47b270f7425e56f136a359368aaf4a50.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 9
 SRJC May 12 th 2008 Younes Ataiiyan Physics 43 University of Rochester, Institute of Optics
SRJC May 12 th 2008 Younes Ataiiyan Physics 43 University of Rochester, Institute of Optics
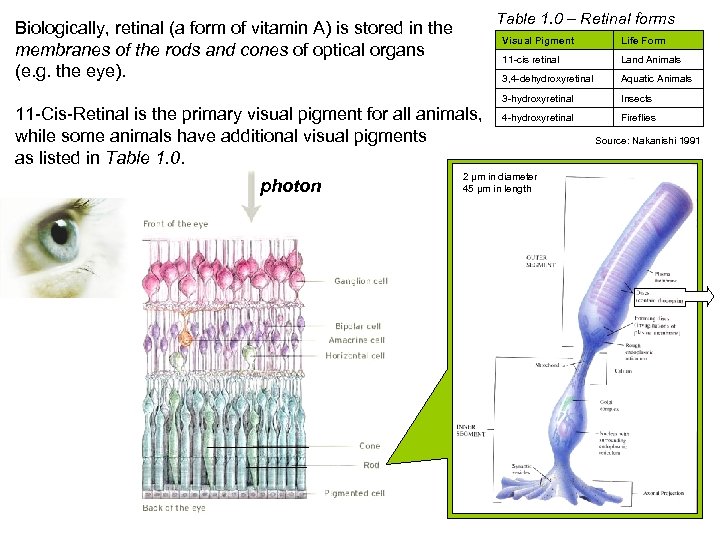 Table 1. 0 – Retinal forms Biologically, retinal (a form of vitamin A) is stored in the membranes of the rods and cones of optical organs (e. g. the eye). Visual Pigment 11 -cis retinal Aquatic Animals 3 -hydroxyretinal photon Land Animals 3, 4 -dehydroxyretinal 11 -Cis-Retinal is the primary visual pigment for all animals, while some animals have additional visual pigments as listed in Table 1. 0. Life Form Insects 4 -hydroxyretinal Fireflies 2 µm in diameter 45 µm in length Rod Cell Source: Nakanishi 1991
Table 1. 0 – Retinal forms Biologically, retinal (a form of vitamin A) is stored in the membranes of the rods and cones of optical organs (e. g. the eye). Visual Pigment 11 -cis retinal Aquatic Animals 3 -hydroxyretinal photon Land Animals 3, 4 -dehydroxyretinal 11 -Cis-Retinal is the primary visual pigment for all animals, while some animals have additional visual pigments as listed in Table 1. 0. Life Form Insects 4 -hydroxyretinal Fireflies 2 µm in diameter 45 µm in length Rod Cell Source: Nakanishi 1991
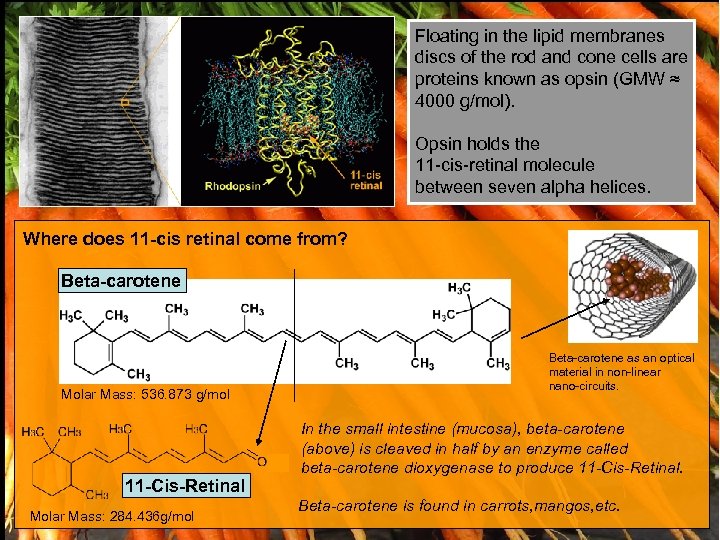 Floating in the lipid membranes discs of the rod and cone cells are proteins known as opsin (GMW ≈ 4000 g/mol). Opsin holds the 11 -cis-retinal molecule between seven alpha helices. Where does 11 -cis retinal come from? Beta-carotene Molar Mass: 536. 873 g/mol 11 -Cis-Retinal Molar Mass: 284. 436 g/mol Beta-carotene as an optical material in non-linear nano-circuits. In the small intestine (mucosa), beta-carotene (above) is cleaved in half by an enzyme called beta-carotene dioxygenase to produce 11 -Cis-Retinal. Beta-carotene is found in carrots, mangos, etc.
Floating in the lipid membranes discs of the rod and cone cells are proteins known as opsin (GMW ≈ 4000 g/mol). Opsin holds the 11 -cis-retinal molecule between seven alpha helices. Where does 11 -cis retinal come from? Beta-carotene Molar Mass: 536. 873 g/mol 11 -Cis-Retinal Molar Mass: 284. 436 g/mol Beta-carotene as an optical material in non-linear nano-circuits. In the small intestine (mucosa), beta-carotene (above) is cleaved in half by an enzyme called beta-carotene dioxygenase to produce 11 -Cis-Retinal. Beta-carotene is found in carrots, mangos, etc.
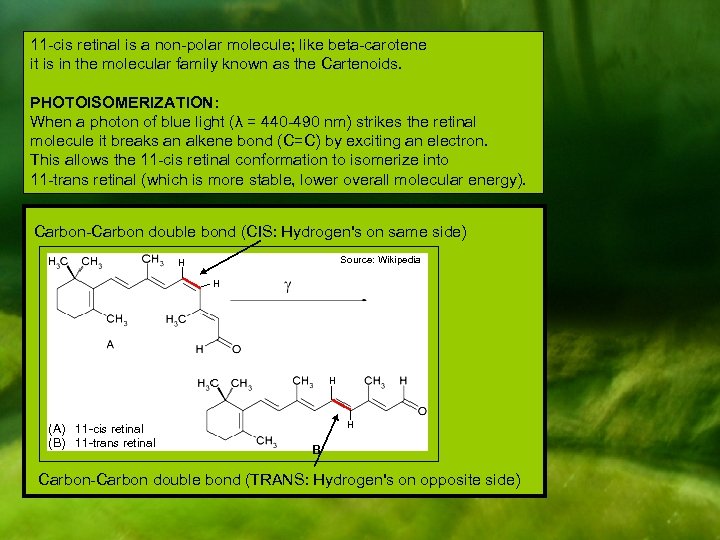 11 -cis retinal is a non-polar molecule; like beta-carotene it is in the molecular family known as the Cartenoids. PHOTOISOMERIZATION: When a photon of blue light (λ = 440 -490 nm) strikes the retinal molecule it breaks an alkene bond (C=C) by exciting an electron. This allows the 11 -cis retinal conformation to isomerize into 11 -trans retinal (which is more stable, lower overall molecular energy). Carbon-Carbon double bond (CIS: Hydrogen's on same side) Source: Wikipedia H H H (A) 11 -cis retinal (B) 11 -trans retinal H B Carbon-Carbon double bond (TRANS: Hydrogen's on opposite side)
11 -cis retinal is a non-polar molecule; like beta-carotene it is in the molecular family known as the Cartenoids. PHOTOISOMERIZATION: When a photon of blue light (λ = 440 -490 nm) strikes the retinal molecule it breaks an alkene bond (C=C) by exciting an electron. This allows the 11 -cis retinal conformation to isomerize into 11 -trans retinal (which is more stable, lower overall molecular energy). Carbon-Carbon double bond (CIS: Hydrogen's on same side) Source: Wikipedia H H H (A) 11 -cis retinal (B) 11 -trans retinal H B Carbon-Carbon double bond (TRANS: Hydrogen's on opposite side)
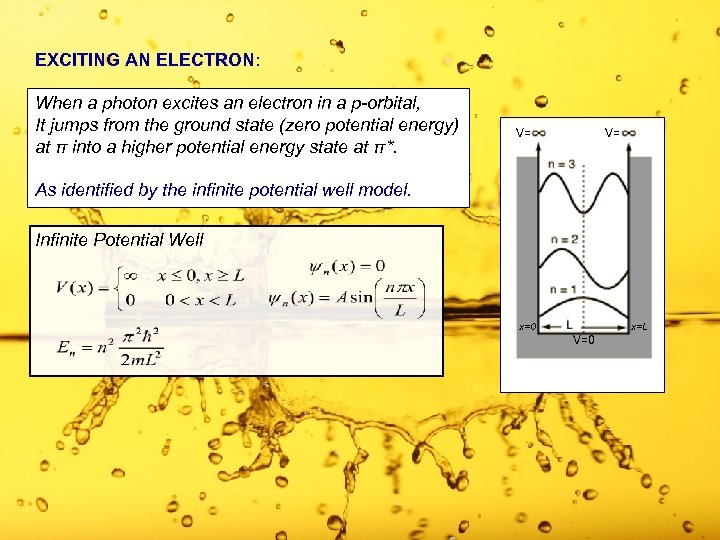 EXCITING AN ELECTRON: When a photon excites an electron in a p-orbital, It jumps from the ground state (zero potential energy) at π into a higher potential energy state at π*. V= V= As identified by the infinite potential well model. Infinite Potential Well x=0 x=L V=0
EXCITING AN ELECTRON: When a photon excites an electron in a p-orbital, It jumps from the ground state (zero potential energy) at π into a higher potential energy state at π*. V= V= As identified by the infinite potential well model. Infinite Potential Well x=0 x=L V=0
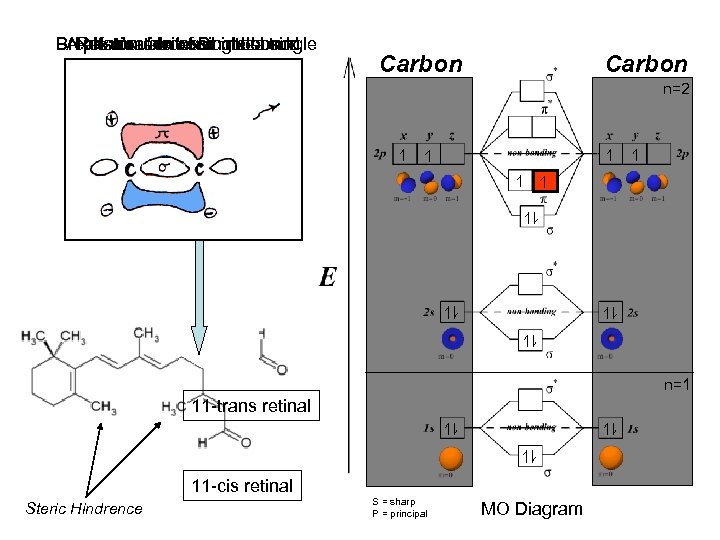 Breaks double bond π electron AReformation of Doublea single Rotationexcitessingle bond photon about a into bond Carbon n=2 n=1 11 -trans retinal 11 -cis retinal Steric Hindrence S = sharp P = principal MO Diagram
Breaks double bond π electron AReformation of Doublea single Rotationexcitessingle bond photon about a into bond Carbon n=2 n=1 11 -trans retinal 11 -cis retinal Steric Hindrence S = sharp P = principal MO Diagram
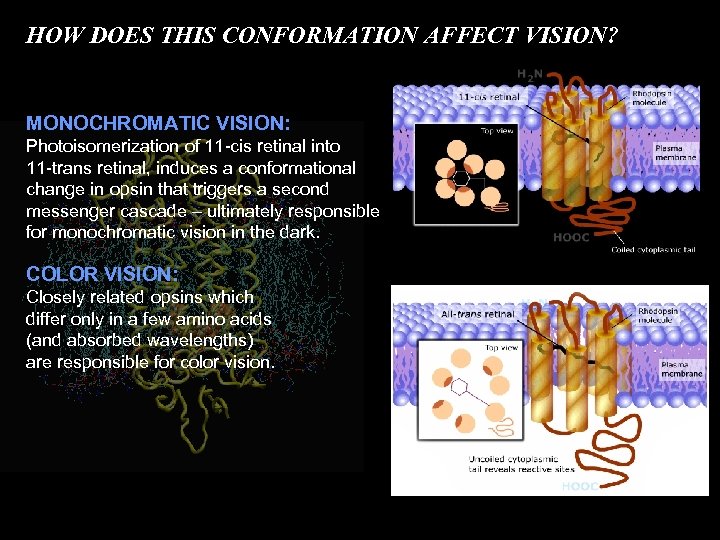 HOW DOES THIS CONFORMATION AFFECT VISION? MONOCHROMATIC VISION: Photoisomerization of 11 -cis retinal into 11 -trans retinal, induces a conformational change in opsin that triggers a second messenger cascade – ultimately responsible for monochromatic vision in the dark. COLOR VISION: Closely related opsins which differ only in a few amino acids (and absorbed wavelengths) are responsible for color vision.
HOW DOES THIS CONFORMATION AFFECT VISION? MONOCHROMATIC VISION: Photoisomerization of 11 -cis retinal into 11 -trans retinal, induces a conformational change in opsin that triggers a second messenger cascade – ultimately responsible for monochromatic vision in the dark. COLOR VISION: Closely related opsins which differ only in a few amino acids (and absorbed wavelengths) are responsible for color vision.
 Conclusion Optical organs are comprised of rods and cones, which in turn house rhodopsin (opsin + retinal). 11 -Cis retinal (cofactor) undergoes photoisomerization, to 11 -trans retinal. More specifically; when an electron in a p-orbital (of the π bond) is excited by a photon (λ = 440 -490 nm), the electron jumps (by infinite well model) into an anti-bonding orbital π* (higher potential energy) - which breaks the π bond. 11 -cis retinal then rotates around the σ bond (C-C) due to steric hinderence of the methyl substituents, and to a trans configuration. The molecule is now in a lower molecular energy conformation. When the electron returns to the ground state (zero potential energy) at π, the double bond reforms (C=C) and the molecule is called 11 -trans retinal is longer in length then 11 -cis retinal which expands the circumference of the seven opsin alpha-helices, and triggers a second massager cascade - which ultimately is responsible for the perception of monochromatic light.
Conclusion Optical organs are comprised of rods and cones, which in turn house rhodopsin (opsin + retinal). 11 -Cis retinal (cofactor) undergoes photoisomerization, to 11 -trans retinal. More specifically; when an electron in a p-orbital (of the π bond) is excited by a photon (λ = 440 -490 nm), the electron jumps (by infinite well model) into an anti-bonding orbital π* (higher potential energy) - which breaks the π bond. 11 -cis retinal then rotates around the σ bond (C-C) due to steric hinderence of the methyl substituents, and to a trans configuration. The molecule is now in a lower molecular energy conformation. When the electron returns to the ground state (zero potential energy) at π, the double bond reforms (C=C) and the molecule is called 11 -trans retinal is longer in length then 11 -cis retinal which expands the circumference of the seven opsin alpha-helices, and triggers a second massager cascade - which ultimately is responsible for the perception of monochromatic light.
 Works Cited Websites: http: //www. diginfo. tv/archives/2006/02/09/national_institute_of_advanced_22. html#more www. ks. uiuc. edu/Research/rhodopsin/ http: //webexhibits. org/colorart/ www. circadian. org/biorhyt. html http: //www. accessexcellence. org/AE/AEC/CC/vision_background. php http: //www. optics. rochester. edu/workgroups/cml/opt 307/spr 06/joe/index. htm http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Retinal http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Rhodopsin Images: http: //www. hortcouncil. ca/images/carrots. jpg http: //upload. wikimedia. org/wikipedia/commons/archive/d/da/20060520170505!Beta-carotene. png http: //education. vetmed. vt. edu/Curriculum/VM 8054/EYE/ROD. HTM http: //www. dark-layouts. net/Backgrounds/purple/images/purple_nebula. jpg
Works Cited Websites: http: //www. diginfo. tv/archives/2006/02/09/national_institute_of_advanced_22. html#more www. ks. uiuc. edu/Research/rhodopsin/ http: //webexhibits. org/colorart/ www. circadian. org/biorhyt. html http: //www. accessexcellence. org/AE/AEC/CC/vision_background. php http: //www. optics. rochester. edu/workgroups/cml/opt 307/spr 06/joe/index. htm http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Retinal http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Rhodopsin Images: http: //www. hortcouncil. ca/images/carrots. jpg http: //upload. wikimedia. org/wikipedia/commons/archive/d/da/20060520170505!Beta-carotene. png http: //education. vetmed. vt. edu/Curriculum/VM 8054/EYE/ROD. HTM http: //www. dark-layouts. net/Backgrounds/purple/images/purple_nebula. jpg


