2471ab6d29cf3b6f56a4e0f900fd8079.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Standard Grade Computing Studies Networks. What is a network?
Standard Grade Computing Studies Networks. What is a network?
 Stand Alone or Networked? • A stand alone computer is one that is not connected to a network • This could be a desktop computer or a laptop that has no wired or wireless connection.
Stand Alone or Networked? • A stand alone computer is one that is not connected to a network • This could be a desktop computer or a laptop that has no wired or wireless connection.
 What is a Network? • A series of computers linked together so that they can send and receive data. • We use them for sending e-mails, downloading files, shopping, etc • You need to know about – Local Area Network (LAN) – The Internet <- What is a network? Local Area Networks ->
What is a Network? • A series of computers linked together so that they can send and receive data. • We use them for sending e-mails, downloading files, shopping, etc • You need to know about – Local Area Network (LAN) – The Internet <- What is a network? Local Area Networks ->
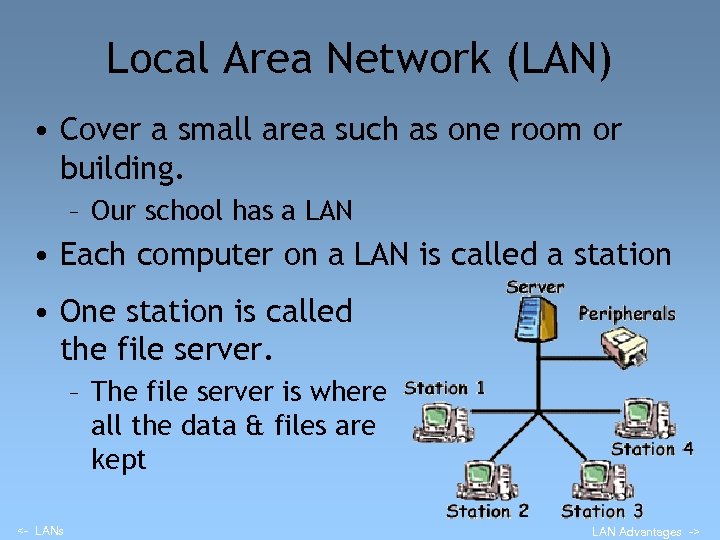 Local Area Network (LAN) • Cover a small area such as one room or building. – Our school has a LAN • Each computer on a LAN is called a station • One station is called the file server. – The file server is where all the data & files are kept <- LANs LAN Advantages ->
Local Area Network (LAN) • Cover a small area such as one room or building. – Our school has a LAN • Each computer on a LAN is called a station • One station is called the file server. – The file server is where all the data & files are kept <- LANs LAN Advantages ->
 Advantages of a LAN • Share data e. g. files in Our school folder • Share devices attached to the network (like a printer) • E-mail • Security. . Passwords. . Different levels of access • You can log onto any station connected to the LAN <- LAN Advantages Ex 1 ->
Advantages of a LAN • Share data e. g. files in Our school folder • Share devices attached to the network (like a printer) • E-mail • Security. . Passwords. . Different levels of access • You can log onto any station connected to the LAN <- LAN Advantages Ex 1 ->
 Exercise 1 1. What is a LAN? 2 Describe your school’s LAN 3. Write down 3 advantages of a LAN <- LAN Advantages Transmission meda ->
Exercise 1 1. What is a LAN? 2 Describe your school’s LAN 3. Write down 3 advantages of a LAN <- LAN Advantages Transmission meda ->
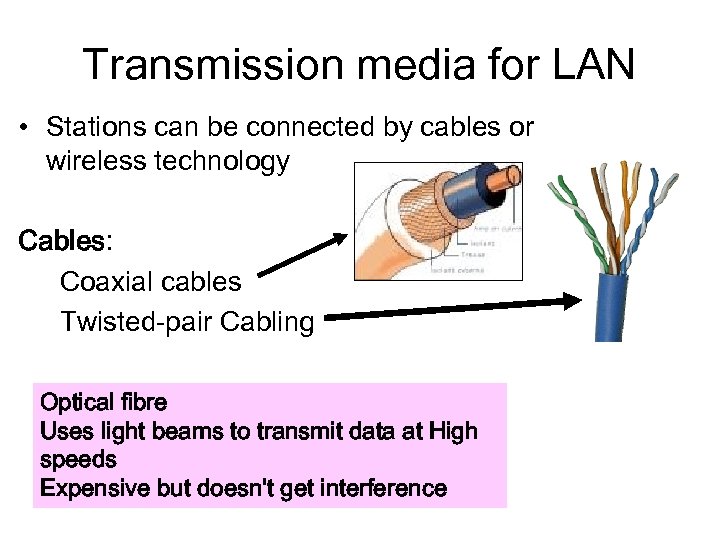 Transmission media for LAN • Stations can be connected by cables or wireless technology Cables: Coaxial cables Twisted-pair Cabling Optical fibre Uses light beams to transmit data at High speeds Expensive but doesn't get interference <- Ex 1 Wireless ->
Transmission media for LAN • Stations can be connected by cables or wireless technology Cables: Coaxial cables Twisted-pair Cabling Optical fibre Uses light beams to transmit data at High speeds Expensive but doesn't get interference <- Ex 1 Wireless ->
 Fibre Optic Cable • High speeds: – Uses light beams to transmit data at High speeds { 100 terabytes per second is possible} • Doesn’t get interference { unlike copper wire cable} • More secure: – Difficult to intercept data on a fibre optic cable • Expensive to install
Fibre Optic Cable • High speeds: – Uses light beams to transmit data at High speeds { 100 terabytes per second is possible} • Doesn’t get interference { unlike copper wire cable} • More secure: – Difficult to intercept data on a fibre optic cable • Expensive to install
 Transmission media for LAN • Wireless – Infrared communication • Used for wireless mouse and keyboard – Bluetooth • Range of about 10 metres – WIFI (Wireless Fidelity Alliance) • Range of about 12 -50 metres Bluetooth & WIFI use radio waves <- Transmission media NICs ->
Transmission media for LAN • Wireless – Infrared communication • Used for wireless mouse and keyboard – Bluetooth • Range of about 10 metres – WIFI (Wireless Fidelity Alliance) • Range of about 12 -50 metres Bluetooth & WIFI use radio waves <- Transmission media NICs ->
 Exercise 2 1. Name 2 types of cable used in a network. 2. What type of cable does the school have on its LAN? 3. How can you link up the computers at home without using cables? <- Client/Server WANs ->
Exercise 2 1. Name 2 types of cable used in a network. 2. What type of cable does the school have on its LAN? 3. How can you link up the computers at home without using cables? <- Client/Server WANs ->
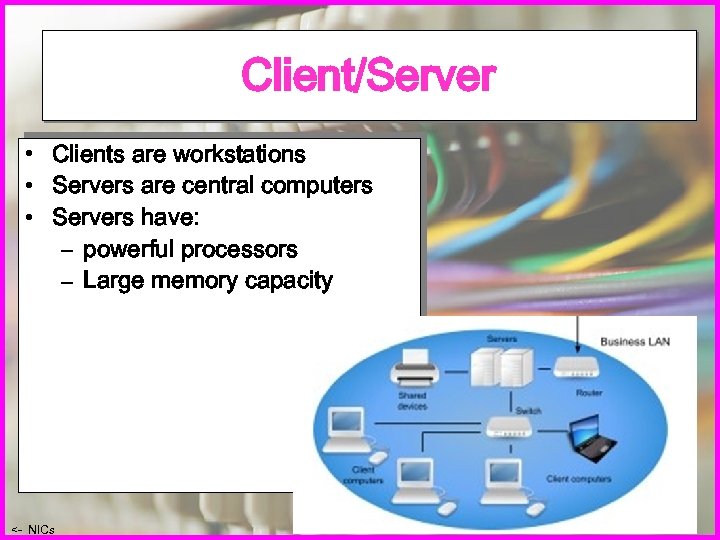 Client/Server • Clients are workstations • Servers are central computers • Servers have: – powerful processors – Large memory capacity <- NICs Ex 2 ->
Client/Server • Clients are workstations • Servers are central computers • Servers have: – powerful processors – Large memory capacity <- NICs Ex 2 ->
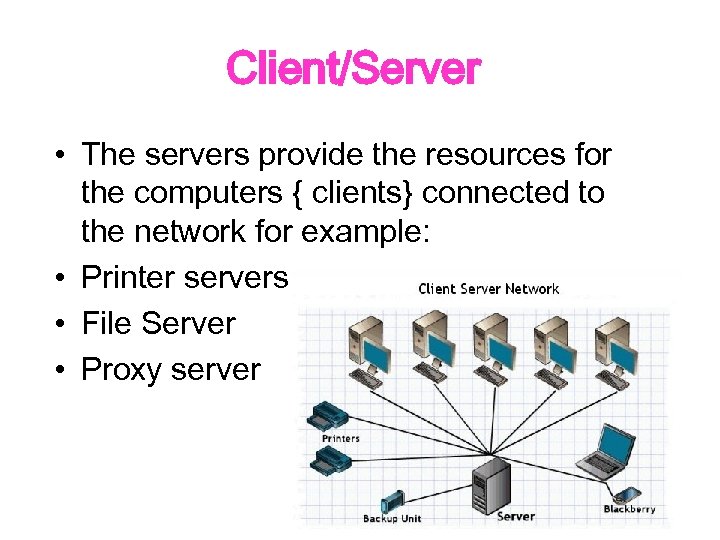 Client/Server • The servers provide the resources for the computers { clients} connected to the network for example: • Printer servers • File Server • Proxy server
Client/Server • The servers provide the resources for the computers { clients} connected to the network for example: • Printer servers • File Server • Proxy server
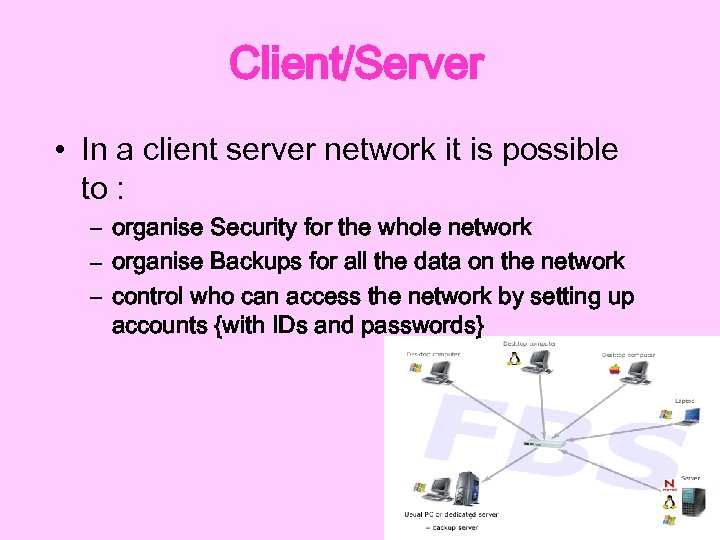 Client/Server • In a client server network it is possible to : – organise Security for the whole network – organise Backups for all the data on the network – control who can access the network by setting up accounts {with IDs and passwords}
Client/Server • In a client server network it is possible to : – organise Security for the whole network – organise Backups for all the data on the network – control who can access the network by setting up accounts {with IDs and passwords}
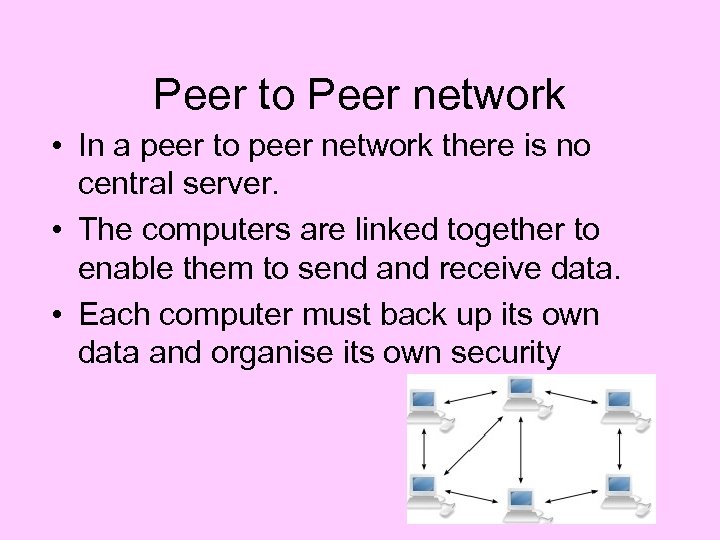 Peer to Peer network • In a peer to peer network there is no central server. • The computers are linked together to enable them to send and receive data. • Each computer must back up its own data and organise its own security
Peer to Peer network • In a peer to peer network there is no central server. • The computers are linked together to enable them to send and receive data. • Each computer must back up its own data and organise its own security
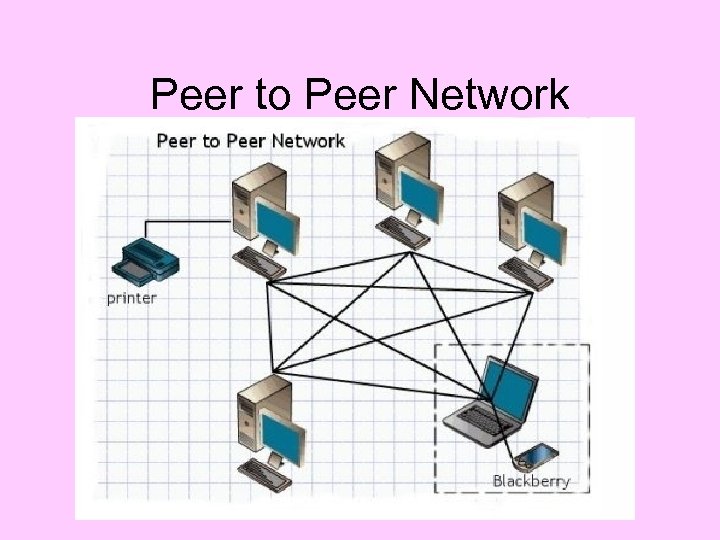 Peer to Peer Network
Peer to Peer Network
 Peer to Peer network • Since there is no centrally organised security of backup system on a Peer to Peer network: • They are only suitable for ‘trusting’ environments’ e. g. home use. • They are not suited to commercial or business use.
Peer to Peer network • Since there is no centrally organised security of backup system on a Peer to Peer network: • They are only suitable for ‘trusting’ environments’ e. g. home use. • They are not suited to commercial or business use.
 The Internet • A network of networks • Can be accessed by any internet-ready computer system. • You need: – A telecommunications connection such as a modem or broadband – A browser – A link to an Internet Service Provider <- Ex 5 Modems and Dialup ->
The Internet • A network of networks • Can be accessed by any internet-ready computer system. • You need: – A telecommunications connection such as a modem or broadband – A browser – A link to an Internet Service Provider <- Ex 5 Modems and Dialup ->
 Transmission Media for The Internet • The Internet uses Telecommunications links – It communicates information around the world using: • Microwave transmission • Satellite links • Optical Fibre • Telephone cables <- WANs Ex 3 ->
Transmission Media for The Internet • The Internet uses Telecommunications links – It communicates information around the world using: • Microwave transmission • Satellite links • Optical Fibre • Telephone cables <- WANs Ex 3 ->
 Services on the Internet • • • < Ex 6 World Wide Web Newsgroups Chat rooms Search Engines E-Commerce WWW >
Services on the Internet • • • < Ex 6 World Wide Web Newsgroups Chat rooms Search Engines E-Commerce WWW >
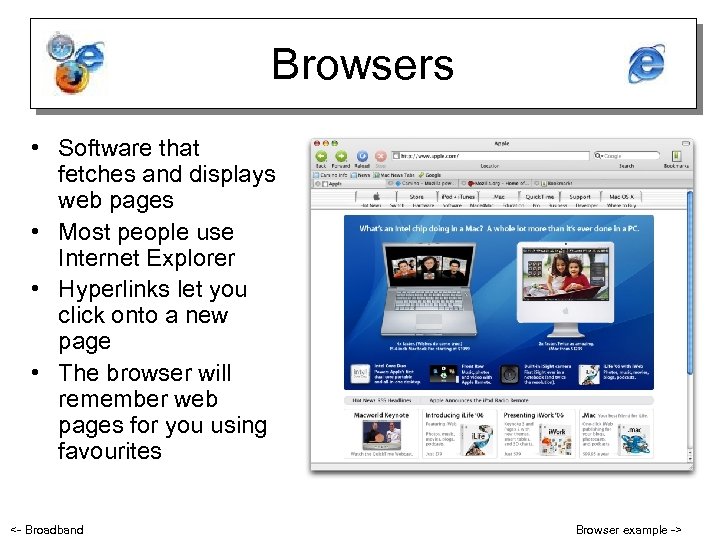 Browsers • Software that fetches and displays web pages • Most people use Internet Explorer • Hyperlinks let you click onto a new page • The browser will remember web pages for you using favourites <- Broadband Browser example ->
Browsers • Software that fetches and displays web pages • Most people use Internet Explorer • Hyperlinks let you click onto a new page • The browser will remember web pages for you using favourites <- Broadband Browser example ->
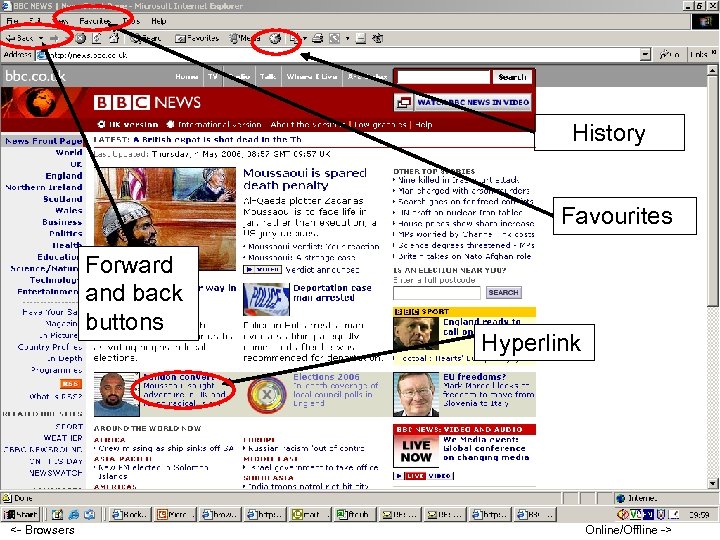 History Favourites Forward and back buttons <- Browsers Hyperlink Online/Offline ->
History Favourites Forward and back buttons <- Browsers Hyperlink Online/Offline ->
 The World Wide Web • Web pages stored in servers round the world • Web pages are multimedia documents • Linked with hyperlinks < Internet services Hyperlinks >
The World Wide Web • Web pages stored in servers round the world • Web pages are multimedia documents • Linked with hyperlinks < Internet services Hyperlinks >
 Other services on the net • Newsgroups let you discuss particular subjects • Chat rooms let you talk live to other people • Netiquette is very important when using these services < Ex 7
Other services on the net • Newsgroups let you discuss particular subjects • Chat rooms let you talk live to other people • Netiquette is very important when using these services < Ex 7
 Newsgroups < Other services Search Engines >
Newsgroups < Other services Search Engines >
 Search Engines • Simple searches – just type in a brief description You can do this on: • Google • Yahoo • Google images Any search engine that you enter your brief description into a single search box uses simple search. < Newsgroups Search example >
Search Engines • Simple searches – just type in a brief description You can do this on: • Google • Yahoo • Google images Any search engine that you enter your brief description into a single search box uses simple search. < Newsgroups Search example >
 Cloud Computing • Instead of buying and setting up a network, they have simple computing devices: • Which they use to access the internet • And use the software, backing storage and servers provided by the Cloud Computing company. • Basically, they rent the use of powerful network resources
Cloud Computing • Instead of buying and setting up a network, they have simple computing devices: • Which they use to access the internet • And use the software, backing storage and servers provided by the Cloud Computing company. • Basically, they rent the use of powerful network resources
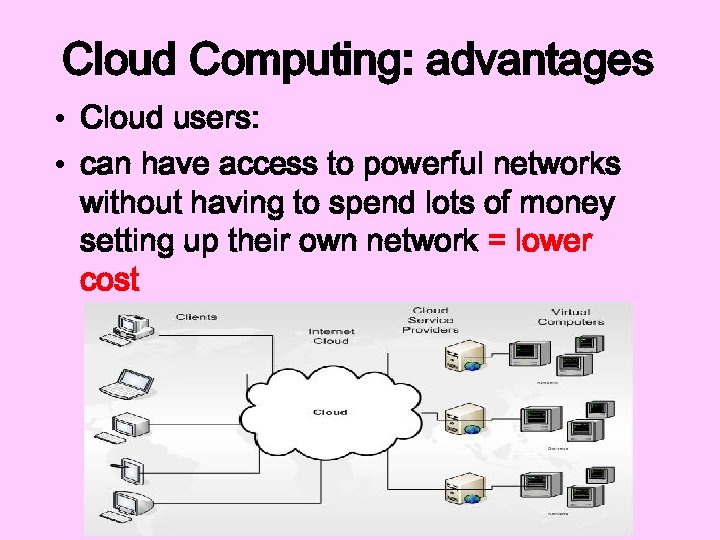 Cloud Computing: advantages • Cloud users: • can have access to powerful networks without having to spend lots of money setting up their own network = lower cost
Cloud Computing: advantages • Cloud users: • can have access to powerful networks without having to spend lots of money setting up their own network = lower cost
 Cloud Computing: advantages • Cloud users: – can update and change their software as their needs change = flexibility – have access to technical support = lower maintenance / staff costs – are billed only for the services they use and the length of time they use them == lower cost – can easily scale up or down their network resources as their needs dictate =flexibility
Cloud Computing: advantages • Cloud users: – can update and change their software as their needs change = flexibility – have access to technical support = lower maintenance / staff costs – are billed only for the services they use and the length of time they use them == lower cost – can easily scale up or down their network resources as their needs dictate =flexibility
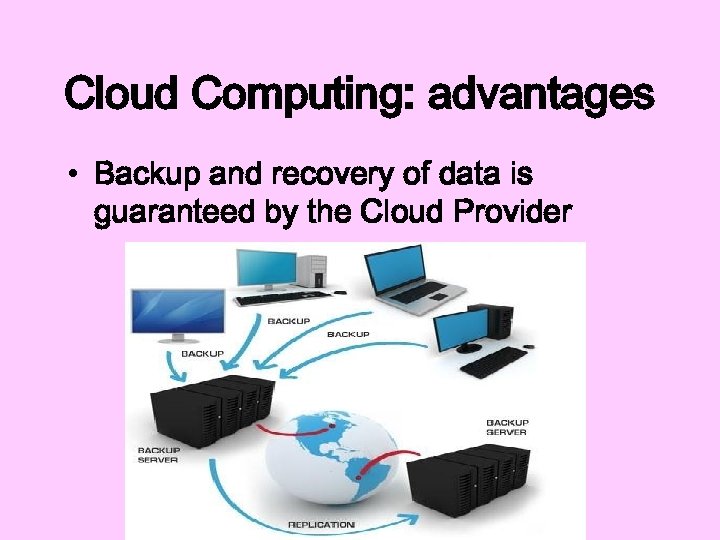 Cloud Computing: advantages • Backup and recovery of data is guaranteed by the Cloud Provider
Cloud Computing: advantages • Backup and recovery of data is guaranteed by the Cloud Provider
 Cloud Computing: disadvantages • Security: having all an organisation’s data stored in ‘ the cloud’ can be a security risk e. g. from hackers, from malware – Many organisations keep ‘critical data’ backed up locally, just in case. • It depends on a reliable speedy internet connection • Can be locked into a contract
Cloud Computing: disadvantages • Security: having all an organisation’s data stored in ‘ the cloud’ can be a security risk e. g. from hackers, from malware – Many organisations keep ‘critical data’ backed up locally, just in case. • It depends on a reliable speedy internet connection • Can be locked into a contract
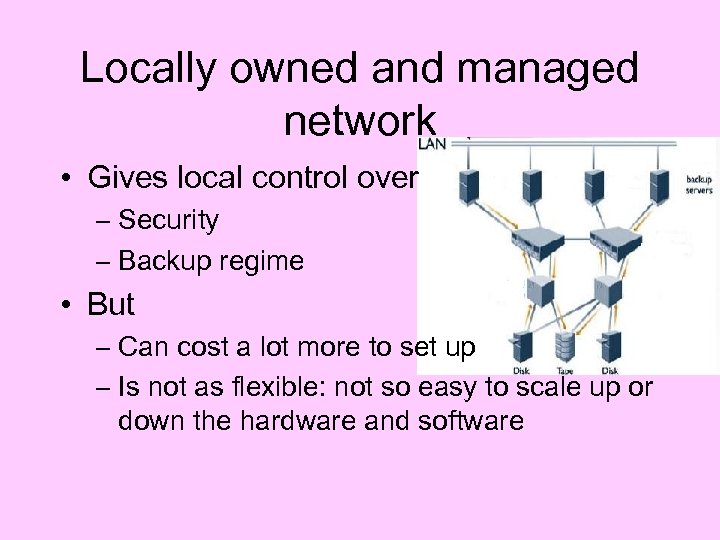 Locally owned and managed network • Gives local control over – Security – Backup regime • But – Can cost a lot more to set up – Is not as flexible: not so easy to scale up or down the hardware and software
Locally owned and managed network • Gives local control over – Security – Backup regime • But – Can cost a lot more to set up – Is not as flexible: not so easy to scale up or down the hardware and software


