511fb9fac89e44f90a3cc22fc547de6a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24

Standards Reorganization

Standards Reorganization Task Force Members: Staff Advisors: • Ainslie Kraeck, Co-Chair • Leanne Woodward, Co -chair • Sharon Butler, DVM • Catherine Mc. Kinnon • Elizabeth Long • Roberta Hirshon • Kristen Sanders • Carrie Garnett • Jeff Kelling • Jama Rice

Standards Reorganization • What – – Moving current standards into new sections Clarifying intent and interpretations Combining like standards No intent change • Why – Professionalism – PAC facilitation – Inclusion of providers • How – New model – not just rearrangement
Current Standards Organization • Core – Admin - 20 – Program -32 – Facilities - 27 • Specialty – – Hippotherapy - 13 Interactive vaulting – 11 Driving - 22 EFP - 8 • Non-profit, therapeutic riding center driven • Isolated development

Current Standard Challenges Core • Admin – non-profit, U. S. centric – Plans, policies and procedures scattered throughout Programs and Facility standards • Program - therapeutic riding centric – Exclusionary to growing EFP/L community • Facility and equine welfare intertwined – Fosters perception of equines as tools

Current Standard Issues Specialty • Repetitive – Same requirements (credentialing, training, conditioning) in specialties • Limited to present concepts – Requires constant update to include new specialized activities • Constantly expanding – EFL coming; new medical models • Downplays professionalism of therapeutic riding, not “specialized” – No session/lesson safety standards for therapeutic riding (driving standards set the example)

What we tried – and abandoned • Task force attempted original reorganization into – Core § Business/admin § Facilities § Equine Welfare/management – Activities § § § Therapeutic Riding Driving Interactive Vaulting (IV) Hippotherapy Equine-facilitated Psychotherapy • We couldn’t do it.

What we tried – and abandoned Problems: • Redundancy in activities – For example mounted hippotherapy and therapeutic riding have similar equipment and safety requirements – All activities have ground components • Policies for activities were in different places – Written helmet standards for interactive vaulting but not for others • No specific therapeutic riding standards – all defined mounted

Why a new model? • We abandoned our attempt and began to explore new models. • When the major categories of SERVICES and ACTIVITIES were identified the individual standards began to fall in to place.

Service Delivery Model • Why do we use equine-assisted activities? • To provide a service – Practicing as a medical professional § Currently, PT, OT and SLP but open to rehab, pediatrics as well as new services. § This model easily accommodates new growth areas in the industry. – Practicing as a mental health professional – Practicing as an educational professional § IEP and/or self growth open to other – spiritual, social, etc. – Providing a therapeutic horsemanship activity § Recreation, sport, competition, etc.

Activities Offered • What activities can we use to deliver EAAT? – – Mounted Driving Interactive vaulting Groundwork

NEW Model

Service Delivery Model • Our common approach in delivering services to clients – – We are businesses We are credentialed professionals We require additional training/proficiencies We select appropriate equine activities from the spectrum – We use a team approach – We respect the equine – We value safety and ethics

Service Delivery Model • Separate delivery of service from activity. – There are only 4 things we do as an activity § § We are on the horse We are off the horse We are on and off the horse We are attached to the horse from behind – All other differentiation is in the goal of the activity

Service Delivery Model • Medical Objective Model – practiced by a licensed and credentialed medical professional – to facilitate a medical treatment goal • Mental Health Objective Model – practiced by a licensed and credentialed mental health professional – to facilitate a mental health treatment goal

Service Delivery Model • Educational Objective Model – practiced by a licensed and credentialed educational professional – to facilitate educational goals • Equestrian Skills Objective Model – provided by a professional credentialed instructor – to facilitate achievement of equestrian skills goals

Activity Types • Mounted – Includes tandem-mounted • Vaulting • Driving • Groundwork – Includes groundwork for all other activities such as grooming, lungeing, long-lining
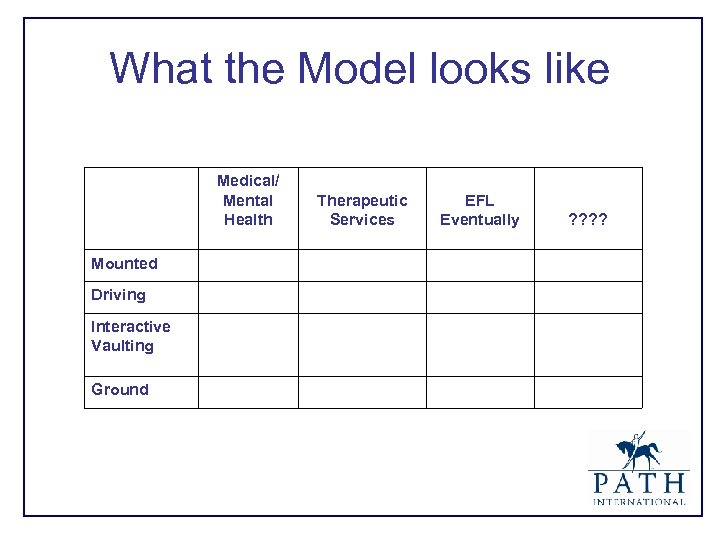
What the Model looks like Medical/ Mental Health Therapeutic Services EFL Eventually ? ? Mounted Driving Interactive Vaulting Ground

New System of Standards Organization • Five sections – Administration and Business Section (old admin) – Facilities Section (old facilities) – Equine Welfare and Management Section (old facilities/program) – Activities Section (old specialty) – Services Section (old specialty)

New System of Standards (continued) • Administration and Business Standards – Plans, policies and procedures – Human resources – Training • Facility Standards – Grounds/Buildings – Equipment storage and maintenance – Activity area • Equine Welfare and Management Standards – – Safety Care Equipment fit and assignment Selection/training/lifecycle

New System of Standards (continued) • Activity Standards – Safety of participant – Activity equipment (safety/selection) – Equine training • Service Standards – Credentialing and certifications – Professional responsibility – Paperwork requirements specific to service

Assumptions • • Baseline certification criteria will include competencies in all ground activities that support other (mounted, driving, interactive vaulting) activities All standards will be reviewed – – – • • Task force has defined policies, procedure and practice Technology update International applicability Reference to PATH Intl. certifications will be stated as “appropriately PATH Intl. Credentialed Professional” Duplicate standards will ultimately be combined resulting in effective organization and reduced redundancy

Benefits • Responds to membership requests for manual organization to facilitate the premier accredited center process success • Positions the association to retain the leadership role in providing EAAT industry best practices • Ultimately increases the professionalism of our Industry

Timeline • August – October 2011 – Review on-site work – Write new standards for repetitive standards • October 2011 – Programs & Standards Oversight Committee comfortable with direction and reorganization • November 2011 – Membership conceptual update • March 2012 – Manual ready for staff to print
511fb9fac89e44f90a3cc22fc547de6a.ppt