Infertility.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46
 State medical University town Infertility Ассистент. Antonova G. A. Assistant Антонова Г. А. Semey
State medical University town Infertility Ассистент. Antonova G. A. Assistant Антонова Г. А. Semey
 • Situation task .
• Situation task .
 Case the 1 • Woman of the 26 years old came to doctor • With complains on absence of pregnancy during 1, 5 years of marriage.
Case the 1 • Woman of the 26 years old came to doctor • With complains on absence of pregnancy during 1, 5 years of marriage.
 What questions do You like to ask her? • Is it interesting for You to know about her menstrual, sexual function? • Do You like to know which type of diseases she had in the past?
What questions do You like to ask her? • Is it interesting for You to know about her menstrual, sexual function? • Do You like to know which type of diseases she had in the past?
 She told for doctor , that she had, periodical on one week before menstruation edema of face and legs, changing of mood, backache, abdominal pains, tenderness of breasts. Date of anamnesis. Menstruations from 12 years, during 3 -4 days, not regular, with delays till 2 months, painful. She has slight growing of hair from period of sexual maturity. She had 1 pregnancy, that finished as missed abortion at 7 weeks. During the next year- no pregnancy.
She told for doctor , that she had, periodical on one week before menstruation edema of face and legs, changing of mood, backache, abdominal pains, tenderness of breasts. Date of anamnesis. Menstruations from 12 years, during 3 -4 days, not regular, with delays till 2 months, painful. She has slight growing of hair from period of sexual maturity. She had 1 pregnancy, that finished as missed abortion at 7 weeks. During the next year- no pregnancy.
 What are the date of objective examination: There are: v Height 175 sm. v Mass- 58 kg. v Female body build. v Breast are developed, v There is growing of hair around areole of nipples, low part of abdomen , femur ‘s.
What are the date of objective examination: There are: v Height 175 sm. v Mass- 58 kg. v Female body build. v Breast are developed, v There is growing of hair around areole of nipples, low part of abdomen , femur ‘s.
 What are the date of special gynecologic examination? Dates are: External sexual organs are developed on the female type. - There is growing of hair at the pubic region. - Urethra, near urethra glands without changes • In speculum : cervix is “ clean”, discharges are mucous P. V. : uterus is smaller in size, mobile, painless. Ovaries with both sides are increased, with soft surface , hard, painless, mobile.
What are the date of special gynecologic examination? Dates are: External sexual organs are developed on the female type. - There is growing of hair at the pubic region. - Urethra, near urethra glands without changes • In speculum : cervix is “ clean”, discharges are mucous P. V. : uterus is smaller in size, mobile, painless. Ovaries with both sides are increased, with soft surface , hard, painless, mobile.
 What is Your preliminary diagnosis? ? ? ? ? ?
What is Your preliminary diagnosis? ? ? ? ? ?
 Diagnosis is • Syndrome of polycystic ovaries. • Missed abortion in anamnesis. • Secondary infertility. Before menstrual syndrome.
Diagnosis is • Syndrome of polycystic ovaries. • Missed abortion in anamnesis. • Secondary infertility. Before menstrual syndrome.
 What is the reason of pregnancy ‘s interruption? ? ? ? ? ?
What is the reason of pregnancy ‘s interruption? ? ? ? ? ?
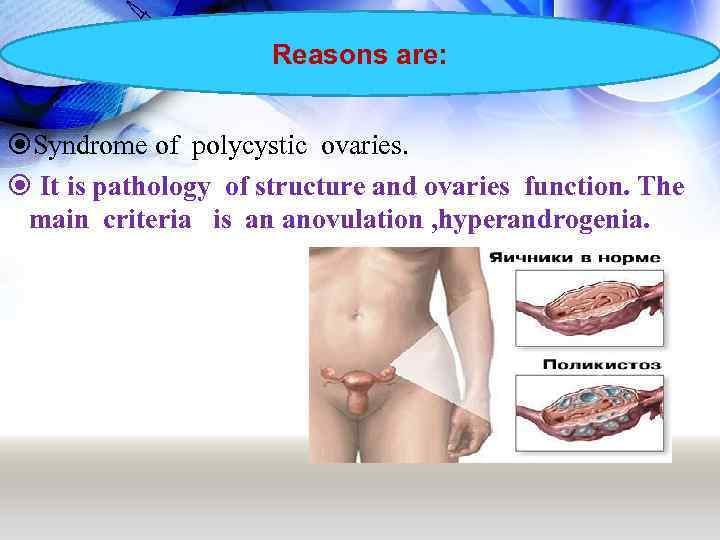 Reasons are: Syndrome of polycystic ovaries. It is pathology of structure and ovaries function. The main criteria is an anovulation , hyperandrogenia.
Reasons are: Syndrome of polycystic ovaries. It is pathology of structure and ovaries function. The main criteria is an anovulation , hyperandrogenia.
 Would You, please, give the conception about PCOS. • It is syndrome of Stein – Levental - poly endocrine syndrome with disturbance of ovary ‘s function ( absence or nor regular ovulation, increasing of androgen’s and estrogen’s secretion, hyper secretion of insulin , supra renal gland ( androgens), hypothalamus and hypophysis.
Would You, please, give the conception about PCOS. • It is syndrome of Stein – Levental - poly endocrine syndrome with disturbance of ovary ‘s function ( absence or nor regular ovulation, increasing of androgen’s and estrogen’s secretion, hyper secretion of insulin , supra renal gland ( androgens), hypothalamus and hypophysis.
 What is the form infertility in this case? • • Tubal? Endocrine? Uterine? Peritoneal form? Psychogenic? Immunolgical? May be male infertility?
What is the form infertility in this case? • • Tubal? Endocrine? Uterine? Peritoneal form? Psychogenic? Immunolgical? May be male infertility?
 What is relationsheep of this syndrome to pre term interruption of pregnancy? v It is the more often reason of habitual abortion v PCOS has frequency among woman of reproductive age - 15 % v 73 -75%- infertility among an ovulation v 68 -85% with hirsutism v 12, 1 -22% among women with interrupted pregnancy.
What is relationsheep of this syndrome to pre term interruption of pregnancy? v It is the more often reason of habitual abortion v PCOS has frequency among woman of reproductive age - 15 % v 73 -75%- infertility among an ovulation v 68 -85% with hirsutism v 12, 1 -22% among women with interrupted pregnancy.
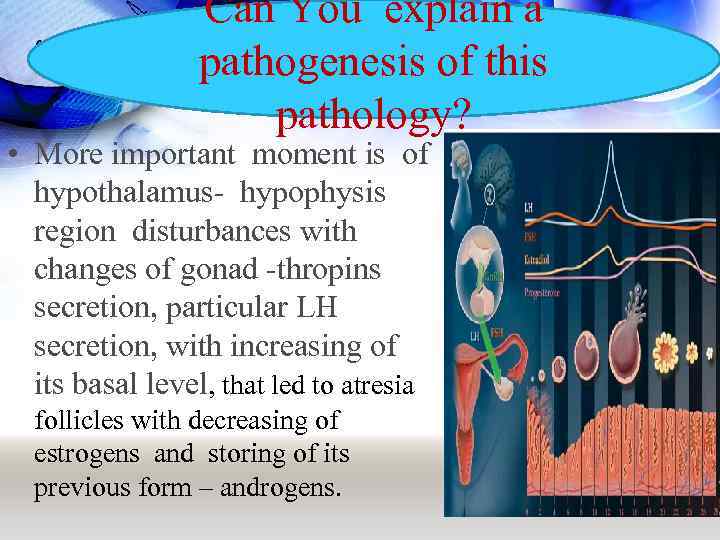 Can You explain a pathogenesis of this pathology? • More important moment is of hypothalamus- hypophysis region disturbances with changes of gonad -thropins secretion, particular LH secretion, with increasing of its basal level, that led to atresia follicles with decreasing of estrogens and storing of its previous form – androgens.
Can You explain a pathogenesis of this pathology? • More important moment is of hypothalamus- hypophysis region disturbances with changes of gonad -thropins secretion, particular LH secretion, with increasing of its basal level, that led to atresia follicles with decreasing of estrogens and storing of its previous form – androgens.
 What are the common symptoms of polycystic ovarian syndrome? Ø Olygomenorrhea, amenorrhea Ø Infertility Ø Increasing of androgen’s level ü Central adipositas ü Androgenic alopecia ü Akantosis ü Stria’s ü Night ‘s apnoae
What are the common symptoms of polycystic ovarian syndrome? Ø Olygomenorrhea, amenorrhea Ø Infertility Ø Increasing of androgen’s level ü Central adipositas ü Androgenic alopecia ü Akantosis ü Stria’s ü Night ‘s apnoae
 • • • Depressionессия Irritability ), agresstion ь, apathy Many cysts in ovaries. On USI – many white vesicles or “ costs from frut’s on all tissue of ovaries;
• • • Depressionессия Irritability ), agresstion ь, apathy Many cysts in ovaries. On USI – many white vesicles or “ costs from frut’s on all tissue of ovaries;
 • There is increasing of ovaries size in 1. 5 till 3 times due to small cysts ; • Thick and hyperplastic endometrium due to chronic over loading by estrogens without progesterone influence;
• There is increasing of ovaries size in 1. 5 till 3 times due to small cysts ; • Thick and hyperplastic endometrium due to chronic over loading by estrogens without progesterone influence;
 • Chronic pains in low part of abdomen due to pressure of enlarged ovaries , hypersecretion of prostaglandins. • The exact reason of pains in low part of abdomen is unknown
• Chronic pains in low part of abdomen due to pressure of enlarged ovaries , hypersecretion of prostaglandins. • The exact reason of pains in low part of abdomen is unknown
 What are the methods of examinations in this case? • • • CBA Coagulogram Smear on purity of vagina LH, FSH, free testosterone Progesterone, estradiolum 17 -CS prolactine; ТТH, Т 3, Т 4 ; IFA, PCR on virus infections
What are the methods of examinations in this case? • • • CBA Coagulogram Smear on purity of vagina LH, FSH, free testosterone Progesterone, estradiolum 17 -CS prolactine; ТТH, Т 3, Т 4 ; IFA, PCR on virus infections
 What are the results of investigation? Ø CBA – norm Ø Coagulogram: в norm Ø Smear on purity of vagina : the 2 degree. Ø 17 -CS - 9, 99 mg/24 hours (norm 7, 5 -9 )0 higher of norm Ø Testosterone- 0, 72 ng/mg (norm 0, 07 -0, 65) higher of norm Ø Prolactinum 482, 7 mc. МЕ/l (30, 3 -818, 1), norm.
What are the results of investigation? Ø CBA – norm Ø Coagulogram: в norm Ø Smear on purity of vagina : the 2 degree. Ø 17 -CS - 9, 99 mg/24 hours (norm 7, 5 -9 )0 higher of norm Ø Testosterone- 0, 72 ng/mg (norm 0, 07 -0, 65) higher of norm Ø Prolactinum 482, 7 mc. МЕ/l (30, 3 -818, 1), norm.
 What are the results of laboratory methods of investigation o o o o Estradiolum-42, 6 pgr/ml ( norm 57 -227) – low norm LH 25, 0 IU/L (0, 7 -24, 5), high the norm. FSH 6, 7 IU/L (2, 2 -15), norm. Progesterone 1, 3 nmoll ( norm 8 -78) low the norm TTH 3, 1 ngr/l (3, 2), - norm. Three IT 1, 42 ngr/l (1, 46), norm. Thyroxin-170 (172± 3, 8 ngr/l-н norm
What are the results of laboratory methods of investigation o o o o Estradiolum-42, 6 pgr/ml ( norm 57 -227) – low norm LH 25, 0 IU/L (0, 7 -24, 5), high the norm. FSH 6, 7 IU/L (2, 2 -15), norm. Progesterone 1, 3 nmoll ( norm 8 -78) low the norm TTH 3, 1 ngr/l (3, 2), - norm. Three IT 1, 42 ngr/l (1, 46), norm. Thyroxin-170 (172± 3, 8 ngr/l-н norm
 Результаты дополнительных методов исследований. What are the results of additional methods of examination ? o Basal temperature during 3 months is mono phase o USI: length of uterus is - 44, 7 mm, wide - 37, 5 mm, right ovary is - 41, 2 mm, left is 39, 7 mm, structure like a many peripheral situated small cysts o Markers of urogenital infections - negative.
Результаты дополнительных методов исследований. What are the results of additional methods of examination ? o Basal temperature during 3 months is mono phase o USI: length of uterus is - 44, 7 mm, wide - 37, 5 mm, right ovary is - 41, 2 mm, left is 39, 7 mm, structure like a many peripheral situated small cysts o Markers of urogenital infections - negative.
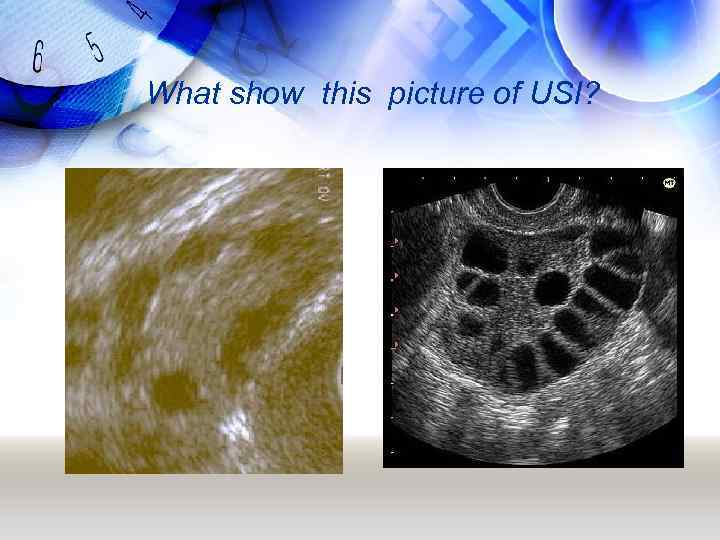 What show this picture of USI?
What show this picture of USI?
 What treatment should be performed in this case? ü Dexametason on ¼ table during 2 - weeks ü Estroferm on 1 table from 5 till 15 -й день day of menstrual cycle ü Clomifen fro stimulation of ovulation from 5 -th till 9 -th day. ü Didrogesteron from 16 -th till 25 -th day on 10 mg 2 times during 4 -months
What treatment should be performed in this case? ü Dexametason on ¼ table during 2 - weeks ü Estroferm on 1 table from 5 till 15 -й день day of menstrual cycle ü Clomifen fro stimulation of ovulation from 5 -th till 9 -th day. ü Didrogesteron from 16 -th till 25 -th day on 10 mg 2 times during 4 -months
 : The results are : v Decreasing of 17 - CS in 2 weeks till- 9, 86 mg/24 hours In one month : v - testosterone is - 0, 39 ngr/mg v - 17 CS - 5, 57 mg/ 24 hours. v In 4 months – pregnancy v Labor with alive boy with mass 3300, 0 height 54 sm.
: The results are : v Decreasing of 17 - CS in 2 weeks till- 9, 86 mg/24 hours In one month : v - testosterone is - 0, 39 ngr/mg v - 17 CS - 5, 57 mg/ 24 hours. v In 4 months – pregnancy v Labor with alive boy with mass 3300, 0 height 54 sm.
 • As a rule, in cases of infertility, which type • of investigation should be done the first and why?
• As a rule, in cases of infertility, which type • of investigation should be done the first and why?
 • Husband should be undergone of investigation the first. Sperm should be investigated. • As a rule, examination of man is more short and result may be seen very quick.
• Husband should be undergone of investigation the first. Sperm should be investigated. • As a rule, examination of man is more short and result may be seen very quick.
 • What are the reasons of male infertility?
• What are the reasons of male infertility?
 Reasons of male infertility are: • Secretory factors: disturbances of spermatogenesis. • Excretory factors: disturbances of going out of sperm. • Varicocele may be, inflammatory diseases, congenital defect of sexual organs.
Reasons of male infertility are: • Secretory factors: disturbances of spermatogenesis. • Excretory factors: disturbances of going out of sperm. • Varicocele may be, inflammatory diseases, congenital defect of sexual organs.
 Clinic case 2 v Pregnant woman of 29 years old came to doctor with complains on absence of pregnancies during 5 years of marriage. v She and her husband attend the special clinic the first and it was found, that husband is completely healthy with position of inability to have a children.
Clinic case 2 v Pregnant woman of 29 years old came to doctor with complains on absence of pregnancies during 5 years of marriage. v She and her husband attend the special clinic the first and it was found, that husband is completely healthy with position of inability to have a children.
 Special gynecologic examination v. Examination of the external sexual organs: External organs developed on the right way, there is developing of hair on female type. v In speculum: cervix without of pathology , discharges are white. v. P. V. Cervix is normal size. External os is closed. Uterus is normal size, to displaced to the right. Adnexa from both side are enlarged till 2 sm. , painful on palpation.
Special gynecologic examination v. Examination of the external sexual organs: External organs developed on the right way, there is developing of hair on female type. v In speculum: cervix without of pathology , discharges are white. v. P. V. Cervix is normal size. External os is closed. Uterus is normal size, to displaced to the right. Adnexa from both side are enlarged till 2 sm. , painful on palpation.
 What is Your tactic and why? • ? Кокрайновское руководство.
What is Your tactic and why? • ? Кокрайновское руководство.
 v. We have to perform antiinflammatory treatment after checking the sensitivity of microorganism to antibiotics, surgical correction of anatomic permeability of tubes- laparoscopy. v. If tubes are blocked at the interstitial or isthmus part – tubes should be removed.
v. We have to perform antiinflammatory treatment after checking the sensitivity of microorganism to antibiotics, surgical correction of anatomic permeability of tubes- laparoscopy. v. If tubes are blocked at the interstitial or isthmus part – tubes should be removed.
 • Treatment should be done during one year. If there is no positive result -extracorporeal fertilization should be done.
• Treatment should be done during one year. If there is no positive result -extracorporeal fertilization should be done.
 v Extracorporeal fertilization is fertilization of ovum in vitro, cultivation and taking of embryo in uterus. v Previously the induction of ovulation should be done for receiving many mature oocytes. v It is possible to perform conservation of oocytes, embryos, sperm in our time , that makes this procedure less expansive.
v Extracorporeal fertilization is fertilization of ovum in vitro, cultivation and taking of embryo in uterus. v Previously the induction of ovulation should be done for receiving many mature oocytes. v It is possible to perform conservation of oocytes, embryos, sperm in our time , that makes this procedure less expansive.
 • What is a doctor’s tactic?
• What is a doctor’s tactic?
 ? ? ? ? ?
? ? ? ? ?
 • • Complex anti – inflammatory treatment with using modern enzymes- distreptase and another.
• • Complex anti – inflammatory treatment with using modern enzymes- distreptase and another.
 In cases of absence of effect – extra corporal fertilization. Extra corporal fertilization has few stages. The first – activation of follicle genesis in ovaries, using of activators over super ovulation. 2. Puncture of all follicles with diameter more 15 mm under the USI control 3. Receiving oocytes are put in special medium , that contents not less, than 100 000 spermatozoon's , 3. Embryons after 48 hours , using a special catheter are putting in uterus ( 2 -3), another one may be as
In cases of absence of effect – extra corporal fertilization. Extra corporal fertilization has few stages. The first – activation of follicle genesis in ovaries, using of activators over super ovulation. 2. Puncture of all follicles with diameter more 15 mm under the USI control 3. Receiving oocytes are put in special medium , that contents not less, than 100 000 spermatozoon's , 3. Embryons after 48 hours , using a special catheter are putting in uterus ( 2 -3), another one may be as
 • What is a treatment in cases of single spermatozoon's?
• What is a treatment in cases of single spermatozoon's?
 • Intra-cytoplasmatic injection of spermatozoon's
• Intra-cytoplasmatic injection of spermatozoon's
 Conclusion • Infertility is a poly etiologic problem, it is not possible to decide a problem in all cases. Due to that the common examination of married couple should be done after one year of common life for detection of reason and proper treatment.
Conclusion • Infertility is a poly etiologic problem, it is not possible to decide a problem in all cases. Due to that the common examination of married couple should be done after one year of common life for detection of reason and proper treatment.
 Conclusion • In cases of in time examination of patient and in time treatment performing before pregnancy, monitory of pregnancy, delivery of alive babies in time may be at 98%.
Conclusion • In cases of in time examination of patient and in time treatment performing before pregnancy, monitory of pregnancy, delivery of alive babies in time may be at 98%.



