deb257b822ff11368cdab33e6da78644.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

SSL VPN
Module Objectives • By the end of this module participants will be able to: • Identify the VPN technologies available on the Forti. Gate device • Identify and configure the SSL VPN operating modes • Define an SSL VPN user group • Configure SSL VPN portals • Configure firewall policies and authentication rules for SSL VPNs
Virtual Private Networks (VPN) Branch Office Corporate Office VPN
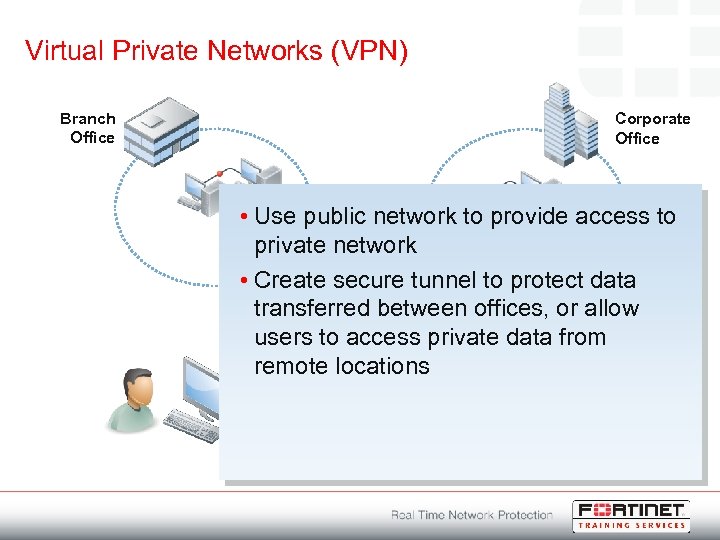
Virtual Private Networks (VPN) Branch Office Corporate Office • Use public network to provide access to private network • Create secure tunnel to protect data transferred between offices, or allow VPN users to access private data from remote locations
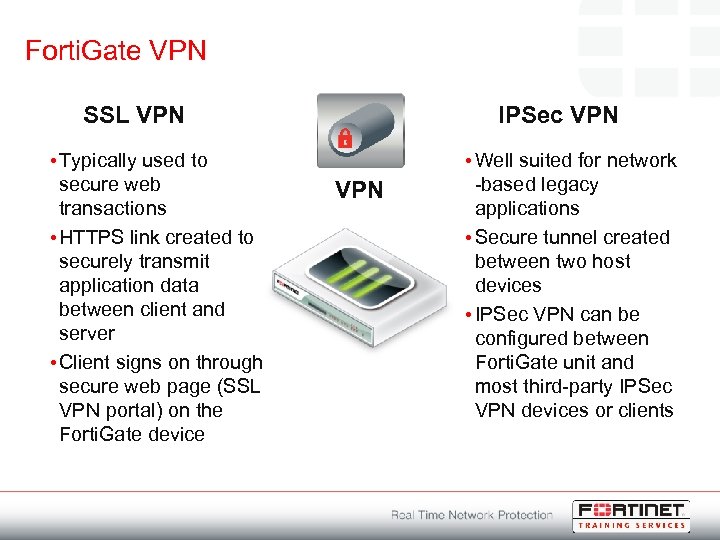
Forti. Gate VPN SSL VPN • Typically used to secure web transactions • HTTPS link created to securely transmit application data between client and server • Client signs on through secure web page (SSL VPN portal) on the Forti. Gate device IPSec VPN • Well suited for network -based legacy applications • Secure tunnel created between two host devices • IPSec VPN can be configured between Forti. Gate unit and most third-party IPSec VPN devices or clients
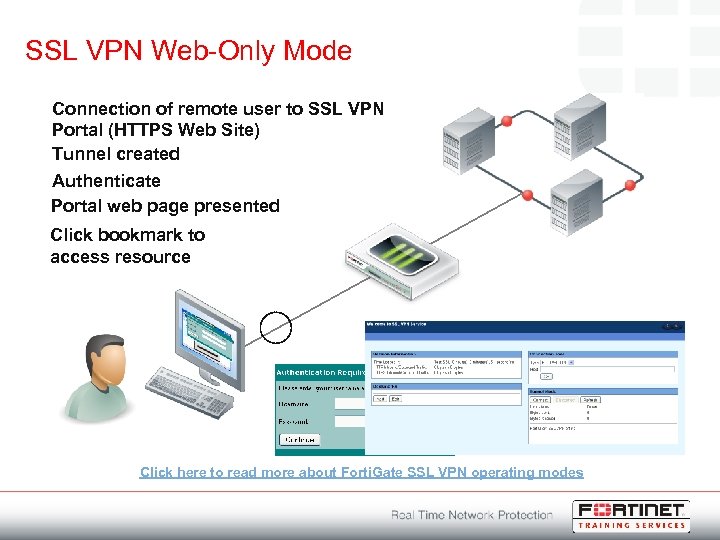
SSL VPN Web-Only Mode Connection of remote user to SSL VPN Portal (HTTPS Web Site) Tunnel created Authenticate Portal web page presented Click bookmark to access resource Click here to read more about Forti. Gate SSL VPN operating modes
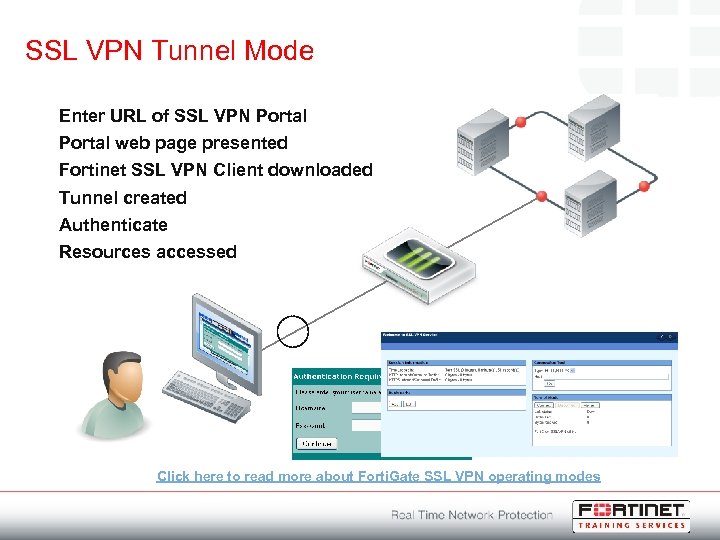
SSL VPN Tunnel Mode Enter URL of SSL VPN Portal web page presented Fortinet SSL VPN Client downloaded Tunnel created Authenticate Resources accessed Click here to read more about Forti. Gate SSL VPN operating modes
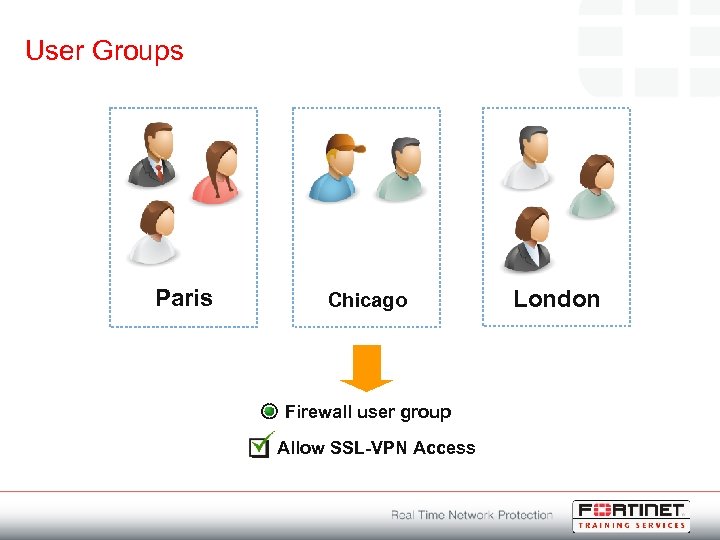
User Groups Paris Chicago Firewall user group Allow SSL-VPN Access London
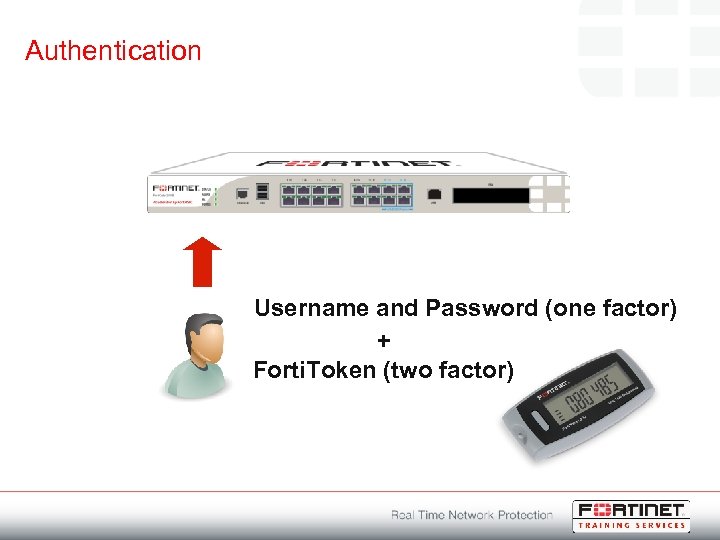
Authentication Username and Password (one factor) + Forti. Token (two factor)
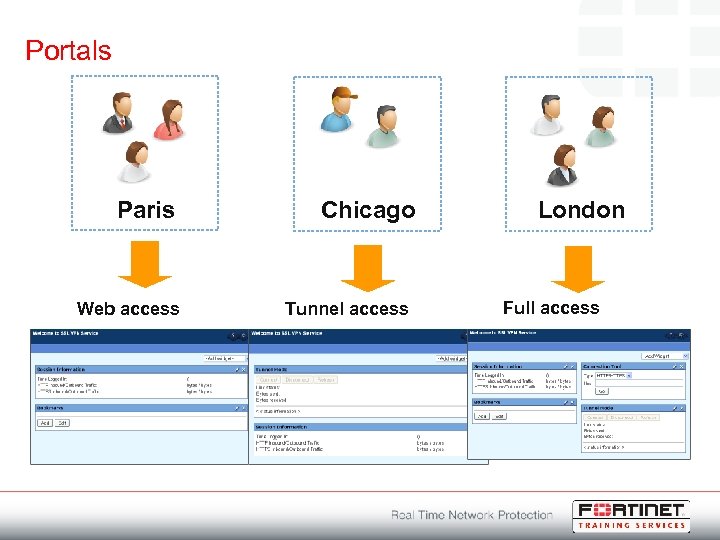
Portals Paris Web access Chicago Tunnel access London Full access
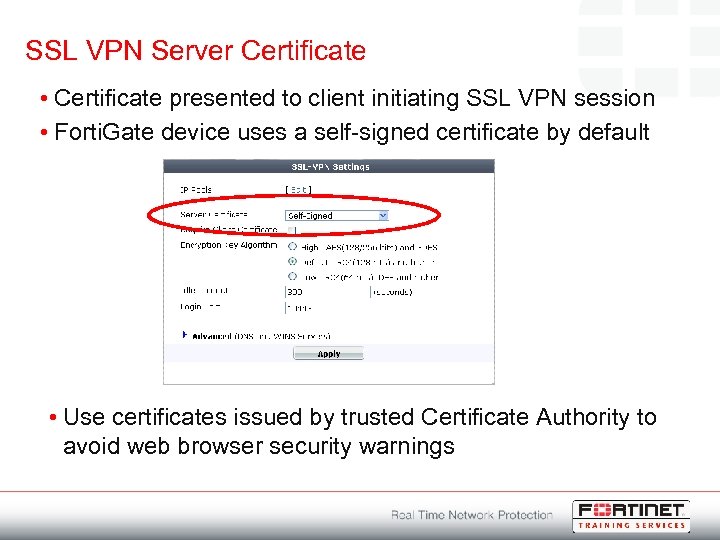
SSL VPN Server Certificate • Certificate presented to client initiating SSL VPN session • Forti. Gate device uses a self-signed certificate by default • Use certificates issued by trusted Certificate Authority to avoid web browser security warnings
Encryption Key Algorithm • Level of encryption used for SSL VPN connections • High, Default, Low • The default setting is RC 4 (128 bits) and higher • If set to High, SSL VPN connections with clients that cannot meet this standard will fail
SSL VPN Web-only Mode Configuration • Enable SSL VPN on the Forti. Gate unit • Create an SSL VPN user group and set SSL VPN portal type to web-access • Add users to SSL VPN user group • Create an SSL VPN firewall policy • Edit authentication rule in firewall policy to add SSL VPN user groups and required protocols
SSL VPN Tunnel Mode Configuration • Enable SSL VPN and select IP Pool • Create an SSL VPN user group and set SSL VPN portal type: • tunnel-access or full-access • Create a static route • Destination = the IP Pool • Device = ssl. root • Add users to SSL VPN user group • Create an SSL VPN firewall policy to authenticate the users • Add SSL VPN user groups and required protocols • Create at least one additional firewall policy • Source = sslvpn tunnel interface • Destination = the internal network • Action is ACCEPT
Web Portal Interface • Web page displayed when client logs into SSL VPN • Includes widgets to access functionality on the portal (such as bookmarks and connection tools) • Software download option for tunnel mode • Default SSL VPN web portal page is accessible at: https: //<Forti. Gate IP address>: 10443 (port 443 can be used in actual deployments as this port is typically open on firewalls)
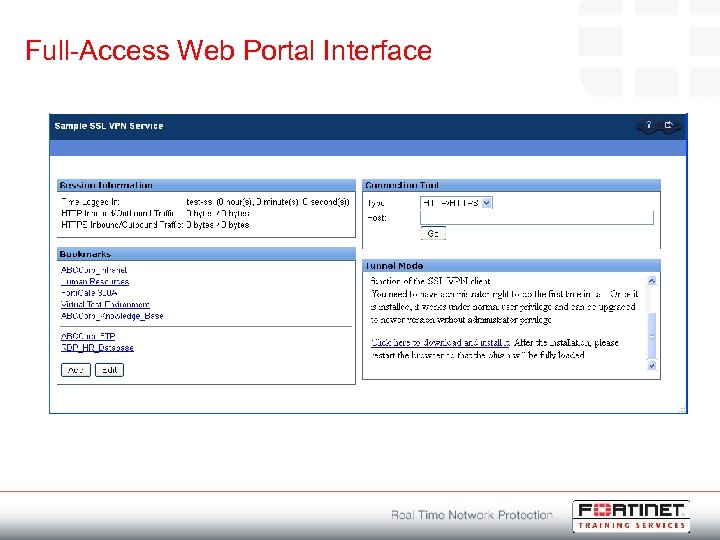
Full-Access Web Portal Interface
Tunnel Mode Split-Tunneling • Only traffic destined for the tunnel IP range network will be routed over the SSL VPN • If access to another inside network is desired, the client will need to create a static route pointing to their own SSL VPN interface • Associated firewall policies must exist
Client Integrity Checking • SSL VPN gateway checks client system • Detects client protection applications (for example, antivirus and personal firewall) • Determines state of applications (active/inactive, current version number and signature updates) • Examples include Cisco Network Admission Control (NAC), MS Network Access Protection (NAP), Trusted Computing Group’s (TCG) Trusted Network Connect
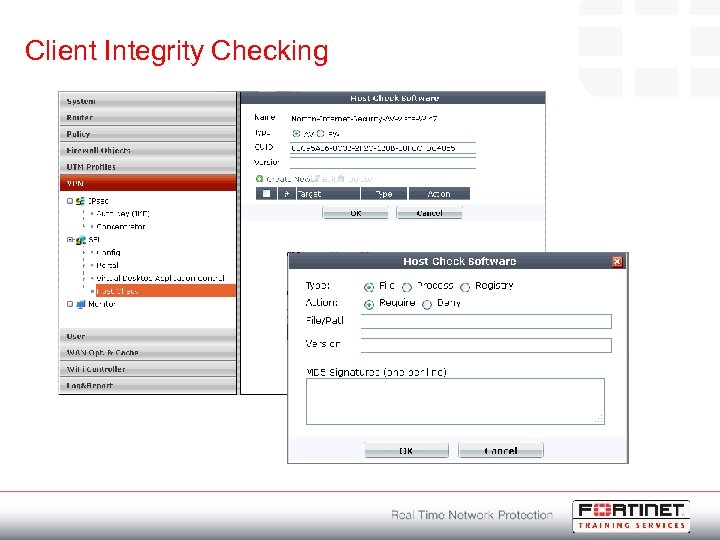
Client Integrity Checking
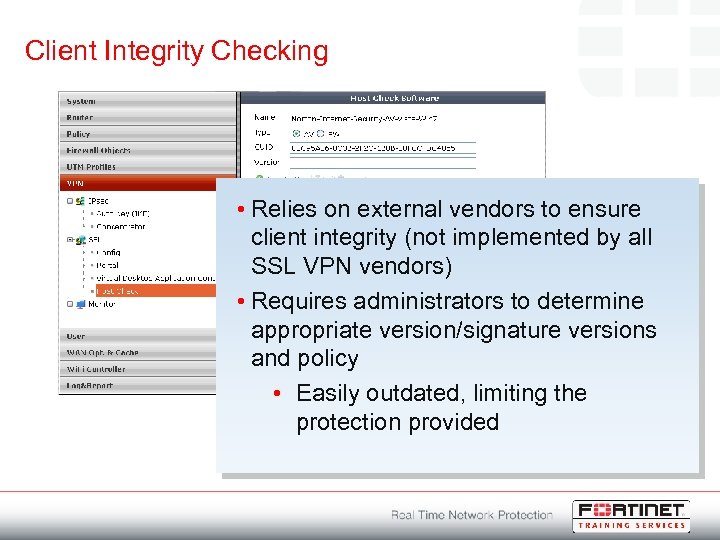
Client Integrity Checking • Relies on external vendors to ensure client integrity (not implemented by all SSL VPN vendors) • Requires administrators to determine appropriate version/signature versions and policy • Easily outdated, limiting the protection provided

SSL VPN Group • The SSL VPN group will be created with full-access and appropriate users selected • The SSL VPN Active X control only needs to be downloaded once
SSL VPN Tunnel Mode Connection • A new network connection called fortissl is created • The connection obtains a virtual IP address • This virtual adapter becomes the preferred default route if split tunneling is disabled • The web portal page will display the status of the SSL VPN client Active. X control • The portal web page must remain open for the tunnel to function
SSL VPN Client Port Forward • Port Forward Mode extends applications supported by Web Application Mode • Application Types: • Port. Forward: for generic port forward application • Citrix: for Citrix server web interface access • RDPNative: for Microsoft Windows native RDP client over port forward • Configured though the CLI using: config vpn ssl web portal edit “SSL Access” set allow-access citrix rdpnative portforward end
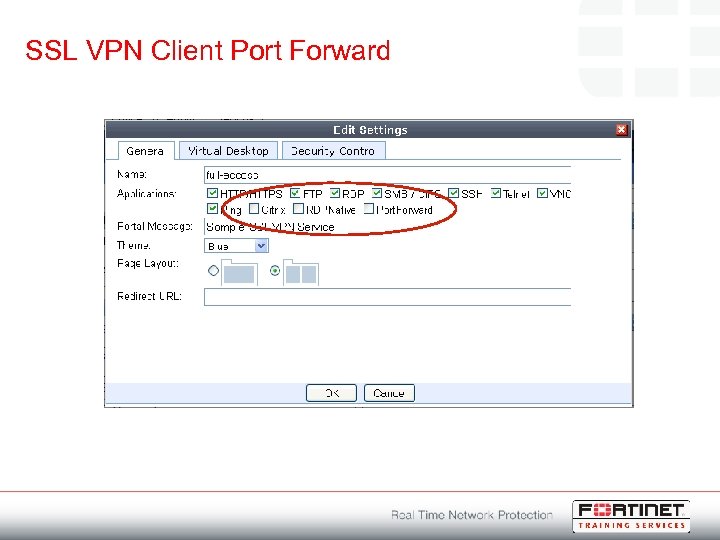
SSL VPN Client Port Forward
SSL VPN IPv 6 Support
SSL-VPN Policy De-Authentication • Firewall policy authentication session is associated with SSL VPN tunnel session • Forces expiration of firewall policy authentication session when associated SSL VPN tunnel session is ended by user • Prevents reuse of authenticated SSL VPN firewall policies (not yet expired) by a different user after the initial user terminates their SSL VPN tunnel session
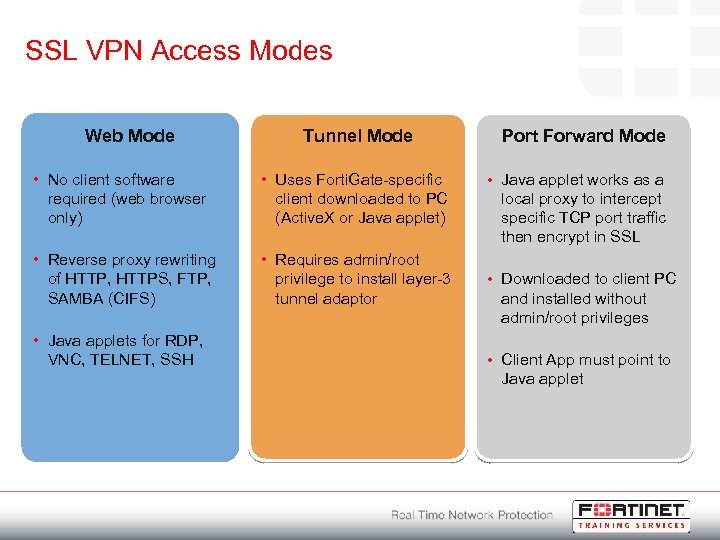
SSL VPN Access Modes Web Mode Tunnel Mode • No client software required (web browser only) • Uses Forti. Gate-specific client downloaded to PC (Active. X or Java applet) • Reverse proxy rewriting of HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, SAMBA (CIFS) • Requires admin/root privilege to install layer-3 tunnel adaptor • Java applets for RDP, VNC, TELNET, SSH Port Forward Mode • Java applet works as a local proxy to intercept specific TCP port traffic then encrypt in SSL • Downloaded to client PC and installed without admin/root privileges • Client App must point to Java applet

Labs • Lab - SSL VPN • Configuring SSL VPN for Web Access • Using the SSL VPN for RDP Access • Configuring the SSL VPN Tunnel Mode with Split Tunneling Click here for step-by-step instructions on completing this lab

Student Resources Click here to view the list of resources used in this module
deb257b822ff11368cdab33e6da78644.ppt