f905e2a2b86a9f4d1b08eedc068734bb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32

Stability Analysis of Positive Linear Switched Systems: A Variational Approach Michael Margaliot School of Elec. Eng. -Systems Tel Aviv University, Israel Joint work with Lior Fainshil and Gal Hochma 1

Outline • Stability of linear switched systems • Variational approach to stability analysis: -Relaxation: a bilinear control system -The “most destabilizing” control • Positive linear switched systems • Variational approach: -Relaxation: a positive bilinear control system -Maximizing the spectral radius of the transition matrix -Main result: a maximum principle 2
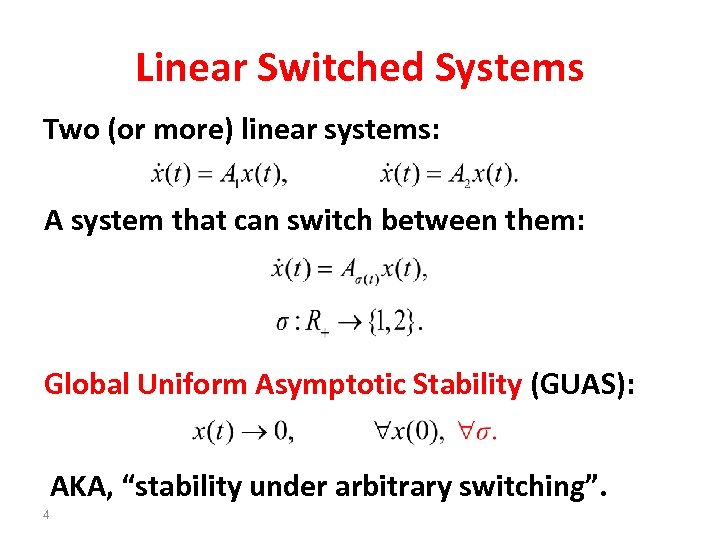
Linear Switched Systems Two (or more) linear systems: A system that can switch between them: Global Uniform Asymptotic Stability (GUAS): AKA, “stability under arbitrary switching”. 4

Why is the GUAS problem difficult? The number of possible switching laws is huge. 5
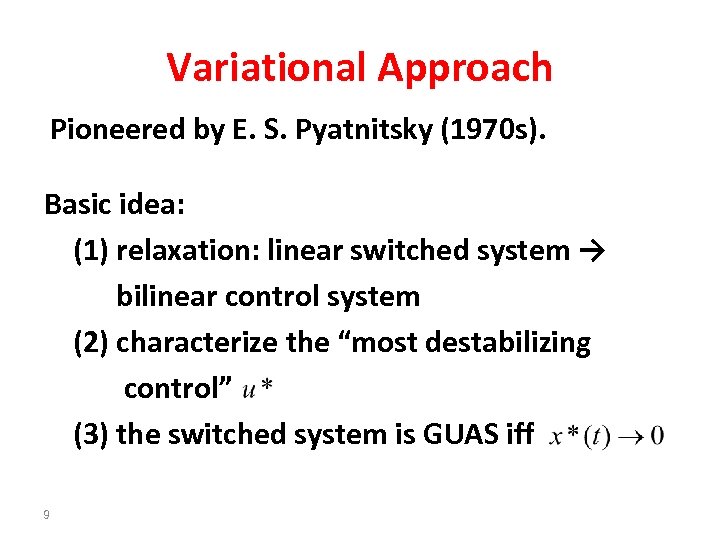
Variational Approach Pioneered by E. S. Pyatnitsky (1970 s). Basic idea: (1) relaxation: linear switched system → bilinear control system (2) characterize the “most destabilizing control” (3) the switched system is GUAS iff 9
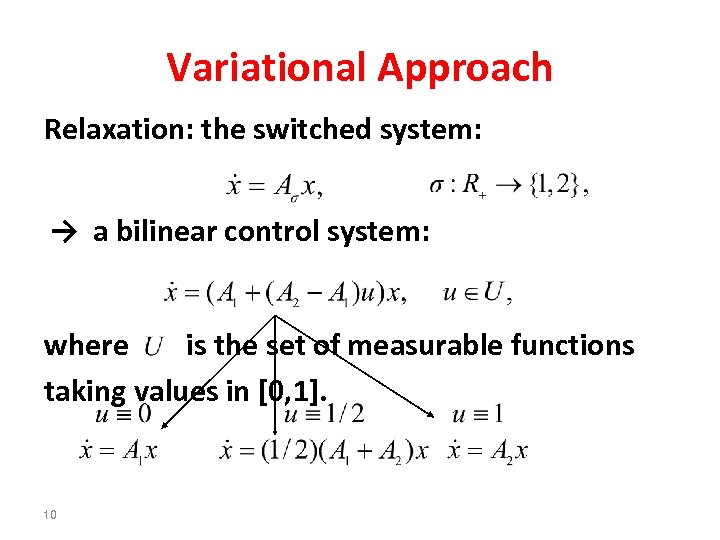
Variational Approach Relaxation: the switched system: → a bilinear control system: where is the set of measurable functions taking values in [0, 1]. 10
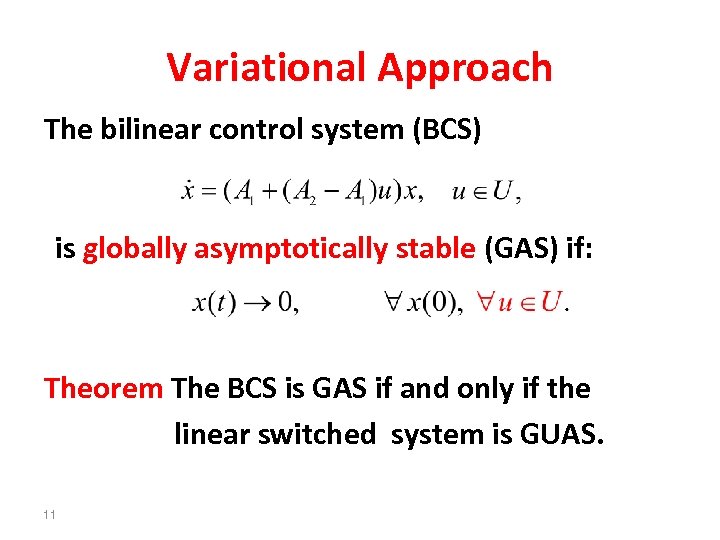
Variational Approach The bilinear control system (BCS) is globally asymptotically stable (GAS) if: Theorem The BCS is GAS if and only if the linear switched system is GUAS. 11

Variational Approach The most destabilizing control: Fix T>0. Let Optimal control problem: find a control that maximizes Intuition: maximize the distance to the origin. 12

Variational Approach and Stability Theorem The BCS is GAS iff 13

Variational Approach Advantages: reduction to a specific control leads to necessary and sufficient conditions for GUAS allows the application of powerful tools (high-order MPs, HJB equation, Liealgebraic ideas, …. ) applicable to nonlinear switched systems Disadvantages: requires characterizing explicit results for particular cases only 14
Variational Approach for Positive Linear Switched Systems Basic idea: (1) positive linear switched system → positive bilinear control system (PBCS) (2) characterize the “most destabilizing control” 15
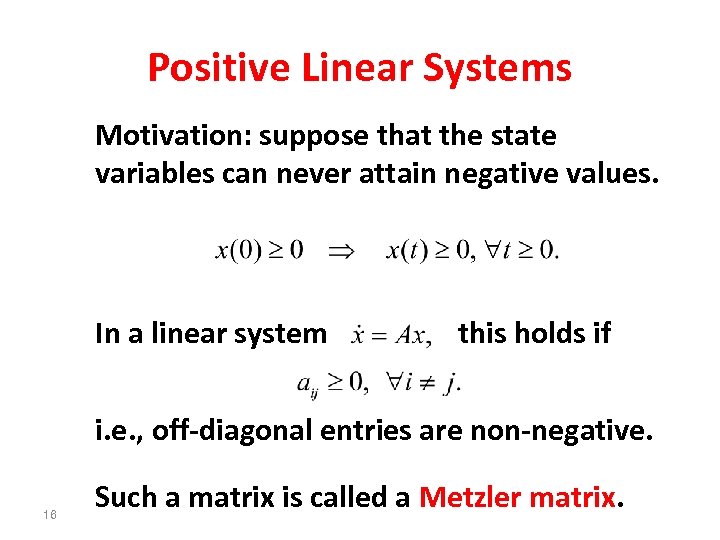
Positive Linear Systems Motivation: suppose that the state variables can never attain negative values. In a linear system this holds if i. e. , off-diagonal entries are non-negative. 16 Such a matrix is called a Metzler matrix.
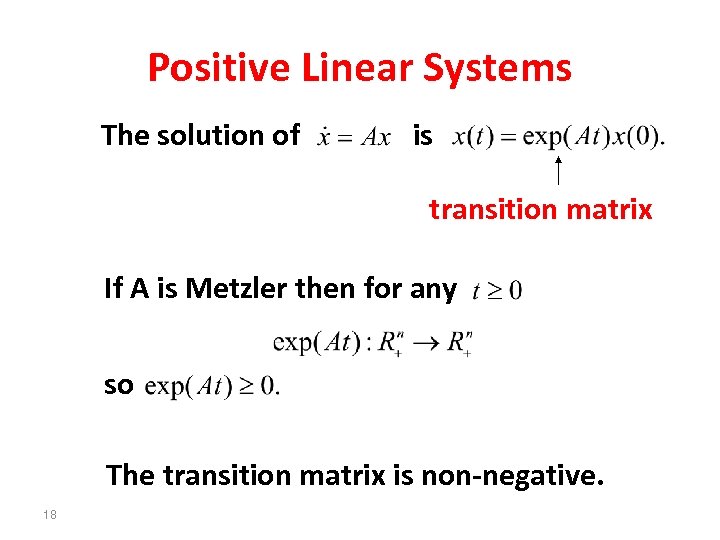
Positive Linear Systems The solution of is transition matrix If A is Metzler then for any so The transition matrix is non-negative. 18
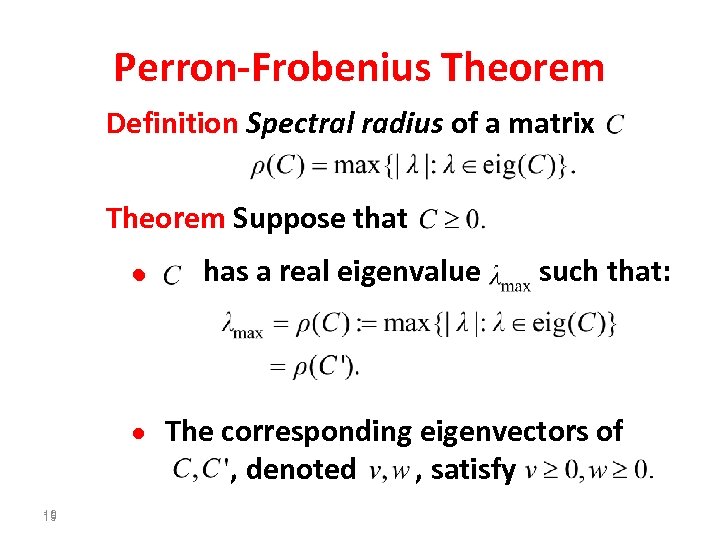
Perron-Frobenius Theorem Definition Spectral radius of a matrix Theorem Suppose that • has a real eigenvalue such that: • The corresponding eigenvectors of , denoted , satisfy 19

Positive Linear Switched Systems: A Variational Approach Relaxation: “Most destabilizing control”: maximize the spectral radius of the transition matrix. 22
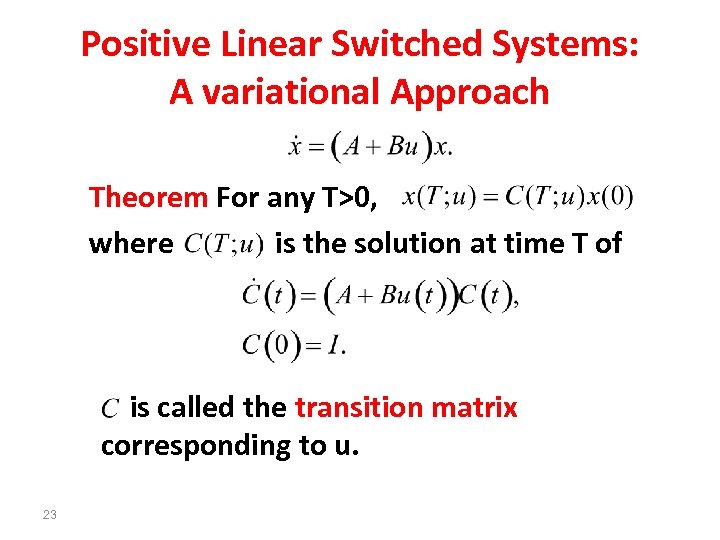
Positive Linear Switched Systems: A variational Approach Theorem For any T>0, where is the solution at time T of is called the transition matrix corresponding to u. 23
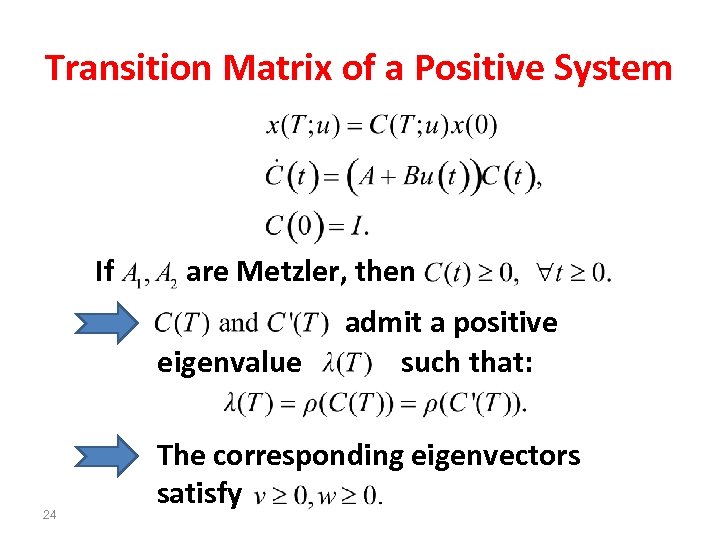
Transition Matrix of a Positive System If are Metzler, then eigenvalue 24 admit a positive such that: The corresponding eigenvectors satisfy
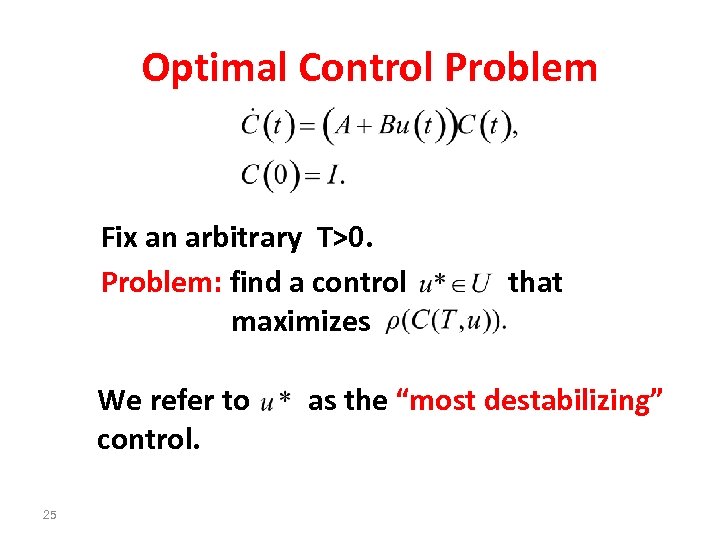
Optimal Control Problem Fix an arbitrary T>0. Problem: find a control maximizes We refer to control. 25 that as the “most destabilizing”
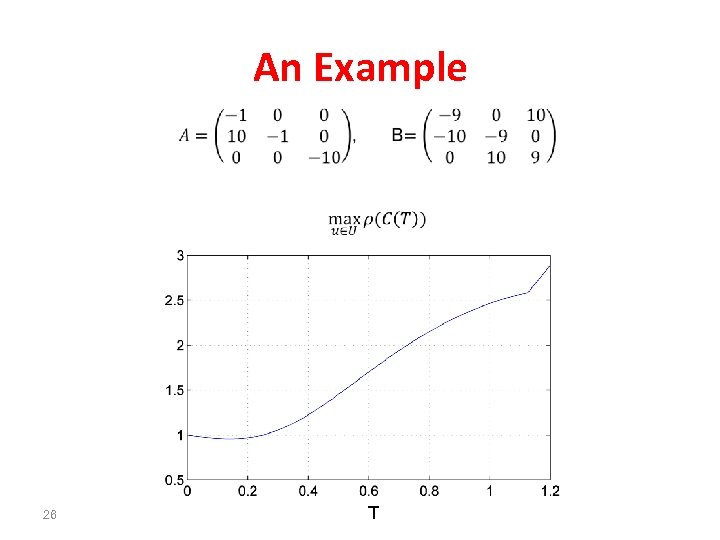
An Example 26 T
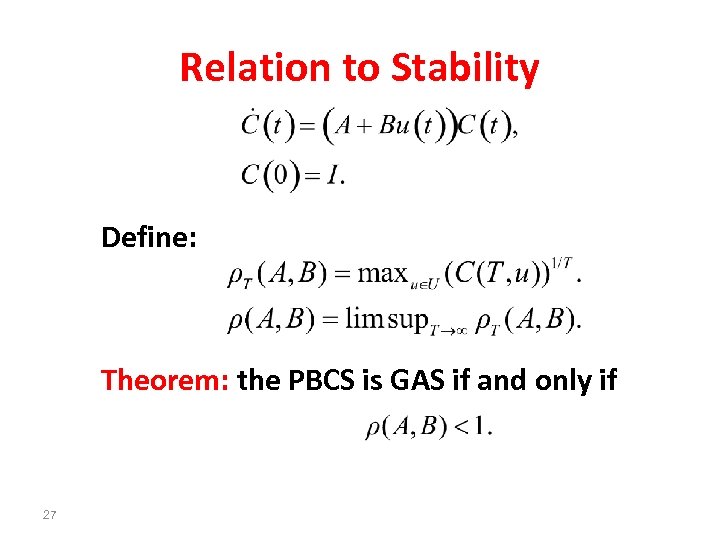
Relation to Stability Define: Theorem: the PBCS is GAS if and only if 27
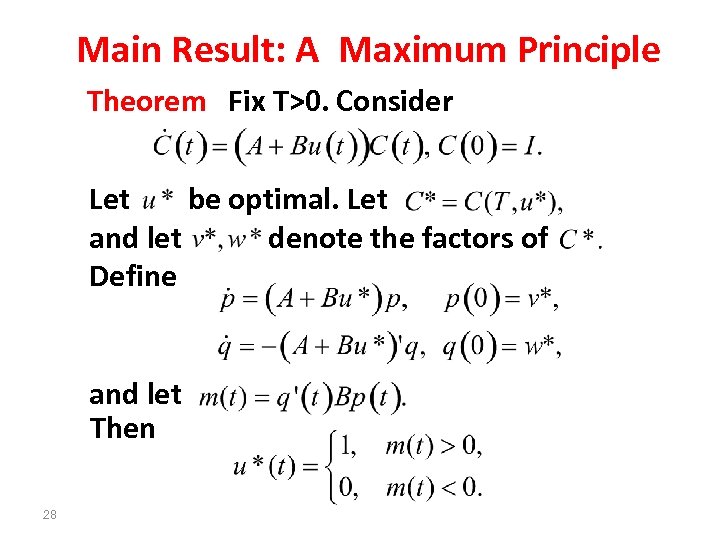
Main Result: A Maximum Principle Theorem Fix T>0. Consider Let be optimal. Let and let denote the factors of Define and let Then 28
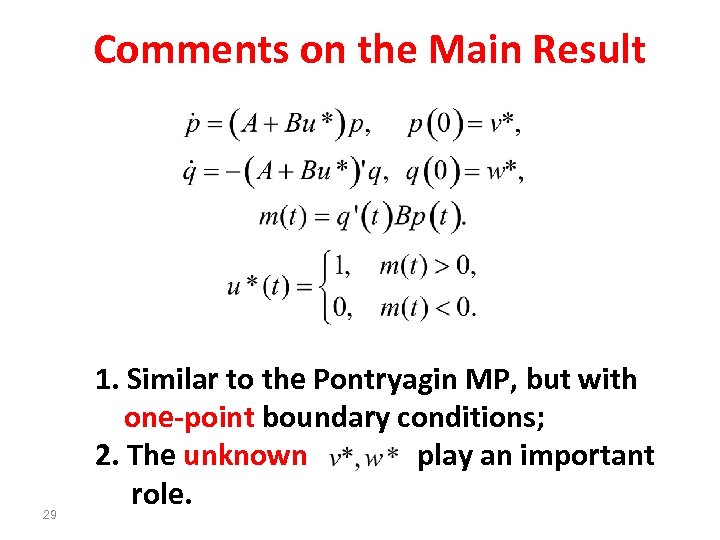
Comments on the Main Result 29 1. Similar to the Pontryagin MP, but with one-point boundary conditions; 2. The unknown play an important role.
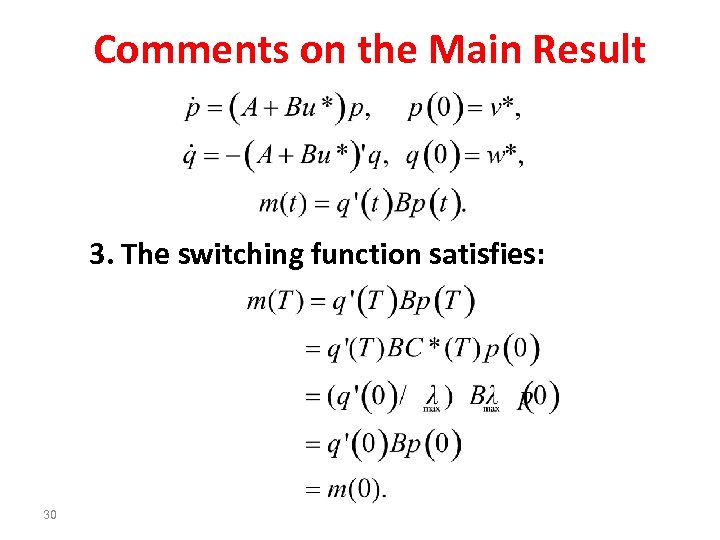
Comments on the Main Result 3. The switching function satisfies: 30
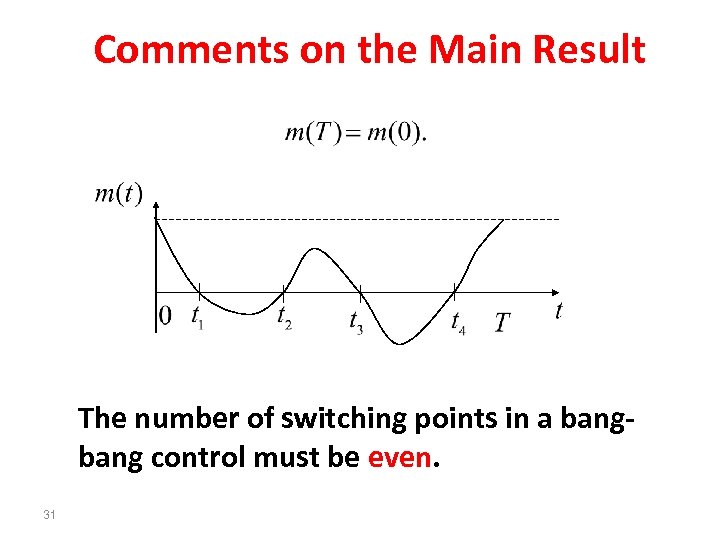
Comments on the Main Result The number of switching points in a bang control must be even. 31
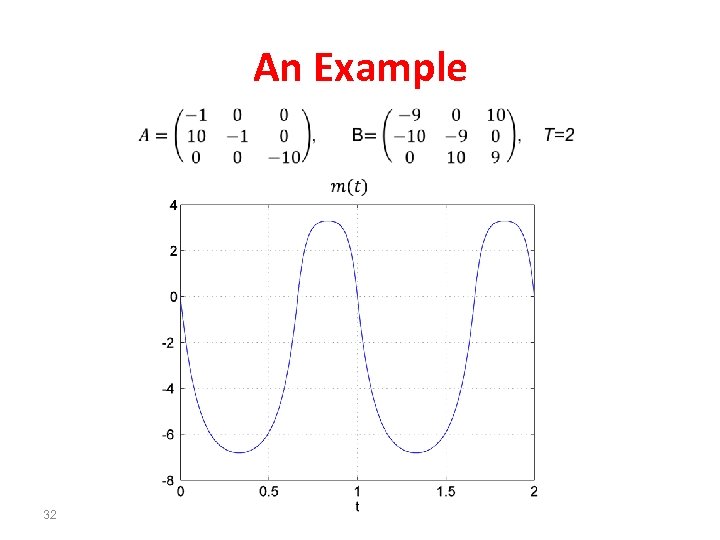
An Example 32
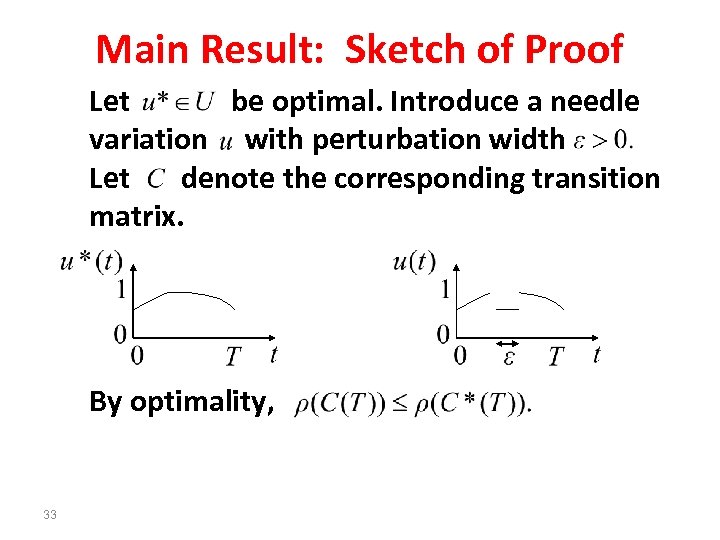
Main Result: Sketch of Proof Let be optimal. Introduce a needle variation with perturbation width Let denote the corresponding transition matrix. By optimality, 33
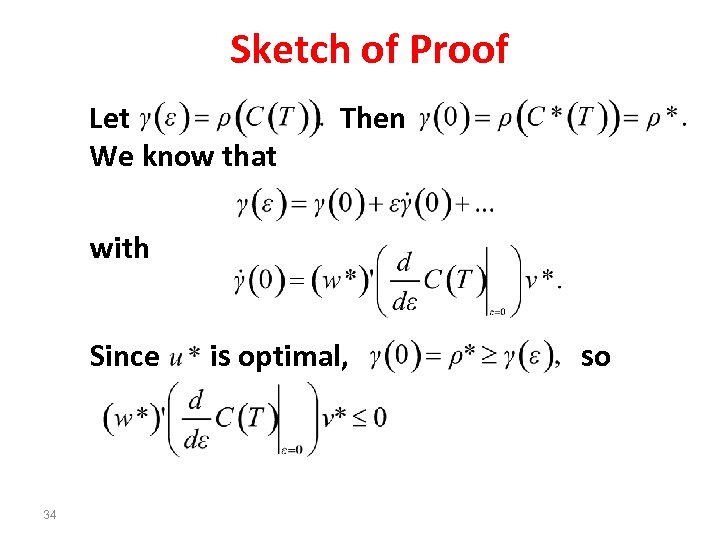
Sketch of Proof Let We know that Then with Since 34 is optimal, so
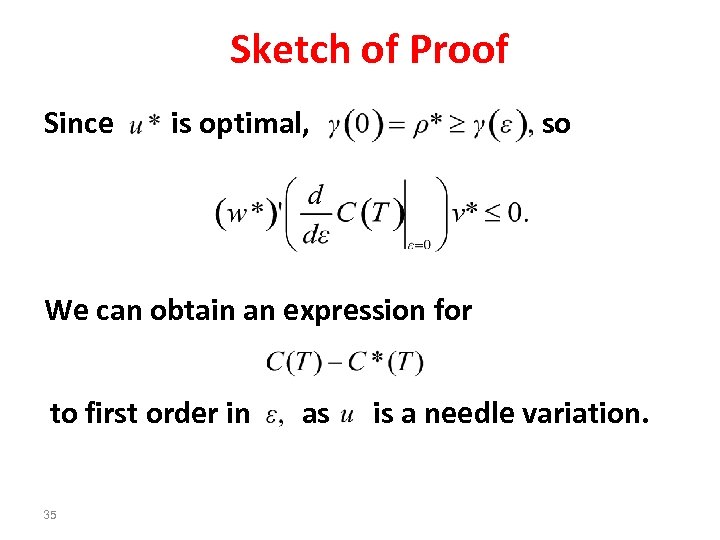
Sketch of Proof Since is optimal, so We can obtain an expression for to first order in 35 as is a needle variation.
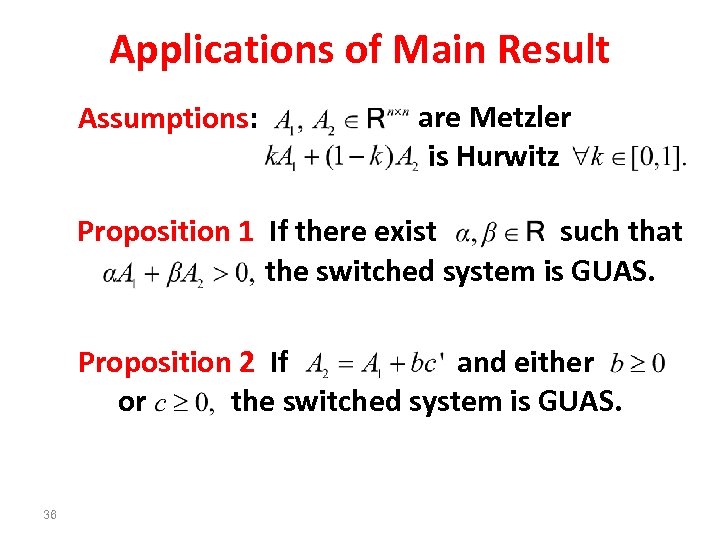
Applications of Main Result Assumptions: are Metzler is Hurwitz Proposition 1 If there exist such that the switched system is GUAS. Proposition 2 If and either the switched system is GUAS. or 36
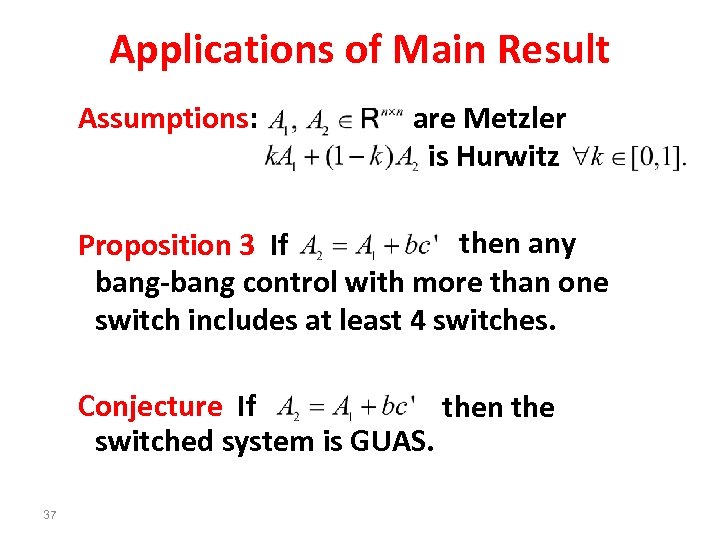
Applications of Main Result Assumptions: are Metzler is Hurwitz then any Proposition 3 If bang-bang control with more than one switch includes at least 4 switches. Conjecture If then the switched system is GUAS. 37

Conclusions We considered the GUAS of positive switched linear systems using a variational approach. The main result is a new MP for the control maximizing the spectral radius of the transition matrix. 38

More Information Margaliot. “Stability analysis of switched systems using variational principles: an introduction”, Automatica, 2006. Sharon & Margaliot. “Third-order nilpotency, nice reachability and asymptotic stability”, JDE, 2007. Margaliot & Branicky. “Nice reachability for planar bilinear control systems with applications to planar linear switched systems”, IEEE TAC, 2009. ---------------------------------------------*Fainshil & Margaliot. “Stability analysis of positive linear switched systems: a variational approach”, SICON, 2012. *Hochma & Margaliot. “High-order maximum principles for the stability analysis of positive bilinear control systems“, OCAM, 39 to appear, 2016.
f905e2a2b86a9f4d1b08eedc068734bb.ppt