b5646ec4a650940545ad81ab50d1b188.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 54
 Standard 3 Market Structures
Standard 3 Market Structures
 Market economies are characterized by competition • The effort of two or more people, acting independently, to get the business of others by offering the best deal – Example: Macintosh and Windows PC
Market economies are characterized by competition • The effort of two or more people, acting independently, to get the business of others by offering the best deal – Example: Macintosh and Windows PC
 Monopoly • Only one seller- a single business controls the supply of a product that has no close substitutes • Control of prices- monopolies act as price makers because they sell products that have no close substitutes and they face no competition • Restricted, regulated market- government regulations or other barriers to entry keep other firms out of the market
Monopoly • Only one seller- a single business controls the supply of a product that has no close substitutes • Control of prices- monopolies act as price makers because they sell products that have no close substitutes and they face no competition • Restricted, regulated market- government regulations or other barriers to entry keep other firms out of the market
 Oligopoly • Few sellers- only a few businesses dominate an entire market • Products can be – Standardized (identical) –ex. Steel, aluminum – differentiated products (different characteristics, quality, function) • More control of prices- decisions one seller makes may cause the other sellers to respond in the same way • Little freedom to enter or exit markethigh start up costs
Oligopoly • Few sellers- only a few businesses dominate an entire market • Products can be – Standardized (identical) –ex. Steel, aluminum – differentiated products (different characteristics, quality, function) • More control of prices- decisions one seller makes may cause the other sellers to respond in the same way • Little freedom to enter or exit markethigh start up costs
 Challenge Question 1. Are Microsoft and Apple monopolies or oligopolies? 2. Is Citizen’s Water, the only water company in Indy a monopoly or oligopoly?
Challenge Question 1. Are Microsoft and Apple monopolies or oligopolies? 2. Is Citizen’s Water, the only water company in Indy a monopoly or oligopoly?
 Dinner for 2 at the Cheesecake Factory $60
Dinner for 2 at the Cheesecake Factory $60
 Dinner for 2 at St. Elmo’s $120
Dinner for 2 at St. Elmo’s $120
 2 Tickets to see your favorite basketball team $100
2 Tickets to see your favorite basketball team $100
 Colts Season Tickets $1500
Colts Season Tickets $1500
 2 Tickets to go see your favorite band or musical $100
2 Tickets to go see your favorite band or musical $100
 Monopolistic Competition • Many sellers- sellers act independently in choosing what kind of product, how much and what price • Similar but differentiated products (ex. hamburger restaurants) • Limited control of prices- consumers will switch to a substitute if the price goes too high • Freedom to enter or exit market- relatively easy to start a small business, if it does not work, equipment can be sold
Monopolistic Competition • Many sellers- sellers act independently in choosing what kind of product, how much and what price • Similar but differentiated products (ex. hamburger restaurants) • Limited control of prices- consumers will switch to a substitute if the price goes too high • Freedom to enter or exit market- relatively easy to start a small business, if it does not work, equipment can be sold
 What makes these restaurants different? • Quality and characteristics of food (non-price competition)
What makes these restaurants different? • Quality and characteristics of food (non-price competition)
 Pure competition • Many buyers and sellers- a large number of buyers and sellers ensures that no one controls prices • Standardized product- all products are essentially the same • Freedom to enter and exit markets- producers can enter or exit the market with no interference • Independent buyers and sellers- buyers and sellers do not band together to influence prices • Well-informed buyers and sellers- both buyers and sellers know the market prices and other conditions
Pure competition • Many buyers and sellers- a large number of buyers and sellers ensures that no one controls prices • Standardized product- all products are essentially the same • Freedom to enter and exit markets- producers can enter or exit the market with no interference • Independent buyers and sellers- buyers and sellers do not band together to influence prices • Well-informed buyers and sellers- both buyers and sellers know the market prices and other conditions
 Challenge Question 1 and 2 1. Is pizza normally bought from companies engaged in monopolistic competition or pure competition? 2. Is wood normally bought from companies engaged in monopolistic competition or pure competition?
Challenge Question 1 and 2 1. Is pizza normally bought from companies engaged in monopolistic competition or pure competition? 2. Is wood normally bought from companies engaged in monopolistic competition or pure competition?
 Challenge Questions 3 -6 What market structure matches the example? 3. Chinese Food- #1 Chinese Buffet, China King, Side Wok Café, King Dragon, Tiger Lily 4. Lettuce 5. Lucy’s gas station, which is the only gas station within 100 miles of her town 6. Coke and Pepsi
Challenge Questions 3 -6 What market structure matches the example? 3. Chinese Food- #1 Chinese Buffet, China King, Side Wok Café, King Dragon, Tiger Lily 4. Lettuce 5. Lucy’s gas station, which is the only gas station within 100 miles of her town 6. Coke and Pepsi
 Impact of Monopolies, Regulation and Deregulation
Impact of Monopolies, Regulation and Deregulation
 Predict • Why do you think monopolies could be bad?
Predict • Why do you think monopolies could be bad?
 Why could it be considered bad to have a monopoly? • Monopolies have extensive control over price without competition- when paired with inelastic demand it could be really bad. • Inequality of wealth developsreally rich and really poor • Wealthy companies can buy out other companies and create monopolies in multiple industries
Why could it be considered bad to have a monopoly? • Monopolies have extensive control over price without competition- when paired with inelastic demand it could be really bad. • Inequality of wealth developsreally rich and really poor • Wealthy companies can buy out other companies and create monopolies in multiple industries
 Predict • How could monopolies be good?
Predict • How could monopolies be good?
 Read 7. 2 and complete notes
Read 7. 2 and complete notes
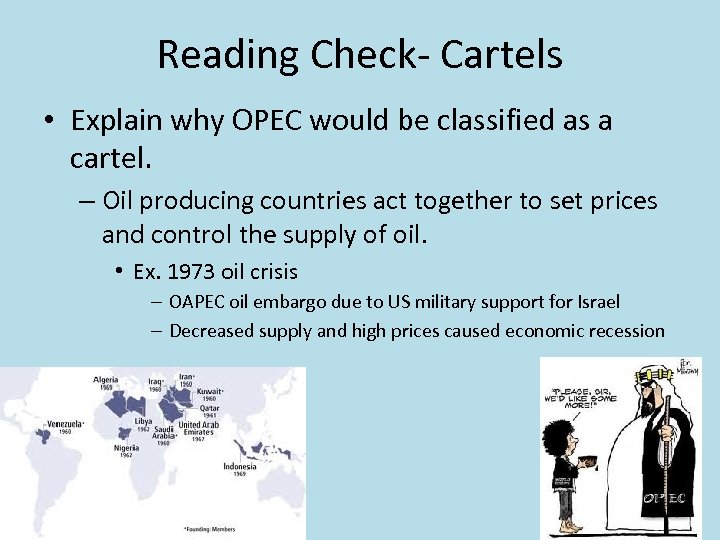 Reading Check- Cartels • Explain why OPEC would be classified as a cartel. – Oil producing countries act together to set prices and control the supply of oil. • Ex. 1973 oil crisis – OAPEC oil embargo due to US military support for Israel – Decreased supply and high prices caused economic recession
Reading Check- Cartels • Explain why OPEC would be classified as a cartel. – Oil producing countries act together to set prices and control the supply of oil. • Ex. 1973 oil crisis – OAPEC oil embargo due to US military support for Israel – Decreased supply and high prices caused economic recession
 Reading Check- Natural Monopoly • Example • Water Company • Why is there only one seller? • Costs are more efficient with one supplier • Why is the market restricted? • Economies of scale- cheaper to produce when larger because can spread fixed costs over larger population of buyers • How does it have control of prices? • Prices subject to government regulation- ensure they don’t charge too much
Reading Check- Natural Monopoly • Example • Water Company • Why is there only one seller? • Costs are more efficient with one supplier • Why is the market restricted? • Economies of scale- cheaper to produce when larger because can spread fixed costs over larger population of buyers • How does it have control of prices? • Prices subject to government regulation- ensure they don’t charge too much
 Reading Check- Government Monopoly • Example • The Postal Service • Why is there only one seller? • Can’t be provided by private terms, not attractive bc insufficient profit • Why is the market restricted? • Market entry limited by government control • How does it have control of prices? • Prices determined by government regulation
Reading Check- Government Monopoly • Example • The Postal Service • Why is there only one seller? • Can’t be provided by private terms, not attractive bc insufficient profit • Why is the market restricted? • Market entry limited by government control • How does it have control of prices? • Prices determined by government regulation
 Reading Check- Technological Monopoly • Example • Polaroid • Why is there only one seller? • Ownership of invention/technology • Why is the market restricted? • Patents cause a barrier to entry (kept Kodak out of instant camera business) • How does it have control of prices? • Charges higher prices while the monopoly lasts
Reading Check- Technological Monopoly • Example • Polaroid • Why is there only one seller? • Ownership of invention/technology • Why is the market restricted? • Patents cause a barrier to entry (kept Kodak out of instant camera business) • How does it have control of prices? • Charges higher prices while the monopoly lasts
 Reading Check- Geographic Monopoly • Example • Professional Sports/ only gas station in town • Why is there only one seller? • No competition in the local area • Why is the market restricted? • Location or size limits # of suppliers • How does it have control of prices? • Charge higher prices due to lack of competition
Reading Check- Geographic Monopoly • Example • Professional Sports/ only gas station in town • Why is there only one seller? • No competition in the local area • Why is the market restricted? • Location or size limits # of suppliers • How does it have control of prices? • Charge higher prices due to lack of competition
 Do 4 Types of Monopolies on BW
Do 4 Types of Monopolies on BW

 Bell Work 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Monopoly C Oligopoly A Monopolistic Competition E Pure Competition H Natural Monopoly G Government Monopoly B Technological Monopoly D Geographic Monopoly F A. Industry in which only a few sellers offer a similar product B. Business (that is typically not very profitable) that is run or authorized by the government that does not have any competitors C. Least competitive market structure D. Business that controls a manufacturing method or invention through a patent E. Industry in which many sellers offer a similar but differentiated product F. Business without nearby competitors G. Business that exists when the lowest production costs occur with only one producer (economies of scale) H. Industry in which many sellers sell a standardized product
Bell Work 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Monopoly C Oligopoly A Monopolistic Competition E Pure Competition H Natural Monopoly G Government Monopoly B Technological Monopoly D Geographic Monopoly F A. Industry in which only a few sellers offer a similar product B. Business (that is typically not very profitable) that is run or authorized by the government that does not have any competitors C. Least competitive market structure D. Business that controls a manufacturing method or invention through a patent E. Industry in which many sellers offer a similar but differentiated product F. Business without nearby competitors G. Business that exists when the lowest production costs occur with only one producer (economies of scale) H. Industry in which many sellers sell a standardized product
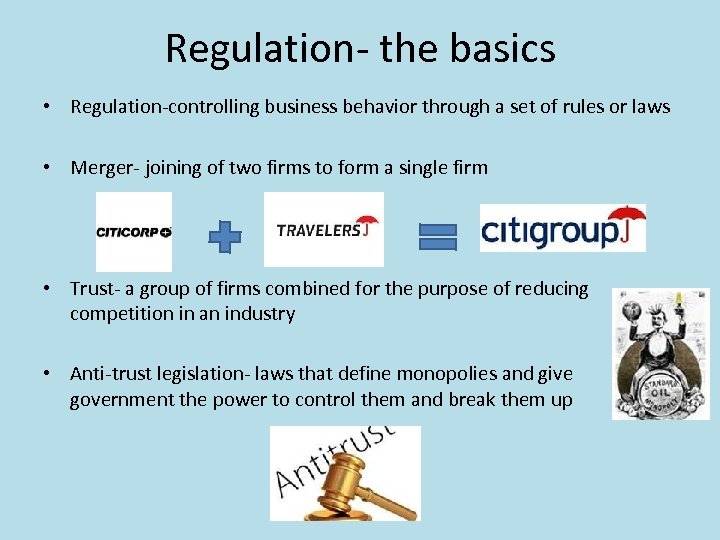 Regulation- the basics • Regulation-controlling business behavior through a set of rules or laws • Merger- joining of two firms to form a single firm • Trust- a group of firms combined for the purpose of reducing competition in an industry • Anti-trust legislation- laws that define monopolies and give government the power to control them and break them up
Regulation- the basics • Regulation-controlling business behavior through a set of rules or laws • Merger- joining of two firms to form a single firm • Trust- a group of firms combined for the purpose of reducing competition in an industry • Anti-trust legislation- laws that define monopolies and give government the power to control them and break them up
 Challenge Questions 1. Anti-Trust Legislation is a form of A) Merger B) Regulation 2. The joining of Chase and Fifth Third Bank would be a A) Merger B) Regulation
Challenge Questions 1. Anti-Trust Legislation is a form of A) Merger B) Regulation 2. The joining of Chase and Fifth Third Bank would be a A) Merger B) Regulation
 Regulation to promote competition • During the 1800’s a few large trusts dominated the oil, steel, and railroad industries. – Standard Oil was comprised of 33 companies that owned 90% of US oil • U. S. government concerned they would use their power to control prices and limit output (supply) • As a result the government passed the Sherman Anti-Trust Act as a way to regulate monopolies – Prevent business practices that would reduce competition
Regulation to promote competition • During the 1800’s a few large trusts dominated the oil, steel, and railroad industries. – Standard Oil was comprised of 33 companies that owned 90% of US oil • U. S. government concerned they would use their power to control prices and limit output (supply) • As a result the government passed the Sherman Anti-Trust Act as a way to regulate monopolies – Prevent business practices that would reduce competition
 Challenge Questions 3 & 4 3. Why was there a need for the Sherman Anti. Trust Act? In the past, a few companies completely controlled the output and prices of their products 4. What does the Sherman Anti-Trust Act do? Regulate Monopolies (prevent practices that reduce competition)
Challenge Questions 3 & 4 3. Why was there a need for the Sherman Anti. Trust Act? In the past, a few companies completely controlled the output and prices of their products 4. What does the Sherman Anti-Trust Act do? Regulate Monopolies (prevent practices that reduce competition)
 Antitrust Legislation Today • The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and Department of Justice are responsible for assessing mergers – Larger firms are more efficient; lower operating costs led to lower prices for consumers – But, the government has to prevent mergers that concentrate the market into the hands of a few firms • Ex: Attempted merger of AT&T and T-Mobile
Antitrust Legislation Today • The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and Department of Justice are responsible for assessing mergers – Larger firms are more efficient; lower operating costs led to lower prices for consumers – But, the government has to prevent mergers that concentrate the market into the hands of a few firms • Ex: Attempted merger of AT&T and T-Mobile
 Ways to level the playing field The FTC prevents these practices that limit competition… • Price fixing- occurs when businesses work together to set the price of competing products – Ex. 1990 s 5 record companies enforced a “minimum advertised price” for CDs • Market allocation- occurs when businesses negotiate to divide up the market. By staying out of each other’s territory, businesses can become geographic monopolies, enabling them to charge higher prices. • Predatory Pricing- setting prices below cost so that smaller producers cannot afford to compete in a market.
Ways to level the playing field The FTC prevents these practices that limit competition… • Price fixing- occurs when businesses work together to set the price of competing products – Ex. 1990 s 5 record companies enforced a “minimum advertised price” for CDs • Market allocation- occurs when businesses negotiate to divide up the market. By staying out of each other’s territory, businesses can become geographic monopolies, enabling them to charge higher prices. • Predatory Pricing- setting prices below cost so that smaller producers cannot afford to compete in a market.
 Consumer Protection Agencies • Government agencies that prevent unfair behavior to competitors and consumers Agency Purpose Federal Trade Commission (FTC) Enforces antitrust laws and monitors unfair business practices, including deceptive advertising Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Protects consumers from unsafe foods, drugs, or cosmetics; requires labels with product information Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Regulates communication industry (radio, tv, cable, telephone services) Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Regulates market for stocks and bonds to protect investors Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Protects human health by enforcing environmental laws regarding pollution and hazardous materials Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) Sets safety standards for thousands of types of consumer products; issues recalls on unsafe products
Consumer Protection Agencies • Government agencies that prevent unfair behavior to competitors and consumers Agency Purpose Federal Trade Commission (FTC) Enforces antitrust laws and monitors unfair business practices, including deceptive advertising Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Protects consumers from unsafe foods, drugs, or cosmetics; requires labels with product information Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Regulates communication industry (radio, tv, cable, telephone services) Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Regulates market for stocks and bonds to protect investors Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Protects human health by enforcing environmental laws regarding pollution and hazardous materials Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) Sets safety standards for thousands of types of consumer products; issues recalls on unsafe products
 Answer Consumer Protection Questions
Answer Consumer Protection Questions
 Deregulation • Deregulation involves actions taken to reduce or to remove government control of a business • Airlines were deregulated by the Airline Deregulation Act of 1978 – The government removed all control of airline routes and rates. Only safety regulations remained. Pros Cons -New carriers entered market -Increased competition led to greater efficiency -Prices dropped -More people began flying than ever before. -Quality of service decreased (ex. food) - Overcrowded airports - Financial pressure led to bankruptcies - Employee layoffs and wage cuts – Ex 2 - Financial Sector • Deregulation allowed mergers of large investment firms that contributed to the economic collapse
Deregulation • Deregulation involves actions taken to reduce or to remove government control of a business • Airlines were deregulated by the Airline Deregulation Act of 1978 – The government removed all control of airline routes and rates. Only safety regulations remained. Pros Cons -New carriers entered market -Increased competition led to greater efficiency -Prices dropped -More people began flying than ever before. -Quality of service decreased (ex. food) - Overcrowded airports - Financial pressure led to bankruptcies - Employee layoffs and wage cuts – Ex 2 - Financial Sector • Deregulation allowed mergers of large investment firms that contributed to the economic collapse
 In General REPUBLICANS • Favor Deregulation DEMOCRATS • Favor Regulation (They like less Government) (They like more government)
In General REPUBLICANS • Favor Deregulation DEMOCRATS • Favor Regulation (They like less Government) (They like more government)
 Forms of business organization • sole proprietorship • partnership • corporation
Forms of business organization • sole proprietorship • partnership • corporation
 Sole Proprietorship • A business owned and managed by a single person Advantages Disadvantages + easy to open or close - limited funds + few regulations* - limited life + freedom and control - unlimited liability* + owner keeps profits Regulation= (gov’t) controlling business behavior through a set of rules or laws Liability= legal responsibility for something, especially costs
Sole Proprietorship • A business owned and managed by a single person Advantages Disadvantages + easy to open or close - limited funds + few regulations* - limited life + freedom and control - unlimited liability* + owner keeps profits Regulation= (gov’t) controlling business behavior through a set of rules or laws Liability= legal responsibility for something, especially costs
 Partnership • A business co-owned by two or more people who agree on how responsibilities, profits and losses will be divided Advantages + easy to open and close + few regulations + access to resources + joint decision making + specialization Disadvantages - unlimited liability - potential for conflict - limited life
Partnership • A business co-owned by two or more people who agree on how responsibilities, profits and losses will be divided Advantages + easy to open and close + few regulations + access to resources + joint decision making + specialization Disadvantages - unlimited liability - potential for conflict - limited life
 Corporation • A business owned by individuals, called shareholders or stockholders Advantages + access to resources + professional managers + limited liability + unlimited life Disadvantages - start-up cost and effort - heavy regulation - double taxation - loss of control
Corporation • A business owned by individuals, called shareholders or stockholders Advantages + access to resources + professional managers + limited liability + unlimited life Disadvantages - start-up cost and effort - heavy regulation - double taxation - loss of control
 • Compare and contrast the following forms of business organization: – sole proprietorship – partnership – corporation
• Compare and contrast the following forms of business organization: – sole proprietorship – partnership – corporation
 Corporation Sole Proprietorship Partnership
Corporation Sole Proprietorship Partnership
 The three basic ways businesses finance operations • Retained earnings – Reinvesting $ they have earned • Stock issues – When people buy stocks, they company gets that $ • Borrowing – Banks lend money to business, just like they do to people
The three basic ways businesses finance operations • Retained earnings – Reinvesting $ they have earned • Stock issues – When people buy stocks, they company gets that $ • Borrowing – Banks lend money to business, just like they do to people
 Economic institutions that help members and clients accomplish their goals without trying to make a profit • Labor unions (an organization of workers who collectively seek to improve work conditions) – Ex. Rail Road workers Union • Nonprofit organizations (aim to benefit society, not to make a profit) – Ex. Red Cross, Salvation Army, Herron High School • Cooperatives (operated for the shared benefit of the owners, who are also its customers) – Ex. Credit Union
Economic institutions that help members and clients accomplish their goals without trying to make a profit • Labor unions (an organization of workers who collectively seek to improve work conditions) – Ex. Rail Road workers Union • Nonprofit organizations (aim to benefit society, not to make a profit) – Ex. Red Cross, Salvation Army, Herron High School • Cooperatives (operated for the shared benefit of the owners, who are also its customers) – Ex. Credit Union
 Nonprofit organizations • With a partner list as many nonprofit organizations as you can
Nonprofit organizations • With a partner list as many nonprofit organizations as you can
 Profit • The profit motive, a key feature of a market economy, insures that resources will be allocated efficiently, since inefficiency would result in lower profits • Serves as a reward for hard work and innovation • Entrepreneurs accept the risks of business failure in return for the possibility of making a profit
Profit • The profit motive, a key feature of a market economy, insures that resources will be allocated efficiently, since inefficiency would result in lower profits • Serves as a reward for hard work and innovation • Entrepreneurs accept the risks of business failure in return for the possibility of making a profit
 Competition • Businesses engage in both: – Price competition – Non-price competition • Celebrity Endorsements • Advertisements • Free Gifts
Competition • Businesses engage in both: – Price competition – Non-price competition • Celebrity Endorsements • Advertisements • Free Gifts
 Review • Which form of business organization is owned by individuals, called shareholders or stockholders? A. Partnership B. Sole proprietorship C. Corporation
Review • Which form of business organization is owned by individuals, called shareholders or stockholders? A. Partnership B. Sole proprietorship C. Corporation
 Review • Which of the following is NOT a basic way that businesses finance operations? A. B. C. D. Stock issues Borrowing Fundraisers Retained earnings
Review • Which of the following is NOT a basic way that businesses finance operations? A. B. C. D. Stock issues Borrowing Fundraisers Retained earnings
 Review • Which is an institution operated for the shared business of the owners, who are also its customers (such as credit unions)? A. Labor unions B. Nonprofit organizations C. Cooperatives
Review • Which is an institution operated for the shared business of the owners, who are also its customers (such as credit unions)? A. Labor unions B. Nonprofit organizations C. Cooperatives
 Review • What are some ways that businesses engage in non-price competition?
Review • What are some ways that businesses engage in non-price competition?
 Review • What is a benefit of natural monopolies? A. Lower cost than if there were several businesses in competition B. They are better for the environment C. There is no way those companies can go out of business
Review • What is a benefit of natural monopolies? A. Lower cost than if there were several businesses in competition B. They are better for the environment C. There is no way those companies can go out of business


