 SQL Server Performance Audit and Tuning Jason Pack
SQL Server Performance Audit and Tuning Jason Pack
 Overview n n n n Using Performance Monitor Hardware and Operating System Performance SQL Server Configuration Settings Database Configuration Settings Index Performance Tuning Application Tuning SQL Profiler on Queries
Overview n n n n Using Performance Monitor Hardware and Operating System Performance SQL Server Configuration Settings Database Configuration Settings Index Performance Tuning Application Tuning SQL Profiler on Queries
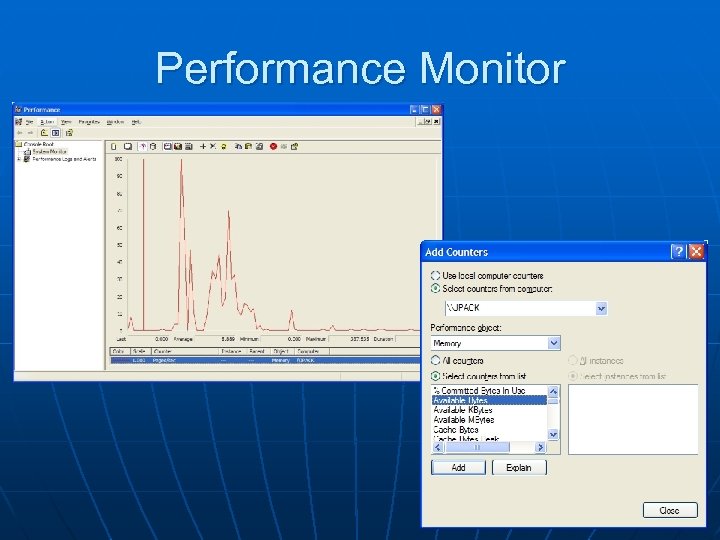 Performance Monitor
Performance Monitor
 Performance Monitor (2) n Typical counters to monitor: • Pages per second (memory) n Want to average less than 20 • Available bytes (memory) n Should be over 5 MB (on dedicated machine) • Percent disk time (physical disk) n Over 55% for 10+ minutes indicates a bottleneck • Percent processor time n Over 80% for 10+ minutes indicates a bottleneck
Performance Monitor (2) n Typical counters to monitor: • Pages per second (memory) n Want to average less than 20 • Available bytes (memory) n Should be over 5 MB (on dedicated machine) • Percent disk time (physical disk) n Over 55% for 10+ minutes indicates a bottleneck • Percent processor time n Over 80% for 10+ minutes indicates a bottleneck
 Tuning Hardware and Operating System Performance n n n More RAM = Good Check disk fragmentation Separate operating system files and SQL Server data files Be sure OS has newest SP Server should be configured as stand -alone server Turn off unnecessary services
Tuning Hardware and Operating System Performance n n n More RAM = Good Check disk fragmentation Separate operating system files and SQL Server data files Be sure OS has newest SP Server should be configured as stand -alone server Turn off unnecessary services
 SQL Server Configuration Settings n n In general, no need to modify If you have to • SP_CONFIGURE, will show your settings • SP_CONFIGURE ['configuration name'], [configuration setting value] GO RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE GO, to change the settings
SQL Server Configuration Settings n n In general, no need to modify If you have to • SP_CONFIGURE, will show your settings • SP_CONFIGURE ['configuration name'], [configuration setting value] GO RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE GO, to change the settings
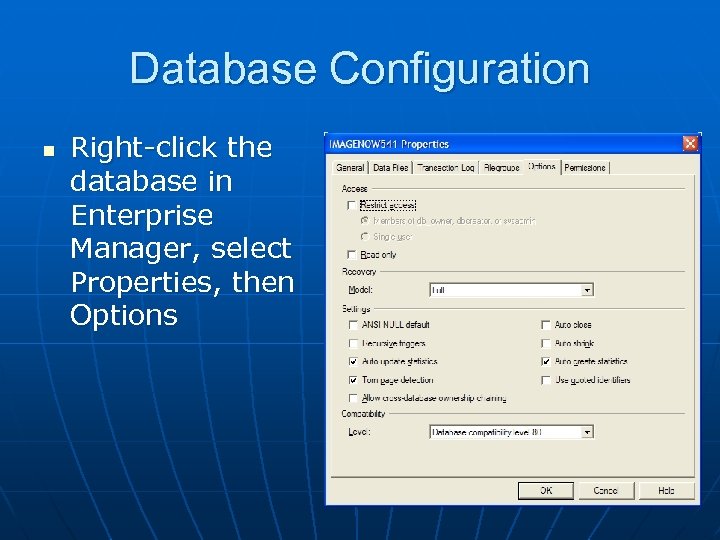 Database Configuration n Right-click the database in Enterprise Manager, select Properties, then Options
Database Configuration n Right-click the database in Enterprise Manager, select Properties, then Options
 Database Configuration (2) n For reporting databases, set to Readonly n Database auto-grow n Transaction log auto-grow • Estimate well, auto-grow creates virtual files, increasing recovery time
Database Configuration (2) n For reporting databases, set to Readonly n Database auto-grow n Transaction log auto-grow • Estimate well, auto-grow creates virtual files, increasing recovery time
 Index Performance Tuning n Run the Index Tuning Wizard • Only available in Enterprise edition n n Start with busiest database, and largest tables Every table, in every database, should have a clustered index on the PK • Allows the data to be stored, physically, in order
Index Performance Tuning n Run the Index Tuning Wizard • Only available in Enterprise edition n n Start with busiest database, and largest tables Every table, in every database, should have a clustered index on the PK • Allows the data to be stored, physically, in order
 Application Tuning n n Most important aspect in improving performance Not always possible
Application Tuning n n Most important aspect in improving performance Not always possible
 Application Tuning (2) n Use stored procedures whenever possible • Include SET NOCOUNT ON in stored procedure n n n Keep transactions as short as possible Choose OLE DB over ODBC, as it is generally faster Don’t return more data than you need
Application Tuning (2) n Use stored procedures whenever possible • Include SET NOCOUNT ON in stored procedure n n n Keep transactions as short as possible Choose OLE DB over ODBC, as it is generally faster Don’t return more data than you need
 SQL Profiler n Events • Stored Procedures n RPC: Completed • TSQL n n SQL: Batch. Completed Filters • Duration > 5000 ms • No system events n Data Columns • • Duration (group by) Event Class Database Identifier Text. Data CPU Writes Reads SPID
SQL Profiler n Events • Stored Procedures n RPC: Completed • TSQL n n SQL: Batch. Completed Filters • Duration > 5000 ms • No system events n Data Columns • • Duration (group by) Event Class Database Identifier Text. Data CPU Writes Reads SPID
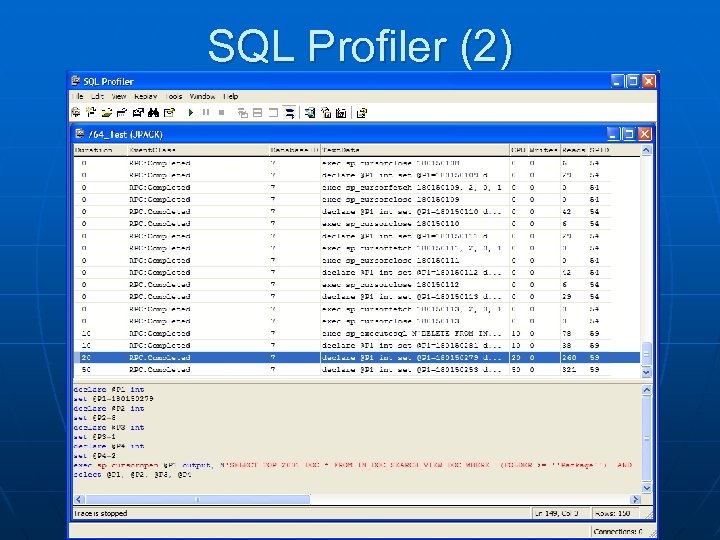 SQL Profiler (2)
SQL Profiler (2)
 References n SQL-Server-Performance. Com, Brad Mc. Gehee, February 2005 • http: //www. sql-server-performance. com/sql_server_performance_audit 10. asp n Microsoft MSDN, Meier, J. D. , Vasireddy, S. , Babbar, A. , et al. , May 2004 • http: //msdn. microsoft. com/library/default. asp? url=/library/enus/dnpag/html/scalenetchapt 14. asp n SQL-Server-Performance. Com, Geert Vanhove, June 2005 • http: //www. sql-server-performance. com/gv_monitoring_8_steps. asp n Microsoft MSDN • http: //msdn. microsoft. com/library/default. asp? url=/library/enus/createdb/cm_8_des_05_2 ri 0. asp
References n SQL-Server-Performance. Com, Brad Mc. Gehee, February 2005 • http: //www. sql-server-performance. com/sql_server_performance_audit 10. asp n Microsoft MSDN, Meier, J. D. , Vasireddy, S. , Babbar, A. , et al. , May 2004 • http: //msdn. microsoft. com/library/default. asp? url=/library/enus/dnpag/html/scalenetchapt 14. asp n SQL-Server-Performance. Com, Geert Vanhove, June 2005 • http: //www. sql-server-performance. com/gv_monitoring_8_steps. asp n Microsoft MSDN • http: //msdn. microsoft. com/library/default. asp? url=/library/enus/createdb/cm_8_des_05_2 ri 0. asp