6bc4e1d48ff4a8c0a9ec210c6a6d14f8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12

Stability and change in public policymaking January, 2009
Goal: better understanding of the political system We use Kuhn and Allison to analyze “the system” Goals: Analyze public policy theories focusing on the political sphere Address the tension with Reut’s main concepts Main concepts in presentation: Serial thinking Parallel thinking Positive feedback Windows of opportunity Punctuated equilibrium Negative feedback Bounded rationality Incrementalism

Our understanding of the political system Short and unstable terms Fragmentation within all parts of the system System overloaded and responding to crises Lack of incentives for strategic long term thinking
Bounded rationality and incrementalism Criticism on rationality Bounded rationality Incrementalism Simon: people cannot deal with several problems at the same time Reliance on standard operating procedures lead towards Incrementalism “The basic problem with Incrementalism surfaced when it was tested empirically” Simon (1954) , Tversky and Kahnman (1974), Lindblum (1959), Thaler, Sunstein (2008) , Allison (1971)
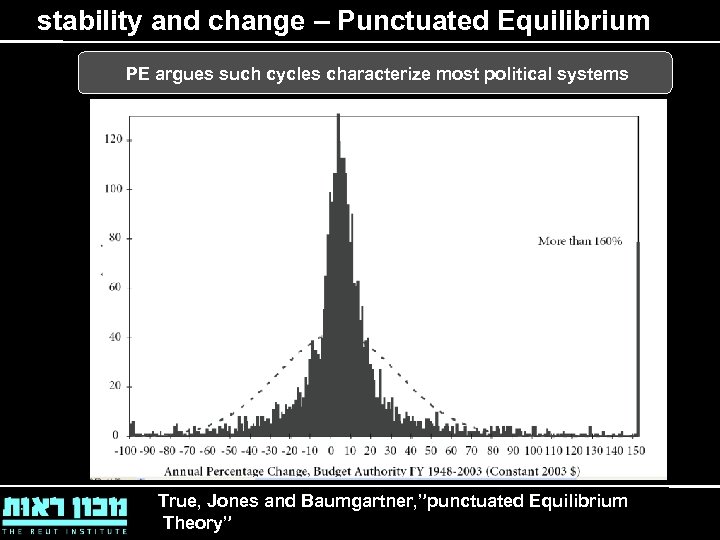
stability and change – Punctuated Equilibrium PE argues such cycles characterize most political systems True, Jones and Baumgartner, ”punctuated Equilibrium Theory”
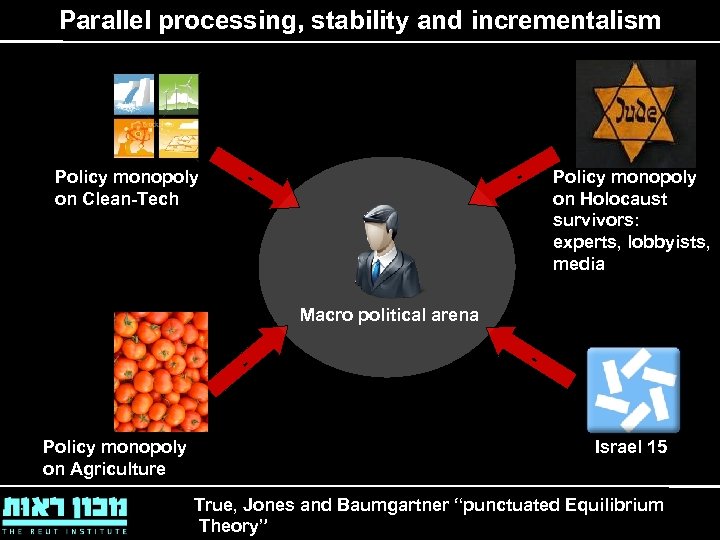
Parallel processing, stability and incrementalism Policy monopoly on Clean-Tech - - Policy monopoly on Holocaust survivors: experts, lobbyists, media Macro political arena - Policy monopoly on Agriculture - Israel 15 True, Jones and Baumgartner “punctuated Equilibrium Theory”
Serial processing, positive feedback, punctuation Policy monopoly on Clean-Tech - Positive feedback punctuation When changes in Policy could circumstancesmonopoly lead to on Holocaust majors changes survivors in policy outcomes in the long run Issue punctuates the equilibrium - Policy monopoly on Agriculture - Israel 15 True, Jones and Baumgartner” punctuated Equilibrium Theory”

Windows of opportunity allow positive feedback Policy Stream Politics Stream Window of opportunity allows positive feedback Problem Stream Kingdon (1995)
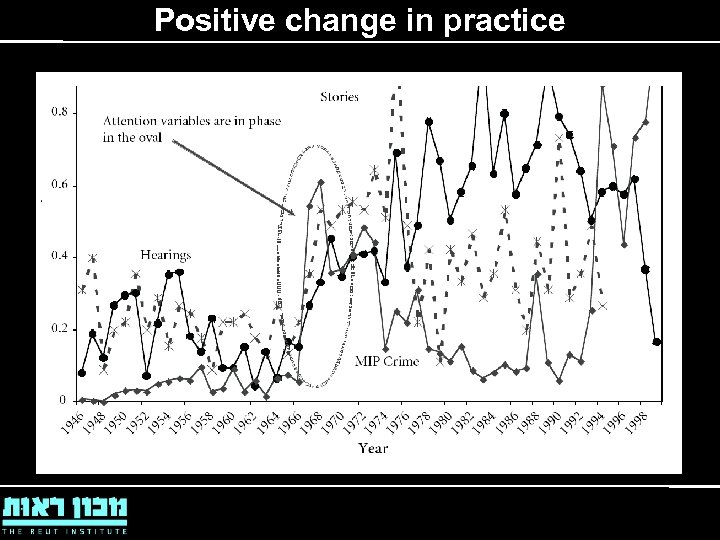
Positive change in practice
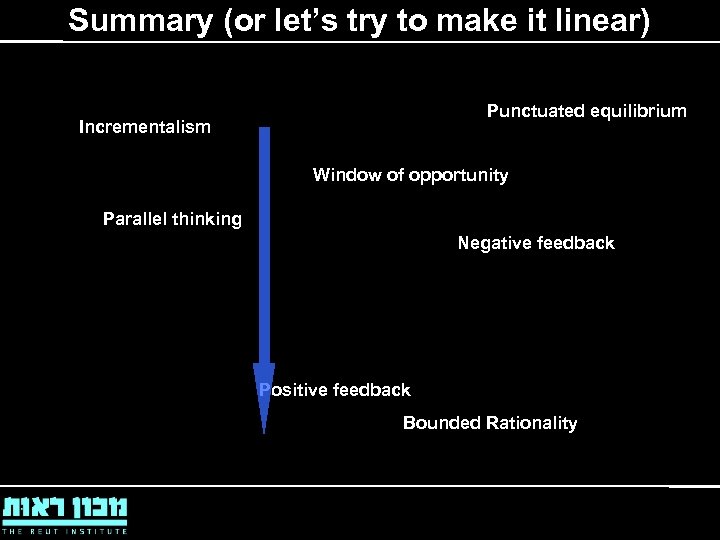
Summary (or let’s try to make it linear) Punctuated equilibrium Incrementalism Window of opportunity Parallel thinking Negative feedback Positive feedback Bounded Rationality

Points for discussion Punctuated Equilibrium and Kuhn’s paradigm shift? How does the window of opportunity relate to Heifetz’s terms? How can these theories help us do more effective ‘sensoring’?

Bibliography • Tversky Amos and Daniel Kahnman. “judgement under uncertainty: Heuristics and Baised. ” Science 185 (1974), 1124 -31 • Kingdon John. 1995. “Agendas, Alternatives and Public Policies”. 2 nd ed. Boston. • Simon, Herbert, A. 1957 “Models of Man. ”New York: willie. • Lindeblom, Charles. 1959 “The science of Muddling Through. ” Public Administration Review 1959. 79 -88. • James, L. True, Bryan, D. Jones, and Frank baumgartner. 2006 “ Punctuated Equilibrium Theory – Explaining Change and Stability in In P. Sabatier Theories of the Policy Process, 1999
6bc4e1d48ff4a8c0a9ec210c6a6d14f8.ppt