4f67f4d7d4721445e06186300a8231ac.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13
 SPLASH Sécurisation des Protoco. Les dans les rése. Aux mobile. S ad Hoc http: //www. inrialpes. fr/planete/splash. html 12 Décembre 2003 Refik Molva Institut EURECOM molva@eurecom. fr
SPLASH Sécurisation des Protoco. Les dans les rése. Aux mobile. S ad Hoc http: //www. inrialpes. fr/planete/splash. html 12 Décembre 2003 Refik Molva Institut EURECOM molva@eurecom. fr
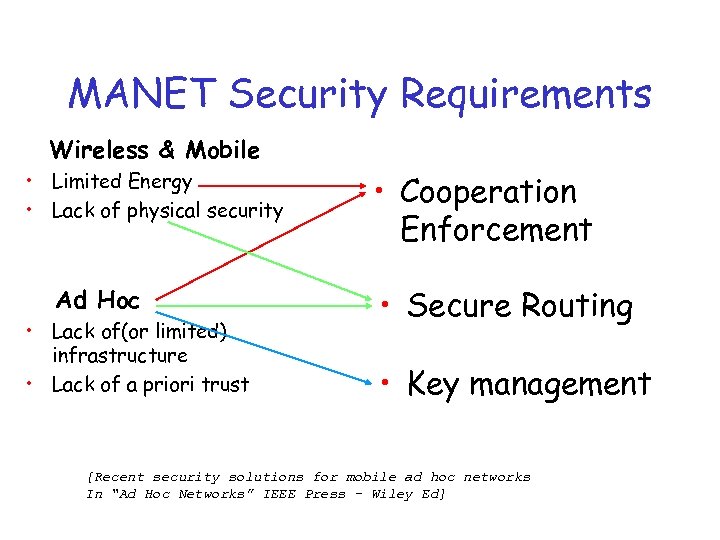 MANET Security Requirements Wireless & Mobile • Limited Energy • Lack of physical security Ad Hoc • Lack of(or limited) infrastructure • Lack of a priori trust • Cooperation Enforcement • Secure Routing • Key management [Recent security solutions for mobile ad hoc networks In “Ad Hoc Networks” IEEE Press - Wiley Ed]
MANET Security Requirements Wireless & Mobile • Limited Energy • Lack of physical security Ad Hoc • Lack of(or limited) infrastructure • Lack of a priori trust • Cooperation Enforcement • Secure Routing • Key management [Recent security solutions for mobile ad hoc networks In “Ad Hoc Networks” IEEE Press - Wiley Ed]
 Key Management Objectives • Bootstrapping from scratch • Fully distributed • Minimum dependency
Key Management Objectives • Bootstrapping from scratch • Fully distributed • Minimum dependency
![Key Management Approaches • Symmetric crypto • (ID, PK) binding [Basagni et al. ] Key Management Approaches • Symmetric crypto • (ID, PK) binding [Basagni et al. ]](https://present5.com/presentation/4f67f4d7d4721445e06186300a8231ac/image-4.jpg) Key Management Approaches • Symmetric crypto • (ID, PK) binding [Basagni et al. ] – Certificate = (ID, PK)CA • Self-organized Authorities [Zhou, Haas] [Kong, et al. ] [Yi, Kravets] [Lehane, et al. ] • Web of trust(PGP) [Hubaux, Buttyan, Capkun] – Certificate-less • Crypto-based IDs: ID = h(PK) [Montenegro, Castellucia] [O’Shea, Roe] [Bobba, et al] • ID-based Crypto: PK = f(ID) [Halili, Katz, Arbaugh] • Context-dependent authentication – location-limited channels [Balfanz, et al. ] – Shared passwords [Asokan, Ginzborg]
Key Management Approaches • Symmetric crypto • (ID, PK) binding [Basagni et al. ] – Certificate = (ID, PK)CA • Self-organized Authorities [Zhou, Haas] [Kong, et al. ] [Yi, Kravets] [Lehane, et al. ] • Web of trust(PGP) [Hubaux, Buttyan, Capkun] – Certificate-less • Crypto-based IDs: ID = h(PK) [Montenegro, Castellucia] [O’Shea, Roe] [Bobba, et al] • ID-based Crypto: PK = f(ID) [Halili, Katz, Arbaugh] • Context-dependent authentication – location-limited channels [Balfanz, et al. ] – Shared passwords [Asokan, Ginzborg]
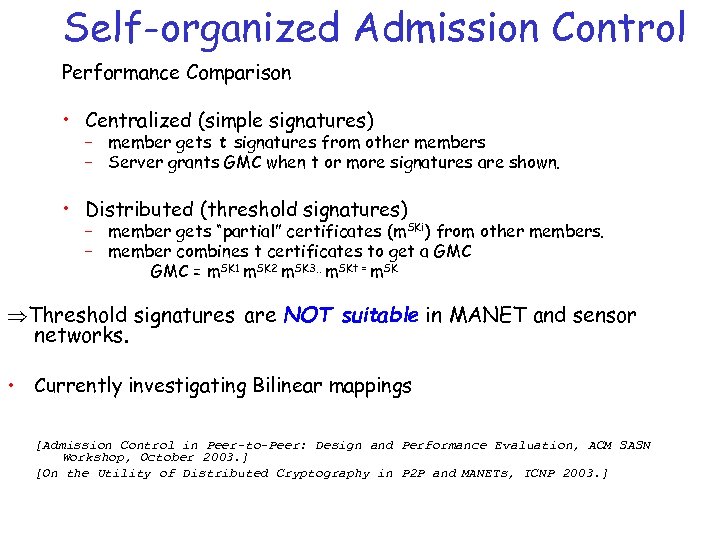 Self-organized Admission Control Performance Comparison • Centralized (simple signatures) – member gets t signatures from other members – Server grants GMC when t or more signatures are shown. • Distributed (threshold signatures) – member gets “partial” certificates (m. SKi) from other members. – member combines t certificates to get a GMC = m. SK 1 m. SK 2 m. SK 3. . m. SKt = m. SK Threshold signatures are NOT suitable in MANET and sensor networks. • Currently investigating Bilinear mappings [Admission Control in Peer-to-Peer: Design and Performance Evaluation, ACM SASN Workshop, October 2003. ] [On the Utility of Distributed Cryptography in P 2 P and MANETs, ICNP 2003. ]
Self-organized Admission Control Performance Comparison • Centralized (simple signatures) – member gets t signatures from other members – Server grants GMC when t or more signatures are shown. • Distributed (threshold signatures) – member gets “partial” certificates (m. SKi) from other members. – member combines t certificates to get a GMC = m. SK 1 m. SK 2 m. SK 3. . m. SKt = m. SK Threshold signatures are NOT suitable in MANET and sensor networks. • Currently investigating Bilinear mappings [Admission Control in Peer-to-Peer: Design and Performance Evaluation, ACM SASN Workshop, October 2003. ] [On the Utility of Distributed Cryptography in P 2 P and MANETs, ICNP 2003. ]
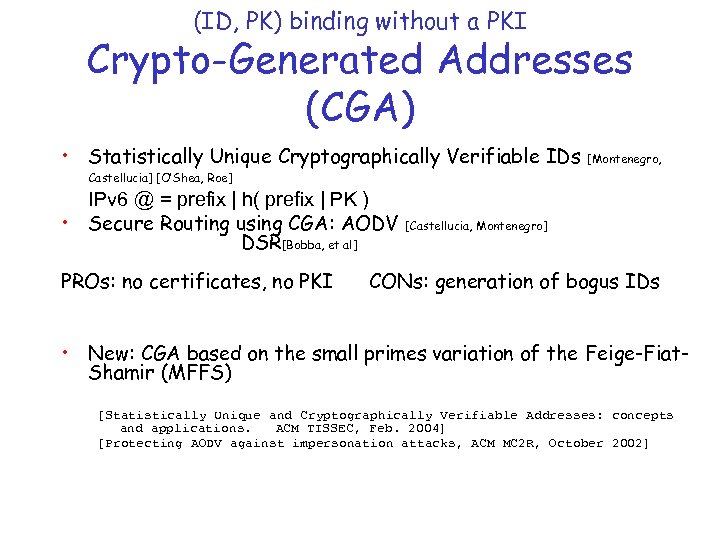 (ID, PK) binding without a PKI Crypto-Generated Addresses (CGA) • Statistically Unique Cryptographically Verifiable IDs [Montenegro, Castellucia] [O’Shea, Roe] IPv 6 @ = prefix | h( prefix | PK ) • Secure Routing using CGA: AODV DSR[Bobba, et al] PROs: no certificates, no PKI [Castellucia, Montenegro] CONs: generation of bogus IDs • New: CGA based on the small primes variation of the Feige-Fiat. Shamir (MFFS) [Statistically Unique and Cryptographically Verifiable Addresses: concepts and applications. ACM TISSEC, Feb. 2004] [Protecting AODV against impersonation attacks, ACM MC 2 R, October 2002]
(ID, PK) binding without a PKI Crypto-Generated Addresses (CGA) • Statistically Unique Cryptographically Verifiable IDs [Montenegro, Castellucia] [O’Shea, Roe] IPv 6 @ = prefix | h( prefix | PK ) • Secure Routing using CGA: AODV DSR[Bobba, et al] PROs: no certificates, no PKI [Castellucia, Montenegro] CONs: generation of bogus IDs • New: CGA based on the small primes variation of the Feige-Fiat. Shamir (MFFS) [Statistically Unique and Cryptographically Verifiable Addresses: concepts and applications. ACM TISSEC, Feb. 2004] [Protecting AODV against impersonation attacks, ACM MC 2 R, October 2002]
![Cooperation enforcement mechanisms Token-based [Yang, Meng, Lu] Nuglets [Buttyan, Hubaux] SPRITE [Zhong, Chen, Yang] Cooperation enforcement mechanisms Token-based [Yang, Meng, Lu] Nuglets [Buttyan, Hubaux] SPRITE [Zhong, Chen, Yang]](https://present5.com/presentation/4f67f4d7d4721445e06186300a8231ac/image-7.jpg) Cooperation enforcement mechanisms Token-based [Yang, Meng, Lu] Nuglets [Buttyan, Hubaux] SPRITE [Zhong, Chen, Yang] CONFIDANT[Buchegger, Le Boudec] CORE [Michiardi, Molva] Beta-Reputation [Josang, Ismail] Threshold cryptography Micro-payment Reputation-based
Cooperation enforcement mechanisms Token-based [Yang, Meng, Lu] Nuglets [Buttyan, Hubaux] SPRITE [Zhong, Chen, Yang] CONFIDANT[Buchegger, Le Boudec] CORE [Michiardi, Molva] Beta-Reputation [Josang, Ismail] Threshold cryptography Micro-payment Reputation-based
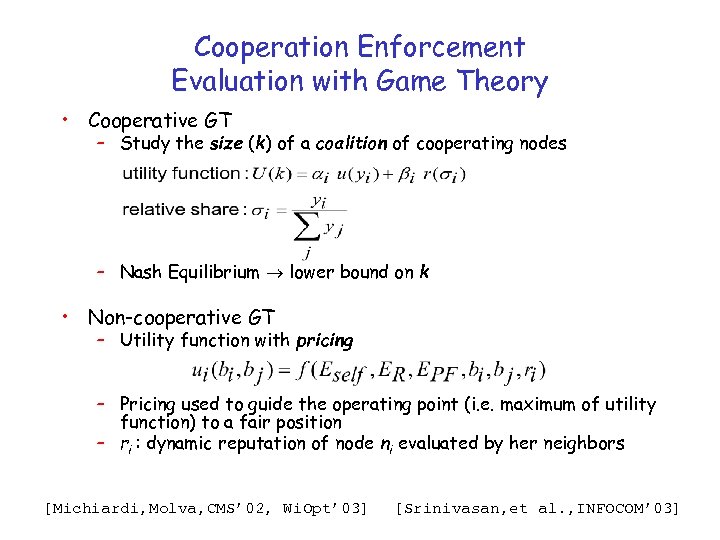 Cooperation Enforcement Evaluation with Game Theory • Cooperative GT – Study the size (k) of a coalition of cooperating nodes – Nash Equilibrium lower bound on k • Non-cooperative GT – Utility function with pricing – Pricing used to guide the operating point (i. e. maximum of utility function) to a fair position – ri : dynamic reputation of node ni evaluated by her neighbors [Michiardi, Molva, CMS’ 02, Wi. Opt’ 03] [Srinivasan, et al. , INFOCOM’ 03]
Cooperation Enforcement Evaluation with Game Theory • Cooperative GT – Study the size (k) of a coalition of cooperating nodes – Nash Equilibrium lower bound on k • Non-cooperative GT – Utility function with pricing – Pricing used to guide the operating point (i. e. maximum of utility function) to a fair position – ri : dynamic reputation of node ni evaluated by her neighbors [Michiardi, Molva, CMS’ 02, Wi. Opt’ 03] [Srinivasan, et al. , INFOCOM’ 03]
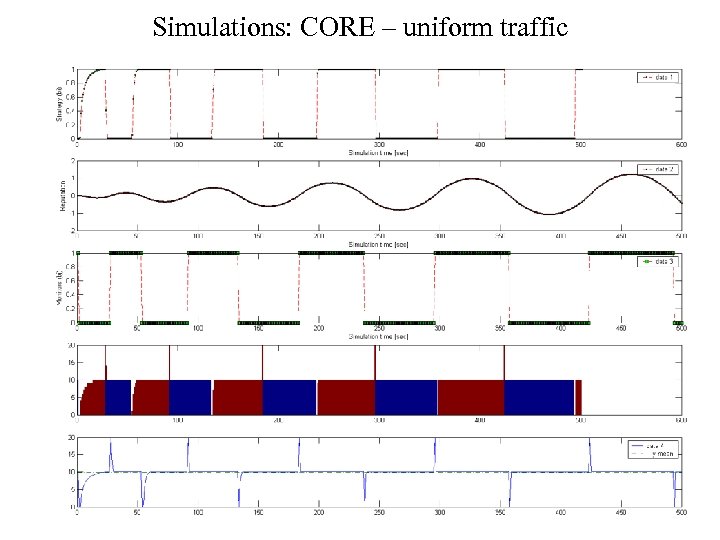 Simulations: CORE – uniform traffic
Simulations: CORE – uniform traffic
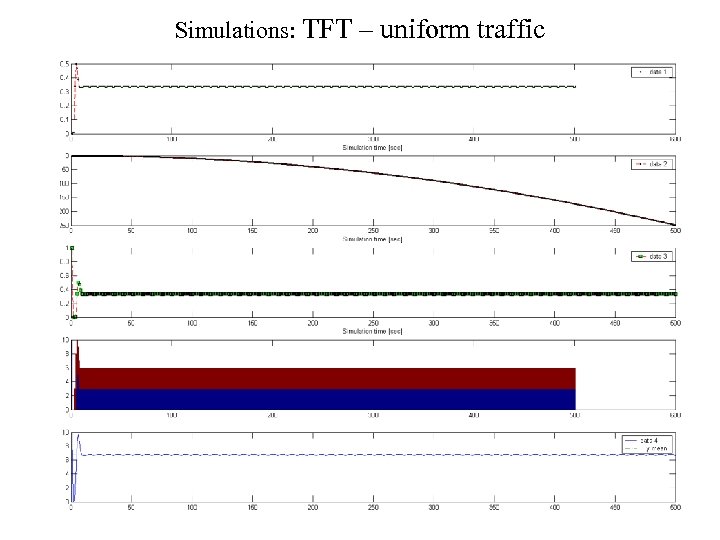 Simulations: TFT – uniform traffic
Simulations: TFT – uniform traffic
 Summary • Specific requirements – Self organized bootstrapping of security associations – Cooperation enforcement • Prospects – New tools from crypto bag of tricks (Id-based crypto, . . . ) – Integrated mechanisms: reputation + key management • Participation in MOBILEMAN project on Ad Hoc Networks • ESAS 2004 1 st European Workshop on Security in Ad-Hoc and Sensor Networks. (5. -6. August, 2004)
Summary • Specific requirements – Self organized bootstrapping of security associations – Cooperation enforcement • Prospects – New tools from crypto bag of tricks (Id-based crypto, . . . ) – Integrated mechanisms: reputation + key management • Participation in MOBILEMAN project on Ad Hoc Networks • ESAS 2004 1 st European Workshop on Security in Ad-Hoc and Sensor Networks. (5. -6. August, 2004)
 ESORICS 2004 – RAID 2004 September 13 -17 Institut EURECOM Sophia Antipolis - FRANCE
ESORICS 2004 – RAID 2004 September 13 -17 Institut EURECOM Sophia Antipolis - FRANCE
 THANK YOU
THANK YOU


