18892ff1495adedb792f17e0f75f5e00.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 “Spray Application Accuracy” Nozzle Selection
“Spray Application Accuracy” Nozzle Selection
 Why are you here? ? Points? ? ? Are you concerned with accuracy? n n n n $$ go bye, bye Changing rates (< an ounce/acre) More foliar applied products (herbicides) More sophisticated equipment - $$$ Environmental impact (water and air) Inefficient Variable rates Site-specific
Why are you here? ? Points? ? ? Are you concerned with accuracy? n n n n $$ go bye, bye Changing rates (< an ounce/acre) More foliar applied products (herbicides) More sophisticated equipment - $$$ Environmental impact (water and air) Inefficient Variable rates Site-specific
 Equipment cost today? How much do these machines cost?
Equipment cost today? How much do these machines cost?
 What about the cost of the nozzle?
What about the cost of the nozzle?
 Regardless of the cost: n Without proper attention to the nozzle, you may end up with a misapplication
Regardless of the cost: n Without proper attention to the nozzle, you may end up with a misapplication
 Nozzles Control n Amount of spray applied n Uniformity of the spray n Coverage on the target n Amount of off-target drift
Nozzles Control n Amount of spray applied n Uniformity of the spray n Coverage on the target n Amount of off-target drift
 Nozzle Types Flat Spray Tips: Extended Range Flat-fan n Drift Reduction Flat-fan n Turbo Flood Flat-fan n Turbo Flat-fan n AI Flat-fan n Turbo. Drop n Cone Spray Tips: n Raindrop
Nozzle Types Flat Spray Tips: Extended Range Flat-fan n Drift Reduction Flat-fan n Turbo Flood Flat-fan n Turbo Flat-fan n AI Flat-fan n Turbo. Drop n Cone Spray Tips: n Raindrop
 Selecting the proper nozzle Legal issues!!
Selecting the proper nozzle Legal issues!!
 Nomenclature: Extended Range Trade Name (S, H, P, K, SS) Stainless Steel Insert Orifice Visi. Flo Color Coding Fan angle and flow rateorifice size Rated Pressure = 40 psi for most nozzle types 10 psi for turbo flood nozzles
Nomenclature: Extended Range Trade Name (S, H, P, K, SS) Stainless Steel Insert Orifice Visi. Flo Color Coding Fan angle and flow rateorifice size Rated Pressure = 40 psi for most nozzle types 10 psi for turbo flood nozzles
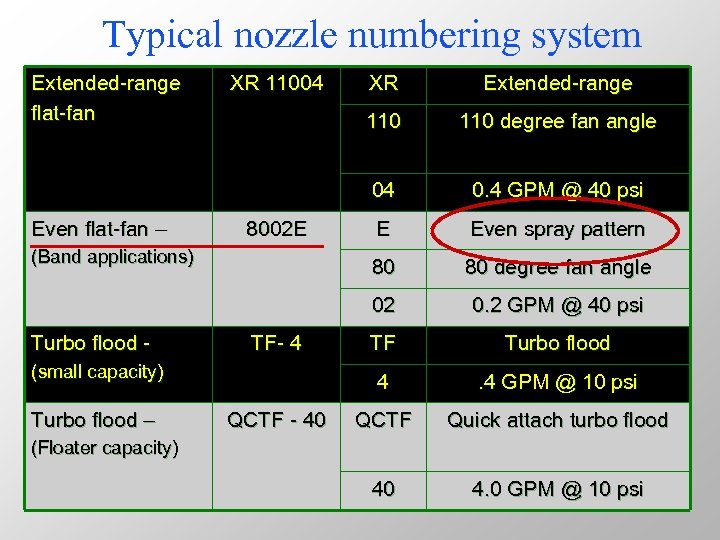 Typical nozzle numbering system Extended-range flat-fan (small capacity) Turbo flood – QCTF - 40 E Even spray pattern 80 degree fan angle 0. 2 GPM @ 40 psi TF Turbo flood 4 TF- 4 0. 4 GPM @ 40 psi 02 Turbo flood - 110 degree fan angle 80 (Band applications) Extended-range 110 8002 E XR 04 Even flat-fan – XR 11004 . 4 GPM @ 10 psi QCTF Quick attach turbo flood 40 4. 0 GPM @ 10 psi (Floater capacity)
Typical nozzle numbering system Extended-range flat-fan (small capacity) Turbo flood – QCTF - 40 E Even spray pattern 80 degree fan angle 0. 2 GPM @ 40 psi TF Turbo flood 4 TF- 4 0. 4 GPM @ 40 psi 02 Turbo flood - 110 degree fan angle 80 (Band applications) Extended-range 110 8002 E XR 04 Even flat-fan – XR 11004 . 4 GPM @ 10 psi QCTF Quick attach turbo flood 40 4. 0 GPM @ 10 psi (Floater capacity)
 Electronics/Rate Controllers n How does your system work when speed changes? n Is it pressure based? n What is the effect of going slower? n What is the effect of going faster?
Electronics/Rate Controllers n How does your system work when speed changes? n Is it pressure based? n What is the effect of going slower? n What is the effect of going faster?
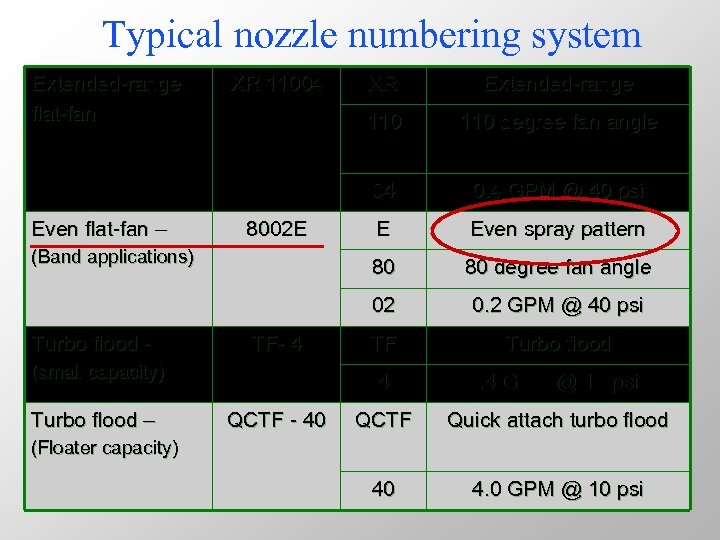 Typical nozzle numbering system Extended-range flat-fan (small capacity) Turbo flood – QCTF - 40 E Even spray pattern 80 degree fan angle 0. 2 GPM @ 40 psi TF Turbo flood 4 TF- 4 0. 4 GPM @ 40 psi 02 Turbo flood - 110 degree fan angle 80 (Band applications) Extended-range 110 8002 E XR 04 Even flat-fan – XR 11004 . 4 GPM @ 10 psi QCTF Quick attach turbo flood 40 4. 0 GPM @ 10 psi (Floater capacity)
Typical nozzle numbering system Extended-range flat-fan (small capacity) Turbo flood – QCTF - 40 E Even spray pattern 80 degree fan angle 0. 2 GPM @ 40 psi TF Turbo flood 4 TF- 4 0. 4 GPM @ 40 psi 02 Turbo flood - 110 degree fan angle 80 (Band applications) Extended-range 110 8002 E XR 04 Even flat-fan – XR 11004 . 4 GPM @ 10 psi QCTF Quick attach turbo flood 40 4. 0 GPM @ 10 psi (Floater capacity)
 Set up for Uniformity Goal is to put the material on evenly from nozzle to nozzle, end of boom to end of boom, and across the entire field. 20 -inch spacing requires 17 -19” above target for 50 -60% overlap.
Set up for Uniformity Goal is to put the material on evenly from nozzle to nozzle, end of boom to end of boom, and across the entire field. 20 -inch spacing requires 17 -19” above target for 50 -60% overlap.
 Set Up For Uniformity What is the first step? n Use label to select the n – application volume – product rate Choose an appropriate travel speed n Effective width of application n – nozzle spacing Calculate GPM – Flow rate per nozzle n Select the correct size of nozzle! n
Set Up For Uniformity What is the first step? n Use label to select the n – application volume – product rate Choose an appropriate travel speed n Effective width of application n – nozzle spacing Calculate GPM – Flow rate per nozzle n Select the correct size of nozzle! n
 Set Up For Uniformity n Label requirements?
Set Up For Uniformity n Label requirements?
 Set Up For Uniformity • Determine Your Field Speed – Know it to maintain it! 200 Feet in 27 seconds 200 27 X 0. 682 = 5 MPH Buy a speed sensor
Set Up For Uniformity • Determine Your Field Speed – Know it to maintain it! 200 Feet in 27 seconds 200 27 X 0. 682 = 5 MPH Buy a speed sensor
 Set Up For Uniformity What is the first step? n Use label to select the n – application volume – product rate Choose an appropriate travel speed n Effective width of application n – nozzle spacing Calculate GPM – Flow rate per nozzle n Select the correct size of nozzle! n
Set Up For Uniformity What is the first step? n Use label to select the n – application volume – product rate Choose an appropriate travel speed n Effective width of application n – nozzle spacing Calculate GPM – Flow rate per nozzle n Select the correct size of nozzle! n
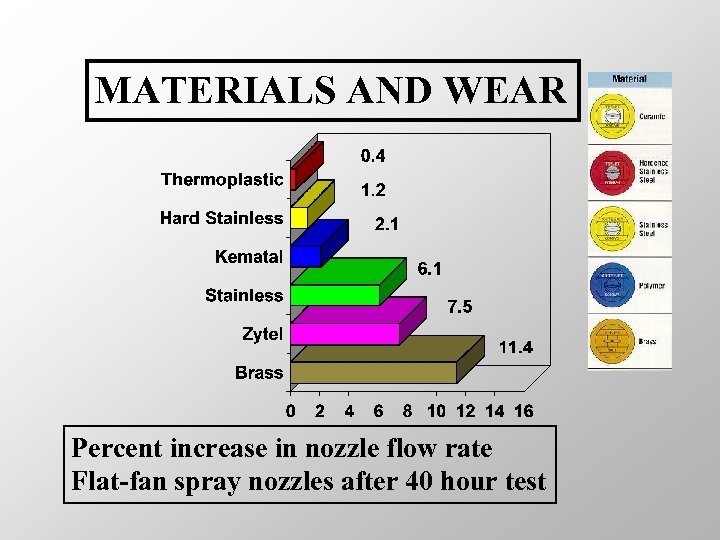 MATERIALS AND WEAR Percent increase in nozzle flow rate Flat-fan spray nozzles after 40 hour test
MATERIALS AND WEAR Percent increase in nozzle flow rate Flat-fan spray nozzles after 40 hour test
 Coverage n Need knowledge of the product being used. – Systemic – Contact n What is the target? – Soil – grass – broadleaf (smooth, hairy, waxy)
Coverage n Need knowledge of the product being used. – Systemic – Contact n What is the target? – Soil – grass – broadleaf (smooth, hairy, waxy)
 #$!@&%! GPA= 5940 Calculations
#$!@&%! GPA= 5940 Calculations
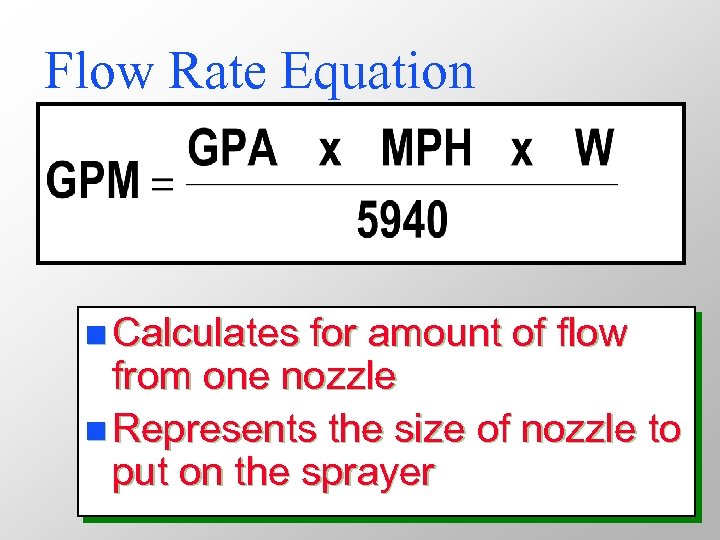 Flow Rate Equation n Calculates for amount of flow from one nozzle n Represents the size of nozzle to put on the sprayer
Flow Rate Equation n Calculates for amount of flow from one nozzle n Represents the size of nozzle to put on the sprayer
 Ok, now I remember! GPA= 5940 Calculations
Ok, now I remember! GPA= 5940 Calculations
 Calibration/Nozzle Selection What is the first step? n Use label to select the n – application volume – product rate Choose an appropriate travel speed n Effective width of application n – nozzle spacing Calculate GPM n Size of nozzle! n
Calibration/Nozzle Selection What is the first step? n Use label to select the n – application volume – product rate Choose an appropriate travel speed n Effective width of application n – nozzle spacing Calculate GPM n Size of nozzle! n
 Nozzle size - Variables n Nozzle flow rate (GPM) n Ground speed (MPH) n Effective sprayed width (W) n Application rate (GPA)
Nozzle size - Variables n Nozzle flow rate (GPM) n Ground speed (MPH) n Effective sprayed width (W) n Application rate (GPA)
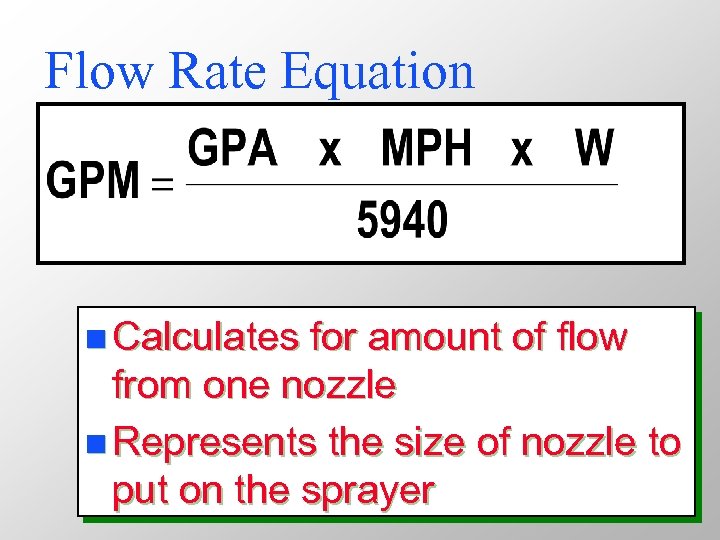 Flow Rate Equation n Calculates for amount of flow from one nozzle n Represents the size of nozzle to put on the sprayer
Flow Rate Equation n Calculates for amount of flow from one nozzle n Represents the size of nozzle to put on the sprayer
 Where: GPA = ___________ gallons per acre gallons per minute GPM = ___________ miles per hour MPH = ___________ nozzle spacing - inches W = ___________ 5940 = a constant to convert gallons per minute, miles per hour, and inches to gallons per acre
Where: GPA = ___________ gallons per acre gallons per minute GPM = ___________ miles per hour MPH = ___________ nozzle spacing - inches W = ___________ 5940 = a constant to convert gallons per minute, miles per hour, and inches to gallons per acre
 Variables 1. Nozzle Flow Rate - Gallons Per Minute (GPM) To double the nozzle output, the pressure must increase 4 times 2. Ground speed - Miles Per Hour (MPH) Doubling the ground speed reduces GPA rate by___ 1/2 3. Effective Sprayed Width (W) (Nozzle spacing, band width, number of nozzles on drop)
Variables 1. Nozzle Flow Rate - Gallons Per Minute (GPM) To double the nozzle output, the pressure must increase 4 times 2. Ground speed - Miles Per Hour (MPH) Doubling the ground speed reduces GPA rate by___ 1/2 3. Effective Sprayed Width (W) (Nozzle spacing, band width, number of nozzles on drop)
 Electronics/Rate Controllers How does your system work when speed changes? n What is the effect of going slower? n What is the effect of going faster? n
Electronics/Rate Controllers How does your system work when speed changes? n What is the effect of going slower? n What is the effect of going faster? n
 GPM Example • You want to broadcast a foliar herbicide at 10 GPA traveling 5 MPH using extended range flat-fan nozzles on 20 -inch spacing. • Use equation to calculate for flow rate?
GPM Example • You want to broadcast a foliar herbicide at 10 GPA traveling 5 MPH using extended range flat-fan nozzles on 20 -inch spacing. • Use equation to calculate for flow rate?
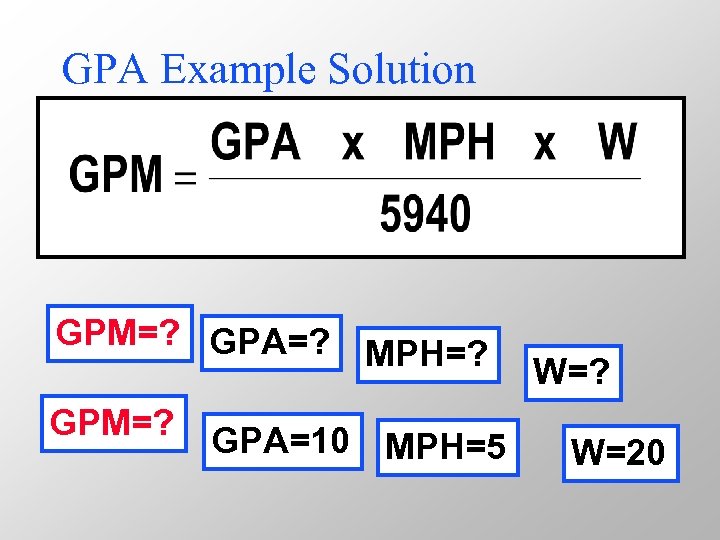 GPA Example Solution GPM=? GPA=? MPH=? GPM=? GPA=10 MPH=5 W=? W=20
GPA Example Solution GPM=? GPA=? MPH=? GPM=? GPA=10 MPH=5 W=? W=20
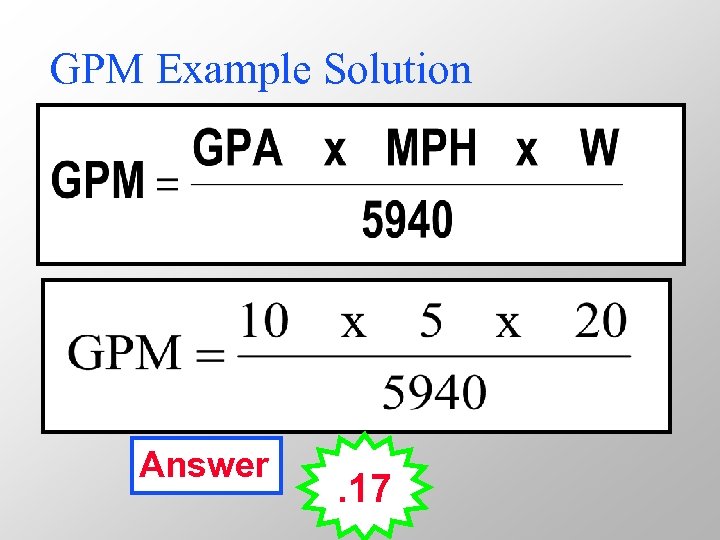 GPM Example Solution Answer . 17
GPM Example Solution Answer . 17
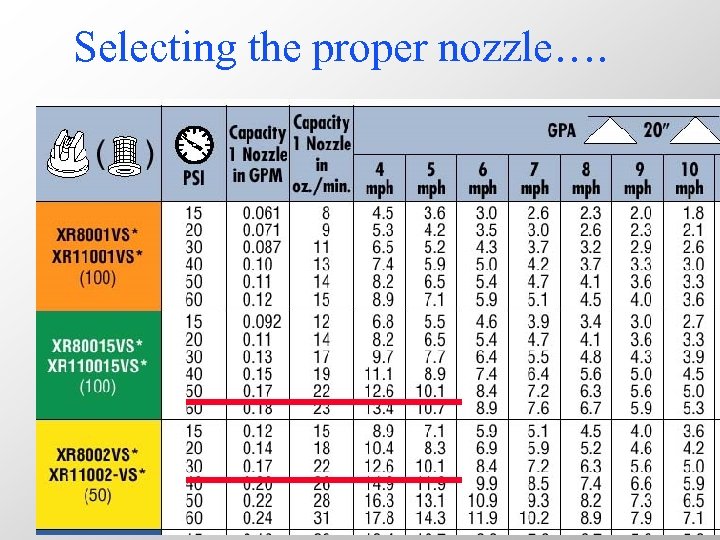
 Selecting the proper nozzle…. n n n Calculate GPM (formula) Look under ‘Capacity of 1 nozzle in GPM’ column Match to pressure-psi Choose the size needed Operate at given pressure and speed to achieve GPA
Selecting the proper nozzle…. n n n Calculate GPM (formula) Look under ‘Capacity of 1 nozzle in GPM’ column Match to pressure-psi Choose the size needed Operate at given pressure and speed to achieve GPA
 Selecting the proper nozzle….
Selecting the proper nozzle….


