5097ad1acf72654faf8380330ed97cf4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 54
 SSMED Emerging Service Science, Management, Engineering, and Design Emerging Service Science and the Future Wealth of Nations Jim Spohrer, Director, Service Research, IBM Almaden Research Center November 7 th, 2008 22 nd Service Conference and Workshop, University of Westminister, UK Acknowledgement: Thanks to IBM and NSF grant IIS-0527770 for support. 1 Service Research and Innovation | Almaden Research Center © 2007 IBM Corporation
SSMED Emerging Service Science, Management, Engineering, and Design Emerging Service Science and the Future Wealth of Nations Jim Spohrer, Director, Service Research, IBM Almaden Research Center November 7 th, 2008 22 nd Service Conference and Workshop, University of Westminister, UK Acknowledgement: Thanks to IBM and NSF grant IIS-0527770 for support. 1 Service Research and Innovation | Almaden Research Center © 2007 IBM Corporation
 Outline § National Wealth 4 Knowledge 4 Specialists 4 Industries § Towards a Science of Service Systems 4 4 Create them 4 2 Improve them A Moore’s Law? Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Outline § National Wealth 4 Knowledge 4 Specialists 4 Industries § Towards a Science of Service Systems 4 4 Create them 4 2 Improve them A Moore’s Law? Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
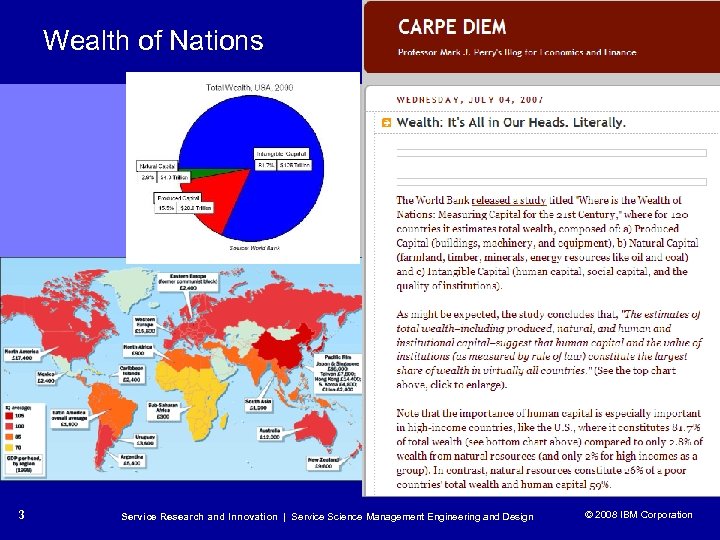 Wealth of Nations 3 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Wealth of Nations 3 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
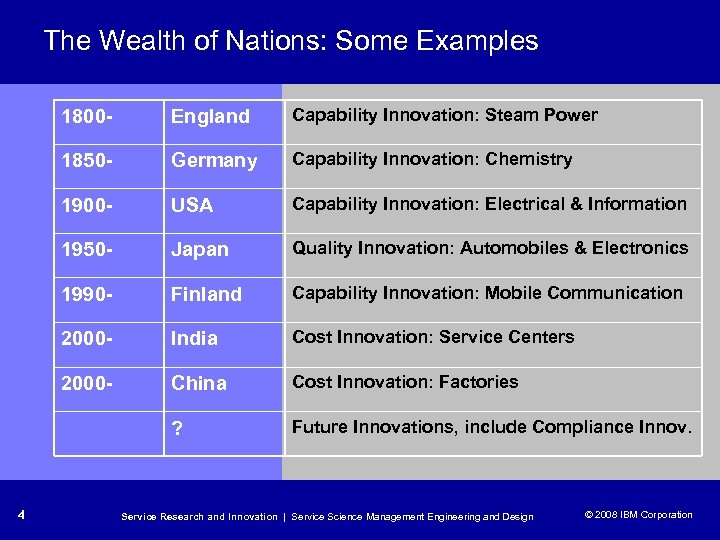 The Wealth of Nations: Some Examples 1800 - Capability Innovation: Steam Power 1850 - Germany Capability Innovation: Chemistry 1900 - USA Capability Innovation: Electrical & Information 1950 - Japan Quality Innovation: Automobiles & Electronics 1990 - Finland Capability Innovation: Mobile Communication 2000 - India Cost Innovation: Service Centers 2000 - China Cost Innovation: Factories ? 4 England Future Innovations, include Compliance Innov. Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
The Wealth of Nations: Some Examples 1800 - Capability Innovation: Steam Power 1850 - Germany Capability Innovation: Chemistry 1900 - USA Capability Innovation: Electrical & Information 1950 - Japan Quality Innovation: Automobiles & Electronics 1990 - Finland Capability Innovation: Mobile Communication 2000 - India Cost Innovation: Service Centers 2000 - China Cost Innovation: Factories ? 4 England Future Innovations, include Compliance Innov. Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
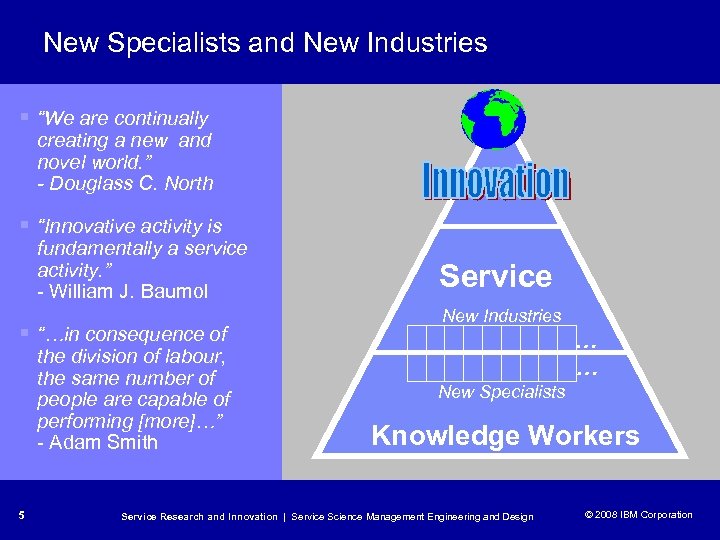 New Specialists and New Industries § “We are continually creating a new and novel world. ” - Douglass C. North § “Innovative activity is fundamentally a service activity. ” - William J. Baumol § “…in consequence of the division of labour, the same number of people are capable of performing [more]…” - Adam Smith 5 Service New Industries … … New Specialists Knowledge Workers Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
New Specialists and New Industries § “We are continually creating a new and novel world. ” - Douglass C. North § “Innovative activity is fundamentally a service activity. ” - William J. Baumol § “…in consequence of the division of labour, the same number of people are capable of performing [more]…” - Adam Smith 5 Service New Industries … … New Specialists Knowledge Workers Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
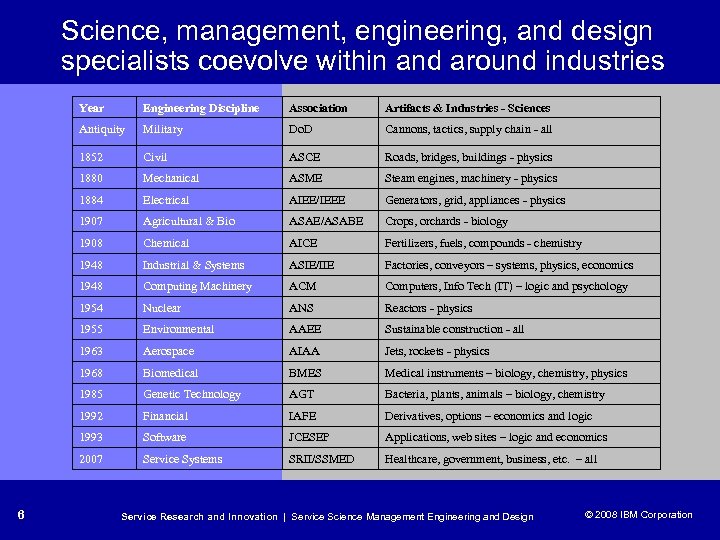 Science, management, engineering, and design specialists coevolve within and around industries Year Association Artifacts & Industries - Sciences Antiquity Military Do. D Cannons, tactics, supply chain - all 1852 Civil ASCE Roads, bridges, buildings - physics 1880 Mechanical ASME Steam engines, machinery - physics 1884 Electrical AIEE/IEEE Generators, grid, appliances - physics 1907 Agricultural & Bio ASAE/ASABE Crops, orchards - biology 1908 Chemical AICE Fertilizers, fuels, compounds - chemistry 1948 Industrial & Systems ASIE/IIE Factories, conveyors – systems, physics, economics 1948 Computing Machinery ACM Computers, Info Tech (IT) – logic and psychology 1954 Nuclear ANS Reactors - physics 1955 Environmental AAEE Sustainable construction - all 1963 Aerospace AIAA Jets, rockets - physics 1968 Biomedical BMES Medical instruments – biology, chemistry, physics 1985 Genetic Technology AGT Bacteria, plants, animals – biology, chemistry 1992 Financial IAFE Derivatives, options – economics and logic 1993 Software JCESEP Applications, web sites – logic and economics 2007 6 Engineering Discipline Service Systems SRII/SSMED Healthcare, government, business, etc. – all Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Science, management, engineering, and design specialists coevolve within and around industries Year Association Artifacts & Industries - Sciences Antiquity Military Do. D Cannons, tactics, supply chain - all 1852 Civil ASCE Roads, bridges, buildings - physics 1880 Mechanical ASME Steam engines, machinery - physics 1884 Electrical AIEE/IEEE Generators, grid, appliances - physics 1907 Agricultural & Bio ASAE/ASABE Crops, orchards - biology 1908 Chemical AICE Fertilizers, fuels, compounds - chemistry 1948 Industrial & Systems ASIE/IIE Factories, conveyors – systems, physics, economics 1948 Computing Machinery ACM Computers, Info Tech (IT) – logic and psychology 1954 Nuclear ANS Reactors - physics 1955 Environmental AAEE Sustainable construction - all 1963 Aerospace AIAA Jets, rockets - physics 1968 Biomedical BMES Medical instruments – biology, chemistry, physics 1985 Genetic Technology AGT Bacteria, plants, animals – biology, chemistry 1992 Financial IAFE Derivatives, options – economics and logic 1993 Software JCESEP Applications, web sites – logic and economics 2007 6 Engineering Discipline Service Systems SRII/SSMED Healthcare, government, business, etc. – all Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
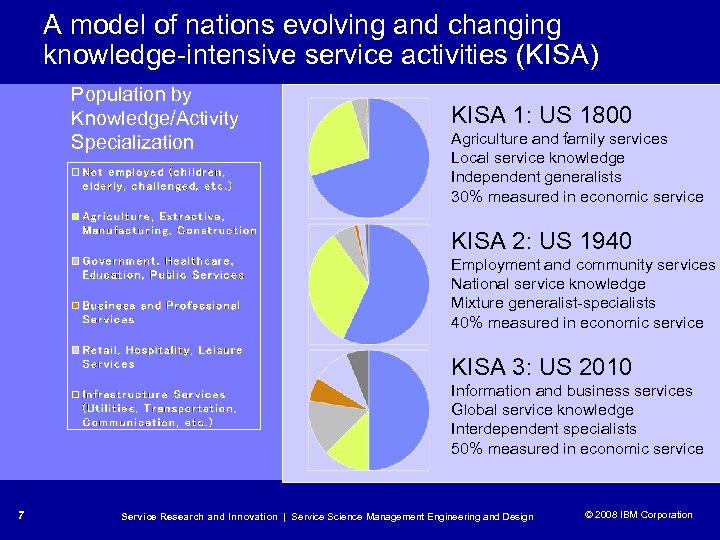 A model of nations evolving and changing knowledge-intensive service activities (KISA) Population by Knowledge/Activity Specialization KISA 1: US 1800 Agriculture and family services Local service knowledge Independent generalists 30% measured in economic service KISA 2: US 1940 Employment and community services National service knowledge Mixture generalist-specialists 40% measured in economic service KISA 3: US 2010 Information and business services Global service knowledge Interdependent specialists 50% measured in economic service 7 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
A model of nations evolving and changing knowledge-intensive service activities (KISA) Population by Knowledge/Activity Specialization KISA 1: US 1800 Agriculture and family services Local service knowledge Independent generalists 30% measured in economic service KISA 2: US 1940 Employment and community services National service knowledge Mixture generalist-specialists 40% measured in economic service KISA 3: US 2010 Information and business services Global service knowledge Interdependent specialists 50% measured in economic service 7 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
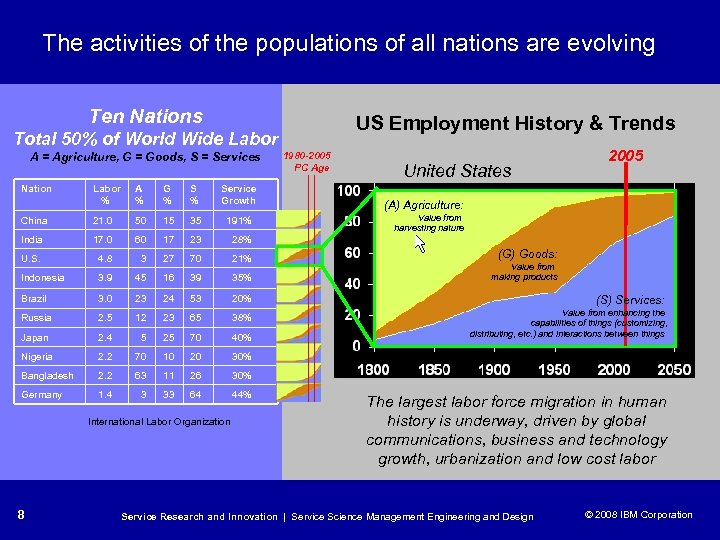 The activities of the populations of all nations are evolving Ten Nations US Employment History & Trends Total 50% of World Wide Labor A = Agriculture, G = Goods, S = Services Nation Labor % A % G % Service Growth China 21. 0 50 15 35 191% India 17. 0 60 17 23 4. 8 3 27 70 21% Indonesia 3. 9 45 16 39 35% Brazil 3. 0 23 24 53 United States 20% 2005 28% U. S. 1980 -2005 PC Age Russia 2. 5 12 23 65 38% Japan 2. 4 5 25 70 40% Nigeria 2. 2 70 10 20 2. 2 63 11 26 1. 4 3 33 64 44% (G) Goods: Value from making products (S) Services: Value from enhancing the capabilities of things (customizing, distributing, etc. ) and interactions between things 30% Germany Value from harvesting nature 30% Bangladesh (A) Agriculture: International Labor Organization 8 The largest labor force migration in human history is underway, driven by global communications, business and technology growth, urbanization and low cost labor Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
The activities of the populations of all nations are evolving Ten Nations US Employment History & Trends Total 50% of World Wide Labor A = Agriculture, G = Goods, S = Services Nation Labor % A % G % Service Growth China 21. 0 50 15 35 191% India 17. 0 60 17 23 4. 8 3 27 70 21% Indonesia 3. 9 45 16 39 35% Brazil 3. 0 23 24 53 United States 20% 2005 28% U. S. 1980 -2005 PC Age Russia 2. 5 12 23 65 38% Japan 2. 4 5 25 70 40% Nigeria 2. 2 70 10 20 2. 2 63 11 26 1. 4 3 33 64 44% (G) Goods: Value from making products (S) Services: Value from enhancing the capabilities of things (customizing, distributing, etc. ) and interactions between things 30% Germany Value from harvesting nature 30% Bangladesh (A) Agriculture: International Labor Organization 8 The largest labor force migration in human history is underway, driven by global communications, business and technology growth, urbanization and low cost labor Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
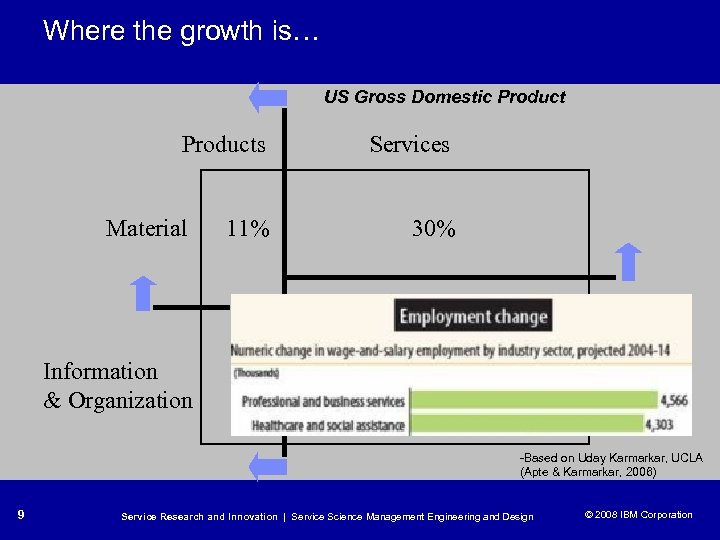 Where the growth is… US Gross Domestic Products Services Material 11% 30% Information & Organization 9% 50% -Based on Uday Karmarkar, UCLA (Apte & Karmarkar, 2006) 9 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Where the growth is… US Gross Domestic Products Services Material 11% 30% Information & Organization 9% 50% -Based on Uday Karmarkar, UCLA (Apte & Karmarkar, 2006) 9 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
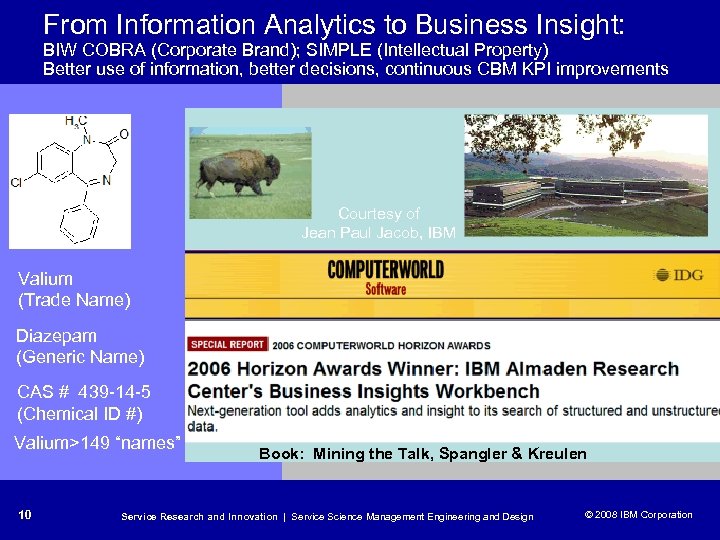 From Information Analytics to Business Insight: BIW COBRA (Corporate Brand); SIMPLE (Intellectual Property) Better use of information, better decisions, continuous CBM KPI improvements Courtesy of Jean Paul Jacob, IBM Valium (Trade Name) Diazepam (Generic Name) CAS # 439 -14 -5 (Chemical ID #) Valium>149 “names” 10 Book: Mining the Talk, Spangler & Kreulen Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
From Information Analytics to Business Insight: BIW COBRA (Corporate Brand); SIMPLE (Intellectual Property) Better use of information, better decisions, continuous CBM KPI improvements Courtesy of Jean Paul Jacob, IBM Valium (Trade Name) Diazepam (Generic Name) CAS # 439 -14 -5 (Chemical ID #) Valium>149 “names” 10 Book: Mining the Talk, Spangler & Kreulen Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
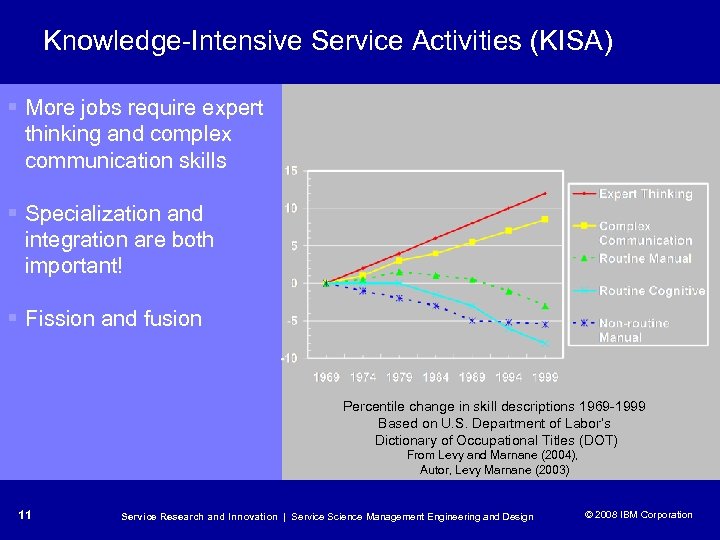 Knowledge-Intensive Service Activities (KISA) § More jobs require expert thinking and complex communication skills § Specialization and integration are both important! § Fission and fusion Percentile change in skill descriptions 1969 -1999 Based on U. S. Department of Labor’s Dictionary of Occupational Titles (DOT) From Levy and Marnane (2004), Autor, Levy Marnane (2003) 11 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Knowledge-Intensive Service Activities (KISA) § More jobs require expert thinking and complex communication skills § Specialization and integration are both important! § Fission and fusion Percentile change in skill descriptions 1969 -1999 Based on U. S. Department of Labor’s Dictionary of Occupational Titles (DOT) From Levy and Marnane (2004), Autor, Levy Marnane (2003) 11 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
 What should a service scientist know? T-shaped professionals: - expert thinking (depth in one or more areas) - complex communications (breadth across many areas) - s-schools (social science) - e-schools (engineering) - i-schools (information) - b-schools (business) complex communication § I. Theoretical & Practical Foundations 41. Concepts & Questions 42. Tools & Methods § II. Disciplines 43. History & Evolution: Economics & Law 44. Customer: Quality Measure & Marketing 45. Provider: Productivity Measure & Operations 46. Authority: Compliance Measure & Governance 47. Competitor: Sustainable Innovation Measure & Strategy 48. Privileged Access: People Resources & S Schools 49. Owned Outright: Tech Resources & E Schools expert thinking Courtesy of Jean Paul Jacob 12 410. Shared Access: Information Resources & I Schools 411. Leased/Contract: Organization Resources & B Schools 412. Future & Investment: Project & Innovation Management § III. Professions 413. Scientists, Entrepreneurs, and Designers 414. Engineers, Managers, Consultants, Practitioners For a service science outline and 200+ annotated references, refer to: http: //www. cob. sjsu. edu/ssme/refmenu. asp Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
What should a service scientist know? T-shaped professionals: - expert thinking (depth in one or more areas) - complex communications (breadth across many areas) - s-schools (social science) - e-schools (engineering) - i-schools (information) - b-schools (business) complex communication § I. Theoretical & Practical Foundations 41. Concepts & Questions 42. Tools & Methods § II. Disciplines 43. History & Evolution: Economics & Law 44. Customer: Quality Measure & Marketing 45. Provider: Productivity Measure & Operations 46. Authority: Compliance Measure & Governance 47. Competitor: Sustainable Innovation Measure & Strategy 48. Privileged Access: People Resources & S Schools 49. Owned Outright: Tech Resources & E Schools expert thinking Courtesy of Jean Paul Jacob 12 410. Shared Access: Information Resources & I Schools 411. Leased/Contract: Organization Resources & B Schools 412. Future & Investment: Project & Innovation Management § III. Professions 413. Scientists, Entrepreneurs, and Designers 414. Engineers, Managers, Consultants, Practitioners For a service science outline and 200+ annotated references, refer to: http: //www. cob. sjsu. edu/ssme/refmenu. asp Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
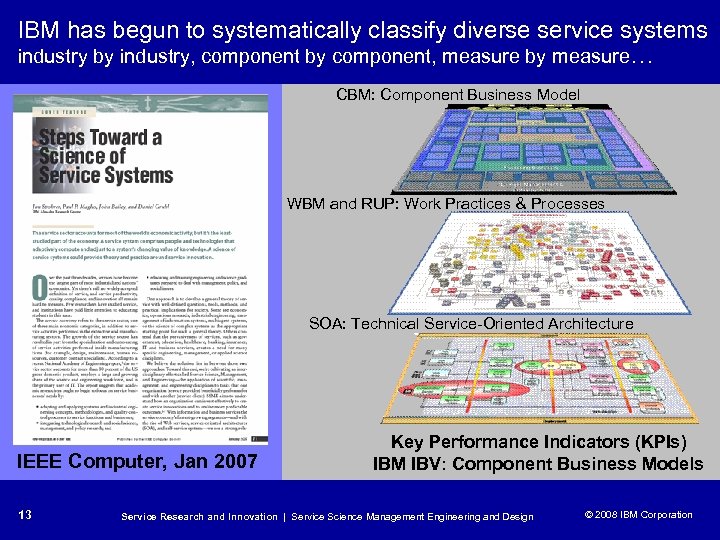 IBM has begun to systematically classify diverse service systems industry by industry, component by component, measure by measure… CBM: Component Business Model WBM and RUP: Work Practices & Processes SOA: Technical Service-Oriented Architecture IEEE Computer, Jan 2007 13 Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) IBM IBV: Component Business Models Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
IBM has begun to systematically classify diverse service systems industry by industry, component by component, measure by measure… CBM: Component Business Model WBM and RUP: Work Practices & Processes SOA: Technical Service-Oriented Architecture IEEE Computer, Jan 2007 13 Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) IBM IBV: Component Business Models Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
 Businesses as service system entities “…of the 100 entities with the largest Gross National Product (GNP), about half were multi -national corporations (MNCs)… The MNCs do not exist on traditional maps. ” Alfred Chandler and Bruce Mazlish, authors of Leviathans “The corporation has evolved constantly during its long history. The MNC of the late twentieth century … were very different from the great trading enterprises of the 1700 s. The type of business organization that is now emerging -- the globally integrated enterprise - marks just as big a leap. “ Sam Palmisano, CEO IBM in Foreign Affairs 14 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Businesses as service system entities “…of the 100 entities with the largest Gross National Product (GNP), about half were multi -national corporations (MNCs)… The MNCs do not exist on traditional maps. ” Alfred Chandler and Bruce Mazlish, authors of Leviathans “The corporation has evolved constantly during its long history. The MNC of the late twentieth century … were very different from the great trading enterprises of the 1700 s. The type of business organization that is now emerging -- the globally integrated enterprise - marks just as big a leap. “ Sam Palmisano, CEO IBM in Foreign Affairs 14 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
 Data Centers as service system entities “All data centers are unique, but they all share the same mission: to protect your company’s valuable information. ” Douglas Alger, author of Build the Best Data Center Facility for Your Business 15 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Data Centers as service system entities “All data centers are unique, but they all share the same mission: to protect your company’s valuable information. ” Douglas Alger, author of Build the Best Data Center Facility for Your Business 15 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
 Call Centers as service system entities “Call Centers For Dummies helps put a value on customer relations efforts undertaken in call centers and helps managers implement new strategies for continual improvement of customer service. ” Réal Bergevin, author of Call Centers For Dummies 16 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Call Centers as service system entities “Call Centers For Dummies helps put a value on customer relations efforts undertaken in call centers and helps managers implement new strategies for continual improvement of customer service. ” Réal Bergevin, author of Call Centers For Dummies 16 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
 Hospitals as service system entities “Modern medicine is one of those incredible works of reason: an elaborate system of specialized knowledge, technical procedures, and rules of behavior. ” Paul Starr, author of The Social Transformation of American Medicine 17 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Hospitals as service system entities “Modern medicine is one of those incredible works of reason: an elaborate system of specialized knowledge, technical procedures, and rules of behavior. ” Paul Starr, author of The Social Transformation of American Medicine 17 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
 Universities as service system entities “The contemporary American university is in fact a knowledge conglomerate in its extensive activities, and this role is costly to sustain. ” Roger L. Geiger, author of Knowledge and Money: Research Universities and the Paradox of the Marketplace 18 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Universities as service system entities “The contemporary American university is in fact a knowledge conglomerate in its extensive activities, and this role is costly to sustain. ” Roger L. Geiger, author of Knowledge and Money: Research Universities and the Paradox of the Marketplace 18 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
 Nations as service system entities “Understanding economic change including everything from the rise of the Western world to the demise of the Soviet Union requires that we cast a net much broader than purely economic change because it is a result of changes in (1) the quantity and quality of human beings; (2) in the stock of human knowledge particularly as applied to human command over nature; and (3) the institutional framework that defines the deliberate incentive structure of a society. ” Douglass C. North, author of Understanding the Process of Economic Change 19 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Nations as service system entities “Understanding economic change including everything from the rise of the Western world to the demise of the Soviet Union requires that we cast a net much broader than purely economic change because it is a result of changes in (1) the quantity and quality of human beings; (2) in the stock of human knowledge particularly as applied to human command over nature; and (3) the institutional framework that defines the deliberate incentive structure of a society. ” Douglass C. North, author of Understanding the Process of Economic Change 19 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
 Cities as service system entities “Cities are the defining artifacts of civilisation. All the achievements and failings of humanity are here… We shape the city, and then it shapes us. Today, almost half the global population lives in cities. ” John Reader, author of Cities IBM Releases ``IBM and the Future of our Cities'' Podcast IBM Press Release 2005 20 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Cities as service system entities “Cities are the defining artifacts of civilisation. All the achievements and failings of humanity are here… We shape the city, and then it shapes us. Today, almost half the global population lives in cities. ” John Reader, author of Cities IBM Releases ``IBM and the Future of our Cities'' Podcast IBM Press Release 2005 20 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
 Families as service system entities "The family is the natural and fundamental group unit of society and is entitled to protection by society and the State". Article 16(3) of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights “Developing a Family Mission Statement” Stephen R. Covey, author of The 7 Habits of Highly Effective Families “In the agricultural age, work-life-and-family blended seamlessly. ” IBM GIO 1. 0 21 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Families as service system entities "The family is the natural and fundamental group unit of society and is entitled to protection by society and the State". Article 16(3) of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights “Developing a Family Mission Statement” Stephen R. Covey, author of The 7 Habits of Highly Effective Families “In the agricultural age, work-life-and-family blended seamlessly. ” IBM GIO 1. 0 21 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
 People as service system entities “All the information workers observed experienced a high level of fragmentation in the execution of their activities. People averaged about three minutes on a task and about two minutes on any electronic device or paper document before switching tasks. ” Gloria Mark and Victor M. Gonzalez, authors of “Research on Multi-tasking in the Workplace” 22 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
People as service system entities “All the information workers observed experienced a high level of fragmentation in the execution of their activities. People averaged about three minutes on a task and about two minutes on any electronic device or paper document before switching tasks. ” Gloria Mark and Victor M. Gonzalez, authors of “Research on Multi-tasking in the Workplace” 22 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
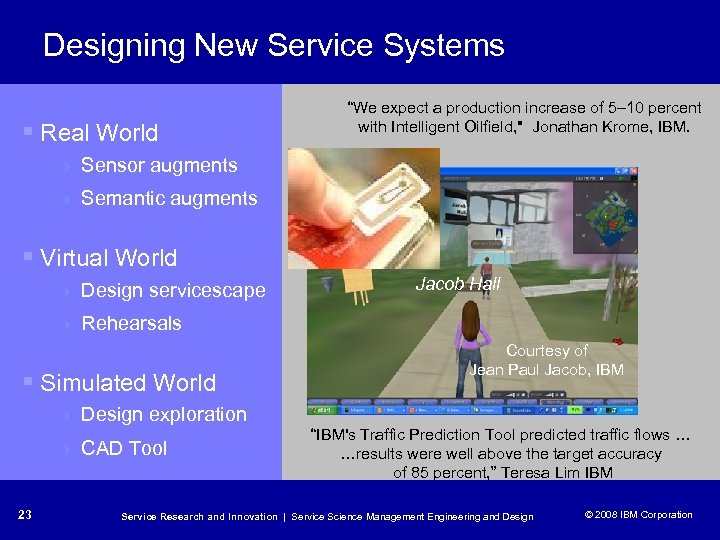 Designing New Service Systems § Real World 4 Sensor augments 4 “We expect a production increase of 5– 10 percent with Intelligent Oilfield, " Jonathan Krome, IBM. Semantic augments § Virtual World 4 Design servicescape 4 Rehearsals § Simulated World 4 4 23 Jacob Hall Design exploration CAD Tool Courtesy of Jean Paul Jacob, IBM “IBM's Traffic Prediction Tool predicted traffic flows … …results were well above the target accuracy of 85 percent, ” Teresa Lim IBM Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Designing New Service Systems § Real World 4 Sensor augments 4 “We expect a production increase of 5– 10 percent with Intelligent Oilfield, " Jonathan Krome, IBM. Semantic augments § Virtual World 4 Design servicescape 4 Rehearsals § Simulated World 4 4 23 Jacob Hall Design exploration CAD Tool Courtesy of Jean Paul Jacob, IBM “IBM's Traffic Prediction Tool predicted traffic flows … …results were well above the target accuracy of 85 percent, ” Teresa Lim IBM Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
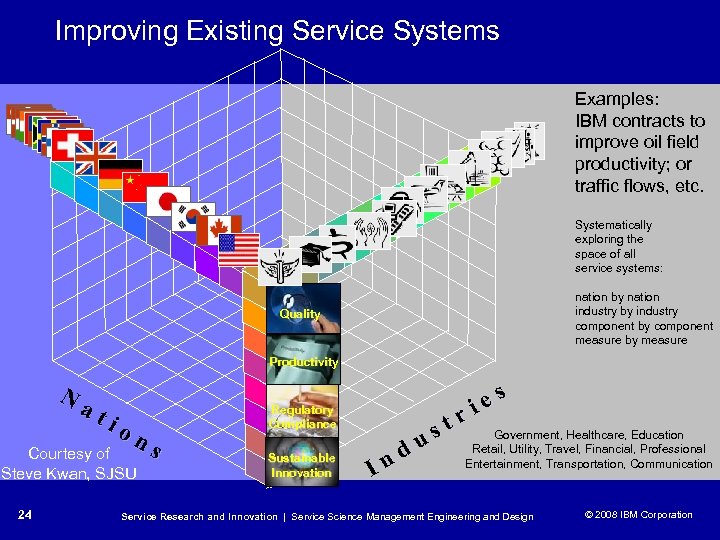 Improving Existing Service Systems Examples: IBM contracts to improve oil field productivity; or traffic flows, etc. Systematically exploring the space of all service systems: nation by nation industry by industry component by component measure by measure Quality Productivity N at io ns Courtesy of Steve Kwan, SJSU 24 Regulatory Compliance Sustainable Innovation nd I st u e ri s Government, Healthcare, Education Retail, Utility, Travel, Financial, Professional Entertainment, Transportation, Communication Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Improving Existing Service Systems Examples: IBM contracts to improve oil field productivity; or traffic flows, etc. Systematically exploring the space of all service systems: nation by nation industry by industry component by component measure by measure Quality Productivity N at io ns Courtesy of Steve Kwan, SJSU 24 Regulatory Compliance Sustainable Innovation nd I st u e ri s Government, Healthcare, Education Retail, Utility, Travel, Financial, Professional Entertainment, Transportation, Communication Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
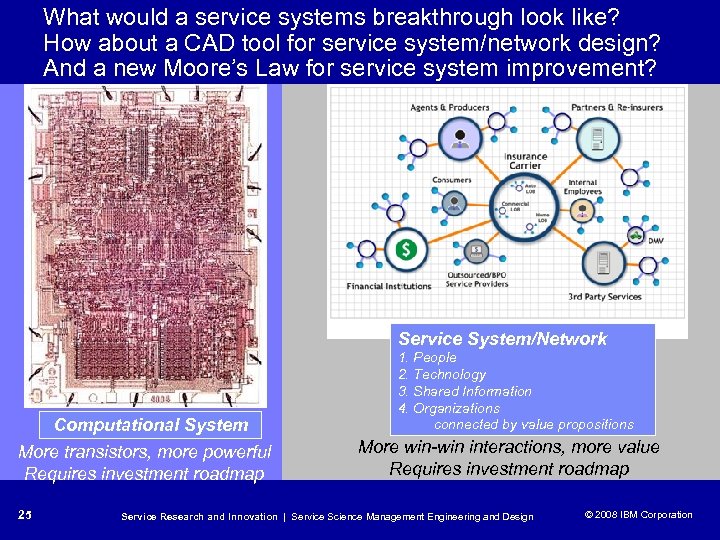 What would a service systems breakthrough look like? How about a CAD tool for service system/network design? And a new Moore’s Law for service system improvement? Service System/Network Computational System More transistors, more powerful Requires investment roadmap 25 1. People 2. Technology 3. Shared Information 4. Organizations connected by value propositions More win-win interactions, more value Requires investment roadmap Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
What would a service systems breakthrough look like? How about a CAD tool for service system/network design? And a new Moore’s Law for service system improvement? Service System/Network Computational System More transistors, more powerful Requires investment roadmap 25 1. People 2. Technology 3. Shared Information 4. Organizations connected by value propositions More win-win interactions, more value Requires investment roadmap Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
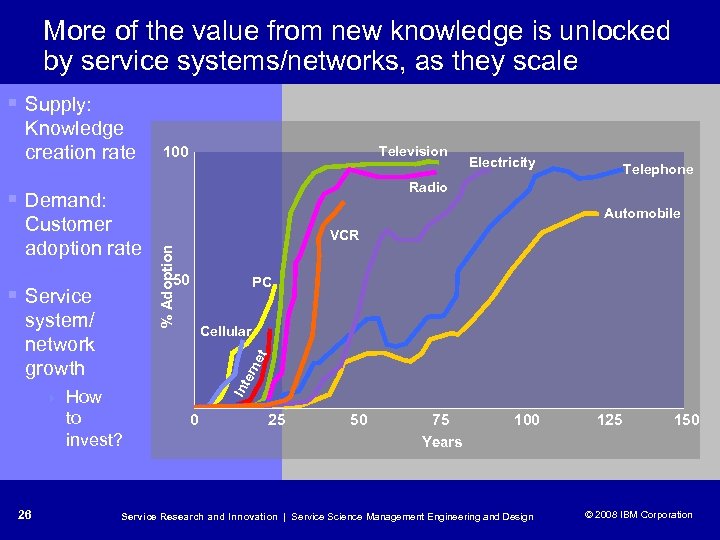 More of the value from new knowledge is unlocked by service systems/networks, as they scale § Supply: Knowledge creation rate Television 100 Automobile VCR % Adoption Customer adoption rate 50 § Service PC Cellular How to invest? Int ern et system/ network growth 26 Telephone Radio § Demand: 4 Electricity 0 25 50 75 Years 100 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design 125 150 © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
More of the value from new knowledge is unlocked by service systems/networks, as they scale § Supply: Knowledge creation rate Television 100 Automobile VCR % Adoption Customer adoption rate 50 § Service PC Cellular How to invest? Int ern et system/ network growth 26 Telephone Radio § Demand: 4 Electricity 0 25 50 75 Years 100 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design 125 150 © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
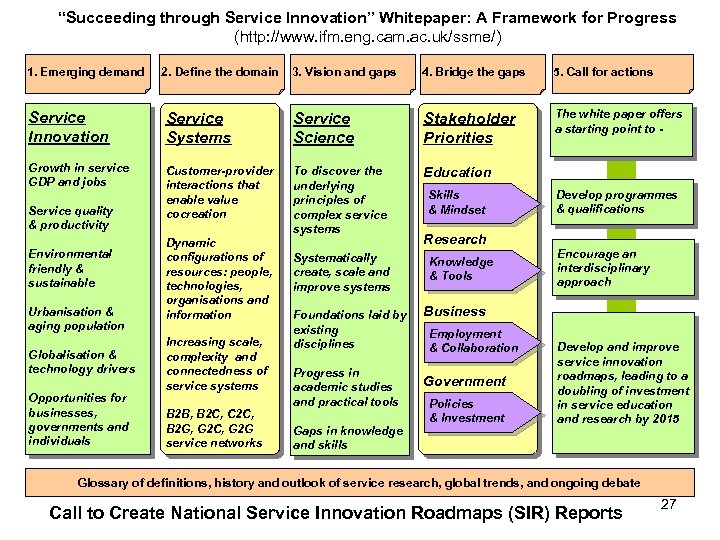 “Succeeding through Service Innovation” Whitepaper: A Framework for Progress (http: //www. ifm. eng. cam. ac. uk/ssme/) 1. Emerging demand 2. Define the domain 3. Vision and gaps 4. Bridge the gaps 5. Call for actions The white paper offers a starting point to - Service Innovation Service Systems Service Science Stakeholder Priorities Growth in service GDP and jobs Customer-provider interactions that enable value cocreation To discover the underlying principles of complex service systems Education Systematically create, scale and improve systems Knowledge & Tools Service quality & productivity Environmental friendly & sustainable Urbanisation & aging population Globalisation & technology drivers Opportunities for businesses, governments and individuals Dynamic configurations of resources: people, technologies, organisations and information Increasing scale, complexity and connectedness of service systems B 2 B, B 2 C, C 2 C, B 2 G, G 2 C, G 2 G service networks Foundations laid by existing disciplines Progress in academic studies and practical tools Gaps in knowledge and skills Skills & Mindset Research Develop programmes & qualifications Encourage an interdisciplinary approach Business Employment & Collaboration Government Policies & Investment Develop and improve service innovation roadmaps, leading to a doubling of investment in service education and research by 2015 Glossary of definitions, history and outlook of service research, global trends, and ongoing debate Call to Create National Service Innovation Roadmaps (SIR) Reports 27
“Succeeding through Service Innovation” Whitepaper: A Framework for Progress (http: //www. ifm. eng. cam. ac. uk/ssme/) 1. Emerging demand 2. Define the domain 3. Vision and gaps 4. Bridge the gaps 5. Call for actions The white paper offers a starting point to - Service Innovation Service Systems Service Science Stakeholder Priorities Growth in service GDP and jobs Customer-provider interactions that enable value cocreation To discover the underlying principles of complex service systems Education Systematically create, scale and improve systems Knowledge & Tools Service quality & productivity Environmental friendly & sustainable Urbanisation & aging population Globalisation & technology drivers Opportunities for businesses, governments and individuals Dynamic configurations of resources: people, technologies, organisations and information Increasing scale, complexity and connectedness of service systems B 2 B, B 2 C, C 2 C, B 2 G, G 2 C, G 2 G service networks Foundations laid by existing disciplines Progress in academic studies and practical tools Gaps in knowledge and skills Skills & Mindset Research Develop programmes & qualifications Encourage an interdisciplinary approach Business Employment & Collaboration Government Policies & Investment Develop and improve service innovation roadmaps, leading to a doubling of investment in service education and research by 2015 Glossary of definitions, history and outlook of service research, global trends, and ongoing debate Call to Create National Service Innovation Roadmaps (SIR) Reports 27
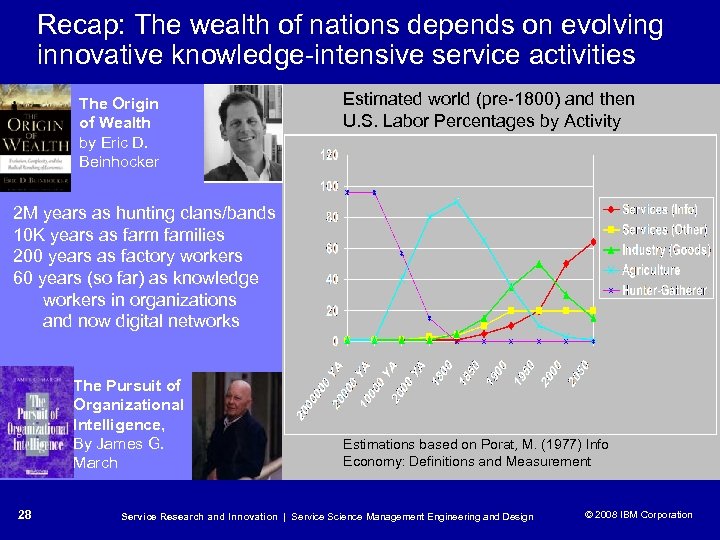 Recap: The wealth of nations depends on evolving innovative knowledge-intensive service activities The Origin of Wealth by Eric D. Beinhocker Estimated world (pre-1800) and then U. S. Labor Percentages by Activity 2 M years as hunting clans/bands 10 K years as farm families 200 years as factory workers 60 years (so far) as knowledge workers in organizations and now digital networks The Pursuit of Organizational Intelligence, By James G. March 28 Estimations based on Porat, M. (1977) Info Economy: Definitions and Measurement Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Recap: The wealth of nations depends on evolving innovative knowledge-intensive service activities The Origin of Wealth by Eric D. Beinhocker Estimated world (pre-1800) and then U. S. Labor Percentages by Activity 2 M years as hunting clans/bands 10 K years as farm families 200 years as factory workers 60 years (so far) as knowledge workers in organizations and now digital networks The Pursuit of Organizational Intelligence, By James G. March 28 Estimations based on Porat, M. (1977) Info Economy: Definitions and Measurement Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
 Questions? Visit us in San Jose, CA USA IBM Almaden Research Center One of eight main IBM Research labs worldwide Email: spohrer@us. ibm. com Blog: http: //forums. thesrii. org/blog? blog. id=main_blog Service Research: http: //www. almaden. ibm. com/asr/ Service Innovation: http: //www. ifm. eng. cam. ac. uk/ssme/ 29 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Questions? Visit us in San Jose, CA USA IBM Almaden Research Center One of eight main IBM Research labs worldwide Email: spohrer@us. ibm. com Blog: http: //forums. thesrii. org/blog? blog. id=main_blog Service Research: http: //www. almaden. ibm. com/asr/ Service Innovation: http: //www. ifm. eng. cam. ac. uk/ssme/ 29 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
 Thanks to Global IBM SSMED Team Research 4 Vivian Ding (CRL) 4 Kazuyoshi Hidaka (TRL) 4 Paul Maglio (ARC) 4 Doug Riecken (WRC) 4 Liba Svobodova (ZRL) 4 Segev Wasserkrug (HRL) and many others… § University Relations 4 Dianne Fodell 4 Wendy Murphy 4 Kevin Wright and many, many others… § Cross IBM 4 Paul Kontogiorgis (SWG) 4 Steve Street (GTS) 4 Moises Cases(Systems) 4 Yuriko Sawatani (TRL) 4 Jakita Thomas (ARC) 4 Gerhard Satzger (Germany) 4 Claudio Pinhanez (Brazil) and many others… § Executive Support 4 Nicholas Donofrio 4 Ginni Rometty 4 John Kelly III 4 Jai Menon 4 Robert Morris 4 Thomas Li 4 Guru Banavar 4 Jim Spohrer 4 David Cohn 4 Mahmoud Nagyshineh 4 Greg Golden 4 Jon Iwata and others… 30 Hundreds of others worldwide… thanks to all! § Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Thanks to Global IBM SSMED Team Research 4 Vivian Ding (CRL) 4 Kazuyoshi Hidaka (TRL) 4 Paul Maglio (ARC) 4 Doug Riecken (WRC) 4 Liba Svobodova (ZRL) 4 Segev Wasserkrug (HRL) and many others… § University Relations 4 Dianne Fodell 4 Wendy Murphy 4 Kevin Wright and many, many others… § Cross IBM 4 Paul Kontogiorgis (SWG) 4 Steve Street (GTS) 4 Moises Cases(Systems) 4 Yuriko Sawatani (TRL) 4 Jakita Thomas (ARC) 4 Gerhard Satzger (Germany) 4 Claudio Pinhanez (Brazil) and many others… § Executive Support 4 Nicholas Donofrio 4 Ginni Rometty 4 John Kelly III 4 Jai Menon 4 Robert Morris 4 Thomas Li 4 Guru Banavar 4 Jim Spohrer 4 David Cohn 4 Mahmoud Nagyshineh 4 Greg Golden 4 Jon Iwata and others… 30 Hundreds of others worldwide… thanks to all! § Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
 A Practical Place to Get Started… § Reaching the Goal: How § “Theory of Constraints (TOC) gets its name from the fact that all enterprises are constrained by something. If they weren’t they could grow as large and as fast as they wanted… So the first step in applying TOC is to figure out precisely where the § John Arthur Ricketts, IBM constraints are… The second step in apply TOC is to utilize the constraint to its fullest extent… The third step in applying TOC is to make sure that non-constraints keep the constraint busy – but otherwise stay out of its way… The fourth step in applying TOC is to improve the productivity of the constraint… The final step in applying TOC is to repeat the previous steps. ” Managers Improve a Services Business Using Goldratt’s Theory of Constraints 31 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
A Practical Place to Get Started… § Reaching the Goal: How § “Theory of Constraints (TOC) gets its name from the fact that all enterprises are constrained by something. If they weren’t they could grow as large and as fast as they wanted… So the first step in applying TOC is to figure out precisely where the § John Arthur Ricketts, IBM constraints are… The second step in apply TOC is to utilize the constraint to its fullest extent… The third step in applying TOC is to make sure that non-constraints keep the constraint busy – but otherwise stay out of its way… The fourth step in applying TOC is to improve the productivity of the constraint… The final step in applying TOC is to repeat the previous steps. ” Managers Improve a Services Business Using Goldratt’s Theory of Constraints 31 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
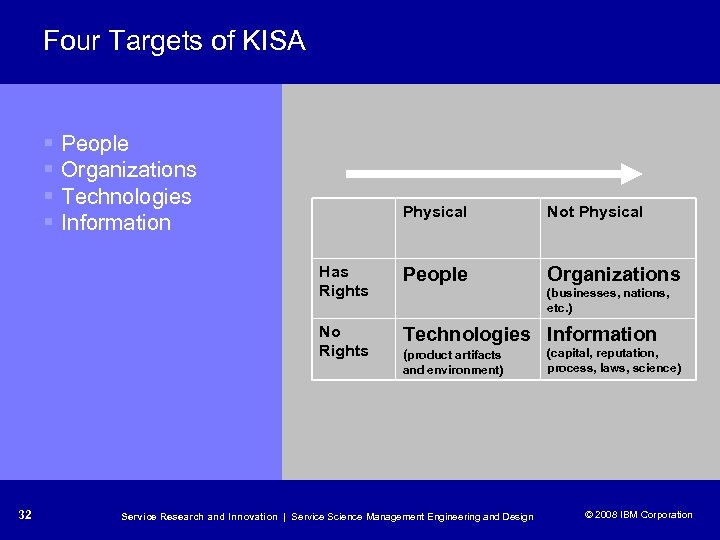 Four Targets of KISA § People § Organizations § Technologies § Information Physical Not Physical Has Rights People Organizations No Rights Technologies Information (businesses, nations, etc. ) (product artifacts and environment) 32 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design (capital, reputation, process, laws, science) © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Four Targets of KISA § People § Organizations § Technologies § Information Physical Not Physical Has Rights People Organizations No Rights Technologies Information (businesses, nations, etc. ) (product artifacts and environment) 32 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design (capital, reputation, process, laws, science) © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
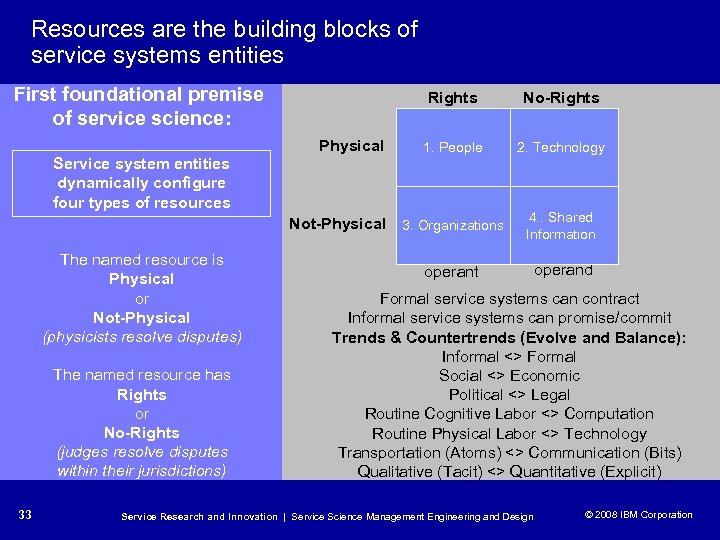 Resources are the building blocks of service systems entities First foundational premise of service science: Rights Physical Service system entities dynamically configure four types of resources No-Rights 1. People 2. Technology Not-Physical 3. Organizations The named resource is Physical or Not-Physical (physicists resolve disputes) The named resource has Rights or No-Rights (judges resolve disputes within their jurisdictions) 33 4. . Shared Information operant operand Formal service systems can contract Informal service systems can promise/commit Trends & Countertrends (Evolve and Balance): Informal <> Formal Social <> Economic Political <> Legal Routine Cognitive Labor <> Computation Routine Physical Labor <> Technology Transportation (Atoms) <> Communication (Bits) Qualitative (Tacit) <> Quantitative (Explicit) Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Resources are the building blocks of service systems entities First foundational premise of service science: Rights Physical Service system entities dynamically configure four types of resources No-Rights 1. People 2. Technology Not-Physical 3. Organizations The named resource is Physical or Not-Physical (physicists resolve disputes) The named resource has Rights or No-Rights (judges resolve disputes within their jurisdictions) 33 4. . Shared Information operant operand Formal service systems can contract Informal service systems can promise/commit Trends & Countertrends (Evolve and Balance): Informal <> Formal Social <> Economic Political <> Legal Routine Cognitive Labor <> Computation Routine Physical Labor <> Technology Transportation (Atoms) <> Communication (Bits) Qualitative (Tacit) <> Quantitative (Explicit) Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
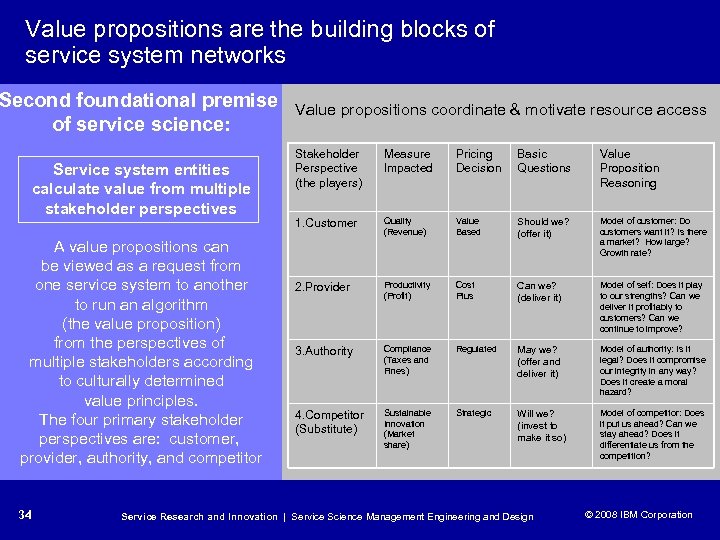 Value propositions are the building blocks of service system networks Second foundational premise of service science: Service system entities calculate value from multiple stakeholder perspectives A value propositions can be viewed as a request from one service system to another to run an algorithm (the value proposition) from the perspectives of multiple stakeholders according to culturally determined value principles. The four primary stakeholder perspectives are: customer, provider, authority, and competitor 34 Value propositions coordinate & motivate resource access Stakeholder Perspective (the players) Measure Impacted Pricing Decision Basic Questions Value Proposition Reasoning 1. Customer Quality (Revenue) Value Based Should we? (offer it) Model of customer: Do customers want it? Is there a market? How large? Growth rate? 2. Provider Productivity (Profit) Cost Plus Can we? (deliver it) Model of self: Does it play to our strengths? Can we deliver it profitably to customers? Can we continue to improve? 3. Authority Compliance (Taxes and Fines) Regulated May we? (offer and deliver it) Model of authority: Is it legal? Does it compromise our integrity in any way? Does it create a moral hazard? 4. Competitor (Substitute) Sustainable Innovation (Market share) Strategic Will we? (invest to make it so) Model of competitor: Does it put us ahead? Can we stay ahead? Does it differentiate us from the competition? Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Value propositions are the building blocks of service system networks Second foundational premise of service science: Service system entities calculate value from multiple stakeholder perspectives A value propositions can be viewed as a request from one service system to another to run an algorithm (the value proposition) from the perspectives of multiple stakeholders according to culturally determined value principles. The four primary stakeholder perspectives are: customer, provider, authority, and competitor 34 Value propositions coordinate & motivate resource access Stakeholder Perspective (the players) Measure Impacted Pricing Decision Basic Questions Value Proposition Reasoning 1. Customer Quality (Revenue) Value Based Should we? (offer it) Model of customer: Do customers want it? Is there a market? How large? Growth rate? 2. Provider Productivity (Profit) Cost Plus Can we? (deliver it) Model of self: Does it play to our strengths? Can we deliver it profitably to customers? Can we continue to improve? 3. Authority Compliance (Taxes and Fines) Regulated May we? (offer and deliver it) Model of authority: Is it legal? Does it compromise our integrity in any way? Does it create a moral hazard? 4. Competitor (Substitute) Sustainable Innovation (Market share) Strategic Will we? (invest to make it so) Model of competitor: Does it put us ahead? Can we stay ahead? Does it differentiate us from the competition? Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
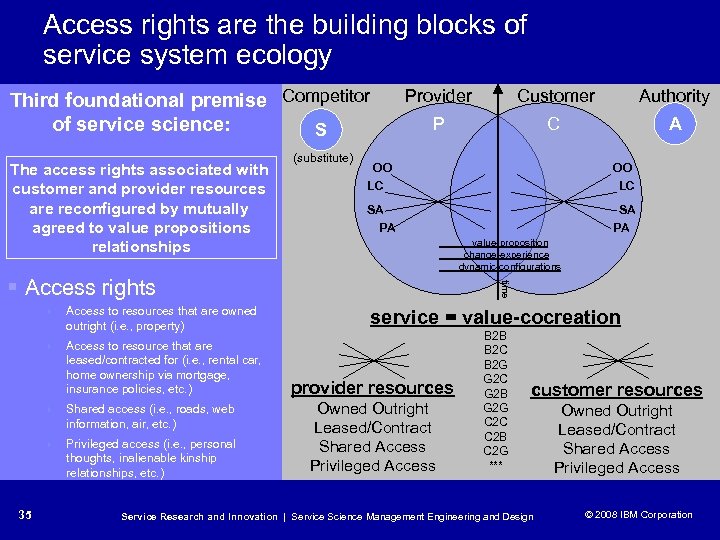 Access rights are the building blocks of service system ecology Third foundational premise Competitor of service science: S The access rights associated with customer and provider resources are reconfigured by mutually agreed to value propositions relationships (substitute) Provider Customer Authority P C A OO LC SA PA value-proposition change-experience dynamic-configurations 4 Access to resources that are owned outright (i. e. , property) 4 Access to resource that are leased/contracted for (i. e. , rental car, home ownership via mortgage, insurance policies, etc. ) 4 4 35 Shared access (i. e. , roads, web information, air, etc. ) Privileged access (i. e. , personal thoughts, inalienable kinship relationships, etc. ) time § Access rights service = value-cocreation provider resources Owned Outright Leased/Contract Shared Access Privileged Access B 2 B B 2 C B 2 G G 2 C G 2 B G 2 G C 2 C C 2 B C 2 G *** customer resources Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design Owned Outright Leased/Contract Shared Access Privileged Access © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Access rights are the building blocks of service system ecology Third foundational premise Competitor of service science: S The access rights associated with customer and provider resources are reconfigured by mutually agreed to value propositions relationships (substitute) Provider Customer Authority P C A OO LC SA PA value-proposition change-experience dynamic-configurations 4 Access to resources that are owned outright (i. e. , property) 4 Access to resource that are leased/contracted for (i. e. , rental car, home ownership via mortgage, insurance policies, etc. ) 4 4 35 Shared access (i. e. , roads, web information, air, etc. ) Privileged access (i. e. , personal thoughts, inalienable kinship relationships, etc. ) time § Access rights service = value-cocreation provider resources Owned Outright Leased/Contract Shared Access Privileged Access B 2 B B 2 C B 2 G G 2 C G 2 B G 2 G C 2 C C 2 B C 2 G *** customer resources Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design Owned Outright Leased/Contract Shared Access Privileged Access © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
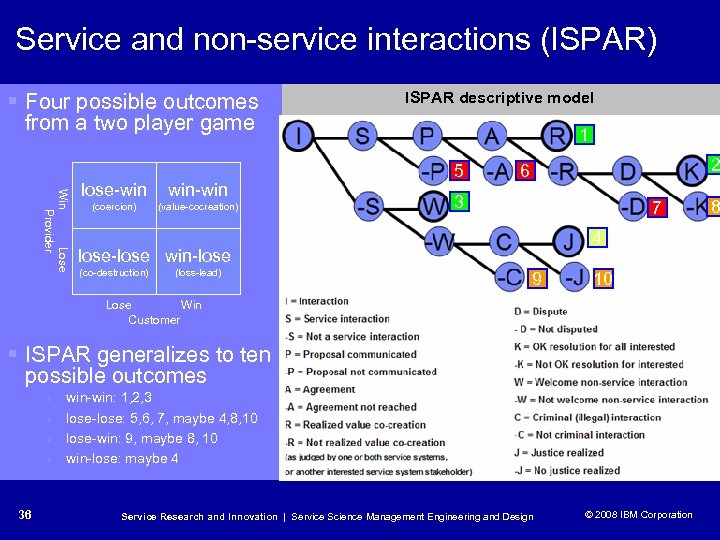 Service and non-service interactions (ISPAR) § Four possible outcomes ISPAR descriptive model from a two player game Win Lose Provider lose-win win-win (coercion) (value-cocreation) 1 5 2 6 3 7 4 lose-lose win-lose (co-destruction) (loss-lead) 9 10 Lose Win Customer § ISPAR generalizes to ten possible outcomes 4 win-win: 1, 2, 3 4 lose-lose: 5, 6, 7, maybe 4, 8, 10 4 lose-win: 9, maybe 8, 10 4 win-lose: maybe 4 36 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation 8
Service and non-service interactions (ISPAR) § Four possible outcomes ISPAR descriptive model from a two player game Win Lose Provider lose-win win-win (coercion) (value-cocreation) 1 5 2 6 3 7 4 lose-lose win-lose (co-destruction) (loss-lead) 9 10 Lose Win Customer § ISPAR generalizes to ten possible outcomes 4 win-win: 1, 2, 3 4 lose-lose: 5, 6, 7, maybe 4, 8, 10 4 lose-win: 9, maybe 8, 10 4 win-lose: maybe 4 36 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation 8
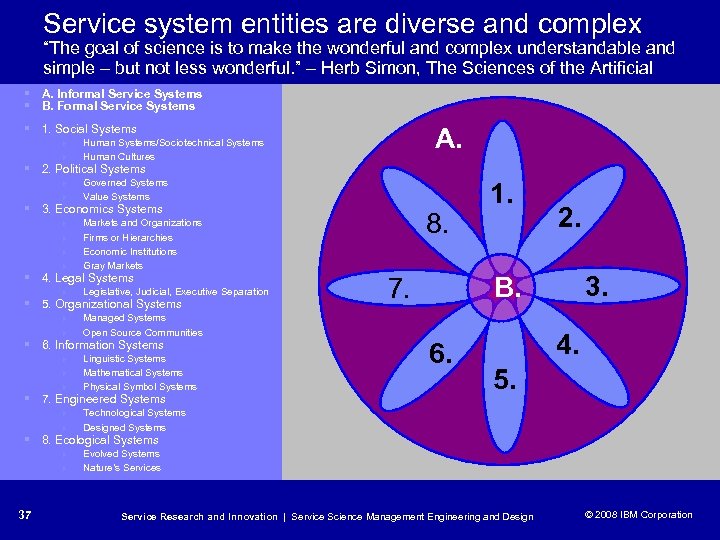 Service system entities are diverse and complex “The goal of science is to make the wonderful and complex understandable and simple – but not less wonderful. ” – Herb Simon, The Sciences of the Artificial § A. Informal Service Systems § B. Formal Service Systems § 1. Social Systems 4 4 A. Human Systems/Sociotechnical Systems Human Cultures § 2. Political Systems 4 4 Governed Systems Value Systems § 3. Economics Systems 4 4 Legislative, Judicial, Executive Separation 4 Managed Systems Open Source Communities 8. Markets and Organizations Firms or Hierarchies Economic Institutions Gray Markets 4 4 4 § 4. Legal Systems § 5. Organizational Systems 4 § 6. Information Systems 4 4 4 Linguistic Systems Mathematical Systems Physical Symbol Systems § 7. Engineered Systems 4 4 1. 2. 3. B. 7. 6. 4. 5. Technological Systems Designed Systems § 8. Ecological Systems 4 4 37 Evolved Systems Nature’s Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Service system entities are diverse and complex “The goal of science is to make the wonderful and complex understandable and simple – but not less wonderful. ” – Herb Simon, The Sciences of the Artificial § A. Informal Service Systems § B. Formal Service Systems § 1. Social Systems 4 4 A. Human Systems/Sociotechnical Systems Human Cultures § 2. Political Systems 4 4 Governed Systems Value Systems § 3. Economics Systems 4 4 Legislative, Judicial, Executive Separation 4 Managed Systems Open Source Communities 8. Markets and Organizations Firms or Hierarchies Economic Institutions Gray Markets 4 4 4 § 4. Legal Systems § 5. Organizational Systems 4 § 6. Information Systems 4 4 4 Linguistic Systems Mathematical Systems Physical Symbol Systems § 7. Engineered Systems 4 4 1. 2. 3. B. 7. 6. 4. 5. Technological Systems Designed Systems § 8. Ecological Systems 4 4 37 Evolved Systems Nature’s Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
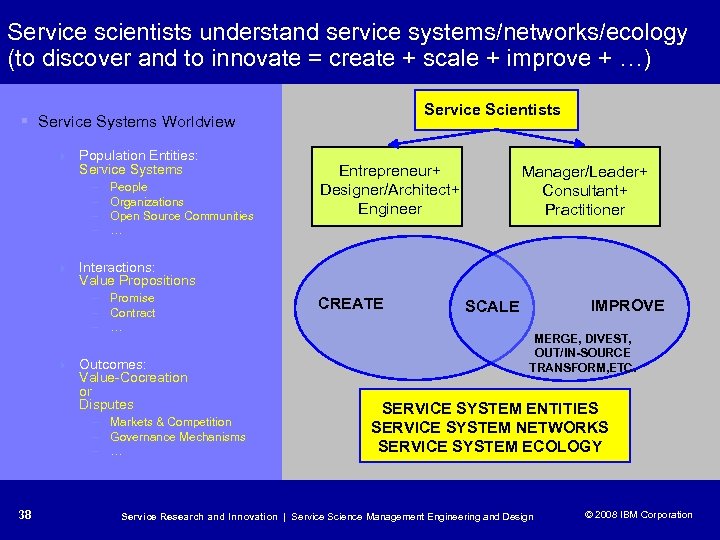 Service scientists understand service systems/networks/ecology (to discover and to innovate = create + scale + improve + …) Service Scientists § Service Systems Worldview 4 Population Entities: Service Systems – – People Organizations Open Source Communities … Entrepreneur+ Designer/Architect+ Engineer Manager/Leader+ Consultant+ Practitioner 4 Interactions: Value Propositions – Promise – Contract – … 4 Outcomes: Value-Cocreation or Disputes – Markets & Competition – Governance Mechanisms – … 38 CREATE IMPROVE SCALE MERGE, DIVEST, OUT/IN-SOURCE TRANSFORM, ETC. SERVICE SYSTEM ENTITIES SERVICE SYSTEM NETWORKS SERVICE SYSTEM ECOLOGY Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Service scientists understand service systems/networks/ecology (to discover and to innovate = create + scale + improve + …) Service Scientists § Service Systems Worldview 4 Population Entities: Service Systems – – People Organizations Open Source Communities … Entrepreneur+ Designer/Architect+ Engineer Manager/Leader+ Consultant+ Practitioner 4 Interactions: Value Propositions – Promise – Contract – … 4 Outcomes: Value-Cocreation or Disputes – Markets & Competition – Governance Mechanisms – … 38 CREATE IMPROVE SCALE MERGE, DIVEST, OUT/IN-SOURCE TRANSFORM, ETC. SERVICE SYSTEM ENTITIES SERVICE SYSTEM NETWORKS SERVICE SYSTEM ECOLOGY Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
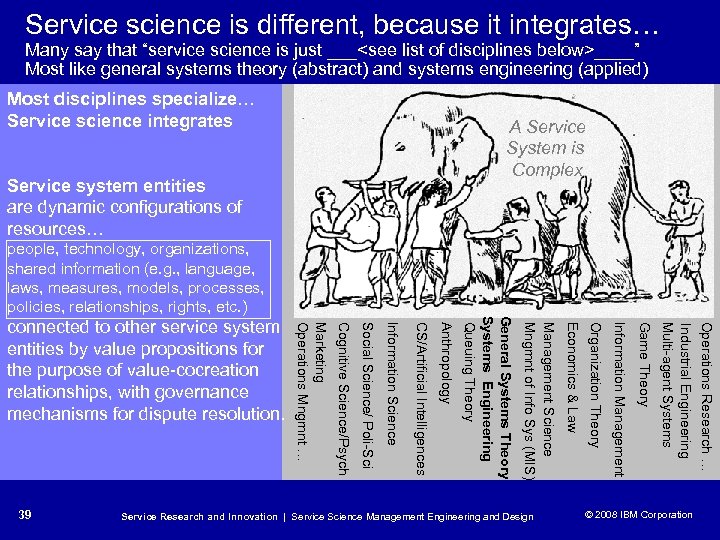 Service science is different, because it integrates… Many say that “service science is just ___
Service science is different, because it integrates… Many say that “service science is just ___
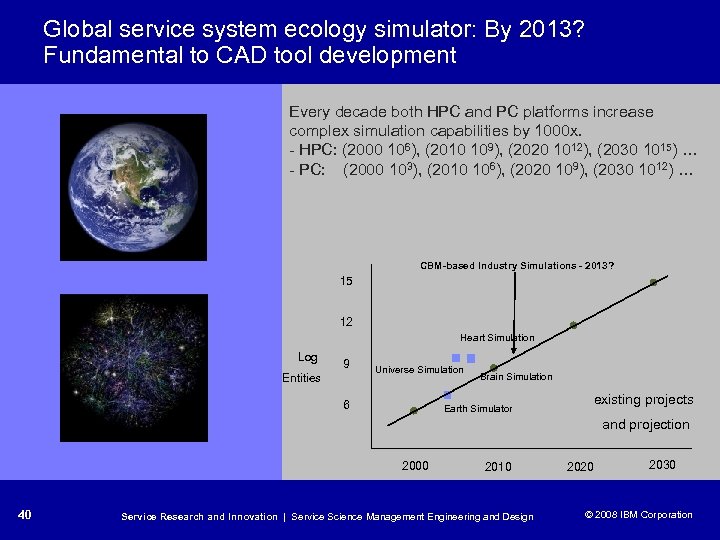 Global service system ecology simulator: By 2013? Fundamental to CAD tool development Every decade both HPC and PC platforms increase complex simulation capabilities by 1000 x. - HPC: (2000 106), (2010 109), (2020 1012), (2030 1015) … - PC: (2000 103), (2010 106), (2020 109), (2030 1012) … CBM-based Industry Simulations - 2013? 15 12 Heart Simulation Log 9 Entities Universe Simulation 6 Brain Simulation Earth Simulator existing projects and projection 2000 40 2010 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design 2020 2030 © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Global service system ecology simulator: By 2013? Fundamental to CAD tool development Every decade both HPC and PC platforms increase complex simulation capabilities by 1000 x. - HPC: (2000 106), (2010 109), (2020 1012), (2030 1015) … - PC: (2000 103), (2010 106), (2020 109), (2030 1012) … CBM-based Industry Simulations - 2013? 15 12 Heart Simulation Log 9 Entities Universe Simulation 6 Brain Simulation Earth Simulator existing projects and projection 2000 40 2010 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design 2020 2030 © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
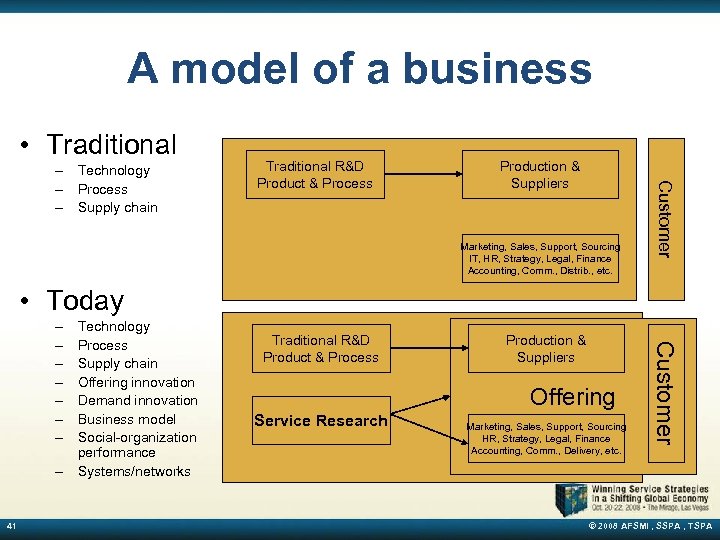 A model of a business • Traditional R&D Product & Process Production & Suppliers Marketing, Sales, Support, Sourcing IT, HR, Strategy, Legal, Finance Accounting, Comm. , Distrib. , etc. Customer – Technology – Process – Supply chain • Today – 41 Technology Process Supply chain Offering innovation Demand innovation Business model Social-organization performance Systems/networks Traditional R&D Product & Process Production & Suppliers Offering Service Research Marketing, Sales, Support, Sourcing HR, Strategy, Legal, Finance Accounting, Comm. , Delivery, etc. Customer – – – – © 2008 AFSMI , SSPA , TSPA
A model of a business • Traditional R&D Product & Process Production & Suppliers Marketing, Sales, Support, Sourcing IT, HR, Strategy, Legal, Finance Accounting, Comm. , Distrib. , etc. Customer – Technology – Process – Supply chain • Today – 41 Technology Process Supply chain Offering innovation Demand innovation Business model Social-organization performance Systems/networks Traditional R&D Product & Process Production & Suppliers Offering Service Research Marketing, Sales, Support, Sourcing HR, Strategy, Legal, Finance Accounting, Comm. , Delivery, etc. Customer – – – – © 2008 AFSMI , SSPA , TSPA
 Evolution of trust The Company of Strangers : A Natural History of Economic Life by Paul Seabright 42 “Evolution of Trust: Human beings are the only species in nature to have developed an elaborate division of labor between strangers. Even something as simple as buying a shirt depends on an astonishing web of interaction and organization that spans the world. But unlike that other uniquely human attribute, language, our ability to cooperate with strangers did not evolve gradually through our prehistory. Only 10, 000 years ago--a blink of an eye in evolutionary time--humans hunted in bands, were intensely suspicious of strangers, and fought those whom they could not flee. Yet since the dawn of agriculture we have refined the division of labor to the point where, today, we live and work amid strangers and depend upon millions more. Every time we travel by rail or air we entrust our lives to individuals we do not know. What institutions have made this possible? ” Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Evolution of trust The Company of Strangers : A Natural History of Economic Life by Paul Seabright 42 “Evolution of Trust: Human beings are the only species in nature to have developed an elaborate division of labor between strangers. Even something as simple as buying a shirt depends on an astonishing web of interaction and organization that spans the world. But unlike that other uniquely human attribute, language, our ability to cooperate with strangers did not evolve gradually through our prehistory. Only 10, 000 years ago--a blink of an eye in evolutionary time--humans hunted in bands, were intensely suspicious of strangers, and fought those whom they could not flee. Yet since the dawn of agriculture we have refined the division of labor to the point where, today, we live and work amid strangers and depend upon millions more. Every time we travel by rail or air we entrust our lives to individuals we do not know. What institutions have made this possible? ” Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
 Evolution of business organizations The Visible Hand: The Managerial Revolution in American Business by Alfred Dupont Chandler 43 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Evolution of business organizations The Visible Hand: The Managerial Revolution in American Business by Alfred Dupont Chandler 43 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
 Biological System Entities: Also diverse and complex “…from so simple a beginning endless forms most beautiful and most wonderful have been, and are being, evolved. ” – Charles Darwin 44 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Biological System Entities: Also diverse and complex “…from so simple a beginning endless forms most beautiful and most wonderful have been, and are being, evolved. ” – Charles Darwin 44 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
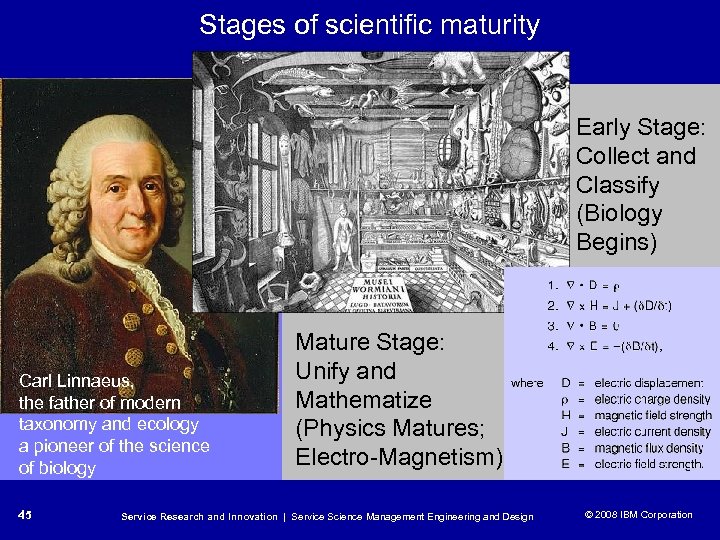 Stages of scientific maturity Early Stage: Collect and Classify (Biology Begins) Carl Linnaeus, the father of modern taxonomy and ecology a pioneer of the science of biology 45 Mature Stage: Unify and Mathematize (Physics Matures; Electro-Magnetism) Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Stages of scientific maturity Early Stage: Collect and Classify (Biology Begins) Carl Linnaeus, the father of modern taxonomy and ecology a pioneer of the science of biology 45 Mature Stage: Unify and Mathematize (Physics Matures; Electro-Magnetism) Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
 Towards a Moore’s Law § Computational power doubles at a predictable rate. § Are there analogous capability-doubling laws that apply in services? § Suppose that traces of human activity in particular service systems double at some rate, and that these human activity data lead to specific opportunities for improved or increased service productivity or quality. § Consider Amazon. com: The quality of recommendations depends on accurate statistics – the more purchases made, the better the statistics for recommendations. § Three improvement “laws” that might be applicable in services: 4 4 The better an activity can be measured (sensor deployment doubling, sensor precision doubling, relevant measurement variables doubling) and modeled, the more opportunities to improve. 4 46 The more an activity is performed (time period doubling, demand doubling), the more opportunities to improve. The more activities that depend on a common sub-step or process (doubling potential demand points), the more likely investment can be raised to improve the sub-step. Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Towards a Moore’s Law § Computational power doubles at a predictable rate. § Are there analogous capability-doubling laws that apply in services? § Suppose that traces of human activity in particular service systems double at some rate, and that these human activity data lead to specific opportunities for improved or increased service productivity or quality. § Consider Amazon. com: The quality of recommendations depends on accurate statistics – the more purchases made, the better the statistics for recommendations. § Three improvement “laws” that might be applicable in services: 4 4 The better an activity can be measured (sensor deployment doubling, sensor precision doubling, relevant measurement variables doubling) and modeled, the more opportunities to improve. 4 46 The more an activity is performed (time period doubling, demand doubling), the more opportunities to improve. The more activities that depend on a common sub-step or process (doubling potential demand points), the more likely investment can be raised to improve the sub-step. Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
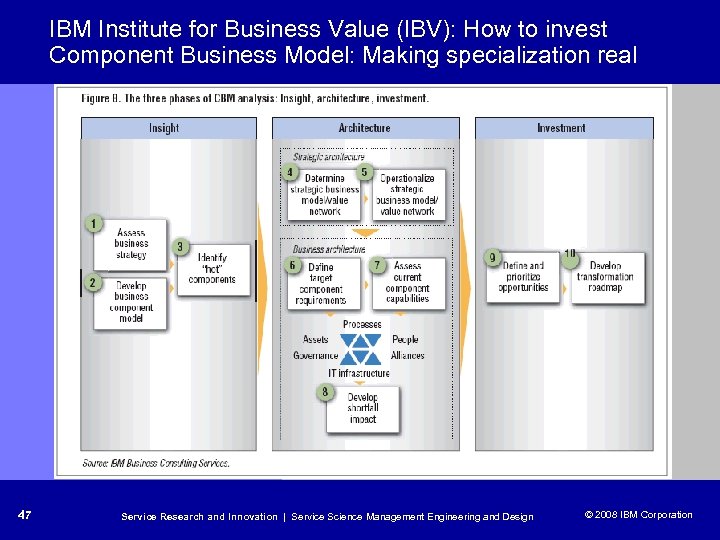 IBM Institute for Business Value (IBV): How to invest Component Business Model: Making specialization real 47 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
IBM Institute for Business Value (IBV): How to invest Component Business Model: Making specialization real 47 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
 Intelligent Document Gateway (IDG): Service System Analysis § Process § Digitization § Business Logic 48 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Intelligent Document Gateway (IDG): Service System Analysis § Process § Digitization § Business Logic 48 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
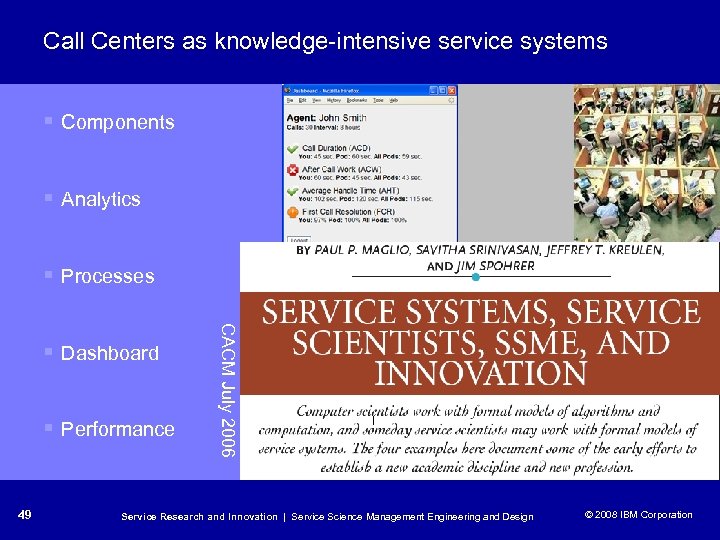 Call Centers as knowledge-intensive service systems § Components § Analytics § Processes § Performance 49 CACM July 2006 § Dashboard Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Call Centers as knowledge-intensive service systems § Components § Analytics § Processes § Performance 49 CACM July 2006 § Dashboard Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
 Fact: 2006 was first year that service jobs overtake agriculture jobs world wide § Correlates with growth of More people, more large cities 4 More technology, more global networks 4 More organizations, more wealth 4 More information, more knowledge 4 § Increase in connectedness Billions of people 4 Billions of devices (computers, phones, TVs, security cameras, routers, etc. ) 4 Millions of organizations 4 Quadrillions of symbol-concepts 4 In 2006 the service sector’s share of global employment overtook agric. for the first time in human history, increasing from 39. 5% to 40%. agric. decreased from 39. 7% to 38. 7%. The industry sector accounted for 21. 3% of total employment. § Increase in interactions Productive (value +) 4 Unproductive (value -) 4 - International Labour Organization 50 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Fact: 2006 was first year that service jobs overtake agriculture jobs world wide § Correlates with growth of More people, more large cities 4 More technology, more global networks 4 More organizations, more wealth 4 More information, more knowledge 4 § Increase in connectedness Billions of people 4 Billions of devices (computers, phones, TVs, security cameras, routers, etc. ) 4 Millions of organizations 4 Quadrillions of symbol-concepts 4 In 2006 the service sector’s share of global employment overtook agric. for the first time in human history, increasing from 39. 5% to 40%. agric. decreased from 39. 7% to 38. 7%. The industry sector accounted for 21. 3% of total employment. § Increase in interactions Productive (value +) 4 Unproductive (value -) 4 - International Labour Organization 50 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
 Global Change and SSMED What is SSMED really? - Focus on service innovation - Proto-discipline & professions - Research area Germany $87 M Innovation with Services EU $100 M NESSI pending China 5 Yr Plan Modern Services Japan $30 M Service Productivity US $4 M+ NSF SEE HR 2272/1106. . . And More! In 2006 the service sector’s share of global employment overtook agric. Related activities to date for the first time, increasing from - ACM, IEEE, INFORMS, SRII SIGs 39. 5% to 40%. Agric. decreased from - 130 Programs, 44 Countries 39. 7% to 38. 7%. The industry sector - Over 100 conference and journal papers accounted for 21. 3% of total - >100 Press, >10, 000 Web site mentions employment. - International Labour Organization 51 - IBM – 400 Service Researchers WW Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Global Change and SSMED What is SSMED really? - Focus on service innovation - Proto-discipline & professions - Research area Germany $87 M Innovation with Services EU $100 M NESSI pending China 5 Yr Plan Modern Services Japan $30 M Service Productivity US $4 M+ NSF SEE HR 2272/1106. . . And More! In 2006 the service sector’s share of global employment overtook agric. Related activities to date for the first time, increasing from - ACM, IEEE, INFORMS, SRII SIGs 39. 5% to 40%. Agric. decreased from - 130 Programs, 44 Countries 39. 7% to 38. 7%. The industry sector - Over 100 conference and journal papers accounted for 21. 3% of total - >100 Press, >10, 000 Web site mentions employment. - International Labour Organization 51 - IBM – 400 Service Researchers WW Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
 US News – Smart Choices Graduate Engineering § ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING It's a growing field, and engineers are needed to clean up existing pollution problems and prevent future ones. § SERVICE SCIENCE, MANAGEMENT, AND ENGINEERING (SSME) This emerging discipline is getting a big push from industry, including IBM and Hewlett-Packard. SSME combines engineering, computer science, economics, and management to improve the service sector. http: //www. usnews. com/usnews/edu/grad/articles/brief/gbeng_brief_2. php http: //www 3. brookings. edu/metro/pubs/20070904_gleiecosystem. pdf 52 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
US News – Smart Choices Graduate Engineering § ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING It's a growing field, and engineers are needed to clean up existing pollution problems and prevent future ones. § SERVICE SCIENCE, MANAGEMENT, AND ENGINEERING (SSME) This emerging discipline is getting a big push from industry, including IBM and Hewlett-Packard. SSME combines engineering, computer science, economics, and management to improve the service sector. http: //www. usnews. com/usnews/edu/grad/articles/brief/gbeng_brief_2. php http: //www 3. brookings. edu/metro/pubs/20070904_gleiecosystem. pdf 52 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
 The U. S. National Innovation Investment Act (America COMPETES) § US House and Senate voted to approve on August 2 nd, , 2007; President has signed. § SEC. 1005. STUDY OF SERVICE SCIENCE. 4 (a) Sense of Congress- It is the sense of Congress that, in order to strengthen the competitiveness of United States enterprises and institutions and to prepare the people of the United States for high-wage, high-skill employment, the Federal Government should better understand respond strategically to the emerging management and learning discipline known as service science. 4 (b) Study- Not later than 270 days after the date of enactment of this Act, the Director of the Office of Science and Technology Policy, through the National Academy of Sciences, shall conduct a study and report to Congress regarding how the Federal Government should support, through research, education, and training, the emerging management and learning discipline known as service science. 4 (c) Outside Resources- In conducting the study under subsection (b), the National Academy of Sciences shall consult with leaders from 2 - and 4 -year institutions of higher education, as defined in section 101(a) of the Higher Education Act of 1965 (20 U. S. C. 1001(a)), leaders from corporations, and other relevant parties. 4 (d) Service Science Defined- In this section, the term `service science' means curricula, training, and research programs that are designed to teach individuals to apply scientific, engineering, and management disciplines that integrate elements of computer science, operations research, industrial engineering, business strategy, management sciences, and social and legal sciences, in order to encourage innovation in how organizations create value for customers and shareholders that could not be achieved through such disciplines working in isolation. http: //thomas. loc. gov/cgi-bin/query/F? c 110: 5: . /temp/~c 110 n. Py 6 Rp: e 19768: 53 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
The U. S. National Innovation Investment Act (America COMPETES) § US House and Senate voted to approve on August 2 nd, , 2007; President has signed. § SEC. 1005. STUDY OF SERVICE SCIENCE. 4 (a) Sense of Congress- It is the sense of Congress that, in order to strengthen the competitiveness of United States enterprises and institutions and to prepare the people of the United States for high-wage, high-skill employment, the Federal Government should better understand respond strategically to the emerging management and learning discipline known as service science. 4 (b) Study- Not later than 270 days after the date of enactment of this Act, the Director of the Office of Science and Technology Policy, through the National Academy of Sciences, shall conduct a study and report to Congress regarding how the Federal Government should support, through research, education, and training, the emerging management and learning discipline known as service science. 4 (c) Outside Resources- In conducting the study under subsection (b), the National Academy of Sciences shall consult with leaders from 2 - and 4 -year institutions of higher education, as defined in section 101(a) of the Higher Education Act of 1965 (20 U. S. C. 1001(a)), leaders from corporations, and other relevant parties. 4 (d) Service Science Defined- In this section, the term `service science' means curricula, training, and research programs that are designed to teach individuals to apply scientific, engineering, and management disciplines that integrate elements of computer science, operations research, industrial engineering, business strategy, management sciences, and social and legal sciences, in order to encourage innovation in how organizations create value for customers and shareholders that could not be achieved through such disciplines working in isolation. http: //thomas. loc. gov/cgi-bin/query/F? c 110: 5: . /temp/~c 110 n. Py 6 Rp: e 19768: 53 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
 Test 54 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation
Test 54 Service Research and Innovation | Service Science Management Engineering and Design © 2008 IBM Corporation © 2005 IBM Corporation


