2dc61183cdce3677522a21fa79d2209f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 79
 Standard Mortality Ratio (SMR) Project: Developing QAPI Without Fear Svetlana (Lana) Kacherova, QI Director Lisle Mukai, QI Coordinator ESRD Network 18 November 12, 2008 1
Standard Mortality Ratio (SMR) Project: Developing QAPI Without Fear Svetlana (Lana) Kacherova, QI Director Lisle Mukai, QI Coordinator ESRD Network 18 November 12, 2008 1
 Special Acknowledgement for Content Contributions: Laura Adams, President and CEO Rhode Island Quality Institute & Quality Improvement Directors From other ESRD Networks! 2
Special Acknowledgement for Content Contributions: Laura Adams, President and CEO Rhode Island Quality Institute & Quality Improvement Directors From other ESRD Networks! 2
 Session Objectives Project Description n Increase understanding of Quality Concepts n Use the Basic Quality Tools n Apply PDSA cycle and project steps n Learn something new n Have some fun n 3
Session Objectives Project Description n Increase understanding of Quality Concepts n Use the Basic Quality Tools n Apply PDSA cycle and project steps n Learn something new n Have some fun n 3
 V 626 QAPI Condition Statement n n The dialysis facility must develop, implement, maintain and evaluate an effective, data driven, quality assessment and performance improvement program with participation by the professional members of the interdisciplinary team. . . …The dialysis facility must maintain and demonstrate evidence of its quality improvement and performance improvement program for review by CMS 4
V 626 QAPI Condition Statement n n The dialysis facility must develop, implement, maintain and evaluate an effective, data driven, quality assessment and performance improvement program with participation by the professional members of the interdisciplinary team. . . …The dialysis facility must maintain and demonstrate evidence of its quality improvement and performance improvement program for review by CMS 4
 Condition 494. 110: Quality Assessment and Performance Improvement Project (QAPI) n n n n Interdisciplinary team (IDT) Must report problems to Medical Director and Quality Improvement committee Outcome- focused Process continuous & on-going Use community accepted standards as targets Include patient satisfaction, infection control, medical injuries & medication errors Plan/Do/Study/Act: Close the loop! 5
Condition 494. 110: Quality Assessment and Performance Improvement Project (QAPI) n n n n Interdisciplinary team (IDT) Must report problems to Medical Director and Quality Improvement committee Outcome- focused Process continuous & on-going Use community accepted standards as targets Include patient satisfaction, infection control, medical injuries & medication errors Plan/Do/Study/Act: Close the loop! 5
 Monitoring Performance Improvement (V 638) The facility must: n Continuously monitor its performance n Take actions that result in performance improvement n Track to assure improvements are sustained over time 6
Monitoring Performance Improvement (V 638) The facility must: n Continuously monitor its performance n Take actions that result in performance improvement n Track to assure improvements are sustained over time 6
 Interdisciplinary Team: Show Me The Progress: 7
Interdisciplinary Team: Show Me The Progress: 7
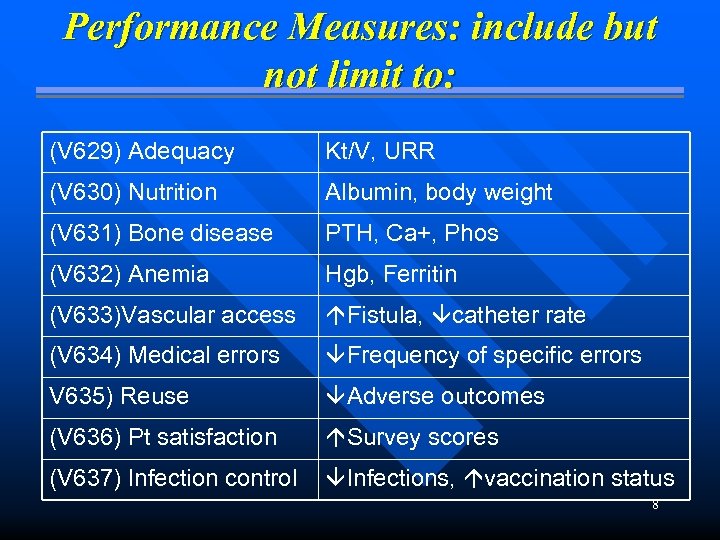 Performance Measures: include but not limit to: (V 629) Adequacy Kt/V, URR (V 630) Nutrition Albumin, body weight (V 631) Bone disease PTH, Ca+, Phos (V 632) Anemia Hgb, Ferritin (V 633)Vascular access Fistula, catheter rate (V 634) Medical errors Frequency of specific errors V 635) Reuse Adverse outcomes (V 636) Pt satisfaction Survey scores (V 637) Infection control Infections, vaccination status 8
Performance Measures: include but not limit to: (V 629) Adequacy Kt/V, URR (V 630) Nutrition Albumin, body weight (V 631) Bone disease PTH, Ca+, Phos (V 632) Anemia Hgb, Ferritin (V 633)Vascular access Fistula, catheter rate (V 634) Medical errors Frequency of specific errors V 635) Reuse Adverse outcomes (V 636) Pt satisfaction Survey scores (V 637) Infection control Infections, vaccination status 8
 SMR Project: Inclusion Criteria for Participating Facilities n SMR rated “Worse than expected” (2008 DFR data) – 27 facilities IMPORTANT: n State Surveyors review DFRs before visiting facilities n SMR information is available on the Dialysis Facility Compare website at www. medicare. gov 9 n
SMR Project: Inclusion Criteria for Participating Facilities n SMR rated “Worse than expected” (2008 DFR data) – 27 facilities IMPORTANT: n State Surveyors review DFRs before visiting facilities n SMR information is available on the Dialysis Facility Compare website at www. medicare. gov 9 n
 SMR Project Goal: All participating facilities will develop to address identified issue(s) for high SMR and implement those processes by May 2008. n Validation of implementation will be verified by supporting documentation and direct observation n 10
SMR Project Goal: All participating facilities will develop to address identified issue(s) for high SMR and implement those processes by May 2008. n Validation of implementation will be verified by supporting documentation and direct observation n 10
 What is QAPI and why do we need it: Quality Assessment and Performance Improvement Project/Program Previously known as a CQI (Continuous Quality Improvement) 11
What is QAPI and why do we need it: Quality Assessment and Performance Improvement Project/Program Previously known as a CQI (Continuous Quality Improvement) 11
 Information that Duels the Growing Emphasis on Quality Two million documents will be lost by the IRS this year n 18, 322 pieces of mail will be mishandled in the next hour n 20, 000 incorrect drug prescriptions will be written in the next 12 months n Data from the early 1990 s 12
Information that Duels the Growing Emphasis on Quality Two million documents will be lost by the IRS this year n 18, 322 pieces of mail will be mishandled in the next hour n 20, 000 incorrect drug prescriptions will be written in the next 12 months n Data from the early 1990 s 12
 Quality in Healthcare Rather then just meeting fixed standards, a never ending search for ways to improve patient outcomes n Focus on outcomes and the process that produce those outcomes n Focus on systems of care not individual cases n Improve the average and the outliers will improve too n 13
Quality in Healthcare Rather then just meeting fixed standards, a never ending search for ways to improve patient outcomes n Focus on outcomes and the process that produce those outcomes n Focus on systems of care not individual cases n Improve the average and the outliers will improve too n 13
 Institute of Medicine Aims for Health Care: 1. 2. 3. 4. Evidence-based Patient centered Outcome improvement driven Systems/team oriented 5. n n n Six aims of health care: Safe Effective Patient centered Timely Efficient Equitable 14
Institute of Medicine Aims for Health Care: 1. 2. 3. 4. Evidence-based Patient centered Outcome improvement driven Systems/team oriented 5. n n n Six aims of health care: Safe Effective Patient centered Timely Efficient Equitable 14
 What is the cost of Poor Quality? No show rates? n Lost charts? n Lost labs? n Train wreck visits? n Lost revenue – improper billing? n Staff turnover? n 15
What is the cost of Poor Quality? No show rates? n Lost charts? n Lost labs? n Train wreck visits? n Lost revenue – improper billing? n Staff turnover? n 15
 Quality Concepts n n n Customers Processes Variation Measurement Root Cause Improvement 16
Quality Concepts n n n Customers Processes Variation Measurement Root Cause Improvement 16
 Basic Principles of Quality Improvement Focus on improving work processes n A systems orientation to service delivery n Services or products tailored to customers needs n Staff involvement n Emphasis on design and improvement of products/services n A focus on continuously improving n 17
Basic Principles of Quality Improvement Focus on improving work processes n A systems orientation to service delivery n Services or products tailored to customers needs n Staff involvement n Emphasis on design and improvement of products/services n A focus on continuously improving n 17
 Introducing the Quality Tools 18
Introducing the Quality Tools 18
 Basic Quality Tools: Process Analysis n Flow Chart n Brainstorming n Fishbone Diagram (Cause and Effect) n Check Sheet n Histogram or Pareto Diagram n Run Chart n Communication n 19
Basic Quality Tools: Process Analysis n Flow Chart n Brainstorming n Fishbone Diagram (Cause and Effect) n Check Sheet n Histogram or Pareto Diagram n Run Chart n Communication n 19
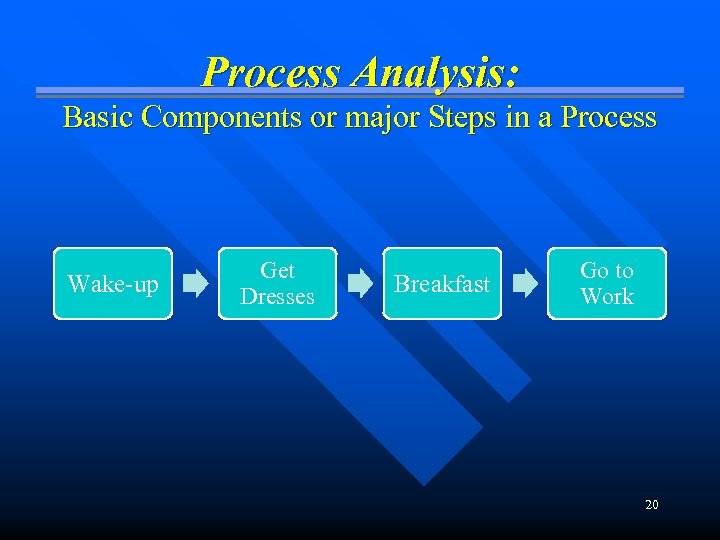 Process Analysis: Basic Components or major Steps in a Process Wake-up Get Dresses Breakfast Go to Work 20
Process Analysis: Basic Components or major Steps in a Process Wake-up Get Dresses Breakfast Go to Work 20
 Use Process Analysis to: Defines and evaluate the overall process n Each box placed in order of occurrence, represents a key part of the process being examined n The amount of time could be added as it could be important for improvement n Once identified which part of the process needs improvement, the box could be further broken down into specific steps using a flow chart n 21
Use Process Analysis to: Defines and evaluate the overall process n Each box placed in order of occurrence, represents a key part of the process being examined n The amount of time could be added as it could be important for improvement n Once identified which part of the process needs improvement, the box could be further broken down into specific steps using a flow chart n 21
 Flow Chart 22
Flow Chart 22
 Use a Flow Chart to: Define specific steps in a process including choices and decision points n If there is a decision to be made and no specific choices – this is a source of variation and a potential problem! n Every process should have a clearly defined beginning and end (all team members must agree on steps) n 23
Use a Flow Chart to: Define specific steps in a process including choices and decision points n If there is a decision to be made and no specific choices – this is a source of variation and a potential problem! n Every process should have a clearly defined beginning and end (all team members must agree on steps) n 23
 Brainstorming n Tool for gathering ideas, particularly about problem causes and solutions 24
Brainstorming n Tool for gathering ideas, particularly about problem causes and solutions 24
 Rules of Brainstorming Don’t criticize n Be creative n Go for quantity not quality n Suspend judgment & evaluation n Piggyback on others’ ideas n Record all ideas n Encourage others n 25
Rules of Brainstorming Don’t criticize n Be creative n Go for quantity not quality n Suspend judgment & evaluation n Piggyback on others’ ideas n Record all ideas n Encourage others n 25
 Fishbone Diagram Also called Ishikawa Diagram in honor of the man who developed this tool n Also called the Cause & Effect Diagram because it’s primary use is to assist in determining the root-cause of a problem n Use this tool (bone by bone) to identify a major source and drill down to the level where action can be taken n 26
Fishbone Diagram Also called Ishikawa Diagram in honor of the man who developed this tool n Also called the Cause & Effect Diagram because it’s primary use is to assist in determining the root-cause of a problem n Use this tool (bone by bone) to identify a major source and drill down to the level where action can be taken n 26
 Fishbone Diagram (cont). Determine the problem and create a problem statement (effect). Write it at the right center of the chart n Brainstorm the major categories of causes of the problem. Write them as the main branches steaming from the center line n Brainstorm all possible causes of the problem. Ask “Why did this happen? ” about each cause. n
Fishbone Diagram (cont). Determine the problem and create a problem statement (effect). Write it at the right center of the chart n Brainstorm the major categories of causes of the problem. Write them as the main branches steaming from the center line n Brainstorm all possible causes of the problem. Ask “Why did this happen? ” about each cause. n
 Fishbone Diagram – (cont). Write sub-causes stemming from the category of causes n Collect data to confirm root-cause n If no further causes can be identified, then you found the root causes of the problem n
Fishbone Diagram – (cont). Write sub-causes stemming from the category of causes n Collect data to confirm root-cause n If no further causes can be identified, then you found the root causes of the problem n
 Check Sheet 30
Check Sheet 30
 Check Shet: Tracking Form 31
Check Shet: Tracking Form 31
 32
32
 Check sheet Used when several possible problem causes are identified, but there is no information on the largest cause n Designed to collect data on the number of times that those causes occur n Collect data and evaluate action taken n The results allow action to be focused in on main causes n 33
Check sheet Used when several possible problem causes are identified, but there is no information on the largest cause n Designed to collect data on the number of times that those causes occur n Collect data and evaluate action taken n The results allow action to be focused in on main causes n 33
 Run Chart 34
Run Chart 34
 Use Run Chart to: Follow performance (Y) over time (X) (“plotting the dots”) n Allow you to visualize how the process is performing and helps you to identify trends (good or bad) n Reveals the impact of improvement actions n Add the goals to the chart to see progress toward achieving the goal n 35
Use Run Chart to: Follow performance (Y) over time (X) (“plotting the dots”) n Allow you to visualize how the process is performing and helps you to identify trends (good or bad) n Reveals the impact of improvement actions n Add the goals to the chart to see progress toward achieving the goal n 35
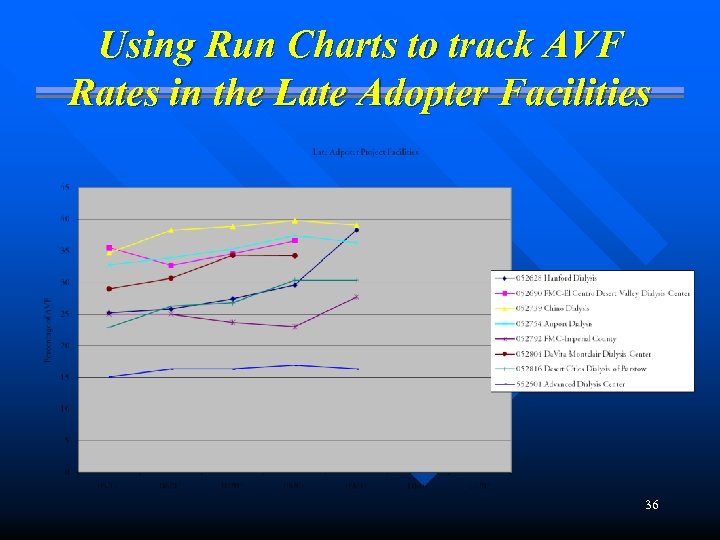 Using Run Charts to track AVF Rates in the Late Adopter Facilities 36
Using Run Charts to track AVF Rates in the Late Adopter Facilities 36
 Using Run Charts as a Tracking Tool Where have you been? n Where is the data going? n Please “plot the dots” n A word about “variation” - normal variation - special cause variation n 37
Using Run Charts as a Tracking Tool Where have you been? n Where is the data going? n Please “plot the dots” n A word about “variation” - normal variation - special cause variation n 37
 Using Run Charts as an Evaluation Tool Compare performance before and after change n Calculate % change between old and new level n 38
Using Run Charts as an Evaluation Tool Compare performance before and after change n Calculate % change between old and new level n 38
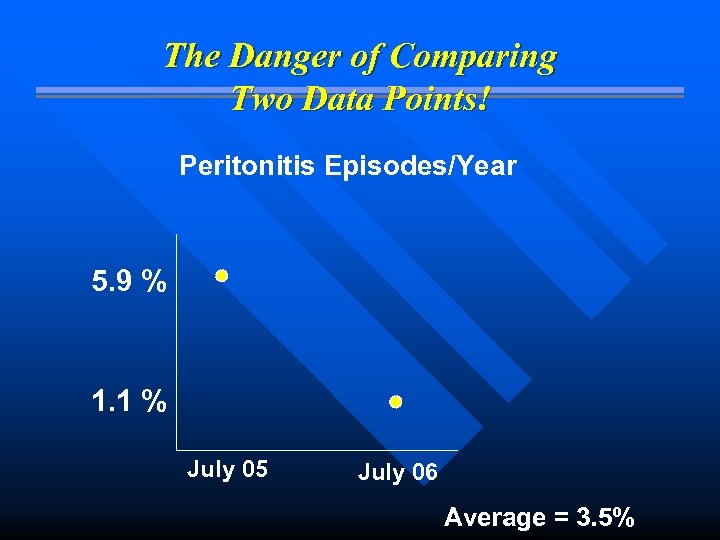 The Danger of Comparing Two Data Points! Peritonitis Episodes/Year 5. 9 % 1. 1 % July 05 July 06 Average = 3. 5%
The Danger of Comparing Two Data Points! Peritonitis Episodes/Year 5. 9 % 1. 1 % July 05 July 06 Average = 3. 5%
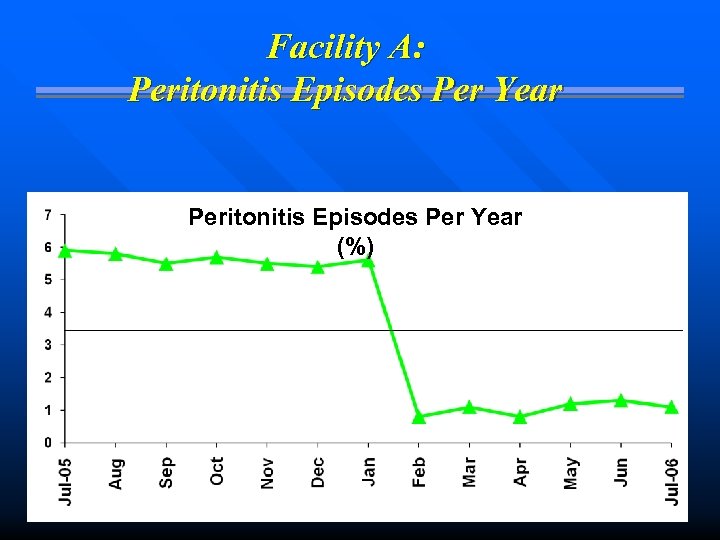 Facility A: Peritonitis Episodes Per Year (%)
Facility A: Peritonitis Episodes Per Year (%)
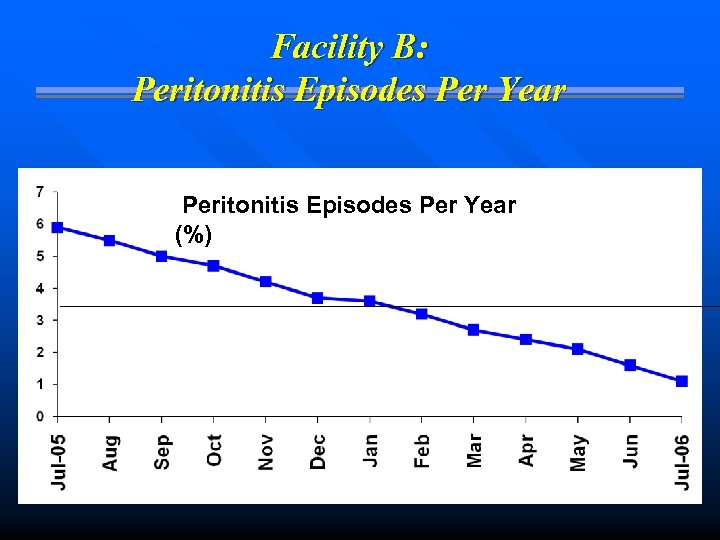 Facility B: Peritonitis Episodes Per Year (%)
Facility B: Peritonitis Episodes Per Year (%)
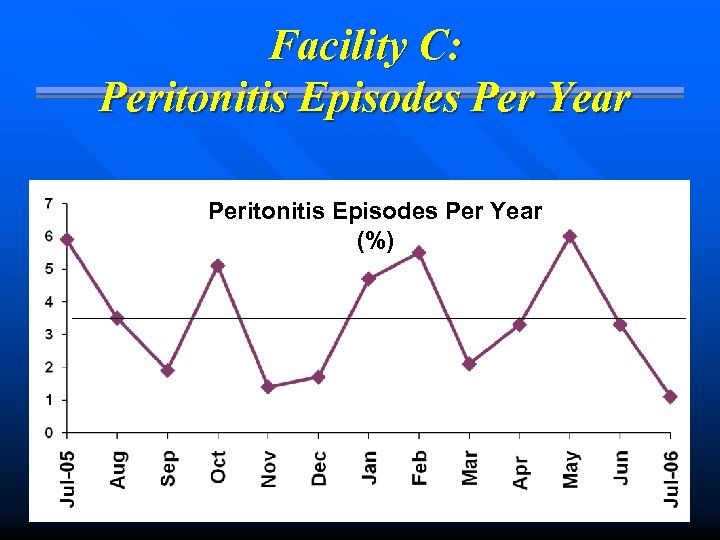 Facility C: Peritonitis Episodes Per Year (%)
Facility C: Peritonitis Episodes Per Year (%)
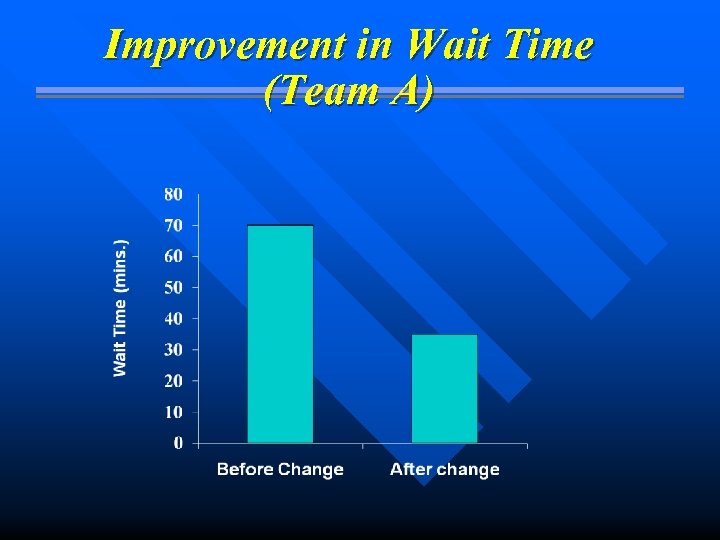 Improvement in Wait Time (Team A)
Improvement in Wait Time (Team A)
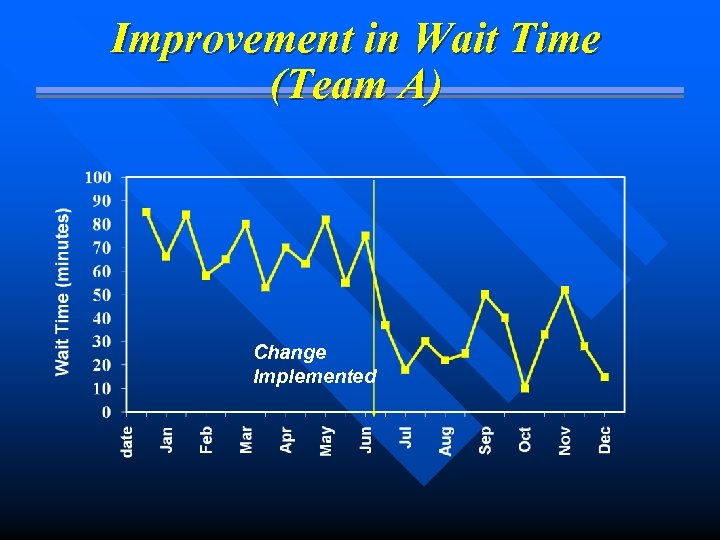 Improvement in Wait Time (Team A) Change Implemented
Improvement in Wait Time (Team A) Change Implemented
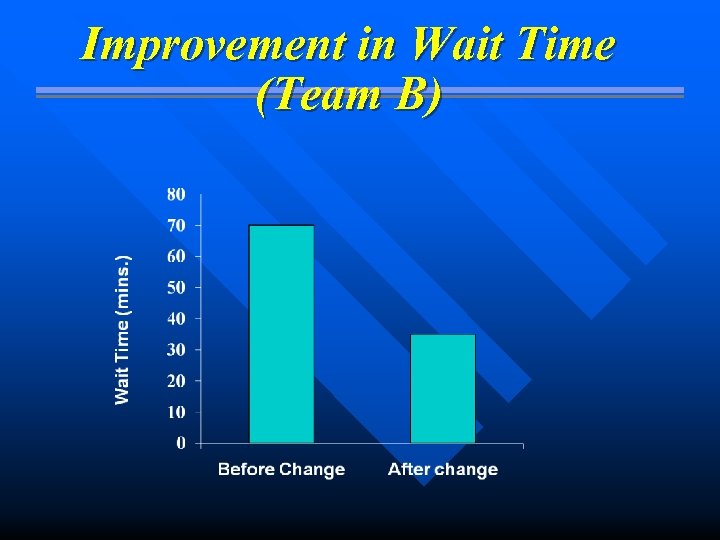 Improvement in Wait Time (Team B)
Improvement in Wait Time (Team B)
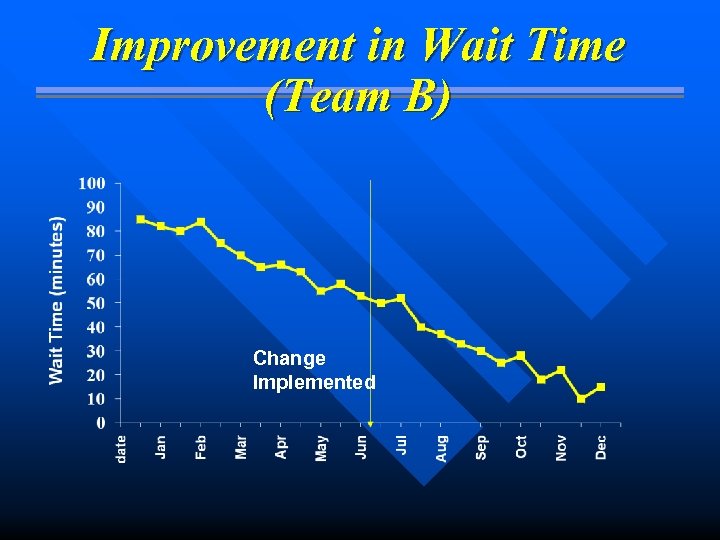 Improvement in Wait Time (Team B) Change Implemented
Improvement in Wait Time (Team B) Change Implemented
 Get more from the Data Segment or stratify - by day - by shift - by machine - by staff, surgeon, physician n Use comparative data n 47
Get more from the Data Segment or stratify - by day - by shift - by machine - by staff, surgeon, physician n Use comparative data n 47
 Pareto Diagram A histogram charted in descending order of frequency n Visually displays the contribution of each cause to the overall problem n This part of problem analysis helps to focus action and resources on main causes n 48
Pareto Diagram A histogram charted in descending order of frequency n Visually displays the contribution of each cause to the overall problem n This part of problem analysis helps to focus action and resources on main causes n 48
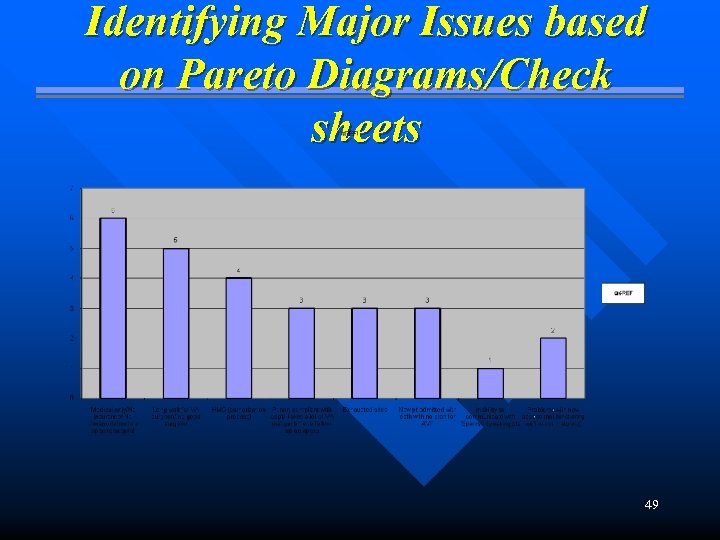 Identifying Major Issues based on Pareto Diagrams/Check sheets 49
Identifying Major Issues based on Pareto Diagrams/Check sheets 49
 Communication Communicate organizational quality definition n Communicate customer/supplier needs n Discuss problems (opportunities for improvement) n Report team progress & project results n Exchange information n 50
Communication Communicate organizational quality definition n Communicate customer/supplier needs n Discuss problems (opportunities for improvement) n Report team progress & project results n Exchange information n 50
 Communication Critical in quality improvement but often ignored tool! n For best results must be frequent and accurate communication among all involved n Communication facilitates buy-in n Let others know what improvement project is going on n Gather input, report progress, celebrate results 51 n
Communication Critical in quality improvement but often ignored tool! n For best results must be frequent and accurate communication among all involved n Communication facilitates buy-in n Let others know what improvement project is going on n Gather input, report progress, celebrate results 51 n
 Listen to Your DATA What does the data say? 52
Listen to Your DATA What does the data say? 52
 Aims to Action: Conducting QAPI utilizing Rapid-Cycle Improvement
Aims to Action: Conducting QAPI utilizing Rapid-Cycle Improvement
 What is Rapid Cycle Improvement? n Variant of process improvement that: relies on existing knowledge – dramatically shortens discovery process – works on “rapid trial & learn” method – relies heavily on action –
What is Rapid Cycle Improvement? n Variant of process improvement that: relies on existing knowledge – dramatically shortens discovery process – works on “rapid trial & learn” method – relies heavily on action –
 PDCA /PDSA Methodology ACT PLAN CHECK DO /STUDY 55
PDCA /PDSA Methodology ACT PLAN CHECK DO /STUDY 55
 Plan-Do-Study-Act n n Plan – Identify Opportunity and plan for change Do – Implement the Change on a small scale Study – Use data to analyze for the change and determine whether it made a difference Act – If the change was successful, implement the plan and continuously monitor results. If the change did not work – start the process again.
Plan-Do-Study-Act n n Plan – Identify Opportunity and plan for change Do – Implement the Change on a small scale Study – Use data to analyze for the change and determine whether it made a difference Act – If the change was successful, implement the plan and continuously monitor results. If the change did not work – start the process again.
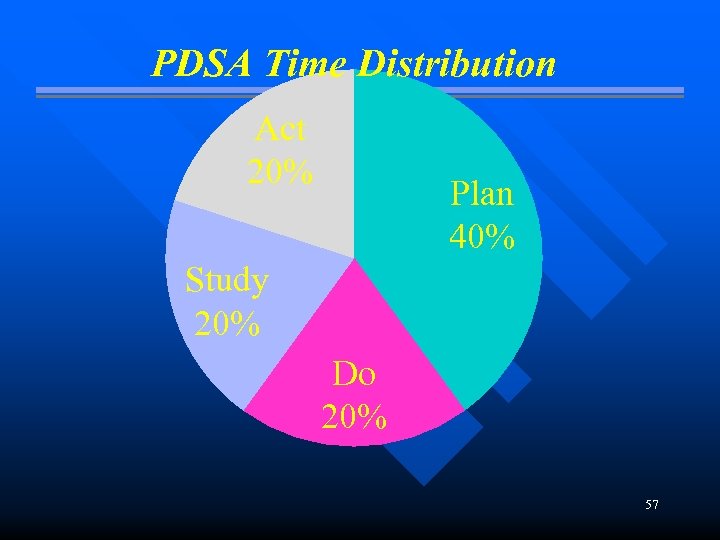 PDSA Time Distribution Act 20% Plan 40% Study 20% Do 20% 57
PDSA Time Distribution Act 20% Plan 40% Study 20% Do 20% 57
 Root Cause Analysis Caution: Avoid the quick fix n Find and fix the root cause of the problem n 58
Root Cause Analysis Caution: Avoid the quick fix n Find and fix the root cause of the problem n 58
 What is Root-Cause Analysis? Finding the basic cause n Use brainstorming n Use the fishbone diagram n Collect data if you need to n Get down to an “actionable” level n Ask “WHY? ” 3 -5 times! n 59
What is Root-Cause Analysis? Finding the basic cause n Use brainstorming n Use the fishbone diagram n Collect data if you need to n Get down to an “actionable” level n Ask “WHY? ” 3 -5 times! n 59
 60
60
 Barriers for facility improvement related to SMR (source: UM-KECC) Accuracy Issues (based on Medicare Billing data and may not capture 100% of patient population) n DFR includes deaths up to 60 days after transfer out from the facility n SMR calculation depends on the accurate completeness of the form by facility staff (results can be a mismatch between 2728 initial data and DFR billing data) n 61
Barriers for facility improvement related to SMR (source: UM-KECC) Accuracy Issues (based on Medicare Billing data and may not capture 100% of patient population) n DFR includes deaths up to 60 days after transfer out from the facility n SMR calculation depends on the accurate completeness of the form by facility staff (results can be a mismatch between 2728 initial data and DFR billing data) n 61
 Barriers identified by Network 18 facilities in the past: High infection rate due to high catheter rate n Medical Insurance Issues (Emergency medical only) n Under-reporting of co-morbidities on the 2728 CMS Medical Evidence Forms n Under-reporting of the number of patients with diabetes as a primary cause of ESRD n 62
Barriers identified by Network 18 facilities in the past: High infection rate due to high catheter rate n Medical Insurance Issues (Emergency medical only) n Under-reporting of co-morbidities on the 2728 CMS Medical Evidence Forms n Under-reporting of the number of patients with diabetes as a primary cause of ESRD n 62
 Facility Process Review Checklist Findings: Clinical At least 85% of patients in the facility have Hemoglobin above 11 gm/dl n Less than 10% of patients in the facility have a catheter as a permanent vascular access n At least 50% of patients in the facility have an AVF as a permanent vascular access n 63
Facility Process Review Checklist Findings: Clinical At least 85% of patients in the facility have Hemoglobin above 11 gm/dl n Less than 10% of patients in the facility have a catheter as a permanent vascular access n At least 50% of patients in the facility have an AVF as a permanent vascular access n 63
 Facility Process Review Checklist Findings: Staff-related Physicians participate in patient care meetings on a regular basis, ensuring that all patients are reviewed at least quarterly n Facility Staff accurately indicates cause of death when completing 2746 Death notification forms on deceased patients n 64
Facility Process Review Checklist Findings: Staff-related Physicians participate in patient care meetings on a regular basis, ensuring that all patients are reviewed at least quarterly n Facility Staff accurately indicates cause of death when completing 2746 Death notification forms on deceased patients n 64
 Model for Improvement What are we trying to accomplish? How will we know that a change is an improvement? What changes can we make that will result in an improvement? Goal Act Plan Stud Do y
Model for Improvement What are we trying to accomplish? How will we know that a change is an improvement? What changes can we make that will result in an improvement? Goal Act Plan Stud Do y
 Developing Your Goal § Write a clear statement of aim--make the target for improvement unambiguous § Include numeric goals § Set “stretch” aims § Focus on issues that are important to your organization - choose appropriate goals
Developing Your Goal § Write a clear statement of aim--make the target for improvement unambiguous § Include numeric goals § Set “stretch” aims § Focus on issues that are important to your organization - choose appropriate goals
 Developing Your Goal § Improvement relies on intention to improve § Senior leaders set & align aim with strategic goals (involve Medical Director!) § Agreement on aim is critical § Include a specific time frame for accomplishing your aim
Developing Your Goal § Improvement relies on intention to improve § Senior leaders set & align aim with strategic goals (involve Medical Director!) § Agreement on aim is critical § Include a specific time frame for accomplishing your aim
 Examples of Goals n n To decrease the number of patients utilizing catheter as a primary source of vascular access by percentage points between November 2008 and May 2009. To increase the number of patients utilizing AVF as a primary vascular access for hemodialysis by 6 percentage points between October 2008 and May 2009
Examples of Goals n n To decrease the number of patients utilizing catheter as a primary source of vascular access by percentage points between November 2008 and May 2009. To increase the number of patients utilizing AVF as a primary vascular access for hemodialysis by 6 percentage points between October 2008 and May 2009
 Model for Improvement What are we trying to accomplish? How will we know that a change is an improvement? What changes can we make that will result in an improvement? Measure Act Plan Stud y Do
Model for Improvement What are we trying to accomplish? How will we know that a change is an improvement? What changes can we make that will result in an improvement? Measure Act Plan Stud y Do
 Measurement Guidelines n The key measures should clarify the goal and make it tangible n Use outcome and process measures n Integrate measurement into the daily routine n Use qualitative as well as quantitative data n Seek usefulness, not perfection
Measurement Guidelines n The key measures should clarify the goal and make it tangible n Use outcome and process measures n Integrate measurement into the daily routine n Use qualitative as well as quantitative data n Seek usefulness, not perfection
 Measures: n Process: n Outcome: n Identify patients with AVFs that were placed after April 2008 but not used yet. Vascular access assessment Cannulation Log P-t referral logs Monitor newly created AVF for maturation n Decrease in number of AVF “placed but not used” Increase in number of functional AVFs n n n 71
Measures: n Process: n Outcome: n Identify patients with AVFs that were placed after April 2008 but not used yet. Vascular access assessment Cannulation Log P-t referral logs Monitor newly created AVF for maturation n Decrease in number of AVF “placed but not used” Increase in number of functional AVFs n n n 71
 Model for Improvement What are we trying to accomplish? How will we know that a change is an improvement? What changes can we make that will result in an improvement? Select Changes Act Plan Stud Do y
Model for Improvement What are we trying to accomplish? How will we know that a change is an improvement? What changes can we make that will result in an improvement? Select Changes Act Plan Stud Do y
 Selecting Changes Blatantly steal: Use the literature, the experience of others, hunches and theories (FFBI suggestions) n Be strategic: Set priorities based on the aim, known problems, and feasibility n
Selecting Changes Blatantly steal: Use the literature, the experience of others, hunches and theories (FFBI suggestions) n Be strategic: Set priorities based on the aim, known problems, and feasibility n
 Objective of the Test: Change or No Change? Probably Change Test Redesign Eliminate Reduce Deliver Implement Probably No Change Recruit Distribute Continue Examine Discuss Teach
Objective of the Test: Change or No Change? Probably Change Test Redesign Eliminate Reduce Deliver Implement Probably No Change Recruit Distribute Continue Examine Discuss Teach
 To Be Considered a Real Test was planned, including a plan for collecting data. n Plan was attempted and data was collected. n Time was set aside to analyze data and study the results. n Action was taken, based on what was learned. n
To Be Considered a Real Test was planned, including a plan for collecting data. n Plan was attempted and data was collected. n Time was set aside to analyze data and study the results. n Action was taken, based on what was learned. n
 Two Key Points n Small scale small change n Success (or failure) in one PDSA cycle success or failure of the project
Two Key Points n Small scale small change n Success (or failure) in one PDSA cycle success or failure of the project
 SMR Project: Network Responsibilities: Project Leader (change agent) n Supply the templates for RCA & PDSA n Supply facilities with tools and knowledge n Periodic monitoring and feedback n Conduct phone interviews to obtain facilityspecific data n Facility site visits for strugglers n 77
SMR Project: Network Responsibilities: Project Leader (change agent) n Supply the templates for RCA & PDSA n Supply facilities with tools and knowledge n Periodic monitoring and feedback n Conduct phone interviews to obtain facilityspecific data n Facility site visits for strugglers n 77
 Facilities Responsibilities: Return agreement letter (signed by MD) n RCA & PDSA due to the Network by November 30, 2008 (PDSA Action Plans must be signed by MD) n Follow the project timelines n 78
Facilities Responsibilities: Return agreement letter (signed by MD) n RCA & PDSA due to the Network by November 30, 2008 (PDSA Action Plans must be signed by MD) n Follow the project timelines n 78
 We are all partners! Thank you! For questions please contact: Svetlana (Lana) Kacherova, RN, MPH, CPHQ Quality Improvement Director ESRD Network 18 323 -962 -2020 skacherova@nw 18. esrd. net 79
We are all partners! Thank you! For questions please contact: Svetlana (Lana) Kacherova, RN, MPH, CPHQ Quality Improvement Director ESRD Network 18 323 -962 -2020 skacherova@nw 18. esrd. net 79


