d15d800b4b8b410c639424c29db4087e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 48

SSWG 3 The student will describe the interaction of physical and human systems that have shaped contemporary North Africa/Southwest Asia.

Importance of North Africa and the Middle East’s Features
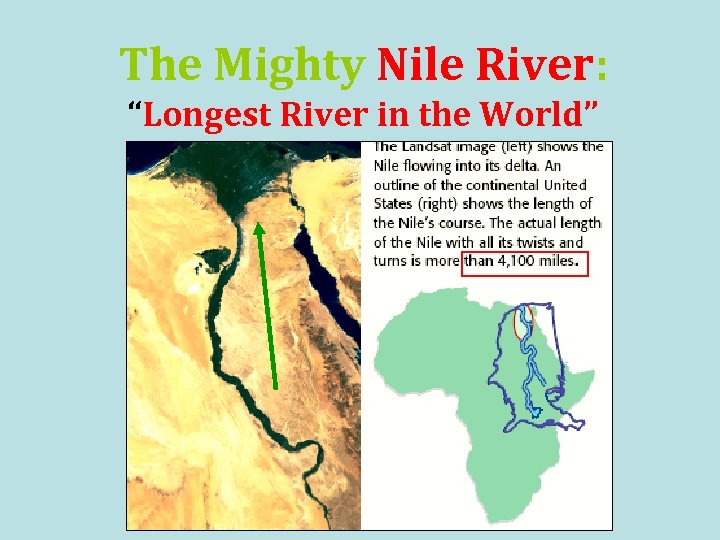
The Mighty Nile River: “Longest River in the World”

Egypt: The “Gift of the Nile” Nile Delta Annual Nile Flooding 95% of the Egyptian people live on 5% of the land!

The Tigris & Euphrates River System Mesopotamia: ”Land Between the Two Rivers” aka the Fertile Crescent

Sinai Peninsula in between Egypt and Arabian Peninsula

Dead Sea: Lowest Point on Earth 2, 300 feet below sea level Highest Salt Content (33%) *9 x saltier than ocean

Suez Canal • Links Med to Red Sea

Suez Canal Completed by the British in 1869

Strait of Hormuz -Most important strait in WORLD b/c only way to LOTS of OIL
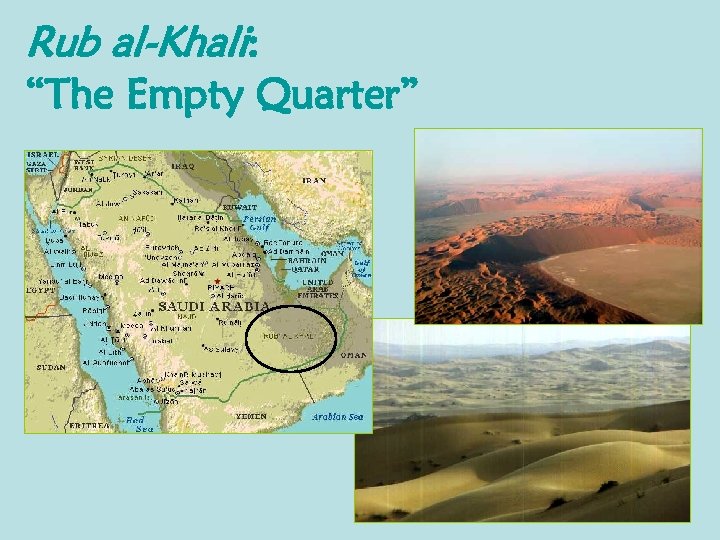
Rub al-Khali: “The Empty Quarter”

Importance of Mountains & Rivers • Why are mountains important to people? – Are NATURAL barriers of protection – Deserts can also be natural boundaries • Why are rivers of great importance? 1. 2. 3. 4. Supply water to drink Supply Food Good source of water for crops Transportation


Climate, Vegetation, and Resources of North Africa/SW Asia
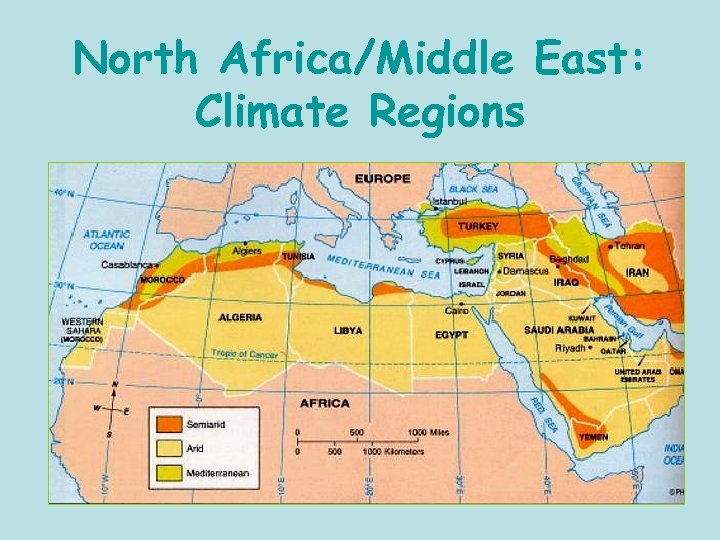
North Africa/Middle East: Climate Regions

Climate • Desert Climate – 50% of N. Africa & S. W. Asia – Semi-Arid (not as dry as desert) – Mediterranean – Highland
The Sahara • Largest desert in the world = 3. 5 million sq. miles • The size of the US

Mediterranean Climate • Hot, dry summers, & cool rainy winters • Found primarily in countries that border bodies of water http: //www. classzone. com/cz/books/world_geography 05/get_ch apter_group. htm? cin=7&rg=map_center&at=maps&var=maps

Highland Climates • Tops of mountains and plateaus • Areas where major food crops are grown cereals • Most rainfall of the region

• Oasis = places in the desert where water is present • Desertification = land becoming more dry and so turns into desert
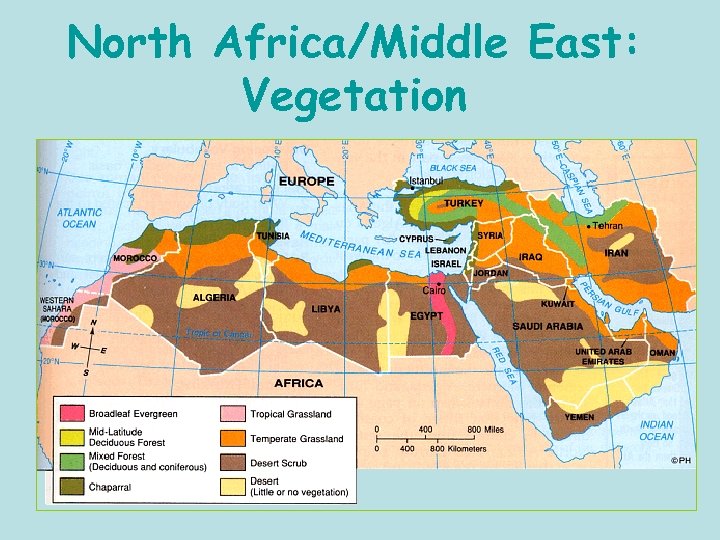
North Africa/Middle East: Vegetation

Desert • The #1 vegetation region throughout North Africa and the Middle East

Steppe/Grasslands • Area surrounding deserts • Grassy areas where people can live and where animals can be raised Pastoralism (domesticating and raising animals and living off them)

The Natural Resources of the North Africa/Middle East

Natural Resources • Petroleum & Natural Gas • 60% of the world’s known petroleum reserves
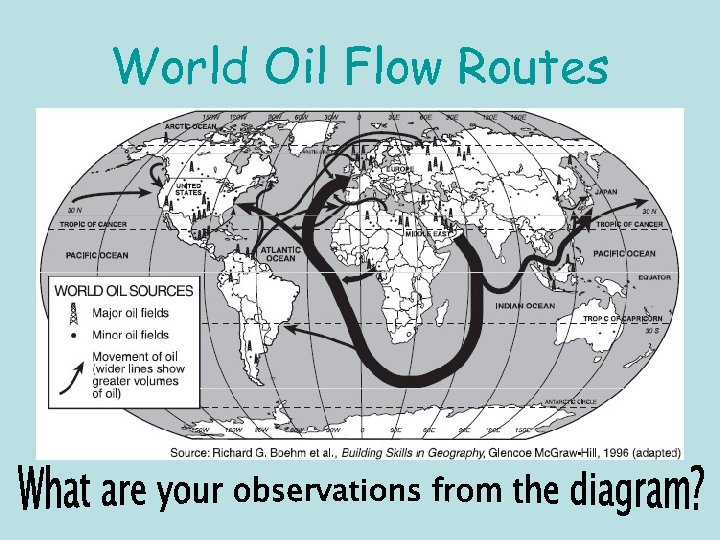
World Oil Flow Routes
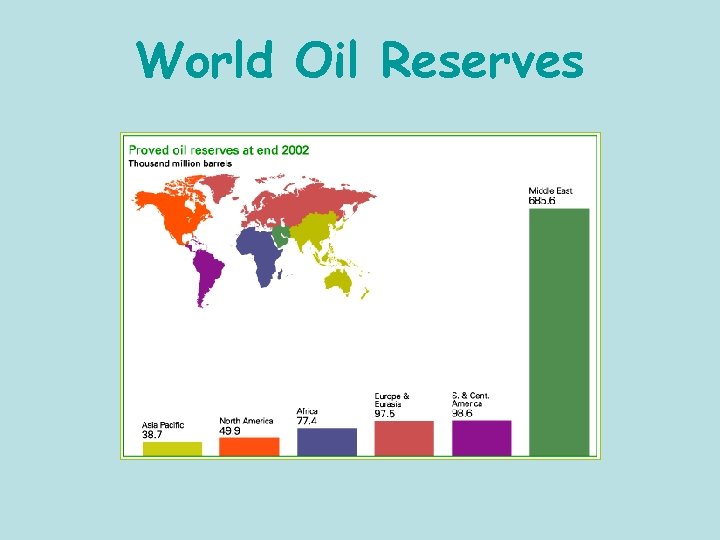
World Oil Reserves
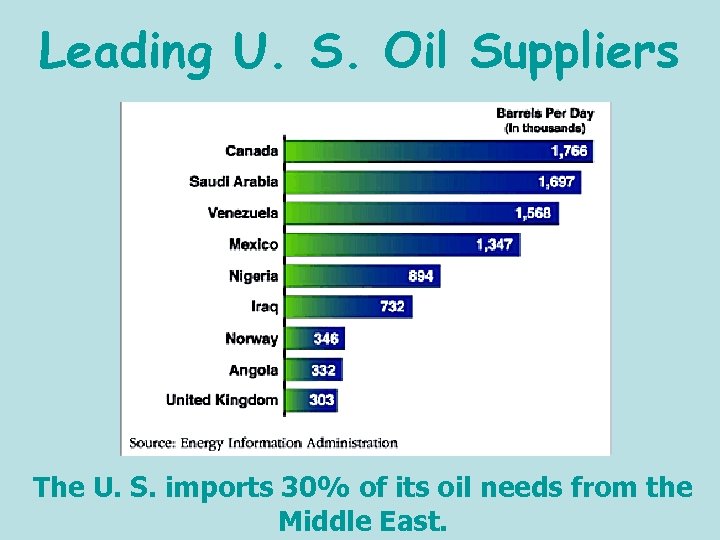
Leading U. S. Oil Suppliers The U. S. imports 30% of its oil needs from the Middle East.

Human Geography The Culture of North Africa and the Middle East
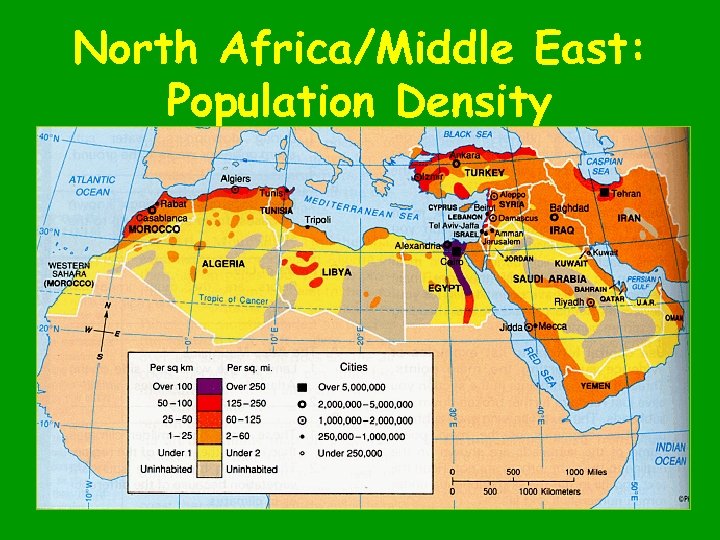
North Africa/Middle East: Population Density

Cairo, Egypt: Most Populated City in the Middle East 17, 000+ People!

Desert Bedouins– people who have no permanent home and live off of the land.

Arabs • Speak Arabic • Mostly Muslims • Most trace ancestry back to the Arabian Peninsula – Civilizations such as Egyptians & Babylonians

Israelis • 6 million people in the region • Citizens of the country of Israel • Of the people 5 million are Jewish, 1 million Arab (Palestinians) • Fighting between Jews and Palestinians is a constant occurrence because both claim rights to the land want to be in control

Turks • Ottoman Turks – ruled an empire in eastern Mediterranean (modern day Turkey) • Not Arab, but most practice Islam • Unique culture that blends Turkish, Islamic, and Western elements TURKEY NOT TURKEY

Iranians • Speak Farsi, an Indo-European language that is related to English • Practice a form of Islam known as Shi’ite • A religious state the religious leaders run the government

Islam

Islam An Abrahamic Religion Z Muslims are strict monotheists. Z They believe in the Judeo. Christian God, which they call Allah. Z Muslims believe that the Torah and the Bible, like the Qur’an, is the word of God.

The Prophetic Tradition Adam Noah Abraham Moses Jesus Muhammad


1. Faith Z The declaration of faith: There is no god worthy of worship except God, and Muhammad is His Messenger [or Prophet]. 1

2. Prayer Z The mandatory prayers performed 5 times a day: * dawn * noon * late afternoon * sunset * before going to bed Z Wash before praying. Z Face Mecca and use a prayer rug. 2

3. Giving to the poor Z Almsgiving (charitable donations). Z Muslims believe that all things belong to God. Z way to both “purification” and “growth. ” Z About 2. 5% of your income. 3

4. Fasting Z Fasting during the holy month of Ramadan. Z Considered a method of selfpurification. Z No eating or drinking from sunrise to sunset during Ramadan. 4

5. The Hajj (pilgrimage) Z The pilgrimage to Mecca. Z Must be done at least once in a Muslim’s lifetime. Z 2 -3 million Muslims make the pilgrimage every year. 5


Judaism Beliefs • Monotheistic • Holy Book=Torah • Prophet=Abraham • 10 Commandments (Laws) • Holidays/Celebration: – Yom Kippur (Day of Atonement) – Rosh Hashanah (Jewish New Year) – Bar/Bat Mitzvah (becoming an adult)
d15d800b4b8b410c639424c29db4087e.ppt