61dd9c83132ff15ccdb155cf310a2ab8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Spring 2008 Economics 98 / 198 De. Cal ` Introduction to Stocks Basics of Investing I www. ocf. berkeley. edu/~jml/decal
Spring 2008 Economics 98 / 198 De. Cal ` Introduction to Stocks Basics of Investing I www. ocf. berkeley. edu/~jml/decal
 Schedule Today n n Administrative Issues Lecture content: Basics of Investing n n n n n What is a stock? How are they traded? What are brokerages? Different types of orders What is the market? Terminology Learning how to use the simulation; IBD Current Events Assignments / Readings
Schedule Today n n Administrative Issues Lecture content: Basics of Investing n n n n n What is a stock? How are they traded? What are brokerages? Different types of orders What is the market? Terminology Learning how to use the simulation; IBD Current Events Assignments / Readings
 Administrative Issues n Attendance & Sign-In n Name Tags n Enrollment n Emails n Webpage n Syllabus Review n News Presentation Sign Ups n Investor’s Business Daily Access
Administrative Issues n Attendance & Sign-In n Name Tags n Enrollment n Emails n Webpage n Syllabus Review n News Presentation Sign Ups n Investor’s Business Daily Access
 Lecture Content
Lecture Content
 What is a stock? n Common stock n Gives you a “share” of ownership of a publicly traded company n Stock ownership n Voting rights n Claim to assets (behind debt holders) and earnings n Potentially entitled to dividends
What is a stock? n Common stock n Gives you a “share” of ownership of a publicly traded company n Stock ownership n Voting rights n Claim to assets (behind debt holders) and earnings n Potentially entitled to dividends
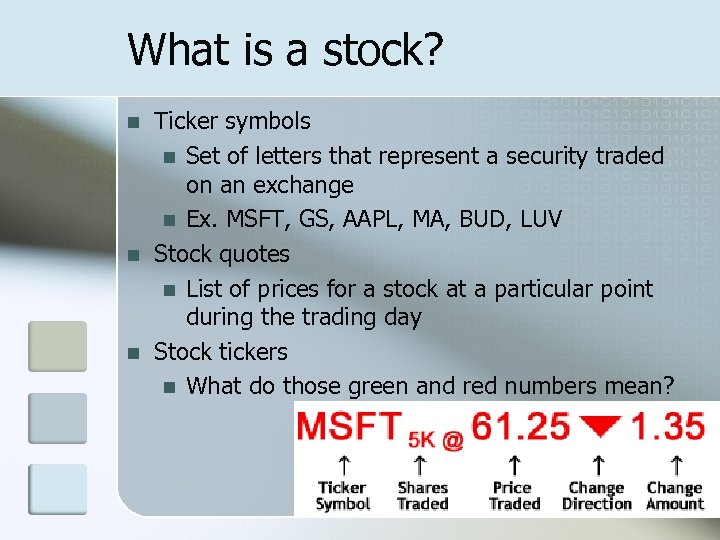 What is a stock? n n n Ticker symbols n Set of letters that represent a security traded on an exchange n Ex. MSFT, GS, AAPL, MA, BUD, LUV Stock quotes n List of prices for a stock at a particular point during the trading day Stock tickers n What do those green and red numbers mean?
What is a stock? n n n Ticker symbols n Set of letters that represent a security traded on an exchange n Ex. MSFT, GS, AAPL, MA, BUD, LUV Stock quotes n List of prices for a stock at a particular point during the trading day Stock tickers n What do those green and red numbers mean?
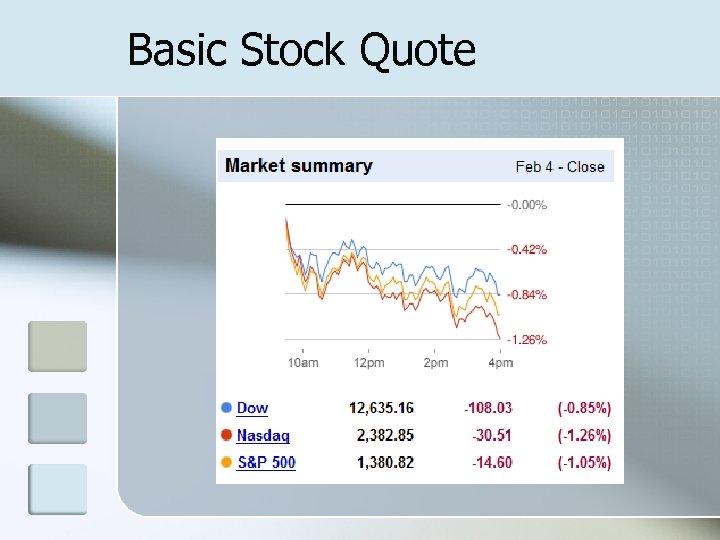 Basic Stock Quote
Basic Stock Quote
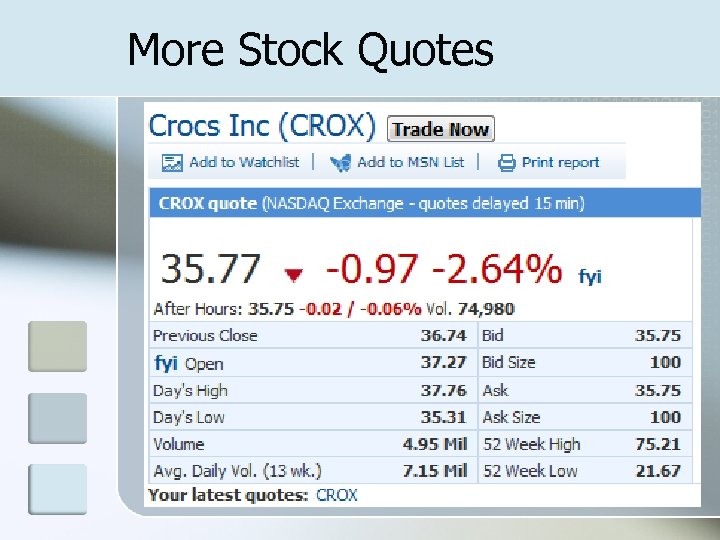 More Stock Quotes
More Stock Quotes
 Different Types of Stock n Preferred Stock n n n Common Stock n n n No voting rights to company issues Issued fixed dividends forever – main form of return Majority of stock we see and hear about in the news Ownership of the company Entitled to portion of the earnings Earn returns mainly through capital gains What are capital gains? n n n Increase in asset value relative to the purchases price Not realized until asset is actually sold Example.
Different Types of Stock n Preferred Stock n n n Common Stock n n n No voting rights to company issues Issued fixed dividends forever – main form of return Majority of stock we see and hear about in the news Ownership of the company Entitled to portion of the earnings Earn returns mainly through capital gains What are capital gains? n n n Increase in asset value relative to the purchases price Not realized until asset is actually sold Example.
 Stocks vs. Bonds n Stocks are equity Generally considered riskier n Quite possible to lose a significant portion, if not all, of your money n Potential for high returns n n Bonds are debt Lower and usually fixed return n Higher claim than stockholders n n What does this mean?
Stocks vs. Bonds n Stocks are equity Generally considered riskier n Quite possible to lose a significant portion, if not all, of your money n Potential for high returns n n Bonds are debt Lower and usually fixed return n Higher claim than stockholders n n What does this mean?
 Dividend Debate n Distribution of a portion of a company's earnings to its shareholders (usually cash) n Bad or Good? n Why?
Dividend Debate n Distribution of a portion of a company's earnings to its shareholders (usually cash) n Bad or Good? n Why?
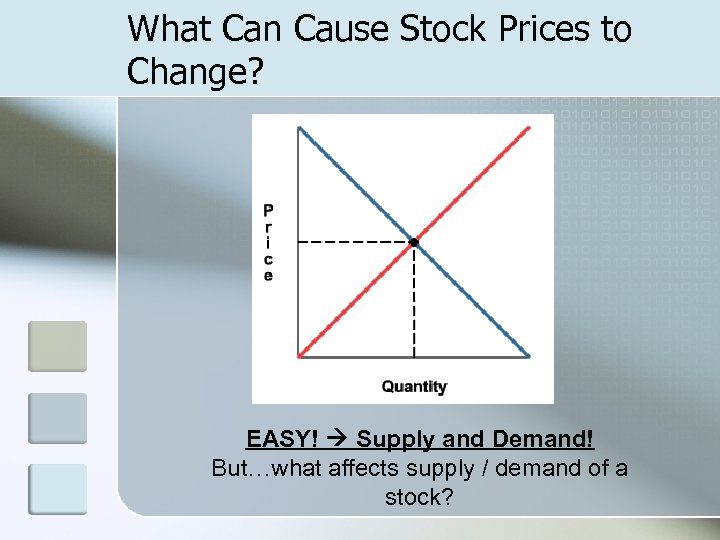 What Can Cause Stock Prices to Change? EASY! Supply and Demand! But…what affects supply / demand of a stock?
What Can Cause Stock Prices to Change? EASY! Supply and Demand! But…what affects supply / demand of a stock?
 What Can Cause Stock Prices to Change? n Earnings & growth expectations n Positive / negative news n Economy sentiment n Investor sentiments & attitudes n Irrational exuberance / behavior
What Can Cause Stock Prices to Change? n Earnings & growth expectations n Positive / negative news n Economy sentiment n Investor sentiments & attitudes n Irrational exuberance / behavior
 Two Markets n Primary Market – market in which investors have first opportunity to buy newly issued shares n n Initial Public Offering (IPO) n First time that company offers its shares to public markets (securities bought directly from company) n Where private companies become public Secondary Market – investors trade alreadyissued shares of companies with each other n n Ie. The stock market Trading of a company’s stock DOES NOT DIRECTLY involve the company financially
Two Markets n Primary Market – market in which investors have first opportunity to buy newly issued shares n n Initial Public Offering (IPO) n First time that company offers its shares to public markets (securities bought directly from company) n Where private companies become public Secondary Market – investors trade alreadyissued shares of companies with each other n n Ie. The stock market Trading of a company’s stock DOES NOT DIRECTLY involve the company financially
 How Stocks Are Traded n Major exchanges n Lists stocks (and other securities), sets policies for how stocks are traded n New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) n American Stock Exchange (AMEX) n National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotation n Only “publicly traded companies” are listed
How Stocks Are Traded n Major exchanges n Lists stocks (and other securities), sets policies for how stocks are traded n New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) n American Stock Exchange (AMEX) n National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotation n Only “publicly traded companies” are listed
 Market Indices (Index) § Definition – Aggregate value of combining several stocks together and intended to represent entire or portion of the stock market § S&P 500 – 500 stocks chosen by Standard & Poor to represent US stock market § NASDAQ Composite § Dow Jones Industrial Average – § § 30 most significant stocks traded S&P 600 Small-Cap Russell 3000 – 3000 of the largest stocks in the US
Market Indices (Index) § Definition – Aggregate value of combining several stocks together and intended to represent entire or portion of the stock market § S&P 500 – 500 stocks chosen by Standard & Poor to represent US stock market § NASDAQ Composite § Dow Jones Industrial Average – § § 30 most significant stocks traded S&P 600 Small-Cap Russell 3000 – 3000 of the largest stocks in the US
 Stocks Markets & Animals n Bull Market n n When everything in the market is going great and stocks are generally heading upwards Bear Market n When everything is NOT GOOD and stocks are generally headed n NOTE: Nothing lasts forever! Good times and bad times will end at some point n Other animal terms: pigs, chickens http: //www. investopedia. com/university/stocks 7. asp
Stocks Markets & Animals n Bull Market n n When everything in the market is going great and stocks are generally heading upwards Bear Market n When everything is NOT GOOD and stocks are generally headed n NOTE: Nothing lasts forever! Good times and bad times will end at some point n Other animal terms: pigs, chickens http: //www. investopedia. com/university/stocks 7. asp
 Brokerages § Need a medium to trade through – this is where brokerages come in § Cash vs. margin account § Criteria – – Full service vs. discount Fees (commission) Services / tools Minimum balance
Brokerages § Need a medium to trade through – this is where brokerages come in § Cash vs. margin account § Criteria – – Full service vs. discount Fees (commission) Services / tools Minimum balance
 Opening an Account n Not a hard process- most of it just some paperwork and mail n n Cash accounts usually never turned down n n Sign-up online and download forms Mail checks, forms, and copy of ID Accounts created within a couple of days Margin accounts difficult if you have pretty bad credit history What you will need: a computer, starting capital, and investing know-how
Opening an Account n Not a hard process- most of it just some paperwork and mail n n Cash accounts usually never turned down n n Sign-up online and download forms Mail checks, forms, and copy of ID Accounts created within a couple of days Margin accounts difficult if you have pretty bad credit history What you will need: a computer, starting capital, and investing know-how
 Brokerages n Some links for brokerage comparisons n n Find something that works for what YOU need No one broker that is best for all investors n http: //www. investingonline. org/gso/broker_ratings. html n http: //www. consumersearch. com/www/internet/onlinebrokers/ n http: //www. stockbrokerguide. com/ n http: //online-stock-trading-review. toptenreviews. com/
Brokerages n Some links for brokerage comparisons n n Find something that works for what YOU need No one broker that is best for all investors n http: //www. investingonline. org/gso/broker_ratings. html n http: //www. consumersearch. com/www/internet/onlinebrokers/ n http: //www. stockbrokerguide. com/ n http: //online-stock-trading-review. toptenreviews. com/
 Different types of Orders n Market Order n Limit Order n Order executes to buy / sell at specified price of better (lower). Limit orders usually cost more, but useful for getting specified price n Stop Order n Order executes when the price surpasses a particular point, which helps buy or sell at a particular price. Limiting loss or locking profits
Different types of Orders n Market Order n Limit Order n Order executes to buy / sell at specified price of better (lower). Limit orders usually cost more, but useful for getting specified price n Stop Order n Order executes when the price surpasses a particular point, which helps buy or sell at a particular price. Limiting loss or locking profits
 Different Types of Orders n Stop Limit Order n Executed at a specified price (or better) after a given stop price has been reached. Order becomes then a limit order to buy (or sell) at the limit price or better n Precision purposes n Good Until Cancelled (GTC) n Good Until End of Day
Different Types of Orders n Stop Limit Order n Executed at a specified price (or better) after a given stop price has been reached. Order becomes then a limit order to buy (or sell) at the limit price or better n Precision purposes n Good Until Cancelled (GTC) n Good Until End of Day
 Things to Internalize n Learn the basics! Need to know what basic terms mean n Articles should help you n n Advantages of starting young n Useful resources for stock tutorials www. investorwords. com n http: //www. investopedia. com/university/ n www. fool. com n
Things to Internalize n Learn the basics! Need to know what basic terms mean n Articles should help you n n Advantages of starting young n Useful resources for stock tutorials www. investorwords. com n http: //www. investopedia. com/university/ n www. fool. com n
 Current Events
Current Events
 Investopedia Simulation
Investopedia Simulation
 Homework / Reading n Set up simulation account & start trading n Online articles (Course website) “The Five Biggest Stock Market Myths” n “Getting Started” n
Homework / Reading n Set up simulation account & start trading n Online articles (Course website) “The Five Biggest Stock Market Myths” n “Getting Started” n


