cda456617a1113c715d965118c2ca2b7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Start. . .
Start. . .
 Power & Energy Technology Energy Sources Mr. Huebsch
Power & Energy Technology Energy Sources Mr. Huebsch
 Behavioral Objectives • Student will know the 10 sources of energy • Students will understand how we measure energy • Students will get a concept of our current supply and demand of energy • Students will understand our energy flow • Energy Picture • The Future through 2010
Behavioral Objectives • Student will know the 10 sources of energy • Students will understand how we measure energy • Students will get a concept of our current supply and demand of energy • Students will understand our energy flow • Energy Picture • The Future through 2010
 I. Sources of Energy • Renewable Sources – Solar (sun) • U. S. produces 0. 1% and uses 0. 1% • Solar collectors • PV – Wind • U. S. produces 0. 1% and uses 0. 1% • Windmills • http: //www. bahrainwtc. com/ – Hydropower • U. S. produces 3. 7% and uses 2. 7% • Falling or Flowing water • Tides – Geothermal • U. S. produces. 06% and uses 0. 3% • Heating and cooling – Biomass • • • U. S. produces 3. 9% and uses 2. 9% Fermentation (corn fuel, methane) Burning (wood) Bacterial Decay (methane from landfills) Conversion (to gas or liquid with chemicals)
I. Sources of Energy • Renewable Sources – Solar (sun) • U. S. produces 0. 1% and uses 0. 1% • Solar collectors • PV – Wind • U. S. produces 0. 1% and uses 0. 1% • Windmills • http: //www. bahrainwtc. com/ – Hydropower • U. S. produces 3. 7% and uses 2. 7% • Falling or Flowing water • Tides – Geothermal • U. S. produces. 06% and uses 0. 3% • Heating and cooling – Biomass • • • U. S. produces 3. 9% and uses 2. 9% Fermentation (corn fuel, methane) Burning (wood) Bacterial Decay (methane from landfills) Conversion (to gas or liquid with chemicals)
 Sources of Energy • Non-renewable sources – Coal • U. S. produces 31. 7% and uses 22. 8% • Top producing states • WY, WV, KY, PA, TX – Natural Gas • U. S. produces 27. 7% and uses 23% • Top producing states • TX, OK, NM, LA, WY – Oil • U. S. produces 18. 3% and uses 38. 3% • Top producing states • TX, AK, CA, LA, NM • Top importing countries • Saudi Arabia, Mexico, Canada, Venezuela, Nigeria – Nuclear Fuels • U. S. produces 11. 4% and uses 8. 3% • Uses uranium 235 to produce steam and create electricity – Propane • U. S. produces 2. 5% and uses 1. 9%
Sources of Energy • Non-renewable sources – Coal • U. S. produces 31. 7% and uses 22. 8% • Top producing states • WY, WV, KY, PA, TX – Natural Gas • U. S. produces 27. 7% and uses 23% • Top producing states • TX, OK, NM, LA, WY – Oil • U. S. produces 18. 3% and uses 38. 3% • Top producing states • TX, AK, CA, LA, NM • Top importing countries • Saudi Arabia, Mexico, Canada, Venezuela, Nigeria – Nuclear Fuels • U. S. produces 11. 4% and uses 8. 3% • Uses uranium 235 to produce steam and create electricity – Propane • U. S. produces 2. 5% and uses 1. 9%
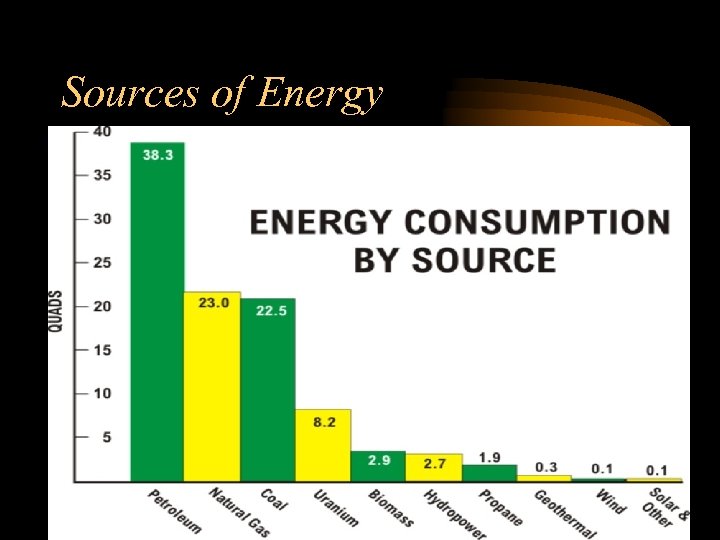 Sources of Energy
Sources of Energy
 2. Energy Units • Barrel – Liquid volume equal to 42 gallons or 159 liters – 1 barrel of crude oil has about the same heat energy as 350 pounds of bituminous coal • Btu (British thermal unit) – Our way of measuring heat – Quantity of heat necessary to raise temp. of one pound of water one degree Fahrenheit – Average American uses 889, 000 Btu’s daily
2. Energy Units • Barrel – Liquid volume equal to 42 gallons or 159 liters – 1 barrel of crude oil has about the same heat energy as 350 pounds of bituminous coal • Btu (British thermal unit) – Our way of measuring heat – Quantity of heat necessary to raise temp. of one pound of water one degree Fahrenheit – Average American uses 889, 000 Btu’s daily
 Energy Units • Calorie – Metric unit of heat energy – Amount of heat needed to raise the temp. of one gram of water on degree Celsius =. 0039 Btu • Watt – Unit of measure for electrical power equal to the transfer of one joule of energy per second
Energy Units • Calorie – Metric unit of heat energy – Amount of heat needed to raise the temp. of one gram of water on degree Celsius =. 0039 Btu • Watt – Unit of measure for electrical power equal to the transfer of one joule of energy per second
 Energy Units • Kilowatt – Measure of power, usually electrical power of heat flow. = 1, 000 watts or 3, 413 Btu • Quad – – Unit for describing very large amounts of energy (1015 Btu) Energy used by an entire country in a year. U. S. uses 1 quad about every 4 days Top three most populated in millions • China @ 1295 pop. = 43. 2 quads • India @ 1050 pop. = 14 quads • U. S. @ 288 pop. = 97. 4 quads
Energy Units • Kilowatt – Measure of power, usually electrical power of heat flow. = 1, 000 watts or 3, 413 Btu • Quad – – Unit for describing very large amounts of energy (1015 Btu) Energy used by an entire country in a year. U. S. uses 1 quad about every 4 days Top three most populated in millions • China @ 1295 pop. = 43. 2 quads • India @ 1050 pop. = 14 quads • U. S. @ 288 pop. = 97. 4 quads
 3. Supply vs. Demand • Supply – Input to a system (what we Have) • Demand – Output to a system (what we need) – Supply and Demand must be equal or problem will arise
3. Supply vs. Demand • Supply – Input to a system (what we Have) • Demand – Output to a system (what we need) – Supply and Demand must be equal or problem will arise
 Supply vs. Demand • Demand Sectors (where our energy goes) – Residential and Commercial • Energy used by homes, offices, schools, churches • 39. 4% – Industrial Sector • Produces goods and products we buy • Manufacturing, Construction, mining, farming, fishing, and forestry. • 33. 4% – Transportation • Energy uses by cars, trucks, buses, trains, ships, and airplanes. • 27. 2%
Supply vs. Demand • Demand Sectors (where our energy goes) – Residential and Commercial • Energy used by homes, offices, schools, churches • 39. 4% – Industrial Sector • Produces goods and products we buy • Manufacturing, Construction, mining, farming, fishing, and forestry. • 33. 4% – Transportation • Energy uses by cars, trucks, buses, trains, ships, and airplanes. • 27. 2%
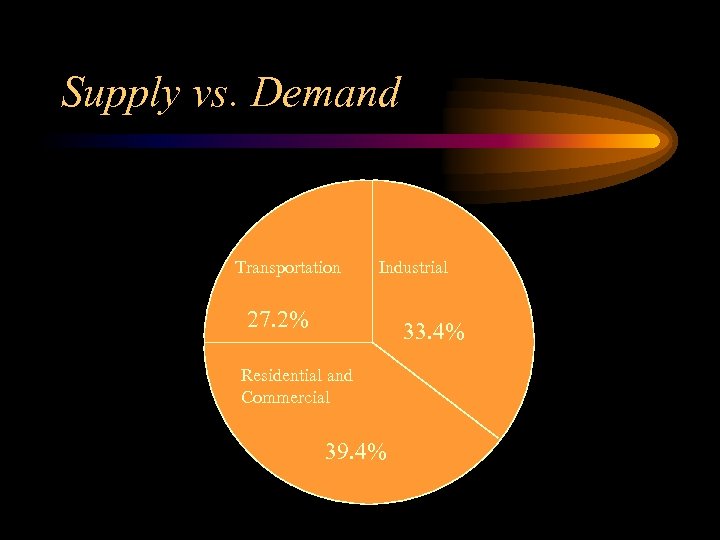 Supply vs. Demand Transportation Industrial 27. 2% 33. 4% Residential and Commercial 39. 4%
Supply vs. Demand Transportation Industrial 27. 2% 33. 4% Residential and Commercial 39. 4%
 4. Energy Flow • Chart show Input and Output – Input = energy resources – Output = demand by sector – Compare old and newer charts
4. Energy Flow • Chart show Input and Output – Input = energy resources – Output = demand by sector – Compare old and newer charts
 Energy Flow • Conclusions about Energy Flow • Compare old and new charts – If an oil shortage were to exist, the transportation sector would be most affected – When any energy resource is changed to electricity, the total efficiency is less – If a coal shortage were to exist all sectors would be affected except transportation – Society is using 51% of energy and wasting 49% – If N. G. ran short, the residential/commercial and industrial sectors would be affected
Energy Flow • Conclusions about Energy Flow • Compare old and new charts – If an oil shortage were to exist, the transportation sector would be most affected – When any energy resource is changed to electricity, the total efficiency is less – If a coal shortage were to exist all sectors would be affected except transportation – Society is using 51% of energy and wasting 49% – If N. G. ran short, the residential/commercial and industrial sectors would be affected
 Energy Picture • OIL 2055 – reserves depleted – If consumption stays the same • N. G. 2060 – depleted – no longer accurate • Coal 2250 – depleted – no longer accurate • Data collected in 1994 @ D. O. E website
Energy Picture • OIL 2055 – reserves depleted – If consumption stays the same • N. G. 2060 – depleted – no longer accurate • Coal 2250 – depleted – no longer accurate • Data collected in 1994 @ D. O. E website
 The Future through 2010 • • Energy use increases 30% Overall energy cost will increase 50% Oil production drops 28% Coal and N. G. will increase 16 & 18%
The Future through 2010 • • Energy use increases 30% Overall energy cost will increase 50% Oil production drops 28% Coal and N. G. will increase 16 & 18%
 End. . .
End. . .


