e0a121836df27b560c84e31835374b29.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 State Farm Insurance Companies
State Farm Insurance Companies
 Agenda • State Farm Overview • State Farm Investment Department • State Farm Fixed Income
Agenda • State Farm Overview • State Farm Investment Department • State Farm Fixed Income
 State Farm Overview
State Farm Overview
 Company Evolution George J. Mecherle Auto Health Life Fire SF Bank & Mutual Funds
Company Evolution George J. Mecherle Auto Health Life Fire SF Bank & Mutual Funds
 “About State Farm” State Farm’s mission is to: • help people manage the risks of everyday life, • recover from the unexpected, • and realize their dreams.
“About State Farm” State Farm’s mission is to: • help people manage the risks of everyday life, • recover from the unexpected, • and realize their dreams.
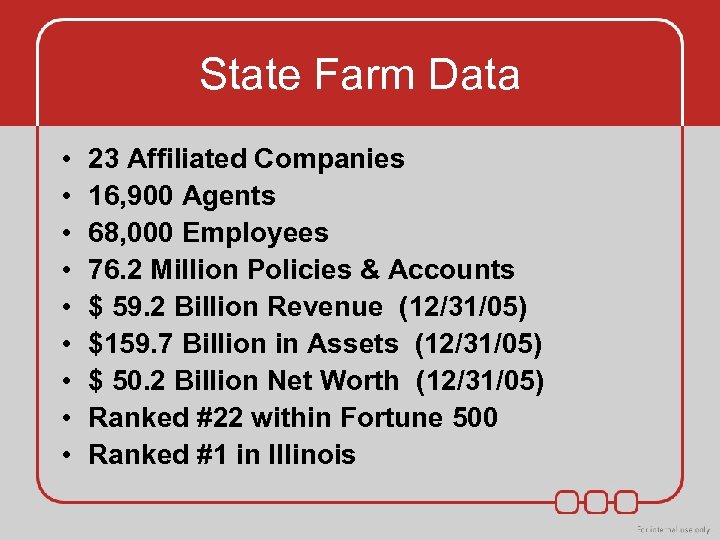 State Farm Data • • • 23 Affiliated Companies 16, 900 Agents 68, 000 Employees 76. 2 Million Policies & Accounts $ 59. 2 Billion Revenue (12/31/05) $159. 7 Billion in Assets (12/31/05) $ 50. 2 Billion Net Worth (12/31/05) Ranked #22 within Fortune 500 Ranked #1 in Illinois
State Farm Data • • • 23 Affiliated Companies 16, 900 Agents 68, 000 Employees 76. 2 Million Policies & Accounts $ 59. 2 Billion Revenue (12/31/05) $159. 7 Billion in Assets (12/31/05) $ 50. 2 Billion Net Worth (12/31/05) Ranked #22 within Fortune 500 Ranked #1 in Illinois
 Industry Positions • #1 U. S. Auto insurer since 1942 • 17. 7% Market Share at end of 2005 • Over 40 million Auto policies • #1 U. S. Home insurer since 1964 • 22. 2% Market Share at end of 2005 • Over 25 million Fire policies • SF Bank • $12. 2 billion in total assets (12/2005) • Top 5% of banks nationwide • Mutual Funds • $2. 8 billion in assets (12/2005)
Industry Positions • #1 U. S. Auto insurer since 1942 • 17. 7% Market Share at end of 2005 • Over 40 million Auto policies • #1 U. S. Home insurer since 1964 • 22. 2% Market Share at end of 2005 • Over 25 million Fire policies • SF Bank • $12. 2 billion in total assets (12/2005) • Top 5% of banks nationwide • Mutual Funds • $2. 8 billion in assets (12/2005)
 State Farm Investment Department
State Farm Investment Department
 Investment Department Invested Assets* ($ Billions) Cash & equivalent Bonds Stocks Mortgages & Real Estate Total xxx xxx $ xxx * (12/31/2006)
Investment Department Invested Assets* ($ Billions) Cash & equivalent Bonds Stocks Mortgages & Real Estate Total xxx xxx $ xxx * (12/31/2006)
 Why does State Farm have an Investment Department? • Amount of “float” the business generates – Premiums – Reserves • Cost of the float – Claims – Operating expenses • Long-term outlook for both these factors – Write more policies
Why does State Farm have an Investment Department? • Amount of “float” the business generates – Premiums – Reserves • Cost of the float – Claims – Operating expenses • Long-term outlook for both these factors – Write more policies
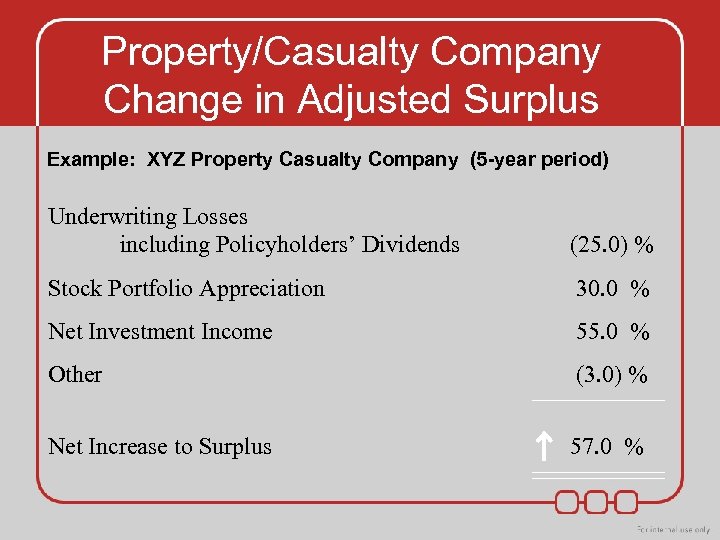 Property/Casualty Company Change in Adjusted Surplus Example: XYZ Property Casualty Company (5 -year period) Underwriting Losses including Policyholders’ Dividends (25. 0) % Stock Portfolio Appreciation 30. 0 % Net Investment Income 55. 0 % Other (3. 0) % Net Increase to Surplus 57. 0 %
Property/Casualty Company Change in Adjusted Surplus Example: XYZ Property Casualty Company (5 -year period) Underwriting Losses including Policyholders’ Dividends (25. 0) % Stock Portfolio Appreciation 30. 0 % Net Investment Income 55. 0 % Other (3. 0) % Net Increase to Surplus 57. 0 %
 Structure Investment Policy to Withstand Worse Case Scenario • Major underwriting losses • Discovery of gross underestimation of cost of unpaid claims • Collapse in stock and long-term bond prices
Structure Investment Policy to Withstand Worse Case Scenario • Major underwriting losses • Discovery of gross underestimation of cost of unpaid claims • Collapse in stock and long-term bond prices
 Insurance Company Financial Adequacy Ratios • Premiums / surplus – tests adequacy of capital to prolonged poor underwriting results • Loss reserves / surplus – tests potential for estimation error relative to capital • Equities / surplus – tests potential for stock market declines to reduce capital
Insurance Company Financial Adequacy Ratios • Premiums / surplus – tests adequacy of capital to prolonged poor underwriting results • Loss reserves / surplus – tests potential for estimation error relative to capital • Equities / surplus – tests potential for stock market declines to reduce capital
 State Farm’s Top 10 Catastrophe Pay-outs (Auto & Fire Combined)
State Farm’s Top 10 Catastrophe Pay-outs (Auto & Fire Combined)
 Investment Department Goals • Support insurance & financial service operations • Invest long-term
Investment Department Goals • Support insurance & financial service operations • Invest long-term
 Support Insurance and Financial Service Operations • State Farm Companies are first and foremost insurance companies with growing financial service operations • Make investment decisions for investment reasons first
Support Insurance and Financial Service Operations • State Farm Companies are first and foremost insurance companies with growing financial service operations • Make investment decisions for investment reasons first
 Long Term Investing Long-term investors have earned higher returns over the years from equity investments versus any other asset class Equities: Goal: Maximize shareholder value Return: Potentially unlimited Fixed Income: Goal: Capital preservation Return: Generally limited to coupon or yield
Long Term Investing Long-term investors have earned higher returns over the years from equity investments versus any other asset class Equities: Goal: Maximize shareholder value Return: Potentially unlimited Fixed Income: Goal: Capital preservation Return: Generally limited to coupon or yield
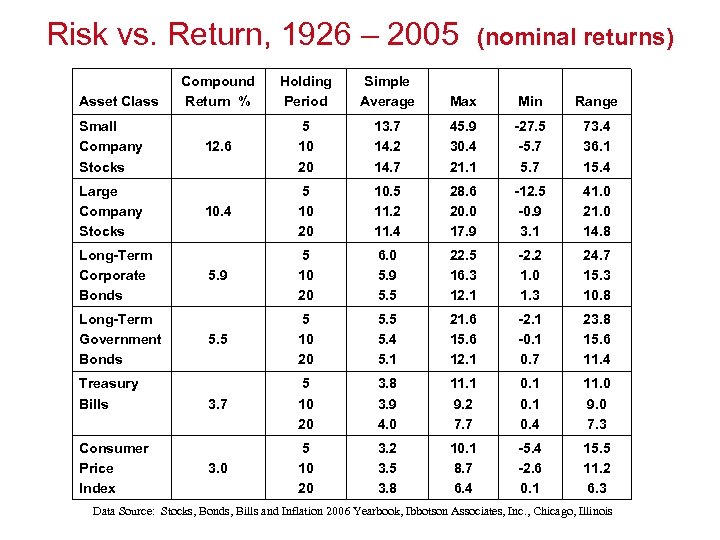 Risk vs. Return, 1926 – 2005 Asset Class Small Company Stocks Large Company Stocks Long-Term Corporate Bonds Long-Term Government Bonds Treasury Bills Consumer Price Index (nominal returns) Compound Return % Holding Period Simple Average Max Min Range 12. 6 5 10 20 13. 7 14. 2 14. 7 45. 9 30. 4 21. 1 -27. 5 -5. 7 73. 4 36. 1 15. 4 10. 4 5 10 20 10. 5 11. 2 11. 4 28. 6 20. 0 17. 9 -12. 5 -0. 9 3. 1 41. 0 21. 0 14. 8 5. 9 5 10 20 6. 0 5. 9 5. 5 22. 5 16. 3 12. 1 -2. 2 1. 0 1. 3 24. 7 15. 3 10. 8 5. 5 5 10 20 5. 5 5. 4 5. 1 21. 6 15. 6 12. 1 -0. 1 0. 7 23. 8 15. 6 11. 4 3. 7 5 10 20 3. 8 3. 9 4. 0 11. 1 9. 2 7. 7 0. 1 0. 4 11. 0 9. 0 7. 3 3. 0 5 10 20 3. 2 3. 5 3. 8 10. 1 8. 7 6. 4 -5. 4 -2. 6 0. 1 15. 5 11. 2 6. 3 Data Source: Stocks, Bonds, Bills and Inflation 2006 Yearbook, Ibbotson Associates, Inc. , Chicago, Illinois
Risk vs. Return, 1926 – 2005 Asset Class Small Company Stocks Large Company Stocks Long-Term Corporate Bonds Long-Term Government Bonds Treasury Bills Consumer Price Index (nominal returns) Compound Return % Holding Period Simple Average Max Min Range 12. 6 5 10 20 13. 7 14. 2 14. 7 45. 9 30. 4 21. 1 -27. 5 -5. 7 73. 4 36. 1 15. 4 10. 4 5 10 20 10. 5 11. 2 11. 4 28. 6 20. 0 17. 9 -12. 5 -0. 9 3. 1 41. 0 21. 0 14. 8 5. 9 5 10 20 6. 0 5. 9 5. 5 22. 5 16. 3 12. 1 -2. 2 1. 0 1. 3 24. 7 15. 3 10. 8 5. 5 5 10 20 5. 5 5. 4 5. 1 21. 6 15. 6 12. 1 -0. 1 0. 7 23. 8 15. 6 11. 4 3. 7 5 10 20 3. 8 3. 9 4. 0 11. 1 9. 2 7. 7 0. 1 0. 4 11. 0 9. 0 7. 3 3. 0 5 10 20 3. 2 3. 5 3. 8 10. 1 8. 7 6. 4 -5. 4 -2. 6 0. 1 15. 5 11. 2 6. 3 Data Source: Stocks, Bonds, Bills and Inflation 2006 Yearbook, Ibbotson Associates, Inc. , Chicago, Illinois
 State Farm Fixed Income
State Farm Fixed Income
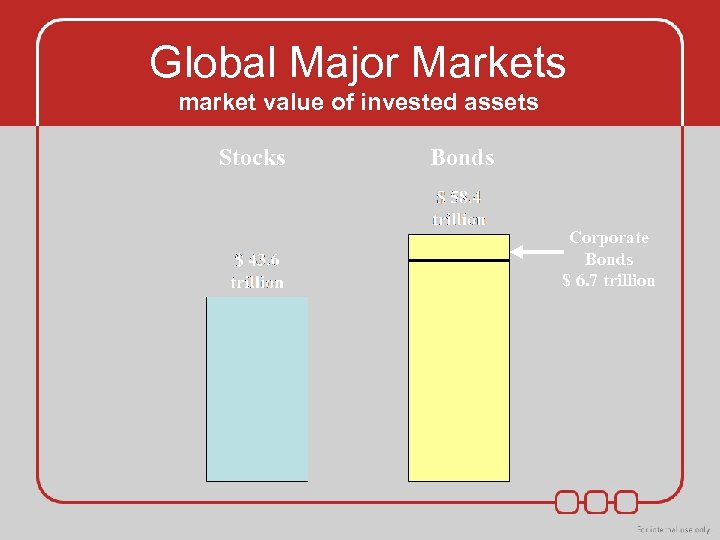 Global Major Markets market value of invested assets Stocks Bonds Corporate Bonds $ 6. 7 trillion
Global Major Markets market value of invested assets Stocks Bonds Corporate Bonds $ 6. 7 trillion
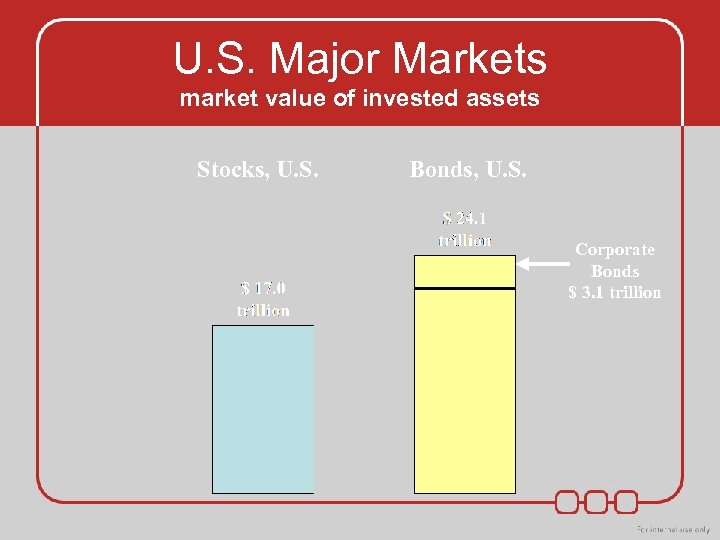 U. S. Major Markets market value of invested assets Stocks, U. S. Bonds, U. S. Corporate Bonds $ 3. 1 trillion
U. S. Major Markets market value of invested assets Stocks, U. S. Bonds, U. S. Corporate Bonds $ 3. 1 trillion
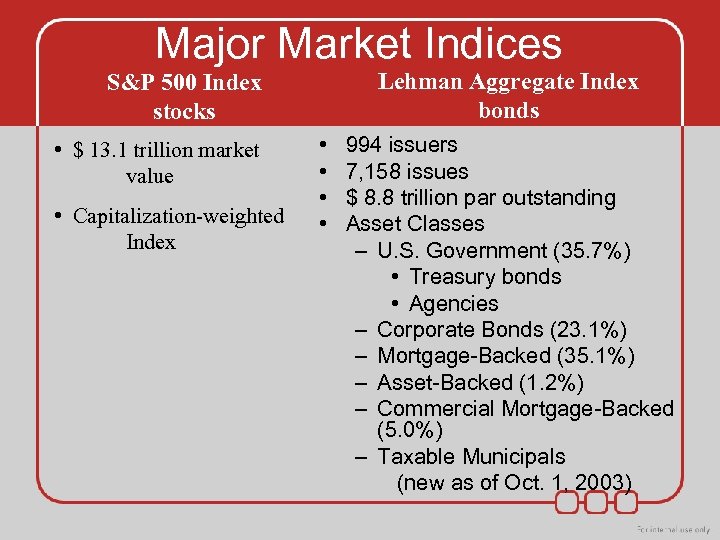 Major Market Indices Lehman Aggregate Index bonds S&P 500 Index stocks • $ 13. 1 trillion market value • Capitalization-weighted Index • • 994 issuers 7, 158 issues $ 8. 8 trillion par outstanding Asset Classes – U. S. Government (35. 7%) • Treasury bonds • Agencies – Corporate Bonds (23. 1%) – Mortgage-Backed (35. 1%) – Asset-Backed (1. 2%) – Commercial Mortgage-Backed (5. 0%) – Taxable Municipals (new as of Oct. 1, 2003)
Major Market Indices Lehman Aggregate Index bonds S&P 500 Index stocks • $ 13. 1 trillion market value • Capitalization-weighted Index • • 994 issuers 7, 158 issues $ 8. 8 trillion par outstanding Asset Classes – U. S. Government (35. 7%) • Treasury bonds • Agencies – Corporate Bonds (23. 1%) – Mortgage-Backed (35. 1%) – Asset-Backed (1. 2%) – Commercial Mortgage-Backed (5. 0%) – Taxable Municipals (new as of Oct. 1, 2003)
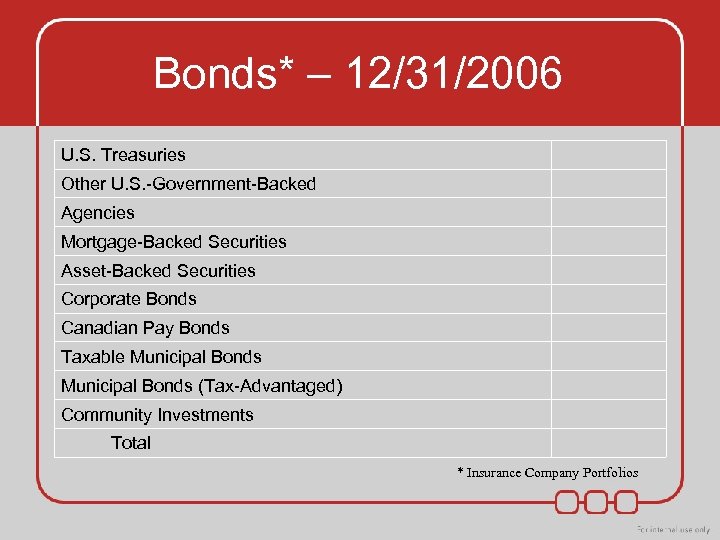 Bonds* – 12/31/2006 U. S. Treasuries Other U. S. -Government-Backed Agencies Mortgage-Backed Securities Asset-Backed Securities Corporate Bonds Canadian Pay Bonds Taxable Municipal Bonds (Tax-Advantaged) Community Investments Total * Insurance Company Portfolios
Bonds* – 12/31/2006 U. S. Treasuries Other U. S. -Government-Backed Agencies Mortgage-Backed Securities Asset-Backed Securities Corporate Bonds Canadian Pay Bonds Taxable Municipal Bonds (Tax-Advantaged) Community Investments Total * Insurance Company Portfolios
 State Farm Investment Philosophies and Disciplines: • • Buy and Hold Dollar-Cost Average Portfolio Ladder Duration Target
State Farm Investment Philosophies and Disciplines: • • Buy and Hold Dollar-Cost Average Portfolio Ladder Duration Target
 Corporate Bonds • Private vs. Public • Analyzing and investing in corporate bonds • Pricing corporate bonds
Corporate Bonds • Private vs. Public • Analyzing and investing in corporate bonds • Pricing corporate bonds
 Fundamental Credit Analysis • Industry Analysis – Porter’s 5 Forces • Business Risk Analysis • Financial Risk Analysis
Fundamental Credit Analysis • Industry Analysis – Porter’s 5 Forces • Business Risk Analysis • Financial Risk Analysis
 Porter’s Five Forces of Competition • • • Barriers to Entry Threat of Substitute Products Power of Suppliers Power of Buyers Rivalry among Existing Competitors Source: Michael Porter, Competitive Strategy
Porter’s Five Forces of Competition • • • Barriers to Entry Threat of Substitute Products Power of Suppliers Power of Buyers Rivalry among Existing Competitors Source: Michael Porter, Competitive Strategy
 Business Risk Analysis • Industry Characteristics • Competitive Position • Management
Business Risk Analysis • Industry Characteristics • Competitive Position • Management
 Financial Risk Analysis • • • Financial Characteristics Financial Policy Profitability Capital Structure Cash Flow Protection Financial Flexibility
Financial Risk Analysis • • • Financial Characteristics Financial Policy Profitability Capital Structure Cash Flow Protection Financial Flexibility
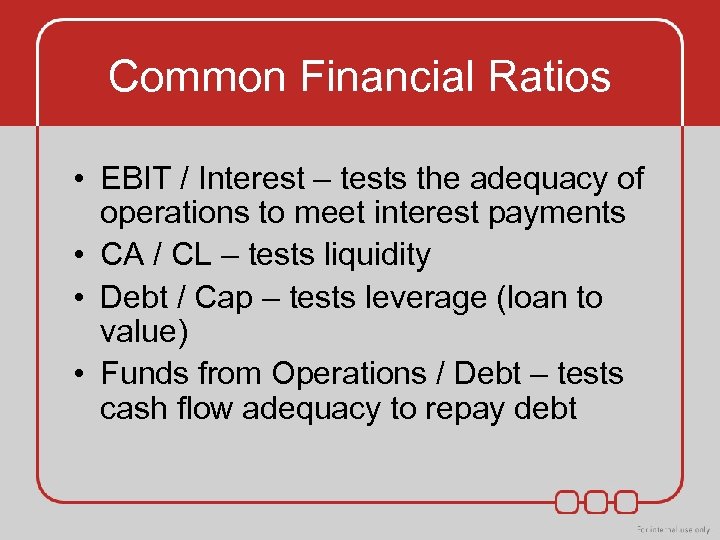 Common Financial Ratios • EBIT / Interest – tests the adequacy of operations to meet interest payments • CA / CL – tests liquidity • Debt / Cap – tests leverage (loan to value) • Funds from Operations / Debt – tests cash flow adequacy to repay debt
Common Financial Ratios • EBIT / Interest – tests the adequacy of operations to meet interest payments • CA / CL – tests liquidity • Debt / Cap – tests leverage (loan to value) • Funds from Operations / Debt – tests cash flow adequacy to repay debt
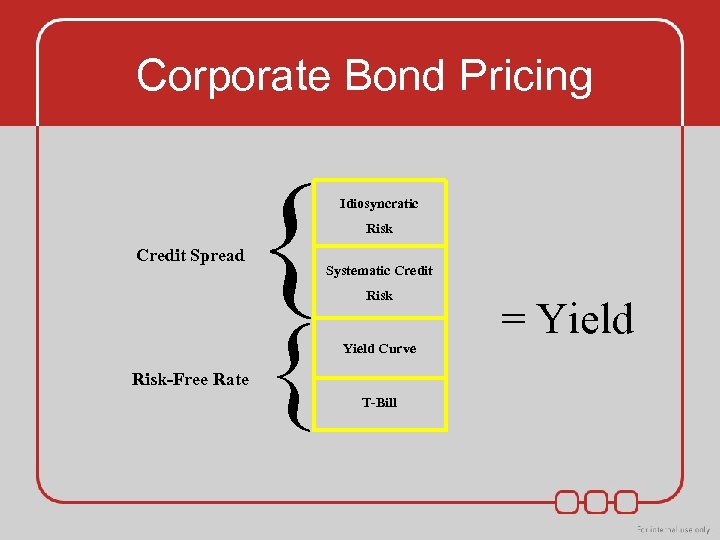 Corporate Bond Pricing Credit Spread Risk-Free Rate { { Idiosyncratic Risk Systematic Credit Risk Yield Curve T-Bill = Yield
Corporate Bond Pricing Credit Spread Risk-Free Rate { { Idiosyncratic Risk Systematic Credit Risk Yield Curve T-Bill = Yield
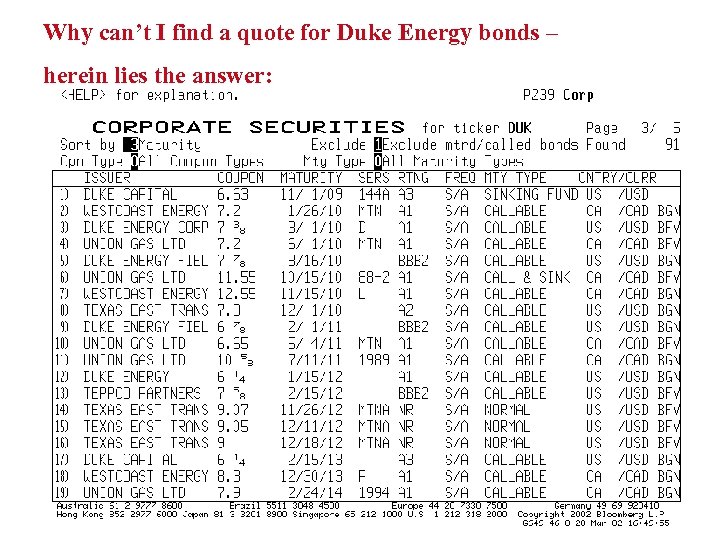 Why can’t I find a quote for Duke Energy bonds – herein lies the answer:
Why can’t I find a quote for Duke Energy bonds – herein lies the answer:
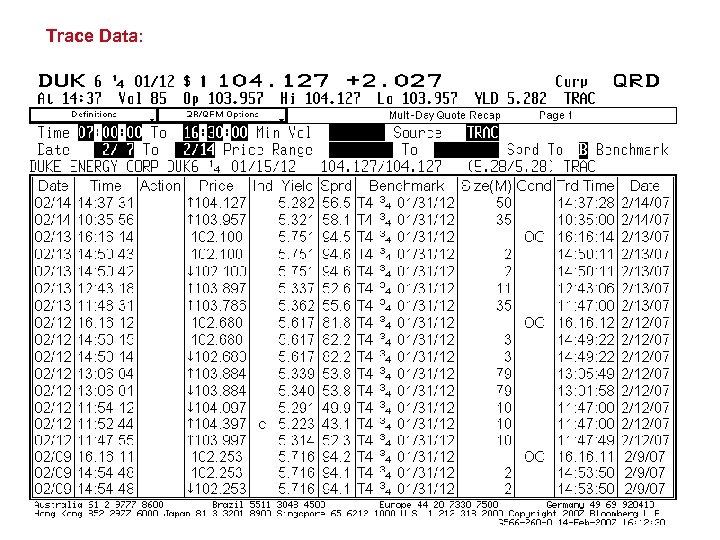 Trace Data:
Trace Data:
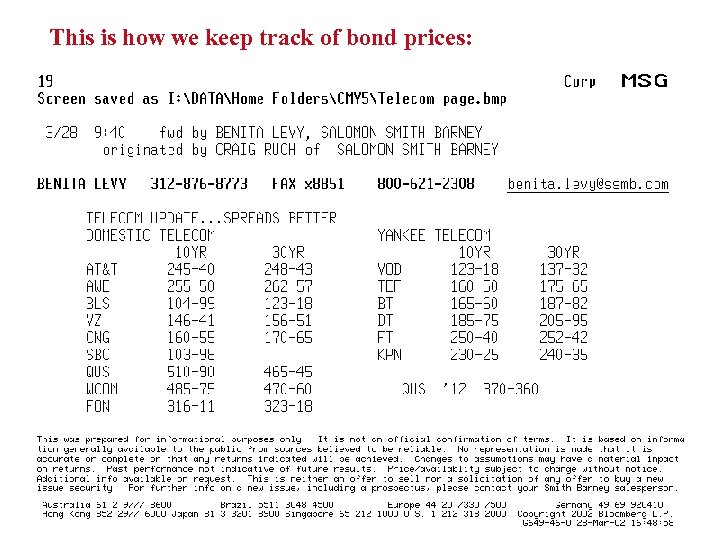 This is how we keep track of bond prices:
This is how we keep track of bond prices:
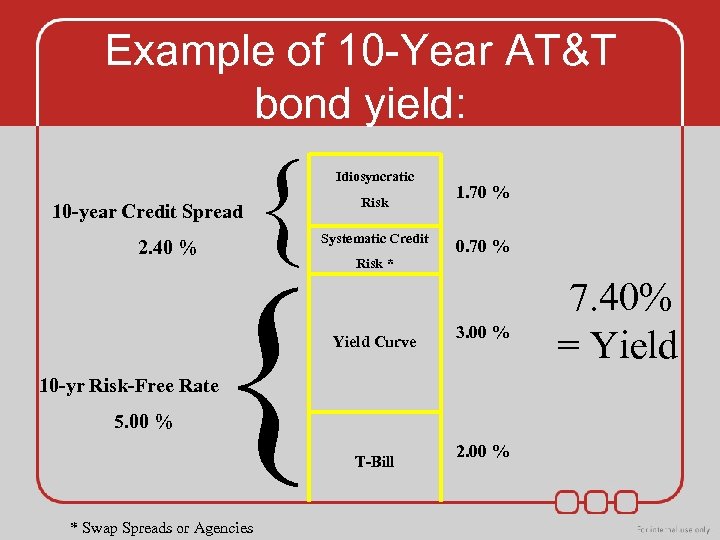 Example of 10 -Year AT&T bond yield: 10 -year Credit Spread 2. 40 % { { Idiosyncratic Risk Systematic Credit Risk * Yield Curve 1. 70 % 0. 70 % 3. 00 % 10 -yr Risk-Free Rate 5. 00 % * Swap Spreads or Agencies T-Bill 2. 00 % 7. 40% = Yield
Example of 10 -Year AT&T bond yield: 10 -year Credit Spread 2. 40 % { { Idiosyncratic Risk Systematic Credit Risk * Yield Curve 1. 70 % 0. 70 % 3. 00 % 10 -yr Risk-Free Rate 5. 00 % * Swap Spreads or Agencies T-Bill 2. 00 % 7. 40% = Yield
 Example of 10 -Year AT&T bond prices: • 6% coupon 10 -year AT&T corporate bond trading at a yield of 7. 4% = $90. 23 (discount) • 8% coupon 10 -year AT&T corporate bond trading at a yield of 7. 4% = $104. 19 (premium) The coupons are different but both bonds trade at the same yield, 7. 4%.
Example of 10 -Year AT&T bond prices: • 6% coupon 10 -year AT&T corporate bond trading at a yield of 7. 4% = $90. 23 (discount) • 8% coupon 10 -year AT&T corporate bond trading at a yield of 7. 4% = $104. 19 (premium) The coupons are different but both bonds trade at the same yield, 7. 4%.
 Example of 10 -Year AT&T bond bid/ask yields: Bid (yield at which you can sell) Assume 10 -Year Treasury is 5. 00% 2. 45% Yield on Bid Side 7. 45% Offer (yield at which you can buy) Assume 10 -Year Treasury is 5. 00% 2. 40% Yield on Offer Side Remember from finance class – bond prices and yields are inversely related – a lower yield means a higher price. 7. 40% Think of bid/ask spread for stocks. You have to buy at a higher price than you can sell. The same holds true for bonds.
Example of 10 -Year AT&T bond bid/ask yields: Bid (yield at which you can sell) Assume 10 -Year Treasury is 5. 00% 2. 45% Yield on Bid Side 7. 45% Offer (yield at which you can buy) Assume 10 -Year Treasury is 5. 00% 2. 40% Yield on Offer Side Remember from finance class – bond prices and yields are inversely related – a lower yield means a higher price. 7. 40% Think of bid/ask spread for stocks. You have to buy at a higher price than you can sell. The same holds true for bonds.
 Investing in a New Public Corporate Bond Issue New deal is announced Perform fundamental credit analysis Price guidance Determine relative value Deal goes “subject” Receive allocation and final spread Road shows, Conference calls, Red-herring prospectus Submit order Price the deal, bill & deliver
Investing in a New Public Corporate Bond Issue New deal is announced Perform fundamental credit analysis Price guidance Determine relative value Deal goes “subject” Receive allocation and final spread Road shows, Conference calls, Red-herring prospectus Submit order Price the deal, bill & deliver
 Questions?
Questions?
 Contact Information State Farm Insurance Human Resources Three State Farm Plaza South, K-1 Bloomington, IL 61791 Need more information? Visit our website! www. statefarm. com E-mail: jobopps. corpsouth@statefarm. com
Contact Information State Farm Insurance Human Resources Three State Farm Plaza South, K-1 Bloomington, IL 61791 Need more information? Visit our website! www. statefarm. com E-mail: jobopps. corpsouth@statefarm. com


