6ce8e15837ea8b039e7af839011753f8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Splinting in the Emergency Room Tammy Whitehead RN, BSN
Splinting in the Emergency Room Tammy Whitehead RN, BSN
 Why Do We Splint? • To stabilize the extremity • To decrease pain • Actually treat the injury
Why Do We Splint? • To stabilize the extremity • To decrease pain • Actually treat the injury
 Complications of Splinting • Abrasions • Sores • Neurovascular compromise (tight fitting splints) • Contact dermatitis • Pressure ulcers • Thermal burns
Complications of Splinting • Abrasions • Sores • Neurovascular compromise (tight fitting splints) • Contact dermatitis • Pressure ulcers • Thermal burns
 How to prevent complications • Apply splint by trained professional • Apply splint correctly • Monitor neurovascular status. U What we do! s ! Collaboratio n with the Docs!
How to prevent complications • Apply splint by trained professional • Apply splint correctly • Monitor neurovascular status. U What we do! s ! Collaboratio n with the Docs!
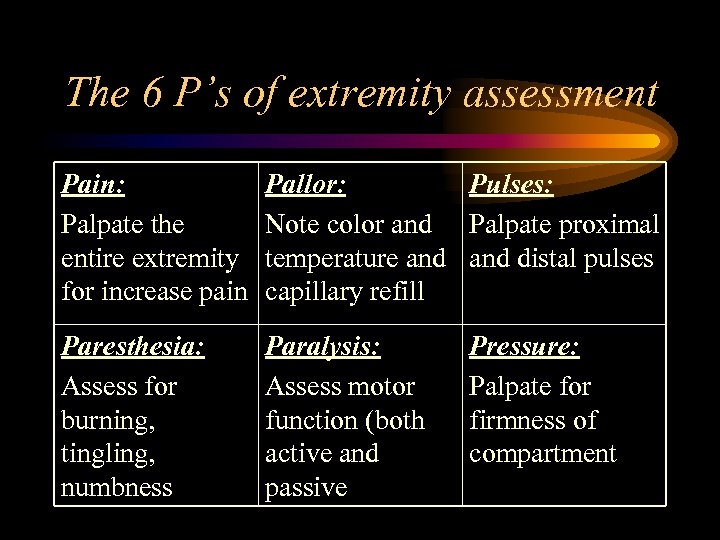 The 6 P’s of extremity assessment Pain: Palpate the entire extremity for increase pain Pallor: Pulses: Note color and Palpate proximal temperature and distal pulses capillary refill Paresthesia: Assess for burning, tingling, numbness Paralysis: Assess motor function (both active and passive Pressure: Palpate for firmness of compartment
The 6 P’s of extremity assessment Pain: Palpate the entire extremity for increase pain Pallor: Pulses: Note color and Palpate proximal temperature and distal pulses capillary refill Paresthesia: Assess for burning, tingling, numbness Paralysis: Assess motor function (both active and passive Pressure: Palpate for firmness of compartment
 Equipment need for application • Cotton bandage( soft roll, cotton roll) Pad entire area to be splinted • Plaster slabs or pre padded fiberglass (Orthoglass), immobilize above and below injury • Room temperature water (apply generously) • Elastic bandage • Adhesive tape or fastners
Equipment need for application • Cotton bandage( soft roll, cotton roll) Pad entire area to be splinted • Plaster slabs or pre padded fiberglass (Orthoglass), immobilize above and below injury • Room temperature water (apply generously) • Elastic bandage • Adhesive tape or fastners
 Types of Splints • Yes, its broken and needs a splint! • Why sure Doctor, not a • problem!
Types of Splints • Yes, its broken and needs a splint! • Why sure Doctor, not a • problem!
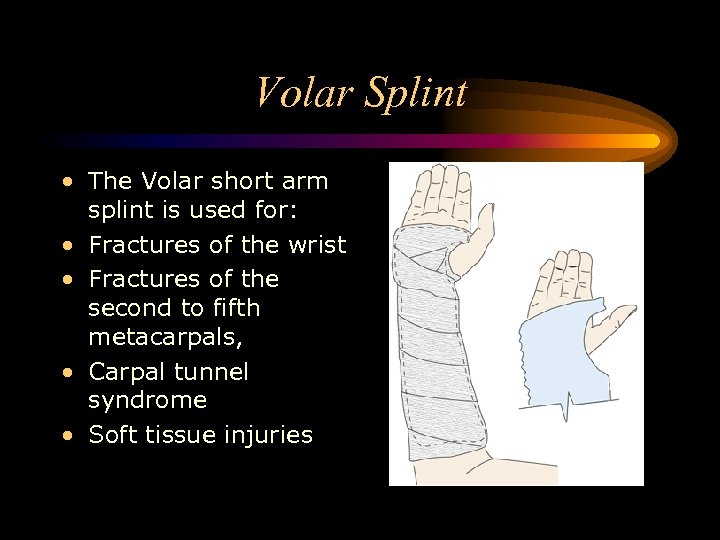 Volar Splint • The Volar short arm splint is used for: • Fractures of the wrist • Fractures of the second to fifth metacarpals, • Carpal tunnel syndrome • Soft tissue injuries
Volar Splint • The Volar short arm splint is used for: • Fractures of the wrist • Fractures of the second to fifth metacarpals, • Carpal tunnel syndrome • Soft tissue injuries
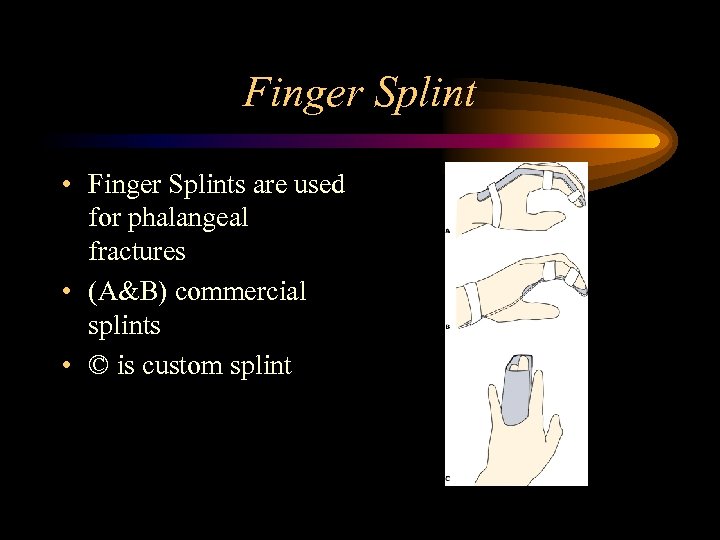 Finger Splint • Finger Splints are used for phalangeal fractures • (A&B) commercial splints • © is custom splint
Finger Splint • Finger Splints are used for phalangeal fractures • (A&B) commercial splints • © is custom splint
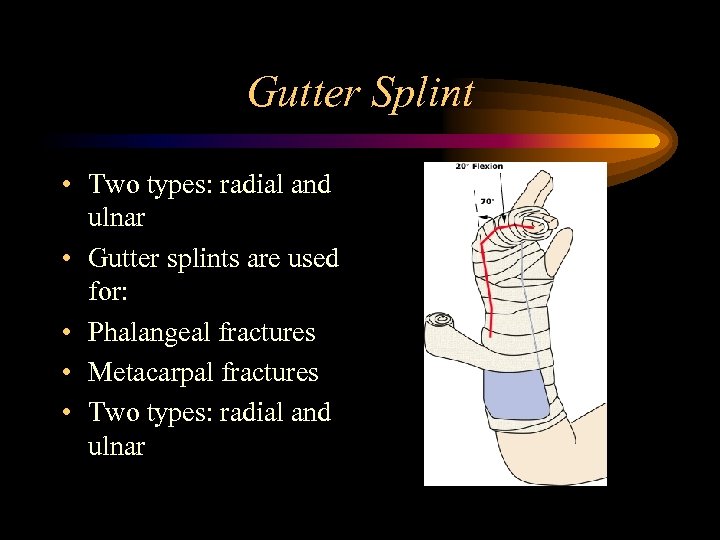 Gutter Splint • Two types: radial and ulnar • Gutter splints are used for: • Phalangeal fractures • Metacarpal fractures • Two types: radial and ulnar
Gutter Splint • Two types: radial and ulnar • Gutter splints are used for: • Phalangeal fractures • Metacarpal fractures • Two types: radial and ulnar
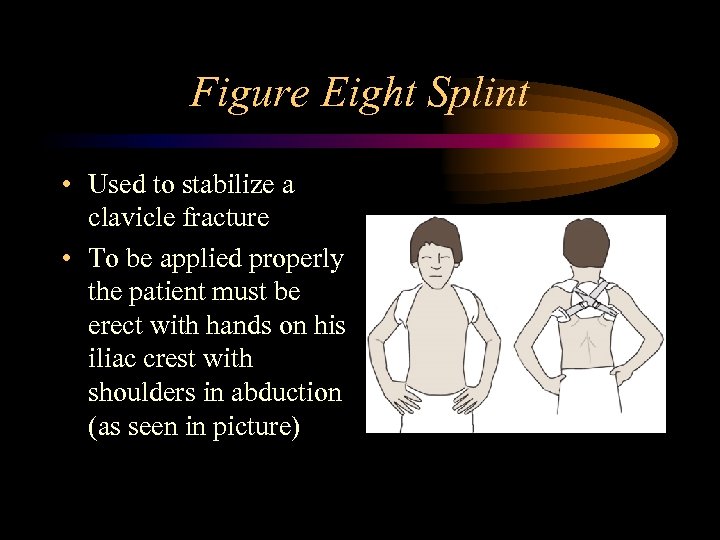 Figure Eight Splint • Used to stabilize a clavicle fracture • To be applied properly the patient must be erect with hands on his iliac crest with shoulders in abduction (as seen in picture)
Figure Eight Splint • Used to stabilize a clavicle fracture • To be applied properly the patient must be erect with hands on his iliac crest with shoulders in abduction (as seen in picture)
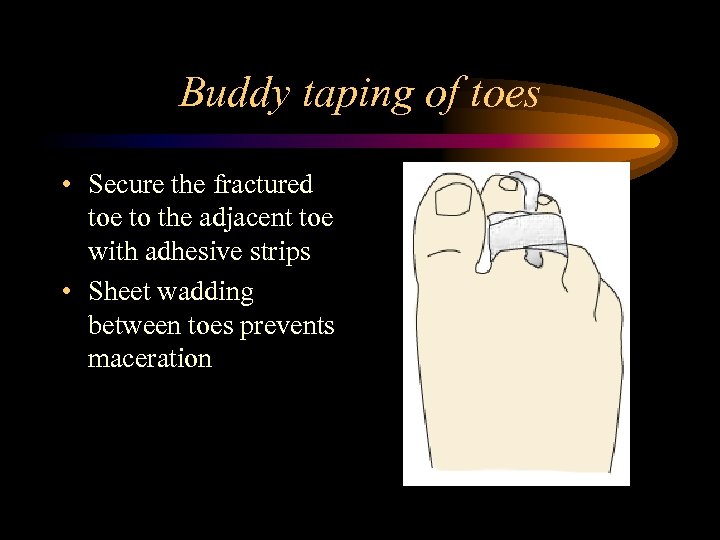 Buddy taping of toes • Secure the fractured toe to the adjacent toe with adhesive strips • Sheet wadding between toes prevents maceration
Buddy taping of toes • Secure the fractured toe to the adjacent toe with adhesive strips • Sheet wadding between toes prevents maceration
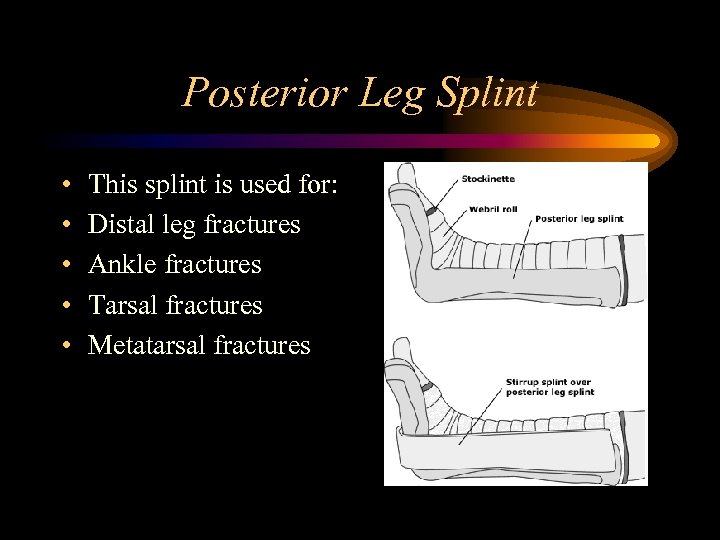 Posterior Leg Splint • • • This splint is used for: Distal leg fractures Ankle fractures Tarsal fractures Metatarsal fractures
Posterior Leg Splint • • • This splint is used for: Distal leg fractures Ankle fractures Tarsal fractures Metatarsal fractures
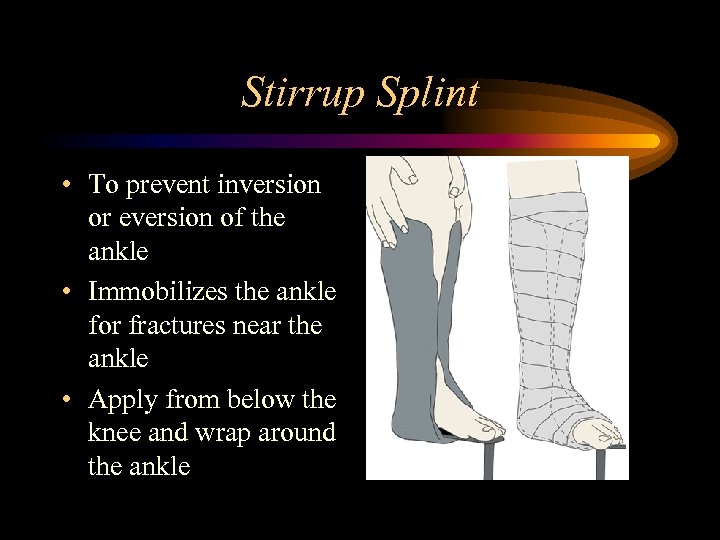 Stirrup Splint • To prevent inversion or eversion of the ankle • Immobilizes the ankle for fractures near the ankle • Apply from below the knee and wrap around the ankle
Stirrup Splint • To prevent inversion or eversion of the ankle • Immobilizes the ankle for fractures near the ankle • Apply from below the knee and wrap around the ankle
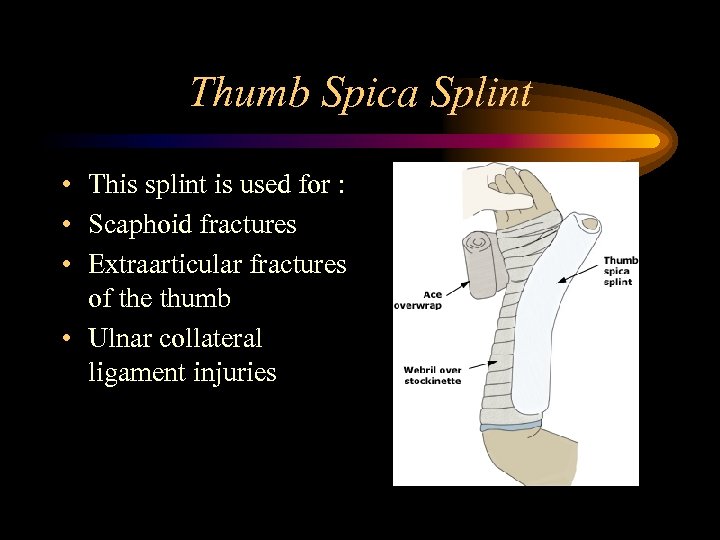 Thumb Spica Splint • This splint is used for : • Scaphoid fractures • Extraarticular fractures of the thumb • Ulnar collateral ligament injuries
Thumb Spica Splint • This splint is used for : • Scaphoid fractures • Extraarticular fractures of the thumb • Ulnar collateral ligament injuries
 What do you do after you have applied your splint? ? ? 1. Have MD/PA evaluate splint 2. Document what you have done!!!
What do you do after you have applied your splint? ? ? 1. Have MD/PA evaluate splint 2. Document what you have done!!!
 Documentation • Which Splint you applied • Which extremity you applied the splint to • 6 P’s • Time you applied the splint • Condition of any wound • How the patient tolerated the procedure • Which MD/PA evaluated splint and time
Documentation • Which Splint you applied • Which extremity you applied the splint to • 6 P’s • Time you applied the splint • Condition of any wound • How the patient tolerated the procedure • Which MD/PA evaluated splint and time
 Application of Splints • Follow up on the floor and perform the following splints under the observation of your preceptor • • • Gutter splint Volar splint Thumb Spica Posterior leg splint Stirrup leg splint Clavicle Brace
Application of Splints • Follow up on the floor and perform the following splints under the observation of your preceptor • • • Gutter splint Volar splint Thumb Spica Posterior leg splint Stirrup leg splint Clavicle Brace
 To Receive Credit for having completed this Review of Splinting : • Certificate of Completion of On-line Module – Splinting in the ED – Complete the Certificate with your name and date of completion – Print and sent to Tammy Whitehead for records.
To Receive Credit for having completed this Review of Splinting : • Certificate of Completion of On-line Module – Splinting in the ED – Complete the Certificate with your name and date of completion – Print and sent to Tammy Whitehead for records.


