931b329ba6484ee4f10c451e09c40bd1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31

Spiele für den Unterricht selbst erstellen mit Story. Tec Johannes Konert, Florian Mehm, Viktor Wendel, Stefan Göbel, Ralf Steinmetz e. Learning – Didaktik Fachtagung, Wien httc – Hessian Telemedia Technology Competence-Center e. V - www. httc. de Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert Johannes. Konert@KOM. tu-darmstadt. de Tel. +49 6151 166887 KOM - Multimedia Communications Lab Prof. Dr. -Ing. Ralf Steinmetz (Director) Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Information Technology Dept. of Computer Science (adjunct Professor) TUD – Technische Universität Darmstadt Rundeturmstr. 10, D-64283 Darmstadt, Germany Tel. +49 6151 166150, Fax. +49 6151 166152 www. KOM. tu-darmstadt. de PPT-for-all___2009. 12. 02. ppt © 2010 author(s) of these slides including research results from the KOM research network and TU Darmstadt. Otherwise it is specified at the respective slide 19 März 2018
Agenda Serious Games Authoring § Motivation und Herausforderungen § Lerner-Modell, Spieler-Modell, Narration Story. Tec § Verwendungsmöglichkeiten und Zielgruppe § Zusammenspiel von Story. Tec und Story. Play § Wiss. Auswertungen in Story. Play Story. Tec und Multiplayer § Offene Aufgabenformate und Peer Education § Ausblick: Multiplayer Storytelling Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert KOM – Multimedia Communications Lab 2
![Serious Games Forschung [Göbel 2010] Serious Games for Learning, Game-based Learning, Digital Educational Games Serious Games Forschung [Göbel 2010] Serious Games for Learning, Game-based Learning, Digital Educational Games](https://present5.com/presentation/931b329ba6484ee4f10c451e09c40bd1/image-3.jpg)
Serious Games Forschung [Göbel 2010] Serious Games for Learning, Game-based Learning, Digital Educational Games Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert KOM – Multimedia Communications Lab 3

Motivation Experten des Faches § Haben Lehrninhalte § Möchten diese mit Serious Games vermitteln Klassiche Spiele-Autorenwerkzeuge sind ungeeignet § Kompliziert § Spezialisiert § Programmierung / Skripting § Aufwendige Inhaltserstellung (3 D/Anim. ) . . . ? Verschiedene Ausgabeformate Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert KOM – Multimedia Communications Lab 4
Herausforderungen - Konzept (Serious) Game Erstellung erfordert Koordination § Spieleprogrammierer § Designer, Künstler, Musiker, … § Fachlichen Experten §… Narrative Paradox Integration und Gleichgewicht zwischen Lernen und Spielen [Louchart 2004] Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert KOM – Multimedia Communications Lab 5

Herausforderungen - Umsetzung Adaption Passe den Spielverlauf an… § … Spiel-Einstellungen und Entscheidungen § … Hintergrund/Vor-Wissen § … Persönlichkeit §… Personalisierung § Anpassung an eine Person § Profilerstellung Game Flow: [Chen 2007] Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert KOM – Multimedia Communications Lab 6
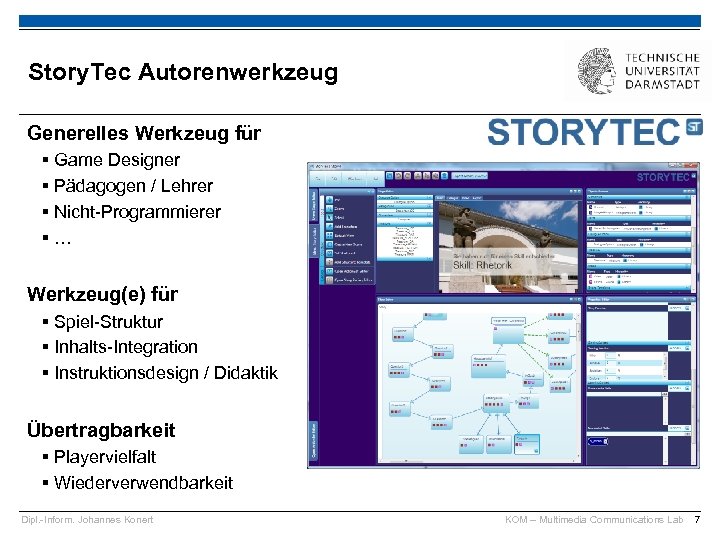
Story. Tec Autorenwerkzeug Generelles Werkzeug für § Game Designer § Pädagogen / Lehrer § Nicht-Programmierer §… Werkzeug(e) für § Spiel-Struktur § Inhalts-Integration § Instruktionsdesign / Didaktik Übertragbarkeit § Playervielfalt § Wiederverwendbarkeit Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert KOM – Multimedia Communications Lab 7
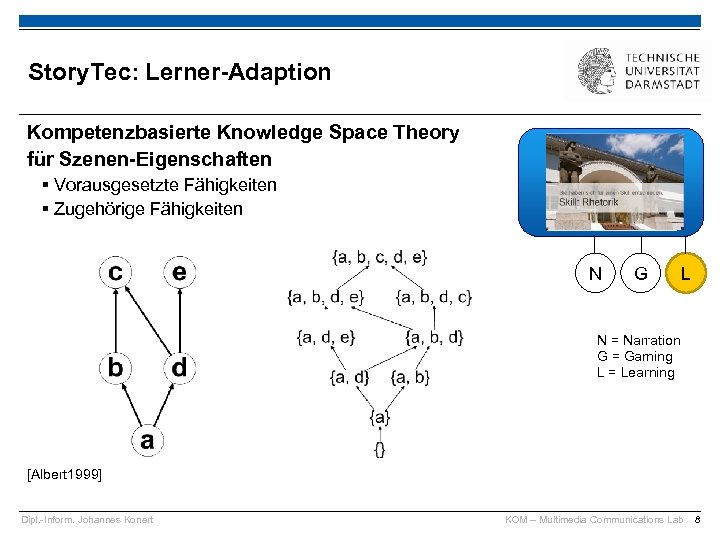
Story. Tec: Lerner-Adaption Kompetenzbasierte Knowledge Space Theory für Szenen-Eigenschaften § Vorausgesetzte Fähigkeiten § Zugehörige Fähigkeiten N G L N = Narration G = Gaming L = Learning [Albert 1999] Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert KOM – Multimedia Communications Lab 8
![Story. Tec: Lerner-Adaption N G L Heldenreise [Campbell 1987] Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert N Story. Tec: Lerner-Adaption N G L Heldenreise [Campbell 1987] Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert N](https://present5.com/presentation/931b329ba6484ee4f10c451e09c40bd1/image-9.jpg)
Story. Tec: Lerner-Adaption N G L Heldenreise [Campbell 1987] Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert N G L [Bartle 1996] KOM – Multimedia Communications Lab 9
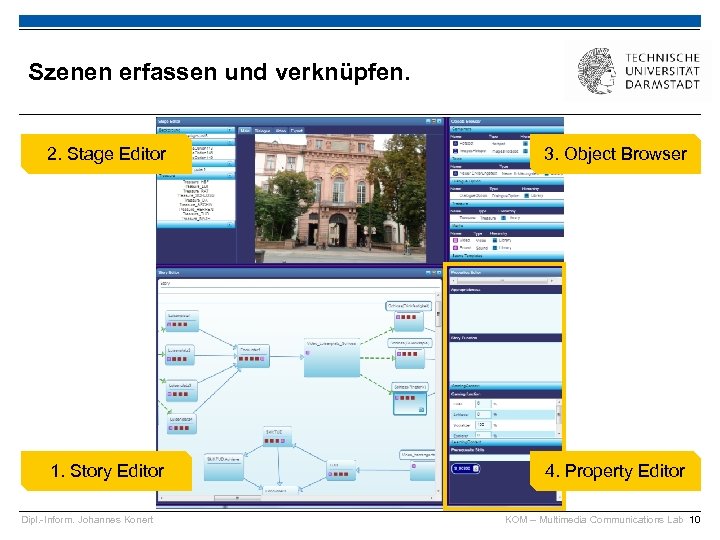
Szenen erfassen und verknüpfen. 2. Stage Editor 3. Object Browser 1. Story Editor 4. Property Editor Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert KOM – Multimedia Communications Lab 10
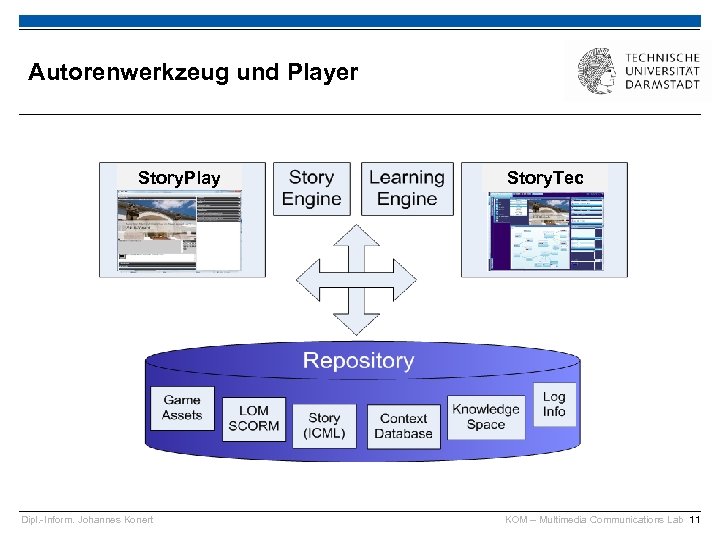
Autorenwerkzeug und Player Story. Play Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert Story. Tec KOM – Multimedia Communications Lab 11

Spiele mit Story. Tec First-Person Adventure Game § Hintergrundbilder § Klickbare Hotspots § Charaktere (als Voice-over) § Multiple Choice Dialoge § Videos, Sounds Leicht zu erstellen § Kein 3 D § Keine Animationen, Modelle § Leicht zu nutzen mit Fotos/Videos Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert KOM – Multimedia Communications Lab 12
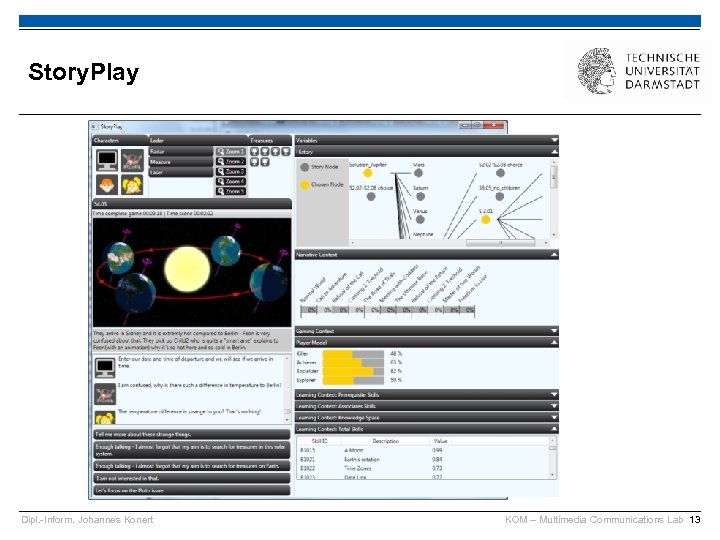
Story. Play Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert KOM – Multimedia Communications Lab 13
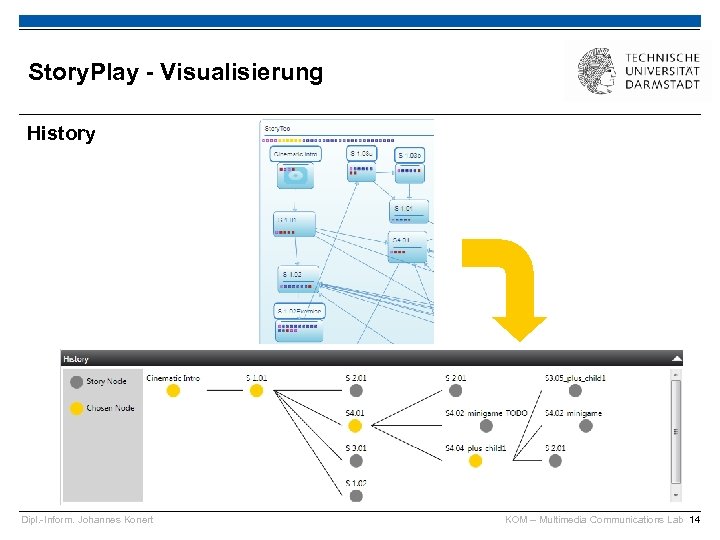
Story. Play - Visualisierung History Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert KOM – Multimedia Communications Lab 14
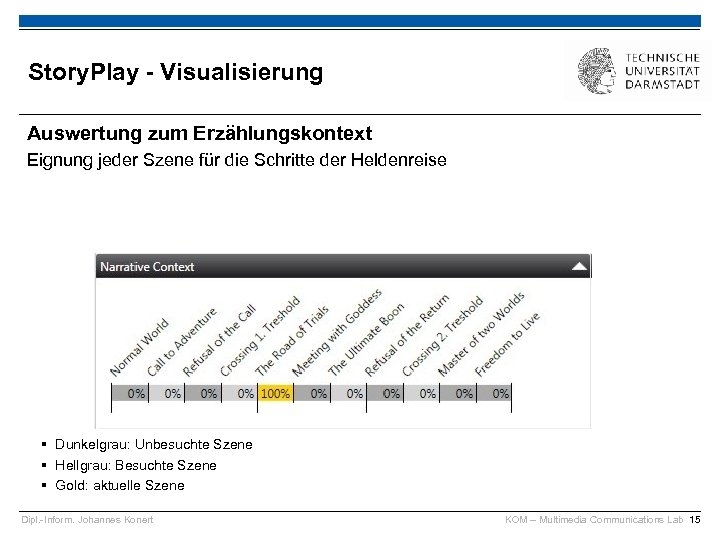
Story. Play - Visualisierung Auswertung zum Erzählungskontext Eignung jeder Szene für die Schritte der Heldenreise § Dunkelgrau: Unbesuchte Szene § Hellgrau: Besuchte Szene § Gold: aktuelle Szene Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert KOM – Multimedia Communications Lab 15
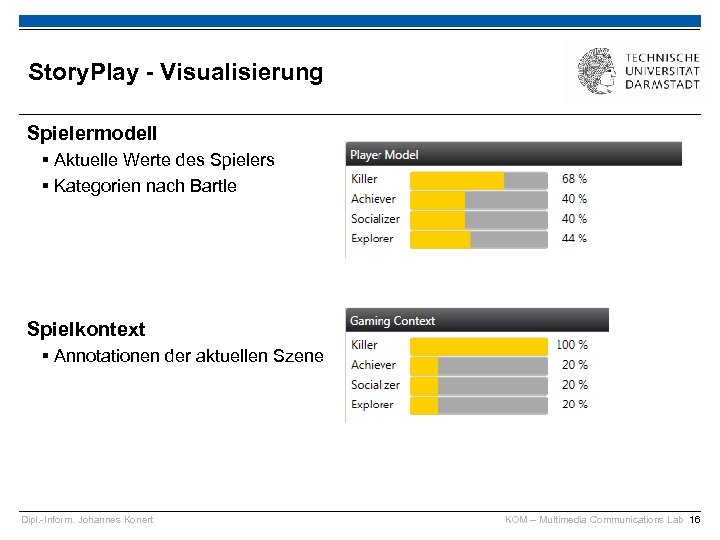
Story. Play - Visualisierung Spielermodell § Aktuelle Werte des Spielers § Kategorien nach Bartle Spielkontext § Annotationen der aktuellen Szene Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert KOM – Multimedia Communications Lab 16
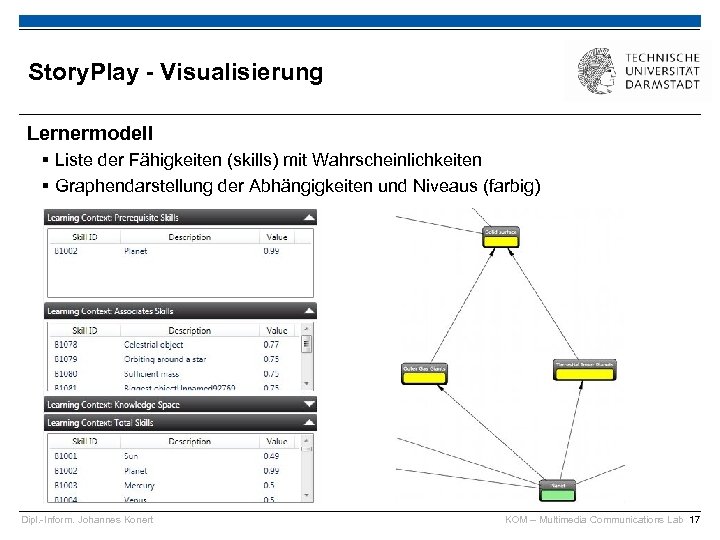
Story. Play - Visualisierung Lernermodell § Liste der Fähigkeiten (skills) mit Wahrscheinlichkeiten § Graphendarstellung der Abhängigkeiten und Niveaus (farbig) Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert KOM – Multimedia Communications Lab 17

Zusammenfassung Story. Tec § Selbst Inhalte erstellen § Keine Programmierung § “Wenig” Aufwand, ohne komplexe Animationen § Flexibel einsetzbar (Adventure, Quiz, Soap, . . ) § Spieler-, Lernermodell Story. Play § Abspielen auf verschiedenen Plattformen § Testen und Auswertung des Spielverlaufs § Dynamische Szenenauswahl Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert KOM – Multimedia Communications Lab 18
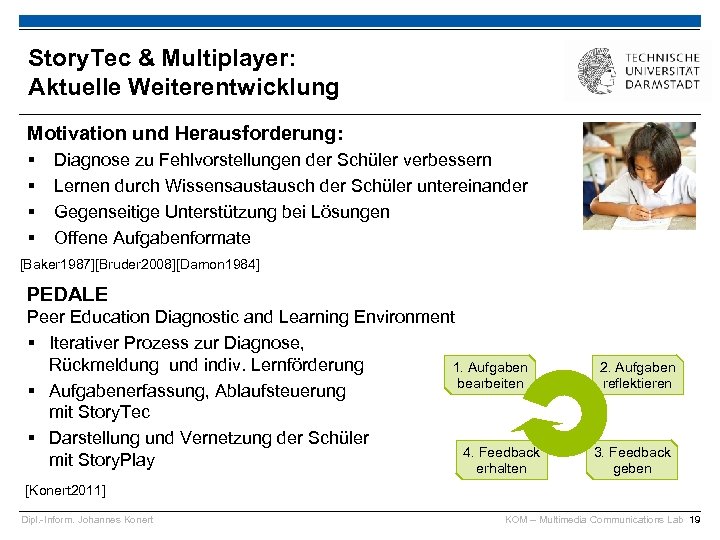
Story. Tec & Multiplayer: Aktuelle Weiterentwicklung Motivation und Herausforderung: § § Diagnose zu Fehlvorstellungen der Schüler verbessern Lernen durch Wissensaustausch der Schüler untereinander Gegenseitige Unterstützung bei Lösungen Offene Aufgabenformate [Baker 1987][Bruder 2008][Damon 1984] PEDALE Peer Education Diagnostic and Learning Environment § Iterativer Prozess zur Diagnose, Rückmeldung und indiv. Lernförderung 1. Aufgaben bearbeiten § Aufgabenerfassung, Ablaufsteuerung mit Story. Tec § Darstellung und Vernetzung der Schüler 4. Feedback mit Story. Play erhalten 2. Aufgaben reflektieren 3. Feedback geben [Konert 2011] Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert KOM – Multimedia Communications Lab 19
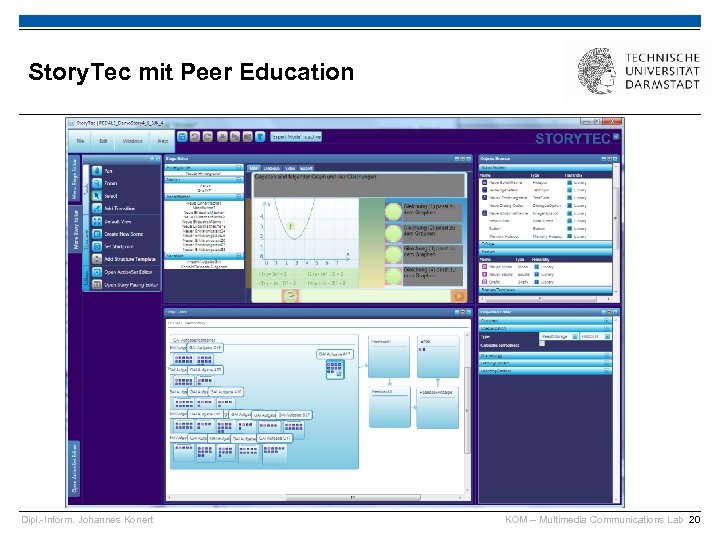
Story. Tec mit Peer Education Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert KOM – Multimedia Communications Lab 20
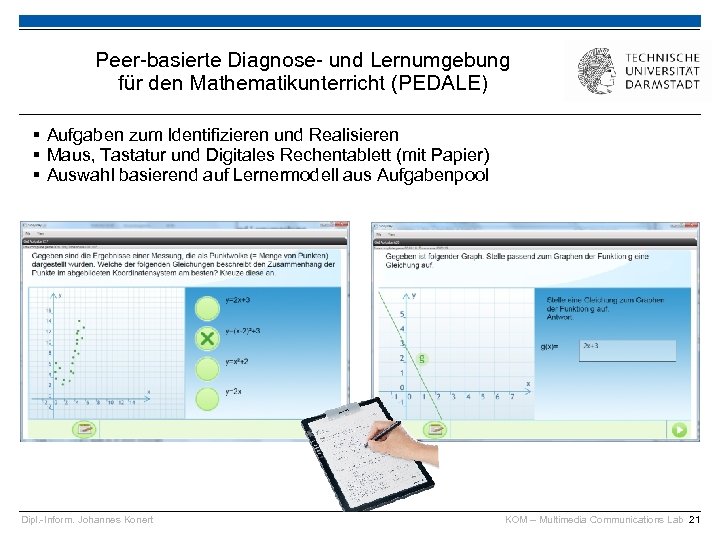
Peer-basierte Diagnose- und Lernumgebung für den Mathematikunterricht (PEDALE) § Aufgaben zum Identifizieren und Realisieren § Maus, Tastatur und Digitales Rechentablett (mit Papier) § Auswahl basierend auf Lernermodell aus Aufgabenpool Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert KOM – Multimedia Communications Lab 21
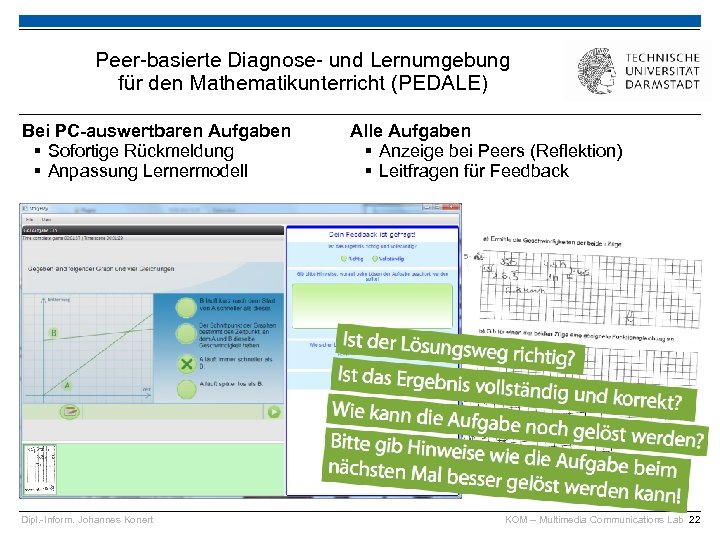
Peer-basierte Diagnose- und Lernumgebung für den Mathematikunterricht (PEDALE) Bei PC-auswertbaren Aufgaben § Sofortige Rückmeldung § Anpassung Lernermodell Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert Alle Aufgaben § Anzeige bei Peers (Reflektion) § Leitfragen für Feedback KOM – Multimedia Communications Lab 22
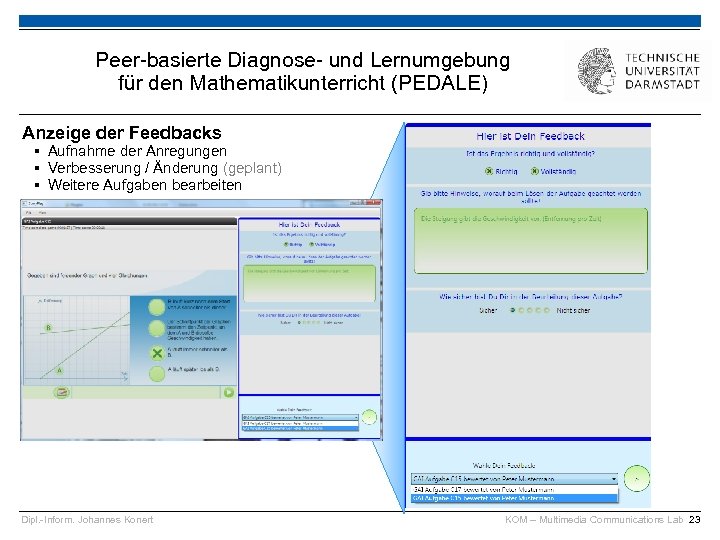
Peer-basierte Diagnose- und Lernumgebung für den Mathematikunterricht (PEDALE) Anzeige der Feedbacks § Aufnahme der Anregungen § Verbesserung / Änderung (geplant) § Weitere Aufgaben bearbeiten Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert KOM – Multimedia Communications Lab 23

Ausblick Weitere Entwicklung: § Multiplayer-Konzepte (Kooperation) für Storytelling § Aufgaben-Szenen erneut bearbeiten § Freie Auswahl von Szenen durch Spieler (kategorisiert) Story. Play: Lehrer-Darstellung § § § Alle Spieler Gelöste Aufgaben Feedbacks Selbst Feedback geben Statistiken Evaluation § Peer Education Konzepte (Schüler) § Diagnostisches Potential (Lehrer) Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert KOM – Multimedia Communications Lab 24

Webseite – www. storytec. de Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert KOM – Multimedia Communications Lab 25

“Game over” Vielen Dank für Ihre § Aufmerksamkeit, § Fragen, § Antworten und § Feedback. Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert KOM – Multimedia Communications Lab 26
![Referenzen [Albert 1999] Albert, D. & Lukas, J. , 1999. Knowledge spaces: Theories, empirical Referenzen [Albert 1999] Albert, D. & Lukas, J. , 1999. Knowledge spaces: Theories, empirical](https://present5.com/presentation/931b329ba6484ee4f10c451e09c40bd1/image-27.jpg)
Referenzen [Albert 1999] Albert, D. & Lukas, J. , 1999. Knowledge spaces: Theories, empirical research, and applications, Lawrence Erlbaum. [Baker 1997] Baker, M. & Lund, K. , 1997. Promoting reflective interactions in a CSCL environment. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 13(3), p. 175 -193. Available at: http: //doi. wiley. com/10. 1046/j. 13652729. 1997. 00019. x. [Bartle 1996] Bartle, R. , 1996. Hearts, clubs, diamonds, spades: Players who suit MUDs. Journal of MUD research, 1(1), p. 19. Available at: http: //www. mud. co. uk/richard/hcds. htm [Accessed January 22, 2011]. [Bruder 2008] Bruder, R. , 2008. Mathematische Kompetenzen nachhaltig entwickeln und sichern. In Mathematikunterricht entwickeln. Bausteine für kompetenzorientiertes Unterrichten. Cornelsen Scriptor, pp. 18 -53. [Campbell] Campbell, J. , 1987. The hero’s journey. Available at: http: //www. worldcat. org/title/herosjourney/oclc/18942516 [Accessed October 11, 2011]. [Charles 2004] Charles, D. & Black, M. , 2004. Dynamic player modeling: A framework for player-centered digital games. In Proc. of the International Conference on Computer Games: Artificial Intelligence, Design and Education. pp. 29– 35. Available at: http: //research. rmutp. ac. th/paper/cu/Dynamic. Player. Modelling. pdf [Accessed January 22, 2011]. [Chen 2007] Chen, J. , 2007. Flow in Games ( and Everything Else ). Communications of the ACM, 50(4), p. 31 -34. Available at: http: //delivery. acm. org/10. 1145/1240000/1232769/p 31 chen. pdf? key 1=1232769&key 2=3643268821&coll=GUIDE&dl=GUIDE&CFID=111187921&CFTOKEN=2 5517040. [Constant 1996] Constant, D. , Sproull, L. & Kiesler, S. , 1996. The Kindness of Strangers: The Usefulness of Electronic Weak Ties for Technical Advice. Organization Science, 7(2), p. 119 -135. Available at: http: //www-2. cs. cmu. edu/~kiesler/publications/PDFs/Constantkindness. pdf. [Csikszentmihalyi 1991] Csikszentmihalyi, M. , 1991. Flow: The Psychology of Optimal Experience First Edit. , Harper Perennial. Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert KOM – Multimedia Communications Lab 27
![Referenzen [Damon 1984] Damon, W. , 1984. Peer education: The untapped potential. Journal of Referenzen [Damon 1984] Damon, W. , 1984. Peer education: The untapped potential. Journal of](https://present5.com/presentation/931b329ba6484ee4f10c451e09c40bd1/image-28.jpg)
Referenzen [Damon 1984] Damon, W. , 1984. Peer education: The untapped potential. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 5(4), p. 331 -343. Available at: http: //linkinghub. elsevier. com/retrieve/pii/0193397384900066. [Dillenbourg 1999] Dillenbourg, P. , 1999. What do you mean by Collaborative Learning? In P. Dillenbourg, ed. Collaborative-learning: Cognitive and Computational Approaches. Oxford: Elsevier, pp. 1 -19. [Göbel 2010] Göbel, S. , 2010. Definition Serious Games Conference. Available at: http: //www. kom. tu-darmstadt. de/~goebel/Cebit 2010/Definition. Serious. Games-SGC 2010_05032010. pdf [Accessed September 6, 2010]. [Konert 2011] Konert, J. , Richter, K. , Göbel, S. & Bruder, R. , 2011. Knowledge Sharing in the classroom - A social network approach for diagnostic assessment and learning together. In Proceedings of the 11 th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies (ICALT). Athens, Georgia, USA: IEEE. [Louchart 2004] Louchart, S. & Ruth, A. , 2004. The Emergent Narrative theoretical investigation. In Narrative and Learning Environments Conference, NILE 04 Edinburgh. pp. 25 -33. Available at: http: //www. macs. hw. ac. uk/~sandy/Publications/Louchart. Aylett. Final. pdf. [Michaelsen 1997] - Michaelsen LK, Fink LD, Hall A. Designing Effective Group Activities : Lessons for Classroom Teaching and Faculty Development. In: De. Zure D, ed. To Improve the Academy: Resources for Faculty, Instructional and Organizational Development. Stollwater, OK: New Forums; 1997. Available at: http: //speech. ipfw. edu/peerreview/TLassignments. pdf. [Mohammad 2009] Mohammad, A. L. S. , Guetl, C. & Kappe, F. , 2009. PASS: Peer-ASSessment Approach for Modern Learning Settings. In Advances in Web Based Learning-ICWL 2009: 8 th International Conference, Aachen, Germany, August 19 -21, 2009, Proceedings. Springer-Verlag New York Inc, p. 44. [Nalebuff 2007] - Nalebuff B. , Brandenburger A. Coopetition — kooperativ konkurrieren. Mit der Spieltheorie zum Unternehmenserfolg. In: Boersch C, Elschen R, eds. Das Summarum des Management. 1 st ed. Gabler; 2007: 217 -230. Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert KOM – Multimedia Communications Lab 28
![Referenzen [Renkl 2003] - Renkl A, Gruber H, Weber S, Lerche T, Schweizer K. Referenzen [Renkl 2003] - Renkl A, Gruber H, Weber S, Lerche T, Schweizer K.](https://present5.com/presentation/931b329ba6484ee4f10c451e09c40bd1/image-29.jpg)
Referenzen [Renkl 2003] - Renkl A, Gruber H, Weber S, Lerche T, Schweizer K. Cognitive Load beim Lernen aus Lösungsbeispielen. Zeitschrift für Pädagogische Psychologie. 2003; 17(2): 93 -101. [Sweetser 2005] – Sweetser P, Wyeth P. Game. Flow : A Model for Evaluating Player Enjoyment in Games. Technology. 2005; 3(3): 1 -24. [Zea 2009] – Zea NP, Sanchez JLG, Gutierrez FL. Collaborative Learning by Means of Video Games: An Entertainment System in the Learning Processes. 2009 Ninth IEEE International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies. 2009: 215 -217 Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert KOM – Multimedia Communications Lab 29

Referenzen Bilder, die nicht aus den wissenschaftlichen Referenzquellen stammen sind von: § § Idea go / Free. Digital. Photos. net Technische Universität Darmstadt (Corporate Design) www. storytec. de http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/File: Cave_of_time. jpg Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert KOM – Multimedia Communications Lab 30

Meta-Data Date 18. 10. 2011 Lecturer Johannes Konert Titel Spiele für den Unterricht selbst erstellen mit Story. Tec Name of Event e. Learning - Didaktik Fachtagung Type Presentation Organizer TGM - Die Schule der Technik in cooperation with Bundesministerium für Unterricht, Kunst und Kultur (Austria) Location Vienna, Austria Dipl. -Inform. Johannes Konert KOM – Multimedia Communications Lab 31
931b329ba6484ee4f10c451e09c40bd1.ppt