222598a24785a76e3e959297a75e4039.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 121
 STAAR Power. Point Review U. S. History Coach Smith Spring 2016
STAAR Power. Point Review U. S. History Coach Smith Spring 2016
 1760 -1800 Foundations of American History 1941 -1945 WWII 1800 -1890 Westward Expansion 1945 -1960 Start of Cold War, 1950 s, & Economic Prosperity 1870 -1900 Gilded Age & Industrial Revolution 1945– 1990 Cold War 1890 -1920 Progressive Era 1954 -1980 Civil Rights 1890 -1920 Imperialism & Expansionism 1960 -1975 1960 s & Vietnam (America’s Rise as World Power) 1970 -1989 1970 s & 1980 s 1920 -1929 Roaring 20 s (Jazz Age) 1990 -2016 1990 s & Modern America 1929 -1941 Great Depression
1760 -1800 Foundations of American History 1941 -1945 WWII 1800 -1890 Westward Expansion 1945 -1960 Start of Cold War, 1950 s, & Economic Prosperity 1870 -1900 Gilded Age & Industrial Revolution 1945– 1990 Cold War 1890 -1920 Progressive Era 1954 -1980 Civil Rights 1890 -1920 Imperialism & Expansionism 1960 -1975 1960 s & Vietnam (America’s Rise as World Power) 1970 -1989 1970 s & 1980 s 1920 -1929 Roaring 20 s (Jazz Age) 1990 -2016 1990 s & Modern America 1929 -1941 Great Depression
 Due to high cost of French & Indian War, British taxed the colonists to help pay the war debt. Colonists objected to these taxes & this eventually led to their Declaration of Independence. Colonists primarily objected to the Stamp, Tea, & Coercive Acts
Due to high cost of French & Indian War, British taxed the colonists to help pay the war debt. Colonists objected to these taxes & this eventually led to their Declaration of Independence. Colonists primarily objected to the Stamp, Tea, & Coercive Acts
 1760 -1800 Foundations of American History 1954 -1980 Civil Rights 1800 -1890 Westward Expansion 1960 -1975 1960 s & Vietnam 1870 -1900 Gilded Age & Industrial Revolution 1970 -1989 1970 s & 1980 s 1890 -1920 Progressive Era 1990 -2016 1990 s & Modern America 1890 -1920 Imperialism & Expansionism (America’s Rise as World Power) 1920 -1929 Roaring 20 s (Jazz Age) 1929 -1941 Great Depression 1941 -1945 WWII 1945 -1960 Start of Cold War, 1950 s, & Economic Prosperity 1945 -1990 Cold War
1760 -1800 Foundations of American History 1954 -1980 Civil Rights 1800 -1890 Westward Expansion 1960 -1975 1960 s & Vietnam 1870 -1900 Gilded Age & Industrial Revolution 1970 -1989 1970 s & 1980 s 1890 -1920 Progressive Era 1990 -2016 1990 s & Modern America 1890 -1920 Imperialism & Expansionism (America’s Rise as World Power) 1920 -1929 Roaring 20 s (Jazz Age) 1929 -1941 Great Depression 1941 -1945 WWII 1945 -1960 Start of Cold War, 1950 s, & Economic Prosperity 1945 -1990 Cold War
 ü Written primarily by Thomas Jefferson üStated reasons why American colonies had the right to separate from England üJuly 4, 1776
ü Written primarily by Thomas Jefferson üStated reasons why American colonies had the right to separate from England üJuly 4, 1776
 ü Rights that cannot be taken away ü Life, liberty, & pursuit of happiness ü Instituted in the Declaration of Independence
ü Rights that cannot be taken away ü Life, liberty, & pursuit of happiness ü Instituted in the Declaration of Independence
 ü Ended the American Revolution üBritain recognized the U. S. as new nation with Mississippi River as the western border
ü Ended the American Revolution üBritain recognized the U. S. as new nation with Mississippi River as the western border
 1787 ü Adoption of Constitution ü Framework for the US gov’t ü Remains a model for representative gov’t
1787 ü Adoption of Constitution ü Framework for the US gov’t ü Remains a model for representative gov’t
 üCreated by the Founding fathers üRevised from the Articles of Confederation üFoundation of the gov’t used today
üCreated by the Founding fathers üRevised from the Articles of Confederation üFoundation of the gov’t used today
 ü 1791 ü 1 st of the ten Bill of Rights üPeople can be well informed through the press üPeople can freely exchange ideas without fear of imprisonment
ü 1791 ü 1 st of the ten Bill of Rights üPeople can be well informed through the press üPeople can freely exchange ideas without fear of imprisonment
 ü 1 st 10 amendments protect basic liberties & individual rights üIndividual rights include freedom of religion, speech, press, etc. ü 17 amendments that follow the Bill of Rights expand individual rights of Americans
ü 1 st 10 amendments protect basic liberties & individual rights üIndividual rights include freedom of religion, speech, press, etc. ü 17 amendments that follow the Bill of Rights expand individual rights of Americans
 üGov’t by popularly elected representatives, not a king üAllows people to be the final source of authority
üGov’t by popularly elected representatives, not a king üAllows people to be the final source of authority
 üIn 1787 the Constitution was drafted, which formed the idea of federalism üStates that power is shared between the national or federal gov’t & the states
üIn 1787 the Constitution was drafted, which formed the idea of federalism üStates that power is shared between the national or federal gov’t & the states
 üSystem where each branch of gov’t has ability to limit power of the other branches to prevent any one branch from becoming too powerful üProvided by the Constitution to ensure that America would never have a monarchy x
üSystem where each branch of gov’t has ability to limit power of the other branches to prevent any one branch from becoming too powerful üProvided by the Constitution to ensure that America would never have a monarchy x
 üGov’t subject to the will of the people üCreated a representative system of gov’t where officials speak on behalf of the people ü New Constitution was based on this idea
üGov’t subject to the will of the people üCreated a representative system of gov’t where officials speak on behalf of the people ü New Constitution was based on this idea
 üGov’t only has the powers the Constitution gives to it
üGov’t only has the powers the Constitution gives to it
 üGovernment principle where power is divided among different branches üLegislative (House & Senate)makes the law ü Executive (President)- enforces the law ü Judicial (Courts)- interprets the law
üGovernment principle where power is divided among different branches üLegislative (House & Senate)makes the law ü Executive (President)- enforces the law ü Judicial (Courts)- interprets the law
 üCottage— Before the Industrial Revolution, most people produced goods at home üIncrease need for cotton by factories üCommercial Industries— Factories created by the Industrial Revolution
üCottage— Before the Industrial Revolution, most people produced goods at home üIncrease need for cotton by factories üCommercial Industries— Factories created by the Industrial Revolution
 üBegan in the 1700’s in Great Britain in the textile industry üIncreased speed of production üMoved production from home to the factory üAfter Civil War, went from rural to industrial society üMore goods at lower prices
üBegan in the 1700’s in Great Britain in the textile industry üIncreased speed of production üMoved production from home to the factory üAfter Civil War, went from rural to industrial society üMore goods at lower prices
 üSubsistence—variety of crops primarily for own use üMarket Oriented—One crop, many hired workers, profit
üSubsistence—variety of crops primarily for own use üMarket Oriented—One crop, many hired workers, profit
 üIdea that America was meant to stretch from coast to coast. üCaused a massive surge of people to settle westward
üIdea that America was meant to stretch from coast to coast. üCaused a massive surge of people to settle westward
 üPresident Andrew Jackson proposed üForced removal of Native Americans to lands west of Mississippi River üMany died üDone to make room for westward expansion.
üPresident Andrew Jackson proposed üForced removal of Native Americans to lands west of Mississippi River üMany died üDone to make room for westward expansion.
 üReasonsreligious freedom, political persecution, & poverty üProblems—hostility, poor working conditions, low wages, isolation, & ghettos. üNativism—preference for native-born Americans & a hatred of immigrants.
üReasonsreligious freedom, political persecution, & poverty üProblems—hostility, poor working conditions, low wages, isolation, & ghettos. üNativism—preference for native-born Americans & a hatred of immigrants.
 1861 -1865 üCivil War in U. S. üIssue of slavery üNorth prevailed üNorth wanted strong central gov’t while the South wanted States’ Rights
1861 -1865 üCivil War in U. S. üIssue of slavery üNorth prevailed üNorth wanted strong central gov’t while the South wanted States’ Rights
 ü 1862 üPresident Abraham Lincoln üAttempted to free all the slaves that lived within states that were rebelling against the Union üEffect-Many African Americans rushed to join the Union army
ü 1862 üPresident Abraham Lincoln üAttempted to free all the slaves that lived within states that were rebelling against the Union üEffect-Many African Americans rushed to join the Union army
 ü 1865 üBanned slavery in America
ü 1865 üBanned slavery in America
 üRatified 1868 üFormer slaves became citizens
üRatified 1868 üFormer slaves became citizens
 ü 1870 üVoting will not be denied based upon race
ü 1870 üVoting will not be denied based upon race

 üBegan in 1862 after the Pacific Railway Act was passed üProvided jobs üMore cities were developed ü Biggest factor that promoted the growth of the West
üBegan in 1862 after the Pacific Railway Act was passed üProvided jobs üMore cities were developed ü Biggest factor that promoted the growth of the West
 1872 -1912 Cattle boom following the Civil War & the Homestead Act (free land for families to move into the Great Plains) caused the settlement of the Western frontier
1872 -1912 Cattle boom following the Civil War & the Homestead Act (free land for families to move into the Great Plains) caused the settlement of the Western frontier
 üCheap labor, new inventions & technology, & raw materials promoted industry üGov’t policies encouraged growth üAndrew Carnegie & John D. Rockefeller were two famous entrepreneurs üLarge corporations became important to the economy ü Railroads, telephones, & telegraphs linked different parts of the country, creating a new nat’l market üLowered cost of products, raised standard of living, & created jobs üPolluted environment, destroyed small companies, & abused workers
üCheap labor, new inventions & technology, & raw materials promoted industry üGov’t policies encouraged growth üAndrew Carnegie & John D. Rockefeller were two famous entrepreneurs üLarge corporations became important to the economy ü Railroads, telephones, & telegraphs linked different parts of the country, creating a new nat’l market üLowered cost of products, raised standard of living, & created jobs üPolluted environment, destroyed small companies, & abused workers
 üDuring Industrial Revolution, immigrants came seeking jobs, African-Americans tried to escape the prejudices of the South, & farmers moved because new technology displaced them üPositives—better paying jobs, bright lights, running water, modern plumbing ü Negatives— overcrowding, dumbell tenements, corrupt politics, riots, poor sanitation, & pollution
üDuring Industrial Revolution, immigrants came seeking jobs, African-Americans tried to escape the prejudices of the South, & farmers moved because new technology displaced them üPositives—better paying jobs, bright lights, running water, modern plumbing ü Negatives— overcrowding, dumbell tenements, corrupt politics, riots, poor sanitation, & pollution
 ü Due to nativism (fear of üAfrican Americans—given foreigners) minorities experience worst jobs, much poverty existed, Jim Crow laws came violence & prejudice into effect & caused violence, lack of voting privileges, KKK üNative Americans— pushed off their land & forced to live on reservations üSpanish speaking Americans—by acquiring the Southwest after the Mexican-American War, many Mexicans became Americans; their land was taken & they were treated badly üWomen— considered the “homemaker”; unable to vote until 1919
ü Due to nativism (fear of üAfrican Americans—given foreigners) minorities experience worst jobs, much poverty existed, Jim Crow laws came violence & prejudice into effect & caused violence, lack of voting privileges, KKK üNative Americans— pushed off their land & forced to live on reservations üSpanish speaking Americans—by acquiring the Southwest after the Mexican-American War, many Mexicans became Americans; their land was taken & they were treated badly üWomen— considered the “homemaker”; unable to vote until 1919
 ü Early 1900’s üFull-time employment of children under the minimum legal age because families needed the income üMore production, less pay üAbuse, exploitation, illiteracy, death üImpact: minimum working age was set at 16
ü Early 1900’s üFull-time employment of children under the minimum legal age because families needed the income üMore production, less pay üAbuse, exploitation, illiteracy, death üImpact: minimum working age was set at 16
 üWorkers realized that they needed to band together to protect and better themselves üEconomic growth caused long working hours, unsafe conditions, & low wages üLate 1880’s workers began to organize into unions, Knights of Labor was 1 st nationwide industrial union üGov’t & big business tried to limit unions, by the early 20 th century gov’t was supportive üThis led to many positive changes for the workers
üWorkers realized that they needed to band together to protect and better themselves üEconomic growth caused long working hours, unsafe conditions, & low wages üLate 1880’s workers began to organize into unions, Knights of Labor was 1 st nationwide industrial union üGov’t & big business tried to limit unions, by the early 20 th century gov’t was supportive üThis led to many positive changes for the workers
 üSupreme Court case that upheld racial segregation üSeparate but equal was OK such as separate drinking fountains, restrooms, schools, etc. üReally hurt equality, but it was eventually overturned by Brown vs. Board of Education (1954)
üSupreme Court case that upheld racial segregation üSeparate but equal was OK such as separate drinking fountains, restrooms, schools, etc. üReally hurt equality, but it was eventually overturned by Brown vs. Board of Education (1954)
 ü 1891 -1896 üDuring the last half of 19 th century, farmers believed the new urban industrial society was dominating American life üThis agrarian malaise was a result of economic complaints, an outgrowth of the isolation of farm life, & a reaction to the departure of increasing numbers of young people who left the farms for the cities üDiscontent contributed to the creation of the Populist Party in the 1890’s üPolitical party pushed for rights of disadvantaged groups such as the farmers
ü 1891 -1896 üDuring the last half of 19 th century, farmers believed the new urban industrial society was dominating American life üThis agrarian malaise was a result of economic complaints, an outgrowth of the isolation of farm life, & a reaction to the departure of increasing numbers of young people who left the farms for the cities üDiscontent contributed to the creation of the Populist Party in the 1890’s üPolitical party pushed for rights of disadvantaged groups such as the farmers
 ü 1899 üPresident William Mc. Kinley üU. S. policy that opened trade in China to all nations
ü 1899 üPresident William Mc. Kinley üU. S. policy that opened trade in China to all nations

 üPublished The Influence of Sea Power Upon History in 1890 üStressed importance of nations needing large navies to protect merchant ships & defend right to trade with other countries üHelped U. S. become a top naval power
üPublished The Influence of Sea Power Upon History in 1890 üStressed importance of nations needing large navies to protect merchant ships & defend right to trade with other countries üHelped U. S. become a top naval power
 ü 1895 - Cuban workers rebelled against Spain seeking their independence üCauses- yellow journalism, American interest in Cuba, sinking of the Maine, the Delome Letter, & moral interests üOutcome- U. S. acquired Philippines, Puerto Rico, & Guam; Cuba became independent; U. S. emerged as a world power
ü 1895 - Cuban workers rebelled against Spain seeking their independence üCauses- yellow journalism, American interest in Cuba, sinking of the Maine, the Delome Letter, & moral interests üOutcome- U. S. acquired Philippines, Puerto Rico, & Guam; Cuba became independent; U. S. emerged as a world power
 üShip exploded in Havana Harbor of Cuba ü 1898 üU. S. blamed Spain üOne of the main instigators of starting the Spanish American War
üShip exploded in Havana Harbor of Cuba ü 1898 üU. S. blamed Spain üOne of the main instigators of starting the Spanish American War
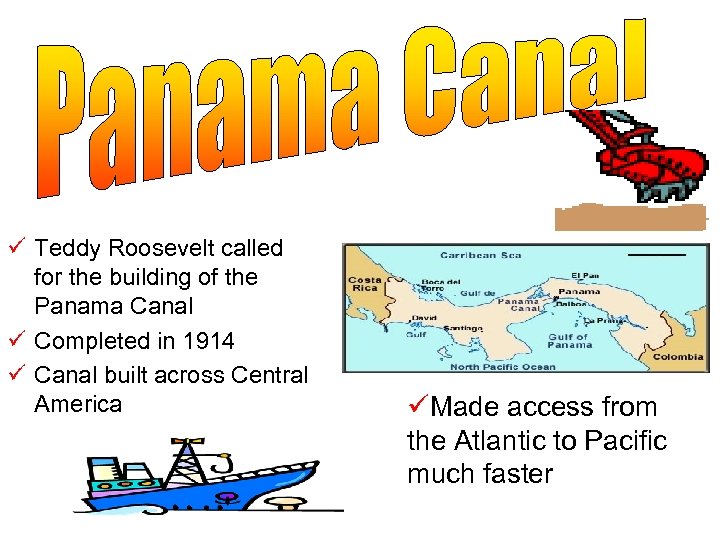 ü Teddy Roosevelt called for the building of the Panama Canal ü Completed in 1914 ü Canal built across Central America üMade access from the Atlantic to Pacific much faster
ü Teddy Roosevelt called for the building of the Panama Canal ü Completed in 1914 ü Canal built across Central America üMade access from the Atlantic to Pacific much faster

 üSeries of movements aimed at renovating or restoring American society, its values, & its institutions ü 1890 -1920 üAreas of reform— industrialization, growing cities, mass immigration, depression, & women’s rights
üSeries of movements aimed at renovating or restoring American society, its values, & its institutions ü 1890 -1920 üAreas of reform— industrialization, growing cities, mass immigration, depression, & women’s rights
 üProgressive president üPresident from 19011909 üAcquired Panama Canal Zone üRoosevelt Corollary (Big Stick Diplomacy) - U. S. would be policeman in Latin America
üProgressive president üPresident from 19011909 üAcquired Panama Canal Zone üRoosevelt Corollary (Big Stick Diplomacy) - U. S. would be policeman in Latin America
 Conservation use limited resources wisely. Gifford Pinchot, adviser to TR on natural resources in this country, favored using federally controlled lands for parks & refuges Preservation To keep something as it is Preserva John Muir was a big preservationist & wanted federally controlled lands to beas it is. To keep something left alone
Conservation use limited resources wisely. Gifford Pinchot, adviser to TR on natural resources in this country, favored using federally controlled lands for parks & refuges Preservation To keep something as it is Preserva John Muir was a big preservationist & wanted federally controlled lands to beas it is. To keep something left alone
 Muckraker A journalist who exposed the corrupt side of business & public life in the early 1900 s The Jungle by Upton Sinclair exposed the meatpacking industry As a result, Pure Food & Drug Act of 1906 banned impure or mislabeled foods & drugs Meat Inspection Act of 1906 provided federal meat inspections take place
Muckraker A journalist who exposed the corrupt side of business & public life in the early 1900 s The Jungle by Upton Sinclair exposed the meatpacking industry As a result, Pure Food & Drug Act of 1906 banned impure or mislabeled foods & drugs Meat Inspection Act of 1906 provided federal meat inspections take place
 Susan B. Anthony ü Leaders of the women’s rights movement from 1851 1906 üArrested for casting a vote in the 1872 Presidential election ü Convinced Congress to grant women the right to vote
Susan B. Anthony ü Leaders of the women’s rights movement from 1851 1906 üArrested for casting a vote in the 1872 Presidential election ü Convinced Congress to grant women the right to vote
 üAllowed a group of citizens to introduce legislation & required the legislature to vote on it üRight that enables voters to remove unsatisfactory elected officials from office üThe practice of letting voters accept or reject measures proposed by the legislature (initiatives) üPopular vote on an issue
üAllowed a group of citizens to introduce legislation & required the legislature to vote on it üRight that enables voters to remove unsatisfactory elected officials from office üThe practice of letting voters accept or reject measures proposed by the legislature (initiatives) üPopular vote on an issue
 th 16 Amendment ü 1913 ü Authorizes US citizens pay income taxes so the gov’t will have money for projects that would benefit all üDirect election of senators – now elected by the people, not the state. ü Puts more power in the hands of the people
th 16 Amendment ü 1913 ü Authorizes US citizens pay income taxes so the gov’t will have money for projects that would benefit all üDirect election of senators – now elected by the people, not the state. ü Puts more power in the hands of the people
 üAdvocated for the “talented tenth” – the most educated 10% of blacks – to lead the fight against segregation üStarted the NAACP ü 1868 -1941 ü Civil Rights movement leader ü Argued that blacks could regain lost ground & achieve full equality only by demanding their rights
üAdvocated for the “talented tenth” – the most educated 10% of blacks – to lead the fight against segregation üStarted the NAACP ü 1868 -1941 ü Civil Rights movement leader ü Argued that blacks could regain lost ground & achieve full equality only by demanding their rights
 ü Migration – moving within the U. S. üGreat Migration 1890 -1930 Blacks moved north & west to escape prejudice
ü Migration – moving within the U. S. üGreat Migration 1890 -1930 Blacks moved north & west to escape prejudice
 ü Opposed imperialism & promoted democracy ü President during WWI ü Progressive president üProposed 14 Points üProposed the League of Nations, but it was not passed
ü Opposed imperialism & promoted democracy ü President during WWI ü Progressive president üProposed 14 Points üProposed the League of Nations, but it was not passed
 1914 -1918
1914 -1918
 ü 194 -1918 ü Known as “Great War” ü U. S. became an international leader üSparked industrial boom & launched the prosperous 20’s
ü 194 -1918 ü Known as “Great War” ü U. S. became an international leader üSparked industrial boom & launched the prosperous 20’s
 ü Viewed WWI as an European conflict ü Though claiming to be neutral, U. S. supplied the Allies with food, supplies, weapons, & other items. ü Germans sank U. S. merchant ships by using unrestricted submarine warfare ü Zimmerman Telegram was a secret message from the German gov’t to Mexico asking them to keep a dispute ongoing with the US
ü Viewed WWI as an European conflict ü Though claiming to be neutral, U. S. supplied the Allies with food, supplies, weapons, & other items. ü Germans sank U. S. merchant ships by using unrestricted submarine warfare ü Zimmerman Telegram was a secret message from the German gov’t to Mexico asking them to keep a dispute ongoing with the US
 ü 1917 ü Cause of US entering WWI ü Germans sank ships, military & commercial, without warning Most famous was the Lusitania, a British passenger liner
ü 1917 ü Cause of US entering WWI ü Germans sank ships, military & commercial, without warning Most famous was the Lusitania, a British passenger liner
 At Home During WWI ü Gov’t sold Liberty Bonds to Americans during WWI üBuying bonds Americans helped finance the war üConserve food & goods for the military in Europe (Meatless Mondays and Wheatless Wednesdays)
At Home During WWI ü Gov’t sold Liberty Bonds to Americans during WWI üBuying bonds Americans helped finance the war üConserve food & goods for the military in Europe (Meatless Mondays and Wheatless Wednesdays)
 Wilson’s 14 Points &League of Nations At the end of WWI, President Wilson worked to get the Allied Powers to accept his 14 points that would help establish & keep peace in the world. The most important of these points was the League of Nations, a peace keeping organization. Henry Cabot Lodge Political Leader noted for the failure of League of Nations & Wilson’s 14 Points because he wanted ta “hands off” approach to world problems (Isolationism)
Wilson’s 14 Points &League of Nations At the end of WWI, President Wilson worked to get the Allied Powers to accept his 14 points that would help establish & keep peace in the world. The most important of these points was the League of Nations, a peace keeping organization. Henry Cabot Lodge Political Leader noted for the failure of League of Nations & Wilson’s 14 Points because he wanted ta “hands off” approach to world problems (Isolationism)

 19 th Amendment ü Gave women the right to vote in state & nat’l elections
19 th Amendment ü Gave women the right to vote in state & nat’l elections
 Changing Roles of Women in the 1920’s ü New household appliances reduced housework, so a greater number of women went to college & worked outside the home ü Flappers were liberated, stylish, & unconventional
Changing Roles of Women in the 1920’s ü New household appliances reduced housework, so a greater number of women went to college & worked outside the home ü Flappers were liberated, stylish, & unconventional
 The Red Scare ü Communists seized power in Russia in 1917 ü After WWI, Americans feared that Communists, “REDS, ” might seize power in the USA ü Many people were wrongly accused of being communists ü Most of the accused were deported or jailed
The Red Scare ü Communists seized power in Russia in 1917 ü After WWI, Americans feared that Communists, “REDS, ” might seize power in the USA ü Many people were wrongly accused of being communists ü Most of the accused were deported or jailed
 Immigration ü After WWI, strong feelings against immigrants arose ü Fear of Communism was seeping into the USA ü Immigration from Southern & Eastern Europe was greatly limited
Immigration ü After WWI, strong feelings against immigrants arose ü Fear of Communism was seeping into the USA ü Immigration from Southern & Eastern Europe was greatly limited
 Prohibition ü In 1920, 18 th Amendment prohibited alcoholic beverages in the U. S. ü Many saw alcohol as cause of poverty & crime, thus pushing for Prohibition üAfter passage of the 18 th amendment, organized crime rose ü 21 st amendment repealed Prohibition because of problem enforcing it & need for more jobs
Prohibition ü In 1920, 18 th Amendment prohibited alcoholic beverages in the U. S. ü Many saw alcohol as cause of poverty & crime, thus pushing for Prohibition üAfter passage of the 18 th amendment, organized crime rose ü 21 st amendment repealed Prohibition because of problem enforcing it & need for more jobs
 Henry Ford • Introduced moving assembly line to automobile production in 1914 • Increased manufacturing efficiency Turned America into a car based society because cars became affordable
Henry Ford • Introduced moving assembly line to automobile production in 1914 • Increased manufacturing efficiency Turned America into a car based society because cars became affordable
 Charles Lindberg • First man to fly nonstop solo across the Atlantic Ocean • Support for commercial flight grew • Show America’s courage & ingenuity
Charles Lindberg • First man to fly nonstop solo across the Atlantic Ocean • Support for commercial flight grew • Show America’s courage & ingenuity
 Clarence Darrow • Lawyer who defended John Scopes’ trial pertained to a high school biology teacher who was arrested for teaching evolution; Scopes was found guilty Trial illustrated the clash between new scientific theories & older fundamentalist religious beliefs
Clarence Darrow • Lawyer who defended John Scopes’ trial pertained to a high school biology teacher who was arrested for teaching evolution; Scopes was found guilty Trial illustrated the clash between new scientific theories & older fundamentalist religious beliefs
 William Jennings Bryan • Beginning in 1896, Bryan ran for President (Populist Party) many times & received many votes, but not quite enough to win • Prosecutor in the Scopes’ trial Delivered the famous “Cross of Gold” speech denouncing bankers for “crucifying mankind on a cross of gold”
William Jennings Bryan • Beginning in 1896, Bryan ran for President (Populist Party) many times & received many votes, but not quite enough to win • Prosecutor in the Scopes’ trial Delivered the famous “Cross of Gold” speech denouncing bankers for “crucifying mankind on a cross of gold”
 Causes of Economic Growth and Prosperity • Higher wages & shorter workdays paved the way for a decade long buying spree that kept the economy booming People began believing in their ability to pay their debt over time, so they started to buy more & more; unfortunately, some bought more on credit faster than their income increased
Causes of Economic Growth and Prosperity • Higher wages & shorter workdays paved the way for a decade long buying spree that kept the economy booming People began believing in their ability to pay their debt over time, so they started to buy more & more; unfortunately, some bought more on credit faster than their income increased
 Harlem Renaissance • Urban Ghetto in New York City with the largest number of African Americans that had traveled to the North from the South during the Great Migration • African American Culture Music (Jazz & Blues) Poetry Art Work • Spread to other major cities Originating in New Orleans from African American Blues & West African rhythms. Jazz was so popular the era was called the Jazz Age. Duke Ellington & Louis Armstrong were the most famous musicians of that time. Langston Hughes Famous African American writer/poet Wrote about racial oppression Known as the “Black Poet Laureate” Jazz
Harlem Renaissance • Urban Ghetto in New York City with the largest number of African Americans that had traveled to the North from the South during the Great Migration • African American Culture Music (Jazz & Blues) Poetry Art Work • Spread to other major cities Originating in New Orleans from African American Blues & West African rhythms. Jazz was so popular the era was called the Jazz Age. Duke Ellington & Louis Armstrong were the most famous musicians of that time. Langston Hughes Famous African American writer/poet Wrote about racial oppression Known as the “Black Poet Laureate” Jazz
 • Young artists, such as poets & writers, became disillusioned with America & materialism • Some big names of the day – F. Scott Fitzgerald – Ernest Hemingway – Robert Frost – Georgia O’Keefe.
• Young artists, such as poets & writers, became disillusioned with America & materialism • Some big names of the day – F. Scott Fitzgerald – Ernest Hemingway – Robert Frost – Georgia O’Keefe.

 The Great Depression • 1929 – 1941 • Presidents Hoover & FDR • Hoover felt that federal gov’t should not get involved; he began some programs, but they were too little, too late §FDR – President during bulk of the Depression; his New Deal domestic plan initiated many programs such as the Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC) & the Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA WWII ended the Depression
The Great Depression • 1929 – 1941 • Presidents Hoover & FDR • Hoover felt that federal gov’t should not get involved; he began some programs, but they were too little, too late §FDR – President during bulk of the Depression; his New Deal domestic plan initiated many programs such as the Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC) & the Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA WWII ended the Depression
 Causes of the Great Depression • Stock Market Crash • Companies were producing more goods than people could afford to buy • Not all groups of people shared in prosperity of the 20’s; farmers really suffered the worst • Real estate speculation & get rich schemes • Many banks made poor decisions about who to loan money to • Over extension of debt by buying on credit
Causes of the Great Depression • Stock Market Crash • Companies were producing more goods than people could afford to buy • Not all groups of people shared in prosperity of the 20’s; farmers really suffered the worst • Real estate speculation & get rich schemes • Many banks made poor decisions about who to loan money to • Over extension of debt by buying on credit
 Decline in World Trade • High US tariffs kept European products out of the US; other countries retaliated by imposing their own high tariffs • World trade came to a halt, a major contributor to the deepening of the Great Depression
Decline in World Trade • High US tariffs kept European products out of the US; other countries retaliated by imposing their own high tariffs • World trade came to a halt, a major contributor to the deepening of the Great Depression
 Stock Market Crash • 1929 • Caused by over speculation & buying stocks on margin • People could not repay their loans or rent • Caused banks to close • One event that led to the Depression
Stock Market Crash • 1929 • Caused by over speculation & buying stocks on margin • People could not repay their loans or rent • Caused banks to close • One event that led to the Depression
 Social Security Act • Provided for old age & disability survivors • Provides workers with Unemployment support • Insurance for families if the parents died • We still have it today, but more money is going out than coming in
Social Security Act • Provided for old age & disability survivors • Provides workers with Unemployment support • Insurance for families if the parents died • We still have it today, but more money is going out than coming in
 Securities Exchange Commission (SEC) • Authorized in 1934 • Protects the public against fraud, deception, & inside manipulation in the stock market. • Continues to be important today.
Securities Exchange Commission (SEC) • Authorized in 1934 • Protects the public against fraud, deception, & inside manipulation in the stock market. • Continues to be important today.
 Effects of the Great Depression on the Economy üExpanded federal gov’t in the economy üGuaranteed a wide range of social & economic benefits üCaused a ripple in society that displaced families, jobs, & fortunes
Effects of the Great Depression on the Economy üExpanded federal gov’t in the economy üGuaranteed a wide range of social & economic benefits üCaused a ripple in society that displaced families, jobs, & fortunes
 sit Insurance Federal Depo ration (FDIC) Corpo Insured individual deposits up to $5, 000 Created as result of the Great Depression in the 30’s when banks failed & people lost their money Still exists today to safeguard our money
sit Insurance Federal Depo ration (FDIC) Corpo Insured individual deposits up to $5, 000 Created as result of the Great Depression in the 30’s when banks failed & people lost their money Still exists today to safeguard our money
 Dust Bowl Depicted in The Grapes of Wrath Drought hit Great Plains, many farmers headed west to CA in hopes of a better life Dorothea Lange, photographer, changed the way public & gov’t viewed the country’s poor 1930’s
Dust Bowl Depicted in The Grapes of Wrath Drought hit Great Plains, many farmers headed west to CA in hopes of a better life Dorothea Lange, photographer, changed the way public & gov’t viewed the country’s poor 1930’s

 ise of R orship ictat D After WWI, Europe was unstable; Dictators took control of Italy & Germany due to much suffering Japan began to expand its empire by moving into China U. S. returned to its traditional policy of isolationism set by Washington
ise of R orship ictat D After WWI, Europe was unstable; Dictators took control of Italy & Germany due to much suffering Japan began to expand its empire by moving into China U. S. returned to its traditional policy of isolationism set by Washington
 945 &1 941 1 1941 - Japan attacked Pearl Harbor & U. S. entered into WWII 1945 - End of WWII with the dropping of the atomic bombs on Japan
945 &1 941 1 1941 - Japan attacked Pearl Harbor & U. S. entered into WWII 1945 - End of WWII with the dropping of the atomic bombs on Japan
 Attack on Pearl H Dec. 7, 1941, Japanese planes attacked Pearl Harbor, Hawaii arbor Caused U. S. to enter into war against Japan Since Italy & Germany had alliance with Japan, these countries declared war on the U. S.
Attack on Pearl H Dec. 7, 1941, Japanese planes attacked Pearl Harbor, Hawaii arbor Caused U. S. to enter into war against Japan Since Italy & Germany had alliance with Japan, these countries declared war on the U. S.
 Rationing in WWII Meat, Sugar, Gasoline & rubber were severely limited Ration books were used Victory gardens were planted Everyone sacrificed to help with war effort
Rationing in WWII Meat, Sugar, Gasoline & rubber were severely limited Ration books were used Victory gardens were planted Everyone sacrificed to help with war effort
 Japanese Internment War produced animosity toward Japanese & Japanese Americans Many feared these people might commit acts of sabotage War relocation authority carried out policy of forcing Japanese Americans into relocation camps Forced to live behind barbed wire in primitive & crowded conditions
Japanese Internment War produced animosity toward Japanese & Japanese Americans Many feared these people might commit acts of sabotage War relocation authority carried out policy of forcing Japanese Americans into relocation camps Forced to live behind barbed wire in primitive & crowded conditions
 Women in WWII Worked outside the home in great numbers Fashions changed because of a shortage of certain materials Rosie the Riveter was the new image of a woman who could work in a factory & do a “man’s” job
Women in WWII Worked outside the home in great numbers Fashions changed because of a shortage of certain materials Rosie the Riveter was the new image of a woman who could work in a factory & do a “man’s” job
 Name given to the mass slaughter of Jews & other groups of people by the Nazis during WWII
Name given to the mass slaughter of Jews & other groups of people by the Nazis during WWII
 Invasion of Normandy “D –Day” June 6, 1944 Allied invasion of France Soviet Union had pushed for this because it opened up a second front in Europe
Invasion of Normandy “D –Day” June 6, 1944 Allied invasion of France Soviet Union had pushed for this because it opened up a second front in Europe
 Battle of Midway June 3 -6, 1942 Most important battle in the Pacific during WWII Turning point of the war in the Pacific Japanese went on defensive & U. S. began to liberate Pacific islands from Japanese control
Battle of Midway June 3 -6, 1942 Most important battle in the Pacific during WWII Turning point of the war in the Pacific Japanese went on defensive & U. S. began to liberate Pacific islands from Japanese control
 t of the Atomic Developmen Bomb Code name: Manhattan Project First atomic bomb was detonated in 1945 in New Mexico Results revealed prompt & utter destruction
t of the Atomic Developmen Bomb Code name: Manhattan Project First atomic bomb was detonated in 1945 in New Mexico Results revealed prompt & utter destruction
 tomic e the A n to us Decisio man’s Tru Bomb Provided a quick end to war in the Pacific in 1945 Saved countless American lives by not invading Japan
tomic e the A n to us Decisio man’s Tru Bomb Provided a quick end to war in the Pacific in 1945 Saved countless American lives by not invading Japan
 The G. I. Bill Passed in 1944 during WWII Provided education, medical care, job training, unemployment pensions, & offered low mortgage loans to veterans These loans led to the growth of the suburbs in the 1950’s
The G. I. Bill Passed in 1944 during WWII Provided education, medical care, job training, unemployment pensions, & offered low mortgage loans to veterans These loans led to the growth of the suburbs in the 1950’s

 old War C Between the U. S. & Soviet Union, the 2 remaining Super Powers There was a great fear of Nuclear warfare The Truman Doctrine U. S. issued policy of containment to prevent spread of Communism throughout the world
old War C Between the U. S. & Soviet Union, the 2 remaining Super Powers There was a great fear of Nuclear warfare The Truman Doctrine U. S. issued policy of containment to prevent spread of Communism throughout the world
 n Doctrine Truma 1947 President Truman’s foreign policy Stated that America would give economic & military aid to any nation threatened by Communism $400 Million in aid went to Greece & Turkey
n Doctrine Truma 1947 President Truman’s foreign policy Stated that America would give economic & military aid to any nation threatened by Communism $400 Million in aid went to Greece & Turkey
 Marshall Plan 1947 Sec. of State George Marshall proposed Granted $12 billion in aid to European nations Plan to help rebuild Europe after WWII to keep Communism from taking over
Marshall Plan 1947 Sec. of State George Marshall proposed Granted $12 billion in aid to European nations Plan to help rebuild Europe after WWII to keep Communism from taking over
 Atlantic Treaty North ization (NATO) Organ Formed after WWII by 10 western European nations declaring that an attack against one member would be construed as a attack against all In response, eastern European nations formed Warsaw Pact The U. S. & Canada also joined
Atlantic Treaty North ization (NATO) Organ Formed after WWII by 10 western European nations declaring that an attack against one member would be construed as a attack against all In response, eastern European nations formed Warsaw Pact The U. S. & Canada also joined
 Berlin Airlift ü 1948 -1949: England, France, & U. S. had merged their occupation zone into a new West Germany Republic. üUSSR prohibited all land traffic between Berlin & West Germany üU. S. dropped supplies until the blockade was lifted. ü 1949: Germany was officially divided.
Berlin Airlift ü 1948 -1949: England, France, & U. S. had merged their occupation zone into a new West Germany Republic. üUSSR prohibited all land traffic between Berlin & West Germany üU. S. dropped supplies until the blockade was lifted. ü 1949: Germany was officially divided.
 Mc. Carthyism ü 1950 s üSenator Joseph Mc. Carthy claimed hundreds of communists had infiltrated U. S. state department üHighly publicized investigation where many people were wrongly accused üCreated fear of a Communist revolution in U. S.
Mc. Carthyism ü 1950 s üSenator Joseph Mc. Carthy claimed hundreds of communists had infiltrated U. S. state department üHighly publicized investigation where many people were wrongly accused üCreated fear of a Communist revolution in U. S.
 Korean War ü 1948 -North Korea was Communist & South Korea was free ü 1950 -North Korea entered South Korea & U. S. entered to help expel North Koreans from South Korea üCommunism was contained without world war or atomic weapons ü 1953 -an agreement was reached, a cease-fire üThe war increased the fear of communism back home
Korean War ü 1948 -North Korea was Communist & South Korea was free ü 1950 -North Korea entered South Korea & U. S. entered to help expel North Koreans from South Korea üCommunism was contained without world war or atomic weapons ü 1953 -an agreement was reached, a cease-fire üThe war increased the fear of communism back home
 Sputnik 1 ü 1957 ü 1 st satellite launched by Soviets ü Showed how Soviets were more advanced than the US üThis meant Soviet Union could also use missiles to carry nuclear weapons üCaused a great increase in science education & research in the U. S.
Sputnik 1 ü 1957 ü 1 st satellite launched by Soviets ü Showed how Soviets were more advanced than the US üThis meant Soviet Union could also use missiles to carry nuclear weapons üCaused a great increase in science education & research in the U. S.
 üFrench lost in 1954 & failure to hold promised free election caused a civil war üU. S. entered to stop the spread of communism. üWar lasted from 1963 to 1975 üCaused protests in U. S. because the war was not “our” war & many lives were being lost üDivided America üThere was no victory üU. S. took more cautious attitude toward foreign affairs
üFrench lost in 1954 & failure to hold promised free election caused a civil war üU. S. entered to stop the spread of communism. üWar lasted from 1963 to 1975 üCaused protests in U. S. because the war was not “our” war & many lives were being lost üDivided America üThere was no victory üU. S. took more cautious attitude toward foreign affairs
 Tet Offensive ü 1968 üTurning Point of Vietnam War üSurprise attack by North Vietnamese on the South üMade Americans see that U. S. would not be able to win & that it would end in a stalemate üIt further divided the country
Tet Offensive ü 1968 üTurning Point of Vietnam War üSurprise attack by North Vietnamese on the South üMade Americans see that U. S. would not be able to win & that it would end in a stalemate üIt further divided the country
 26 th Amendment ü 1971 üDue to Vietnam War, legal voting age was lowered from 21 to 18
26 th Amendment ü 1971 üDue to Vietnam War, legal voting age was lowered from 21 to 18

 ü 1954—Polio Vaccine ü 1963—Measles vaccine improved public health, decreased infant mortality rate, & increased life expectancy
ü 1954—Polio Vaccine ü 1963—Measles vaccine improved public health, decreased infant mortality rate, & increased life expectancy
 üReversed Plessey vs. Ferguson ü 1954 Supreme Court ruled segregation of blacks & whites in public schools was unconstitutional ü 1 st step toward school desegregation üProcess of desegregating took until the early 1970 s
üReversed Plessey vs. Ferguson ü 1954 Supreme Court ruled segregation of blacks & whites in public schools was unconstitutional ü 1 st step toward school desegregation üProcess of desegregating took until the early 1970 s
 üProhibited discrimination by employers & unions üGuaranteed equal access to school & public accommodations
üProhibited discrimination by employers & unions üGuaranteed equal access to school & public accommodations
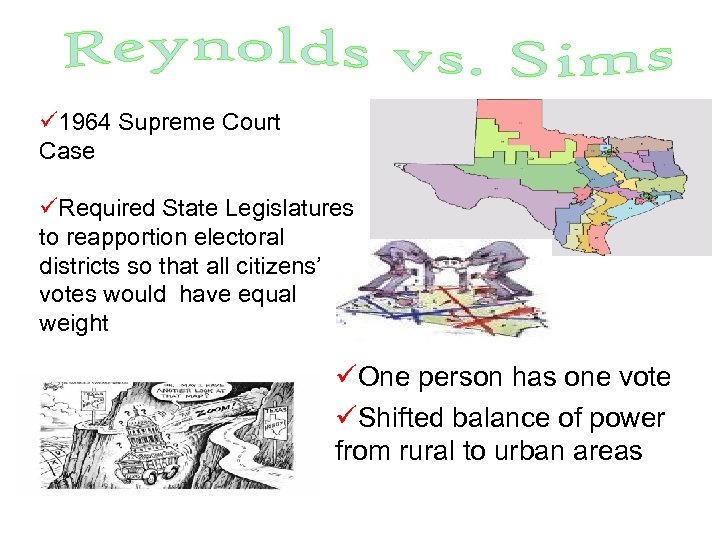 ü 1964 Supreme Court Case üRequired State Legislatures to reapportion electoral districts so that all citizens’ votes would have equal weight üOne person has one vote üShifted balance of power from rural to urban areas
ü 1964 Supreme Court Case üRequired State Legislatures to reapportion electoral districts so that all citizens’ votes would have equal weight üOne person has one vote üShifted balance of power from rural to urban areas
 Martin Luther King Jr üLed Montgomery Bus Boycott üBaptist Minister üAssassinated in 1968 üAdvocated passive, nonviolent resistance as a means of protesting & encouraged other blacks to employ such methods
Martin Luther King Jr üLed Montgomery Bus Boycott üBaptist Minister üAssassinated in 1968 üAdvocated passive, nonviolent resistance as a means of protesting & encouraged other blacks to employ such methods
 üProblems in the environment: smog, oil spills, garbage, toxic waste ü 1970 President Nixon created the EPA üGoals were to set & enforce pollution standards, promote research, reduce air pollution üTo the present day, this movement is still very active
üProblems in the environment: smog, oil spills, garbage, toxic waste ü 1970 President Nixon created the EPA üGoals were to set & enforce pollution standards, promote research, reduce air pollution üTo the present day, this movement is still very active
 ü 1990 üPresident George Bush üIraq’s Saddam Hussein sent soldiers to invade Kuwait, an oil rich country üHoping Iraq would withdraw, the UN, led by the U. S. imposed economic sanctions on Iraq ü 1991 Operation Desert Storm went into effect since Iraq would not withdraw. This meant full scale war üKuwait was liberated
ü 1990 üPresident George Bush üIraq’s Saddam Hussein sent soldiers to invade Kuwait, an oil rich country üHoping Iraq would withdraw, the UN, led by the U. S. imposed economic sanctions on Iraq ü 1991 Operation Desert Storm went into effect since Iraq would not withdraw. This meant full scale war üKuwait was liberated
 ü 1978 Supreme Court Case üA white student had to be admitted to the University of California Medical School üExample of reverse discrimination
ü 1978 Supreme Court Case üA white student had to be admitted to the University of California Medical School üExample of reverse discrimination
 ü 1964 üAbolished poll tax, no longer need to pay to vote üHelped the poor & minorities
ü 1964 üAbolished poll tax, no longer need to pay to vote üHelped the poor & minorities
 üRatified 1993 üLowered tariffs üBrought Mexico into the free trade zone with US & Canada
üRatified 1993 üLowered tariffs üBrought Mexico into the free trade zone with US & Canada
 üMilitant organization üFormed in 1968 üFighting for rights of Native Americans üStand off at Wounded Knee, South Dakota
üMilitant organization üFormed in 1968 üFighting for rights of Native Americans üStand off at Wounded Knee, South Dakota


