da9a2e99c8a54fb8326ee385bc6fa58f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 ® Speech Technology Opportunities and Challenges David Nahamoo Speech CTO, IBM Research Dec 12, 2006
® Speech Technology Opportunities and Challenges David Nahamoo Speech CTO, IBM Research Dec 12, 2006
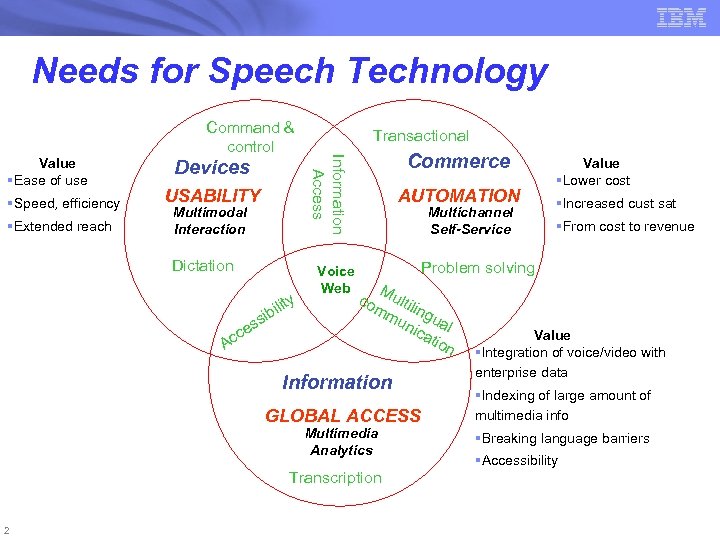 Needs for Speech Technology §Speed, efficiency §Extended reach Devices USABILITY Multimodal Interaction Dictation y ilit c Ac ib ss e Transactional Commerce Information Access Value §Ease of use Command & control Voice Web AUTOMATION Multichannel Self-Service §Increased cust sat §From cost to revenue Problem solving co Mu mm ltiling un ual ica tio n Information GLOBAL ACCESS Multimedia Analytics Transcription 2 Value §Lower cost Value §Integration of voice/video with enterprise data §Indexing of large amount of multimedia info §Breaking language barriers §Accessibility
Needs for Speech Technology §Speed, efficiency §Extended reach Devices USABILITY Multimodal Interaction Dictation y ilit c Ac ib ss e Transactional Commerce Information Access Value §Ease of use Command & control Voice Web AUTOMATION Multichannel Self-Service §Increased cust sat §From cost to revenue Problem solving co Mu mm ltiling un ual ica tio n Information GLOBAL ACCESS Multimedia Analytics Transcription 2 Value §Lower cost Value §Integration of voice/video with enterprise data §Indexing of large amount of multimedia info §Breaking language barriers §Accessibility
 Major Speech Application Opportunities § Commerce – Contact Centers – Unified Communication § Global Access – Speech To Speech Translation – Translingual Multi. Media Mining – Accessibility § Devices – Automotive – Set Top Box – Mobile Phones 3
Major Speech Application Opportunities § Commerce – Contact Centers – Unified Communication § Global Access – Speech To Speech Translation – Translingual Multi. Media Mining – Accessibility § Devices – Automotive – Set Top Box – Mobile Phones 3
 Speech Technology Innovation that Matters • Conversational Interaction – Dealing with Complexity • Speech Analytics – Extracting Insight / Knowledge • Multilingual Dimension – 4 Globalization
Speech Technology Innovation that Matters • Conversational Interaction – Dealing with Complexity • Speech Analytics – Extracting Insight / Knowledge • Multilingual Dimension – 4 Globalization
 ® Contact Centers Of Future
® Contact Centers Of Future
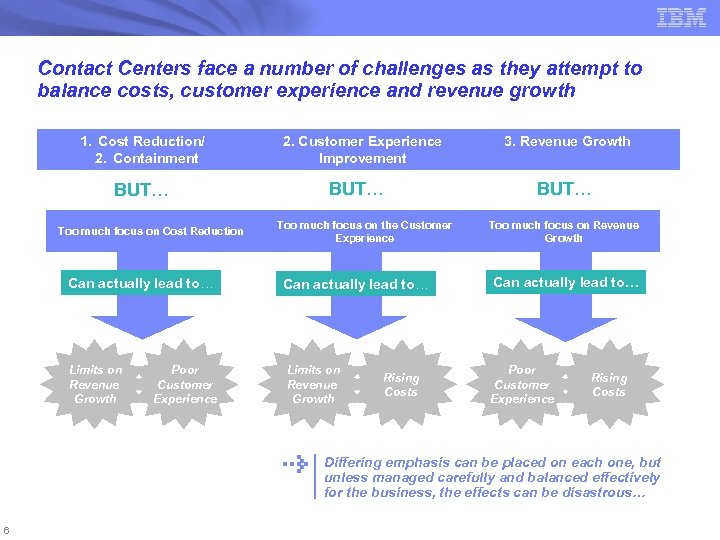 Contact Centers face a number of challenges as they attempt to balance costs, customer experience and revenue growth 1. Cost Reduction/ 2. Containment BUT… Too much focus on Cost Reduction 2. Customer Experience Improvement BUT… Too much focus on the Customer Experience 3. Revenue Growth BUT… Too much focus on Revenue Growth Can actually lead to… Limits on Revenue Growth Poor Customer Experience Rising Costs Differing emphasis can be placed on each one, but unless managed carefully and balanced effectively for the business, the effects can be disastrous… 6
Contact Centers face a number of challenges as they attempt to balance costs, customer experience and revenue growth 1. Cost Reduction/ 2. Containment BUT… Too much focus on Cost Reduction 2. Customer Experience Improvement BUT… Too much focus on the Customer Experience 3. Revenue Growth BUT… Too much focus on Revenue Growth Can actually lead to… Limits on Revenue Growth Poor Customer Experience Rising Costs Differing emphasis can be placed on each one, but unless managed carefully and balanced effectively for the business, the effects can be disastrous… 6
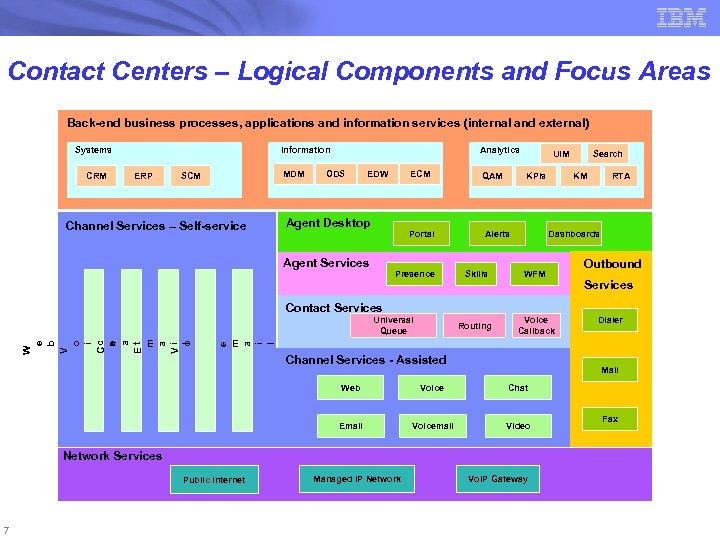 Contact Centers – Logical Components and Focus Areas Back-end business processes, applications and information services (internal and external) Systems CRM Information ERP SCM Channel Services – Self-service MDM Analytics ODS EDW Agent Desktop Portal Agent Services W e b V o Data Services i c C e h a Et m a Vi l o i c e m a i l ECM Presence QAM UIM KPIs Alerts Skills WFM RTA Routing Voice Callback Outbound Services Contact Services Universal Queue Channel Services - Assisted Dialer Mail Voice Chat Email Voicemail Video Network Services 7 KM Dashboards Web Public Internet Search Managed IP Network Vo. IP Gateway Fax
Contact Centers – Logical Components and Focus Areas Back-end business processes, applications and information services (internal and external) Systems CRM Information ERP SCM Channel Services – Self-service MDM Analytics ODS EDW Agent Desktop Portal Agent Services W e b V o Data Services i c C e h a Et m a Vi l o i c e m a i l ECM Presence QAM UIM KPIs Alerts Skills WFM RTA Routing Voice Callback Outbound Services Contact Services Universal Queue Channel Services - Assisted Dialer Mail Voice Chat Email Voicemail Video Network Services 7 KM Dashboards Web Public Internet Search Managed IP Network Vo. IP Gateway Fax
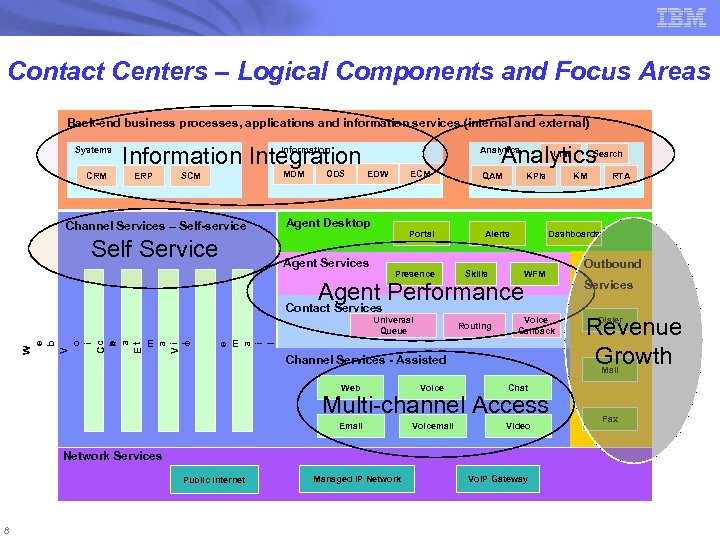 Contact Centers – Logical Components and Focus Areas Back-end business processes, applications and information services (internal and external) Systems CRM Information Integration Analytics Information ERP SCM Channel Services – Self-service W e b V o Data Services i c C e h a Et m a Vi l o i c e m a i l Self Service MDM ODS Analytics EDW ECM Agent Desktop Agent Services Portal Presence UIM QAM KPIs Alerts KM Skills WFM Routing Voice Callback Channel Services - Assisted Voice Services Revenue Growth Dialer Chat Email Voicemail Video Multi-channel Access Network Services 8 Outbound Mail Web Public Internet RTA Dashboards Agent Performance Contact Services Universal Queue Search Managed IP Network Vo. IP Gateway Fax
Contact Centers – Logical Components and Focus Areas Back-end business processes, applications and information services (internal and external) Systems CRM Information Integration Analytics Information ERP SCM Channel Services – Self-service W e b V o Data Services i c C e h a Et m a Vi l o i c e m a i l Self Service MDM ODS Analytics EDW ECM Agent Desktop Agent Services Portal Presence UIM QAM KPIs Alerts KM Skills WFM Routing Voice Callback Channel Services - Assisted Voice Services Revenue Growth Dialer Chat Email Voicemail Video Multi-channel Access Network Services 8 Outbound Mail Web Public Internet RTA Dashboards Agent Performance Contact Services Universal Queue Search Managed IP Network Vo. IP Gateway Fax
 ® Self-Service
® Self-Service
 Increased Self-Service § Self-service to 80% levels and higher is possible in at least some centers – Today’s contact centers are typically 10 to 20% self-service in most industries, but at least some companies claim 80% self-service now where Web-based interaction predominates; when voice predominates, numbers are much lower – Live-agent costs are an order of magnitude higher than the costs of self-service § Self-service adoption has been slow to take off (8% growth 2003 -2005) – Self-service is more challenging technically than agent performance because of the difficulty of achieving high customer satisfaction – Self-service is often run by another group than the one that runs the contact center – Self-service will be the end-game as labor-arbitrage becomes increasingly more difficult § Whichever vendor develops ways to drive self-service fastest (while maintaining customer satisfaction) will have a commanding position in the marketplace – Self-service is clearly a huge cost-savings opportunity 10
Increased Self-Service § Self-service to 80% levels and higher is possible in at least some centers – Today’s contact centers are typically 10 to 20% self-service in most industries, but at least some companies claim 80% self-service now where Web-based interaction predominates; when voice predominates, numbers are much lower – Live-agent costs are an order of magnitude higher than the costs of self-service § Self-service adoption has been slow to take off (8% growth 2003 -2005) – Self-service is more challenging technically than agent performance because of the difficulty of achieving high customer satisfaction – Self-service is often run by another group than the one that runs the contact center – Self-service will be the end-game as labor-arbitrage becomes increasingly more difficult § Whichever vendor develops ways to drive self-service fastest (while maintaining customer satisfaction) will have a commanding position in the marketplace – Self-service is clearly a huge cost-savings opportunity 10
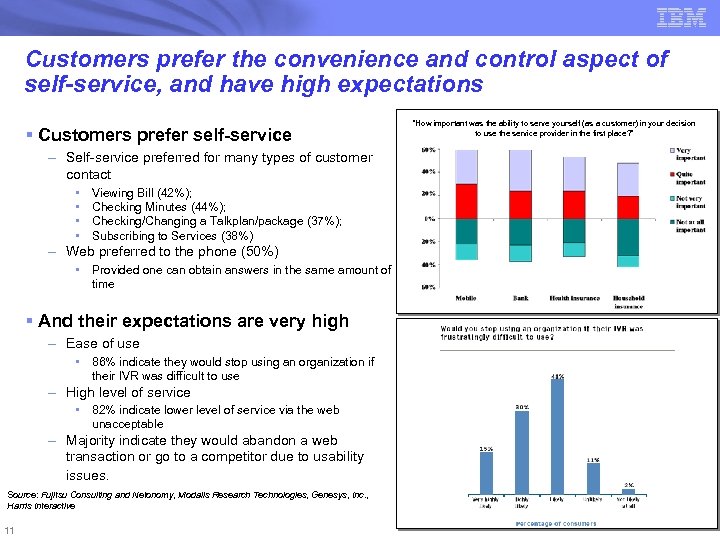 Customers prefer the convenience and control aspect of self-service, and have high expectations § Customers prefer self-service – Self-service preferred for many types of customer contact • • Viewing Bill (42%); Checking Minutes (44%); Checking/Changing a Talkplan/package (37%); Subscribing to Services (38%) – Web preferred to the phone (50%) • Provided one can obtain answers in the same amount of time § And their expectations are very high – Ease of use • 86% indicate they would stop using an organization if their IVR was difficult to use – High level of service • 82% indicate lower level of service via the web unacceptable – Majority indicate they would abandon a web transaction or go to a competitor due to usability issues. Source: Fujitsu Consulting and Netonomy, Modalis Research Technologies, Genesys, Inc. , Harris Interactive 11 “How important was the ability to serve yourself (as a customer) in your decision to use the service provider in the first place? ”
Customers prefer the convenience and control aspect of self-service, and have high expectations § Customers prefer self-service – Self-service preferred for many types of customer contact • • Viewing Bill (42%); Checking Minutes (44%); Checking/Changing a Talkplan/package (37%); Subscribing to Services (38%) – Web preferred to the phone (50%) • Provided one can obtain answers in the same amount of time § And their expectations are very high – Ease of use • 86% indicate they would stop using an organization if their IVR was difficult to use – High level of service • 82% indicate lower level of service via the web unacceptable – Majority indicate they would abandon a web transaction or go to a competitor due to usability issues. Source: Fujitsu Consulting and Netonomy, Modalis Research Technologies, Genesys, Inc. , Harris Interactive 11 “How important was the ability to serve yourself (as a customer) in your decision to use the service provider in the first place? ”
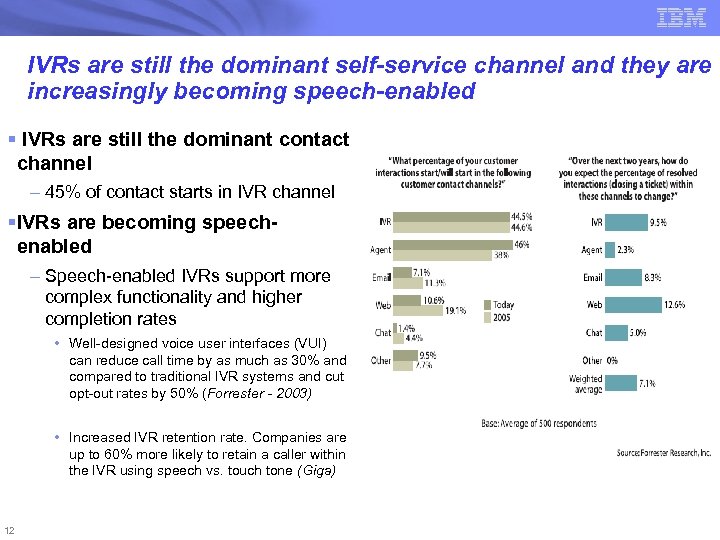 IVRs are still the dominant self-service channel and they are increasingly becoming speech-enabled § IVRs are still the dominant contact channel – 45% of contact starts in IVR channel §IVRs are becoming speechenabled – Speech-enabled IVRs support more complex functionality and higher completion rates • Well-designed voice user interfaces (VUI) can reduce call time by as much as 30% and compared to traditional IVR systems and cut opt-out rates by 50% (Forrester - 2003) • Increased IVR retention rate. Companies are up to 60% more likely to retain a caller within the IVR using speech vs. touch tone (Giga) 12
IVRs are still the dominant self-service channel and they are increasingly becoming speech-enabled § IVRs are still the dominant contact channel – 45% of contact starts in IVR channel §IVRs are becoming speechenabled – Speech-enabled IVRs support more complex functionality and higher completion rates • Well-designed voice user interfaces (VUI) can reduce call time by as much as 30% and compared to traditional IVR systems and cut opt-out rates by 50% (Forrester - 2003) • Increased IVR retention rate. Companies are up to 60% more likely to retain a caller within the IVR using speech vs. touch tone (Giga) 12
 Conversational Interaction § Should support the gap between user mental model and the application model – Task Complexity – User Familiarity – User Patience § Should minimize the user effort and task completion time – Consistent – Rapid – Efficient 13
Conversational Interaction § Should support the gap between user mental model and the application model – Task Complexity – User Familiarity – User Patience § Should minimize the user effort and task completion time – Consistent – Rapid – Efficient 13
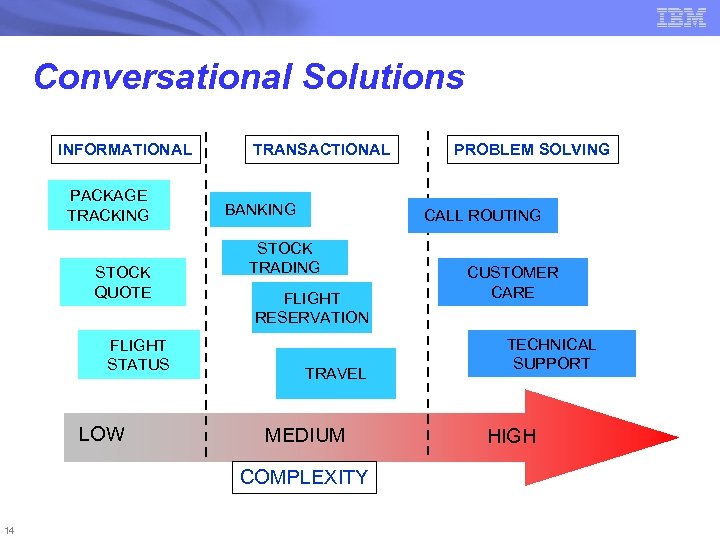 Conversational Solutions INFORMATIONAL PACKAGE TRACKING STOCK QUOTE FLIGHT STATUS LOW TRANSACTIONAL BANKING CALL ROUTING STOCK TRADING FLIGHT RESERVATION TRAVEL MEDIUM COMPLEXITY 14 PROBLEM SOLVING CUSTOMER CARE TECHNICAL SUPPORT HIGH
Conversational Solutions INFORMATIONAL PACKAGE TRACKING STOCK QUOTE FLIGHT STATUS LOW TRANSACTIONAL BANKING CALL ROUTING STOCK TRADING FLIGHT RESERVATION TRAVEL MEDIUM COMPLEXITY 14 PROBLEM SOLVING CUSTOMER CARE TECHNICAL SUPPORT HIGH
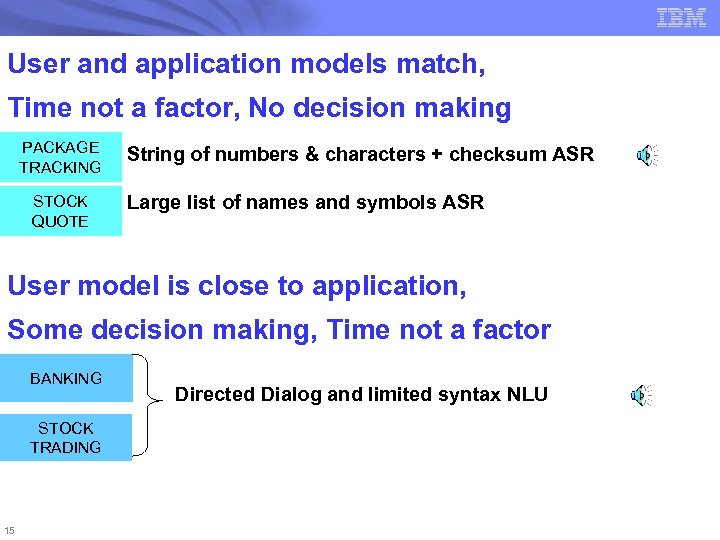 User and application models match, Time not a factor, No decision making PACKAGE TRACKING STOCK QUOTE String of numbers & characters + checksum ASR Large list of names and symbols ASR User model is close to application, Some decision making, Time not a factor BANKING STOCK TRADING 15 Directed Dialog and limited syntax NLU
User and application models match, Time not a factor, No decision making PACKAGE TRACKING STOCK QUOTE String of numbers & characters + checksum ASR Large list of names and symbols ASR User model is close to application, Some decision making, Time not a factor BANKING STOCK TRADING 15 Directed Dialog and limited syntax NLU
 User’s model might not match application’s, Involved decision making, Time a factor TRAVEL Substantial Dialog (& Language Understanding) User and application models match, No decision making, Long list of concepts CALL ROUTING 16 Substantial Language Understanding
User’s model might not match application’s, Involved decision making, Time a factor TRAVEL Substantial Dialog (& Language Understanding) User and application models match, No decision making, Long list of concepts CALL ROUTING 16 Substantial Language Understanding
 Conversational Help Desk Challenges § Help Desk is the most complex of all three types of conversational speech applications § Complexity is based on Nature of the Call • User domain model is limited at best • User is usually upset • Complex dialog and language understanding § Current Market Solution • No Industry “best practices” have been established 17
Conversational Help Desk Challenges § Help Desk is the most complex of all three types of conversational speech applications § Complexity is based on Nature of the Call • User domain model is limited at best • User is usually upset • Complex dialog and language understanding § Current Market Solution • No Industry “best practices” have been established 17
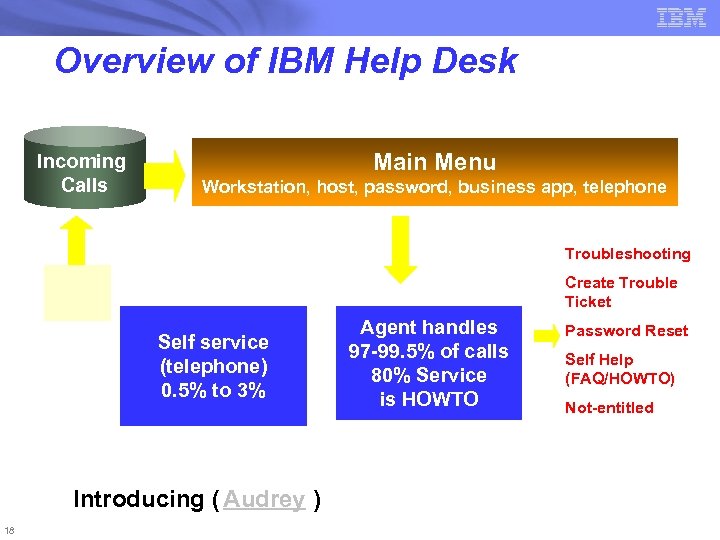 Overview of IBM Help Desk Incoming Calls Main Menu Workstation, host, password, business app, telephone Troubleshooting Create Trouble Ticket Self service (telephone) 0. 5% to 3% Introducing ( Audrey ) 18 Agent handles 97 -99. 5% of calls 80% Service is HOWTO Password Reset Self Help (FAQ/HOWTO) Not-entitled
Overview of IBM Help Desk Incoming Calls Main Menu Workstation, host, password, business app, telephone Troubleshooting Create Trouble Ticket Self service (telephone) 0. 5% to 3% Introducing ( Audrey ) 18 Agent handles 97 -99. 5% of calls 80% Service is HOWTO Password Reset Self Help (FAQ/HOWTO) Not-entitled
 ® Speech Analytics
® Speech Analytics
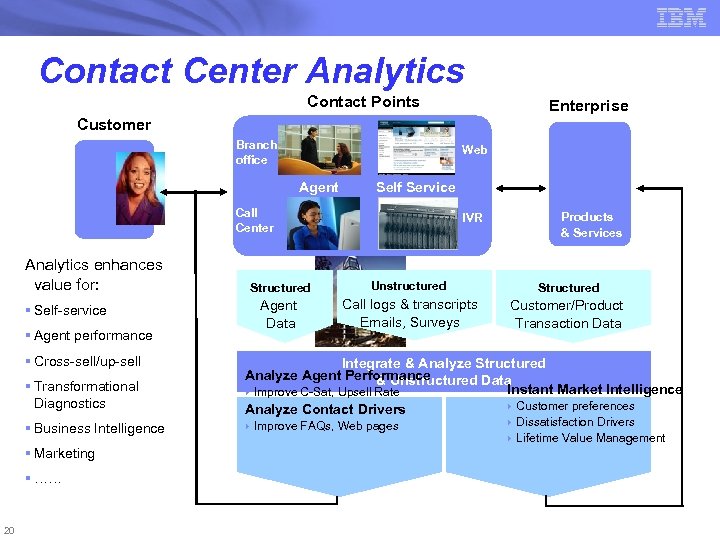 Contact Center Analytics Contact Points Enterprise Customer Branch office Web Agent Self Service Call Center Analytics enhances value for: Structured § Agent performance § Transformational Diagnostics § Business Intelligence § Marketing § …… 20 Unstructured Structured Agent Data § Self-service § Cross-sell/up-sell Products & Services IVR Call logs & transcripts Emails, Surveys Customer/Product Transaction Data Integrate & Analyze Structured Analyze Agent Performance & Unstructured Data Instant Market Intelligence } Improve C-Sat, Upsell Rate } Customer preferences Analyze Contact Drivers } Improve FAQs, Web pages } } Dissatisfaction Drivers Lifetime Value Management
Contact Center Analytics Contact Points Enterprise Customer Branch office Web Agent Self Service Call Center Analytics enhances value for: Structured § Agent performance § Transformational Diagnostics § Business Intelligence § Marketing § …… 20 Unstructured Structured Agent Data § Self-service § Cross-sell/up-sell Products & Services IVR Call logs & transcripts Emails, Surveys Customer/Product Transaction Data Integrate & Analyze Structured Analyze Agent Performance & Unstructured Data Instant Market Intelligence } Improve C-Sat, Upsell Rate } Customer preferences Analyze Contact Drivers } Improve FAQs, Web pages } } Dissatisfaction Drivers Lifetime Value Management
 Call Center Operation Quality Millions of Calls Everyday § Want general information: – Are callers happy? – Are processes followed? – What are people asking for? – What is the trend of occurrence of known problems? – Are there new problems? § 21 Need to know where to take action: – Save a customer from defecting – Apologize for mishandled calls – Show call to agent for coaching – Follow up on a missed sales opportunity Currently § Human monitoring is necessary for these things § Only a small fraction of calls can be checked § Most checking is wasted § There is no permanent record of the calls
Call Center Operation Quality Millions of Calls Everyday § Want general information: – Are callers happy? – Are processes followed? – What are people asking for? – What is the trend of occurrence of known problems? – Are there new problems? § 21 Need to know where to take action: – Save a customer from defecting – Apologize for mishandled calls – Show call to agent for coaching – Follow up on a missed sales opportunity Currently § Human monitoring is necessary for these things § Only a small fraction of calls can be checked § Most checking is wasted § There is no permanent record of the calls
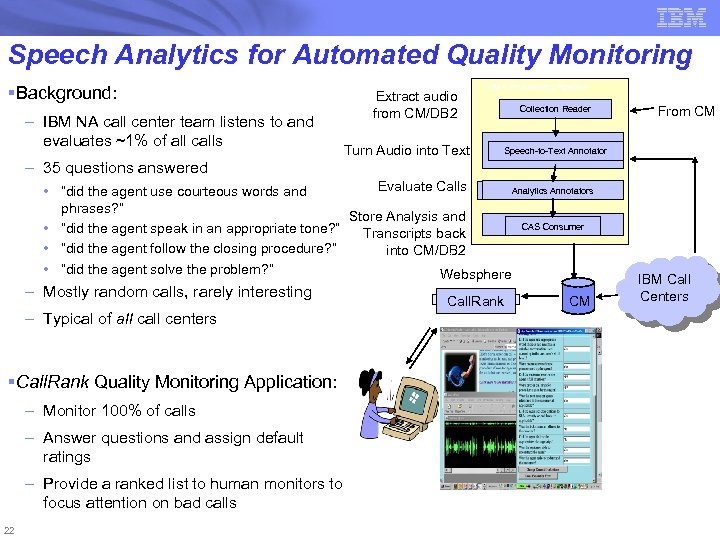 Speech Analytics for Automated Quality Monitoring § Background: – IBM NA call center team listens to and evaluates ~1% of all calls – 35 questions answered Extract audio from CM/DB 2 UIMA Processing Pipeline Turn Audio into Text Collection Reader Speech-to-Text Annotator Evaluate Calls Analytics Annotators • “did the agent use courteous words and phrases? ” Store Analysis and CAS Consumer • “did the agent speak in an appropriate tone? ” Transcripts back • “did the agent follow the closing procedure? ” into CM/DB 2 Transcribed & Analyzed audio • “did the agent solve the problem? ” Websphere – Mostly random calls, rarely interesting – Typical of all centers § Call. Rank Quality Monitoring Application: – Monitor 100% of calls – Answer questions and assign default ratings – Provide a ranked list to human monitors to focus attention on bad calls 22 Call. Rank From CM Calls & Stored Analysis CM audio IBM Call Centers
Speech Analytics for Automated Quality Monitoring § Background: – IBM NA call center team listens to and evaluates ~1% of all calls – 35 questions answered Extract audio from CM/DB 2 UIMA Processing Pipeline Turn Audio into Text Collection Reader Speech-to-Text Annotator Evaluate Calls Analytics Annotators • “did the agent use courteous words and phrases? ” Store Analysis and CAS Consumer • “did the agent speak in an appropriate tone? ” Transcripts back • “did the agent follow the closing procedure? ” into CM/DB 2 Transcribed & Analyzed audio • “did the agent solve the problem? ” Websphere – Mostly random calls, rarely interesting – Typical of all centers § Call. Rank Quality Monitoring Application: – Monitor 100% of calls – Answer questions and assign default ratings – Provide a ranked list to human monitors to focus attention on bad calls 22 Call. Rank From CM Calls & Stored Analysis CM audio IBM Call Centers
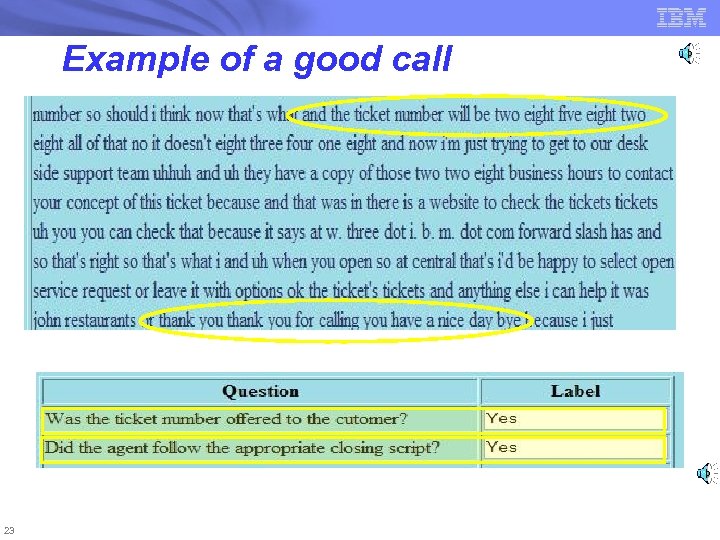 Example of a good call 23
Example of a good call 23
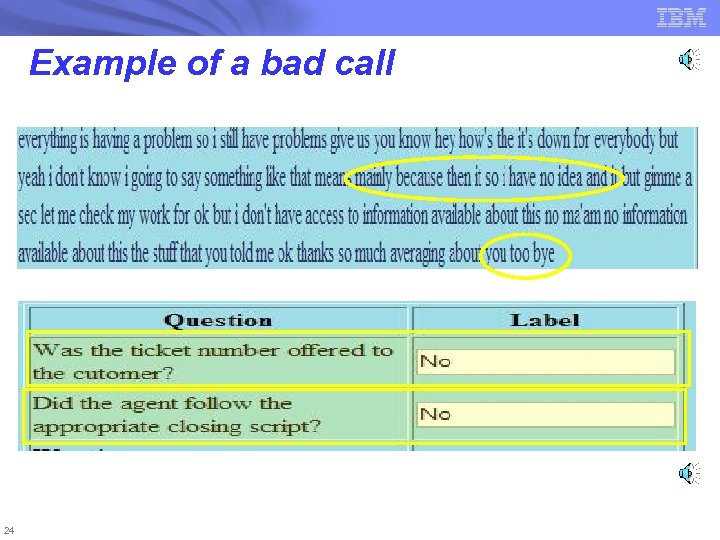 Example of a bad call 24
Example of a bad call 24
 Automated Quality Monitoring • Status: ü Three times as many bad calls found for same listening effort ü Processing ~ 3000 calls/day now from all North American centers • Technology: ü Answer many questions with pattern matching on decoded text § Did the agent follow the appropriate closing script? § Search for “THANK YOU FOR CALLING”, “ANYTHING ELSE”, “SERVICE REQUEST” ü Use other linguistic cues to improve the accuracy of the system § Number of hesitations (UH, UM, HUM, etc), total silence, longest silence, … 25
Automated Quality Monitoring • Status: ü Three times as many bad calls found for same listening effort ü Processing ~ 3000 calls/day now from all North American centers • Technology: ü Answer many questions with pattern matching on decoded text § Did the agent follow the appropriate closing script? § Search for “THANK YOU FOR CALLING”, “ANYTHING ELSE”, “SERVICE REQUEST” ü Use other linguistic cues to improve the accuracy of the system § Number of hesitations (UH, UM, HUM, etc), total silence, longest silence, … 25
 ® Agent Performance
® Agent Performance
 Agent Performance § Personnel costs are by far the largest component of existing contact center costs – Move to off-shore operations has resulted in significant (up to 75%) labor cost reductions – Large contact centers have very large numbers of personnel – Estimated 6 M agents in U. S. in 2004 and continuing to grow § Even with the rise of self-service, a percentage of calls will still be handled by live agents § Numerous opportunities exist to improve performance by automation: – Integration of systems across the business for use in the contact center – On-boarding process (e. g. , accent monitoring) – Training (on-boarding, continuing education, real-time training) – Agent quality monitoring – Call logging (30% of agent time in some contact centers) – Helping the agent find the answer to the customer’s question – Workforce management – Intelligent call routing globally – Expert “multi-channel” agents – Activity-centric computing and other collaborative projects 27
Agent Performance § Personnel costs are by far the largest component of existing contact center costs – Move to off-shore operations has resulted in significant (up to 75%) labor cost reductions – Large contact centers have very large numbers of personnel – Estimated 6 M agents in U. S. in 2004 and continuing to grow § Even with the rise of self-service, a percentage of calls will still be handled by live agents § Numerous opportunities exist to improve performance by automation: – Integration of systems across the business for use in the contact center – On-boarding process (e. g. , accent monitoring) – Training (on-boarding, continuing education, real-time training) – Agent quality monitoring – Call logging (30% of agent time in some contact centers) – Helping the agent find the answer to the customer’s question – Workforce management – Intelligent call routing globally – Expert “multi-channel” agents – Activity-centric computing and other collaborative projects 27
 Agent Performance: Voice Assessment/Training Increased number of off-shore centers § e. g. , India (>50% growth) Key focus in off-shore contact centers § Hiring – § Shrinking candidate pool and high agent attrition rates Training – Train agents to have neutral accents to improve customer experience Voice Assessment/Training System § Candidate screening for – – – § Accent training – 28 Grammar Pronunciation Spoken language comprehension Correctness of pronunciation, intonation, speaking rate and syllable stress
Agent Performance: Voice Assessment/Training Increased number of off-shore centers § e. g. , India (>50% growth) Key focus in off-shore contact centers § Hiring – § Shrinking candidate pool and high agent attrition rates Training – Train agents to have neutral accents to improve customer experience Voice Assessment/Training System § Candidate screening for – – – § Accent training – 28 Grammar Pronunciation Spoken language comprehension Correctness of pronunciation, intonation, speaking rate and syllable stress
 Contact Centers Summary § § Contact Centers face a number of challenges as they attempt to balance costs, customer experience and revenue growth § Customers increasingly prefer self-service and speech self-service is now ready for prime time § Enterprises can achieve improved agent performance with agent productivity tools and agent hiring/training tools § Enterprises should focus on revenue growth transforming their contact centers from cost centers to profit centers § Customer demand for choice, convenience and consistency is driving the adoption of multi-channel enablement in contact centers § 29 Contact centers are focal points in an enterprise from which all customer contacts are managed Actionable intelligence from real-time and offline analytics of structured and unstructured customer interaction data will lead to new opportunities for cost reduction, revenue growth and improved customer experience
Contact Centers Summary § § Contact Centers face a number of challenges as they attempt to balance costs, customer experience and revenue growth § Customers increasingly prefer self-service and speech self-service is now ready for prime time § Enterprises can achieve improved agent performance with agent productivity tools and agent hiring/training tools § Enterprises should focus on revenue growth transforming their contact centers from cost centers to profit centers § Customer demand for choice, convenience and consistency is driving the adoption of multi-channel enablement in contact centers § 29 Contact centers are focal points in an enterprise from which all customer contacts are managed Actionable intelligence from real-time and offline analytics of structured and unstructured customer interaction data will lead to new opportunities for cost reduction, revenue growth and improved customer experience
 ® Increasing Global Reach
® Increasing Global Reach
 Global Language Barriers Different languages spoken by people living in different regions or even by different ethnic groups living in the same region § Language barriers cause… – High cost for agents – need both subject matter expertise and language skills • Call centers, insurance agents, etc. – Unreachable to broad international business or tourism travel market – Life threatening in • medical emergency • natural disaster situations • military – Multilingual on demand media and entertainment 31
Global Language Barriers Different languages spoken by people living in different regions or even by different ethnic groups living in the same region § Language barriers cause… – High cost for agents – need both subject matter expertise and language skills • Call centers, insurance agents, etc. – Unreachable to broad international business or tourism travel market – Life threatening in • medical emergency • natural disaster situations • military – Multilingual on demand media and entertainment 31
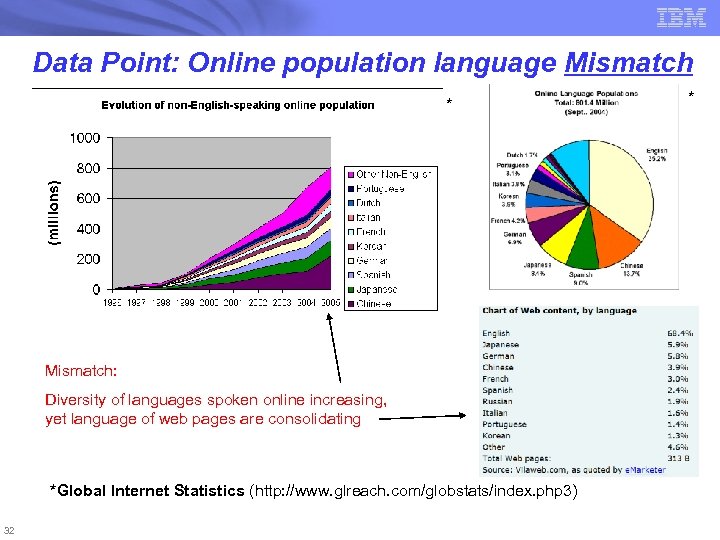 Data Point: Online population language Mismatch * Mismatch: Diversity of languages spoken online increasing, yet language of web pages are consolidating *Global Internet Statistics (http: //www. glreach. com/globstats/index. php 3) 32 *
Data Point: Online population language Mismatch * Mismatch: Diversity of languages spoken online increasing, yet language of web pages are consolidating *Global Internet Statistics (http: //www. glreach. com/globstats/index. php 3) 32 *
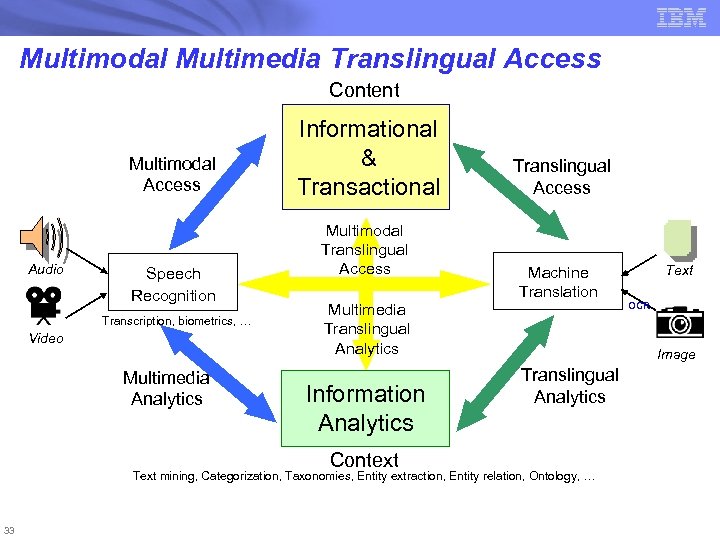 Multimodal Multimedia Translingual Access Content Multimodal Access Audio Speech Recognition Transcription, biometrics, … Video Multimedia Analytics Informational & Transactional Multimodal Translingual Access Machine Translation Multimedia Translingual Analytics Information Analytics Context OCR Image Translingual Analytics Text mining, Categorization, Taxonomies, Entity extraction, Entity relation, Ontology, … 33 Text
Multimodal Multimedia Translingual Access Content Multimodal Access Audio Speech Recognition Transcription, biometrics, … Video Multimedia Analytics Informational & Transactional Multimodal Translingual Access Machine Translation Multimedia Translingual Analytics Information Analytics Context OCR Image Translingual Analytics Text mining, Categorization, Taxonomies, Entity extraction, Entity relation, Ontology, … 33 Text
 S 2 S Translation call for innovation § Speech Recognition Challenges – Needs to work in noisy environments, with spontaneous, conversational speech in multiple languages, could be emotional speech when under stress. § Translation has to handle output of ASR system – Recognition errors – Spoken language: different from written language • Non-grammatical disfluencies • Imperfect syntax • Lack of formal characteristics of text: no punctuation or paragraphing § Translated text must be "speakable" for oral communication – not enough to translate content adequately; output must be fluent – Need to carefully consider and tune interactions between ASR, MT and NLG – need access to all components § Cost-effective development of new languages and domains § Intonation translation remains a grand challenge 34
S 2 S Translation call for innovation § Speech Recognition Challenges – Needs to work in noisy environments, with spontaneous, conversational speech in multiple languages, could be emotional speech when under stress. § Translation has to handle output of ASR system – Recognition errors – Spoken language: different from written language • Non-grammatical disfluencies • Imperfect syntax • Lack of formal characteristics of text: no punctuation or paragraphing § Translated text must be "speakable" for oral communication – not enough to translate content adequately; output must be fluent – Need to carefully consider and tune interactions between ASR, MT and NLG – need access to all components § Cost-effective development of new languages and domains § Intonation translation remains a grand challenge 34
 Speech Technology Driving New Business Opportunities • Increasing Self Service: More natural interaction • Increasing Agent Productivity, Monitoring Quality, and Increasing Sales Opportunity: with more difficult tasks is made possible Extracting insight from the content of conversation • 35 Increasing the Global Reach: Breaking the language barrier
Speech Technology Driving New Business Opportunities • Increasing Self Service: More natural interaction • Increasing Agent Productivity, Monitoring Quality, and Increasing Sales Opportunity: with more difficult tasks is made possible Extracting insight from the content of conversation • 35 Increasing the Global Reach: Breaking the language barrier


