0cf25ed235c8309d132ba869a8828423.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 78
 Speed Dating You are to research your randomly assigned psychologist using the guide below (#1) l Bring with you to class: l 1. A notecard (or notecard size paper) with the essential information from your research. l l l The psychologist’s name, details of their research and/or importance, what school of thought (cognitive, behaviorist, psychoanalytic) if appropriate, etc. Basically, its a cheat-sheet to ensure you cover all the relevant information and correctly represent yourself. 2. A prop of some kind to represent your research. l For example, Phil Zimbardo who did the prison study (among many others) could bring a guy behind bars (made out of clay, a picture, a drawing) For Pavlov a stuffed dog with a jingle bell, etc. . Be creative.
Speed Dating You are to research your randomly assigned psychologist using the guide below (#1) l Bring with you to class: l 1. A notecard (or notecard size paper) with the essential information from your research. l l l The psychologist’s name, details of their research and/or importance, what school of thought (cognitive, behaviorist, psychoanalytic) if appropriate, etc. Basically, its a cheat-sheet to ensure you cover all the relevant information and correctly represent yourself. 2. A prop of some kind to represent your research. l For example, Phil Zimbardo who did the prison study (among many others) could bring a guy behind bars (made out of clay, a picture, a drawing) For Pavlov a stuffed dog with a jingle bell, etc. . Be creative.
 Stop & Look & Listen
Stop & Look & Listen
 History and Approaches What do we Know about Psychology? What is Psychology?
History and Approaches What do we Know about Psychology? What is Psychology?
 Complete Questionnaire l Please select True or False for Each Question (use what you know to the best of your ability) l How did you feel after taking the test? How well do you think you did? How did you know the information that you did?
Complete Questionnaire l Please select True or False for Each Question (use what you know to the best of your ability) l How did you feel after taking the test? How well do you think you did? How did you know the information that you did?
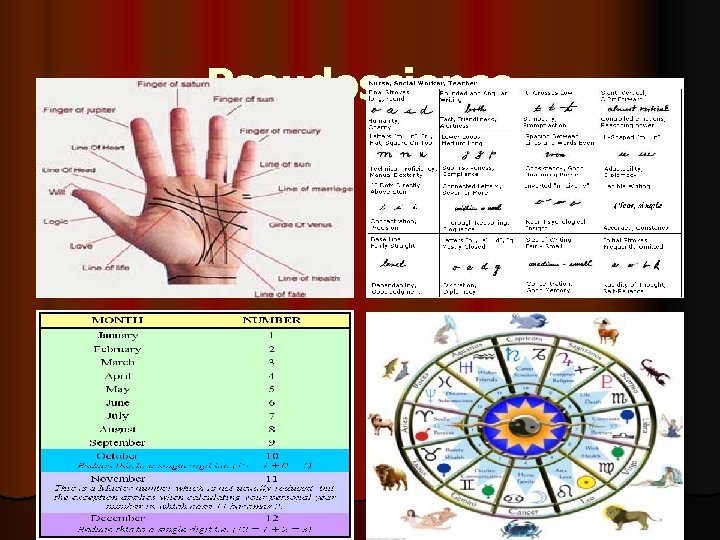
 PSEUDOSCIENCE l Promises easy fixes to life’s problems and challenges l Love l Unhappiness l Get both halves of your brain working
PSEUDOSCIENCE l Promises easy fixes to life’s problems and challenges l Love l Unhappiness l Get both halves of your brain working
 Pseudoscience
Pseudoscience
 NUMEROLOGY
NUMEROLOGY
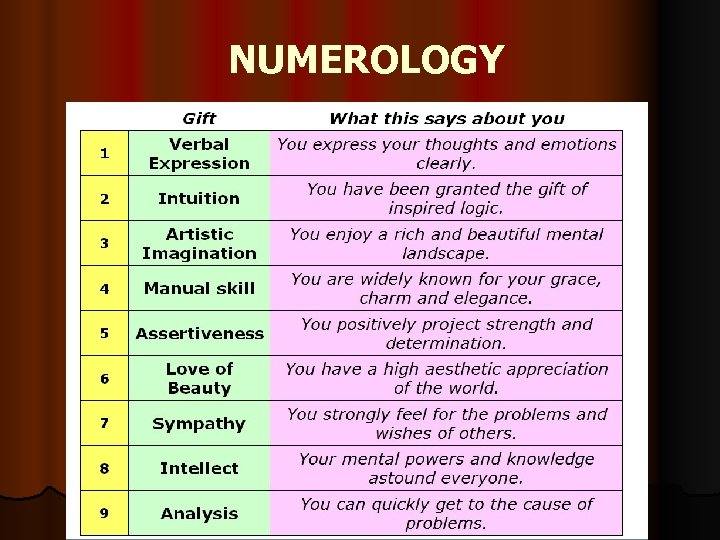
 Do You Believe? l Do you believe in astrology, psychics, numerology, graphology? l Why or why not?
Do You Believe? l Do you believe in astrology, psychics, numerology, graphology? l Why or why not?
 FORTUNE-TELLING/PSYCHICS
FORTUNE-TELLING/PSYCHICS
 PSYCHIC FAILS Sylvia Browne – most noted psychic predicated 2005 Saddam Hussein would die before his trial l Wrote of John Ritter- “Having a Virgo sun sign helps keep his career ticking” l Published hours after Ritter died of a ruptured Aorta l
PSYCHIC FAILS Sylvia Browne – most noted psychic predicated 2005 Saddam Hussein would die before his trial l Wrote of John Ritter- “Having a Virgo sun sign helps keep his career ticking” l Published hours after Ritter died of a ruptured Aorta l
 Linda & Terry Jamison l "We are seeing terrorist attacks on federal government – excuse me, federal buildings. Particularly South Carolina or Georgia, by July 2002. And also the New York Trade Center – the World Trade Center in 2002, with something, with a terrorist attack.
Linda & Terry Jamison l "We are seeing terrorist attacks on federal government – excuse me, federal buildings. Particularly South Carolina or Georgia, by July 2002. And also the New York Trade Center – the World Trade Center in 2002, with something, with a terrorist attack.
 What is Psychology?
What is Psychology?
 What Fields Can A Psychologist go into?
What Fields Can A Psychologist go into?
 What kind of different fields can you get into with a Psych Degree? l You & a Partner will be assigned a field. l Research it (what they do, where they work) l Come up with a skit to show an example of why you would need such a psychologist l Ex: If you’re a sports psych. You can do a skit of a kid playing a sport and then something happens l Be ready to present on Friday (skit first, then explanation) l
What kind of different fields can you get into with a Psych Degree? l You & a Partner will be assigned a field. l Research it (what they do, where they work) l Come up with a skit to show an example of why you would need such a psychologist l Ex: If you’re a sports psych. You can do a skit of a kid playing a sport and then something happens l Be ready to present on Friday (skit first, then explanation) l
 Careers in Psychology
Careers in Psychology
 Psychologist l Need a doctorate graduate degree l May take 4 -6 years to earn a doctorate in a subfield
Psychologist l Need a doctorate graduate degree l May take 4 -6 years to earn a doctorate in a subfield
 Clinical Psychologist l Diagnose and treat patients with psychological problems l Day to day issues l Largest number of professional psychologists
Clinical Psychologist l Diagnose and treat patients with psychological problems l Day to day issues l Largest number of professional psychologists
 Basic Research/ Experimental Psychologist l Pure science or research l Research for the sake of finding new information and expanding the knowledge base of psychology l Conducts research in a lab
Basic Research/ Experimental Psychologist l Pure science or research l Research for the sake of finding new information and expanding the knowledge base of psychology l Conducts research in a lab
 Neuropsychologist l Also called biological psychologists or biopsychologists l Explore how the brain works l Most often work in university/college settings
Neuropsychologist l Also called biological psychologists or biopsychologists l Explore how the brain works l Most often work in university/college settings
 Social Psychologist Explore how behaviors, feelings, and beliefs are influenced by others l Study conformity, attitudes, leadership, prejudice, group behavior, etc. l Work in the business setting, government, and universities l
Social Psychologist Explore how behaviors, feelings, and beliefs are influenced by others l Study conformity, attitudes, leadership, prejudice, group behavior, etc. l Work in the business setting, government, and universities l
 Developmental Psychologist l Study the growth or development that takes place from the womb to death l Work in senior centers, hospitals, daycares or universities
Developmental Psychologist l Study the growth or development that takes place from the womb to death l Work in senior centers, hospitals, daycares or universities
 Cognitive Psychologist l Study thought processes including intelligence, problem solving, attention, decision making, language, etc. l Work in educational settings and the business world
Cognitive Psychologist l Study thought processes including intelligence, problem solving, attention, decision making, language, etc. l Work in educational settings and the business world
 Forensic Psychologist l Apply law and psychology to legal issues l Studies Actions and Motives of criminals l Work in correctional settings, law enforcement, and academic settings
Forensic Psychologist l Apply law and psychology to legal issues l Studies Actions and Motives of criminals l Work in correctional settings, law enforcement, and academic settings
 Sports Psychologist l Explore psychological issues in improving athletic performance as well as recovering from a loss or injury l Work for sports teams or in private practice
Sports Psychologist l Explore psychological issues in improving athletic performance as well as recovering from a loss or injury l Work for sports teams or in private practice
 Educational Psychologist l l l Study how humans learn and how to improve the learning process Search for ways to improve educational systems Memory Rewards/punishment for achievement Work in school systems, the government, or at universities
Educational Psychologist l l l Study how humans learn and how to improve the learning process Search for ways to improve educational systems Memory Rewards/punishment for achievement Work in school systems, the government, or at universities
 PSYCHOMETRIC PSYCHOLOGIST l Design and evaluate tests of mental abilities, aptitudes, interests, and personality
PSYCHOMETRIC PSYCHOLOGIST l Design and evaluate tests of mental abilities, aptitudes, interests, and personality
 School Psychologist l Use psychology to improve the development of children in the school system l Are involved in assessments (testing) l Work for school systems, the government or universities
School Psychologist l Use psychology to improve the development of children in the school system l Are involved in assessments (testing) l Work for school systems, the government or universities
 Consumer Psychologist l Study why people buy certain products and not others l Work in the business or academic world
Consumer Psychologist l Study why people buy certain products and not others l Work in the business or academic world
 Rehabilitation Psychologist l Help those who have been involved in an accident or have been ill l Work in medical rehabilitation centers
Rehabilitation Psychologist l Help those who have been involved in an accident or have been ill l Work in medical rehabilitation centers
 Social Worker l Only have an undergraduate or masters degree in psychology or social work l Work to improve the lives of others l Work for the government, schools, and residential facilities
Social Worker l Only have an undergraduate or masters degree in psychology or social work l Work to improve the lives of others l Work for the government, schools, and residential facilities
 INDUSTRIAL/ORGANIZATIONAL l Try to apply psychology to help business and organizations operate l Behavior at the workplace l Group decision making l Employee morale l Work motivation l Productivity l Job stress l Personnel selection l Marketing strategies
INDUSTRIAL/ORGANIZATIONAL l Try to apply psychology to help business and organizations operate l Behavior at the workplace l Group decision making l Employee morale l Work motivation l Productivity l Job stress l Personnel selection l Marketing strategies
 Where do Psychologists work? l 36% -Academic Institutions l 22% - Clinical Settings (Private Practice) l 17% - Hospitals and Clinics l 12% - Business and Government l 6% - Counseling and Guidance Centers l 5% - School Systems l 1% - Other
Where do Psychologists work? l 36% -Academic Institutions l 22% - Clinical Settings (Private Practice) l 17% - Hospitals and Clinics l 12% - Business and Government l 6% - Counseling and Guidance Centers l 5% - School Systems l 1% - Other
 Practice Question #1 1. Martha is pursuing a career in psychology. She wants to help employees become more productive in the workplace. Which field of psychology should Martha select for school? a. Physiological b. Cognitive c. Educational d. Clinical e. Industrial-organizational
Practice Question #1 1. Martha is pursuing a career in psychology. She wants to help employees become more productive in the workplace. Which field of psychology should Martha select for school? a. Physiological b. Cognitive c. Educational d. Clinical e. Industrial-organizational
 What is Psychology?
What is Psychology?
 ↓Root Words↓ Psyche: the soul Ology: the study of
↓Root Words↓ Psyche: the soul Ology: the study of
 What is psychology? The scientific study of behavior & mental processes l. Science: making verifiable, objective predictions l. Behavior: observable acts l. Mental Processes: storing, recalling, using info/feelings
What is psychology? The scientific study of behavior & mental processes l. Science: making verifiable, objective predictions l. Behavior: observable acts l. Mental Processes: storing, recalling, using info/feelings
 What is Psychology? l Affected by (response to) l Physical state l Mental state l External environment
What is Psychology? l Affected by (response to) l Physical state l Mental state l External environment
 Hippocrates & Aristotle Greek philosopher: Founder of modern medicine l Brain is ultimate source of (feelings such as pleasure and pain (Biological perspective) l - Use senses to get information - Use information to solve problems - motivated to act in good or bad ways
Hippocrates & Aristotle Greek philosopher: Founder of modern medicine l Brain is ultimate source of (feelings such as pleasure and pain (Biological perspective) l - Use senses to get information - Use information to solve problems - motivated to act in good or bad ways
 Historical Origins of Psychology l Rene Descartes l True knowledge comes through reasoning l Heredity provides individuals with inborn knowledge and abilities and we use this to reason l We are to doubt everything – that’s the only way we can be certain about anything l I think, therefore I am (because we think, we exist)
Historical Origins of Psychology l Rene Descartes l True knowledge comes through reasoning l Heredity provides individuals with inborn knowledge and abilities and we use this to reason l We are to doubt everything – that’s the only way we can be certain about anything l I think, therefore I am (because we think, we exist)
 Historical Origins of Psychology l John Locke l Saw the mind as receptive and passive, with its main goal as sensing and perceiving l Tabula rasa – we are born as a blank slate, l everything learned we know is
Historical Origins of Psychology l John Locke l Saw the mind as receptive and passive, with its main goal as sensing and perceiving l Tabula rasa – we are born as a blank slate, l everything learned we know is
 Who’s Right? ?
Who’s Right? ?
 Practice Question #2 1. Which of the following characterizes a behavioral approach to psychology? A study of the unconscious motives involved in behavior b. An introspective study of mental imagery used in problem solving c. An analysis of the neurons involved in memory storage d. The use of a projective test to assess personality a. e. A study of how reinforcement affects learning
Practice Question #2 1. Which of the following characterizes a behavioral approach to psychology? A study of the unconscious motives involved in behavior b. An introspective study of mental imagery used in problem solving c. An analysis of the neurons involved in memory storage d. The use of a projective test to assess personality a. e. A study of how reinforcement affects learning
 Psychological Perspectives Why is a person the way they are? Depends on who you ask… I’m gonna need 6 participants
Psychological Perspectives Why is a person the way they are? Depends on who you ask… I’m gonna need 6 participants
 The Blind Men & The Elephant
The Blind Men & The Elephant

 The Father of Psychology l Wilhelm Wundt Opened 1 st Psychology lab (1879) - Germany Est. Psych as a Science - lab experiments - empirical evidence
The Father of Psychology l Wilhelm Wundt Opened 1 st Psychology lab (1879) - Germany Est. Psych as a Science - lab experiments - empirical evidence
 Could you hang with Wilheim Wundt? Wilhelm Wundt’s Volunteers had to make 10, 000 practice observations about themselves before considered for studies l Come up with 50 observations about thoughts, sensations, images, and feelings. 5 minutes l Who thinks they can do more? l Nothing can be repeated l
Could you hang with Wilheim Wundt? Wilhelm Wundt’s Volunteers had to make 10, 000 practice observations about themselves before considered for studies l Come up with 50 observations about thoughts, sensations, images, and feelings. 5 minutes l Who thinks they can do more? l Nothing can be repeated l
 The Father of Psychology l Wilhelm l. Focus l Wundt on consciousness could be broken down (or reduced) to its basic elements l. Introspection l. Self-observation: ‘seeing’ mental processes in immediate experience l record thoughts, sensations, feeling, and images and to analyze them when you are experiencing something l Reactions to simple stimuli
The Father of Psychology l Wilhelm l. Focus l Wundt on consciousness could be broken down (or reduced) to its basic elements l. Introspection l. Self-observation: ‘seeing’ mental processes in immediate experience l record thoughts, sensations, feeling, and images and to analyze them when you are experiencing something l Reactions to simple stimuli
 The First Schools of Psychology l Structuralism there) (what happened, what is sensation & perception and breaking those down into minute detail l Edward Bradford Titchner (Wundt’s student) l Three basic mental elements l Images, feelings & sensations 1. Introspection 2. Wanted to understand the structural elements of the mind (FEELING) l a. Mind operates by combining subjective emotions and objective sensations
The First Schools of Psychology l Structuralism there) (what happened, what is sensation & perception and breaking those down into minute detail l Edward Bradford Titchner (Wundt’s student) l Three basic mental elements l Images, feelings & sensations 1. Introspection 2. Wanted to understand the structural elements of the mind (FEELING) l a. Mind operates by combining subjective emotions and objective sensations
 The First Schools of Psychology l Functionalism 1890 (how and why did it happen) l Applying Darwin’s theory of natural selection to mental processes (what was the purpose of thinking? ) l William James (Father of American Psychology) l How and why (purpose) of behavior l The nose is structured to smell, but why do we need the nose to smell? ? What’s its function?
The First Schools of Psychology l Functionalism 1890 (how and why did it happen) l Applying Darwin’s theory of natural selection to mental processes (what was the purpose of thinking? ) l William James (Father of American Psychology) l How and why (purpose) of behavior l The nose is structured to smell, but why do we need the nose to smell? ? What’s its function?
 Other Early Schools of Psychology l Gestalt psychology (1890) l. Wholes vs. multiple individual elements l. A whole is greater than the sum of it’s parts l. Examine a person’s who experience l Don’t dissect an experience into separate elements to discover truths – instead, look at the ‘whole’
Other Early Schools of Psychology l Gestalt psychology (1890) l. Wholes vs. multiple individual elements l. A whole is greater than the sum of it’s parts l. Examine a person’s who experience l Don’t dissect an experience into separate elements to discover truths – instead, look at the ‘whole’
 WHAT DO YOU SEE? ? Next slide
WHAT DO YOU SEE? ? Next slide

 Autumn by Giuseppe Arcimboldo (1573) How does this painting illustrate Gestalt Psychology? ?
Autumn by Giuseppe Arcimboldo (1573) How does this painting illustrate Gestalt Psychology? ?
 What do you see when you see this car?
What do you see when you see this car?
 Sigmund Freud (1856 -1939) Austrian physician, and his followers emphasized the importance of the unconscious mind and its effects on human behavior.
Sigmund Freud (1856 -1939) Austrian physician, and his followers emphasized the importance of the unconscious mind and its effects on human behavior.

 ‘Modern’ Schools of Psychology l Freud’s Psychodynamic (Psychoanalytic) Theory (20 th century) l Conscious vs. unconscious conflicts l. Behavior results from unconscious drives & conflicts l memories of which we are not aware & cannot control especially sexual drives from childhood
‘Modern’ Schools of Psychology l Freud’s Psychodynamic (Psychoanalytic) Theory (20 th century) l Conscious vs. unconscious conflicts l. Behavior results from unconscious drives & conflicts l memories of which we are not aware & cannot control especially sexual drives from childhood
 Behaviorism Pioneered by Ivan Pavlov (1849 -1936) l CLASSICAL CONDITIONING = behavior as the product of prior experience l famous experiment where he rang a bell every time he fed some dogs, the dogs would salivate with the food. Eventually the dogs began salivating when Pavlov rang the bell l Unintentional (studying the digestion of dogs) l
Behaviorism Pioneered by Ivan Pavlov (1849 -1936) l CLASSICAL CONDITIONING = behavior as the product of prior experience l famous experiment where he rang a bell every time he fed some dogs, the dogs would salivate with the food. Eventually the dogs began salivating when Pavlov rang the bell l Unintentional (studying the digestion of dogs) l
 John B. Watson (18781958) l First to use the term ‘behaviorism’ (founder) l Famous experiment with Little Albert (1920) l Emotions like fear could be conditioned l Science of behavior
John B. Watson (18781958) l First to use the term ‘behaviorism’ (founder) l Famous experiment with Little Albert (1920) l Emotions like fear could be conditioned l Science of behavior
 B. F. Skinner (1904 -1990) l Huge influence on behaviorism l Introduced the idea of REINFORCEMENT, and Operant Conditioning l Behavior is a result of reinforcement & punishment
B. F. Skinner (1904 -1990) l Huge influence on behaviorism l Introduced the idea of REINFORCEMENT, and Operant Conditioning l Behavior is a result of reinforcement & punishment
 Behavioral Perspective l All Behavior is LEARNED Modeling l Imitating l Reinforcements l “You are what you learned” l l Focuses on OBSERVABLE behaviors over inner experiences. l Only cares about the behaviors that get in the way of our living, and attempts to change them. If you bit your fingernails when you were nervous, a behaviorist would not focus on calming you down, but rather focus on how to stop you from biting your nails.
Behavioral Perspective l All Behavior is LEARNED Modeling l Imitating l Reinforcements l “You are what you learned” l l Focuses on OBSERVABLE behaviors over inner experiences. l Only cares about the behaviors that get in the way of our living, and attempts to change them. If you bit your fingernails when you were nervous, a behaviorist would not focus on calming you down, but rather focus on how to stop you from biting your nails.

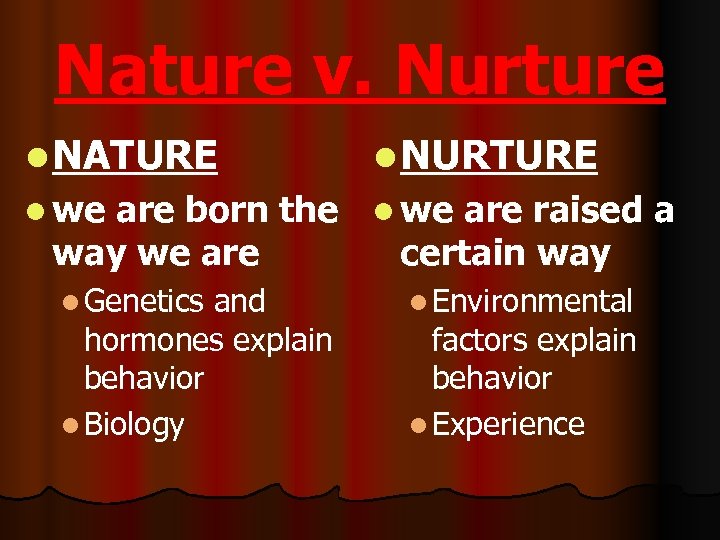 Nature v. Nurture l NATURE l NURTURE l we are born the l we are raised a way we are certain way l Genetics and hormones explain behavior l Biology l Environmental factors explain behavior l Experience
Nature v. Nurture l NATURE l NURTURE l we are born the l we are raised a way we are certain way l Genetics and hormones explain behavior l Biology l Environmental factors explain behavior l Experience
 Nature v. Nurture Am I the way I am because I was born that way or because of my Can I ever be like these people, or surroundings? does nature give me limitations?
Nature v. Nurture Am I the way I am because I was born that way or because of my Can I ever be like these people, or surroundings? does nature give me limitations?
 Biological Perspective l impact of biology on our behavior lhow the brain, nervous system, hormones, & genetics influence our behavior l referred to as psychobiologists
Biological Perspective l impact of biology on our behavior lhow the brain, nervous system, hormones, & genetics influence our behavior l referred to as psychobiologists
 Neuroscience/Biological Perspective If you could not remember the names of your parents and went to a psychologist who adheres to the neuroscience perspective, what might they say?
Neuroscience/Biological Perspective If you could not remember the names of your parents and went to a psychologist who adheres to the neuroscience perspective, what might they say?
 Cognitive Perspective l Cognitive = Thinking l how we process, store, and use information l how info. influences our thinking, language, reasoning, problem solving, and creativity l Behavior influenced by mental processes, perceptions, beliefs memories & expectations
Cognitive Perspective l Cognitive = Thinking l how we process, store, and use information l how info. influences our thinking, language, reasoning, problem solving, and creativity l Behavior influenced by mental processes, perceptions, beliefs memories & expectations
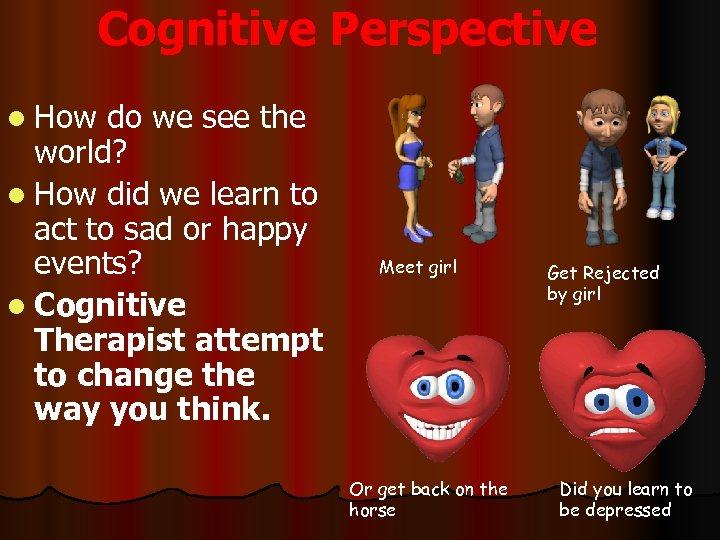 Cognitive Perspective l How do we see the world? l How did we learn to act to sad or happy events? l Cognitive Therapist attempt to change the way you think. Meet girl Or get back on the horse Get Rejected by girl Did you learn to be depressed
Cognitive Perspective l How do we see the world? l How did we learn to act to sad or happy events? l Cognitive Therapist attempt to change the way you think. Meet girl Or get back on the horse Get Rejected by girl Did you learn to be depressed
 Humanistic Psychology l Individual or self-directed choices influence our behavior l Reaching our full potential SELF ACTUALIZATION l The environment and other outside forces simply serve as a background to our own internal growth l Carl Rogers and Abraham Maslow “Hierarchy of Needs”
Humanistic Psychology l Individual or self-directed choices influence our behavior l Reaching our full potential SELF ACTUALIZATION l The environment and other outside forces simply serve as a background to our own internal growth l Carl Rogers and Abraham Maslow “Hierarchy of Needs”
 Humanistic Perspective l Focuses on positive growth l Attempt to seek self-actualization l Therapists use active listening and unconditional positive regard. Mr. Rogers would have made a great Humanistic Therapist!!!
Humanistic Perspective l Focuses on positive growth l Attempt to seek self-actualization l Therapists use active listening and unconditional positive regard. Mr. Rogers would have made a great Humanistic Therapist!!!
 Socio-cultural Perspective l Studying the influence of cultural and ethnic similarities and differences on behavior and social functioning l Rules, Roles, Social Norms & Groups
Socio-cultural Perspective l Studying the influence of cultural and ethnic similarities and differences on behavior and social functioning l Rules, Roles, Social Norms & Groups
 Social-Cultural Perspective Even in the same high school, behaviors can change in accordance to the various subcultures.
Social-Cultural Perspective Even in the same high school, behaviors can change in accordance to the various subcultures.
 Evolutionary Psychology l Charles l All Darwin behavior stems from survival of the fittest l Instinctual behavior l Motivated to spread genetic material
Evolutionary Psychology l Charles l All Darwin behavior stems from survival of the fittest l Instinctual behavior l Motivated to spread genetic material
 Practice Question #2 1. Which of the following characterizes a behavioral approach to psychology? A study of the unconscious motives involved in behavior b. An introspective study of mental imagery used in problem solving c. An analysis of the neurons involved in memory storage d. The use of a projective test to assess personality a. e. A study of how reinforcement affects learning
Practice Question #2 1. Which of the following characterizes a behavioral approach to psychology? A study of the unconscious motives involved in behavior b. An introspective study of mental imagery used in problem solving c. An analysis of the neurons involved in memory storage d. The use of a projective test to assess personality a. e. A study of how reinforcement affects learning
 Practice Question #2 #2. Of the following topics, which would a cognitive psychologist be most likely to study? a. b. c. d. e. Conformity behavior of college students Genetic determinants of behavior Problem-solving strategies in chess Personnel selection problems Maturational processes in adolescent
Practice Question #2 #2. Of the following topics, which would a cognitive psychologist be most likely to study? a. b. c. d. e. Conformity behavior of college students Genetic determinants of behavior Problem-solving strategies in chess Personnel selection problems Maturational processes in adolescent
 Practice Question #3 1. John B. Watson is best known as the founder of a. Behaviorism b. Functionalism c. Rationalism d. Structuralism e. Mechanism
Practice Question #3 1. John B. Watson is best known as the founder of a. Behaviorism b. Functionalism c. Rationalism d. Structuralism e. Mechanism
 Perspectives Through Music l https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=2 uz. K 3 Vwzra. M l https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=7 yg 0 5 sv. Xp 98 l Which perspective does this music video represent and why/how?
Perspectives Through Music l https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=2 uz. K 3 Vwzra. M l https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=7 yg 0 5 sv. Xp 98 l Which perspective does this music video represent and why/how?


