 Standards for CSR SA 8000 p AA 1000 p GRI p ISO 9000 p ISO 26000 p Sarbanes-Oxley p UN Global Compact p
Standards for CSR SA 8000 p AA 1000 p GRI p ISO 9000 p ISO 26000 p Sarbanes-Oxley p UN Global Compact p
 United Nations Initiatives p UN Global Compact p UN Principles for Responsible Investment p UNEP Equator Principles p ILO Tripartite Declaration of Principles concerning Multinational Enterprises and Social Policy (MNE Declaration) p UNHCHR Business and Human Rights p UNODC Anti-corruption p UNCTAD Corporate Responsibility Reporting, World Investment Report
United Nations Initiatives p UN Global Compact p UN Principles for Responsible Investment p UNEP Equator Principles p ILO Tripartite Declaration of Principles concerning Multinational Enterprises and Social Policy (MNE Declaration) p UNHCHR Business and Human Rights p UNODC Anti-corruption p UNCTAD Corporate Responsibility Reporting, World Investment Report
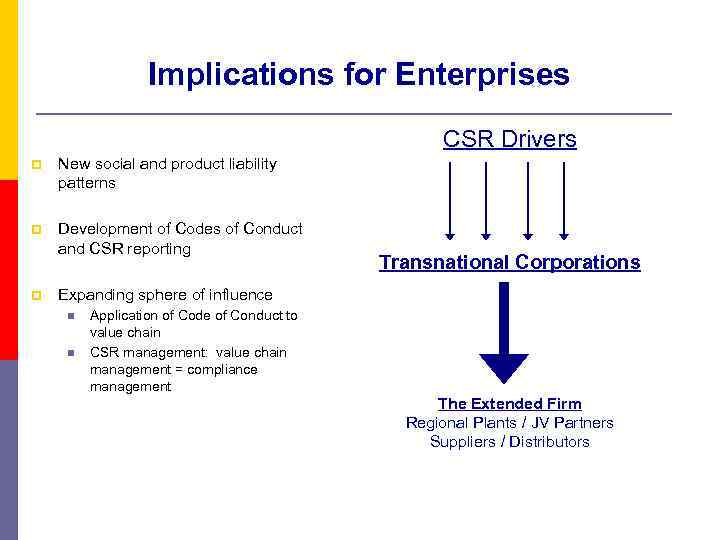 Implications for Enterprises CSR Drivers p New social and product liability patterns p Development of Codes of Conduct and CSR reporting p Transnational Corporations Expanding sphere of influence n n Application of Code of Conduct to value chain CSR management: value chain management = compliance management The Extended Firm Regional Plants / JV Partners Suppliers / Distributors
Implications for Enterprises CSR Drivers p New social and product liability patterns p Development of Codes of Conduct and CSR reporting p Transnational Corporations Expanding sphere of influence n n Application of Code of Conduct to value chain CSR management: value chain management = compliance management The Extended Firm Regional Plants / JV Partners Suppliers / Distributors
 Implications for Enterprises: CSR Management How do companies address socio-environmental & legal compliance issues? • Policies - Code of Conduct • Systems - Compliance Management • Reporting - Accounting and Reporting
Implications for Enterprises: CSR Management How do companies address socio-environmental & legal compliance issues? • Policies - Code of Conduct • Systems - Compliance Management • Reporting - Accounting and Reporting
 CSR Management: Systems approach Sustainable business development does not come about of its own accord. Rather, commitment to sustainability demands that corporate processes be reliably controlled and that everyone's actions in finance as much as in environmental and social areas - be coordinated. Prerequisites for this are binding guidelines, unambiguous corporate goals and a clear organizational structure. - Deutsche Telekom
CSR Management: Systems approach Sustainable business development does not come about of its own accord. Rather, commitment to sustainability demands that corporate processes be reliably controlled and that everyone's actions in finance as much as in environmental and social areas - be coordinated. Prerequisites for this are binding guidelines, unambiguous corporate goals and a clear organizational structure. - Deutsche Telekom
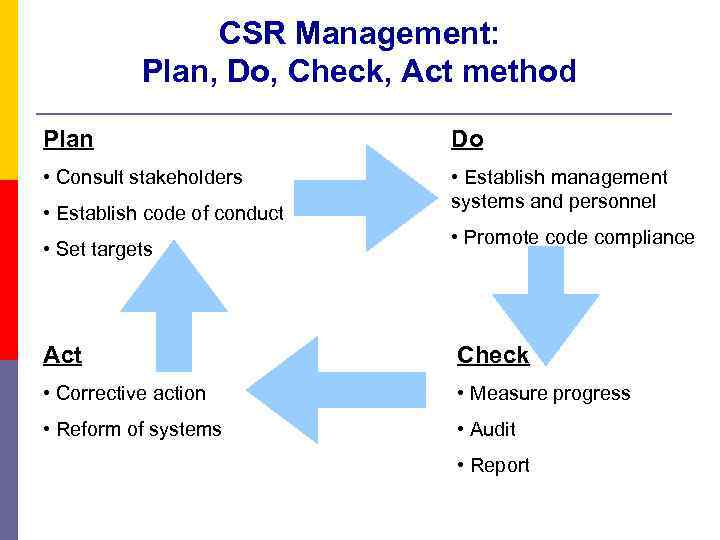 CSR Management: Plan, Do, Check, Act method Plan Do • Consult stakeholders • Establish management systems and personnel • Establish code of conduct • Set targets • Promote code compliance Act Check • Corrective action • Measure progress • Reform of systems • Audit • Report
CSR Management: Plan, Do, Check, Act method Plan Do • Consult stakeholders • Establish management systems and personnel • Establish code of conduct • Set targets • Promote code compliance Act Check • Corrective action • Measure progress • Reform of systems • Audit • Report
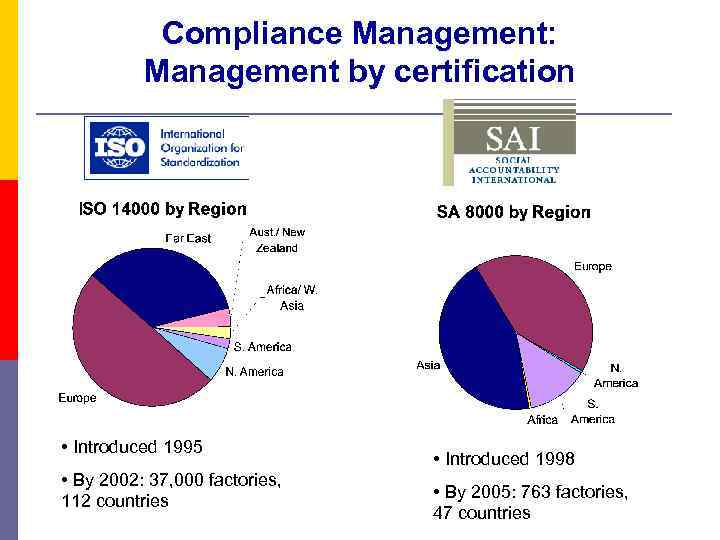 Compliance Management: Management by certification • Introduced 1995 • By 2002: 37, 000 factories, 112 countries • Introduced 1998 • By 2005: 763 factories, 47 countries
Compliance Management: Management by certification • Introduced 1995 • By 2002: 37, 000 factories, 112 countries • Introduced 1998 • By 2005: 763 factories, 47 countries
 Compliance Management: Management by certification ISO 26000: Social Responsibility • To be Introduced in 2009 or 2010 • NOT a Management System (? ) • NOT a Certifiable Standard (? )
Compliance Management: Management by certification ISO 26000: Social Responsibility • To be Introduced in 2009 or 2010 • NOT a Management System (? ) • NOT a Certifiable Standard (? )
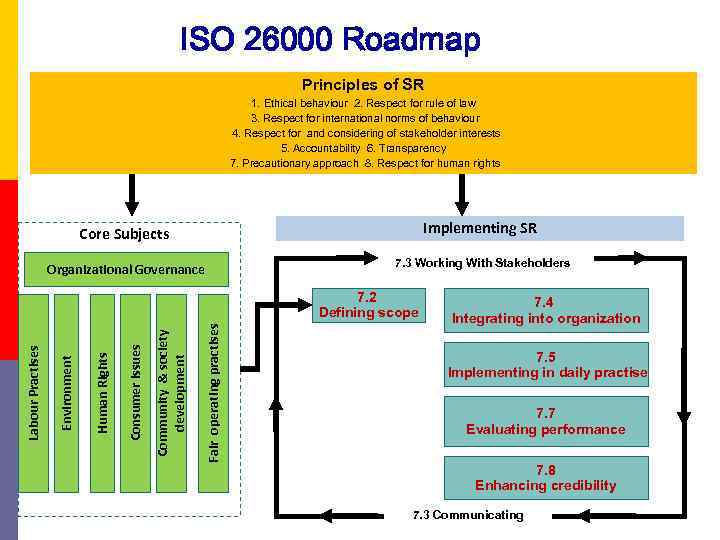 ISO 26000 Roadmap Principles of SR 1. Ethical behaviour 2. Respect for rule of law 3. Respect for international norms of behaviour 4. Respect for and considering of stakeholder interests 5. Accountability 6. Transparency 7. Precautionary approach 8. Respect for human rights Core Subjects Implementing SR Organizational Governance 7. 3 Working With Stakeholders Fair operating practises Community & society development Consumer issues Human Rights Environment Labour Practises 7. 2 Defining scope 7. 4 Integrating into organization 7. 5 Implementing in daily practise 7. 7 Evaluating performance 7. 8 Enhancing credibility 7. 3 Communicating
ISO 26000 Roadmap Principles of SR 1. Ethical behaviour 2. Respect for rule of law 3. Respect for international norms of behaviour 4. Respect for and considering of stakeholder interests 5. Accountability 6. Transparency 7. Precautionary approach 8. Respect for human rights Core Subjects Implementing SR Organizational Governance 7. 3 Working With Stakeholders Fair operating practises Community & society development Consumer issues Human Rights Environment Labour Practises 7. 2 Defining scope 7. 4 Integrating into organization 7. 5 Implementing in daily practise 7. 7 Evaluating performance 7. 8 Enhancing credibility 7. 3 Communicating
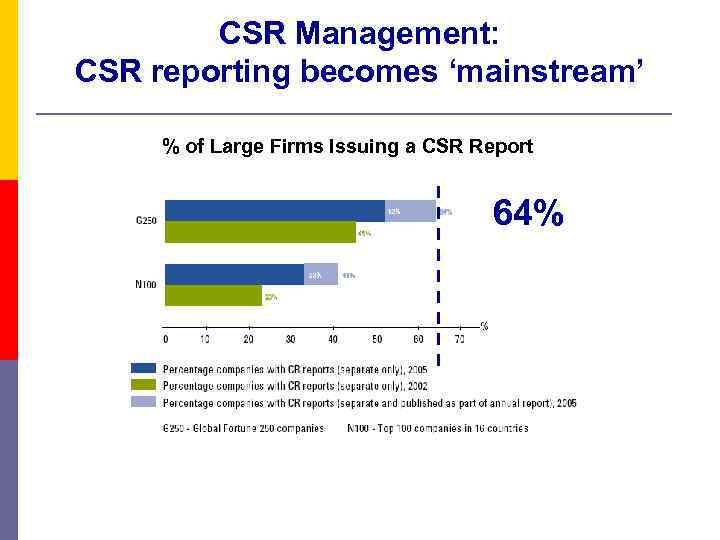 CSR Management: CSR reporting becomes ‘mainstream’ % of Large Firms Issuing a CSR Report 64%
CSR Management: CSR reporting becomes ‘mainstream’ % of Large Firms Issuing a CSR Report 64%
 CSR Management: Emerging standards in CSR Reporting Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) A multi-stakeholder initiative www. globalreporting. org International Standards of Accounting and Reporting (ISAR) A project of UNCTAD www. unctad. org/isar
CSR Management: Emerging standards in CSR Reporting Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) A multi-stakeholder initiative www. globalreporting. org International Standards of Accounting and Reporting (ISAR) A project of UNCTAD www. unctad. org/isar
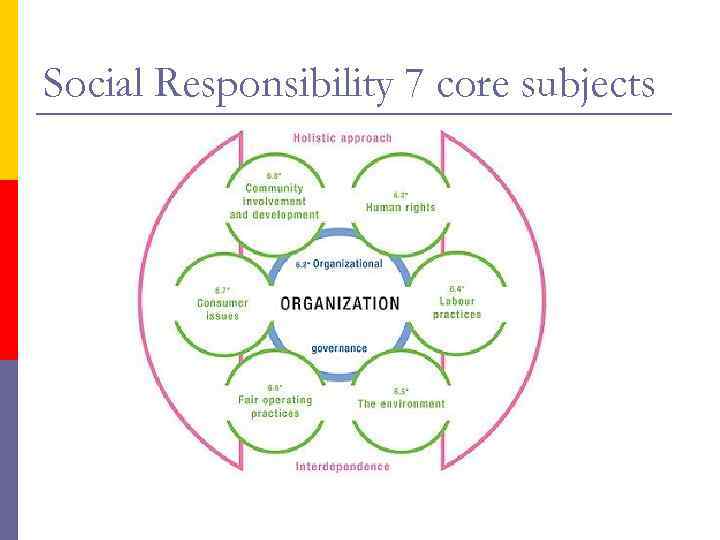 Social Responsibility 7 core subjects
Social Responsibility 7 core subjects
 Evolution of Social Reporting p „triple bottom line”
Evolution of Social Reporting p „triple bottom line”
 3. Stakeholders & the social contract What is a stakeholder? Multiple stakeholding. The classification of stakeholders p Stakeholder Theory p Regulation and its implications p Risk Reducing p
3. Stakeholders & the social contract What is a stakeholder? Multiple stakeholding. The classification of stakeholders p Stakeholder Theory p Regulation and its implications p Risk Reducing p
 What is a stakeholder? Those groups without whose support the organization would cease to exist p Any group or individual who can affect or is affected by the achievement of the organization's objectives p
What is a stakeholder? Those groups without whose support the organization would cease to exist p Any group or individual who can affect or is affected by the achievement of the organization's objectives p
 The most common groups who we consider to be stakeholders include: p Managers p Employees p Customers p Investors p Shareholders p Suppliers p
The most common groups who we consider to be stakeholders include: p Managers p Employees p Customers p Investors p Shareholders p Suppliers p
 Then there are some more generic groups who are often included: p Government p Society at large p The local community p
Then there are some more generic groups who are often included: p Government p Society at large p The local community p
 The classification of stakeholders p p Internal v external Internal stakeholders are those included within the organisation such as employees or managers whereas external stakeholders are such groups as suppliers or customers who are not generally considered to be a part of the organisation. Voluntary v Involuntary Voluntary stakeholders can choose whether or not to be a stakeholder to an organisation whereas involuntary stakeholders cannot.
The classification of stakeholders p p Internal v external Internal stakeholders are those included within the organisation such as employees or managers whereas external stakeholders are such groups as suppliers or customers who are not generally considered to be a part of the organisation. Voluntary v Involuntary Voluntary stakeholders can choose whether or not to be a stakeholder to an organisation whereas involuntary stakeholders cannot.
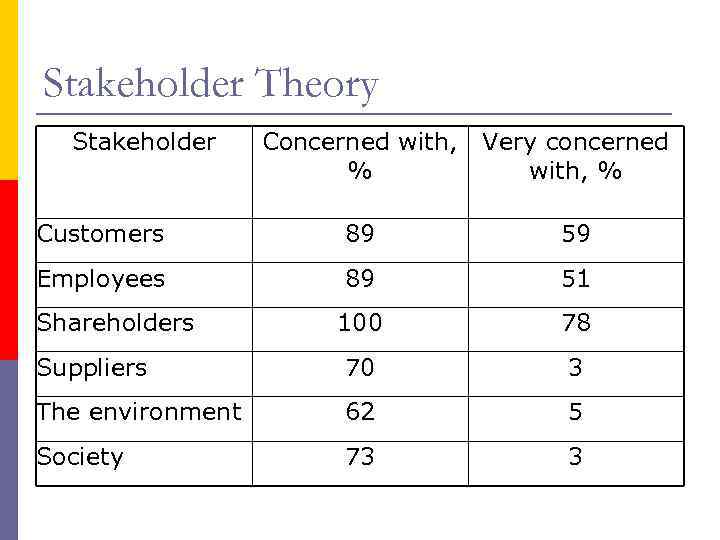 Stakeholder Theory Stakeholder Concerned with, % Very concerned with, % Customers 89 59 Employees 89 51 100 78 Suppliers 70 3 The environment 62 5 Society 73 3 Shareholders
Stakeholder Theory Stakeholder Concerned with, % Very concerned with, % Customers 89 59 Employees 89 51 100 78 Suppliers 70 3 The environment 62 5 Society 73 3 Shareholders
 Setting priorities criteria - 1 p p the significance of the effect of the firm in the view of the stakeholder (e. g. , layoffs at the only plant in town will be very significant to workers, their families and other residents); the importance of the stakeholder group to operations (e. g. , customers and key suppliers); the risk of gathering incomplete information by excluding a group (e. g. , when a foreign subsidiary’s only contacts are with government officials, it will be difficult to learn the concerns of local workers or residents); the opportunity to access new ideas (e. g. , engaging a group that is likely to challenge current practices may provide fresh insight into a difficult problem—but the firm had better be prepared to actually change its approach);
Setting priorities criteria - 1 p p the significance of the effect of the firm in the view of the stakeholder (e. g. , layoffs at the only plant in town will be very significant to workers, their families and other residents); the importance of the stakeholder group to operations (e. g. , customers and key suppliers); the risk of gathering incomplete information by excluding a group (e. g. , when a foreign subsidiary’s only contacts are with government officials, it will be difficult to learn the concerns of local workers or residents); the opportunity to access new ideas (e. g. , engaging a group that is likely to challenge current practices may provide fresh insight into a difficult problem—but the firm had better be prepared to actually change its approach);
 Setting priorities criteria - 2 p p p the requirements of regulators or permit-issuing bodies (e. g. , to get an operating licence in certain countries, a firm may be required to engage indigenous peoples); some operations (e. g. , emissions to land or water) may have extra-territorial impacts or implications that give legal or other grounds for special-issue groups to intervene; and the opportunity to share costs in addressing a specific challenge (e. g. , by partnering with another firm or NGO working on the issue).
Setting priorities criteria - 2 p p p the requirements of regulators or permit-issuing bodies (e. g. , to get an operating licence in certain countries, a firm may be required to engage indigenous peoples); some operations (e. g. , emissions to land or water) may have extra-territorial impacts or implications that give legal or other grounds for special-issue groups to intervene; and the opportunity to share costs in addressing a specific challenge (e. g. , by partnering with another firm or NGO working on the issue).
 Risk Reducing
Risk Reducing
 Benchmarking and assessing sustainability performance with respect to laws, norms, codes, performance standards, and voluntary initiatives; p Demonstrating how the organization influences and is influenced by expectations about sustainable development; and p Comparing performance within an organization and between different organizations over time. p
Benchmarking and assessing sustainability performance with respect to laws, norms, codes, performance standards, and voluntary initiatives; p Demonstrating how the organization influences and is influenced by expectations about sustainable development; and p Comparing performance within an organization and between different organizations over time. p

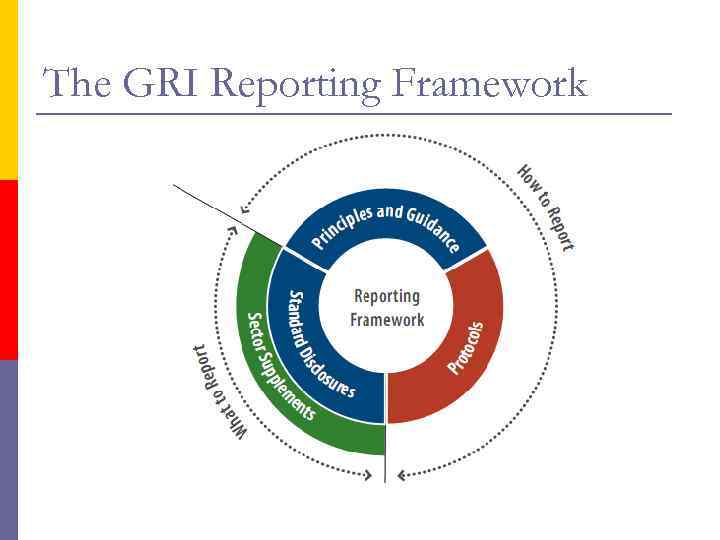 The GRI Reporting Framework
The GRI Reporting Framework