09595499b436d33d38332ad61df6054e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 Spectrophotometer
Spectrophotometer
 Definition : • A spectrophotometer is an instrument that measure the amount of light absorbed or transmitted by the sample.
Definition : • A spectrophotometer is an instrument that measure the amount of light absorbed or transmitted by the sample.
 Purpose : • Spectrophotometer is used to: 1)measure the concentration of the solution. 2)identify organic compounds by determining the absorption maximum.
Purpose : • Spectrophotometer is used to: 1)measure the concentration of the solution. 2)identify organic compounds by determining the absorption maximum.
 Principle: • Spectrophotometer consists of two instruments: 1 -spectrometer to produce light for any selected wave length. 2 -photometer to measure the intensity of light, and the analyte is put between them.
Principle: • Spectrophotometer consists of two instruments: 1 -spectrometer to produce light for any selected wave length. 2 -photometer to measure the intensity of light, and the analyte is put between them.
 Single and double beams : • In the early days of spectroscopy, double beam spectrophotometers were popular but now it is thought that the single beam spectrophotometer is more advantageous.
Single and double beams : • In the early days of spectroscopy, double beam spectrophotometers were popular but now it is thought that the single beam spectrophotometer is more advantageous.
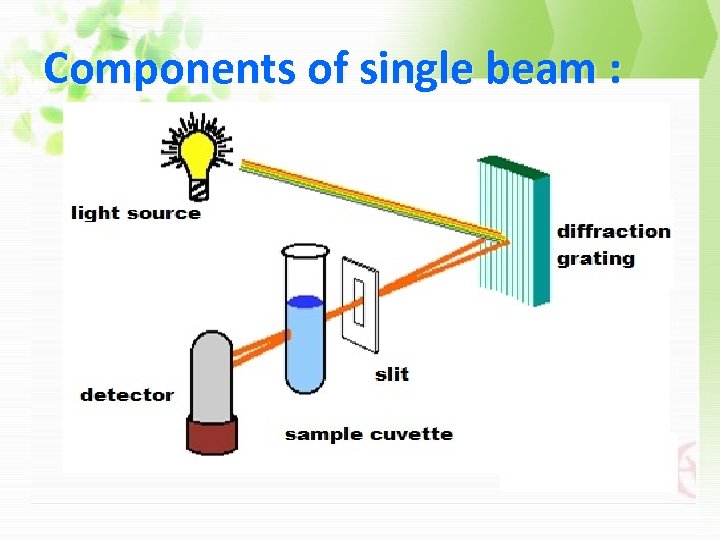 Components of single beam :
Components of single beam :
 1 - Light source. • For ultraviolet absorption spectrophotometer • for visible absorption spectrophotometer
1 - Light source. • For ultraviolet absorption spectrophotometer • for visible absorption spectrophotometer
 q For ultraviolet absorption spectrophotometer we use • # H 2 lamp its wave length ranges from 190 to 380 nm.
q For ultraviolet absorption spectrophotometer we use • # H 2 lamp its wave length ranges from 190 to 380 nm.
 • #D 2 (deuterium) lamp its wave length ranges from 185 to 400 nm. We prefer D 2 lamp because of its higher stability & it emits continuous radiation.
• #D 2 (deuterium) lamp its wave length ranges from 185 to 400 nm. We prefer D 2 lamp because of its higher stability & it emits continuous radiation.
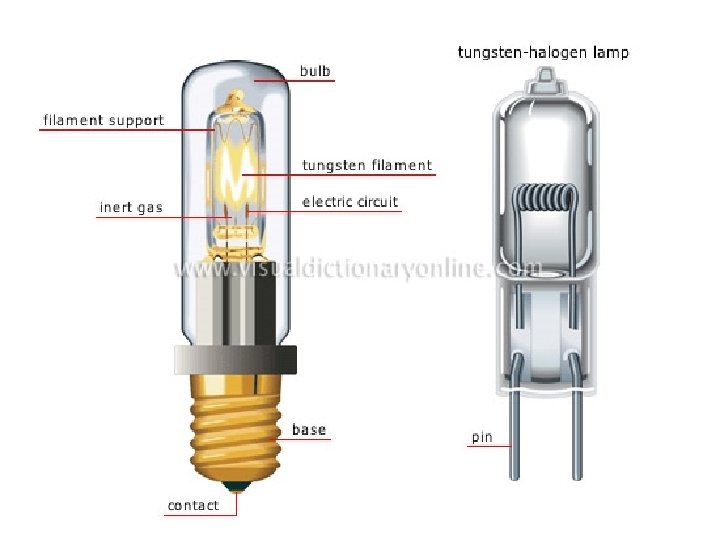
 q for visible absorption spectrophotometer we use • #tungsten lamp (350~2200 nm) • #tungsten halogen lamp (240~2500 nm) We prefer tungsten halogen lamp because it has longer life, can be used at lower wave length.
q for visible absorption spectrophotometer we use • #tungsten lamp (350~2200 nm) • #tungsten halogen lamp (240~2500 nm) We prefer tungsten halogen lamp because it has longer life, can be used at lower wave length.
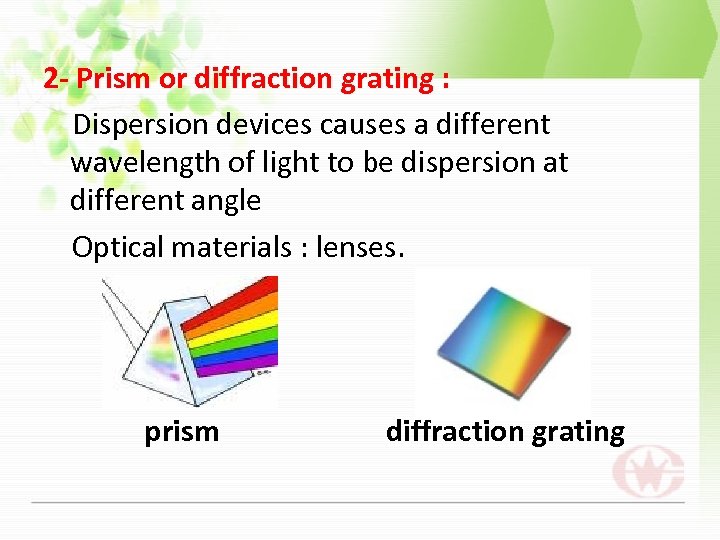 2 - Prism or diffraction grating : Dispersion devices causes a different wavelength of light to be dispersion at different angle Optical materials : lenses. prism diffraction grating
2 - Prism or diffraction grating : Dispersion devices causes a different wavelength of light to be dispersion at different angle Optical materials : lenses. prism diffraction grating
 3 - slit : monochromators used for selecting one wave length.
3 - slit : monochromators used for selecting one wave length.
 4 - cell (cuvette): The cuvette or absorption cells, must made from material that is transparent to radiation in the spectral region of interest.
4 - cell (cuvette): The cuvette or absorption cells, must made from material that is transparent to radiation in the spectral region of interest.
 5 - Detector (photometer): a device used to convert the radiant energy to electrical signal.
5 - Detector (photometer): a device used to convert the radiant energy to electrical signal.
 6 - Read out device (Digital galvanometer) : The data from the detector are displayed by a readout device , such as an analog meter , digital display or liquid crystal display. The out put can also transmitted to computer or printer.
6 - Read out device (Digital galvanometer) : The data from the detector are displayed by a readout device , such as an analog meter , digital display or liquid crystal display. The out put can also transmitted to computer or printer.
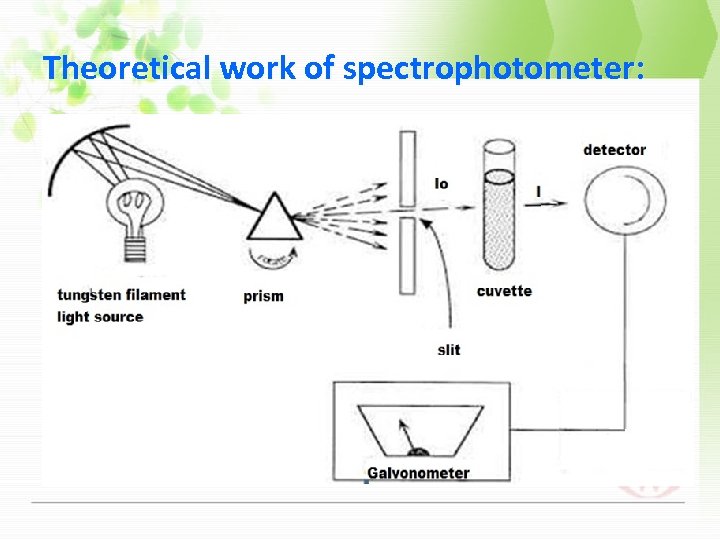 Theoretical work of spectrophotometer:
Theoretical work of spectrophotometer:

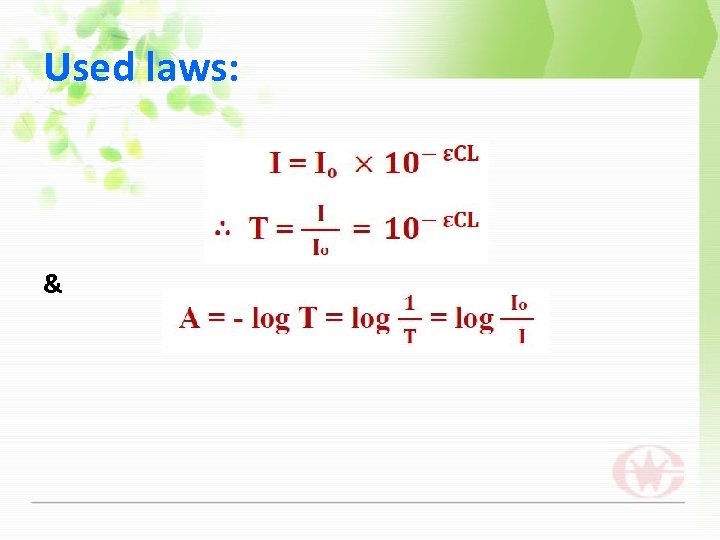 Used laws: &
Used laws: &
 Where T: transmittance of solution. I: intensity of transmitted light. (Watt/cm 2) Io: intensity of incident light. (watt/cm 2) : Coefficient absorptivity. (L/mole. cm) : Concentration of solution. (Mole/L) : Thickness of cuvette. (cm) A: the absorption of light by the sample
Where T: transmittance of solution. I: intensity of transmitted light. (Watt/cm 2) Io: intensity of incident light. (watt/cm 2) : Coefficient absorptivity. (L/mole. cm) : Concentration of solution. (Mole/L) : Thickness of cuvette. (cm) A: the absorption of light by the sample
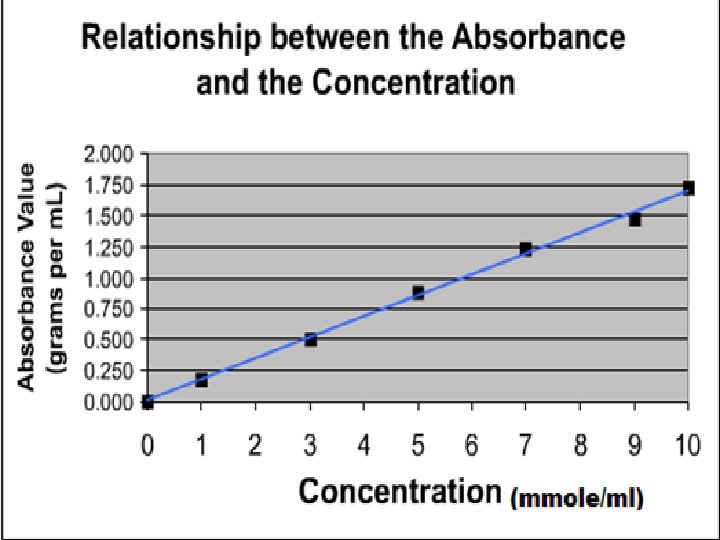
 Beer's Law: • Beer's Law explains the relationship between absorbance, at a given wavelength and concentration. A = CL Where: A = absorbance. = molar absorptivity coefficient. (L/mole. cm) L = length of the light path. (cm) C = concentration of the solute. (mole/L)
Beer's Law: • Beer's Law explains the relationship between absorbance, at a given wavelength and concentration. A = CL Where: A = absorbance. = molar absorptivity coefficient. (L/mole. cm) L = length of the light path. (cm) C = concentration of the solute. (mole/L)
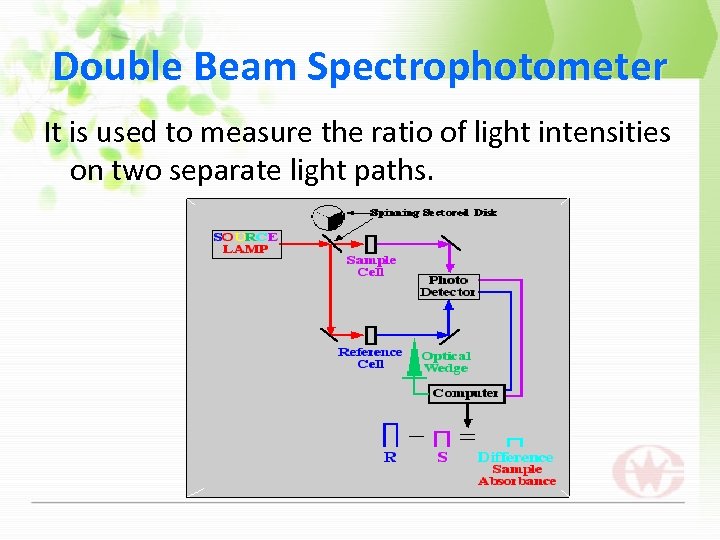 Double Beam Spectrophotometer It is used to measure the ratio of light intensities on two separate light paths.
Double Beam Spectrophotometer It is used to measure the ratio of light intensities on two separate light paths.
 Advantages : 1) Wide applicability. 2) High sensitivity. 3) Good accuracy. 4) Ease and convenience.
Advantages : 1) Wide applicability. 2) High sensitivity. 3) Good accuracy. 4) Ease and convenience.
 Disadvantages : 1. Error in reading due to » the change in temperature » nature of solution. 2. It is subject to false wavelength setting
Disadvantages : 1. Error in reading due to » the change in temperature » nature of solution. 2. It is subject to false wavelength setting
 3. an error in wavelength setting of ± 0. 3 nm results in an error. 4. The equipment is generally expensive.
3. an error in wavelength setting of ± 0. 3 nm results in an error. 4. The equipment is generally expensive.
 Applications in our life • • Clinical Food and Drink Industrial / Pharmaceutical Life Sciences
Applications in our life • • Clinical Food and Drink Industrial / Pharmaceutical Life Sciences
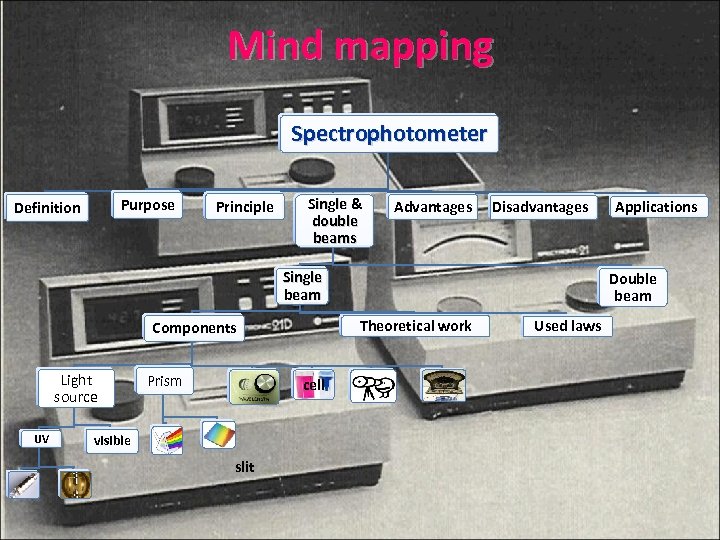 Mind mapping Spectrophotometer Purpose Definition Principle Single & double beams Advantages Disadvantages Single beam Light source UV Prism cell visible slit Double beam Theoretical work Components Applications Used laws
Mind mapping Spectrophotometer Purpose Definition Principle Single & double beams Advantages Disadvantages Single beam Light source UV Prism cell visible slit Double beam Theoretical work Components Applications Used laws
 The End ‘‘ best wishes ’’
The End ‘‘ best wishes ’’


