e8b0b6099713ffe441117a222d20ca1f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 65
 SS 4115 Group Project Analysis of Integrated Social Work Practice in Welfare Organizations ---- Focused study on IFSC
SS 4115 Group Project Analysis of Integrated Social Work Practice in Welfare Organizations ---- Focused study on IFSC
 Group Members: Lee Yin King Hung Yuen Chun Chan Kit Ying Siu Lok Ming Yau Yuen King Lin Hau Yin Yeung Man Cham Wong Lai Ping 50564784 50573756 50547646 50552411 50383739 50547425 50487946 50459310
Group Members: Lee Yin King Hung Yuen Chun Chan Kit Ying Siu Lok Ming Yau Yuen King Lin Hau Yin Yeung Man Cham Wong Lai Ping 50564784 50573756 50547646 50552411 50383739 50547425 50487946 50459310
 Table of Contents l l l Introduction of One- Stop Service Historical development of Integrated Service Ideal model of IFSC Model of integration on IFSC Advantages of integration Disadvantages of integration Difficulties in implementing integrated practice Ways of solving difficulties Positive and Negative Comments Conclusion Reference
Table of Contents l l l Introduction of One- Stop Service Historical development of Integrated Service Ideal model of IFSC Model of integration on IFSC Advantages of integration Disadvantages of integration Difficulties in implementing integrated practice Ways of solving difficulties Positive and Negative Comments Conclusion Reference
 Introduction of One –Stop Service
Introduction of One –Stop Service
 One- Stop Services provides a diversify, comprehensive and preventive services on the community. Its major functions and services are: ü Hotlines Services ü Understanding Local Community ü Trust-building among the residents
One- Stop Services provides a diversify, comprehensive and preventive services on the community. Its major functions and services are: ü Hotlines Services ü Understanding Local Community ü Trust-building among the residents
 One-Stop Services The principles of One-Stop Services are, to respond proactively on local needs and allocated resources with flexibility and elasticity in the following areas: l Human Resources l Financial Resources l Equipment l Spatial which are also corresponding to the idea of “Cost Effectiveness”. Another major principles of One-Stop Services are to responds swiftly and directly again on the local needs.
One-Stop Services The principles of One-Stop Services are, to respond proactively on local needs and allocated resources with flexibility and elasticity in the following areas: l Human Resources l Financial Resources l Equipment l Spatial which are also corresponding to the idea of “Cost Effectiveness”. Another major principles of One-Stop Services are to responds swiftly and directly again on the local needs.
 One-Stop Services Example of carrying out one-stop service Target A Background Information: Middle-aged woman, approached the center and seek helps on financial assistance. Flow of providing one-stop services: services Comprehensive Assessment at the center Apart from the financial difficulties, Problems on Spousal Relationship and Parenting also discovered Social Worker encouraged Target A to join training services / Attending Family Education Group / Participated in Counseling Services Being employed after the training program / Improvement in Spousal Relationship / Improvement in Parenting Skills. (Cheng, 2001) v From the above example, it helps to illustrate that One-stop services merge from remedy services to developmental services.
One-Stop Services Example of carrying out one-stop service Target A Background Information: Middle-aged woman, approached the center and seek helps on financial assistance. Flow of providing one-stop services: services Comprehensive Assessment at the center Apart from the financial difficulties, Problems on Spousal Relationship and Parenting also discovered Social Worker encouraged Target A to join training services / Attending Family Education Group / Participated in Counseling Services Being employed after the training program / Improvement in Spousal Relationship / Improvement in Parenting Skills. (Cheng, 2001) v From the above example, it helps to illustrate that One-stop services merge from remedy services to developmental services.
 Historical Development of Integrated Service 1991 White Paper - government announced that children and youth centers, outreach social work and school social work were to be integrated and co-operated together under neighborhood basis meaning that the same team of workers serve young people within the same area Children and youth were the first target group to be under integration services l
Historical Development of Integrated Service 1991 White Paper - government announced that children and youth centers, outreach social work and school social work were to be integrated and co-operated together under neighborhood basis meaning that the same team of workers serve young people within the same area Children and youth were the first target group to be under integration services l
 Historical Development of Integrated Service--IFSC l 1993 - The Hong Kong Council of Social Services suggested to establish Integrated Family Services Center so that family services centers, family life education, senior social workers and family guidance services were to be integrated. However, it was due to the extra expenditure needed for integration, the plan has been left aside.
Historical Development of Integrated Service--IFSC l 1993 - The Hong Kong Council of Social Services suggested to establish Integrated Family Services Center so that family services centers, family life education, senior social workers and family guidance services were to be integrated. However, it was due to the extra expenditure needed for integration, the plan has been left aside.
 Historical Development of Integrated Service--- IFSC 2000 -2001 - Study of family services reviewed that family problems were more and more popular and serious - Family services were involved with youth services in which the allocation of services was not concentrated and repeated with existing family services - Integration of family services was established under three elements: primary prevention (family resources unit), secondary prevention (family support unit, tertiary prevention (family counseling unit) l
Historical Development of Integrated Service--- IFSC 2000 -2001 - Study of family services reviewed that family problems were more and more popular and serious - Family services were involved with youth services in which the allocation of services was not concentrated and repeated with existing family services - Integration of family services was established under three elements: primary prevention (family resources unit), secondary prevention (family support unit, tertiary prevention (family counseling unit) l
 l To review, because: ¡ remedial services absorbed most resources ¡ preventive services were neglected
l To review, because: ¡ remedial services absorbed most resources ¡ preventive services were neglected
 IDEAL MODEL OF IFSC
IDEAL MODEL OF IFSC
 Direction and Rationale l Child-centered l Family-focused (兒童為重) (家庭為本) l Community-based (社區為基礎)
Direction and Rationale l Child-centered l Family-focused (兒童為重) (家庭為本) l Community-based (社區為基礎)
 Basic Principles 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Accessibility Early identification Prevention Integration Partnership
Basic Principles 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Accessibility Early identification Prevention Integration Partnership
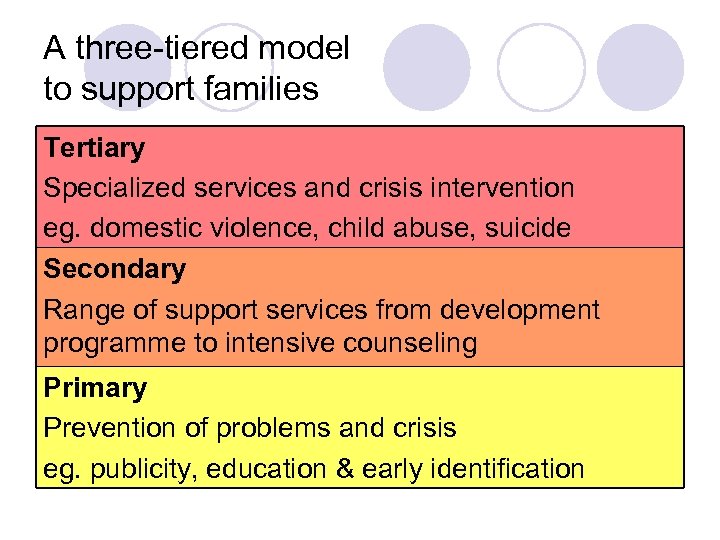 A three-tiered model to support families Tertiary Specialized services and crisis intervention eg. domestic violence, child abuse, suicide Secondary Range of support services from development programme to intensive counseling Primary Prevention of problems and crisis eg. publicity, education & early identification
A three-tiered model to support families Tertiary Specialized services and crisis intervention eg. domestic violence, child abuse, suicide Secondary Range of support services from development programme to intensive counseling Primary Prevention of problems and crisis eg. publicity, education & early identification
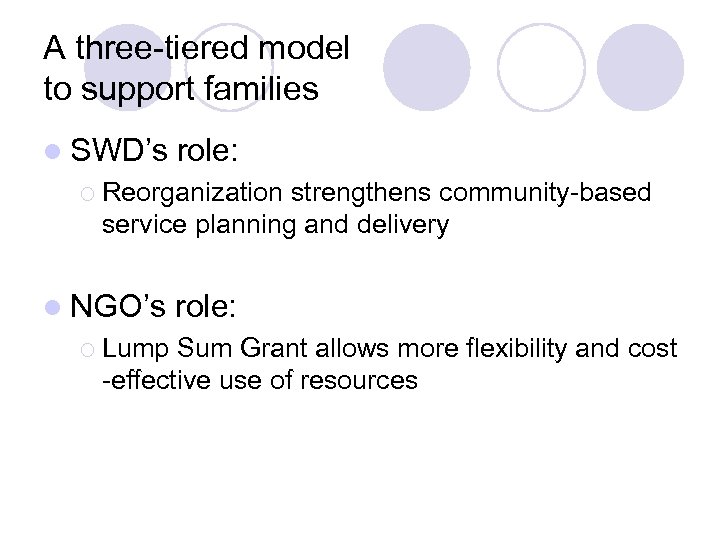 A three-tiered model to support families l SWD’s role: ¡ Reorganization strengthens community-based service planning and delivery l NGO’s ¡ Lump role: Sum Grant allows more flexibility and cost -effective use of resources
A three-tiered model to support families l SWD’s role: ¡ Reorganization strengthens community-based service planning and delivery l NGO’s ¡ Lump role: Sum Grant allows more flexibility and cost -effective use of resources
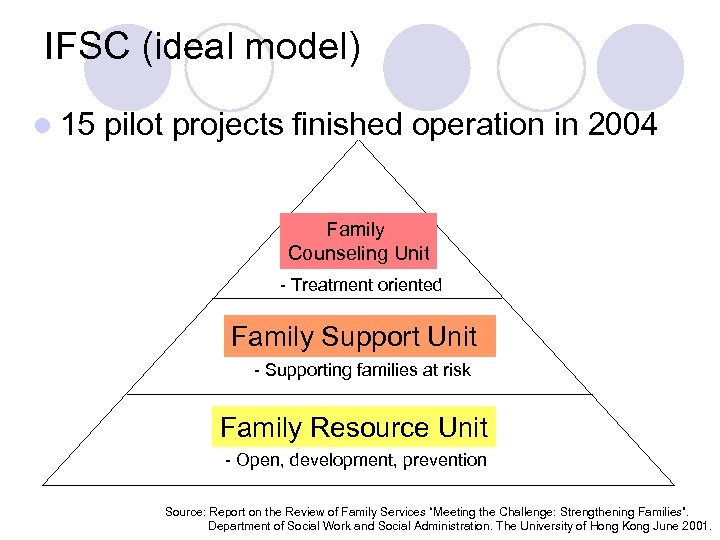 IFSC (ideal model) l 15 pilot projects finished operation in 2004 Family Counseling Unit - Treatment oriented Family Support Unit - Supporting families at risk Family Resource Unit - Open, development, prevention Source: Report on the Review of Family Services “Meeting the Challenge: Strengthening Families”. Department of Social Work and Social Administration. The University of Hong Kong June 2001.
IFSC (ideal model) l 15 pilot projects finished operation in 2004 Family Counseling Unit - Treatment oriented Family Support Unit - Supporting families at risk Family Resource Unit - Open, development, prevention Source: Report on the Review of Family Services “Meeting the Challenge: Strengthening Families”. Department of Social Work and Social Administration. The University of Hong Kong June 2001.
 Family Resource Unit l Functions: ¡ Easy to catch cases ¡ Early identification ¡ Educational, developmental ¡ Support and preventive ¡ Empowerment and advocacy Source: Report on the Review of Family Services “Meeting the Challenge: Strengthening Families”. Department of Social Work and Social Administration. The University of Hong Kong June 2001. p. 79.
Family Resource Unit l Functions: ¡ Easy to catch cases ¡ Early identification ¡ Educational, developmental ¡ Support and preventive ¡ Empowerment and advocacy Source: Report on the Review of Family Services “Meeting the Challenge: Strengthening Families”. Department of Social Work and Social Administration. The University of Hong Kong June 2001. p. 79.
 Family Resource Unit l Core Services: ¡ Drop-in services ¡ Information giving ¡ Family life education ¡ Developmental groups ¡ Mutual help groups ¡ Volunteer development ¡ outreach Source: Report on the Review of Family Services “Meeting the Challenge: Strengthening Families”. Department of Social Work and Social Administration. The University of Hong Kong June 2001. p. 79.
Family Resource Unit l Core Services: ¡ Drop-in services ¡ Information giving ¡ Family life education ¡ Developmental groups ¡ Mutual help groups ¡ Volunteer development ¡ outreach Source: Report on the Review of Family Services “Meeting the Challenge: Strengthening Families”. Department of Social Work and Social Administration. The University of Hong Kong June 2001. p. 79.
 Family Resource Unit l Complementary ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Service Hotlines Employment skills training After school care / tutoring Child minding / occasional child care Respite care Play groups Recreational / social activities Toy library Research Source: Report on the Review of Family Services “Meeting the Challenge: Strengthening Families”. Department of Social Work and Social Administration. The University of Hong Kong June 2001. p. 79.
Family Resource Unit l Complementary ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Service Hotlines Employment skills training After school care / tutoring Child minding / occasional child care Respite care Play groups Recreational / social activities Toy library Research Source: Report on the Review of Family Services “Meeting the Challenge: Strengthening Families”. Department of Social Work and Social Administration. The University of Hong Kong June 2001. p. 79.
 Family Support Unit l Functions: ¡ Some remedial ¡ Preventive ¡ Support ¡ Advocacy Source: Report on the Review of Family Services “Meeting the Challenge: Strengthening Families”. Department of Social Work and Social Administration. The University of Hong Kong June 2001. p. 79.
Family Support Unit l Functions: ¡ Some remedial ¡ Preventive ¡ Support ¡ Advocacy Source: Report on the Review of Family Services “Meeting the Challenge: Strengthening Families”. Department of Social Work and Social Administration. The University of Hong Kong June 2001. p. 79.
 Family Support Unit l Core Services: ¡ Brief counseling ¡ Emotional support ¡ Referral for tangible services ¡ mutual help groups ¡ Family education l Complementary Service: ¡ Family aide service Source: Report on the Review of Family Services “Meeting the Challenge: Strengthening Families”. Department of Social Work and Social Administration. The University of Hong Kong June 2001. p. 79.
Family Support Unit l Core Services: ¡ Brief counseling ¡ Emotional support ¡ Referral for tangible services ¡ mutual help groups ¡ Family education l Complementary Service: ¡ Family aide service Source: Report on the Review of Family Services “Meeting the Challenge: Strengthening Families”. Department of Social Work and Social Administration. The University of Hong Kong June 2001. p. 79.
 Family Counseling Unit l Functions: ¡ Remedial l Core Services: ¡ Intensive counseling ¡ Therapeutic groups ¡ Crisis intervention Source: Report on the Review of Family Services “Meeting the Challenge: Strengthening Families”. Department of Social Work and Social Administration. The University of Hong Kong June 2001. p. 79.
Family Counseling Unit l Functions: ¡ Remedial l Core Services: ¡ Intensive counseling ¡ Therapeutic groups ¡ Crisis intervention Source: Report on the Review of Family Services “Meeting the Challenge: Strengthening Families”. Department of Social Work and Social Administration. The University of Hong Kong June 2001. p. 79.
 Partnership with the community and the Social Services System 1. IFSC ↔ Community-based social services unit 2. IFSC ↔ Social service units 3. IFSC ↔ Community organizations 4. IFSC ↔ Specialized units 5. IFSC ↔ Educational bodies 6. IFSC ↔ Other professionals 7. IFSC ↔ Government Offices
Partnership with the community and the Social Services System 1. IFSC ↔ Community-based social services unit 2. IFSC ↔ Social service units 3. IFSC ↔ Community organizations 4. IFSC ↔ Specialized units 5. IFSC ↔ Educational bodies 6. IFSC ↔ Other professionals 7. IFSC ↔ Government Offices
 Partnership with the community and the Social Services System Service/Worker-oriented Integration (Different service units or workers join together) 1. IFSC ↔ Community-based social services unit eg. FARC/GWU, FARC/CC, IT, C&YC l Type of relationship: ¡ ¡ early identification & referral Screening & referral of cases to IFSC Cooperation at project level collaboration Source: Report on the Review of Family Services “Meeting the Challenge: Strengthening Families”. Department of Social Work and Social Administration. The University of Hong Kong June 2001. p. 80.
Partnership with the community and the Social Services System Service/Worker-oriented Integration (Different service units or workers join together) 1. IFSC ↔ Community-based social services unit eg. FARC/GWU, FARC/CC, IT, C&YC l Type of relationship: ¡ ¡ early identification & referral Screening & referral of cases to IFSC Cooperation at project level collaboration Source: Report on the Review of Family Services “Meeting the Challenge: Strengthening Families”. Department of Social Work and Social Administration. The University of Hong Kong June 2001. p. 80.
 Partnership with the community and the Social Services System Service/Worker-oriented Integration 2. IFSC ↔ Social service units eg. SSFU, SSW, MSS, M/E, children’s homes, rehabilitation units, elderly centers, PMCs, SPCs, CD projects, etc. l Type of relationship: ¡ ¡ early identification & referral Cooperation at project level Source: Report on the Review of Family Services “Meeting the Challenge: Strengthening Families”. Department of Social Work and Social Administration. The University of Hong Kong June 2001. p. 80.
Partnership with the community and the Social Services System Service/Worker-oriented Integration 2. IFSC ↔ Social service units eg. SSFU, SSW, MSS, M/E, children’s homes, rehabilitation units, elderly centers, PMCs, SPCs, CD projects, etc. l Type of relationship: ¡ ¡ early identification & referral Cooperation at project level Source: Report on the Review of Family Services “Meeting the Challenge: Strengthening Families”. Department of Social Work and Social Administration. The University of Hong Kong June 2001. p. 80.
 Partnership with the community and the Social Services System Service/Worker-oriented Integration 3. IFSC ↔ Community organizations eg. women’s labour & residents’ associations, self-help groups, disabled & parent organizations, etc. l Type of relationship: ¡ early identification & referral Source: Report on the Review of Family Services “Meeting the Challenge: Strengthening Families”. Department of Social Work and Social Administration. The University of Hong Kong June 2001. p. 80.
Partnership with the community and the Social Services System Service/Worker-oriented Integration 3. IFSC ↔ Community organizations eg. women’s labour & residents’ associations, self-help groups, disabled & parent organizations, etc. l Type of relationship: ¡ early identification & referral Source: Report on the Review of Family Services “Meeting the Challenge: Strengthening Families”. Department of Social Work and Social Administration. The University of Hong Kong June 2001. p. 80.
 Partnership with the community and the Social Services System 4. IFSC ↔ Specialized units eg. FCPSU, CCSU, CP, FLERC, Child assessment center, etc. l Type of relationship: ¡ Referral and support Source: Report on the Review of Family Services “Meeting the Challenge: Strengthening Families”. Department of Social Work and Social Administration. The University of Hong Kong June 2001. p. 80.
Partnership with the community and the Social Services System 4. IFSC ↔ Specialized units eg. FCPSU, CCSU, CP, FLERC, Child assessment center, etc. l Type of relationship: ¡ Referral and support Source: Report on the Review of Family Services “Meeting the Challenge: Strengthening Families”. Department of Social Work and Social Administration. The University of Hong Kong June 2001. p. 80.
 Partnership with the community and the Social Services System Agency-oriented Integration (different agencies join together) 5. IFSC ↔ Educational bodies eg. child care centers, kindergartens, primary schools, special schools, skill centers, SGO/SGT, PATs, etc. l Type of relationship: ¡ ¡ early identification & referral Cooperation at project level Source: Report on the Review of Family Services “Meeting the Challenge: Strengthening Families”. Department of Social Work and Social Administration. The University of Hong Kong June 2001. p. 80.
Partnership with the community and the Social Services System Agency-oriented Integration (different agencies join together) 5. IFSC ↔ Educational bodies eg. child care centers, kindergartens, primary schools, special schools, skill centers, SGO/SGT, PATs, etc. l Type of relationship: ¡ ¡ early identification & referral Cooperation at project level Source: Report on the Review of Family Services “Meeting the Challenge: Strengthening Families”. Department of Social Work and Social Administration. The University of Hong Kong June 2001. p. 80.
 Partnership with the community and the Social Services System Profession-oriented Integration (Different professionals join together) 6. IFSC ↔ Other professionals eg. lawyers, medical practitioners, psychiatrists, educational psychologists, etc. l Type of relationship: ¡ early identification & referral Source: Report on the Review of Family Services “Meeting the Challenge: Strengthening Families”. Department of Social Work and Social Administration. The University of Hong Kong June 2001. p. 80.
Partnership with the community and the Social Services System Profession-oriented Integration (Different professionals join together) 6. IFSC ↔ Other professionals eg. lawyers, medical practitioners, psychiatrists, educational psychologists, etc. l Type of relationship: ¡ early identification & referral Source: Report on the Review of Family Services “Meeting the Challenge: Strengthening Families”. Department of Social Work and Social Administration. The University of Hong Kong June 2001. p. 80.
 Partnership with the community and the Social Services System Agency-oriented Integration 7. IFSC ↔ Government Offices eg. Hospital & MCHCs, Department of Housing, Labour & Legal Aid, Marriage Registry, etc. l Type of relationship: ¡ ¡ early identification & referral Cooperation at project level Source: Report on the Review of Family Services “Meeting the Challenge: Strengthening Families”. Department of Social Work and Social Administration. The University of Hong Kong June 2001. p. 80.
Partnership with the community and the Social Services System Agency-oriented Integration 7. IFSC ↔ Government Offices eg. Hospital & MCHCs, Department of Housing, Labour & Legal Aid, Marriage Registry, etc. l Type of relationship: ¡ ¡ early identification & referral Cooperation at project level Source: Report on the Review of Family Services “Meeting the Challenge: Strengthening Families”. Department of Social Work and Social Administration. The University of Hong Kong June 2001. p. 80.
 Further Illustration on Models of integration exist in IFSC l. Method-oriented integration l. Profession-oriented integration l. Networking & Case management l. Agency-oriented integration
Further Illustration on Models of integration exist in IFSC l. Method-oriented integration l. Profession-oriented integration l. Networking & Case management l. Agency-oriented integration
 Method-oriented integration l Using all three social work interventions– casework (e. g. counselling service), group work( e. g. parenting group) , community work (e. g. mass programme: community education) l In dealing with cases which involve parenting difficulties, case workers may refer clients to join some parenting groups. l i. e. casework+group work
Method-oriented integration l Using all three social work interventions– casework (e. g. counselling service), group work( e. g. parenting group) , community work (e. g. mass programme: community education) l In dealing with cases which involve parenting difficulties, case workers may refer clients to join some parenting groups. l i. e. casework+group work
 Profession-oriented integration E. g. l In dealing with cases which involve suspected child abuse, social workers may call different professions such as psychologists, doctors, and police to join together for a case conference to investigate the case and discuss the welfare of the victim l i. e. Multiple Professional Case Conference l (MPCC) Social workers+psychologists+doctors+police
Profession-oriented integration E. g. l In dealing with cases which involve suspected child abuse, social workers may call different professions such as psychologists, doctors, and police to join together for a case conference to investigate the case and discuss the welfare of the victim l i. e. Multiple Professional Case Conference l (MPCC) Social workers+psychologists+doctors+police
 Networking & Case Management E. g. l Referring clients to food banks in case they could not support their meals or are not entitled to apply for financial assistance l Referring clients to non-profit corporations such as Crossroads International to obtain tangible goods (furniture and electronic appliances) l Referring clients to join Intensive Employment Assistance Projects to help them find jobs IFSC+Tangible assistance IFSC+Employment assistance
Networking & Case Management E. g. l Referring clients to food banks in case they could not support their meals or are not entitled to apply for financial assistance l Referring clients to non-profit corporations such as Crossroads International to obtain tangible goods (furniture and electronic appliances) l Referring clients to join Intensive Employment Assistance Projects to help them find jobs IFSC+Tangible assistance IFSC+Employment assistance
 Agency oriented integration E. g. l Community Harmony Project held from June 18 to July 19 in 2006 in Tuen Mun l IFSCs under the SWD l + Hong Kong Police Force l + Tuen Mun District Women’s Association l + IFSC under the Caritas
Agency oriented integration E. g. l Community Harmony Project held from June 18 to July 19 in 2006 in Tuen Mun l IFSCs under the SWD l + Hong Kong Police Force l + Tuen Mun District Women’s Association l + IFSC under the Caritas
 Looking at Reality --Opinions gathered from observation/ interviews of workers/discussion
Looking at Reality --Opinions gathered from observation/ interviews of workers/discussion
 Advantages of integration For Service Users: l User friendly, physically convenient for clients ( Past: service users approach different agencies by themselves Now in IFSC: one-stop service or workers make referral , reduce intake procedures) l Quantity of services increases while the same resources are introduced l More prevention programs held at district level For Workers: l Training programs for improving skills which match IFSC services l Workers can develop diversified skills in handling varieties of cases / and for using different intervention approaches/ wider exposure
Advantages of integration For Service Users: l User friendly, physically convenient for clients ( Past: service users approach different agencies by themselves Now in IFSC: one-stop service or workers make referral , reduce intake procedures) l Quantity of services increases while the same resources are introduced l More prevention programs held at district level For Workers: l Training programs for improving skills which match IFSC services l Workers can develop diversified skills in handling varieties of cases / and for using different intervention approaches/ wider exposure
 Advantages of integration For Center: l l l Better coordination and communication between the staff in the centre Can get in touch with different types of problems and services. Services are diversified and elastic which matched the ideas of “Cost-Effectiveness”. Share materials of programme : reducing cost Efficient services to community needs.
Advantages of integration For Center: l l l Better coordination and communication between the staff in the centre Can get in touch with different types of problems and services. Services are diversified and elastic which matched the ideas of “Cost-Effectiveness”. Share materials of programme : reducing cost Efficient services to community needs.
 Provide the total integration (one-stop service): -can have total assessment for the client -can find the different needs of one client The client can obtain the total service l Increase the co-operation among different professionals and service units -the resources can be used more flexibly -不同專業: 互相配合, 互補不足 ( mutual complementary) -the quality of services can be increased and guaranteed l
Provide the total integration (one-stop service): -can have total assessment for the client -can find the different needs of one client The client can obtain the total service l Increase the co-operation among different professionals and service units -the resources can be used more flexibly -不同專業: 互相配合, 互補不足 ( mutual complementary) -the quality of services can be increased and guaranteed l
 Example In the past, the Family Resources Centre had an annual fund about $330000 for holding programs and groups for the whole district in Tuen Mun l At present, there are four Integrated Family Service Centres in Tuen Mun, each has about $90000 for programs and groups l IFSCs have to meet the service quota under the Funding Service Agreement Services l
Example In the past, the Family Resources Centre had an annual fund about $330000 for holding programs and groups for the whole district in Tuen Mun l At present, there are four Integrated Family Service Centres in Tuen Mun, each has about $90000 for programs and groups l IFSCs have to meet the service quota under the Funding Service Agreement Services l
 Disadvantages of integration For Centre l Unable to provide one-stop services l IFSCs are not competent in every aspect of services. l In comparison to some specialized units, IFSCs may not be able to provide the same quality of services in some areas as those specialized units l It is uncertain whether it is more cost effective because it is difficult to measure the quality of services
Disadvantages of integration For Centre l Unable to provide one-stop services l IFSCs are not competent in every aspect of services. l In comparison to some specialized units, IFSCs may not be able to provide the same quality of services in some areas as those specialized units l It is uncertain whether it is more cost effective because it is difficult to measure the quality of services
 Disadvantages of integration (Cont’) For service users l Service users are sometimes transferred from one centre to another, this creates confusion for them For workers l Workers’ burden increase a lot, this certainly creates discontent and adjustment difficulties among the workers l Demand workers to have multiple skills ( case, group and community work) and increases their stress l The support system for workers is not enough
Disadvantages of integration (Cont’) For service users l Service users are sometimes transferred from one centre to another, this creates confusion for them For workers l Workers’ burden increase a lot, this certainly creates discontent and adjustment difficulties among the workers l Demand workers to have multiple skills ( case, group and community work) and increases their stress l The support system for workers is not enough
 Disadvantage and Side-effects of integration l For further explanation of the disadvantages on integration, it can be divided into 2 major aspects, each aspect could also be divided into 2 areas to look into the problems l They are the worker side and the center side l To explore these area, we have read some reports and interview some social workers to understand more
Disadvantage and Side-effects of integration l For further explanation of the disadvantages on integration, it can be divided into 2 major aspects, each aspect could also be divided into 2 areas to look into the problems l They are the worker side and the center side l To explore these area, we have read some reports and interview some social workers to understand more
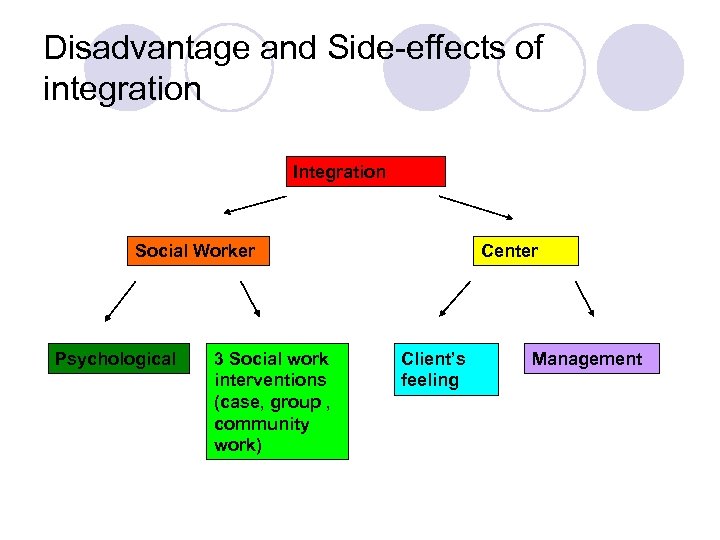 Disadvantage and Side-effects of integration Integration Social Worker Psychological 3 Social work interventions (case, group , community work) Center Client’s feeling Management
Disadvantage and Side-effects of integration Integration Social Worker Psychological 3 Social work interventions (case, group , community work) Center Client’s feeling Management
 Social worker psychological aspects l According to a report of SWAC 11/03 on the evaluation report of integration services l Worker’s worry - Loss of work - Cannot adapt the changes - New services need to introduces
Social worker psychological aspects l According to a report of SWAC 11/03 on the evaluation report of integration services l Worker’s worry - Loss of work - Cannot adapt the changes - New services need to introduces
 Social working interventions (case, group , community work) l Social Worker’s difficulties - Integrated in services but workers lack of integrated experiences - Worker’s should also work in the interventions who are not familiar and interest in - Worker’s work load increase as holding variety of work in (individual, clients level – case, group and the society level community work sometimes) - A worker is handling 60 - 80 cases at the same time, still need to spend much time on group and programme preparation - Always worry about the cases would have life danger but worker have insufficient time to handle– extremely high pressure
Social working interventions (case, group , community work) l Social Worker’s difficulties - Integrated in services but workers lack of integrated experiences - Worker’s should also work in the interventions who are not familiar and interest in - Worker’s work load increase as holding variety of work in (individual, clients level – case, group and the society level community work sometimes) - A worker is handling 60 - 80 cases at the same time, still need to spend much time on group and programme preparation - Always worry about the cases would have life danger but worker have insufficient time to handle– extremely high pressure
 Center level’s side effects l Client aspect - Although it provide the convenience, some workers are not so good at different working skills, it affects the quality of service - Too much workload of worker also lower the quality of service received by service users - Finally, they still need to be wait and take more time for the referral and intervention - But actually the clients think less of integration, they most concern about how the service can help them
Center level’s side effects l Client aspect - Although it provide the convenience, some workers are not so good at different working skills, it affects the quality of service - Too much workload of worker also lower the quality of service received by service users - Finally, they still need to be wait and take more time for the referral and intervention - But actually the clients think less of integration, they most concern about how the service can help them
 Family services center level side effects l Management - Center in-charge need to spend more time on communicating the difficulties during the integration (However, not so many I. C. do so) - There may have different management method and culture in various IFSC , the center-in-charges apply their own way in organize the resources. As a result, the integration culture is not consistent.
Family services center level side effects l Management - Center in-charge need to spend more time on communicating the difficulties during the integration (However, not so many I. C. do so) - There may have different management method and culture in various IFSC , the center-in-charges apply their own way in organize the resources. As a result, the integration culture is not consistent.
 Family services center level side effects -worker’s communication also plays important role in integration the services as the case transfer internally in the centre, however, one social worker point out these kinds of software on integration are not well developed and prepared for the integration
Family services center level side effects -worker’s communication also plays important role in integration the services as the case transfer internally in the centre, however, one social worker point out these kinds of software on integration are not well developed and prepared for the integration
 Family services center level side effects - Provide some training to worker on the specific working intervention that they are not good at (However, the daily work are too heavy to process on-job training) To code an example一名家庭生活教育 作員服務有50, 000名 10至 50歲市民之社區
Family services center level side effects - Provide some training to worker on the specific working intervention that they are not good at (However, the daily work are too heavy to process on-job training) To code an example一名家庭生活教育 作員服務有50, 000名 10至 50歲市民之社區
 Difficulties in implementing integrated practice and solutions Not much cases can be treated by group work, casework remain the focus l Workers’ inadequate knowledge on group work because they used to deal with cases only, and those who used to work in Community Centres find difficulty in dealing with cases l Worker’s inadequate knowledge in carrying out therapeutic groups for intensive treatment for clients l
Difficulties in implementing integrated practice and solutions Not much cases can be treated by group work, casework remain the focus l Workers’ inadequate knowledge on group work because they used to deal with cases only, and those who used to work in Community Centres find difficulty in dealing with cases l Worker’s inadequate knowledge in carrying out therapeutic groups for intensive treatment for clients l
 Difficulties in implementing integrated practice Group session is limited the group’s culture in IFSC is 4 sessions per group both supportive / therapeutic group there is limited time to develop the group cohesion difficult to reach the aims of therapeutic in short time l
Difficulties in implementing integrated practice Group session is limited the group’s culture in IFSC is 4 sessions per group both supportive / therapeutic group there is limited time to develop the group cohesion difficult to reach the aims of therapeutic in short time l
 Difficulties in implementing integrated practice Limitation in reality Integration give service users an impression that it can provide any kind of services IFSC also has its limitation in resources l Thus, maintain close contact and referral to other community resources is common
Difficulties in implementing integrated practice Limitation in reality Integration give service users an impression that it can provide any kind of services IFSC also has its limitation in resources l Thus, maintain close contact and referral to other community resources is common
 Difficulties in implementing integrated practice Confused responsibility /service boundary -since the integration aims to provide one-shop service to the service user, sometimes other service will transfer their client for service -there is a misunderstanding about service delivery -”throw ball” between other agency may arise - the reality is IFSC may not get responsibility in the situation l -IFSC also has its limitation in resources and boundary
Difficulties in implementing integrated practice Confused responsibility /service boundary -since the integration aims to provide one-shop service to the service user, sometimes other service will transfer their client for service -there is a misunderstanding about service delivery -”throw ball” between other agency may arise - the reality is IFSC may not get responsibility in the situation l -IFSC also has its limitation in resources and boundary
 Ways to solve the difficulties Solution to Confused responsibility /service boundary -maintain good cooperation , clear communication and setting guidelines/ agreement with other agency for service delivery -When some case arguments are raised, use client’s benefit as priority -seek for alternative solution between agencies
Ways to solve the difficulties Solution to Confused responsibility /service boundary -maintain good cooperation , clear communication and setting guidelines/ agreement with other agency for service delivery -When some case arguments are raised, use client’s benefit as priority -seek for alternative solution between agencies
 Ways to solve the difficulties Solutions to improve service quality: l Provide flexible and concise training courses and workshops for workers on group work and therapies l More work supervision l Increase mutual support between workers l exchange professional ideas with expertise l Better utilize the strength of different worker –- more division of work / a certain level of specialization inside the team e. g. ASWO focuses more on casework and therapeutic group l Increase no. of workers ( increase funding needed) l Comprehensive training needed in institution
Ways to solve the difficulties Solutions to improve service quality: l Provide flexible and concise training courses and workshops for workers on group work and therapies l More work supervision l Increase mutual support between workers l exchange professional ideas with expertise l Better utilize the strength of different worker –- more division of work / a certain level of specialization inside the team e. g. ASWO focuses more on casework and therapeutic group l Increase no. of workers ( increase funding needed) l Comprehensive training needed in institution
 Our Comments on the integration Positive Comments It is a diversify and large-scale model which provides varieties services which are easily assess to. Ø It helps to shorten the period in the process of referring cases and could make intervention within a shorter period of time. Ø It integrated with different kinds of services could lessen the duration for the residents in seeking information. Ø There are different kinds of services available within the setting and services users could choose their suitable and best services under the supervisions and suggestions from IFSC. Ø
Our Comments on the integration Positive Comments It is a diversify and large-scale model which provides varieties services which are easily assess to. Ø It helps to shorten the period in the process of referring cases and could make intervention within a shorter period of time. Ø It integrated with different kinds of services could lessen the duration for the residents in seeking information. Ø There are different kinds of services available within the setting and services users could choose their suitable and best services under the supervisions and suggestions from IFSC. Ø
 Positive Comments The services ranged from preventive to remedial, served as a more professional image on the community and could help to strengthen its foundation in the locality, as a result, the residents in the community will be clearer on where and how they can seek helps and information. Ø It helps to lessen the financial expenses of the government as IFSC is running under the “Cost-Effectiveness” principle. Ø As IFSC is working on the whole community, it helps to balance different kinds of services’ needs and development, which as a result turns to be more favorable to the locality as their needs can be better satisfied. Ø IFSC also work at advocating new services to meet the changing needs on the community and as a result, it helps to bring better services to the residents. Ø
Positive Comments The services ranged from preventive to remedial, served as a more professional image on the community and could help to strengthen its foundation in the locality, as a result, the residents in the community will be clearer on where and how they can seek helps and information. Ø It helps to lessen the financial expenses of the government as IFSC is running under the “Cost-Effectiveness” principle. Ø As IFSC is working on the whole community, it helps to balance different kinds of services’ needs and development, which as a result turns to be more favorable to the locality as their needs can be better satisfied. Ø IFSC also work at advocating new services to meet the changing needs on the community and as a result, it helps to bring better services to the residents. Ø
 Comments on the integration l Negative - - - comments The integration actually contain a lot of good ideas and the effectiveness of using resources. However, the “software” of integration are not enough to support the workers and the center. It seems that integration is to save resources instead of using resources more effectively since the effectiveness of integration on family services is unsure. The results on it varies according to the perspectives that the researcher adopts , the reports done by Hong Kong University are supported by H. K. government and therefore contains bias Under the Funding Service Agreement, each IFSC has to try hard to meet the quota, it emphasizes too much on quantity of service provided but the quality of services is not ensured
Comments on the integration l Negative - - - comments The integration actually contain a lot of good ideas and the effectiveness of using resources. However, the “software” of integration are not enough to support the workers and the center. It seems that integration is to save resources instead of using resources more effectively since the effectiveness of integration on family services is unsure. The results on it varies according to the perspectives that the researcher adopts , the reports done by Hong Kong University are supported by H. K. government and therefore contains bias Under the Funding Service Agreement, each IFSC has to try hard to meet the quota, it emphasizes too much on quantity of service provided but the quality of services is not ensured
 To code some example, software of S. W. support is limited, no spare time to have further training, no ways to share the pressure when facing changes. Moreover, even for the worker, they are not open to recognize the difficulties and release pressure during the integration as some workers think that social worker should be strong……therefore, such kinds of software not developed well, the result of integration must have many aspects to be improved as our presentation mention
To code some example, software of S. W. support is limited, no spare time to have further training, no ways to share the pressure when facing changes. Moreover, even for the worker, they are not open to recognize the difficulties and release pressure during the integration as some workers think that social worker should be strong……therefore, such kinds of software not developed well, the result of integration must have many aspects to be improved as our presentation mention
 Service delivery is confused and do not have a clear guild line. -sometimes other agency transfer case to IFSC which they think that IFSC has one-stop service -however there is limitation in service delivery -misunderstanding arise between IFSC and other agency -it is time consuming to struggle between the event -and affect the service delivery towards client
Service delivery is confused and do not have a clear guild line. -sometimes other agency transfer case to IFSC which they think that IFSC has one-stop service -however there is limitation in service delivery -misunderstanding arise between IFSC and other agency -it is time consuming to struggle between the event -and affect the service delivery towards client
 Conclusion To conclude, the rationale of IFSC deserves us to promote and support. l Because…. l It is more efficient for the service users to search and use the service when practicing the one-stop service. The service users can save more time in the service use. The service can be centralized in one district that the service users can be more convenient to use different kinds of services at the same time. l The service duplication can be decreased after practicing the one-stop service that the service user can receive a more effective and congruent service (a better support and intervention from the social worker). l
Conclusion To conclude, the rationale of IFSC deserves us to promote and support. l Because…. l It is more efficient for the service users to search and use the service when practicing the one-stop service. The service users can save more time in the service use. The service can be centralized in one district that the service users can be more convenient to use different kinds of services at the same time. l The service duplication can be decreased after practicing the one-stop service that the service user can receive a more effective and congruent service (a better support and intervention from the social worker). l
 Despite the fact that agencies and social workers are facing the changes brought by integration, they are also facing the challenges brought by lump-sum grant and funding services agreement (F. S. A. ): l Front line social workers need more time and resources for adapting the changes l More resources should be allocated to agencies so as to provide spaces for front line social workers to receive further training and support l To cope with the diversifying and ever-changing needs of clients, concerning parties should go through the carrying out and implementation of integration services in details as well as do more research on the influence towards social service agencies brought by integration so that the aim of services, “provide effective support for people in need in society” could be achieved. l
Despite the fact that agencies and social workers are facing the changes brought by integration, they are also facing the challenges brought by lump-sum grant and funding services agreement (F. S. A. ): l Front line social workers need more time and resources for adapting the changes l More resources should be allocated to agencies so as to provide spaces for front line social workers to receive further training and support l To cope with the diversifying and ever-changing needs of clients, concerning parties should go through the carrying out and implementation of integration services in details as well as do more research on the influence towards social service agencies brought by integration so that the aim of services, “provide effective support for people in need in society” could be achieved. l
 References 社會福利諮詢委員會會議記錄2003年 10月28日 http: //www. hwfb. gov. hk/cn/committees/swac/minutes 031 028_c. htm l 剖析服務綜合化 http: //www. hkcs. org/info/cnews/c 224_11. htm l 家庭服務檢討之回應二(探討服務目標、服務策劃及整合 家庭服務模式) 游達裕 朱志強 林嘉麗 黃美菁 http: //swforum. socialnet. org. hk/article/001112. htm l 鄭麗玲. (2002). 一切由「綜合」開始—東涌新體驗. 社聯季 刊. 香港: 香港社會服務聯會. l
References 社會福利諮詢委員會會議記錄2003年 10月28日 http: //www. hwfb. gov. hk/cn/committees/swac/minutes 031 028_c. htm l 剖析服務綜合化 http: //www. hkcs. org/info/cnews/c 224_11. htm l 家庭服務檢討之回應二(探討服務目標、服務策劃及整合 家庭服務模式) 游達裕 朱志強 林嘉麗 黃美菁 http: //swforum. socialnet. org. hk/article/001112. htm l 鄭麗玲. (2002). 一切由「綜合」開始—東涌新體驗. 社聯季 刊. 香港: 香港社會服務聯會. l


