 Spectroscopy of Diamondoid Molecules From the far IR to the vacuum UV O. Pirali, Laboratoire de Photophysique Moléculaire, France; Synchrotron SOLEIL, AILES Beamline, France J. Oomens, H. Alvaro Galue FOM Institute for Plasma Physics “Rijnhuizen”, The Netherlands G. Garcia, L. Nahon, M. Vervloet Synchrotron SOLEIL, DESIRS Beamline, France S. Boyé-Peronne, S. Douin Laboratoire de Photophysique Moléculaire, France V. Boudon, Institut Carnot de Bourgogne, France Columbus 2009/ Spectroscopy of diamondoids
Spectroscopy of Diamondoid Molecules From the far IR to the vacuum UV O. Pirali, Laboratoire de Photophysique Moléculaire, France; Synchrotron SOLEIL, AILES Beamline, France J. Oomens, H. Alvaro Galue FOM Institute for Plasma Physics “Rijnhuizen”, The Netherlands G. Garcia, L. Nahon, M. Vervloet Synchrotron SOLEIL, DESIRS Beamline, France S. Boyé-Peronne, S. Douin Laboratoire de Photophysique Moléculaire, France V. Boudon, Institut Carnot de Bourgogne, France Columbus 2009/ Spectroscopy of diamondoids
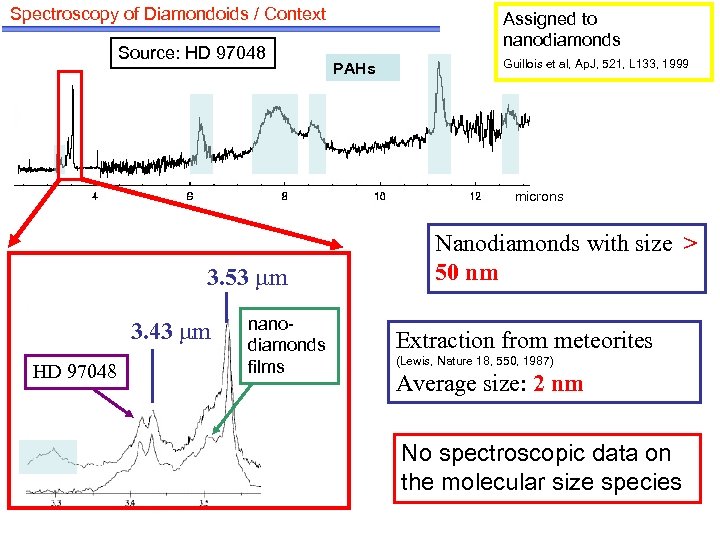 Spectroscopy of Diamondoids / Context Source: HD 97048 Assigned to nanodiamonds PAHs Guillois et al, Ap. J, 521, L 133, 1999 microns 3. 53 m 3. 43 m HD 97048 nanodiamonds films Nanodiamonds with size > 50 nm Extraction from meteorites (Lewis, Nature 18, 550, 1987) Average size: 2 nm No spectroscopic data on the molecular size species
Spectroscopy of Diamondoids / Context Source: HD 97048 Assigned to nanodiamonds PAHs Guillois et al, Ap. J, 521, L 133, 1999 microns 3. 53 m 3. 43 m HD 97048 nanodiamonds films Nanodiamonds with size > 50 nm Extraction from meteorites (Lewis, Nature 18, 550, 1987) Average size: 2 nm No spectroscopic data on the molecular size species
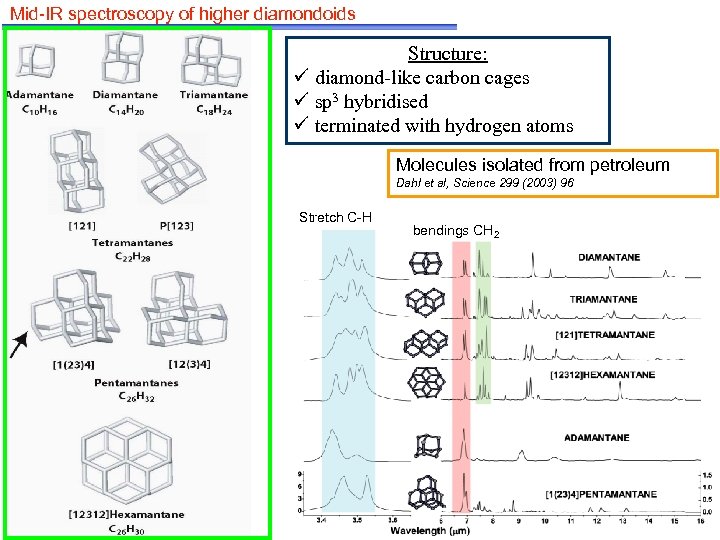 Mid-IR spectroscopy of higher diamondoids Structure: ü diamond-like carbon cages ü sp 3 hybridised ü terminated with hydrogen atoms Molecules isolated from petroleum Dahl et al, Science 299 (2003) 96 Stretch C-H bendings CH 2
Mid-IR spectroscopy of higher diamondoids Structure: ü diamond-like carbon cages ü sp 3 hybridised ü terminated with hydrogen atoms Molecules isolated from petroleum Dahl et al, Science 299 (2003) 96 Stretch C-H bendings CH 2
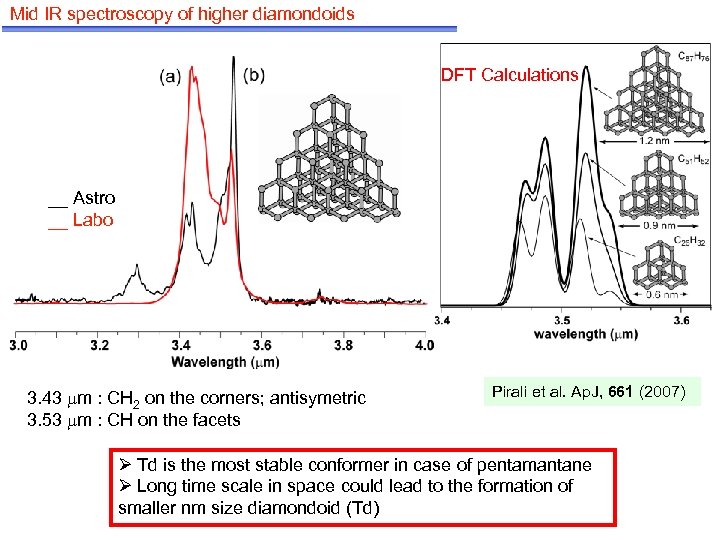 Mid IR spectroscopy of higher diamondoids DFT Calculations __ Astro __ Labo 3. 43 m : CH 2 on the corners; antisymetric 3. 53 m : CH on the facets Pirali et al. Ap. J, 661 (2007) Ø Td is the most stable conformer in case of pentamantane Ø Long time scale in space could lead to the formation of smaller nm size diamondoid (Td)
Mid IR spectroscopy of higher diamondoids DFT Calculations __ Astro __ Labo 3. 43 m : CH 2 on the corners; antisymetric 3. 53 m : CH on the facets Pirali et al. Ap. J, 661 (2007) Ø Td is the most stable conformer in case of pentamantane Ø Long time scale in space could lead to the formation of smaller nm size diamondoid (Td)
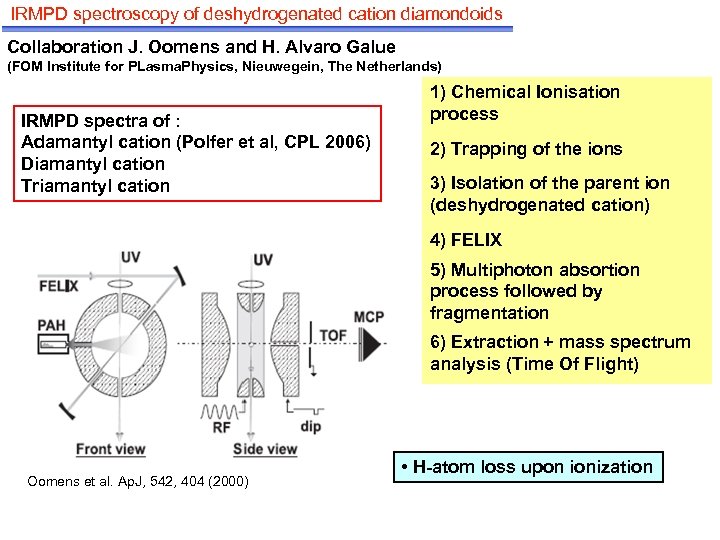 IRMPD spectroscopy of deshydrogenated cation diamondoids Collaboration J. Oomens and H. Alvaro Galue (FOM Institute for PLasma. Physics, Nieuwegein, The Netherlands) IRMPD spectra of : Adamantyl cation (Polfer et al, CPL 2006) Diamantyl cation Triamantyl cation 1) Chemical Ionisation process 2) Trapping of the ions 3) Isolation of the parent ion (deshydrogenated cation) 4) FELIX 5) Multiphoton absortion process followed by fragmentation 6) Extraction + mass spectrum analysis (Time Of Flight) Oomens et al. Ap. J, 542, 404 (2000) • H-atom loss upon ionization
IRMPD spectroscopy of deshydrogenated cation diamondoids Collaboration J. Oomens and H. Alvaro Galue (FOM Institute for PLasma. Physics, Nieuwegein, The Netherlands) IRMPD spectra of : Adamantyl cation (Polfer et al, CPL 2006) Diamantyl cation Triamantyl cation 1) Chemical Ionisation process 2) Trapping of the ions 3) Isolation of the parent ion (deshydrogenated cation) 4) FELIX 5) Multiphoton absortion process followed by fragmentation 6) Extraction + mass spectrum analysis (Time Of Flight) Oomens et al. Ap. J, 542, 404 (2000) • H-atom loss upon ionization
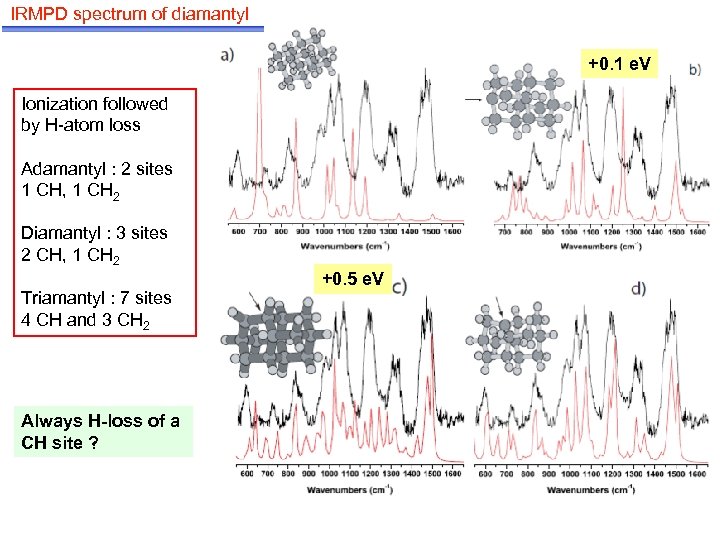 IRMPD spectrum of diamantyl +0. 1 e. V Ionization followed by H-atom loss Adamantyl : 2 sites 1 CH, 1 CH 2 Diamantyl : 3 sites 2 CH, 1 CH 2 Triamantyl : 7 sites 4 CH and 3 CH 2 Always H-loss of a CH site ? +0. 5 e. V
IRMPD spectrum of diamantyl +0. 1 e. V Ionization followed by H-atom loss Adamantyl : 2 sites 1 CH, 1 CH 2 Diamantyl : 3 sites 2 CH, 1 CH 2 Triamantyl : 7 sites 4 CH and 3 CH 2 Always H-loss of a CH site ? +0. 5 e. V
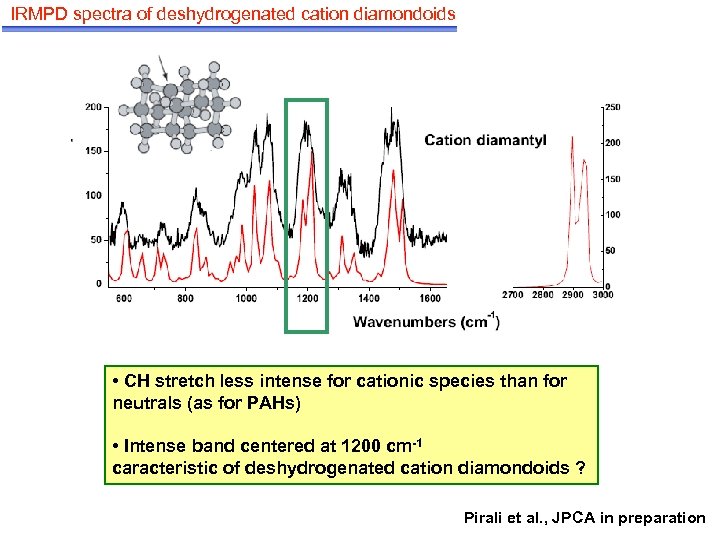 IRMPD spectra of deshydrogenated cation diamondoids • CH stretch less intense for cationic species than for neutrals (as for PAHs) • Intense band centered at 1200 cm-1 caracteristic of deshydrogenated cation diamondoids ? Pirali et al. , JPCA in preparation
IRMPD spectra of deshydrogenated cation diamondoids • CH stretch less intense for cationic species than for neutrals (as for PAHs) • Intense band centered at 1200 cm-1 caracteristic of deshydrogenated cation diamondoids ? Pirali et al. , JPCA in preparation
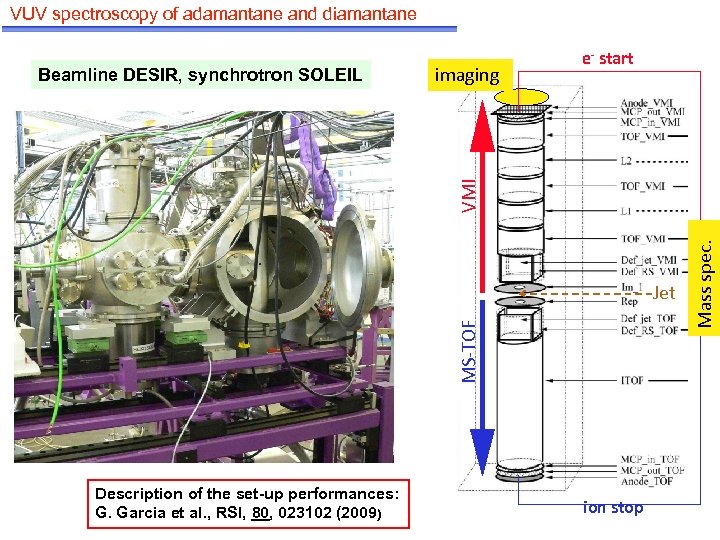 VUV spectroscopy of adamantane and diamantane imaging MS-TOF Jet Description of the set-up performances: G. Garcia et al. , RSI, 80, 023102 (2009) ion stop Mass spec. VMI Beamline DESIR, synchrotron SOLEIL e- start
VUV spectroscopy of adamantane and diamantane imaging MS-TOF Jet Description of the set-up performances: G. Garcia et al. , RSI, 80, 023102 (2009) ion stop Mass spec. VMI Beamline DESIR, synchrotron SOLEIL e- start
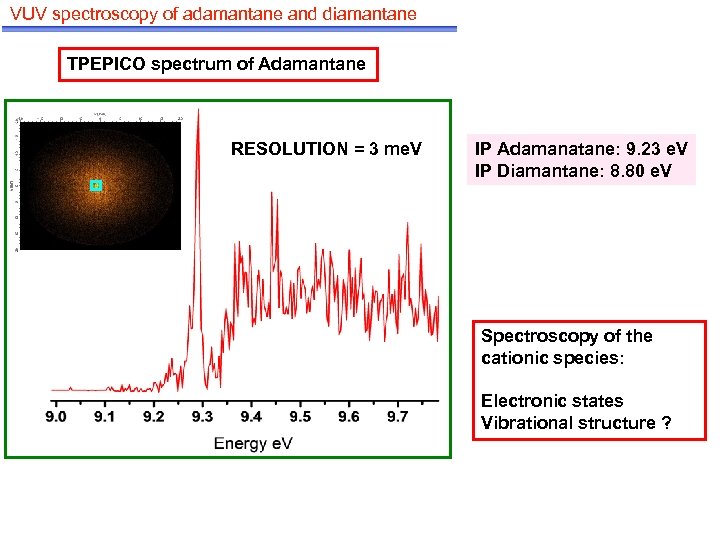 VUV spectroscopy of adamantane and diamantane TPEPICO spectrum of Adamantane RESOLUTION = 3 me. V IP Adamanatane: 9. 23 e. V IP Diamantane: 8. 80 e. V Spectroscopy of the cationic species: Electronic states Vibrational structure ?
VUV spectroscopy of adamantane and diamantane TPEPICO spectrum of Adamantane RESOLUTION = 3 me. V IP Adamanatane: 9. 23 e. V IP Diamantane: 8. 80 e. V Spectroscopy of the cationic species: Electronic states Vibrational structure ?
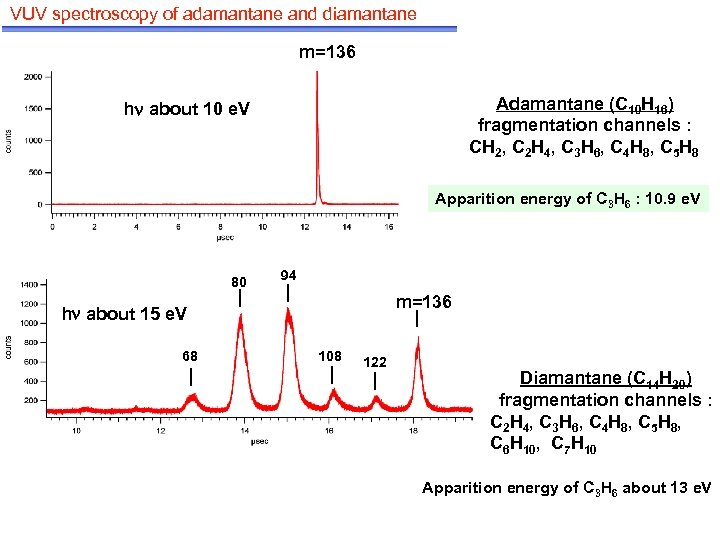 VUV spectroscopy of adamantane and diamantane m=136 Adamantane (C 10 H 16) fragmentation channels : CH 2, C 2 H 4, C 3 H 6, C 4 H 8, C 5 H 8 h about 10 e. V Apparition energy of C 3 H 6 : 10. 9 e. V 80 94 m=136 h about 15 e. V 68 108 122 Diamantane (C 14 H 20) fragmentation channels : C 2 H 4, C 3 H 6, C 4 H 8, C 5 H 8, C 6 H 10, C 7 H 10 Apparition energy of C 3 H 6 about 13 e. V
VUV spectroscopy of adamantane and diamantane m=136 Adamantane (C 10 H 16) fragmentation channels : CH 2, C 2 H 4, C 3 H 6, C 4 H 8, C 5 H 8 h about 10 e. V Apparition energy of C 3 H 6 : 10. 9 e. V 80 94 m=136 h about 15 e. V 68 108 122 Diamantane (C 14 H 20) fragmentation channels : C 2 H 4, C 3 H 6, C 4 H 8, C 5 H 8, C 6 H 10, C 7 H 10 Apparition energy of C 3 H 6 about 13 e. V
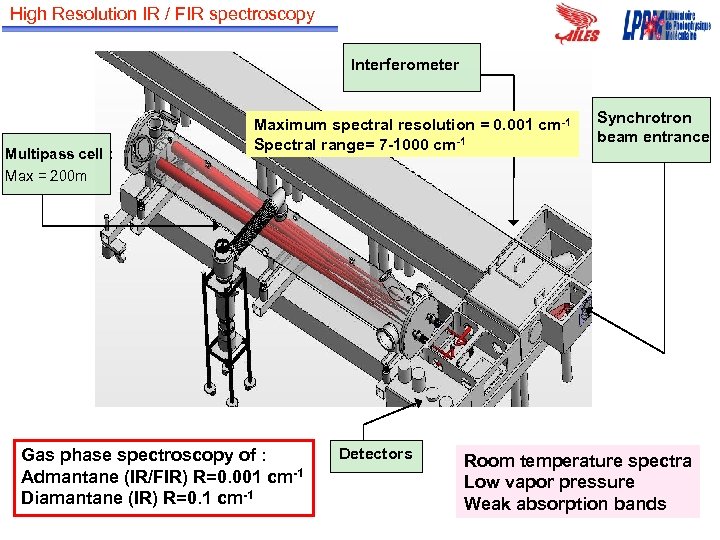 High Resolution IR / FIR spectroscopy Interferometer Multipass cell : Max = 200 m Maximum spectral resolution = 0. 001 cm-1 Spectral range= 7 -1000 cm-1 Gas phase spectroscopy of : Admantane (IR/FIR) R=0. 001 cm-1 Diamantane (IR) R=0. 1 cm-1 Detectors Synchrotron beam entrance Room temperature spectra Low vapor pressure Weak absorption bands
High Resolution IR / FIR spectroscopy Interferometer Multipass cell : Max = 200 m Maximum spectral resolution = 0. 001 cm-1 Spectral range= 7 -1000 cm-1 Gas phase spectroscopy of : Admantane (IR/FIR) R=0. 001 cm-1 Diamantane (IR) R=0. 1 cm-1 Detectors Synchrotron beam entrance Room temperature spectra Low vapor pressure Weak absorption bands
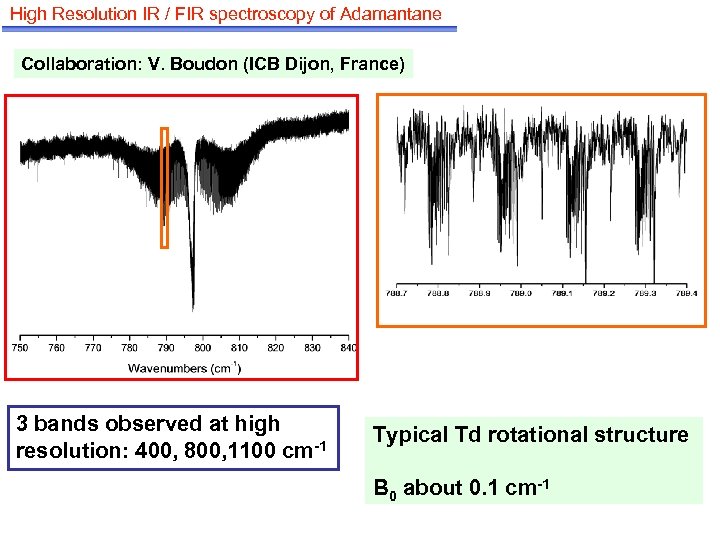 High Resolution IR / FIR spectroscopy of Adamantane Collaboration: V. Boudon (ICB Dijon, France) 3 bands observed at high resolution: 400, 800, 1100 cm-1 Typical Td rotational structure B 0 about 0. 1 cm-1
High Resolution IR / FIR spectroscopy of Adamantane Collaboration: V. Boudon (ICB Dijon, France) 3 bands observed at high resolution: 400, 800, 1100 cm-1 Typical Td rotational structure B 0 about 0. 1 cm-1
 Conclusions and perspectives • IR spectra and analysis of « higher » diamondoid molecules • IRMPD spectra of adamantyl, diamantyl and triamantyl • VUV TPEPICO spectra of adamantane and diamantane • FIR / IR high resolution gas phase spectra of adamantane Thank You !
Conclusions and perspectives • IR spectra and analysis of « higher » diamondoid molecules • IRMPD spectra of adamantyl, diamantyl and triamantyl • VUV TPEPICO spectra of adamantane and diamantane • FIR / IR high resolution gas phase spectra of adamantane Thank You !


