1f54f5f63fd3163a0167d52b9d2e36e8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20

 Standards & Open Systems Session # 50 Presented by: Russell Judd Chief Industry and Government Relations Officer Great Lakes Educational Loan Services Michael Sessa Executive Director Postsecondary Electronic Standards Council (PESC) 2
Standards & Open Systems Session # 50 Presented by: Russell Judd Chief Industry and Government Relations Officer Great Lakes Educational Loan Services Michael Sessa Executive Director Postsecondary Electronic Standards Council (PESC) 2
 Agenda n n n n “Standard” Defined Benefits of Standards Open Standards Players & Stakeholders Hierarchy History in Financial Aid Relevance – Today and Tomorrow Getting Involved 3
Agenda n n n n “Standard” Defined Benefits of Standards Open Standards Players & Stakeholders Hierarchy History in Financial Aid Relevance – Today and Tomorrow Getting Involved 3
 “Standard” Defined n Specific guidelines for data exchange that can include: – Transport/transmission of data – Data itself (format, element names, definitions, transactions, etc) – Security (protocols to protect data) – Authentication (identity recognition and verification) 4
“Standard” Defined n Specific guidelines for data exchange that can include: – Transport/transmission of data – Data itself (format, element names, definitions, transactions, etc) – Security (protocols to protect data) – Authentication (identity recognition and verification) 4
 “Standard” Defined n Agreed upon guidelines set: – By government regulation or legislation n Formally through cooperation, study, and approval by designated accredited standards -setting bodies: – National and/or international – Industry agreement and collaboration 5
“Standard” Defined n Agreed upon guidelines set: – By government regulation or legislation n Formally through cooperation, study, and approval by designated accredited standards -setting bodies: – National and/or international – Industry agreement and collaboration 5
 “Standard” Defined n Data standards must be supported by business standards, agreement on common policy and process – Common policy (Common Manual) – Common terminology and definitions – Common business purpose and transactions (Common. Line) 6
“Standard” Defined n Data standards must be supported by business standards, agreement on common policy and process – Common policy (Common Manual) – Common terminology and definitions – Common business purpose and transactions (Common. Line) 6
 “Standard” Defined n Proprietary methods: – Are often misrepresented as standards – Become a duplicate of existing or new standard – Are often created intentionally to “capture” or “lock-in” customers or partners – Are often controlled by small but influential groups without open or public participation – Raise costs for everyone – Become impediments for industry progression road blocking ability to move forward with new features and technologies 7
“Standard” Defined n Proprietary methods: – Are often misrepresented as standards – Become a duplicate of existing or new standard – Are often created intentionally to “capture” or “lock-in” customers or partners – Are often controlled by small but influential groups without open or public participation – Raise costs for everyone – Become impediments for industry progression road blocking ability to move forward with new features and technologies 7
 Benefits of Standards n n Streamline processes – eliminate unnecessary complexities Improve service to customers by expanding functionality and reducing costs Decreases delivery time of new services to customers Future services can be added to a standard framework 8
Benefits of Standards n n Streamline processes – eliminate unnecessary complexities Improve service to customers by expanding functionality and reducing costs Decreases delivery time of new services to customers Future services can be added to a standard framework 8
 Benefits of Standards n n n Reduces or eliminates the cost of maintaining multiple methods “Level the playing field” and promote competition based on service, not on process or technology Ability to plug-n-play and interoperate – Partners can integrate, communicate, and exchange information easier which enables value -added services – Simpler interconnectivity between partners allows new business alliances 9
Benefits of Standards n n n Reduces or eliminates the cost of maintaining multiple methods “Level the playing field” and promote competition based on service, not on process or technology Ability to plug-n-play and interoperate – Partners can integrate, communicate, and exchange information easier which enables value -added services – Simpler interconnectivity between partners allows new business alliances 9
 Open Standards n n n Ensure input from all interested parties Are developed by an objective body who is NOT itself a stakeholder (the standards body doesn’t benefit directly from the services which use the standard) Are available and accessible for public comment 10
Open Standards n n n Ensure input from all interested parties Are developed by an objective body who is NOT itself a stakeholder (the standards body doesn’t benefit directly from the services which use the standard) Are available and accessible for public comment 10
 Open Standards n n n Allows interoperability between implementers Precludes a participation cost or fee to use Do not require participants to use proprietary software/hardware 11
Open Standards n n n Allows interoperability between implementers Precludes a participation cost or fee to use Do not require participants to use proprietary software/hardware 11
 Players & Stakeholders n Technical, industry-independent groups – OASIS, W 3 C, X 12 n n Government groups - FSA Higher Education – Postsecondary Electronic Standards Council (PESC) – AACRAO’s Postsecondary Education Electronic Data Exchange (SPEEDE) Committee for EDI Academic Transcripts and Test Scores – NCHELP’s Electronic Standards Committee (ESC) for Common. Line 12
Players & Stakeholders n Technical, industry-independent groups – OASIS, W 3 C, X 12 n n Government groups - FSA Higher Education – Postsecondary Electronic Standards Council (PESC) – AACRAO’s Postsecondary Education Electronic Data Exchange (SPEEDE) Committee for EDI Academic Transcripts and Test Scores – NCHELP’s Electronic Standards Committee (ESC) for Common. Line 12
 Hierarchy Standards are built upon standards Stakeholder Implementations (Common. Line, COD, Meteor, NSLDS II) Financial Aid Industry Technical and Business Standards Data definitions, XML Standards Web Services and Technical Standards (XML, Authentication, Data Transport, Data encryption, Interoperability protocols) 13
Hierarchy Standards are built upon standards Stakeholder Implementations (Common. Line, COD, Meteor, NSLDS II) Financial Aid Industry Technical and Business Standards Data definitions, XML Standards Web Services and Technical Standards (XML, Authentication, Data Transport, Data encryption, Interoperability protocols) 13
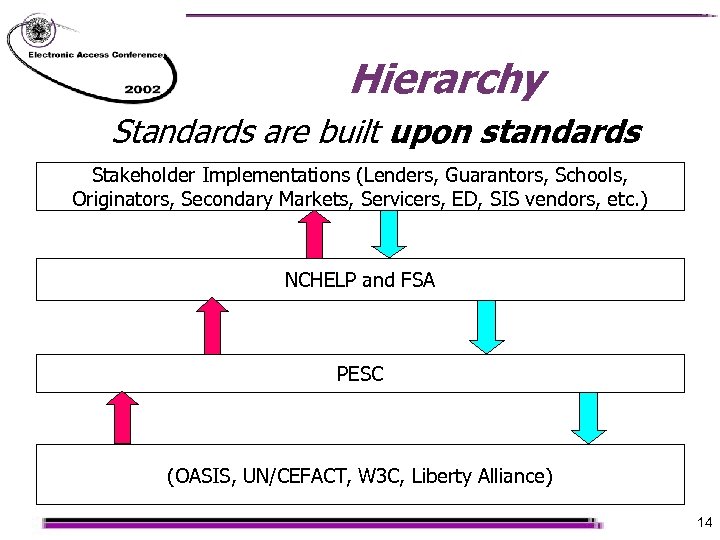 Hierarchy Standards are built upon standards Stakeholder Implementations (Lenders, Guarantors, Schools, Originators, Secondary Markets, Servicers, ED, SIS vendors, etc. ) NCHELP and FSA PESC (OASIS, UN/CEFACT, W 3 C, Liberty Alliance) 14
Hierarchy Standards are built upon standards Stakeholder Implementations (Lenders, Guarantors, Schools, Originators, Secondary Markets, Servicers, ED, SIS vendors, etc. ) NCHELP and FSA PESC (OASIS, UN/CEFACT, W 3 C, Liberty Alliance) 14
 History in Financial Aid n n n n Common. Line Common Account Maintenance (CAM) NSLDS E-Sign Common Record Common. Line/Common Record Convergence PESC Core Data Dictionary and Web Services 15
History in Financial Aid n n n n Common. Line Common Account Maintenance (CAM) NSLDS E-Sign Common Record Common. Line/Common Record Convergence PESC Core Data Dictionary and Web Services 15
 Relevance – Today and Tomorrow n n n Real-time services – another evolutionary step Standards are the necessary linchpin to make new technology happen FSA is committed and active in standardssetting and development (PESC, Common. Line/Common Record convergence, Web Services) 16
Relevance – Today and Tomorrow n n n Real-time services – another evolutionary step Standards are the necessary linchpin to make new technology happen FSA is committed and active in standardssetting and development (PESC, Common. Line/Common Record convergence, Web Services) 16
 Relevance – Today and Tomorrow n n n Meteor – developing communication, authentication, and data definitions built on work of public and industry standards-setting bodies (PESC, OASIS, JA-SIG, Internet 2) Common. Line/Common Record convergence XML-based data transmission Web Services Decreasing and limited role for proprietary processes and layouts 17
Relevance – Today and Tomorrow n n n Meteor – developing communication, authentication, and data definitions built on work of public and industry standards-setting bodies (PESC, OASIS, JA-SIG, Internet 2) Common. Line/Common Record convergence XML-based data transmission Web Services Decreasing and limited role for proprietary processes and layouts 17
 Getting Involved n n n Participate in the standards process – your participation provides a voice and influence for you institution and service providers Practice and promote the standards – this will maximize time and monetary investment Pre-empt efforts to develop proprietary methods 18
Getting Involved n n n Participate in the standards process – your participation provides a voice and influence for you institution and service providers Practice and promote the standards – this will maximize time and monetary investment Pre-empt efforts to develop proprietary methods 18
 Getting Involved! n PESC – Join PESC and the XML Forum – membership info available at www. Standards. Council. org n NCHELP – Visit www. NCHELP. org – Join the ESC – Join the School Advisory Group 19
Getting Involved! n PESC – Join PESC and the XML Forum – membership info available at www. Standards. Council. org n NCHELP – Visit www. NCHELP. org – Join the ESC – Join the School Advisory Group 19
 Contact Information n Russell Judd – 608 -246 -1500 – rjudd@glhec. org n Michael Sessa – 202 -293 -7383 – sessa@standardscouncil. org 20
Contact Information n Russell Judd – 608 -246 -1500 – rjudd@glhec. org n Michael Sessa – 202 -293 -7383 – sessa@standardscouncil. org 20


