4047e0782c0d8ad68897b9afeef154c9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
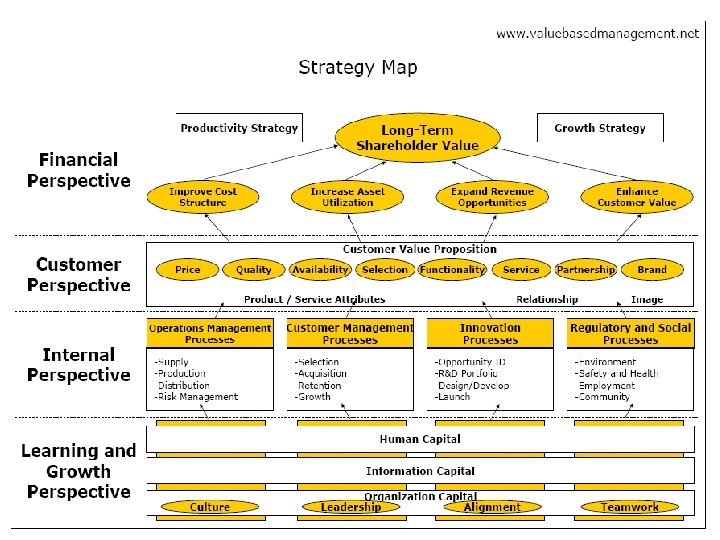
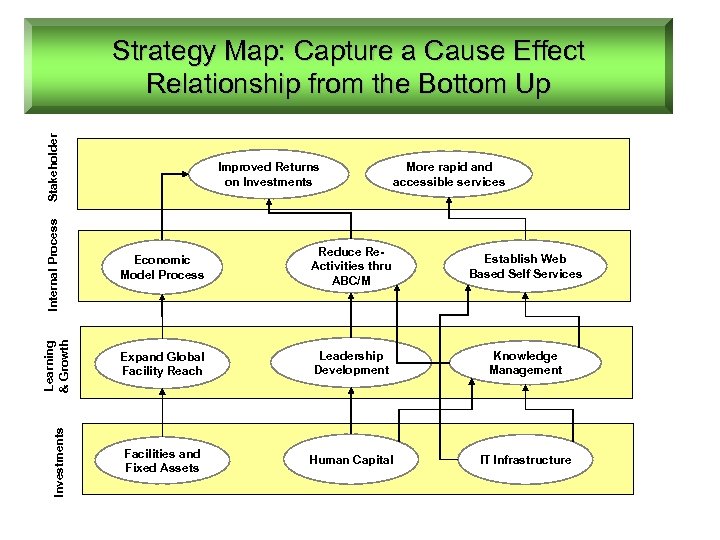 Stakeholder Strategy Map: Capture a Cause Effect Relationship from the Bottom Up Internal Process Economic Model Process Reduce Re. Activities thru ABC/M Establish Web Based Self Services Learning & Growth More rapid and accessible services Expand Global Facility Reach Leadership Development Knowledge Management Investments Improved Returns on Investments Facilities and Fixed Assets Human Capital IT Infrastructure
Stakeholder Strategy Map: Capture a Cause Effect Relationship from the Bottom Up Internal Process Economic Model Process Reduce Re. Activities thru ABC/M Establish Web Based Self Services Learning & Growth More rapid and accessible services Expand Global Facility Reach Leadership Development Knowledge Management Investments Improved Returns on Investments Facilities and Fixed Assets Human Capital IT Infrastructure
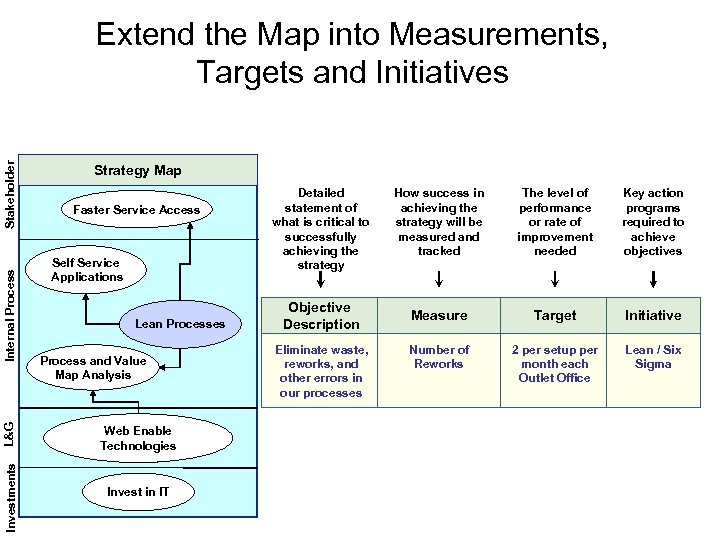 Strategy Map Faster Service Access Self Service Applications Lean Processes L&G Process and Value Map Analysis Web Enable Technologies Investments Internal Process Stakeholder Extend the Map into Measurements, Targets and Initiatives Invest in IT Detailed statement of what is critical to successfully achieving the strategy Objective Description Eliminate waste, reworks, and other errors in our processes How success in achieving the strategy will be measured and tracked The level of performance or rate of improvement needed Key action programs required to achieve objectives Measure Target Initiative Number of Reworks 2 per setup per month each Outlet Office Lean / Six Sigma
Strategy Map Faster Service Access Self Service Applications Lean Processes L&G Process and Value Map Analysis Web Enable Technologies Investments Internal Process Stakeholder Extend the Map into Measurements, Targets and Initiatives Invest in IT Detailed statement of what is critical to successfully achieving the strategy Objective Description Eliminate waste, reworks, and other errors in our processes How success in achieving the strategy will be measured and tracked The level of performance or rate of improvement needed Key action programs required to achieve objectives Measure Target Initiative Number of Reworks 2 per setup per month each Outlet Office Lean / Six Sigma
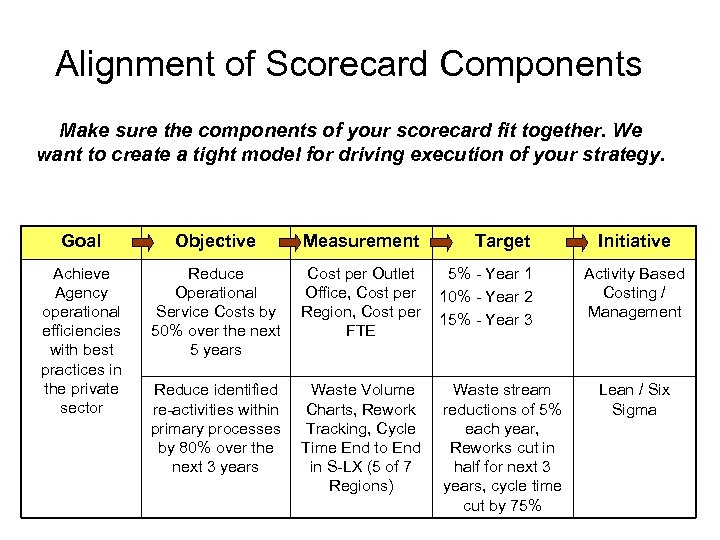 Alignment of Scorecard Components Make sure the components of your scorecard fit together. We want to create a tight model for driving execution of your strategy. Goal Objective Measurement Target Achieve Agency operational efficiencies with best practices in the private sector Reduce Operational Service Costs by 50% over the next 5 years Cost per Outlet Office, Cost per Region, Cost per FTE 5% - Year 1 10% - Year 2 15% - Year 3 Reduce identified re-activities within primary processes by 80% over the next 3 years Waste Volume Charts, Rework Tracking, Cycle Time End to End in S-LX (5 of 7 Regions) Waste stream reductions of 5% each year, Reworks cut in half for next 3 years, cycle time cut by 75% Initiative Activity Based Costing / Management Lean / Six Sigma
Alignment of Scorecard Components Make sure the components of your scorecard fit together. We want to create a tight model for driving execution of your strategy. Goal Objective Measurement Target Achieve Agency operational efficiencies with best practices in the private sector Reduce Operational Service Costs by 50% over the next 5 years Cost per Outlet Office, Cost per Region, Cost per FTE 5% - Year 1 10% - Year 2 15% - Year 3 Reduce identified re-activities within primary processes by 80% over the next 3 years Waste Volume Charts, Rework Tracking, Cycle Time End to End in S-LX (5 of 7 Regions) Waste stream reductions of 5% each year, Reworks cut in half for next 3 years, cycle time cut by 75% Initiative Activity Based Costing / Management Lean / Six Sigma
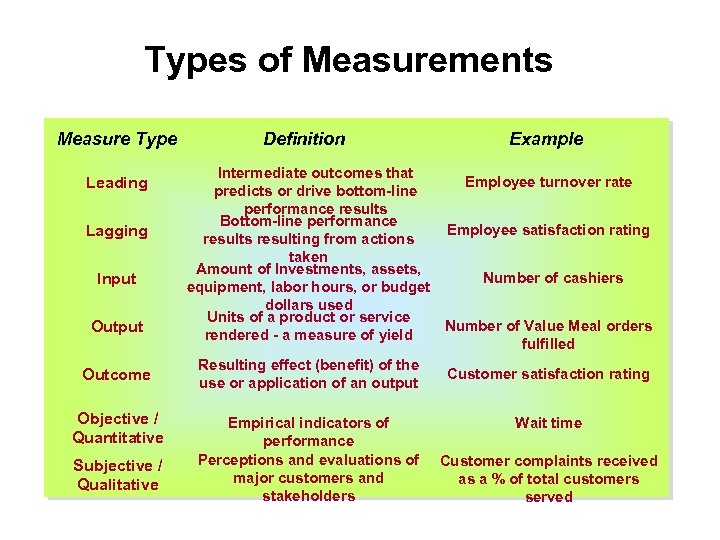 Types of Measurements Measure Type Leading Lagging Input Outcome Objective / Quantitative Subjective / Qualitative Definition Example Intermediate outcomes that Employee turnover rate predicts or drive bottom-line performance results Bottom-line performance Employee satisfaction rating results resulting from actions taken Amount of Investments, assets, Number of cashiers equipment, labor hours, or budget dollars used Units of a product or service Number of Value Meal orders rendered - a measure of yield fulfilled Resulting effect (benefit) of the Customer satisfaction rating use or application of an output Empirical indicators of performance Perceptions and evaluations of major customers and stakeholders Wait time Customer complaints received as a % of total customers served
Types of Measurements Measure Type Leading Lagging Input Outcome Objective / Quantitative Subjective / Qualitative Definition Example Intermediate outcomes that Employee turnover rate predicts or drive bottom-line performance results Bottom-line performance Employee satisfaction rating results resulting from actions taken Amount of Investments, assets, Number of cashiers equipment, labor hours, or budget dollars used Units of a product or service Number of Value Meal orders rendered - a measure of yield fulfilled Resulting effect (benefit) of the Customer satisfaction rating use or application of an output Empirical indicators of performance Perceptions and evaluations of major customers and stakeholders Wait time Customer complaints received as a % of total customers served
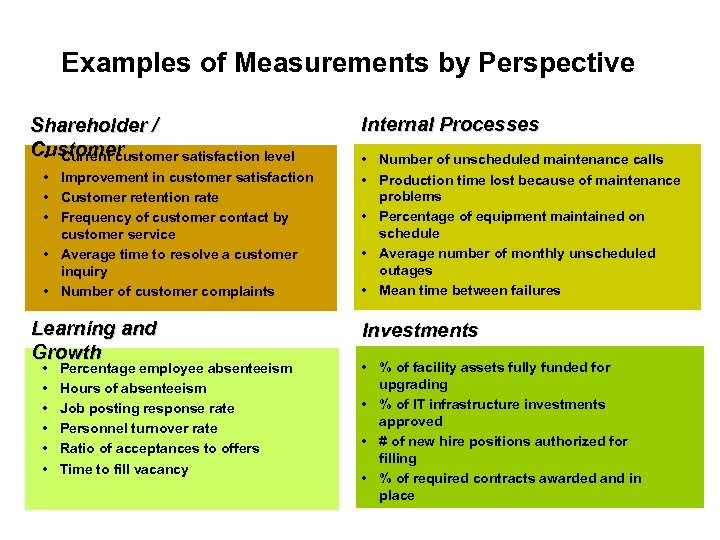 Examples of Measurements by Perspective Shareholder / Customer • Current customer satisfaction level • Improvement in customer satisfaction • Customer retention rate • Frequency of customer contact by customer service • Average time to resolve a customer inquiry • Number of customer complaints Learning and Growth • • • Percentage employee absenteeism Hours of absenteeism Job posting response rate Personnel turnover rate Ratio of acceptances to offers Time to fill vacancy Internal Processes • Number of unscheduled maintenance calls • Production time lost because of maintenance problems • Percentage of equipment maintained on schedule • Average number of monthly unscheduled outages • Mean time between failures Investments • % of facility assets fully funded for upgrading • % of IT infrastructure investments approved • # of new hire positions authorized for filling • % of required contracts awarded and in place
Examples of Measurements by Perspective Shareholder / Customer • Current customer satisfaction level • Improvement in customer satisfaction • Customer retention rate • Frequency of customer contact by customer service • Average time to resolve a customer inquiry • Number of customer complaints Learning and Growth • • • Percentage employee absenteeism Hours of absenteeism Job posting response rate Personnel turnover rate Ratio of acceptances to offers Time to fill vacancy Internal Processes • Number of unscheduled maintenance calls • Production time lost because of maintenance problems • Percentage of equipment maintained on schedule • Average number of monthly unscheduled outages • Mean time between failures Investments • % of facility assets fully funded for upgrading • % of IT infrastructure investments approved • # of new hire positions authorized for filling • % of required contracts awarded and in place
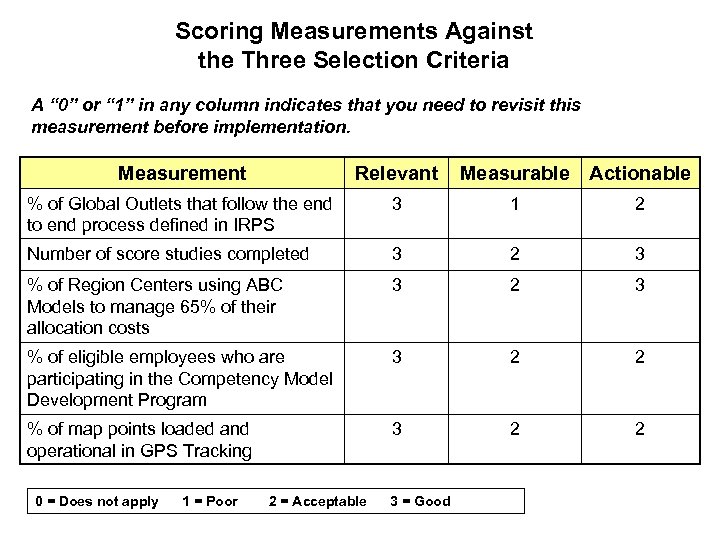 Scoring Measurements Against the Three Selection Criteria A “ 0” or “ 1” in any column indicates that you need to revisit this measurement before implementation. Measurement Relevant % of Global Outlets that follow the end to end process defined in IRPS 3 1 2 Number of score studies completed 3 2 3 % of Region Centers using ABC Models to manage 65% of their allocation costs 3 2 3 % of eligible employees who are participating in the Competency Model Development Program 3 2 2 % of map points loaded and operational in GPS Tracking 3 2 2 0 = Does not apply 1 = Poor 2 = Acceptable 3 = Good Measurable Actionable
Scoring Measurements Against the Three Selection Criteria A “ 0” or “ 1” in any column indicates that you need to revisit this measurement before implementation. Measurement Relevant % of Global Outlets that follow the end to end process defined in IRPS 3 1 2 Number of score studies completed 3 2 3 % of Region Centers using ABC Models to manage 65% of their allocation costs 3 2 3 % of eligible employees who are participating in the Competency Model Development Program 3 2 2 % of map points loaded and operational in GPS Tracking 3 2 2 0 = Does not apply 1 = Poor 2 = Acceptable 3 = Good Measurable Actionable
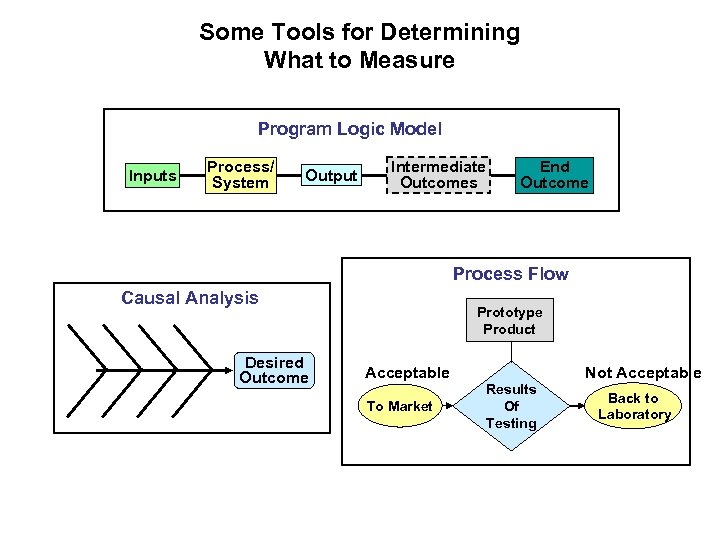 Some Tools for Determining What to Measure Program Logic Model Inputs Process/ System Output Intermediate Outcomes End Outcome Process Flow Causal Analysis Desired Outcome Prototype Product Acceptable To Market Not Acceptable Results Of Testing Back to Laboratory
Some Tools for Determining What to Measure Program Logic Model Inputs Process/ System Output Intermediate Outcomes End Outcome Process Flow Causal Analysis Desired Outcome Prototype Product Acceptable To Market Not Acceptable Results Of Testing Back to Laboratory
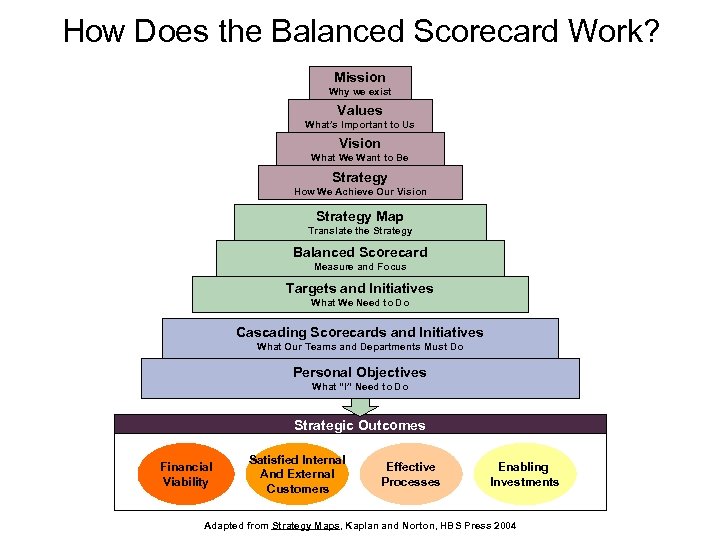 How Does the Balanced Scorecard Work? Mission Why we exist Values What’s Important to Us Vision What We Want to Be Strategy How We Achieve Our Vision Strategy Map Translate the Strategy Balanced Scorecard Measure and Focus Targets and Initiatives What We Need to Do Cascading Scorecards and Initiatives What Our Teams and Departments Must Do Personal Objectives What “I” Need to Do Strategic Outcomes Financial Viability Satisfied Internal And External Customers Effective Processes Enabling Investments Adapted from Strategy Maps, Kaplan and Norton, HBS Press 2004
How Does the Balanced Scorecard Work? Mission Why we exist Values What’s Important to Us Vision What We Want to Be Strategy How We Achieve Our Vision Strategy Map Translate the Strategy Balanced Scorecard Measure and Focus Targets and Initiatives What We Need to Do Cascading Scorecards and Initiatives What Our Teams and Departments Must Do Personal Objectives What “I” Need to Do Strategic Outcomes Financial Viability Satisfied Internal And External Customers Effective Processes Enabling Investments Adapted from Strategy Maps, Kaplan and Norton, HBS Press 2004
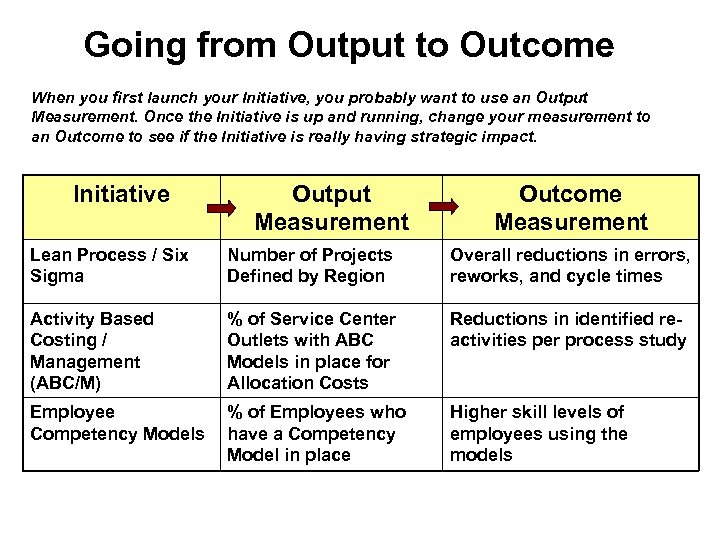 Going from Output to Outcome When you first launch your Initiative, you probably want to use an Output Measurement. Once the Initiative is up and running, change your measurement to an Outcome to see if the Initiative is really having strategic impact. Initiative Output Measurement Outcome Measurement Lean Process / Six Sigma Number of Projects Defined by Region Overall reductions in errors, reworks, and cycle times Activity Based Costing / Management (ABC/M) % of Service Center Outlets with ABC Models in place for Allocation Costs Reductions in identified reactivities per process study Employee Competency Models % of Employees who have a Competency Model in place Higher skill levels of employees using the models
Going from Output to Outcome When you first launch your Initiative, you probably want to use an Output Measurement. Once the Initiative is up and running, change your measurement to an Outcome to see if the Initiative is really having strategic impact. Initiative Output Measurement Outcome Measurement Lean Process / Six Sigma Number of Projects Defined by Region Overall reductions in errors, reworks, and cycle times Activity Based Costing / Management (ABC/M) % of Service Center Outlets with ABC Models in place for Allocation Costs Reductions in identified reactivities per process study Employee Competency Models % of Employees who have a Competency Model in place Higher skill levels of employees using the models
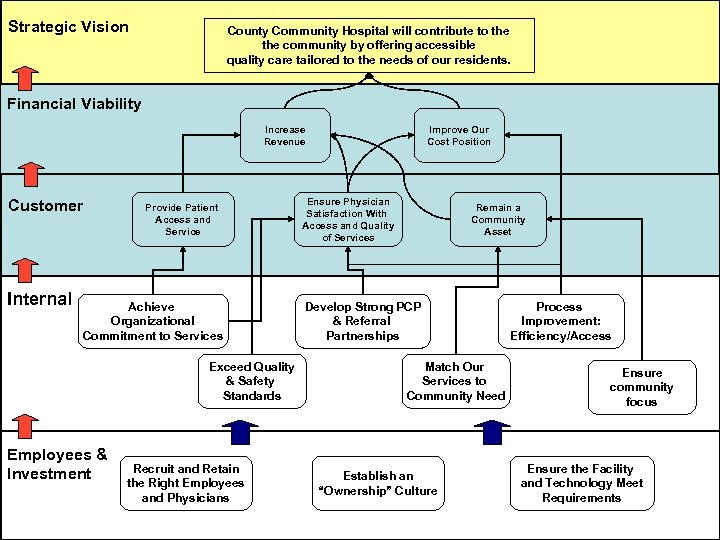 Strategic Vision County Community Hospital will contribute to the community by offering accessible quality care tailored to the needs of our residents. Financial Viability Increase Revenue Customer Internal Provide Patient Access and Service Achieve Organizational Commitment to Services Exceed Quality & Safety Standards Employees & Investment Recruit and Retain the Right Employees and Physicians Improve Our Cost Position Ensure Physician Satisfaction With Access and Quality of Services Remain a Community Asset Develop Strong PCP & Referral Partnerships Match Our Services to Community Need Establish an “Ownership” Culture Process Improvement: Efficiency/Access Ensure community focus Ensure the Facility and Technology Meet Requirements
Strategic Vision County Community Hospital will contribute to the community by offering accessible quality care tailored to the needs of our residents. Financial Viability Increase Revenue Customer Internal Provide Patient Access and Service Achieve Organizational Commitment to Services Exceed Quality & Safety Standards Employees & Investment Recruit and Retain the Right Employees and Physicians Improve Our Cost Position Ensure Physician Satisfaction With Access and Quality of Services Remain a Community Asset Develop Strong PCP & Referral Partnerships Match Our Services to Community Need Establish an “Ownership” Culture Process Improvement: Efficiency/Access Ensure community focus Ensure the Facility and Technology Meet Requirements
 Making the connection to the Baldrige Criteria Malcolm Baldrige Balanced Scorecard Leadership Learning & Growth Perspective Human Resource Capital Learning & Growth Perspective Business Results Measurements and Targets Process Management Internal Process Perspective Strategic Planning Strategy Map Customer Focus Stakeholder / Customer Perspective
Making the connection to the Baldrige Criteria Malcolm Baldrige Balanced Scorecard Leadership Learning & Growth Perspective Human Resource Capital Learning & Growth Perspective Business Results Measurements and Targets Process Management Internal Process Perspective Strategic Planning Strategy Map Customer Focus Stakeholder / Customer Perspective
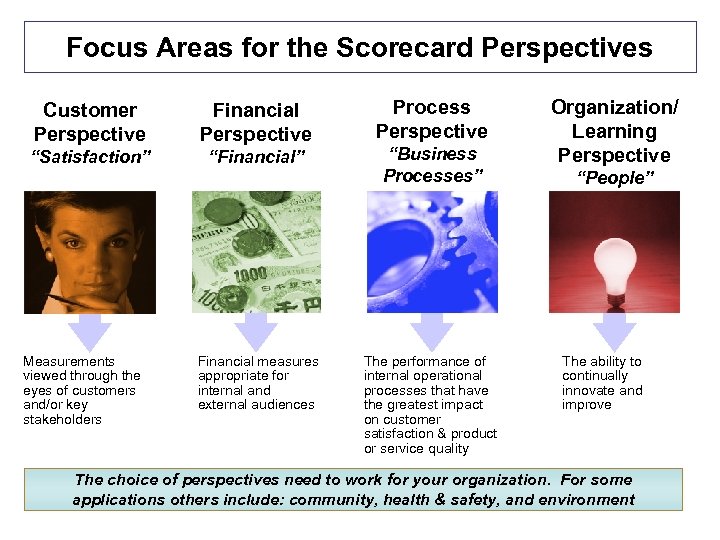 Focus Areas for the Scorecard Perspectives Customer Perspective Financial Perspective “Satisfaction” “Financial” Measurements viewed through the eyes of customers and/or key stakeholders Financial measures appropriate for internal and external audiences Process Perspective “Business Processes” The performance of internal operational processes that have the greatest impact on customer satisfaction & product or service quality Organization/ Learning Perspective “People” The ability to continually innovate and improve The choice of perspectives need to work for your organization. For some applications others include: community, health & safety, and environment
Focus Areas for the Scorecard Perspectives Customer Perspective Financial Perspective “Satisfaction” “Financial” Measurements viewed through the eyes of customers and/or key stakeholders Financial measures appropriate for internal and external audiences Process Perspective “Business Processes” The performance of internal operational processes that have the greatest impact on customer satisfaction & product or service quality Organization/ Learning Perspective “People” The ability to continually innovate and improve The choice of perspectives need to work for your organization. For some applications others include: community, health & safety, and environment
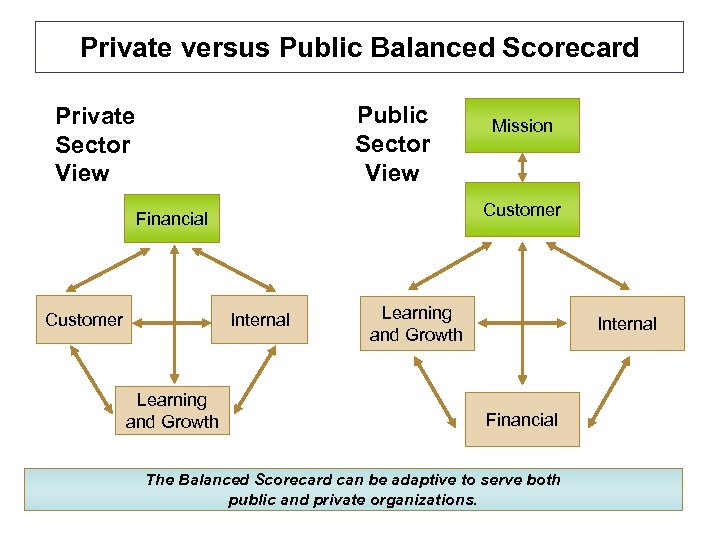 Private versus Public Balanced Scorecard Public Sector View Private Sector View Customer Financial Customer Internal Learning and Growth Mission Learning and Growth Internal Financial The Balanced Scorecard can be adaptive to serve both public and private organizations.
Private versus Public Balanced Scorecard Public Sector View Private Sector View Customer Financial Customer Internal Learning and Growth Mission Learning and Growth Internal Financial The Balanced Scorecard can be adaptive to serve both public and private organizations.
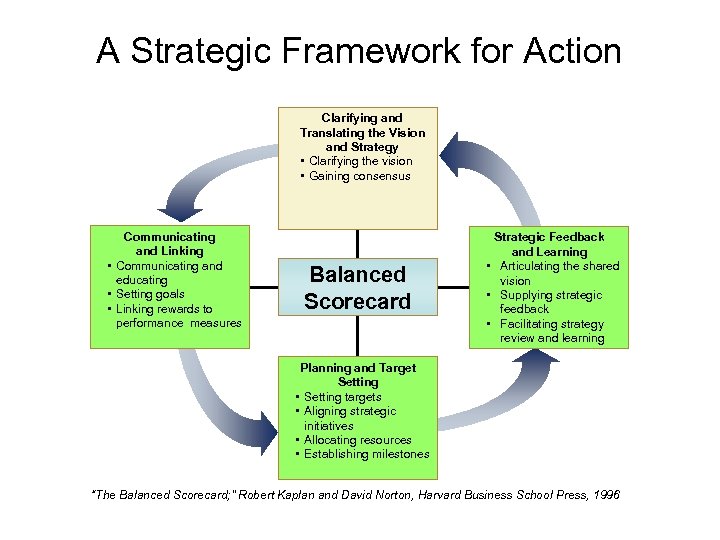 A Strategic Framework for Action Clarifying and Translating the Vision and Strategy • Clarifying the vision • Gaining consensus Communicating and Linking • Communicating and educating • Setting goals • Linking rewards to performance measures Balanced Scorecard Strategic Feedback and Learning • Articulating the shared vision • Supplying strategic feedback • Facilitating strategy review and learning Planning and Target Setting • Setting targets • Aligning strategic initiatives • Allocating resources • Establishing milestones “The Balanced Scorecard; ” Robert Kaplan and David Norton, Harvard Business School Press, 1996
A Strategic Framework for Action Clarifying and Translating the Vision and Strategy • Clarifying the vision • Gaining consensus Communicating and Linking • Communicating and educating • Setting goals • Linking rewards to performance measures Balanced Scorecard Strategic Feedback and Learning • Articulating the shared vision • Supplying strategic feedback • Facilitating strategy review and learning Planning and Target Setting • Setting targets • Aligning strategic initiatives • Allocating resources • Establishing milestones “The Balanced Scorecard; ” Robert Kaplan and David Norton, Harvard Business School Press, 1996
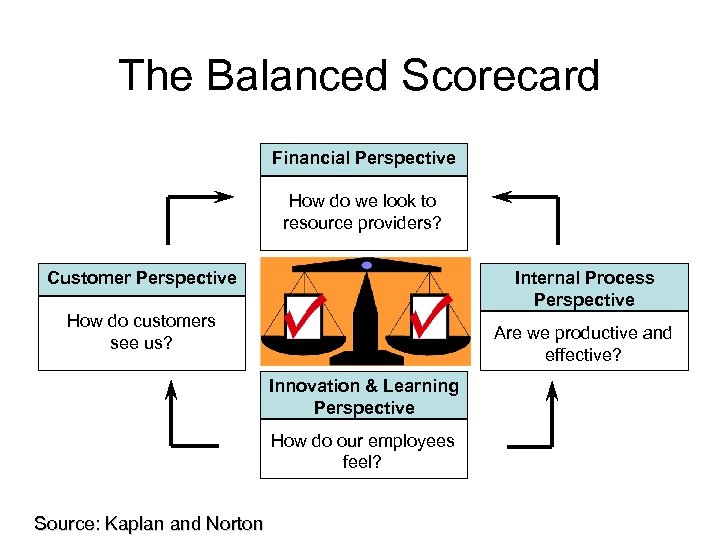 The Balanced Scorecard Financial Perspective How do we look to resource providers? Customer Perspective Internal Process Perspective How do customers see us? Are we productive and effective? Innovation & Learning Perspective How do our employees feel? Source: Kaplan and Norton
The Balanced Scorecard Financial Perspective How do we look to resource providers? Customer Perspective Internal Process Perspective How do customers see us? Are we productive and effective? Innovation & Learning Perspective How do our employees feel? Source: Kaplan and Norton
 EVA Reporting at Best Buy The EVA model: Revenues (Oper Exp) +/- Adjustments =NOPBT (Tax) =NOPAT (Cap Charge) =EVA
EVA Reporting at Best Buy The EVA model: Revenues (Oper Exp) +/- Adjustments =NOPBT (Tax) =NOPAT (Cap Charge) =EVA
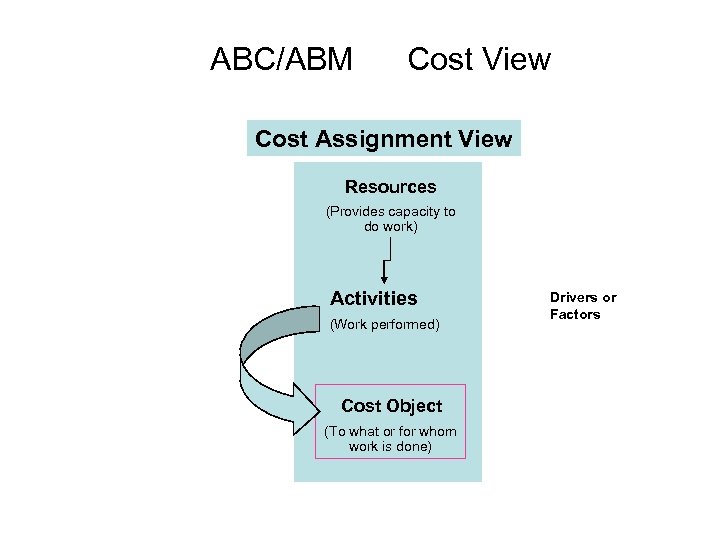 ABC/ABM Cost View Cost Assignment View Resources (Provides capacity to do work) Activities (Work performed) Cost Object (To what or for whom work is done) Drivers or Factors
ABC/ABM Cost View Cost Assignment View Resources (Provides capacity to do work) Activities (Work performed) Cost Object (To what or for whom work is done) Drivers or Factors
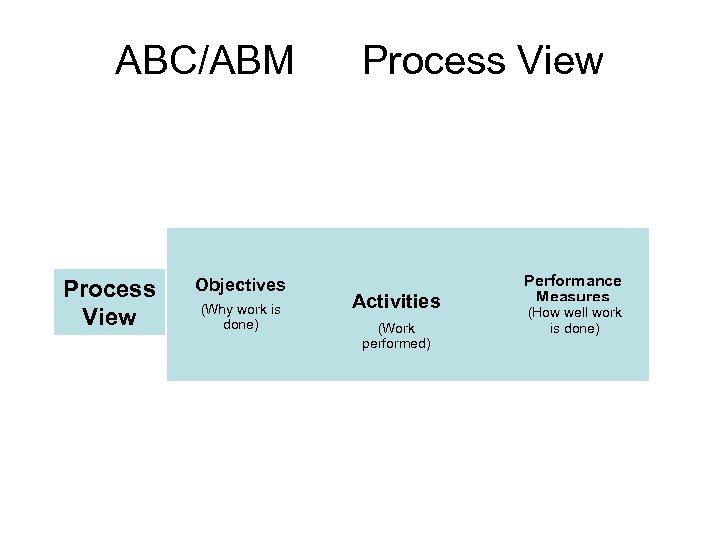 ABC/ABM Process View Objectives (Why work is done) Process View Activities (Work performed) Performance Measures (How well work is done)
ABC/ABM Process View Objectives (Why work is done) Process View Activities (Work performed) Performance Measures (How well work is done)
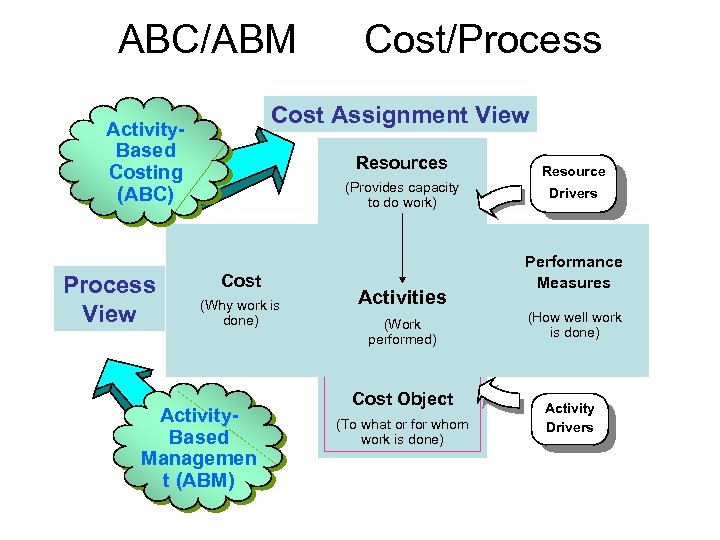 ABC/ABM Cost Assignment View Activity. Based Costing (ABC) Process View Cost/Process Resources (Provides capacity to do work) Cost Drivers (Why work is done) Activity. Based Managemen t (ABM) Activities (Work performed) Cost Object (To what or for whom work is done) Resource Drivers Performance Measures (How well work is done) Activity Drivers
ABC/ABM Cost Assignment View Activity. Based Costing (ABC) Process View Cost/Process Resources (Provides capacity to do work) Cost Drivers (Why work is done) Activity. Based Managemen t (ABM) Activities (Work performed) Cost Object (To what or for whom work is done) Resource Drivers Performance Measures (How well work is done) Activity Drivers
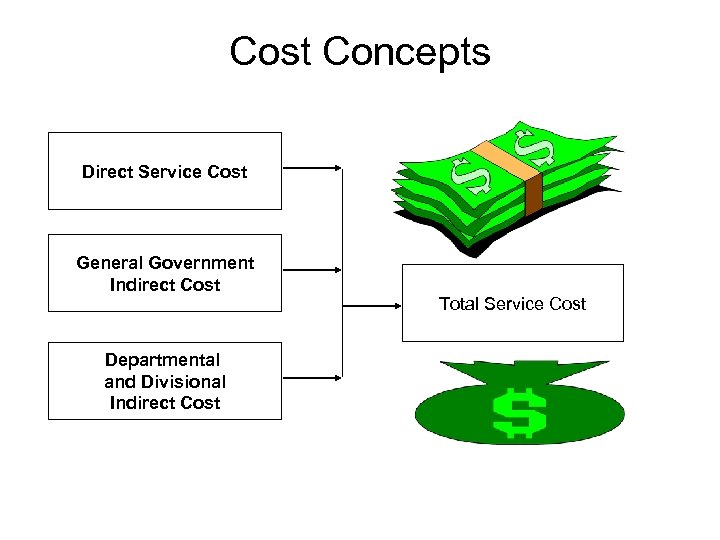 Cost Concepts Direct Service Cost General Government Indirect Cost Departmental and Divisional Indirect Cost Total Service Cost
Cost Concepts Direct Service Cost General Government Indirect Cost Departmental and Divisional Indirect Cost Total Service Cost
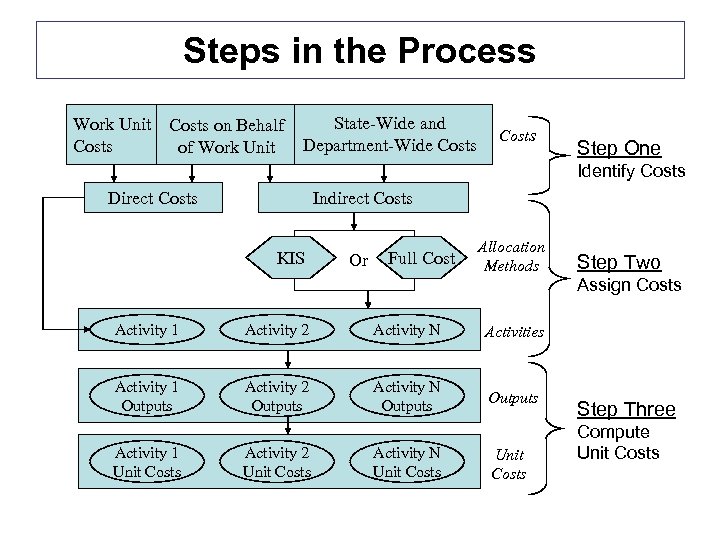 Steps in the Process Work Unit Costs on Behalf of Work Unit State-Wide and Department-Wide Costs Step One Identify Costs Direct Costs Indirect Costs KIS Or Full Cost Allocation Methods Step Two Assign Costs Activity 1 Activity 2 Activity N Activities Activity 1 Outputs Activity 2 Outputs Activity N Outputs Activity 1 Unit Costs Activity 2 Unit Costs Activity N Unit Costs Step Three Compute Unit Costs
Steps in the Process Work Unit Costs on Behalf of Work Unit State-Wide and Department-Wide Costs Step One Identify Costs Direct Costs Indirect Costs KIS Or Full Cost Allocation Methods Step Two Assign Costs Activity 1 Activity 2 Activity N Activities Activity 1 Outputs Activity 2 Outputs Activity N Outputs Activity 1 Unit Costs Activity 2 Unit Costs Activity N Unit Costs Step Three Compute Unit Costs
 We cannot solve the problems we have by the same methods by which we have created them. Albert Einstein
We cannot solve the problems we have by the same methods by which we have created them. Albert Einstein
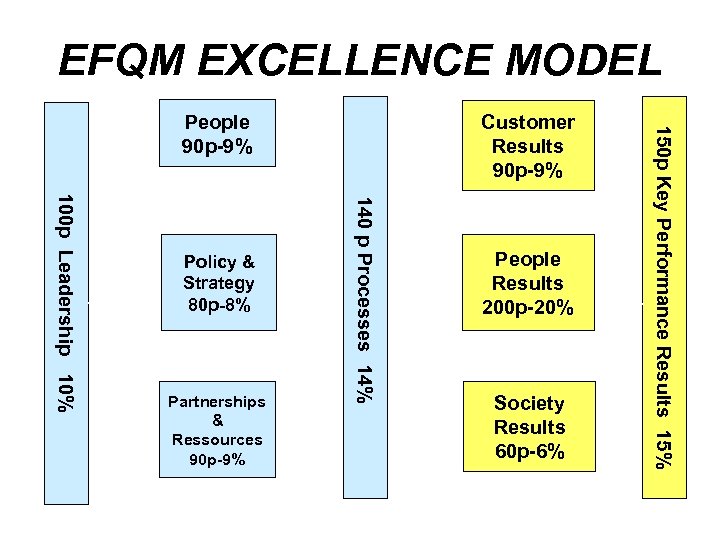 EFQM EXCELLENCE MODEL Partnerships & Ressources 90 p-9% 140 p Processes 14% 100 p Leadership 10% Policy & Strategy 80 p-8% Customer Results 90 p-9% People Results 200 p-20% Society Results 60 p-6% 150 p Key Performance Results 15% People 90 p-9%
EFQM EXCELLENCE MODEL Partnerships & Ressources 90 p-9% 140 p Processes 14% 100 p Leadership 10% Policy & Strategy 80 p-8% Customer Results 90 p-9% People Results 200 p-20% Society Results 60 p-6% 150 p Key Performance Results 15% People 90 p-9%
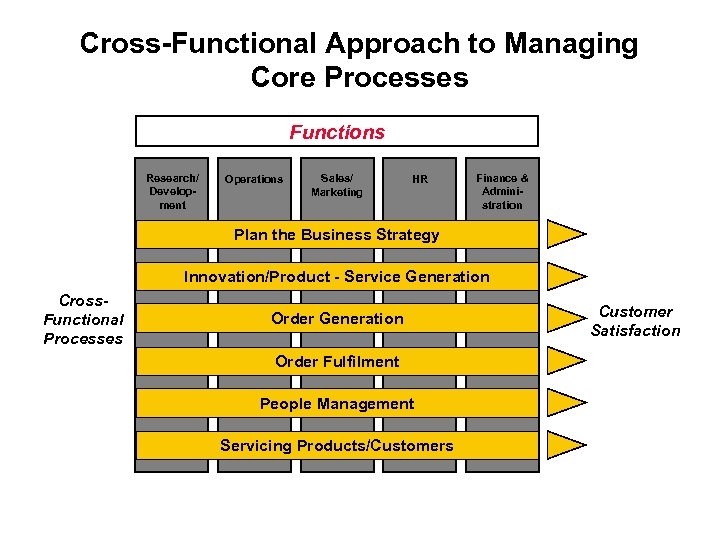 Cross-Functional Approach to Managing Core Processes Functions Research/ Development Operations Sales/ Marketing HR Finance & Administration Plan the Business Strategy Innovation/Product - Service Generation Cross. Functional Processes Order Generation Order Fulfilment People Management Servicing Products/Customers Customer Satisfaction
Cross-Functional Approach to Managing Core Processes Functions Research/ Development Operations Sales/ Marketing HR Finance & Administration Plan the Business Strategy Innovation/Product - Service Generation Cross. Functional Processes Order Generation Order Fulfilment People Management Servicing Products/Customers Customer Satisfaction
 E Q Award
E Q Award


