c863b8a6699a716377004bc5b80f7b3a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Spoken Dialogue Technology Achievements and Challenges Michael Mc. Tear University of Ulster
Spoken Dialogue Technology Achievements and Challenges Michael Mc. Tear University of Ulster
 Overview l l Introduction - What is a spoken dialogue system? Examples of spoken dialogue systems Technical issues and challenges Future Prospects
Overview l l Introduction - What is a spoken dialogue system? Examples of spoken dialogue systems Technical issues and challenges Future Prospects
 What is a spoken dialogue system? A spoken dialogue system is an automated system that engages in a dialogue with a human user using spoken language as the medium of interaction.
What is a spoken dialogue system? A spoken dialogue system is an automated system that engages in a dialogue with a human user using spoken language as the medium of interaction.
 Types of dialogue system Two main types of spoken dialogue system l Task-oriented: involves the use of dialogues to accomplish a task, e. g. making a hotel booking, or planning a family holiday l Non-task-oriented: engaging in conversational interaction, but without necessarily being involved in a task that needs to be accomplished e. g conversational companion for the elderly
Types of dialogue system Two main types of spoken dialogue system l Task-oriented: involves the use of dialogues to accomplish a task, e. g. making a hotel booking, or planning a family holiday l Non-task-oriented: engaging in conversational interaction, but without necessarily being involved in a task that needs to be accomplished e. g conversational companion for the elderly
 Application Domains for SDS l Telephone-based services and transactions l l l l Call-routing, Directory assistance, Travel enquiries, Bank balance, Bank transactions, Flight / hotel / car rental reservations In-car interactive and entertainment systems Automated trouble-shooting Smart homes applications Health-care systems e. g. patient monitoring Educational e, g. Intelligent Tutoring Systems, Foreign Language Learning Computer games
Application Domains for SDS l Telephone-based services and transactions l l l l Call-routing, Directory assistance, Travel enquiries, Bank balance, Bank transactions, Flight / hotel / car rental reservations In-car interactive and entertainment systems Automated trouble-shooting Smart homes applications Health-care systems e. g. patient monitoring Educational e, g. Intelligent Tutoring Systems, Foreign Language Learning Computer games
 Three generations of taskoriented spoken dialogue system l l l Informational – to retrieve information e. g. flight times, football scores, … Transactional – to assist the user to perform a transaction e. g. book a flight, pay a bill Problem-solving – to support the user in solving a problem e. g. to troubleshoot a PC that is not working
Three generations of taskoriented spoken dialogue system l l l Informational – to retrieve information e. g. flight times, football scores, … Transactional – to assist the user to perform a transaction e. g. book a flight, pay a bill Problem-solving – to support the user in solving a problem e. g. to troubleshoot a PC that is not working
 Why is dialogue interesting? l Fundamental aspect of human behaviour l l l Model human conversational competence Simulate human conversational behaviour Provide tool for interacting with data, services, resources on computers l l l Research challenges Applications in assistive and educational environments Commercial opportunities
Why is dialogue interesting? l Fundamental aspect of human behaviour l l l Model human conversational competence Simulate human conversational behaviour Provide tool for interacting with data, services, resources on computers l l l Research challenges Applications in assistive and educational environments Commercial opportunities
 Commercial Systems l Focus on l l l Business opportunities, return on investment (ROI) Benefits for end users Benefits for providers Human factors: performance, usability Tools and languages for design and maintainability Application areas: call centre, enquiries, transactions, healthcare, …
Commercial Systems l Focus on l l l Business opportunities, return on investment (ROI) Benefits for end users Benefits for providers Human factors: performance, usability Tools and languages for design and maintainability Application areas: call centre, enquiries, transactions, healthcare, …
 Academic Systems l Focus on l l Technologies: speech recognition, spoken language understanding, dialogue management AI inspired: planning, reasoning, machine learning Statistical v symbolic approaches Advanced dialogue control, error handling, adaptivity, context representation
Academic Systems l Focus on l l Technologies: speech recognition, spoken language understanding, dialogue management AI inspired: planning, reasoning, machine learning Statistical v symbolic approaches Advanced dialogue control, error handling, adaptivity, context representation
 Overview l l Introduction - What is a spoken dialogue system? Examples of spoken dialogue systems Technical issues and challenges Future Prospects
Overview l l Introduction - What is a spoken dialogue system? Examples of spoken dialogue systems Technical issues and challenges Future Prospects
 Example 1: Voice Menu System: Hello and welcome …. Main menu. For customer service, say ‘service’. To enquire about an existing order, say ‘order’ … User: Service System: Customer service. Would you like to report a fault or enquire about an extended warranty? User: Fault System: Do you have a PC or a laptop? User: Laptop System: And the name of the manufacturer? User: Sony System: Thank you. Please hold while I transfer you to the Sony … http: //www. speechstorm. com/
Example 1: Voice Menu System: Hello and welcome …. Main menu. For customer service, say ‘service’. To enquire about an existing order, say ‘order’ … User: Service System: Customer service. Would you like to report a fault or enquire about an extended warranty? User: Fault System: Do you have a PC or a laptop? User: Laptop System: And the name of the manufacturer? User: Sony System: Thank you. Please hold while I transfer you to the Sony … http: //www. speechstorm. com/
 Example 2: Research System (Mercury: MIT) l l l Open ended prompt How may I help you? Disfluencies in input August twenty-first no August twelfth I'd like to fly from Boston to Minneapolis on Tuesday no Wednesday November 21 st Inexact response Prompt: Can you provide the approximate departure time or airline preference User: Yeah I'd like to fly United and I'd like to leave in the afternoon http: //groups. csail. mit. edu/sls/research/mercury. shtml
Example 2: Research System (Mercury: MIT) l l l Open ended prompt How may I help you? Disfluencies in input August twenty-first no August twelfth I'd like to fly from Boston to Minneapolis on Tuesday no Wednesday November 21 st Inexact response Prompt: Can you provide the approximate departure time or airline preference User: Yeah I'd like to fly United and I'd like to leave in the afternoon http: //groups. csail. mit. edu/sls/research/mercury. shtml
 Example 2: continued l Response generation There are more than 3 flights. The earliest departure leaves at 1. 45 pm. l Mixed initiative: user asks question Do you have something leaving around 4. 45? l Relative date reference I’d like to return the following Tuesday
Example 2: continued l Response generation There are more than 3 flights. The earliest departure leaves at 1. 45 pm. l Mixed initiative: user asks question Do you have something leaving around 4. 45? l Relative date reference I’d like to return the following Tuesday
 Example 3: Voice Search GOOG 411 GOOG-411 (or Google Voice Local Search) is Google's new 411 service. With GOOG-411, you can find local business information completely free, directly from your phone. You can access 1 -800 -GOOG-411 from any phone, anywhere, at anytime. http: //www. google. com/goog 411/
Example 3: Voice Search GOOG 411 GOOG-411 (or Google Voice Local Search) is Google's new 411 service. With GOOG-411, you can find local business information completely free, directly from your phone. You can access 1 -800 -GOOG-411 from any phone, anywhere, at anytime. http: //www. google. com/goog 411/
 GOOG 411: Prompts What city and state? What business name or category? (Lists services) Number one, …. . Connects to requested service
GOOG 411: Prompts What city and state? What business name or category? (Lists services) Number one, …. . Connects to requested service
 GOOG 411: What can you say? At any point in the call: To go back say "go back" To start over say "start over" or press *All phones When asked for a city and state: Say the full names for example, "Palo Alto California“ To enter a zip code say it or enter with keypad When asked for business name or category: Say the full names for example, "Joe's Pizzaria" or "Pizza“ When given results: To navigate between results say or press the listing number To receive an SMS say "text message" To receive a map say "map it" To get more details say "details"
GOOG 411: What can you say? At any point in the call: To go back say "go back" To start over say "start over" or press *All phones When asked for a city and state: Say the full names for example, "Palo Alto California“ To enter a zip code say it or enter with keypad When asked for business name or category: Say the full names for example, "Joe's Pizzaria" or "Pizza“ When given results: To navigate between results say or press the listing number To receive an SMS say "text message" To receive a map say "map it" To get more details say "details"
 Overview l l Introduction - What is a spoken dialogue system? Examples of spoken dialogue systems Technical issues and challenges Future Prospects
Overview l l Introduction - What is a spoken dialogue system? Examples of spoken dialogue systems Technical issues and challenges Future Prospects
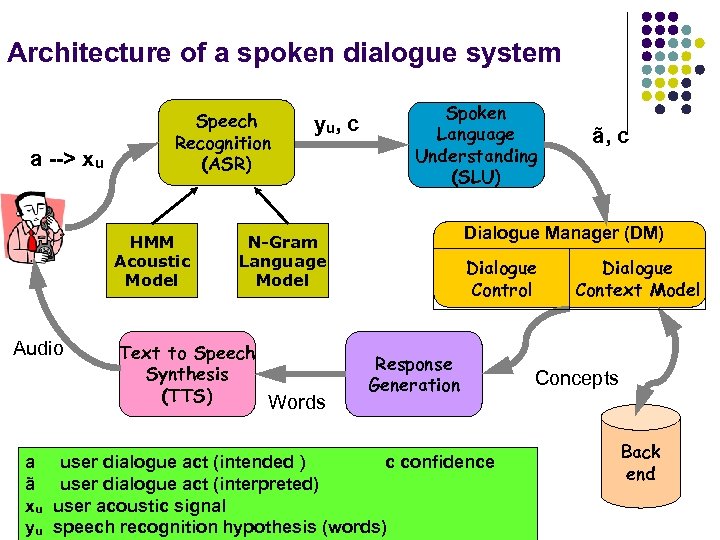 Architecture of a spoken dialogue system a --> xu Speech Recognition (ASR) HMM Acoustic Model Audio a ã xu yu yu , c Spoken Language Understanding (SLU) Dialogue Manager (DM) N-Gram Language Model Text to Speech Synthesis (TTS) Words ã, c Dialogue Control Response Generation user dialogue act (intended ) c confidence user dialogue act (interpreted) user acoustic signal speech recognition hypothesis (words) Dialogue Context Model Concepts Back end
Architecture of a spoken dialogue system a --> xu Speech Recognition (ASR) HMM Acoustic Model Audio a ã xu yu yu , c Spoken Language Understanding (SLU) Dialogue Manager (DM) N-Gram Language Model Text to Speech Synthesis (TTS) Words ã, c Dialogue Control Response Generation user dialogue act (intended ) c confidence user dialogue act (interpreted) user acoustic signal speech recognition hypothesis (words) Dialogue Context Model Concepts Back end
 Component Technologies l l l Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) Spoken Language Understanding (SLU) Response Generation (RG) Text to speech synthesis (TTS) Dialogue Management (DM)
Component Technologies l l l Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) Spoken Language Understanding (SLU) Response Generation (RG) Text to speech synthesis (TTS) Dialogue Management (DM)
 Issues in ASR for Dialogue l l recognising spontaneous speech in noisy environments word accuracy does not have to be 100% use of confidence scores in combination with other information to determine DM actions use of additional information (ASR and parse probabilities, semantic and contextual features) to re-score recognition hypotheses
Issues in ASR for Dialogue l l recognising spontaneous speech in noisy environments word accuracy does not have to be 100% use of confidence scores in combination with other information to determine DM actions use of additional information (ASR and parse probabilities, semantic and contextual features) to re-score recognition hypotheses
 Issues in SLU for Dialogue l l grammars and parsers for spontaneous speech (disfluencies, errors) robust understanding l l l problems with hand-crafted approaches use of statistical/ data-driven methods combined approaches e. g TINA (MIT) l l hand-crafted rules with trained probabilities robust strategy – if full sentence cannot be parsed, parse and combine fragments, else use word spotting
Issues in SLU for Dialogue l l grammars and parsers for spontaneous speech (disfluencies, errors) robust understanding l l l problems with hand-crafted approaches use of statistical/ data-driven methods combined approaches e. g TINA (MIT) l l hand-crafted rules with trained probabilities robust strategy – if full sentence cannot be parsed, parse and combine fragments, else use word spotting
 Issues in Response Generation for Dialogue l Content selection l l Discourse planning l l l Determining what to say, selecting and ranking options discourse relations e. g. comparison, contrast user-adapted information Presentation ordering Referring expression generation Aggregation – grouping propositions into clauses and sentences Use of discourse cues (e. g. firstly, finally, however, moreover, …)
Issues in Response Generation for Dialogue l Content selection l l Discourse planning l l l Determining what to say, selecting and ranking options discourse relations e. g. comparison, contrast user-adapted information Presentation ordering Referring expression generation Aggregation – grouping propositions into clauses and sentences Use of discourse cues (e. g. firstly, finally, however, moreover, …)
 Issues in Dialogue Management l Dialogue Control l l Representations l l l Scripts, frames, intelligent agents Information State Theory Error handling Dialogue design l l Traditional approaches Statistical approaches l l Reinforcement learning Corpus / example based approaches
Issues in Dialogue Management l Dialogue Control l l Representations l l l Scripts, frames, intelligent agents Information State Theory Error handling Dialogue design l l Traditional approaches Statistical approaches l l Reinforcement learning Corpus / example based approaches
 Overview l l Introduction - What is a spoken dialogue system? Examples of spoken dialogue systems Technical issues and challenges Future Prospects
Overview l l Introduction - What is a spoken dialogue system? Examples of spoken dialogue systems Technical issues and challenges Future Prospects
 A vision for the future Develop systems that can interact intelligently and co-operatively across a range of environments using a range of appropriate modalities to support people in the activities of their daily lives.
A vision for the future Develop systems that can interact intelligently and co-operatively across a range of environments using a range of appropriate modalities to support people in the activities of their daily lives.
 Fundamental research topics l l l Modelling human conversational competence Dialogue-related issues for ASR, SLU, NLG, TTS Comparison of methods for dialogue management: rule-based v stochastic Representation and use of contextual information Integration and usage of modalities to complement and supplement speech Incremental processing in dialogue
Fundamental research topics l l l Modelling human conversational competence Dialogue-related issues for ASR, SLU, NLG, TTS Comparison of methods for dialogue management: rule-based v stochastic Representation and use of contextual information Integration and usage of modalities to complement and supplement speech Incremental processing in dialogue
 Areas of application l l l Voice search Dialogue in vehicles Mobile speech applications Multimodal embodied and situated systems Troubleshooting applications Dialogue systems for ambient intelligence and as assistive technologies
Areas of application l l l Voice search Dialogue in vehicles Mobile speech applications Multimodal embodied and situated systems Troubleshooting applications Dialogue systems for ambient intelligence and as assistive technologies
 Concluding remarks Spoken Dialogue Technology l embraces a range of speech and language technologies l poses lots of theoretical as well as practical challenges l is interesting for commercial developers as well as academic researchers l has a wide range of potential applications
Concluding remarks Spoken Dialogue Technology l embraces a range of speech and language technologies l poses lots of theoretical as well as practical challenges l is interesting for commercial developers as well as academic researchers l has a wide range of potential applications
 Recommended reading Mc. Tear, M. (2004) Spoken Dialogue Technology. Springer. Lopez Cozar, R. & Araki, M. (2005) Spoken, multilingual and multimodal dialogue systems. John Wiley & Sons. Aghajan, H. , Augusto, J. C. , Lopez Cozar, R. (2009) Human -Centric Interfaces for Ambient Intelligence. Elsevier. Jokinen, K. & Mc. Tear, M. (2010) Spoken Dialogue Systems. Morgan Claypool Publishers. Wilks, Y. (ed. ) (2010) Close Engagements with Artificial Companions: Key social, psychological, ethical and design issues. John Benjamins Publishing Company.
Recommended reading Mc. Tear, M. (2004) Spoken Dialogue Technology. Springer. Lopez Cozar, R. & Araki, M. (2005) Spoken, multilingual and multimodal dialogue systems. John Wiley & Sons. Aghajan, H. , Augusto, J. C. , Lopez Cozar, R. (2009) Human -Centric Interfaces for Ambient Intelligence. Elsevier. Jokinen, K. & Mc. Tear, M. (2010) Spoken Dialogue Systems. Morgan Claypool Publishers. Wilks, Y. (ed. ) (2010) Close Engagements with Artificial Companions: Key social, psychological, ethical and design issues. John Benjamins Publishing Company.
 Thank you Questions?
Thank you Questions?


