333a8b61a13ad67aded37242c8115300.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 90

STAFFING FOR EFFICIENCY IN RADIOTHERAPY: ROLES & RESPONSIBILITIES Dr. M. RAVIKUMAR Professor & Head Department of Radiation Physics Kidwai Memorial Institute of Oncology Bangalore 560029

OUTLINE • • • Radiation professional requirement Roles & Responsibilities E- Lora Necessary equipment Steps to be followed for various facility establishment Conclusion

Therapeutic Applications of Ionizing Radiation Tele Therapy - High energy beams from dedicated equipment (Gamma rays, X-rays, Electrons, Protons, Heavy Ions) Brachytherapy - Encapsulated sources – Manual or remotely operated Gamma/X-rays and Beta emitting

Atomic Energy Act, RPR & AERB The mission of AERB is to ensure the use of ionizing radiation and nuclear energy in India does not cause undue risk to the health of people and environment

Radiation Protection Rules (2004)

Radiation Protection Rules (2004)

Radiation Protection Rules (2004)
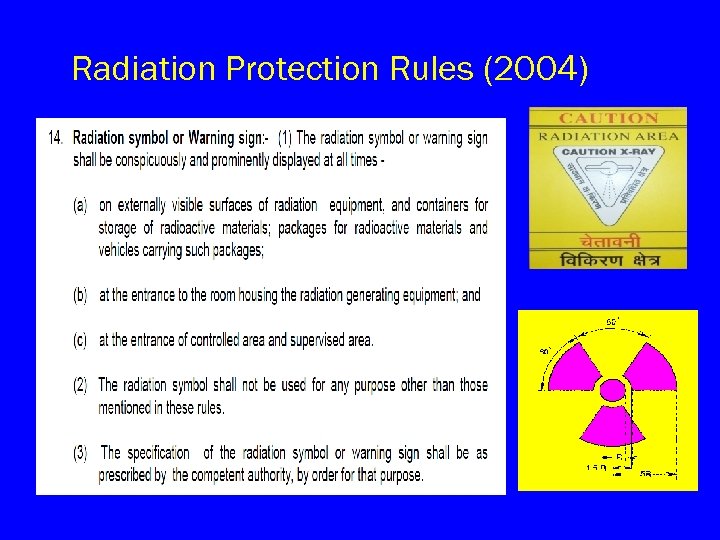
Radiation Protection Rules (2004)

Manpower Required for RT March 2011 www. aerb. gov. in 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) RO MP RSO (Med) Dosimetrist RTT RT Service Engineer

Objectives of Staffs Requirement Effective use of radiation technology Protection from harmful effects of ionizing radiation without unduly limiting the use of techniques that may cause radiation exposure: - People (workers, public, patients) - Environment

Impact of Trained Professionals A high standard supervision; of clinical service and Improvement in work practices and working environment; Decrease in individual and average personnel radiation doses in the institution; Increase in confidence level in handling the emergencies; and Downward trend in the number of the incidents/emergencies in the relevant practices.







Minimum Personnel Requirement Category Staffing Chief Radiation Oncologist 1 per centre Radiation Oncologist 1 additional for each 400 patients treated annually. Not more than 40 patients under treatment by a single physician per day Medical Physicist 1 per centre for up to 500 patients treated annually, additional in ratio of 1 per 500 patients treated annually. Radiological Safety Officer 1 per centre

Minimum Personnel Requirement Chief RTT 1 per centre RTTs 2 per teletherapy unit up to 40 patients treated daily per unit, 4 per teletherapy unit up to 80 patients treated daily. Technologist (Simulator) 2 for every 500 patients simulated yearly Technologist (Brachy) As needed Technologist (Mould room) 1 per 600 patients treated annually Dosimetrist/Phys Assts 1 per 500 patients treated annually. Auxiliary Staffs: May be employed as per requirement Nurse, Social Worker, Dietician, Physiotherapist, Occupational Therapist, Psychologists, Maintenance Engineer

Blue Book 20

Roles & Responsibilities of RT Staffs Radiation Oncologist

Medical Physicist

Medical Physicist

Radiation Therapy Technologist

Radiation Therapy Technologist

RSO

RSO conti nued

Responsibilities of the employer (1) Every employer shall Ensure that provisions of these rules are implemented by the licensee, Radiological Safety Officer and other worker(s). Provide facilities and equipment to the Radiological Safety Officer , licensee and other worker(s) to carry out their functions effectively in conformity with regulatory constraint. Prior to employment of a worker, procure from his former employer, where applicable, the dose records and health surveillance reports

Responsibilities of the employer Upon termination of service of worker provide to his new employer on request his dose records and health surveillance reports. Furnish to each worker dose records and health surveillance reports of the worker in his employment annually, as and when requested by the worker and at the termination of his service. Inform the competent authority if the licensee or the Radiological Safety Officer or any worker leaves the employment. Arrange for health surveillance of workers as specified under rule 25.

Responsibilities of the employer The employer shall be the custodian of radiation sources in his possession and shall ensure physical security of the sources at all times. The employer shall inform the competent authority, within twenty four hours, of any accident involving a source or loss of source of which he is the custodian

Responsibilities of the licensee The responsibility for implementing the terms and conditions of the licence shall rest with the licensee The licensee shall comply with the surveillance procedures, safety codes and safety standards specified by the competent authority. Every licensee shall establish written procedures and plans for controlling, monitoring and assessment of exposure for ensuring adequate protection of workers, members of the public and the environment and patients, wherever applicable.

Responsibilities of the licensee The licensee shall comply with the provision of rules for safe disposal of radioactive waste issued under the Act. Without prejudice to the generality of the above, the licensee shall not allow workers, other than those specified in subclause (ii) of clause of sub-rule (2) of rule 7 and already dealt with under rule 17. maintain records of workers as specified under rule 24. arrange for preventive and remedial maintenance of radiation protection equipment, and monitoring instruments

Responsibilities of the licensee in consultation with the Radiological Safety Officer, investigate any case of exposure in excess of regulatory constraints received by individual workers and maintain records of such investigations. inform competent authority promptly of the occurrence, investigation and follow-up actions in cases of exposure in excess of regulatory constraints, including steps to prevent recurrence of such incidents. carry out physical verification of radioactive material periodically and maintain inventory.

Responsibilities of the licensee inform appropriate law enforcement agency in the locality of any loss of source. inform the employer and the competent authority of any loss of source investigate and inform the competent authority of any accident involving source and maintain record of investigations verify the performance of radiation monitoring systems, safety interlocks, protective devices and any other safety systems in the radiation installation

Responsibilities of the licensee in consultation with Radiological Safety Officer, prepare emergency plans, for responding to accident to mitigate their consequences and ensure emergency preparedness measures. conduct or arrange for quality assurance tests of structures, systems, components and sources and related equipment. advise the employer about the modifications in working condition of a pregnant worker.

Responsibilities of the licensee inform the competent authority if the Radiological Safety Officer or a worker leaves the employment; and inform the competent authority when he leaves the employment • The licensee shall ensure that the workers are familiarised with contents of the relevant surveillance procedures, safety standards, safety codes, safety guides and safety manuals issued by the competent authority and emergency response plans.

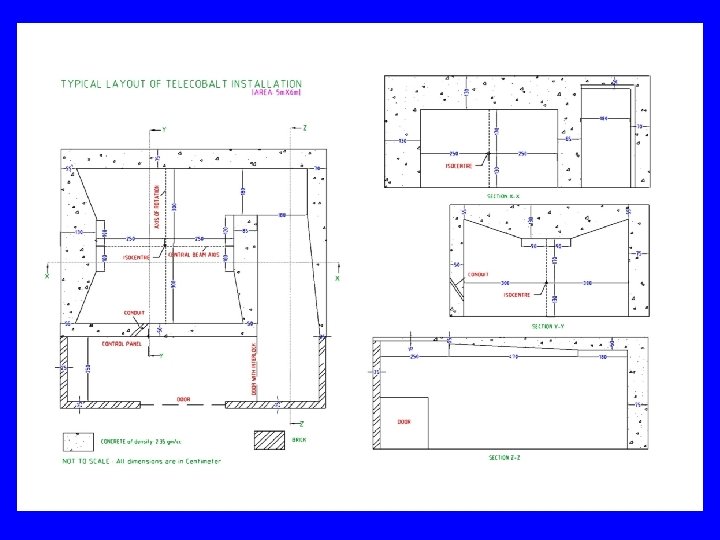
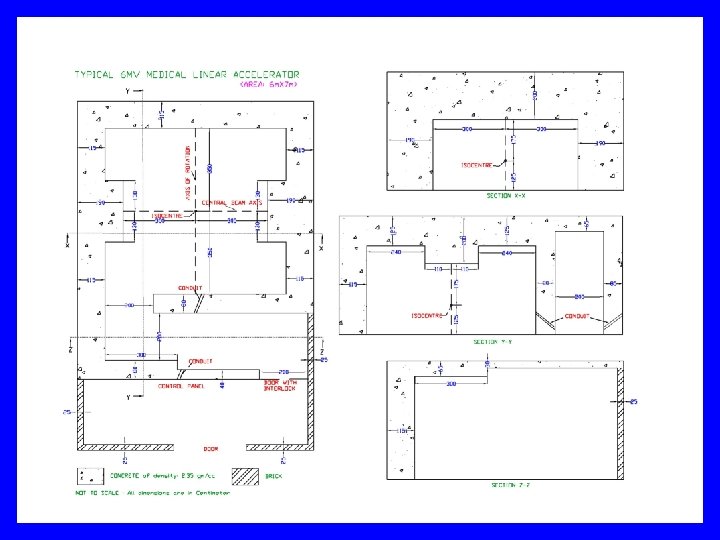
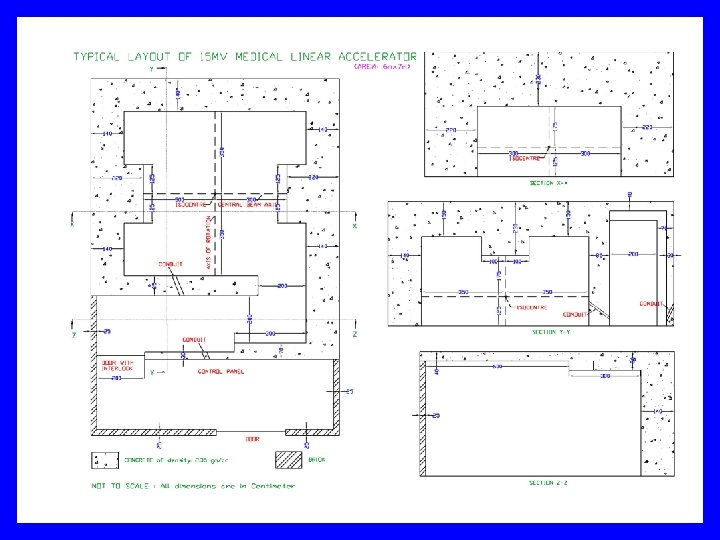
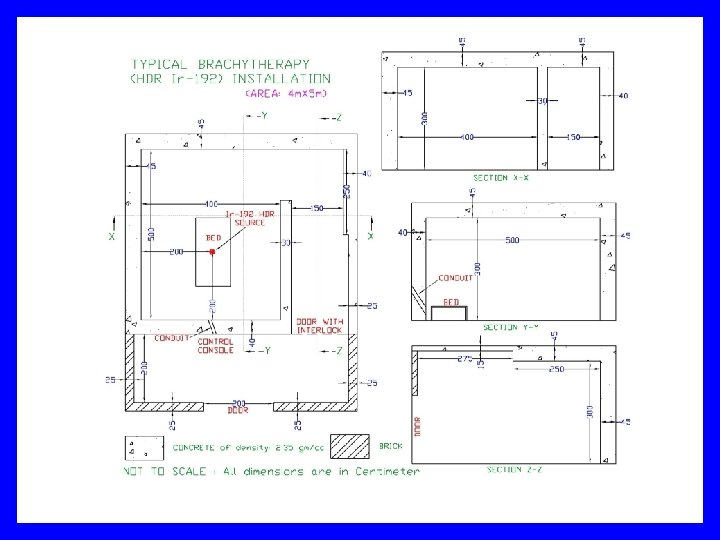
Procedures for RT facility AERB/RSD/RT/GUIDELINES Provides Guidelines to Establish a Radiation Therapy Facility including step by step procedures needed to be followed by the Institution and the forms needed to be filled at various stages. AERB/RSD/RT/PLAN-TECHNOTE-1 Provides Specifications to prepare layout plan of a Radiation Therapy Facility. For downloading some of the standard plans, click the link given below: Telecobalt Installation 6 MV Accelerator Installation 15 MV Accelerator Installation Ir-192 HDR Brachytherapy Installation

Procedures for RT facility AERB/RSD/RT/PROC/TC-SOURCE REPLACEMENT Provides step by step procedures needed to be followed by the Institution for Replacement of telecobalt source and the forms needed to be filled at various stages. AERB/RSD/RT/PROC/BT-SOURCE REPLACEMENT Provides step by step procedures needed to be followed by the Institution for Replacement of HDR Brachytherapy source and the forms needed to be filled at various stages. AERB/RSD/RT/PROC/DECOMMISSIONING Provides step by step procedures needed to be followed by the Institution for Decommissioning a Radiotherapy Unit. AERB/RSD/RT/PROC/DISPOSAL Provides step by step procedures needed to be followed by the Institution for Disposal of Brachytherapy/discrete sources.

AERB/RSD/RT/GUIDELINES REQUIREMENTS AND GUIDELINES TO START A RADIATION THERAPY FACILITY 1). AERB clearance of the unit - type approved 2). Layout Plan approval of Radiation Therapy Installation - AERB/RSD/RT/PLAN -commence construction on receipt of the approved plan 3). Concurrence from AERB prior to modification 4). Appointment of Radiation Therapy Staff 5). Nomination and Approval of RSO - AERB/441/RSOM-II/III-FORM

REQUIREMENTS AND GUIDELINES TO START A RADIATION THERAPY FACILITY 6). Procurement of Personnel Monitors 7). Measuring and Monitoring instruments Measuring instruments Thimble Ionisation Chamber, Parallel Plate Ionisation Chamber, Well type Ionization Chamber, Electrometer, Radiation Field Analyser etc. Monitoring instruments for area monitoring Survey Meters, Contamination Monitors, Gamma Zone Monitors etc. 8). Associated equipment Simulator / CT-Simulator – Layout approval necessary 9). Associated Accessories Treatment Planning System (TPS), beam modifiers, patient immobilisation devices such as moulds, quality assurance test tools

REQUIREMENTS AND GUIDELINES TO START A RADIATION THERAPY FACILITY 10). Authorisation to procure Radiation Sources - AERB/RSD/RT/ATH Includes sealed radioactive sources, depleted uranium and Medical Accelerator and Simulator 11). Procure only equipments in authorization letter 12). Road Transport Approval 13). Receipt of Sources - AERB/RSD/RT/SRI 14). Installation of the Unit 15). Loading of the source/Switching on Radiation in case of Radiation Generating Equipment AERB/RSD/RT/SSA & AERB/RSD/RT/ST-REPORT

REQUIREMENTS AND GUIDELINES TO START A RADIATION THERAPY FACILITY 16). Ensure personnel monitoring instruments before operation of unit 17). Carryout radiation protection survey 18). Quality Assurance/Acceptance test 19). Commissioning Approval for Patient Treatment - AERB/RSD/RT/UT-COM & AERB/RSD/RT/COM 20). Periodic Performance/ Quality Assurance test 21). Annual status report- AERB/RSD/RT/ASR/2 K 1
e. LORA: e-Licensing of Radiation Applications e-Governance initiative by AERB Web-based application for automation of regulatory processes Objective: Enhance efficiency and transparency in the regulatory processes of AERB Aimed at achieving paperless licensing

Need for e-LORA knowledge All activities including registration of institute to applying for license, from declaring of RSO to decommissioning of equipment, everything is approved / monitored / rejected through e. LORA only e. LORA to be operated on need basis Better understanding is essential to have hassle free environment If deficiencies are there, correcting them may take time
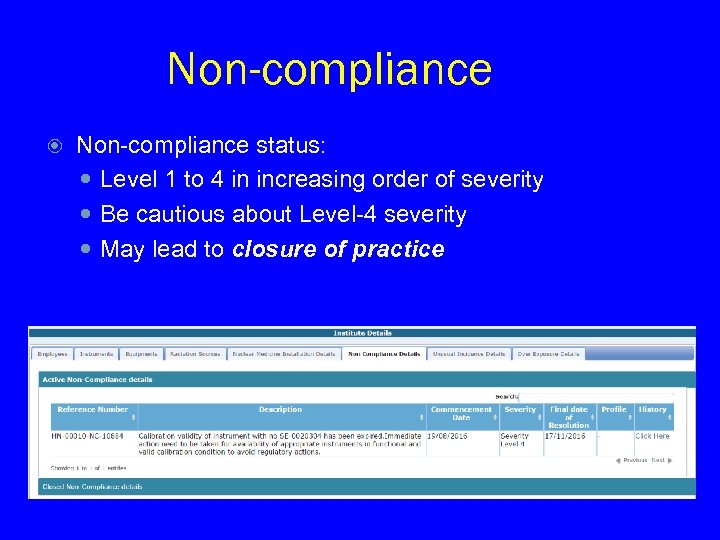
Non-compliance status: Level 1 to 4 in increasing order of severity Be cautious about Level-4 severity May lead to closure of practice

Role of RSO Every institute shall have a e. LORA account Employer is the ‘operator’ of this account AERB recognizes employer ONLY, for all practical purposes Usually employer will ‘empower’ Medical Physicist-cum-RSO to operate the account on his/her behalf

Procedure for E-Licensing of Radiation Applications (e. LORA): RT STEP 1: Register your Institute. After successful registration you will receive a User ID and Password (login details) for the employer, whose details has been accepted in the Institute registration process. STEP 2: Staff members such as Radiation Oncologist, Medical Physicist and Radiotherapy Technologist of the facility needs to be added

STEP 3: Instruments to be added Measuring instruments ( Secondary Standard Dosimeter, Parallel Plate Chamber, RFA ion chambers, Isotope calibrator, etc. Monitoring instruments (Survey meters, Gamma Zone monitors, etc. ) QA tools (Different phantoms, Thermo meter, Barometer, etc. ) Safety tools (Emergency container, T-Rod etc. ) source storage

STEP 4: RSO approval Application for RSO approval can be initiated through employer. Please Note: Regulatory clearances will not be processed till adequate number of staff members (considering them as radiation professional), approved RSO, Measuring/Monitoring instruments, QA tools and Safety tools are successfully added in e. LORA. Visit e. LORA home page regularly for guidelines and frequently asked questions (FAQs)

Steps inside e. LORA: Linac
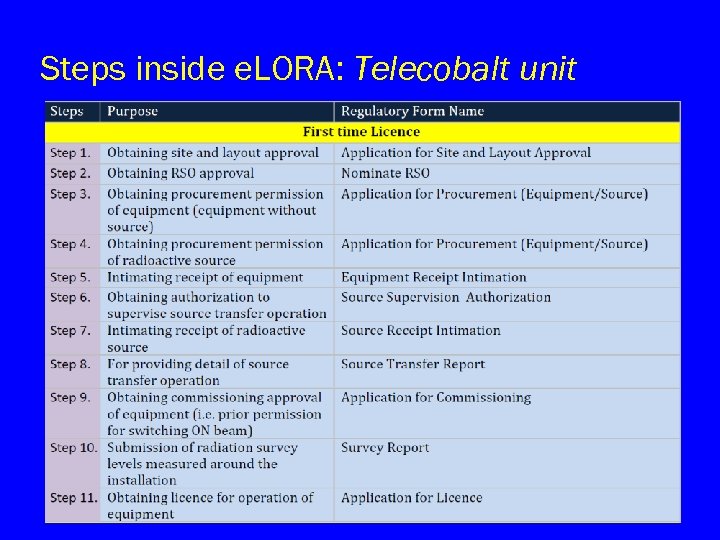
Steps inside e. LORA: Telecobalt unit
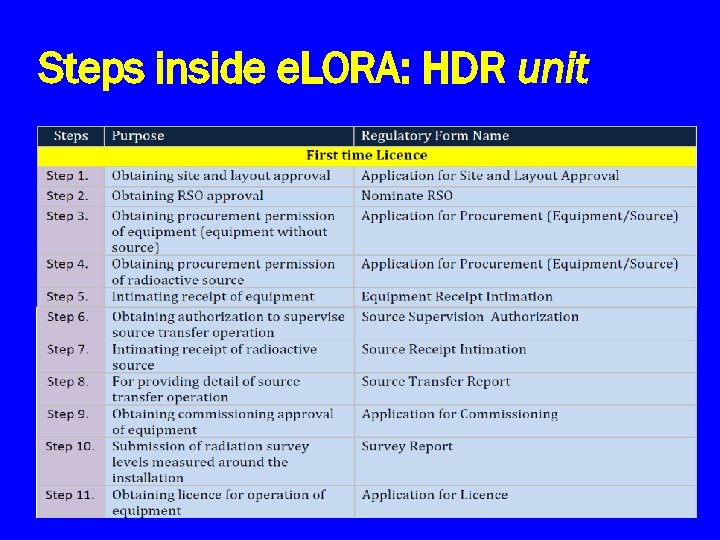
Steps inside e. LORA: HDR unit

Steps for a simulator / CT-simulator
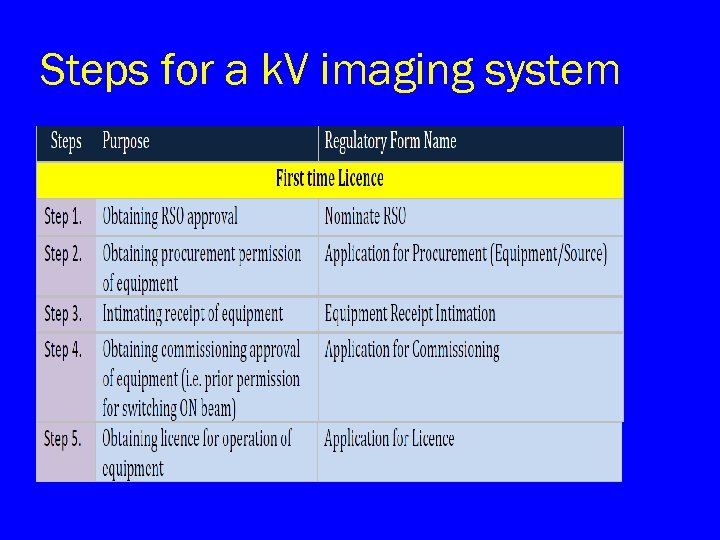
Steps for a k. V imaging system

Obtaining permission from AERB for equipment Verify from the supplier that the unit to be installed is either type approved by Atomic Energy Regulatory Board (AERB) or a NOC is issued The local supplier has to produce the copy of type approval certificate or NOC (issued by AERB) whenever its demanded Type approval : When a new model is to be imported to INDIA for the first time, AERB issues NOC to the local supplier to import only ONE unit Once it is imported, AERB checks the performance of the unit and check whether the unit meets the required standards The type approval certificate is issued based on the physical evaluation of the unit, to the local supplier

Source transfer operations Every source transfer, especially telecobalt source transfer requires special attention & preparation prior to the process RSO will be authorised by AERB for supervising the source transfer operation For authorisation, RSO should submit the duly filled in form prior to 15 days of actual date of source transfer If the physicist/RSO doesn’t have experience, then institute should seek the help of other centers Follow all documentation Source transfer only in the presence of MP who will submit a report after the transfer

Source transfer operations Only required personnel All have PMS badges Survey after transfer The first thing to be done before any other activity If levels are not within limits, then STOP & inform AERB All QA tests Documentation
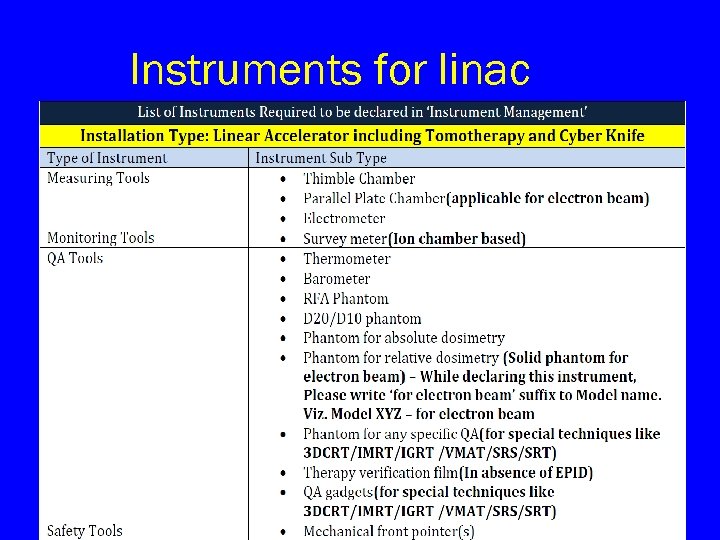
Instruments for linac
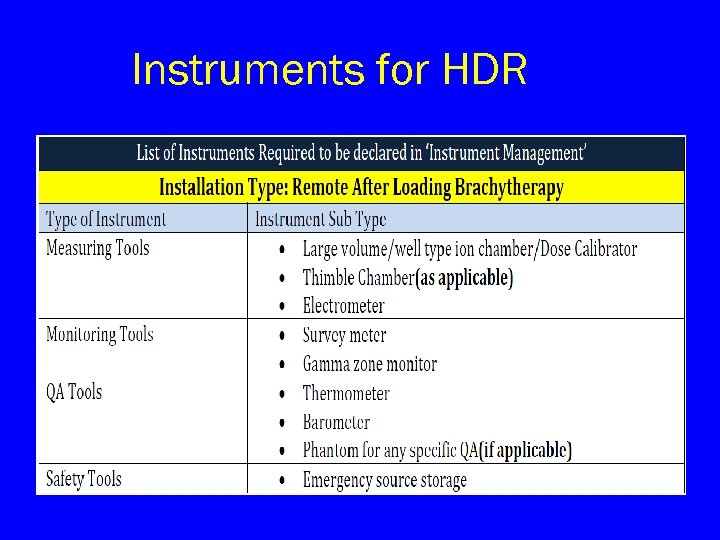
Instruments for HDR

Orphaned source almost always results in accident Goiania, Brazil (Sep 1987) Istanbul, Turkey (Dec 1998) Bangkok, Thailand (Jan 2000) New Delhi, India (Apr 2010) Prevent orphaned source situation Accountability at all times Cradle-to-grave

Care in preparing site & layout plan drawings Site plan Scale 1: 200 Two copies + application to Head, RSD, AERB Show all facilities up to 20 m from the external walls of RT room Write like ‘Ward’, ‘Toilet’, ‘Corridor’, ‘Accounts Office’, ‘Open Land open to sky’ ○ Do not write as ‘Full Occupancy’, ‘Partial Occupancy’ etc. Indicate distance between external walls of RT room to plot boundary ○ At least 2 -3 meter clearance

Care in preparing site & layout plan drawings Main drawing showing RT room etc. , Indicate floor ○ If floors above/below, attach their floor plans too Write like ‘Ward’, ‘Toilet’, ‘Corridor’, ‘Accounts Office’, ‘Open Land open to sky’ ○ Do not write as ‘Full Occupancy’, ‘Partial Occupancy’ etc. Mark isocenter, central axis, axis of gantry rotation Source position, bed position Position of LMOS No construction work without AERB approval

Information Required for shielding calculation Equipment Source, Energy/Activity Dose rate Workload (W) Target dose (Dose/fraction) Use factor (U) Distance to the area of interest (d) Occupancy of area to be shielded (T) Dose Limit value in area to be shielded (P)

Method of Shielding Calculation A. Primary Barrier: The number (n) of TVTs required n = no. of TVTs = log(RF) = log Thickness of primary wall (tpri) = n x TVT Note: Wall thicknesses determined for primary barriers will be more than adequate to shield leakage and scattered radiation and no further calculations are required.

RADIAION PROTECTION STANDRDS To prevent deterministic effects To reduce the probability of stochastic risk at an acceptable level
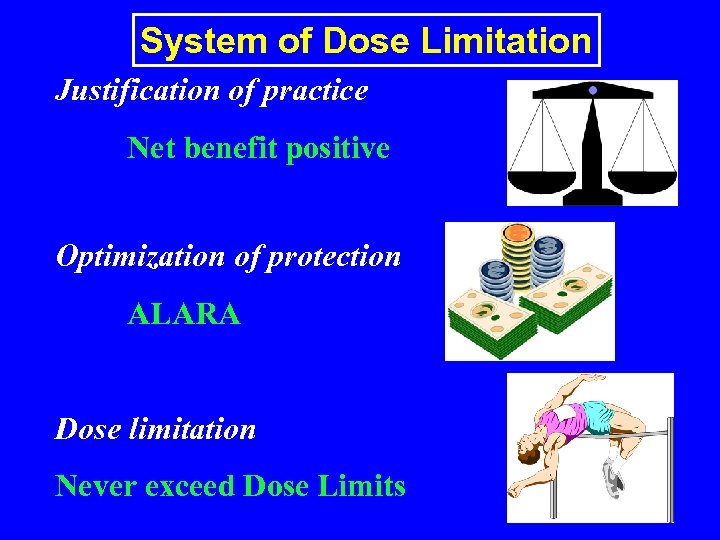
System of Dose Limitation Justification of practice Net benefit positive Optimization of protection ALARA Dose limitation Never exceed Dose Limits

DOSE LIMITS Part of the body Occupational Exposure Public Exposure Whole body (Effective dose) 20 m. Sv/year averaged over 1 m. Sv/y 5 consecutive years; 30 m. Sv in any single year Lens of eyes (Equivalent dose) 150 m. Sv in a year 15 m. Sv/y Skin (Equivalent dose) 500 m. Sv in a year 50 m. Sv/y Extremities (Hands and Feet) Equivalent dose 500 m. Sv in a year -
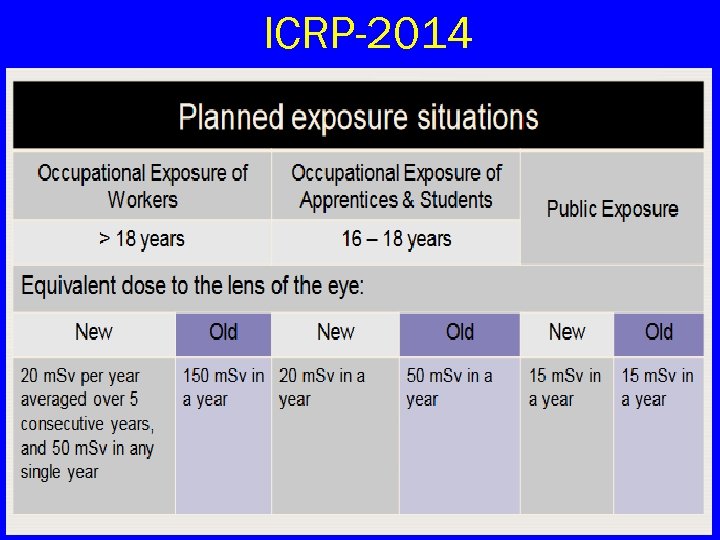
ICRP-2014

INSTRUMENTS REQUIRED

INSTRUMENTS REQUIRED

INSTRUMENTS REQUIRED

Radiation Safety Total Radiation Safety is achieved by Built-in safety + Operational Safety

Built-in Radiation Safety Sources - Standards Equipment - Shielding and design Installation - Siting, shielding & design Transport package - Design

Example: Built-in Radiation Safety Sealed Source: Classification (safety of worker and public) Equipment : Type-approval Electrical, Mechanical, Radiological (safety of Rad. worker and patient) 79

Operational Safety Components of operational safety Qualified and certified personnel Work place monitoring Personnel monitoring Safe and secure storage place Preventive maintenance of equipment Interaction with regulatory body Emergency planning and preparedness Working together as a team Knowledge and skill commensurate with the technology Safety culture

Commissioning, QA/QC of RT Equipment Commissioning: Performance Assessment of the equipment - Generation of Dosimetry Data for Clinical and Regulatory purposes QA/QC: Periodic Evaluation for establishing the stability in performance Performance Criteria: IEC/Regulatory Board has prescribed criteria and tolerance values for performance evaluation of different RT equipment

Category & Frequency of QA Test for Radiotherapy Equipment Electrical Tests Daily Mechanical tests Weekly Dosimetry Tests Radiation Safety Tests Monthly Yearly
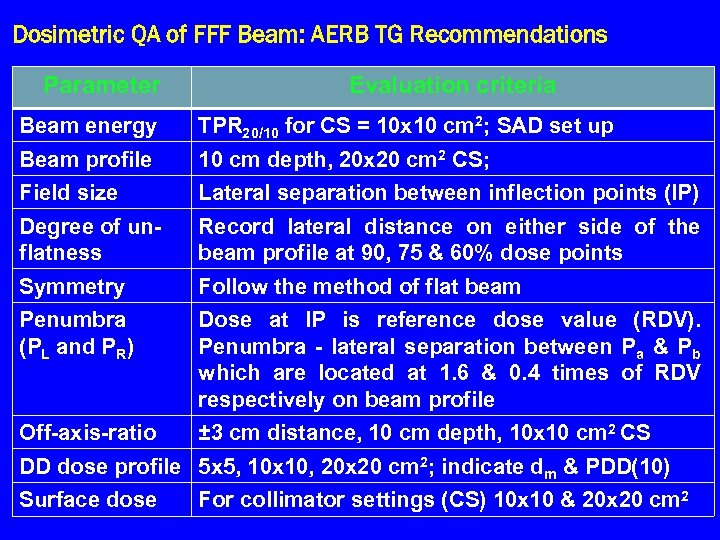
Dosimetric QA of FFF Beam: AERB TG Recommendations Parameter Evaluation criteria Beam energy TPR 20/10 for CS = 10 x 10 cm 2; SAD set up Beam profile 10 cm depth, 20 x 20 cm 2 CS; Field size Lateral separation between inflection points (IP) Degree of unflatness Record lateral distance on either side of the beam profile at 90, 75 & 60% dose points Symmetry Follow the method of flat beam Penumbra (PL and PR) Dose at IP is reference dose value (RDV). Penumbra - lateral separation between Pa & Pb which are located at 1. 6 & 0. 4 times of RDV respectively on beam profile Off-axis-ratio ± 3 cm distance, 10 cm depth, 10 x 10 cm 2 CS DD dose profile 5 x 5, 10 x 10, 20 x 20 cm 2; indicate dm & PDD(10) Surface dose For collimator settings (CS) 10 x 10 & 20 x 20 cm 2
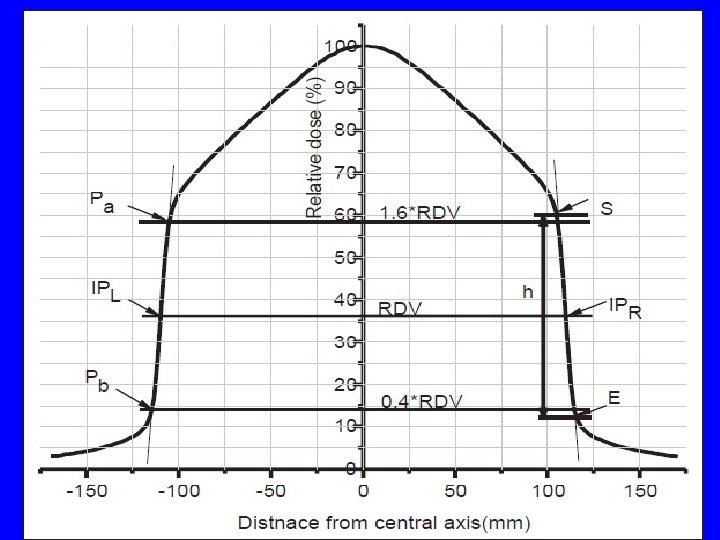

Pre-requisites for license · Type approval of sources and equipment · Approval · Safe of installation and secure source storage · Radiation (area / personal) monitoring · Qualified, Trained and certified staff · Emergency · Licensee’s response plans Commitment to return spent sources to original supplier

Licensee’s responsibilities include Safety & Security of sources all the time at all stages of life cycle of sources Periodic status reports Reporting off-normal incidents Reporting loss or theft of sources to police and AERB Regulator’s role: Source inventory Inspection & Enforcement Investigation of off-normal events

Post Use • Permission for decommissioning of the source installation including DU • Permission to transport the source to the supplier for safe disposal • Verification of safe arrival of the disused source to its destination • Updating the inventory of the sources

Concluding Remarks M The society is drawing immense benefits from the medical applications of ionizing radiation – qualified and skilled staffs are necessary for effective and safe use of radiation technology, M Roles and responsibilities of the staffs are prescribed in the regulatory code for RT, M Proper care need to be taken while handling these sources

Kidwai Memorial Institute of Oncology, Bangalore Thank you for your attention
333a8b61a13ad67aded37242c8115300.ppt