4e5064727d806182eaa1aa44900f8c26.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 10
Spinal Cord Compression Surgical Students’ Society of Melbourne Presentation Felicity Victoria Connon
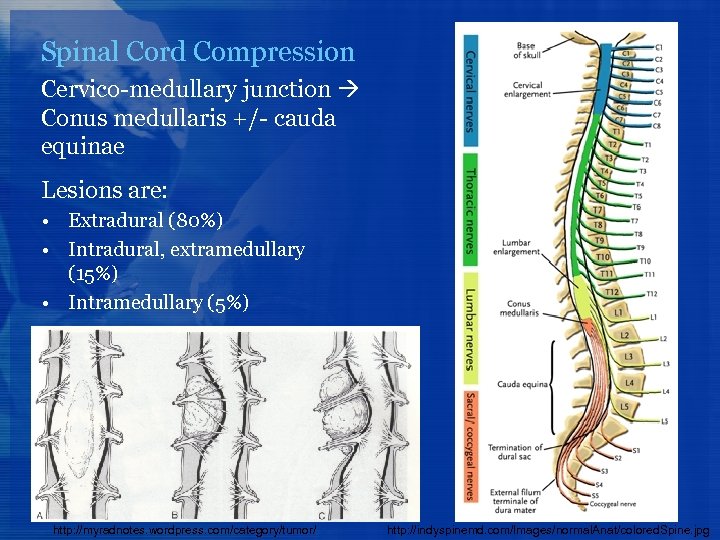
Spinal Cord Compression Cervico-medullary junction Conus medullaris +/- cauda equinae Lesions are: • Extradural (80%) • Intradural, extramedullary (15%) • Intramedullary (5%) http: //myradnotes. wordpress. com/category/tumor/ http: //indyspinemd. com/Images/normal. Anat/colored. Spine. jpg
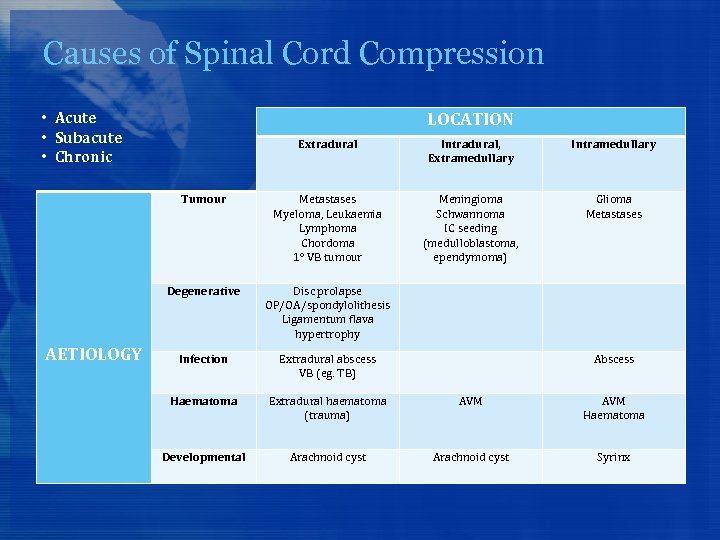
Causes of Spinal Cord Compression • Acute • Subacute • Chronic LOCATION Intradural, Extramedullary Intramedullary Tumour Metastases Myeloma, Leukaemia Lymphoma Chordoma 1° VB tumour Meningioma Schwannoma IC seeding (medulloblastoma, ependymoma) Glioma Metastases Degenerative Extradural Disc prolapse OP/OA/spondylolithesis Ligamentum flava hypertrophy Infection Extradural abscess VB (eg. TB) Abscess Haematoma Extradural haematoma (trauma) AVM Haematoma Developmental Arachnoid cyst Syrinx AETIOLOGY
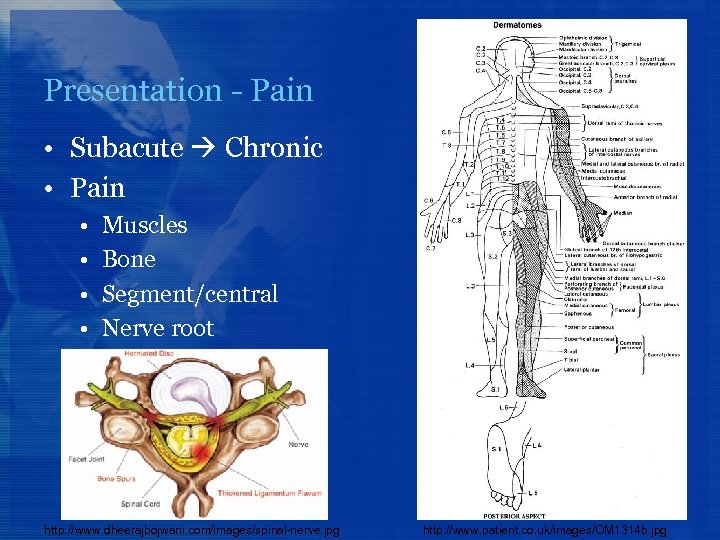
Presentation - Pain • Subacute Chronic • Pain • • Muscles Bone Segment/central Nerve root http: //www. dheerajbojwani. com/images/spinal-nerve. jpg http: //www. patient. co. uk/images/OM 1314 b. jpg

Presentation – Altered Sensation and Power Brown-Sequard Syndrome/Hemisection Syringomyelia/Central cord Posterior Column Spinal Cord Posterior Compressive Lesion Dorsal Column +/- Corticospinal & Autonomic Lateral Compressive Lesion Corticospinal Dorsal column Spinothalamic Central Cord Lesion 1. Spinothalamic 2. Interomediolateral columns (autonomic) 3. Corticospinal Motor Deficit Ipsilateral weakness LMN at level of lesion UMN below Bilateral weakness LMN at level of lesion UMN below Ipsilateral/Bilateral weakness LMN at level of lesion +/- UMN below Sensory Deficit Ipsilateral loss of vibration, proprioception and fine touch Contralateral loss of pain and temperature Bilateral pain and temperature Cervical - Cape distribution extending downwards Sacral sparing Bilateral loss of vibration and proprioception Bladder and Bowel Usually unaffected Late incontinence Tracts Affected
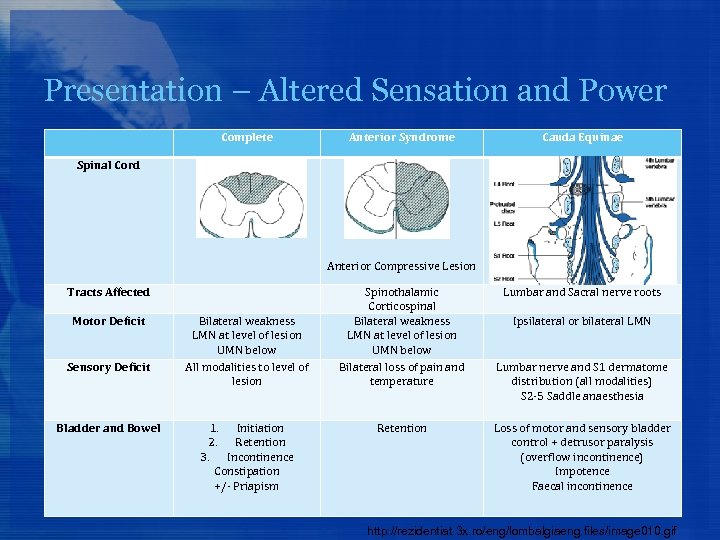
Presentation – Altered Sensation and Power Complete Anterior Syndrome Cauda Equinae Spinal Cord Anterior Compressive Lesion Tracts Affected Motor Deficit Sensory Deficit Bladder and Bowel Bilateral weakness LMN at level of lesion UMN below All modalities to level of lesion 1. Initiation 2. Retention 3. Incontinence Constipation +/- Priapism Spinothalamic Corticospinal Bilateral weakness LMN at level of lesion UMN below Bilateral loss of pain and temperature Retention Lumbar and Sacral nerve roots Ipsilateral or bilateral LMN Lumbar nerve and S 1 dermatome distribution (all modalities) S 2 -5 Saddle anaesthesia Loss of motor and sensory bladder control + detrusor paralysis (overflow incontinence) Impotence Faecal incontinence http: //rezidentiat. 3 x. ro/eng/lombalgiaeng. files/image 010. gif
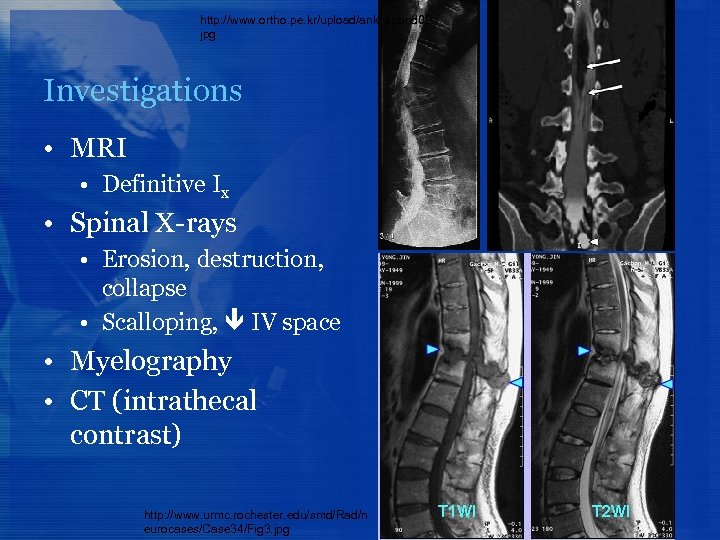
http: //www. ortho. pe. kr/upload/ank_spond 02. jpg Investigations • MRI • Definitive Ix • Spinal X-rays • Erosion, destruction, collapse • Scalloping, IV space • Myelography • CT (intrathecal contrast) http: //www. urmc. rochester. edu/smd/Rad/n eurocases/Case 34/Fig 3. jpg

Management – Neurosurgical Emergency Conservative Specific • Rest • Weight loss • Epidural steroid injections • Analgesia, antiinflammatories • Muscle relaxants • Physiotherapy • Malignancy • Extramedullary/Vertebral • Laminectomy (post. ) • Vertebrectomy + fusion (ant. ) • XRT, chemo • Intramedullary: • Macroscopic excision • XRT • + Dexamethasone
Management • Spinal canal stenosis • • Laminectomy Discectomy Foramenectomy ACDF • Abscess • Drainage +/decompression • Antibiotics • AVM • Dural: nidus excision or venous obliteration • Intradural http: //img. springerimages. com/Images/Springer/PUB=Springer-Verlag. Berlin. Heidelberg/JOU=00586/VOL=2009. 18/ISU=S 2/ART=2009_895/Media

References • Essential Neurosurgery, Kaye, 3 rd ed. , 2005, Blackwell Publishing • Neurology and Neurosurgery Illustrated, Lindsay & Bone, 4 th ed. , 2004, Churchill Livingstone • www. uptodate. com • Treatment and prognosis of neoplastic epidural spinal cord compression, including cauda equinae. Schiff et al, 2010 • Anatomy and localisation of spinal cord disorders, Eisen et al, 2010
4e5064727d806182eaa1aa44900f8c26.ppt