1538e960bb8cab4f80defd833dc34f70.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 STANDARD(S): 11. 1 Students analyze the significant events in the founding of the nation. LESSON OBJECTIVES/ GOALS/ SWBAT • 1. Describe the impact of new markets, entrepreneurs, and inventions on the 19 thcentury American economy. • 2. Explain the ways in which workplaces changed during the market revolution. • 3. Summarize the efforts of workers to improve their economic security.
STANDARD(S): 11. 1 Students analyze the significant events in the founding of the nation. LESSON OBJECTIVES/ GOALS/ SWBAT • 1. Describe the impact of new markets, entrepreneurs, and inventions on the 19 thcentury American economy. • 2. Explain the ways in which workplaces changed during the market revolution. • 3. Summarize the efforts of workers to improve their economic security.

 Section 4 The Market Revolution Inventions and economic developments in the early 19 th century helps transform American society. NEXT
Section 4 The Market Revolution Inventions and economic developments in the early 19 th century helps transform American society. NEXT
 SECTION 4 The Market Revolution U. S. Markets Expand • Market revolution—people buy and sell goods rather than make them • In 1840 s economy grows more than in previous 40 years • Free enterprise—private businesses free to operate for profit • Entrepreneurs invest own money in new industries Continued. . . NEXT
SECTION 4 The Market Revolution U. S. Markets Expand • Market revolution—people buy and sell goods rather than make them • In 1840 s economy grows more than in previous 40 years • Free enterprise—private businesses free to operate for profit • Entrepreneurs invest own money in new industries Continued. . . NEXT
 SECTION 4: THE MARKET REVOLUTION Known as the Market Revolution, people increasingly bought and sold goods rather than make them for themselves A 19 th century market
SECTION 4: THE MARKET REVOLUTION Known as the Market Revolution, people increasingly bought and sold goods rather than make them for themselves A 19 th century market
 U. S. Markets Expand • The first half of the 19 th century in America, brought vast changes to technology, transportation, and production • Inventions and economic developments in the early 19 th century helps transform American society.
U. S. Markets Expand • The first half of the 19 th century in America, brought vast changes to technology, transportation, and production • Inventions and economic developments in the early 19 th century helps transform American society.
 How did these innovations and inventions help expand the national market economy? 1. Entrepreneurial activity Provided investment capital to create new companies and industries that boosted U. S. industrial output
How did these innovations and inventions help expand the national market economy? 1. Entrepreneurial activity Provided investment capital to create new companies and industries that boosted U. S. industrial output
 CHP 3: SECTION 4: A • A – How did entrepreneurs contribute to the market revolution? – Entrepreneurs created new businesses and new products to be bought and sold.
CHP 3: SECTION 4: A • A – How did entrepreneurs contribute to the market revolution? – Entrepreneurs created new businesses and new products to be bought and sold.
 SECTION 4 continued The Market Revolution Inventions and Improvements • Samuel F. B. Morse’s telegraph helps business, railroads communicate • Improved transportation systems cut freight costs, speed travel NEXT
SECTION 4 continued The Market Revolution Inventions and Improvements • Samuel F. B. Morse’s telegraph helps business, railroads communicate • Improved transportation systems cut freight costs, speed travel NEXT
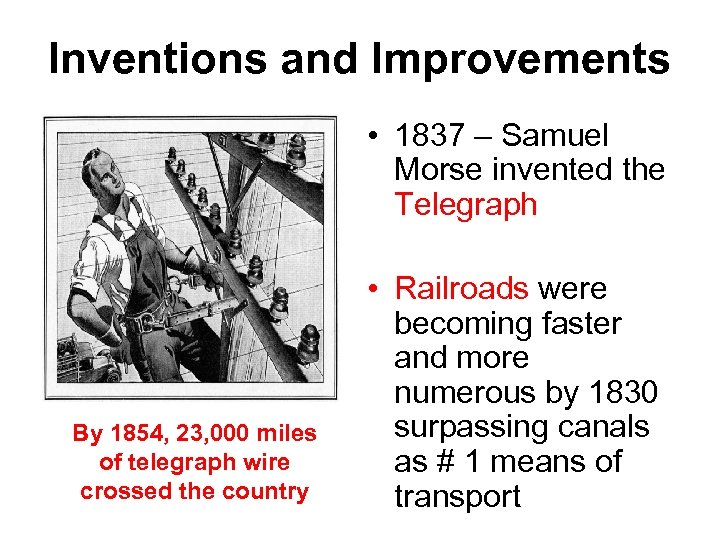 Inventions and Improvements • 1837 – Samuel Morse invented the Telegraph By 1854, 23, 000 miles of telegraph wire crossed the country • Railroads were becoming faster and more numerous by 1830 surpassing canals as # 1 means of transport
Inventions and Improvements • 1837 – Samuel Morse invented the Telegraph By 1854, 23, 000 miles of telegraph wire crossed the country • Railroads were becoming faster and more numerous by 1830 surpassing canals as # 1 means of transport
 How did these innovations and inventions help expand the national market economy? 2. Telegraph Improved communication; allowed businesspersons to stay in contact; helped trains move more efficiently and safely; linked regions of the country
How did these innovations and inventions help expand the national market economy? 2. Telegraph Improved communication; allowed businesspersons to stay in contact; helped trains move more efficiently and safely; linked regions of the country
 SECTION 4 continued The Market Revolution Transforms the Nation • Many manufactured goods become affordable in early 1800 s • Transportation, communication links make regions interdependent • Northeast becomes industrial, commercial; farmers go to Midwest NEXT
SECTION 4 continued The Market Revolution Transforms the Nation • Many manufactured goods become affordable in early 1800 s • Transportation, communication links make regions interdependent • Northeast becomes industrial, commercial; farmers go to Midwest NEXT
 The Market Revolution Transforms the Nation • Robert Fulton invented the Steamboat and by 1830, 200 were on the Mississippi
The Market Revolution Transforms the Nation • Robert Fulton invented the Steamboat and by 1830, 200 were on the Mississippi
 How did these innovations and inventions help expand the national market economy? 3. Steamboat Improved transportation; reduced travel time for goods and people, allowing agricultural and industrial expansion; decreased freight charges
How did these innovations and inventions help expand the national market economy? 3. Steamboat Improved transportation; reduced travel time for goods and people, allowing agricultural and industrial expansion; decreased freight charges
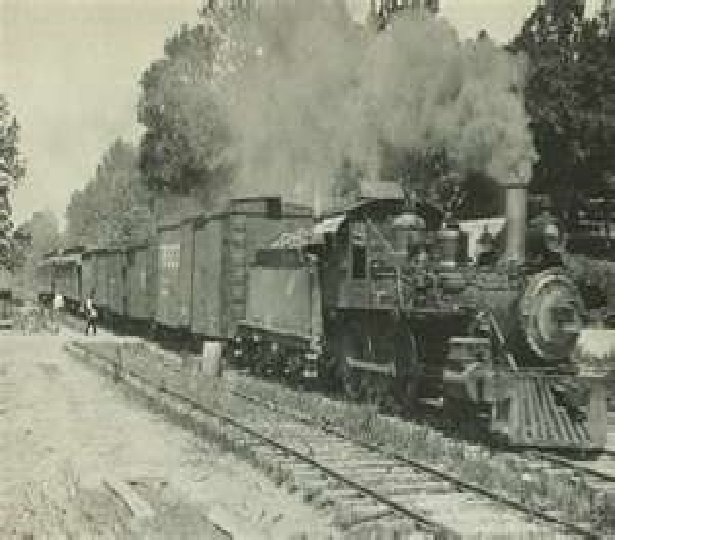

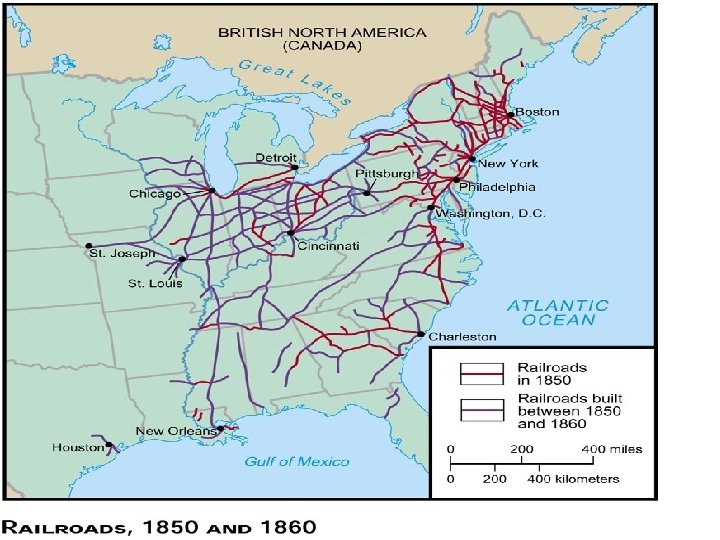
 How did these innovations and inventions help expand the national market economy? 4. Railroad Decreased travel time for goods and people; linked regions of the country
How did these innovations and inventions help expand the national market economy? 4. Railroad Decreased travel time for goods and people; linked regions of the country
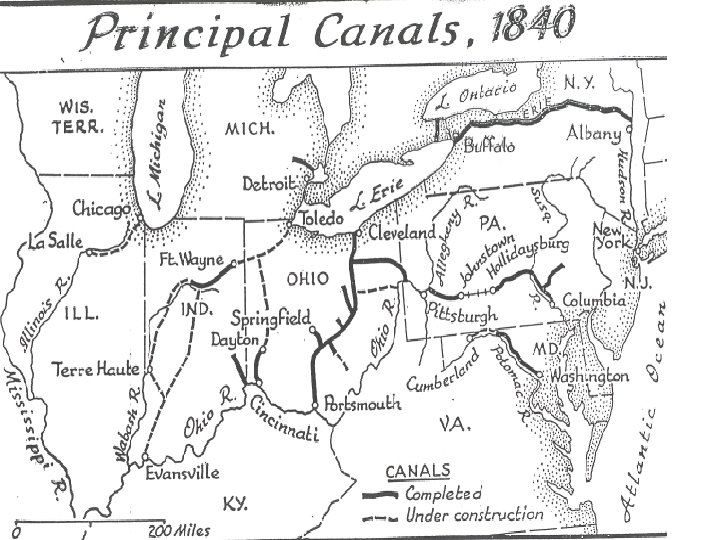

 How did these innovations and inventions help expand the national market economy? 5. Canals Opened more efficient trade routes; decreased freight charges; linked regions
How did these innovations and inventions help expand the national market economy? 5. Canals Opened more efficient trade routes; decreased freight charges; linked regions
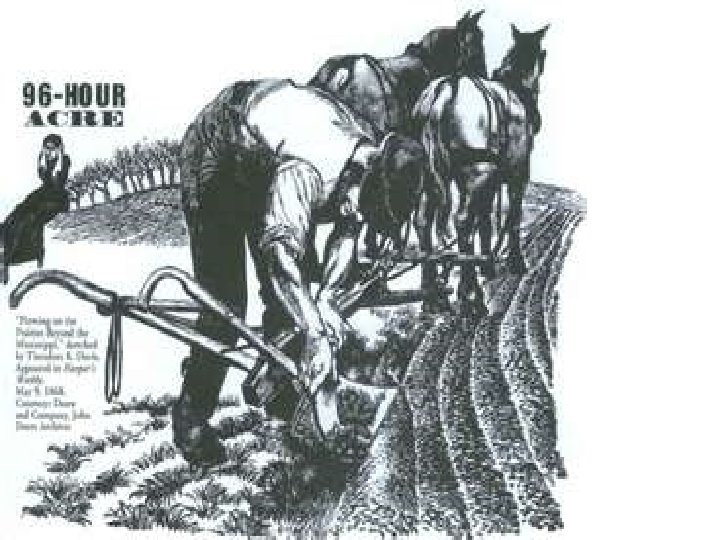

 How did these innovations and inventions help expand the national market economy? 6. Steel plow Made farming more efficient; allowed farmers to shift from subsistence fanning to growing cash crops
How did these innovations and inventions help expand the national market economy? 6. Steel plow Made farming more efficient; allowed farmers to shift from subsistence fanning to growing cash crops
 CHP 3: 4: A • B – How did technology influence both the North and Midwest in the 1840’s? – Technology influenced the North and Midwest by improving means of transportation and communication. – Inventions such as the steel plow and the reaper also improved farming in the Midwest.
CHP 3: 4: A • B – How did technology influence both the North and Midwest in the 1840’s? – Technology influenced the North and Midwest by improving means of transportation and communication. – Inventions such as the steel plow and the reaper also improved farming in the Midwest.
 SECTION 4 Changing Workplaces Effect of Factories • Families split, towns created, employer-worker relationships change • Machines allow unskilled workers to do jobs of skilled artisans NEXT
SECTION 4 Changing Workplaces Effect of Factories • Families split, towns created, employer-worker relationships change • Machines allow unskilled workers to do jobs of skilled artisans NEXT
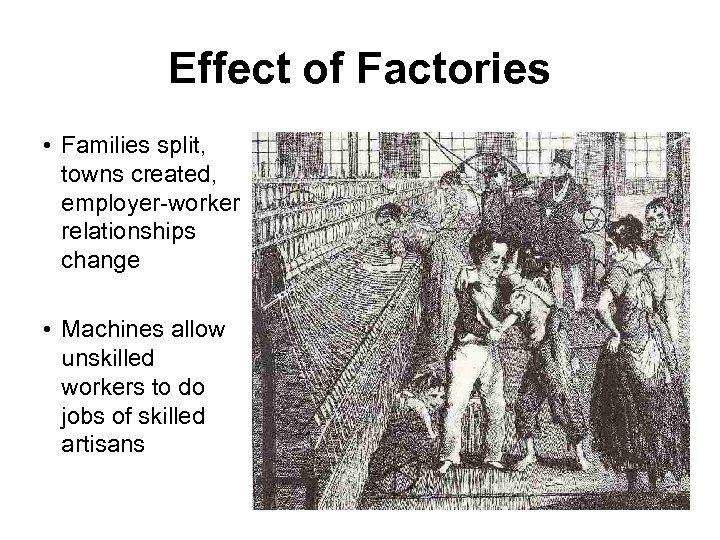 Effect of Factories • Families split, towns created, employer-worker relationships change • Machines allow unskilled workers to do jobs of skilled artisans
Effect of Factories • Families split, towns created, employer-worker relationships change • Machines allow unskilled workers to do jobs of skilled artisans
 SECTION 4 Changing Workplaces The Lowell Textile Mills • In 1820 s, Lowell textile mills employ young farm women • Women get lower pay than men, but factories pay more than other jobs • Conditions worsen: work over 12 hours; dark, hot, cramped factories NEXT
SECTION 4 Changing Workplaces The Lowell Textile Mills • In 1820 s, Lowell textile mills employ young farm women • Women get lower pay than men, but factories pay more than other jobs • Conditions worsen: work over 12 hours; dark, hot, cramped factories NEXT
 • employ young farm women • Women get lower pay than men, but factories pay more than other jobs • Conditions worsen: work over 12 hours; dark, hot, cramped factories
• employ young farm women • Women get lower pay than men, but factories pay more than other jobs • Conditions worsen: work over 12 hours; dark, hot, cramped factories
 How did these developments affect the lives of workers? 7. Textile mills Brought workers into factory to make goods; introduced workers to industrial work discipline; allowed unskilled workers to replace skilled artisans
How did these developments affect the lives of workers? 7. Textile mills Brought workers into factory to make goods; introduced workers to industrial work discipline; allowed unskilled workers to replace skilled artisans
 SECTION 4 Workers Seek Better Conditions Workers Strike • 1830 s, 1840 s U. S. workers go on strike— work stoppage over job issues • Employers defeat strikes, replace workers with immigrants NEXT
SECTION 4 Workers Seek Better Conditions Workers Strike • 1830 s, 1840 s U. S. workers go on strike— work stoppage over job issues • Employers defeat strikes, replace workers with immigrants NEXT
 Workers Strike In 1834, Lowell, Massachusetts textile workers went on strike after their wages were lowered – one example of the dozens of strikes in the U. S. in the 1830 s and 1840 s
Workers Strike In 1834, Lowell, Massachusetts textile workers went on strike after their wages were lowered – one example of the dozens of strikes in the U. S. in the 1830 s and 1840 s
 SECTION 4 Workers Seek Better Conditions Immigration Increases • Immigration—moving to a new country— of 3 million people (1830– 1860) NEXT
SECTION 4 Workers Seek Better Conditions Immigration Increases • Immigration—moving to a new country— of 3 million people (1830– 1860) NEXT
 Immigration Increases —moving to a new country— 3 million people (1830– 1860)
Immigration Increases —moving to a new country— 3 million people (1830– 1860)
 SECTION 4 Workers Seek Better Conditions National Trades’ Union • 1830 s, trade unions in different towns join to expand their power • Groups from several industries form National Trades’ Union (1834) • Commonwealth v. Hunt: MA Supreme Court supports right to strike NEXT
SECTION 4 Workers Seek Better Conditions National Trades’ Union • 1830 s, trade unions in different towns join to expand their power • Groups from several industries form National Trades’ Union (1834) • Commonwealth v. Hunt: MA Supreme Court supports right to strike NEXT
 • Several industries formed the National Trade Union in 1834 in hopes of bettering their conditions STRIKES AND UNIONS BECAME MORE NUMEROUS AFTER 1830
• Several industries formed the National Trade Union in 1834 in hopes of bettering their conditions STRIKES AND UNIONS BECAME MORE NUMEROUS AFTER 1830
 How did these developments affect the lives of workers? 8. National Trades’ Union Offered workers a chance to expand their power in the workplace by organizing efforts to improve pay and working conditions
How did these developments affect the lives of workers? 8. National Trades’ Union Offered workers a chance to expand their power in the workplace by organizing efforts to improve pay and working conditions
 National Trades’ Union • Commonwealth v. Hunt: MA Supreme Court supports right to strike
National Trades’ Union • Commonwealth v. Hunt: MA Supreme Court supports right to strike
 How did these developments affect the lives of workers? Declared that 9. Commonwealth v. workers had the legal right to Hunt organize to protect their rights
How did these developments affect the lives of workers? Declared that 9. Commonwealth v. workers had the legal right to Hunt organize to protect their rights
 CHP 3: 4: A • C – What was the attitude of many factory owners toward their workers? – Most factory owners regarded their workers in the same way that they regarded their machinery. – They were to be maintained to provide maximum production and discarded when no longer of any use.
CHP 3: 4: A • C – What was the attitude of many factory owners toward their workers? – Most factory owners regarded their workers in the same way that they regarded their machinery. – They were to be maintained to provide maximum production and discarded when no longer of any use.

 How did these developments affect the lives of workers? 10. Industrialization Created many jobs; produced goods efficiently; created new markets; produced new goods for use in other sectors of the economy (agriculture, transportation)
How did these developments affect the lives of workers? 10. Industrialization Created many jobs; produced goods efficiently; created new markets; produced new goods for use in other sectors of the economy (agriculture, transportation)
 CHP 3: 4: A • D – Why were most labor strikes of the 1830’s and 1840’s ineffective? – Workers were not well organized, they had little public support, and strikers could be easily replaced.
CHP 3: 4: A • D – Why were most labor strikes of the 1830’s and 1840’s ineffective? – Workers were not well organized, they had little public support, and strikers could be easily replaced.


