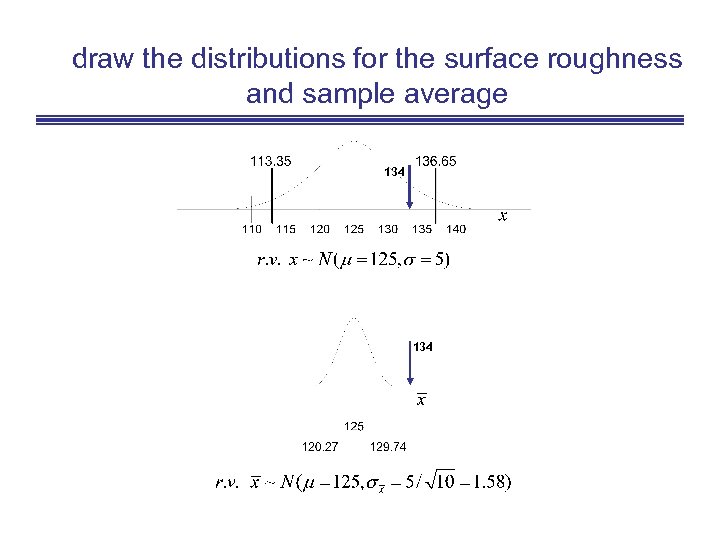 draw the distributions for the surface roughness and sample average 134
draw the distributions for the surface roughness and sample average 134
 e. g. Surface Roughness • Find the probability that the sample of size 10, and with an average of 134 does not come from a population with mean 125 and standard deviation of 5. = • Should I accept this shipment?
e. g. Surface Roughness • Find the probability that the sample of size 10, and with an average of 134 does not come from a population with mean 125 and standard deviation of 5. = • Should I accept this shipment?
 e. g. Surface Roughness Cont'd • For future shipments, suggest good cutoff values for the sample average – (i. e. , accept shipment if average of 10 observations is between what and what)? • We know that encompasses over 99% of the probability mass of the distribution for x
e. g. Surface Roughness Cont'd • For future shipments, suggest good cutoff values for the sample average – (i. e. , accept shipment if average of 10 observations is between what and what)? • We know that encompasses over 99% of the probability mass of the distribution for x
 Concept Map for Hypothesis Tests
Concept Map for Hypothesis Tests
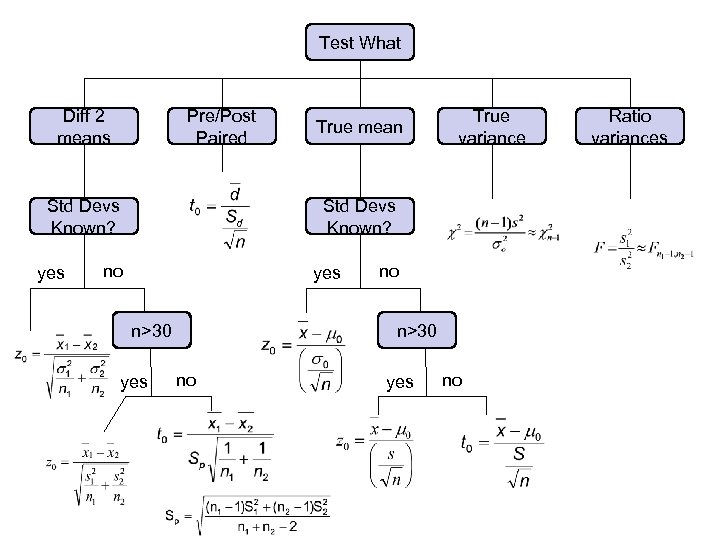 Test What Diff 2 means Pre/Post Paired Std Devs Known? yes True mean True variance Std Devs Known? no yes n>30 yes no n>30 no yes no Ratio variances
Test What Diff 2 means Pre/Post Paired Std Devs Known? yes True mean True variance Std Devs Known? no yes n>30 yes no n>30 no yes no Ratio variances


