48bff8df4b450725b127a78f6a2fde18.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27

Sponsor Based Leveraged Acquisition Market Overview Joseph V. Rizzi Amsterdam Institute of Finance October, 2014
Acquisition/Leveraged Finance Transaction: Buyout, Acquisition or Recapitalization Leverage: Resulting in highly leveraged (i. e. , non investment grade) obligor – f. D/EBITDA > 3 X Subject to market availability and pricing (function of risk appetite Deal Types: Acquisition Recapitalization Refinance PTP (Public to Private) STS (Sponsor to Sponsor, aka Pass the Parcel) PE Importance: Provides 1/3 of all I/B Revenues and up to 25% of M&A Amsterdam Institute of Finance October, 2014 2

Global M&A (1 H 14) 7 Year High – 1. 77 T U. S. - 41% ROW - 59% Drivers Cash Balances Low Rates Exhausted Cost Cuts and Buybacks Pent-up Demand Positive Response Confidence Rising Stock Prices Increase in Hostile T/O 20% of total v single digits post crisis PE: Dog that didn’t bark – Strategic Acquirers crowd-out 20% of total v 27% 4 year average Reflects dearth of larger PTP deals Volume up 6% 2014 v double digit M&A increase PPX: 14 X+ Drop in cash in favor of stock/stock + cash All cash at lowest level since 2001 Amsterdam Averages reflect return of the “big deal” Institute of Finance October, 2014 3
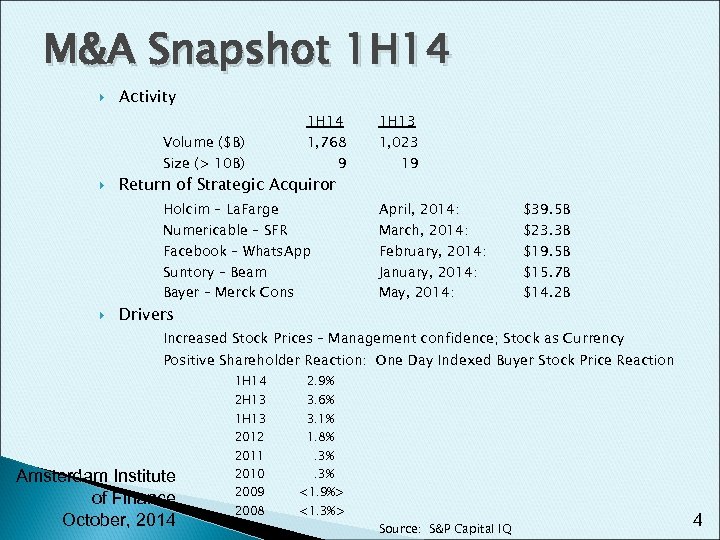
M&A Snapshot 1 H 14 Activity Volume ($B) Size (> 10 B) 1 H 14 1, 768 9 Return of Strategic Acquiror Holcim – La. Farge 1, 023 19 April, 2014: Numericable – SFR Facebook – Whats. App Suntory – Beam Bayer – Merck Cons 1 H 13 March, 2014: February, 2014: January, 2014: May, 2014: Drivers $39. 5 B $23. 3 B $19. 5 B $15. 7 B $14. 2 B Increased Stock Prices – Management confidence; Stock as Currency Positive Shareholder Reaction: One Day Indexed Buyer Stock Price Reaction 1 H 14 2. 9% 2 H 13 3. 6% 2012 1. 8% 1 H 13 2011 Amsterdam Institute of Finance October, 2014 2010 2009 2008 3. 1%. 3% <1. 9%> <1. 3%> Source: S&P Capital IQ 4
Success Factors Tests Amsterdam Institute of Finance October, 2014 Deal Size Timing Price Financing Consideration Buyer Execution Type Best Owner Iron Law 5
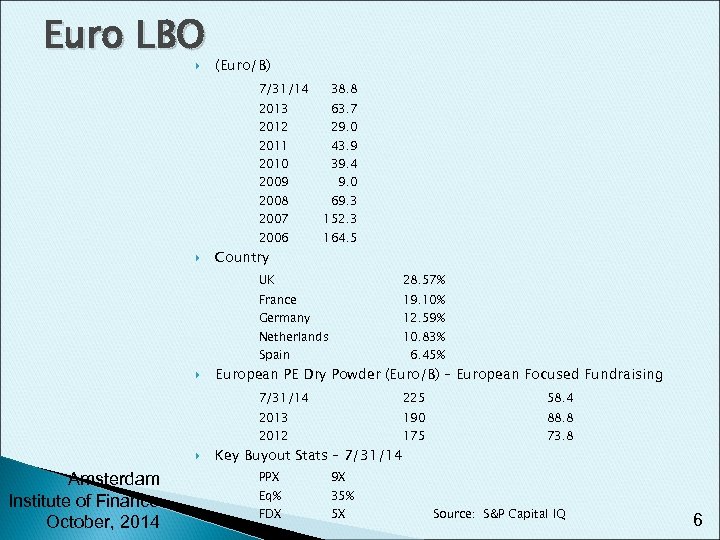
Euro LBO (Euro/B) 7/31/14 38. 8 2013 63. 7 2011 43. 9 2012 29. 0 2010 39. 4 2009 2008 2007 2006 Country 9. 0 69. 3 152. 3 164. 5 UK 28. 57% France 19. 10% Netherlands 10. 83% Germany 12. 59% Spain 6. 45% European PE Dry Powder (Euro/B) – European Focused Fundraising 7/31/14 225 58. 4 2013 190 88. 8 2012 Amsterdam Institute of Finance October, 2014 Key Buyout Stats – 7/31/14 PPX 35% 73. 8 9 X Eq% 175 FDX 5 X Source: S&P Capital IQ 6

Euro Market European LL Volume: Highest Level Post Crisis June/July YTD Volume € 59. 5 B up 19% same period 2013/LY Includes M&A and PE Leverage Up: 5 X+ Return of Cov-lite: Reduced Terms 2 L Increasing CLO: Returning – 6 Mo 16 v 20 for YE 13 Costs dropped from E+200 2013 to E+100 1 H 14 MEZ N/A: 2 L Wipeout HYB (7/31/14): € 61. 3 B v € 47. 2 B LY Amsterdam Institute of Finance October, 2014 7
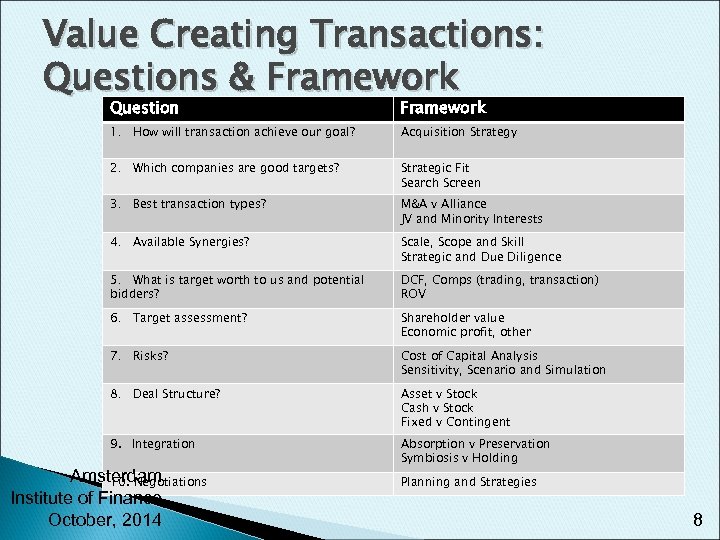
Value Creating Transactions: Questions & Framework Question Framework 1. How will transaction achieve our goal? Acquisition Strategy 2. Which companies are good targets? Strategic Fit Search Screen 3. Best transaction types? M&A v Alliance JV and Minority Interests 4. Available Synergies? Scale, Scope and Skill Strategic and Due Diligence 5. What is target worth to us and potential bidders? DCF, Comps (trading, transaction) ROV 6. Target assessment? Shareholder value Economic profit, other 7. Risks? Cost of Capital Analysis Sensitivity, Scenario and Simulation 8. Deal Structure? Asset v Stock Cash v Stock Fixed v Contingent 9. Integration Absorption v Preservation Symbiosis v Holding Amsterdam 10. Negotiations Institute of Finance October, 2014 Planning and Strategies 8

M&A Danger Signs CEO only believer: headstrong; magazine cover effect Only revenue synergies with no investment plan Prefunctory Due Diligence Reservation price changes during bidding Must close deal Failure to identify why buyer is best owner Emphasis on time, effort, cost and reputation sunk into deal msterdam Institute of nance October, 2014 9
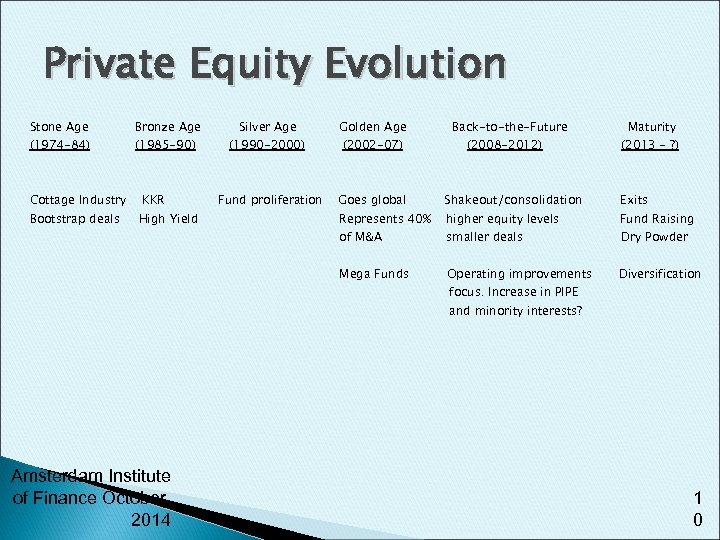
Private Equity Evolution Stone Age (1974 -84) Cottage Industry Bootstrap deals Bronze Age (1985 -90) KKR High Yield Silver Age Golden Age Fund proliferation Goes global Shakeout/consolidation of M&A smaller deals (1990 -2000) (2002 -07) Represents 40% Mega Funds Back-to-the-Future (2008 -2012) Maturity (2013 - ? ) Exits higher equity levels Fund Raising Operating improvements Diversification focus. Increase in PIPE Dry Powder and minority interests? Amsterdam Institute of Finance October, 2014 1 0

PE Sector PE Fund Performance Persistence – declining due to competition Access Networks Signaling Crowded (> 5, 000) 2, 200 funds seeking funds as of July, 2014 Raise $750 B Dry Powder LP Selection Issues Strategy Returns Team Terms Relationship Amsterdam Institute of Finance October, 2014 1 1
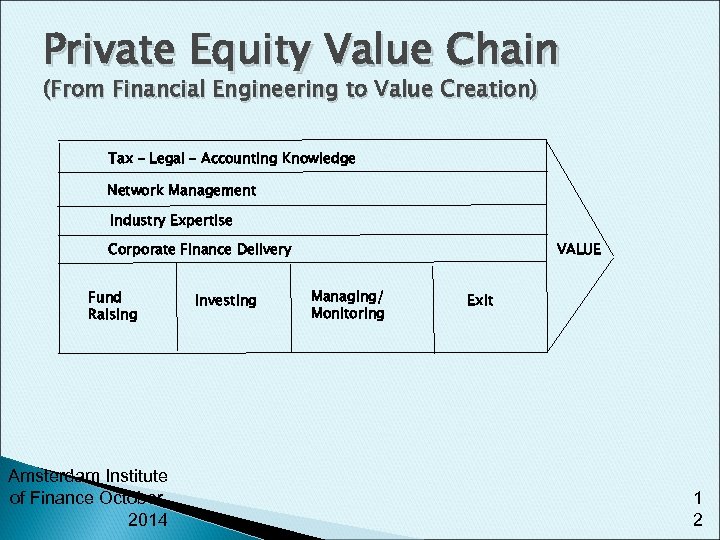
Private Equity Value Chain (From Financial Engineering to Value Creation) Tax – Legal – Accounting Knowledge Network Management Industry Expertise Corporate Finance Delivery Fund Raising Amsterdam Institute of Finance October, 2014 Investing VALUE Managing/ Monitoring Exit 1 2
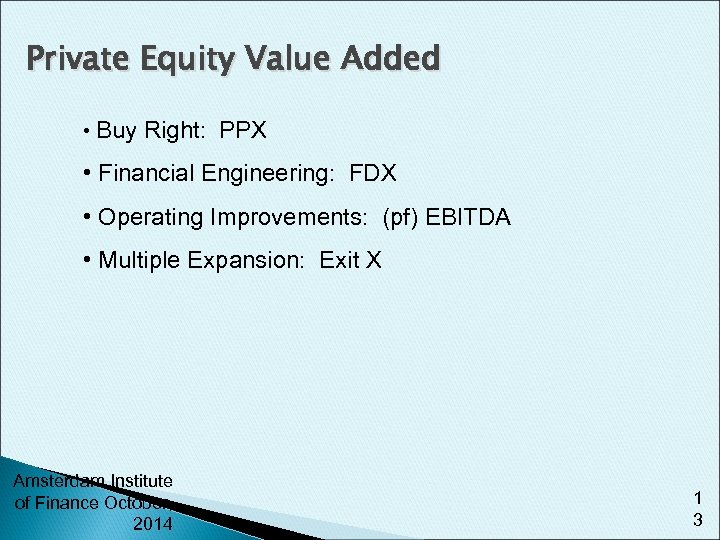
Private Equity Value Added • Buy Right: PPX • Financial Engineering: FDX • Operating Improvements: (pf) EBITDA • Multiple Expansion: Exit X Amsterdam Institute of Finance October, 2014 1 3
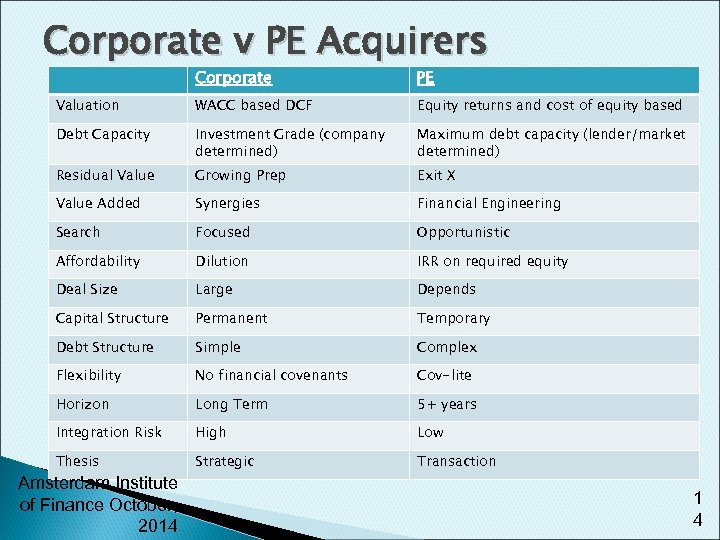
Corporate v PE Acquirers Corporate PE Valuation WACC based DCF Equity returns and cost of equity based Debt Capacity Investment Grade (company determined) Maximum debt capacity (lender/market determined) Residual Value Growing Prep Exit X Value Added Synergies Financial Engineering Search Focused Opportunistic Affordability Dilution IRR on required equity Deal Size Large Depends Capital Structure Permanent Temporary Debt Structure Simple Complex Flexibility No financial covenants Cov-lite Horizon Long Term 5+ years Integration Risk High Low Thesis Strategic Transaction Amsterdam Institute of Finance October, 2014 1 4
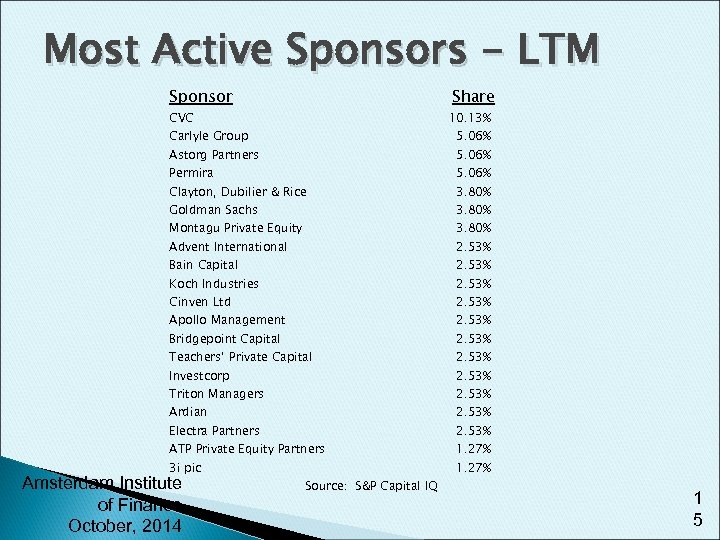
Most Active Sponsors - LTM Sponsor Share CVC 10. 13% Carlyle Group 5. 06% Astorg Partners 5. 06% Clayton, Dubilier & Rice 3. 80% Permira Goldman Sachs Montagu Private Equity 2. 53% Bain Capital 2. 53% Koch Industries 2. 53% Cinven Ltd 2. 53% Apollo Management 2. 53% Bridgepoint Capital Teachers’ Private Capital Investcorp Triton Managers 2. 53% Ardian 2. 53% Electra Partners ATP Private Equity Partners Amsterdam Institute of Finance October, 2014 3. 80% Advent International 3 i pic 5. 06% Source: S&P Capital IQ 2. 53% 1. 27% 1 5
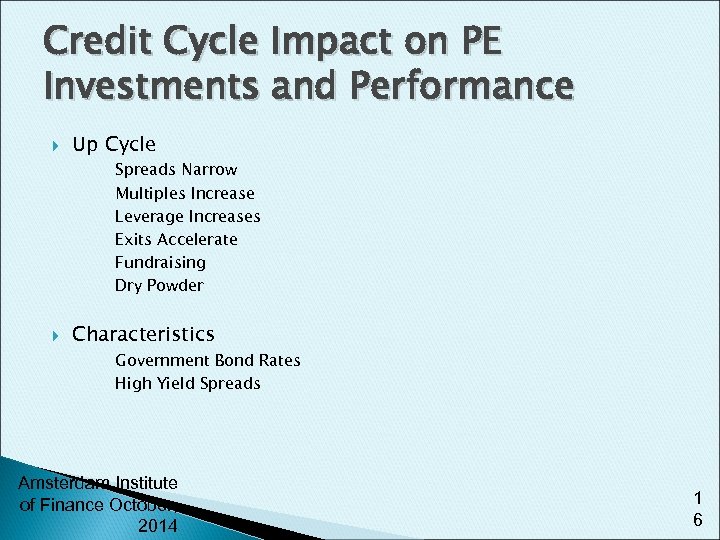
Credit Cycle Impact on PE Investments and Performance Up Cycle Spreads Narrow Multiples Increase Leverage Increases Exits Accelerate Fundraising Dry Powder Characteristics Government Bond Rates High Yield Spreads Amsterdam Institute of Finance October, 2014 1 6
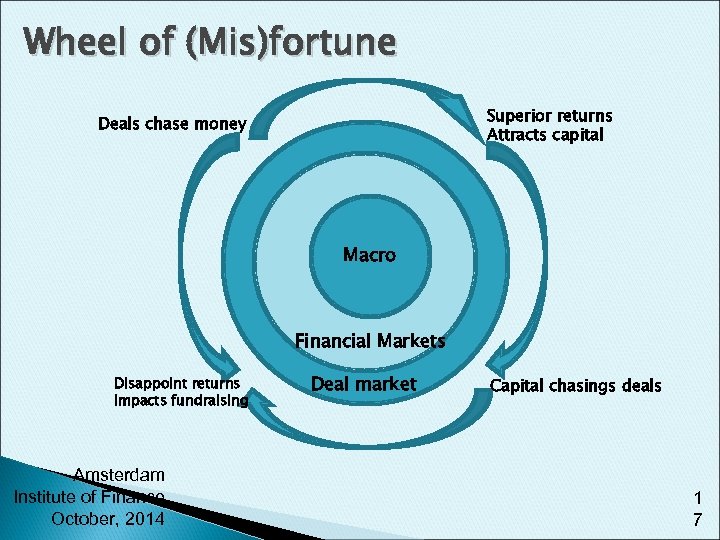
Wheel of (Mis)fortune Superior returns Attracts capital Deals chase money Macro Financial Markets Disappoint returns Impacts fundraising Amsterdam Institute of Finance October, 2014 Deal market Capital chasings deals 1 7
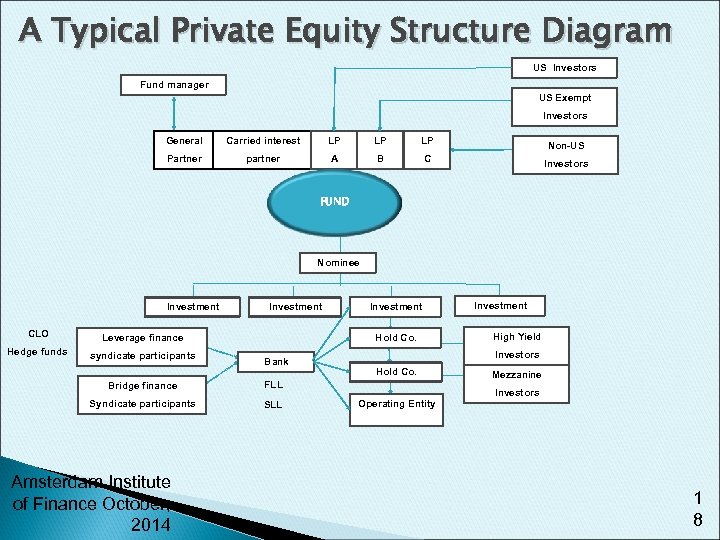
A Typical Private Equity Structure Diagram US Investors Fund manager US Exempt Investors General Carried interest LP LP LP Non-US Partner partner A B C Investors FUND Nominee Investment CLO Leverage finance Hedge funds syndicate participants Investment Hold Co. Bank Bridge finance SLL Amsterdam Institute of Finance October, 2014 High Yield Investors Hold Co. FLL Syndicate participants Investment Operating Entity Mezzanine Investors 1 8
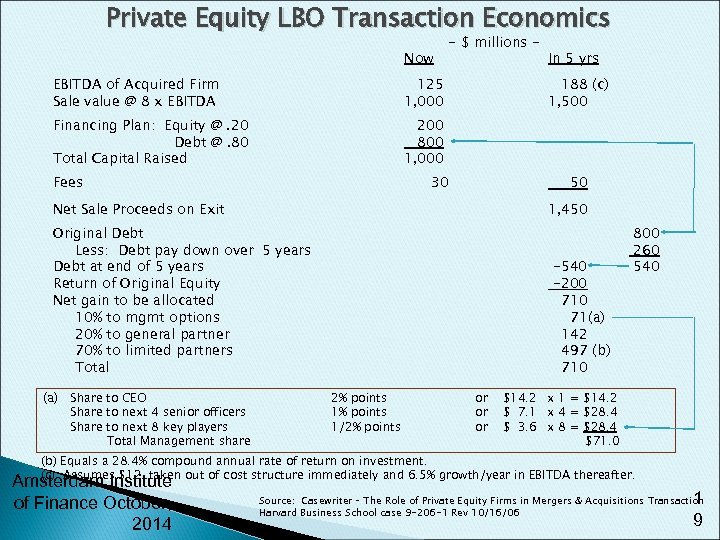
Private Equity LBO Transaction Economics Now EBITDA of Acquired Firm Sale value @ 8 x EBITDA 125 1, 000 Financing Plan: Equity @. 20 Debt @. 80 Total Capital Raised - $ millions - In 5 yrs 200 800 1, 000 Fees 188 (c) 1, 500 30 50 Net Sale Proceeds on Exit 1, 450 Original Debt Less: Debt pay down over 5 years Debt at end of 5 years Return of Original Equity Net gain to be allocated 10% to mgmt options 20% to general partner 70% to limited partners Total (a) Share to CEO Share to next 4 senior officers Share to next 8 key players Total Management share -540 -200 71(a) 142 497 (b) 710 2% points 1/2% points or or or 800 260 540 $14. 2 x 1 = $14. 2 $ 7. 1 x 4 = $28. 4 $ 3. 6 x 8 = $28. 4 $71. 0 (b) Equals a 28. 4% compound annual rate of return on investment. (c) Assumes $12 taken out of cost structure immediately and 6. 5% growth/year in EBITDA thereafter. Amsterdam Institute of Finance October, 2014 1 9 Source: Casewriter – The Role of Private Equity Firms in Mergers & Acquisitions Transaction Harvard Business School case 9 -206 -1 Rev 10/16/06
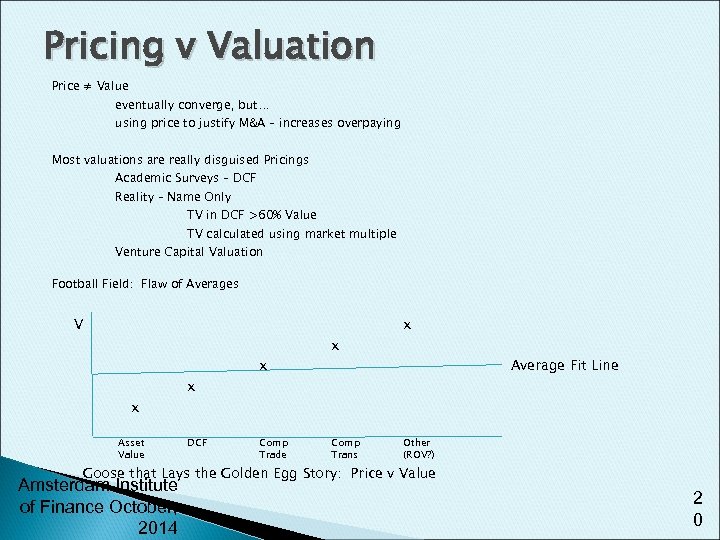
Pricing v Valuation Price ≠ Value eventually converge, but… using price to justify M&A – increases overpaying Most valuations are really disguised Pricings Academic Surveys – DCF Reality – Name Only TV in DCF >60% Value TV calculated using market multiple Venture Capital Valuation Football Field: Flaw of Averages V x Asset Value x DCF x Comp Trade x Comp Trans x Average Fit Line Other (ROV? ) Goose that Lays the Golden Egg Story: Price v Value Amsterdam Institute of Finance October, 2014 2 0

Anatomy of a Premium Stupidity & Bias Fantasy Competitive Necessity Outlook/Information Advantage Synergies Lower Buyer WACC Undervaluation ROT: Greater than 40% premium over pre-bid market price is difficult to justify for any sizeable acquisition. Amsterdam Institute of Finance October, 2014 2 1

LBO Analysis Focus on return: what is the maximum price I can pay based on given set of projections and earn X% return not risk adjusted? Tradition Valuation = Projected cash flows Discounted rate Terminal value LBO Perspective = IRR (Equity discount rate) Projected cash flows Purchase Price Sale Price (Terminal Value) Debt Policy Ratings/Corp Value Transfer from LP’s Amsterdam Institute of Finance October, 2014 2 2

LBO Valuation (Pricing/Affordability) How much can I borrow (XEBITDA) Usually 4 - 6 X depending on market Equity Percentage Required (% of PP) Usually 30% - 45% dependent on market Compare Market PPX IRR Adjustments FD Exit Multiple Equity PP EBITDA adjustment (pro forma EBITDA) Example – assume € 100 EBITDA FDX – 5 X Equity % - 35% Amsterdam Institute bid 7500 or 7. 5 x EBITDA Affordable of Finance October, 2014 2 3

Cash Flow Available for Debt Service (CFADS) DCF CFADS Net Income + Dep/Amt +/_ Change in deferred taxes +/- Other noncash items +/- Change in working capital Cash flow from operations +After tax interest (hypo Ƭ) - CAPEX - Unleveraged FCF Net Income Dep/Amt Change in deferred taxes Other non cash changes Change in working capital Cash flow from operations Non interest expense adjustment Capex CFADS Amsterdam Institute of Finance October, 2014 2 4

Converting IRR into Equivalent Multiple of Capital (MOIC) IRR 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% Amsterdam Institute of Finance October, 2014 Equivalent MOIC Over 6 Years 1. 8 X 3. 0 X 4. 8 X 7. 5 X 11. 4 X 2 5
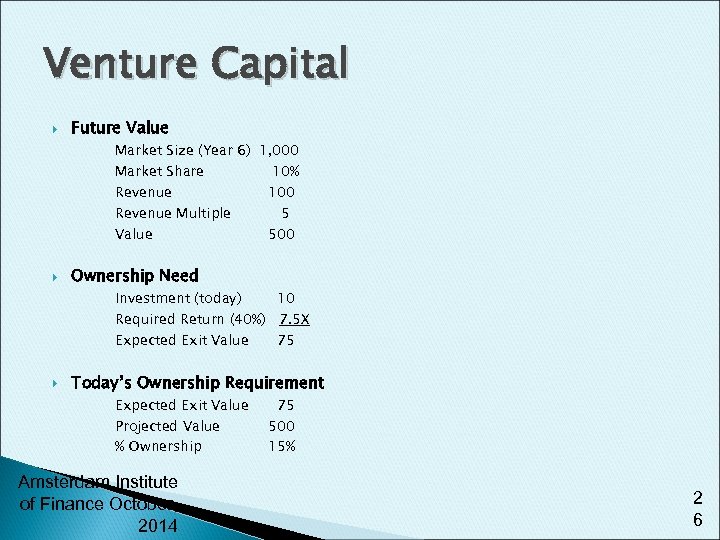
Venture Capital Future Value Market Size (Year 6) 1, 000 Market Share 10% Revenue 100 Revenue Multiple 5 Value 500 Ownership Need Investment (today) 10 Required Return (40%) 7. 5 X Expected Exit Value 75 Today’s Ownership Requirement Expected Exit Value Projected Value % Ownership Amsterdam Institute of Finance October, 2014 75 500 15% 2 6

Fixing the Broken Deal – Price and Structural Flex Increase spread Recycled Original issue discount Eliminate PIK Reduce debt Add a subordinate tranche More equity Add covenants Reduce Price Seller Paper Amsterdam Institute of Finance October, 2014 2 7
48bff8df4b450725b127a78f6a2fde18.ppt