e45730829b8837b236deab01d8be44cd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 STAT 3 and the Immune System Maureen Sherry Lynes February 29, 2012
STAT 3 and the Immune System Maureen Sherry Lynes February 29, 2012
 Overview § STAT family; STAT 3 signaling and structure § Role of STAT 3 revealed by tissue specific knockouts § STAT 3 and the anti-tumor immune response §Therapeutic approaches for targeting STAT 3 §Paper discussion
Overview § STAT family; STAT 3 signaling and structure § Role of STAT 3 revealed by tissue specific knockouts § STAT 3 and the anti-tumor immune response §Therapeutic approaches for targeting STAT 3 §Paper discussion
 The STAT Family of Transcription Factors § 7 mammalian STAT proteins § latent cytoplasmic transcription factors § Important in a wide range of physiological processes Adapted from Darnell and Levy, 2002
The STAT Family of Transcription Factors § 7 mammalian STAT proteins § latent cytoplasmic transcription factors § Important in a wide range of physiological processes Adapted from Darnell and Levy, 2002
 How is the STAT 3 pathway activated? • Cytokines, growth factors • Secreted by diverse cell types in response to diverse processes • Receptor specific Minegishi et al 2011
How is the STAT 3 pathway activated? • Cytokines, growth factors • Secreted by diverse cell types in response to diverse processes • Receptor specific Minegishi et al 2011
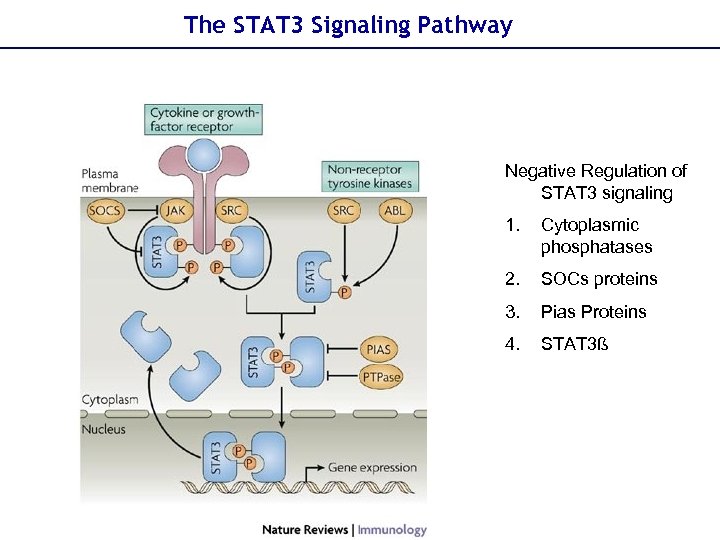 The STAT 3 Signaling Pathway Negative Regulation of STAT 3 signaling 1. Cytoplasmic phosphatases 2. SOCs proteins 3. Pias Proteins 4. STAT 3ß
The STAT 3 Signaling Pathway Negative Regulation of STAT 3 signaling 1. Cytoplasmic phosphatases 2. SOCs proteins 3. Pias Proteins 4. STAT 3ß
 Domain Structure of STAT 3
Domain Structure of STAT 3
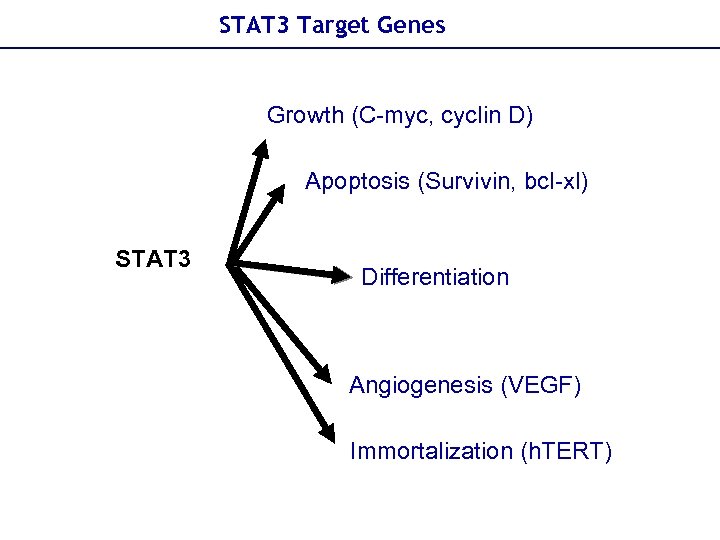 STAT 3 Target Genes Growth (C-myc, cyclin D) Apoptosis (Survivin, bcl-xl) STAT 3 Differentiation Angiogenesis (VEGF) Immortalization (h. TERT)
STAT 3 Target Genes Growth (C-myc, cyclin D) Apoptosis (Survivin, bcl-xl) STAT 3 Differentiation Angiogenesis (VEGF) Immortalization (h. TERT)
 Tissue Specific STAT 3 Knockouts • Brain: obesity, inability to control temperature, diabetes • Skin: impaired wound healing, resistance to skin cancer • Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells: loss of pluripotency • Lung • Macrophages and Neutrophils • Liver • Th 17 development Gao et al, 2004.
Tissue Specific STAT 3 Knockouts • Brain: obesity, inability to control temperature, diabetes • Skin: impaired wound healing, resistance to skin cancer • Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells: loss of pluripotency • Lung • Macrophages and Neutrophils • Liver • Th 17 development Gao et al, 2004.
 STAT 3 and the Acute Phase Response • Liver: site of integration of signals from tissue, toxins and bacterial products in blood, etc • Macrophages in the periphery: cytokine release • Hepatocytes respond to cytokines (IL-6, IL-1 for example) and upregulate appropriate response proteins (clotting, innate responses to bacterial infection, toxins, etc) • Hepatocyte deletion of STAT 3 - polymicrobial sepsis LPS injection or cecal ligation and puncture: Sakamori et al 2007 Similar bacterial load; decreased acute phase proteins, increased inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and TNFa
STAT 3 and the Acute Phase Response • Liver: site of integration of signals from tissue, toxins and bacterial products in blood, etc • Macrophages in the periphery: cytokine release • Hepatocytes respond to cytokines (IL-6, IL-1 for example) and upregulate appropriate response proteins (clotting, innate responses to bacterial infection, toxins, etc) • Hepatocyte deletion of STAT 3 - polymicrobial sepsis LPS injection or cecal ligation and puncture: Sakamori et al 2007 Similar bacterial load; decreased acute phase proteins, increased inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and TNFa
 STAT 3 in macrophages and neutrophils • STAT 3 deleted in cells expressing lysozyme M • Mice were susceptible to LPS-induced endotoxic shock • Macrophages constitutively activated Takeda et al, 1999.
STAT 3 in macrophages and neutrophils • STAT 3 deleted in cells expressing lysozyme M • Mice were susceptible to LPS-induced endotoxic shock • Macrophages constitutively activated Takeda et al, 1999.
 STAT 3 in macrophages and neutrophils • STAT 3 -/- macrophages are resistant to IL-10 • IL-10 normally dampens macrophage activation and response • Lysm. Cre STAT 3 mice develop chronic enterocholitis
STAT 3 in macrophages and neutrophils • STAT 3 -/- macrophages are resistant to IL-10 • IL-10 normally dampens macrophage activation and response • Lysm. Cre STAT 3 mice develop chronic enterocholitis
 STAT 3 in the lung epithelium • House dustmite extract: induces allergic inflammation in the lung, as well as STAT 3 activation • Lung specific STAT 3 KO: appears normal • STAT 3 lung KO: decreased airway hyperresponsiveness, immune infiltration upon HDM challenge Simeone et al, 2007.
STAT 3 in the lung epithelium • House dustmite extract: induces allergic inflammation in the lung, as well as STAT 3 activation • Lung specific STAT 3 KO: appears normal • STAT 3 lung KO: decreased airway hyperresponsiveness, immune infiltration upon HDM challenge Simeone et al, 2007.
 STAT 3 in Th 17 Differentiation • CD 4+, defense against extracellular bacteria, fungi • Pathogenic autoimmune responses • Celiac, IBD, etc Fischer 2008
STAT 3 in Th 17 Differentiation • CD 4+, defense against extracellular bacteria, fungi • Pathogenic autoimmune responses • Celiac, IBD, etc Fischer 2008
 STAT 3 in hyper Ig. E syndrome activation DNA binding
STAT 3 in hyper Ig. E syndrome activation DNA binding
 STAT 3 in hyper Ig. E syndrome Recurrent skin and lung infections (Th 17, lung epithelial defects? )
STAT 3 in hyper Ig. E syndrome Recurrent skin and lung infections (Th 17, lung epithelial defects? )
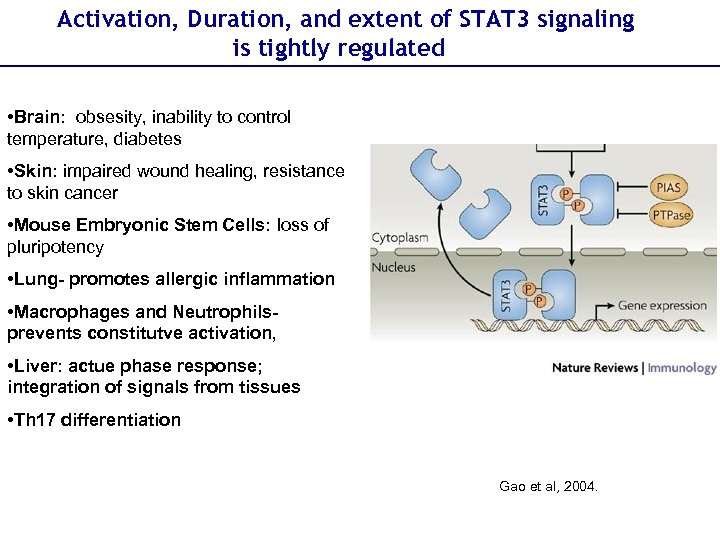 Activation, Duration, and extent of STAT 3 signaling is tightly regulated • Brain: obsesity, inability to control temperature, diabetes • Skin: impaired wound healing, resistance to skin cancer • Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells: loss of pluripotency • Lung- promotes allergic inflammation • Macrophages and Neutrophilsprevents constitutve activation, • Liver: actue phase response; integration of signals from tissues • Th 17 differentiation Gao et al, 2004.
Activation, Duration, and extent of STAT 3 signaling is tightly regulated • Brain: obsesity, inability to control temperature, diabetes • Skin: impaired wound healing, resistance to skin cancer • Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells: loss of pluripotency • Lung- promotes allergic inflammation • Macrophages and Neutrophilsprevents constitutve activation, • Liver: actue phase response; integration of signals from tissues • Th 17 differentiation Gao et al, 2004.
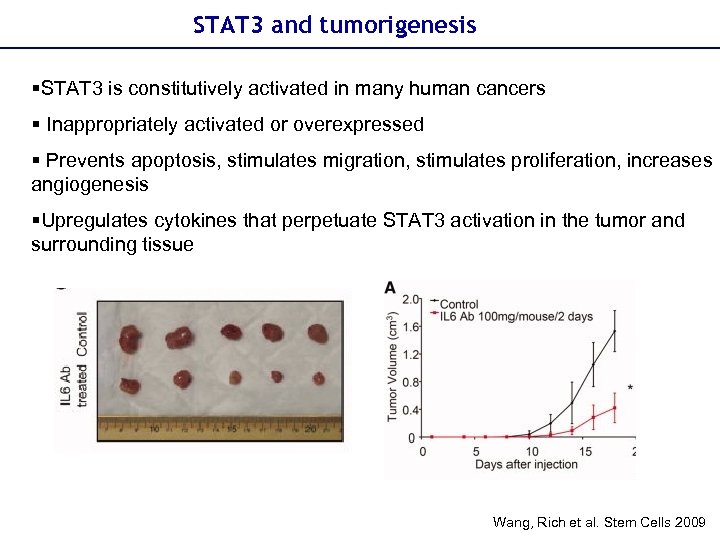 STAT 3 and tumorigenesis §STAT 3 is constitutively activated in many human cancers § Inappropriately activated or overexpressed § Prevents apoptosis, stimulates migration, stimulates proliferation, increases angiogenesis §Upregulates cytokines that perpetuate STAT 3 activation in the tumor and surrounding tissue Wang, Rich et al. Stem Cells 2009
STAT 3 and tumorigenesis §STAT 3 is constitutively activated in many human cancers § Inappropriately activated or overexpressed § Prevents apoptosis, stimulates migration, stimulates proliferation, increases angiogenesis §Upregulates cytokines that perpetuate STAT 3 activation in the tumor and surrounding tissue Wang, Rich et al. Stem Cells 2009
 DN STAT 3 induces melanoma regression in a mouse model §Transfection of B 16 tumors with dominant negative STAT 3 induces tumor regression § Bystander effect: regression disproportionate to transfection Niu et al Cancer Research 1999
DN STAT 3 induces melanoma regression in a mouse model §Transfection of B 16 tumors with dominant negative STAT 3 induces tumor regression § Bystander effect: regression disproportionate to transfection Niu et al Cancer Research 1999
 STAT 3 Suppresses Anti-Tumor Immunity §Cultured B 16 cells transfected with DN STAT 3: increased production of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines (TNFa, RANTES, IP-10) § In vivo: enhances macrophage and neutrophil infiltration Wang et al Nature Med 2004
STAT 3 Suppresses Anti-Tumor Immunity §Cultured B 16 cells transfected with DN STAT 3: increased production of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines (TNFa, RANTES, IP-10) § In vivo: enhances macrophage and neutrophil infiltration Wang et al Nature Med 2004
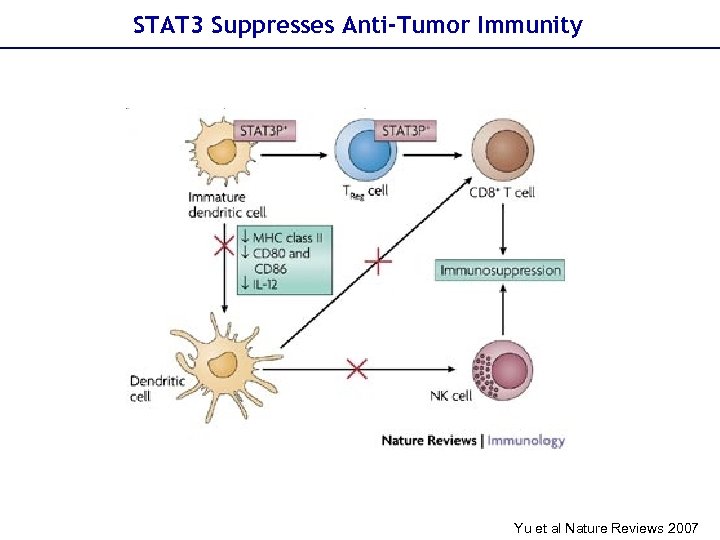 STAT 3 Suppresses Anti-Tumor Immunity Yu et al Nature Reviews 2007
STAT 3 Suppresses Anti-Tumor Immunity Yu et al Nature Reviews 2007
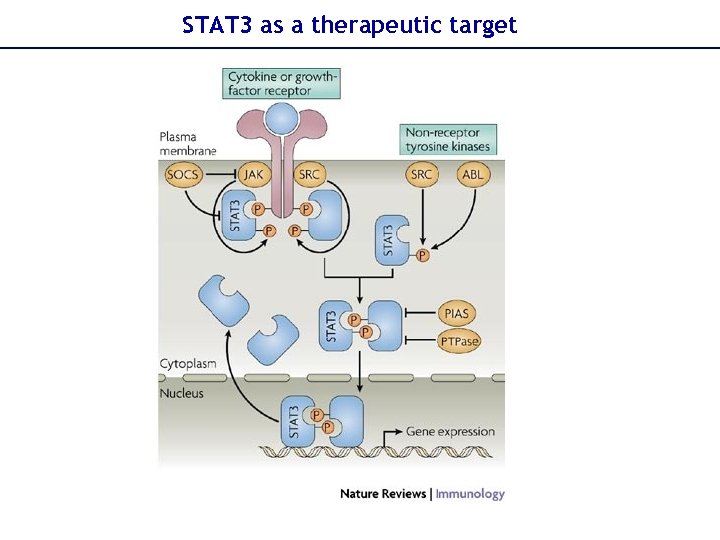 STAT 3 as a therapeutic target
STAT 3 as a therapeutic target
 STAT 3 as a therapeutic target §Activation §EGFR antibodies; small molecules §Jak inhibitors §Multi-receptor kinase inhibitors §Protein-protein interactions §Small molecules to prevent dimerization §phospho. Tyr peptides §DNA binding §Double stranded oligonucleotides §Nuclear translocation, natural inhibitors
STAT 3 as a therapeutic target §Activation §EGFR antibodies; small molecules §Jak inhibitors §Multi-receptor kinase inhibitors §Protein-protein interactions §Small molecules to prevent dimerization §phospho. Tyr peptides §DNA binding §Double stranded oligonucleotides §Nuclear translocation, natural inhibitors
 Summary §STAT 3 is a cytokine and growth factor activated transcription factor § STAT 3 has a wide range of functions, both anti and pro inflammatory depending on the tissue and physiological context §STAT 3 is also involved in disease states, such as asthma, colitis, and cancer §STAT 3 can suppress anti-tumor immunity §STAT 3 directed therapeutics is an active area of research
Summary §STAT 3 is a cytokine and growth factor activated transcription factor § STAT 3 has a wide range of functions, both anti and pro inflammatory depending on the tissue and physiological context §STAT 3 is also involved in disease states, such as asthma, colitis, and cancer §STAT 3 can suppress anti-tumor immunity §STAT 3 directed therapeutics is an active area of research



