3ee4046b68c38cf91dd9b84595be08fc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Stanford Authority Manager Privilege management use case Integration CAMP Denver, June 27, 2005 Lynn Mc. Rae Stanford University lmcrae@stanford. edu
Stanford Authority Manager Privilege management use case Integration CAMP Denver, June 27, 2005 Lynn Mc. Rae Stanford University lmcrae@stanford. edu
 Stanford Authority Manager • Initial production, November 2001 • Created in conjunction with ERP migration from mainframe • Student Administration (People. Soft/SA) • Sept 2001 • Human Resources (People. Soft/HR) • Sept 2002 • Oracle Financials • Sept 2004 2
Stanford Authority Manager • Initial production, November 2001 • Created in conjunction with ERP migration from mainframe • Student Administration (People. Soft/SA) • Sept 2001 • Human Resources (People. Soft/HR) • Sept 2002 • Oracle Financials • Sept 2004 2
 Stanford Authority Goals • Simplify authority policy, management and interpretation. • Manage and summarize the privileges of an individual in one place. • Support consistent application of authority across systems via the infrastructure. • Provide automatic revocation of authority based on affiliation changes. • Evolve role-based authority -- managing privileges based on job function. 3
Stanford Authority Goals • Simplify authority policy, management and interpretation. • Manage and summarize the privileges of an individual in one place. • Support consistent application of authority across systems via the infrastructure. • Provide automatic revocation of authority based on affiliation changes. • Evolve role-based authority -- managing privileges based on job function. 3
 Stanford Authority Architecture • Central Authority Management • Common user interface. • based on business functions and language, not system-specific or in technical terms • Rich privileges -- e. g. , scope, direct qualifiers, indirect qualifiers • Supports a model of distributed Authority management. • Integrated with Organizational Registry • Records “chain of delegation” 4
Stanford Authority Architecture • Central Authority Management • Common user interface. • based on business functions and language, not system-specific or in technical terms • Rich privileges -- e. g. , scope, direct qualifiers, indirect qualifiers • Supports a model of distributed Authority management. • Integrated with Organizational Registry • Records “chain of delegation” 4
 Stanford Authority Architecture • Central Authority Management • A repository of authority assignments and resulting privilege information. • Does not replace the security systems in each local system. • Requires integration/synchronization of data between Authority system and local systems. • Features to facilitate mapping of user assignments to target systems. 5
Stanford Authority Architecture • Central Authority Management • A repository of authority assignments and resulting privilege information. • Does not replace the security systems in each local system. • Requires integration/synchronization of data between Authority system and local systems. • Features to facilitate mapping of user assignments to target systems. 5
 Authority Manager Assignments • 45, 000+ active assignments (70 k to date) • • • 32, 000+ financial 5, 500+ hr 3, 500+ student 4, 000+ Enterprise Reporting 58 Research Administration (conflict-of-interest) 4 Space Management (new) • 144 are “authority” assignments • For “granting proxy” within Authority Manager Statistics gathered week of June 20 -25, 2005 6
Authority Manager Assignments • 45, 000+ active assignments (70 k to date) • • • 32, 000+ financial 5, 500+ hr 3, 500+ student 4, 000+ Enterprise Reporting 58 Research Administration (conflict-of-interest) 4 Space Management (new) • 144 are “authority” assignments • For “granting proxy” within Authority Manager Statistics gathered week of June 20 -25, 2005 6
 Authority Manager Assignments • 381 current grantors (2. 6% of ~14, 000 faculty/staff) • 329 financial • 45 hr • 116 student • 5, 106 current grantees (36% of faculty/staff) • 2, 899 financial • 795 hr • 1, 183 student • 897 grantees (18%) can delegate to others 7
Authority Manager Assignments • 381 current grantors (2. 6% of ~14, 000 faculty/staff) • 329 financial • 45 hr • 116 student • 5, 106 current grantees (36% of faculty/staff) • 2, 899 financial • 795 hr • 1, 183 student • 897 grantees (18%) can delegate to others 7
 Prerequisites • Prerequisites control auto-activation • 2, 950 assignments are “pending” • Manage HR Records Training • Alcohol Approver • Sign Confidentiality Statement • Cost Policy Training • DPA • i. Budget Training • Labor Distribution Training • Labor Distribution Adjustments Training • GFS Policy and Entry Training • GFS Read Only Access Training • Student Records Dept Course Setup • Student Admin Basics Training • FERPA GLB, Student Financial Acct Training • Most: nightly feed from LMS (STARS Stanford Training and Registration System) • Some: direct workgroup maintenance 8
Prerequisites • Prerequisites control auto-activation • 2, 950 assignments are “pending” • Manage HR Records Training • Alcohol Approver • Sign Confidentiality Statement • Cost Policy Training • DPA • i. Budget Training • Labor Distribution Training • Labor Distribution Adjustments Training • GFS Policy and Entry Training • GFS Read Only Access Training • Student Records Dept Course Setup • Student Admin Basics Training • FERPA GLB, Student Financial Acct Training • Most: nightly feed from LMS (STARS Stanford Training and Registration System) • Some: direct workgroup maintenance 8
 Conditions • Conditions control auto-revocation • 462 assignments have expiration date • 1. 1% of 42, 000 active assignments • All others have “While at Stanford” • Based on “stanford administrative” -- faculty, staff (including casual/temps) and sponsored affiliates • Mostly great, but not precise enough -- need “while in department” 9
Conditions • Conditions control auto-revocation • 462 assignments have expiration date • 1. 1% of 42, 000 active assignments • All others have “While at Stanford” • Based on “stanford administrative” -- faculty, staff (including casual/temps) and sponsored affiliates • Mostly great, but not precise enough -- need “while in department” 9
 Security • Granting authority governed by two principles • You can only give what you have, or less • Permission use or to give to others is separate and explicit • Stanford Authority Manager is open to the “Stanford administrative” community • Any user can see all privileges for any other user 10
Security • Granting authority governed by two principles • You can only give what you have, or less • Permission use or to give to others is separate and explicit • Stanford Authority Manager is open to the “Stanford administrative” community • Any user can see all privileges for any other user 10
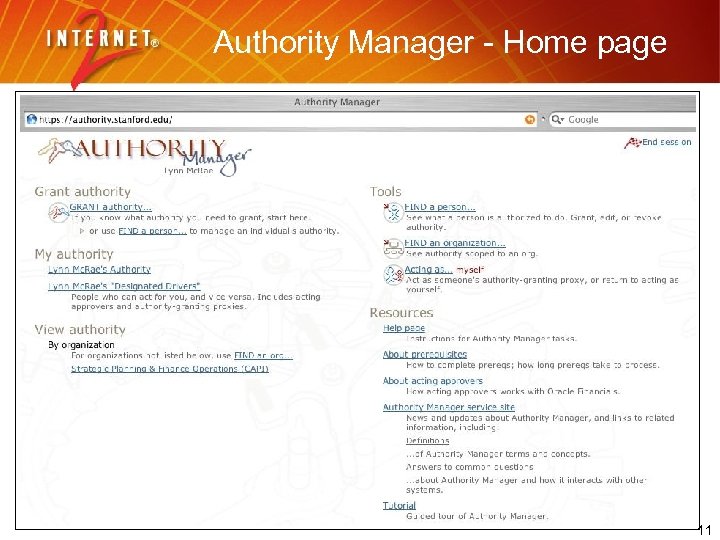 Authority Manager - Home page 11
Authority Manager - Home page 11
 Authority Manager - Home page 12
Authority Manager - Home page 12
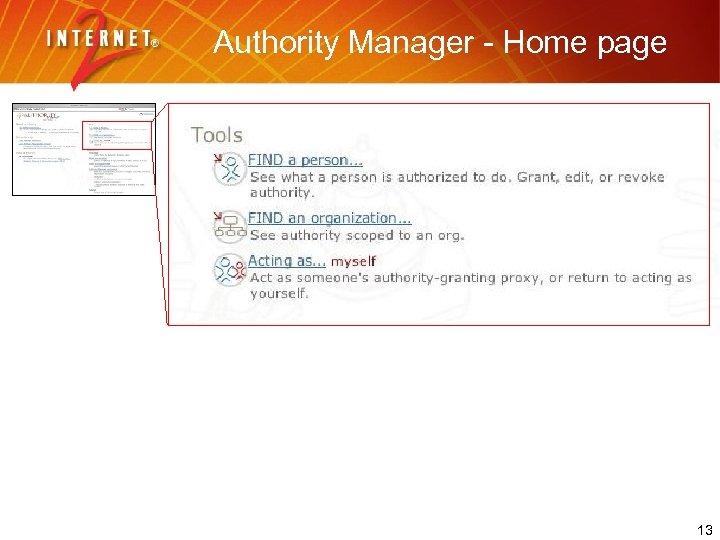 Authority Manager - Home page 13
Authority Manager - Home page 13
 Designated drivers • Granting proxy • Acting in Authority Manager for someone else who has Authority • Can “grant only”; does not actually have privileges • Cultural necessity • Acting approver • Assumes privileges temporarily 14
Designated drivers • Granting proxy • Acting in Authority Manager for someone else who has Authority • Can “grant only”; does not actually have privileges • Cultural necessity • Acting approver • Assumes privileges temporarily 14
 Authority Manager - Home page 15
Authority Manager - Home page 15
 Help and Training • Core system owned by Stanford IT (ITSS) • General use/availability/problem reports through central Help Desk • Tier 1 help, else direct user to central office or IT staff. • Web based training • IT developed module for basic system commands and concepts • Subsystem owners responsible for training module in their own realm • Online Tutorial available through the UI 16
Help and Training • Core system owned by Stanford IT (ITSS) • General use/availability/problem reports through central Help Desk • Tier 1 help, else direct user to central office or IT staff. • Web based training • IT developed module for basic system commands and concepts • Subsystem owners responsible for training module in their own realm • Online Tutorial available through the UI 16
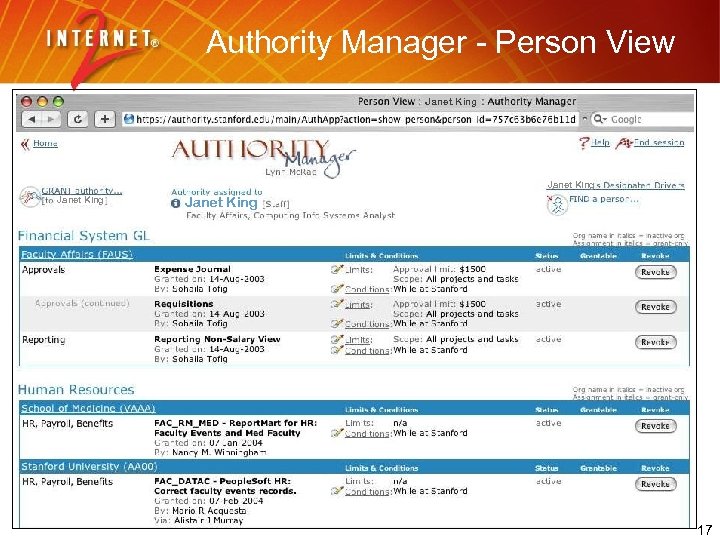 Authority Manager - Person View Janet King 17
Authority Manager - Person View Janet King 17
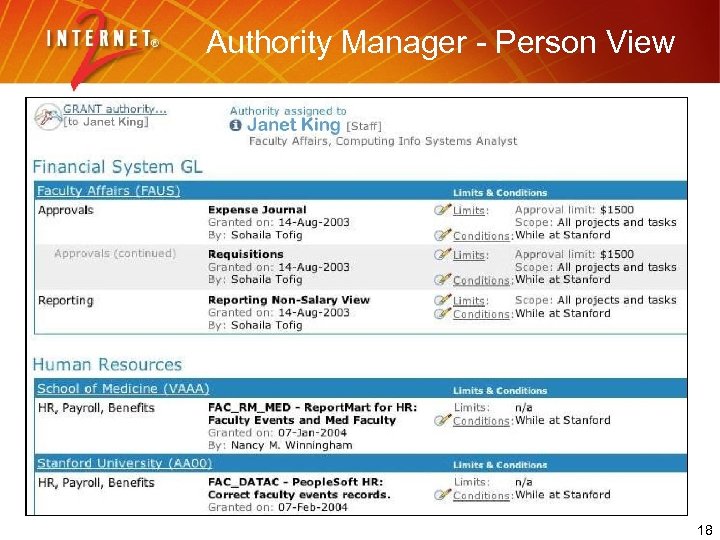 Authority Manager - Person View 18
Authority Manager - Person View 18
 Integration Challenges • People. Soft and Oracle do not have security No user serviceable parts APIs Warranty void if opened • Custom development to process “privileges” XML document into local system • Inadequate resource planning for the scope of integration work • Skill set issues • Has led to more centralized support for integration 19
Integration Challenges • People. Soft and Oracle do not have security No user serviceable parts APIs Warranty void if opened • Custom development to process “privileges” XML document into local system • Inadequate resource planning for the scope of integration work • Skill set issues • Has led to more centralized support for integration 19
 Integration Challenges • People. Soft still uses manual integration • Nightly email/printed report • Staff job to transfer data into People. Soft security panels • Being automated this summer • Audits • Required to establish trust in Authority Manager assertions • Non-trivial independent effort • Effort is ongoing 20
Integration Challenges • People. Soft still uses manual integration • Nightly email/printed report • Staff job to transfer data into People. Soft security panels • Being automated this summer • Audits • Required to establish trust in Authority Manager assertions • Non-trivial independent effort • Effort is ongoing 20
 Integration Challenges • Authority/business system functional gaps • Oracle Financials, more than 1 active approver • Oracle Financials, workflow referrals up • People. Soft: cross associations (false positives) • Bootstrap grantor issues • “real” authorization chain • schools vs central office model • bulk loading at initial conversion, no recorded chain of authorization 21
Integration Challenges • Authority/business system functional gaps • Oracle Financials, more than 1 active approver • Oracle Financials, workflow referrals up • People. Soft: cross associations (false positives) • Bootstrap grantor issues • “real” authorization chain • schools vs central office model • bulk loading at initial conversion, no recorded chain of authorization 21
 Reporting • Online views • Good for person details • Weak for organization level details • Lack of independent reporting • Priority for new development • Controls for reporting down a hierarchy • Upcoming work to integrate with Report. Mart 22
Reporting • Online views • Good for person details • Weak for organization level details • Lack of independent reporting • Priority for new development • Controls for reporting down a hierarchy • Upcoming work to integrate with Report. Mart 22
 UI Challenges • Style of business language • Nouns/verbs, roles/action, non-system-specific • Perceived complexity of wizard interactions for repetitive tasks • Ameliorated by some wrap-around controls • Performance/scalability problems in Web app, esp. for users with a lot of authority 23
UI Challenges • Style of business language • Nouns/verbs, roles/action, non-system-specific • Perceived complexity of wizard interactions for repetitive tasks • Ameliorated by some wrap-around controls • Performance/scalability problems in Web app, esp. for users with a lot of authority 23
 Functional needs • • • Granting to Groups or Roles Transfer of authority from old to new person Revoke all Bulk grantor updates Lack of administrative interface • Supported centrally by IT staff • Changes in metadata complex and confusing • Option to limit granting to only one level 24
Functional needs • • • Granting to Groups or Roles Transfer of authority from old to new person Revoke all Bulk grantor updates Lack of administrative interface • Supported centrally by IT staff • Changes in metadata complex and confusing • Option to limit granting to only one level 24
 Successes • Distributed delegation model • Auto-activation and revocation • Near realtime integration • Stanford events service • Consistency of UI across domains • Re-use across systems (report mart) • Stanford model adopted for I 2/NMI Signet Privilege Management software 25
Successes • Distributed delegation model • Auto-activation and revocation • Near realtime integration • Stanford events service • Consistency of UI across domains • Re-use across systems (report mart) • Stanford model adopted for I 2/NMI Signet Privilege Management software 25
 Fini Questions… Contact: Lynn Mc. Rae, lmcrae@stanford. edu 26
Fini Questions… Contact: Lynn Mc. Rae, lmcrae@stanford. edu 26


