cd22a9c57f9afbedd09c873eb6e3680d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 95
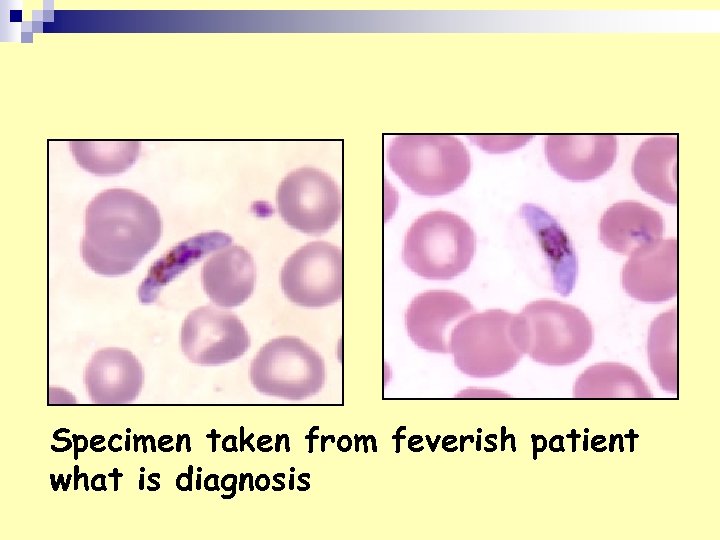 Specimen taken from feverish patient what is diagnosis
Specimen taken from feverish patient what is diagnosis
 1. Falcipram gametocyte Banana shape P. f gametocytes n Vector: female Anopheles mosquito n Mode of infection: injection of sporozoite during Anopheles bite.
1. Falcipram gametocyte Banana shape P. f gametocytes n Vector: female Anopheles mosquito n Mode of infection: injection of sporozoite during Anopheles bite.
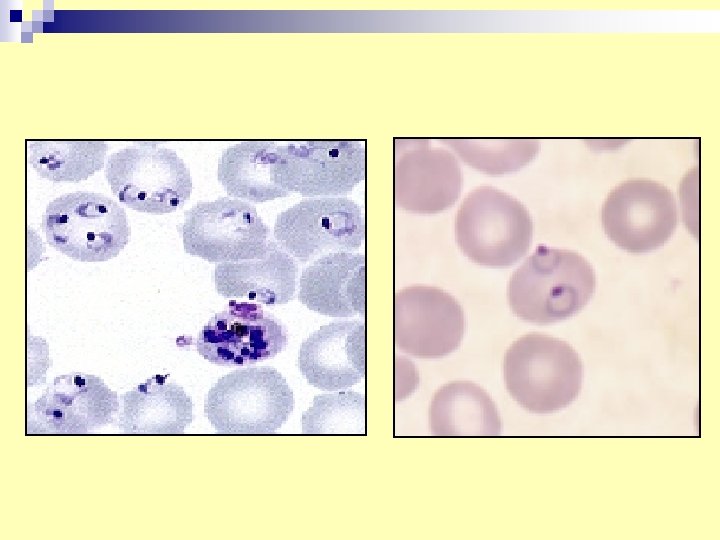
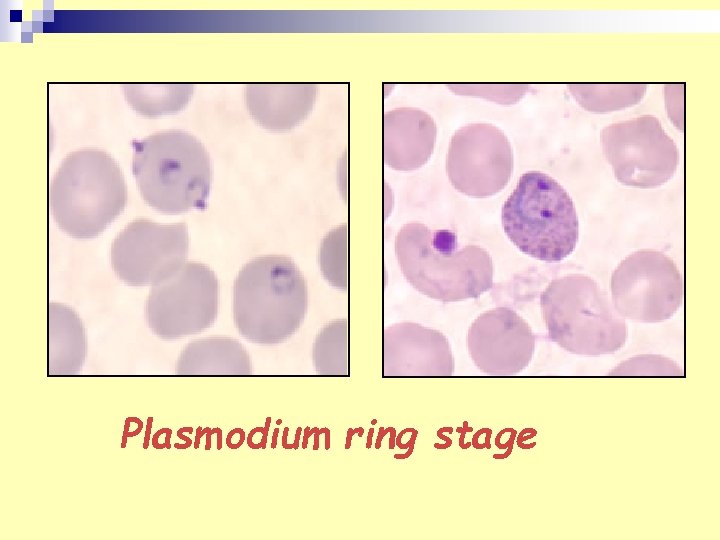 Plasmodium ring stage
Plasmodium ring stage
 2. Plasmodium ring stage n Diagnosis: blood film (thin and thick) n Vector: female Anopheles n Infective stage: Sporozoite
2. Plasmodium ring stage n Diagnosis: blood film (thin and thick) n Vector: female Anopheles n Infective stage: Sporozoite
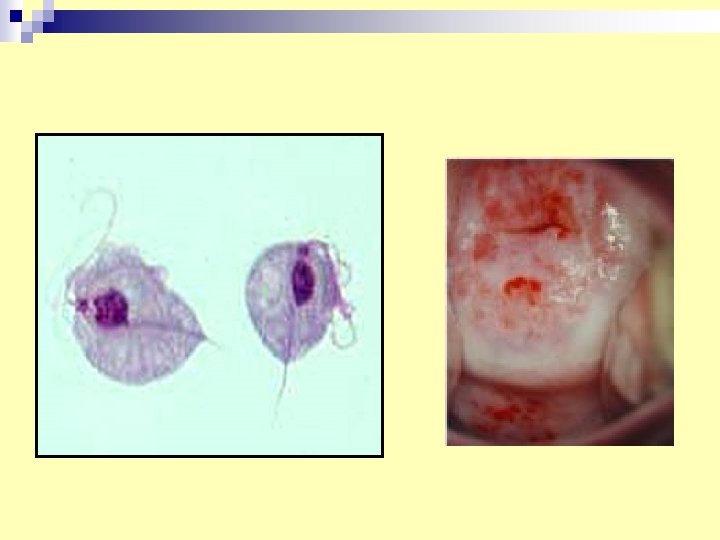
 3. Trichomonas vaginalis n Diagnosis: vaginal, urethral smear, occasionally in urine analysis n Trophozoite is the infective stage. n transmitted sexually.
3. Trichomonas vaginalis n Diagnosis: vaginal, urethral smear, occasionally in urine analysis n Trophozoite is the infective stage. n transmitted sexually.
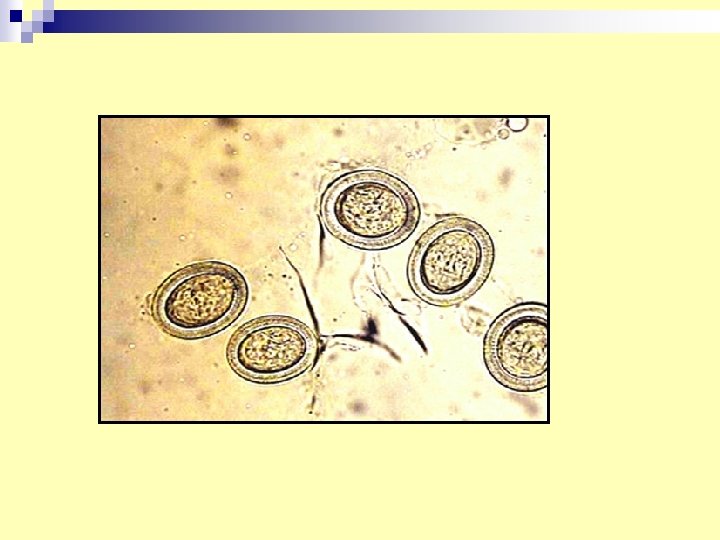
 4. Eggs of Taenia species n n n -T. saginata -T. solium -Echinoccus granulosus
4. Eggs of Taenia species n n n -T. saginata -T. solium -Echinoccus granulosus
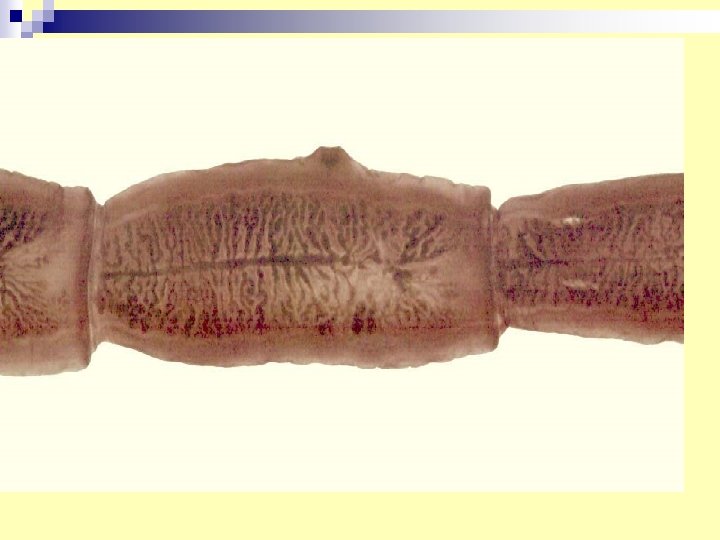
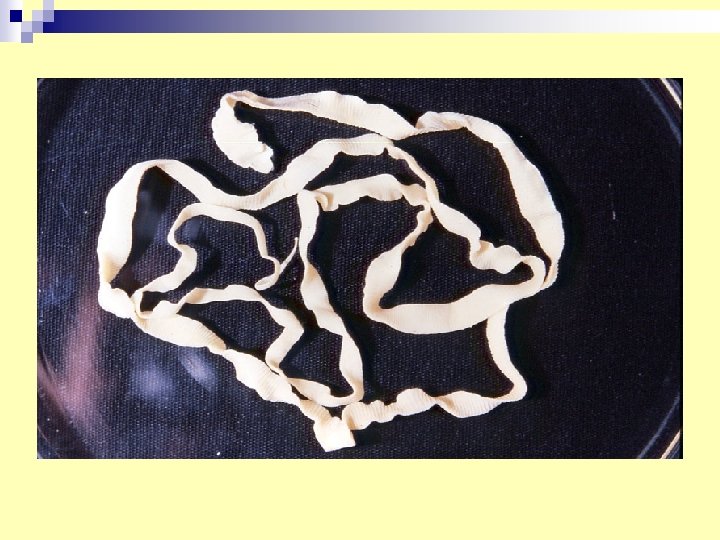

 5. Taenia saginata (adult tape) Diagnosis: stool examination for - eggs - gravid segments. n Infective stage : cysticercus bovis-in under cooked meat (beef). n Adult habitat small intestine n
5. Taenia saginata (adult tape) Diagnosis: stool examination for - eggs - gravid segments. n Infective stage : cysticercus bovis-in under cooked meat (beef). n Adult habitat small intestine n

 6. Soft tick 1. 2. Relapsing fever (endemic). Tick paralysis
6. Soft tick 1. 2. Relapsing fever (endemic). Tick paralysis

 7. Hard tick n Rocky mountain spotted fever n Q fever n Babesiosis
7. Hard tick n Rocky mountain spotted fever n Q fever n Babesiosis
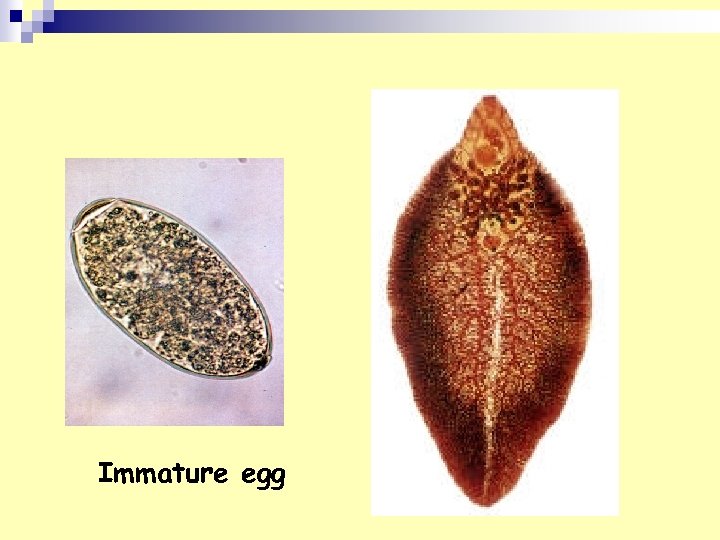 Immature egg
Immature egg
 8. Adult Fasciola hepatica n Diagnosis : egg in -stools examination -duodenal aspirate. n Infective stage : encysted metacercaria (on water plants). n Habitat : biliary passage in liver.
8. Adult Fasciola hepatica n Diagnosis : egg in -stools examination -duodenal aspirate. n Infective stage : encysted metacercaria (on water plants). n Habitat : biliary passage in liver.

 emale. Trichuris trichiura (whip worm) n Diagnosis : egg in stools n Infective stage, mode of infection: ingestion of embryonated egg in soil.
emale. Trichuris trichiura (whip worm) n Diagnosis : egg in stools n Infective stage, mode of infection: ingestion of embryonated egg in soil.
 Scotch tape preparation Clear adhensive tape slide
Scotch tape preparation Clear adhensive tape slide
 Scotch tape preparation Clear adhensive tape slide n Used in detection of Enterobius vermicularis infection n Collect eggs from perianal area
Scotch tape preparation Clear adhensive tape slide n Used in detection of Enterobius vermicularis infection n Collect eggs from perianal area
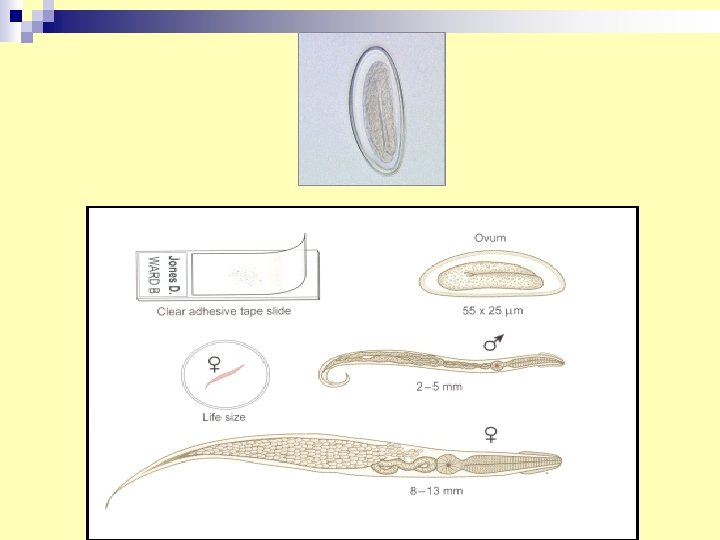
 10. Enterobius vermicularis egg (Pin worm, Oxyuris worm) n Diagnosis: Scotch tape preparation to collect eggs from perianal area and microscopical examination.
10. Enterobius vermicularis egg (Pin worm, Oxyuris worm) n Diagnosis: Scotch tape preparation to collect eggs from perianal area and microscopical examination.
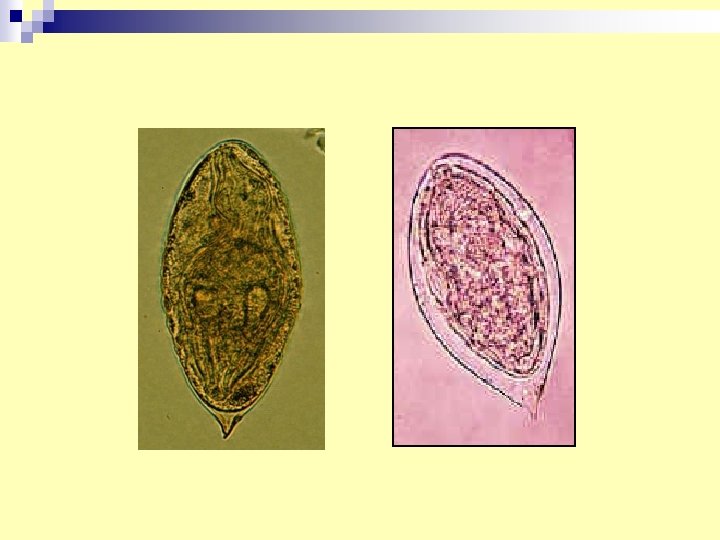
 11. Schistosoma haematobium egg (Urinary schistosomiasis) n Diagnosis: - Urine analysis - Serology in chronic cases. n Infective stage : cercaria in water penetrate skin. n Pathology : periportal fibrosis. ppf
11. Schistosoma haematobium egg (Urinary schistosomiasis) n Diagnosis: - Urine analysis - Serology in chronic cases. n Infective stage : cercaria in water penetrate skin. n Pathology : periportal fibrosis. ppf
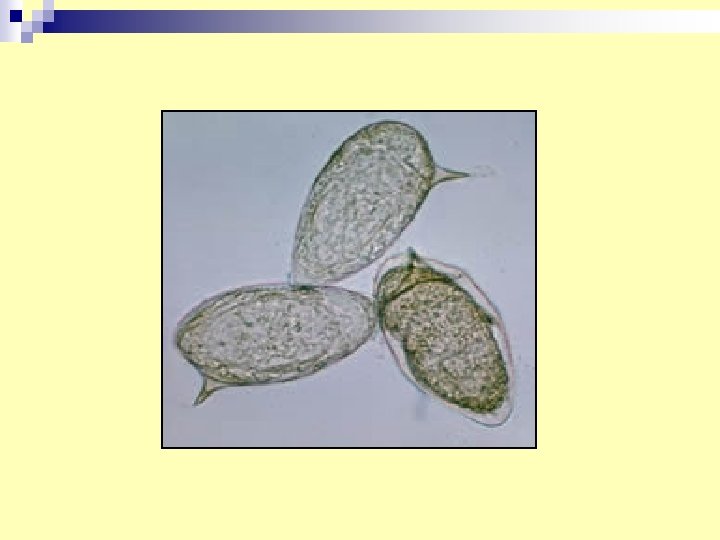
 12. Schistosoma mansoni egg in stools specimen (intestinal schistosomiasis) n Other methods of diagnosis : - rectal swab. - rectal snip biopsy. - serology: to detect antibodies in patient serum.
12. Schistosoma mansoni egg in stools specimen (intestinal schistosomiasis) n Other methods of diagnosis : - rectal swab. - rectal snip biopsy. - serology: to detect antibodies in patient serum.
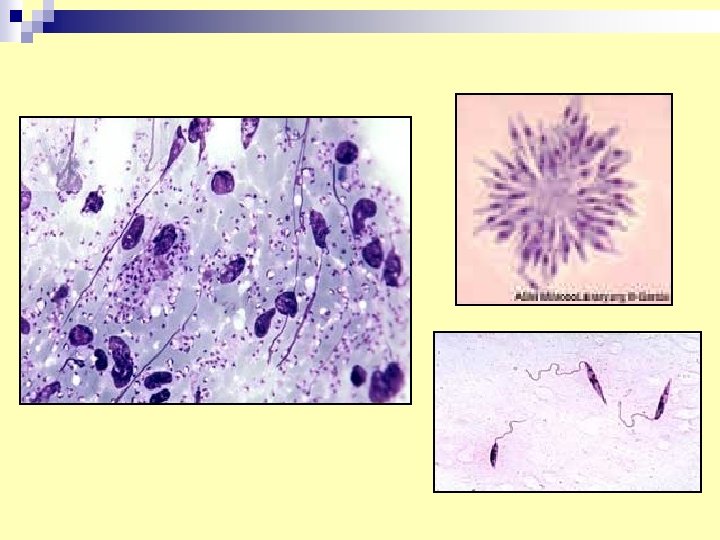
 n 13. Leishmania donovani bodies in smear (skin, B. M, spleen) (amastigotes) n Vector : sand fly. n Infective stage: promastigote. n for diagnosis of leishmaniasis Culture smear amastigotes from (skin , BM, spleen) on NNN media grow and multiply in promastigote form.
n 13. Leishmania donovani bodies in smear (skin, B. M, spleen) (amastigotes) n Vector : sand fly. n Infective stage: promastigote. n for diagnosis of leishmaniasis Culture smear amastigotes from (skin , BM, spleen) on NNN media grow and multiply in promastigote form.
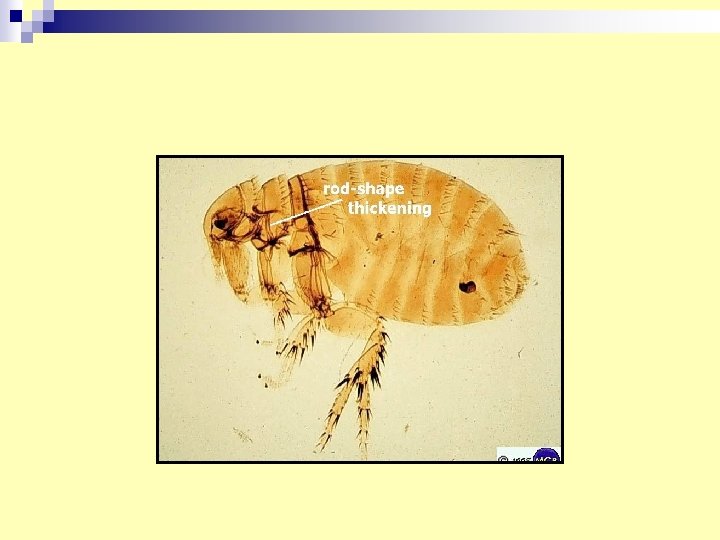
 14. Fleas n Medical importance: - Plague (Yerisinia pestis). - Murine (endemic )Typhus. -Tunga penetrance (chigger`s disease) Jigger`s
14. Fleas n Medical importance: - Plague (Yerisinia pestis). - Murine (endemic )Typhus. -Tunga penetrance (chigger`s disease) Jigger`s
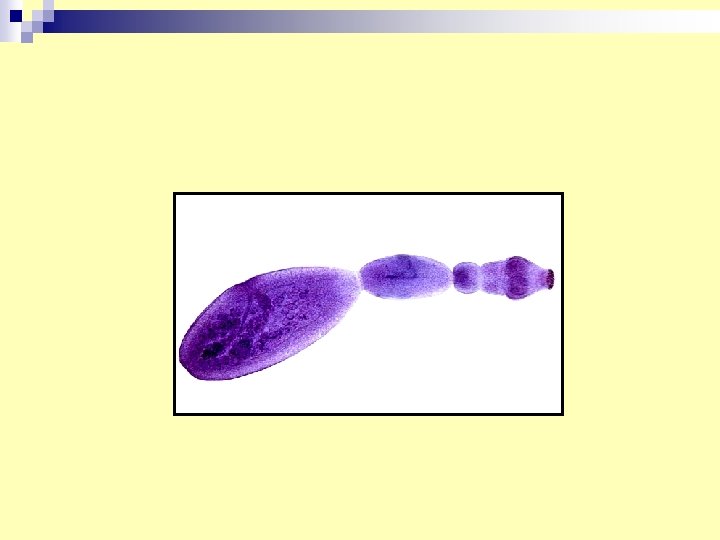
 15. Echinococcus granulosus adult n Dog cestode n Dog take infection after eating hydatid cyst (from infected animals). n Man get hydatid disease by ingestion of egg from infected dog.
15. Echinococcus granulosus adult n Dog cestode n Dog take infection after eating hydatid cyst (from infected animals). n Man get hydatid disease by ingestion of egg from infected dog.

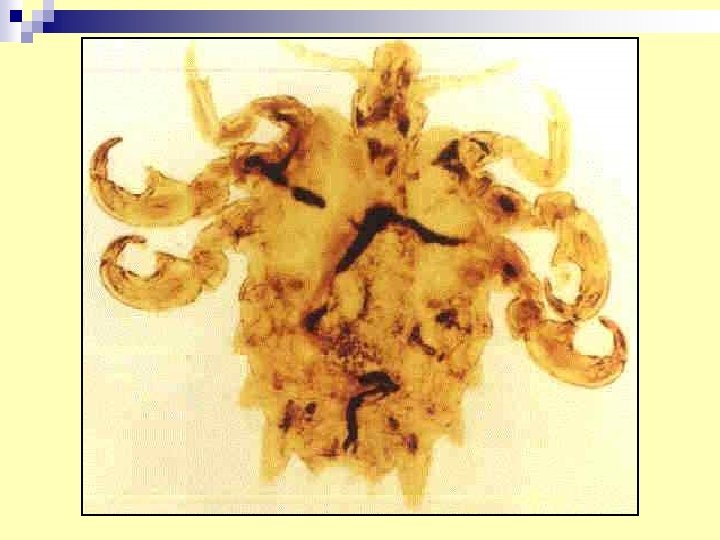
 16. Pediculus humanus (head and body lice) n Medical importance: - Epidemic typhus - Trench fever - Epidemic relapsing fever - Pediculosis
16. Pediculus humanus (head and body lice) n Medical importance: - Epidemic typhus - Trench fever - Epidemic relapsing fever - Pediculosis
 n. Diagnosis : nits visible by naked eye, and fluoresce under UV light (wood's lamp for screening). -
n. Diagnosis : nits visible by naked eye, and fluoresce under UV light (wood's lamp for screening). -
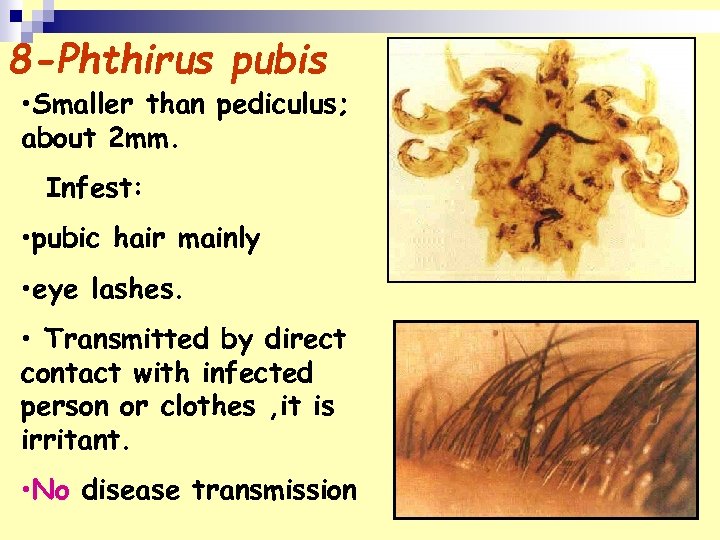 8 -Phthirus pubis • Smaller than pediculus; about 2 mm. Infest: • pubic hair mainly • eye lashes. • Transmitted by direct contact with infected person or clothes , it is irritant. • No disease transmission
8 -Phthirus pubis • Smaller than pediculus; about 2 mm. Infest: • pubic hair mainly • eye lashes. • Transmitted by direct contact with infected person or clothes , it is irritant. • No disease transmission
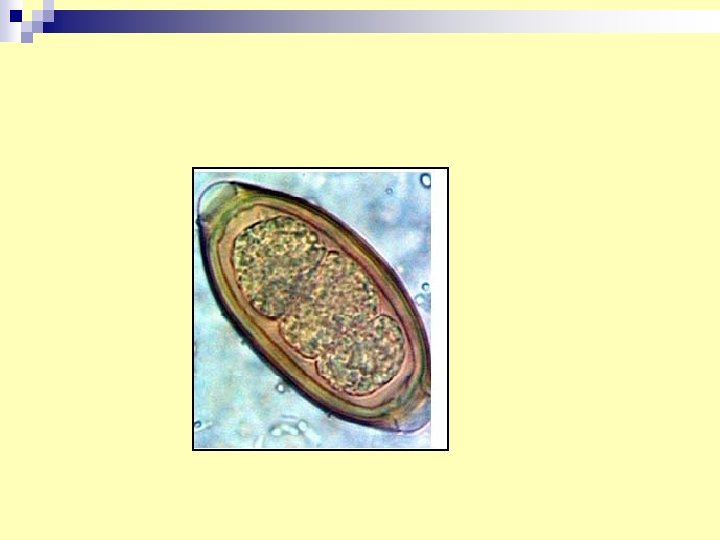
 17. Trichuris trichiura egg n Diagnosis : egg in stools. n Infective stage : embryonated egg.
17. Trichuris trichiura egg n Diagnosis : egg in stools. n Infective stage : embryonated egg.
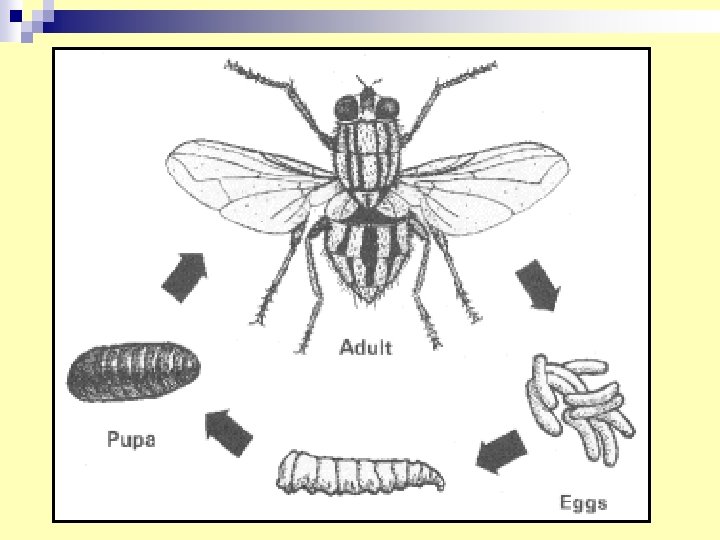
 18. Musca demostica Egg—larvae–- pupa--- adult. House fly developmental stage (Life cycle) n Medical importance mechanical transmation of virus, bacterial and parasitic diseases.
18. Musca demostica Egg—larvae–- pupa--- adult. House fly developmental stage (Life cycle) n Medical importance mechanical transmation of virus, bacterial and parasitic diseases.
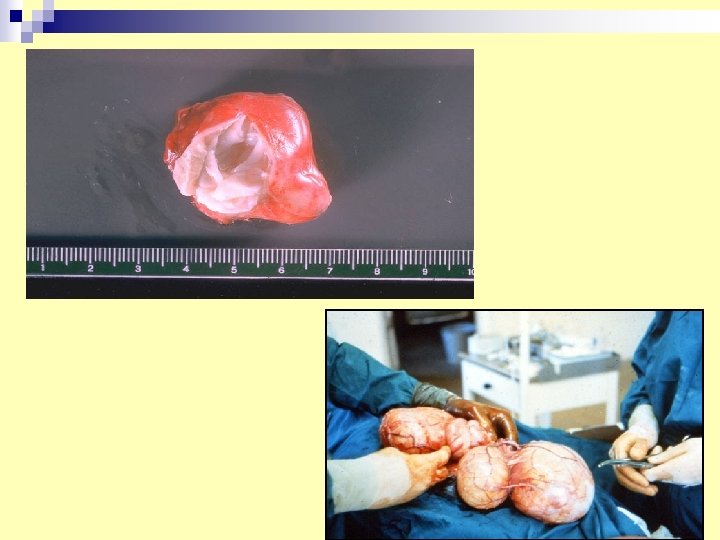
 19. Hydatid cyst in liver * diagnosis can confirmed by: n 1 - examination of hydatid fluid after surgical removal. n 2 - serology. * Infective stage: ingestion of Echinococcus egg (dog cestod).
19. Hydatid cyst in liver * diagnosis can confirmed by: n 1 - examination of hydatid fluid after surgical removal. n 2 - serology. * Infective stage: ingestion of Echinococcus egg (dog cestod).
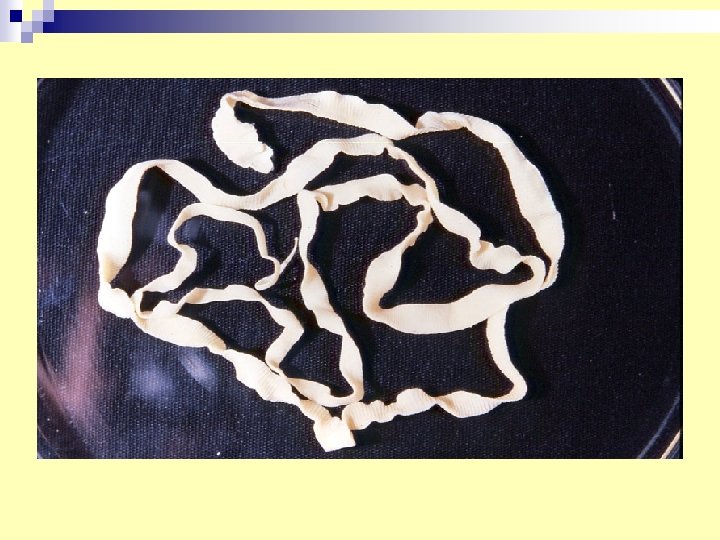
 20 -Taenia (tape worm) n T. saginata --cysticercus bovis in beef. n T. solium--cysticercus cellulose in pig. n Diagnosis ----eggs or gravid segment in stools.
20 -Taenia (tape worm) n T. saginata --cysticercus bovis in beef. n T. solium--cysticercus cellulose in pig. n Diagnosis ----eggs or gravid segment in stools.
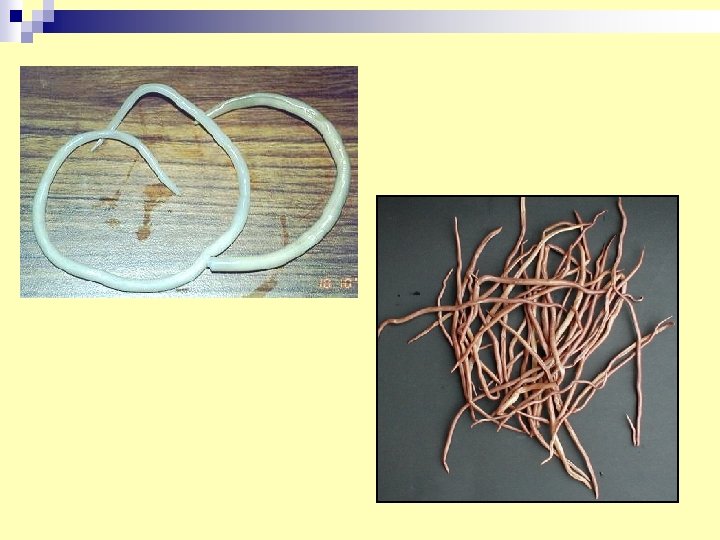

 21. Ascaris lumbricoid adult n Diagnosis : eggs in stools (sometime adult) n Infection : ingestion of embryonated egg. (soil transmitted disease) n Habitat : small intestine.
21. Ascaris lumbricoid adult n Diagnosis : eggs in stools (sometime adult) n Infection : ingestion of embryonated egg. (soil transmitted disease) n Habitat : small intestine.
 22. Ascaris lumbricoid Diagnosis : eggs in stools n Infective stage: embryonated egg. n
22. Ascaris lumbricoid Diagnosis : eggs in stools n Infective stage: embryonated egg. n
 23. N N N media n used in culture of Leishmania bodies (amastigote) n to diagnose leishmaniasis (visceral & cutaneous). n Amastigotes in smear or aspirate culture promastigotes.
23. N N N media n used in culture of Leishmania bodies (amastigote) n to diagnose leishmaniasis (visceral & cutaneous). n Amastigotes in smear or aspirate culture promastigotes.
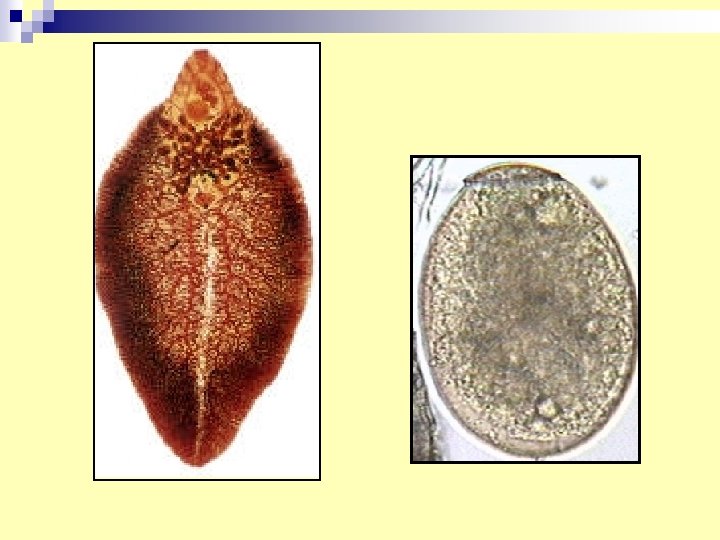
 24. Fasciola hepatica egg n diagnosis: finding egg by: -stools examination -duodenal aspirate n infective stage: encysted metacercaria n Adult habitat: biliary passage (liver)
24. Fasciola hepatica egg n diagnosis: finding egg by: -stools examination -duodenal aspirate n infective stage: encysted metacercaria n Adult habitat: biliary passage (liver)
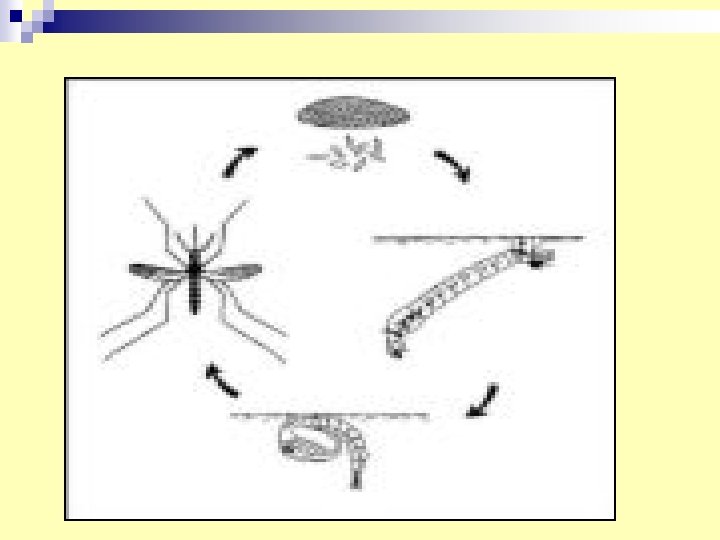
 25. Mosquitoe life cycle Egg—larvae–- pupa--- adult. Medical importance. n Anopheles: vector of malaria and filaria. n Culex : vector of filaria and viruses. n Aedes : (viruses) yellow fever, dengue and rift valley fever.
25. Mosquitoe life cycle Egg—larvae–- pupa--- adult. Medical importance. n Anopheles: vector of malaria and filaria. n Culex : vector of filaria and viruses. n Aedes : (viruses) yellow fever, dengue and rift valley fever.
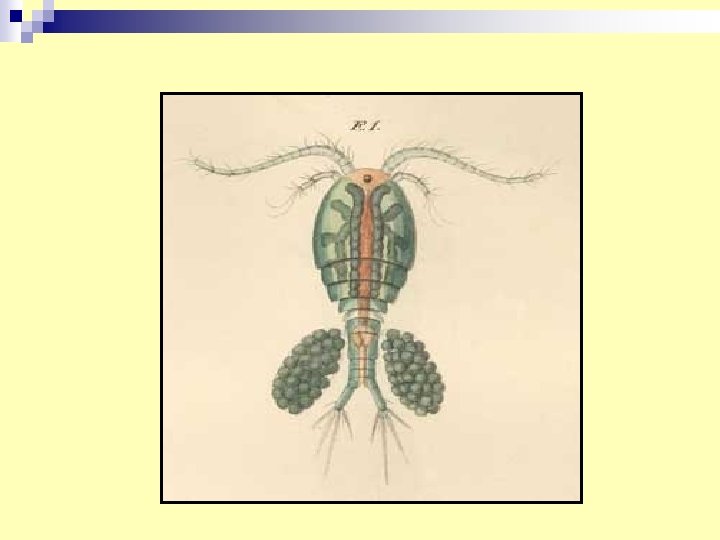
 26. Cyclops n Vector for transmission of Madina worm Dracunculus medinesis
26. Cyclops n Vector for transmission of Madina worm Dracunculus medinesis
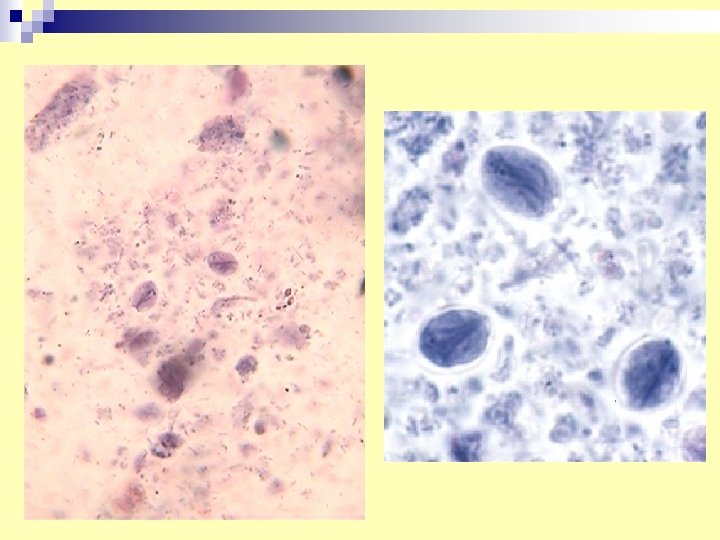
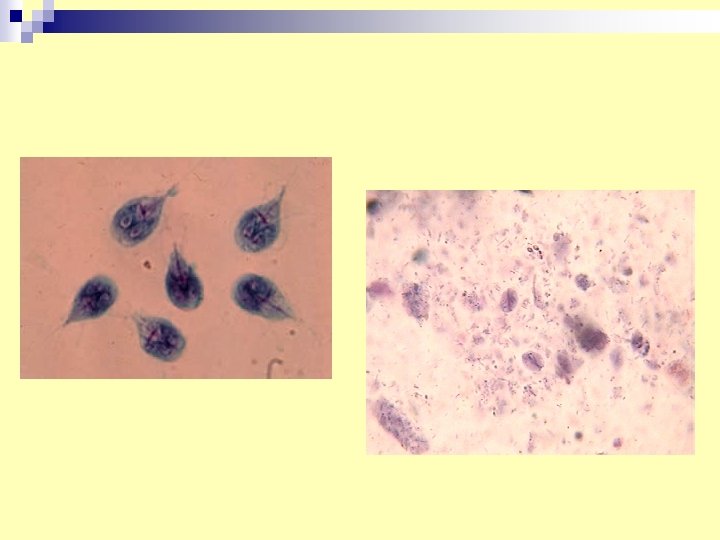
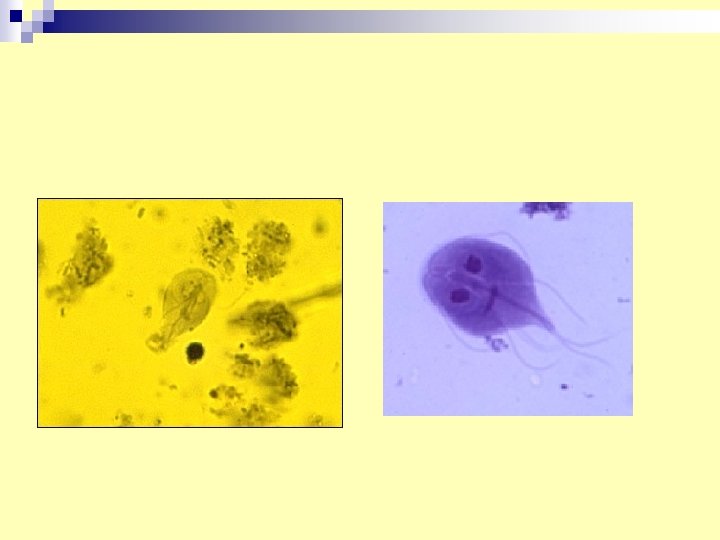
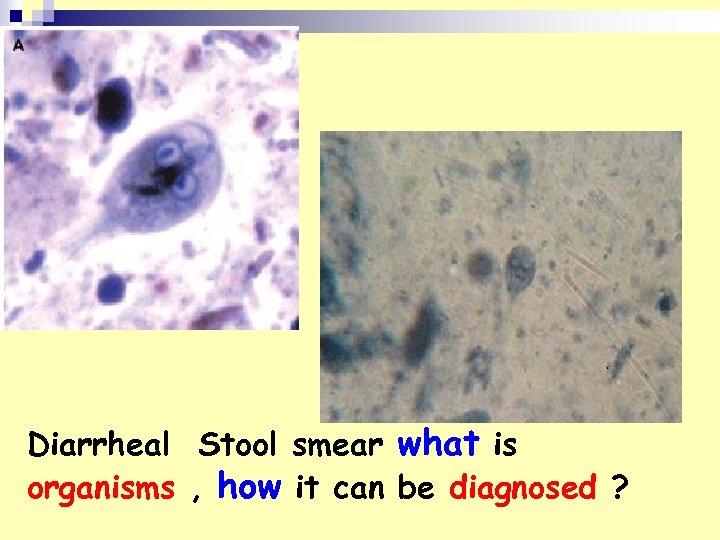 Diarrheal Stool smear what is organisms , how it can be diagnosed ?
Diarrheal Stool smear what is organisms , how it can be diagnosed ?
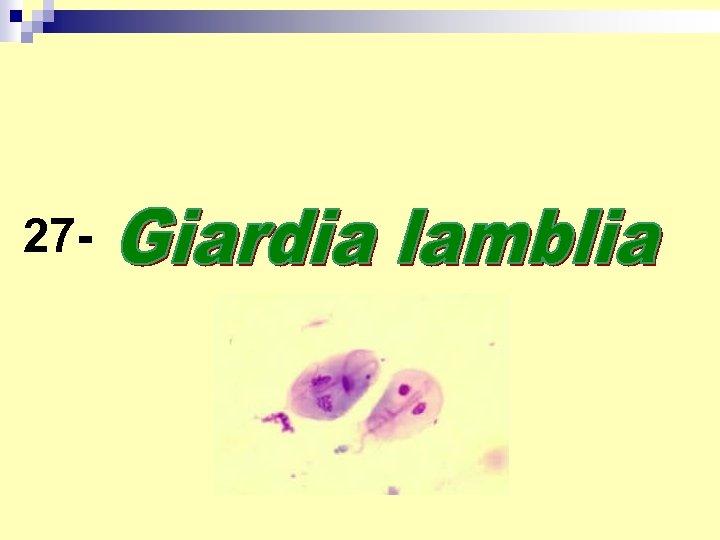 27 -
27 -
 n. Diagnosis -Stool examination daily for three days for cyst or trophozoites. -duodenal aspirate examination, or by string (enterotest)
n. Diagnosis -Stool examination daily for three days for cyst or trophozoites. -duodenal aspirate examination, or by string (enterotest)
 Feature of human intestinal nematodes n Adult live in intestinal tract. n Female are oviparous, i. e. lay eggs. n Humans are host of major intestinal nematodes of medical importance. n Most species are spread by fecal pollution of soil transmitted disease
Feature of human intestinal nematodes n Adult live in intestinal tract. n Female are oviparous, i. e. lay eggs. n Humans are host of major intestinal nematodes of medical importance. n Most species are spread by fecal pollution of soil transmitted disease
 n larvae (free or in egg) develops to its infective stage in soil. n Infection by n - swallowing of infective eggs. (A. lumbricoides , T. trichiura, E. vermicularis ) n - or penetration of skin by infective larvae (Hook worms , S. stercoralis) Larvae of A. lumbricoid , S. stercoralis and Hookworms (undergo heart to lung migration).
n larvae (free or in egg) develops to its infective stage in soil. n Infection by n - swallowing of infective eggs. (A. lumbricoides , T. trichiura, E. vermicularis ) n - or penetration of skin by infective larvae (Hook worms , S. stercoralis) Larvae of A. lumbricoid , S. stercoralis and Hookworms (undergo heart to lung migration).
 n filariform larvae is infective stage of S. stercoralis and Hookworm by penetration of skin. n Rabditiform larvae is used to describe larvae that hatch from egg in intestine (S. stercoralis ) or in soil in (hook worms).
n filariform larvae is infective stage of S. stercoralis and Hookworm by penetration of skin. n Rabditiform larvae is used to describe larvae that hatch from egg in intestine (S. stercoralis ) or in soil in (hook worms).
 n Laboratory confirmation: A. lumbricoid, T. trichiura, and Hookworms is by finding eggs in feces and with S. stercoralis by finding larvae in stool. n E. vermicularis by scotch tape from skin around anus. n Some time worms of A. lumbricodis and E. vermicularis can be recovered in stool.
n Laboratory confirmation: A. lumbricoid, T. trichiura, and Hookworms is by finding eggs in feces and with S. stercoralis by finding larvae in stool. n E. vermicularis by scotch tape from skin around anus. n Some time worms of A. lumbricodis and E. vermicularis can be recovered in stool.
 Feature of intestinal and tissue protozoa: n n Entamoeba histolytica, G. lamblia are motile organisms that multiply and encyst in intestinal tract. they form cyst which excreted in faces. Invasive strains of E histolytica multiply in intestinal wall. Cryptospordium multiply intracellular in cells. It produces oocysts which are excreted in feces. T. gondii muliply intracelluler in reticuloendothelial cell and cell of brain and other organs of body. T. vaginalis is motile and multiplies in the urogenital tract cyst forms are unknown.
Feature of intestinal and tissue protozoa: n n Entamoeba histolytica, G. lamblia are motile organisms that multiply and encyst in intestinal tract. they form cyst which excreted in faces. Invasive strains of E histolytica multiply in intestinal wall. Cryptospordium multiply intracellular in cells. It produces oocysts which are excreted in feces. T. gondii muliply intracelluler in reticuloendothelial cell and cell of brain and other organs of body. T. vaginalis is motile and multiplies in the urogenital tract cyst forms are unknown.
 Infection is by ingesting cysts (E. histolytica, G. lamblia) or n oocyst (Cryptosporidium, T. gondii) in food, water, or from hands contaminated with infected feces. T. gondii can also be transmitted congenitally and by ingesting the parasites in under-cooked meat of intermediate hosts. T. vaginalis is transmitted sexually (no cyst). Humans are important hosts of E. histolytica, G. lamblia and T. vaginalis. Animal are natural definitive hosts of Cryptosporidium and T. gondii. n
Infection is by ingesting cysts (E. histolytica, G. lamblia) or n oocyst (Cryptosporidium, T. gondii) in food, water, or from hands contaminated with infected feces. T. gondii can also be transmitted congenitally and by ingesting the parasites in under-cooked meat of intermediate hosts. T. vaginalis is transmitted sexually (no cyst). Humans are important hosts of E. histolytica, G. lamblia and T. vaginalis. Animal are natural definitive hosts of Cryptosporidium and T. gondii. n
 n n n Laboratory confirmation of E. histolytica infection is by finding amoebae or cysts in feces or by detecting antibodies in serum (invasive amoebiasis) Giardiasis diagnosed by finding motile flagellates or cysts in feces or flagellates in duodenal aspirates. Infection with Cryptosporidium is diagnosed by finding oocyst in feces Toxoplasmosis is usually diagnosed serologically. T. vaginalis infection is usually confirmed by detecting flagellates in vaginal or uretheral discharge or urine
n n n Laboratory confirmation of E. histolytica infection is by finding amoebae or cysts in feces or by detecting antibodies in serum (invasive amoebiasis) Giardiasis diagnosed by finding motile flagellates or cysts in feces or flagellates in duodenal aspirates. Infection with Cryptosporidium is diagnosed by finding oocyst in feces Toxoplasmosis is usually diagnosed serologically. T. vaginalis infection is usually confirmed by detecting flagellates in vaginal or uretheral discharge or urine

 n Pyrexia is not caused by: 1. Fascioliasis 2. Toxoplamosis 3. Oxyuriasis 4. Kala-azar
n Pyrexia is not caused by: 1. Fascioliasis 2. Toxoplamosis 3. Oxyuriasis 4. Kala-azar
 The following parasites cause fever except: 1. Trichinella spiralis 2. Naegleria fowleri 3. Hymenolepis nana 4. Plasmodium vivax.
The following parasites cause fever except: 1. Trichinella spiralis 2. Naegleria fowleri 3. Hymenolepis nana 4. Plasmodium vivax.
 Infection with Giardia lamblia is through: 1. Ingestion of trophozoite stage 2. Ingestion of cyst stage 3. Ingestion of oocyste 4. Ingestion of eggs
Infection with Giardia lamblia is through: 1. Ingestion of trophozoite stage 2. Ingestion of cyst stage 3. Ingestion of oocyste 4. Ingestion of eggs
 Parasite causing duodenites is: 1. 2. 3. 4. Giardia lamblia Entamoeba histolytica Toxoplasma Acanthamoeba
Parasite causing duodenites is: 1. 2. 3. 4. Giardia lamblia Entamoeba histolytica Toxoplasma Acanthamoeba
 There is lymphadenopathy in following infection EXCEPT 1. African trypanosomiasis 2. Toxoplasmosis 3. Schitosomiasis 4. Kala-azar
There is lymphadenopathy in following infection EXCEPT 1. African trypanosomiasis 2. Toxoplasmosis 3. Schitosomiasis 4. Kala-azar
 Splenomegaly not caused by: Schistosomaiasis 2. Malaria 3. Ascariasis 4. Kala-azar 1.
Splenomegaly not caused by: Schistosomaiasis 2. Malaria 3. Ascariasis 4. Kala-azar 1.
 The following diseases occur as zoonoses: 1. Fasciolasis hydatid disease 3. Toxoplasmosis 4. African trypanosomiasis 5. Cryptospordium 6. Plasmodium vivax 7. Leishmania major 2.
The following diseases occur as zoonoses: 1. Fasciolasis hydatid disease 3. Toxoplasmosis 4. African trypanosomiasis 5. Cryptospordium 6. Plasmodium vivax 7. Leishmania major 2.
 For treatment of clinical attack of malaria we can use 1. 2. 3. 4. 4 -aminoquinolines (chloroquine) Pentavalent antimonials 8 -aminoquinoline (primaquine) All of above
For treatment of clinical attack of malaria we can use 1. 2. 3. 4. 4 -aminoquinolines (chloroquine) Pentavalent antimonials 8 -aminoquinoline (primaquine) All of above
 For treatment of clinical relapse of P. vivax we can use 1. 4 -aminoquinolines 2. Pentavalent antimonials 3. 8 -aminoquinoline 4. All of above
For treatment of clinical relapse of P. vivax we can use 1. 4 -aminoquinolines 2. Pentavalent antimonials 3. 8 -aminoquinoline 4. All of above
 Duodenal aspirate is a good specimen for diagnosis of 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Taeniasis Giardiasis Amoebic dysentery Cysticercosis hydatidosis
Duodenal aspirate is a good specimen for diagnosis of 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Taeniasis Giardiasis Amoebic dysentery Cysticercosis hydatidosis
 Diagnosis by duodenal aspirate n Strongyloides stercoralis n Fasciolasis n Cryptospordium n Giardia pavarum. lamblia ( enterotest)
Diagnosis by duodenal aspirate n Strongyloides stercoralis n Fasciolasis n Cryptospordium n Giardia pavarum. lamblia ( enterotest)
 Regarding Hymenolepis nana 1. 2. 3. 4. Diagnosed by finding eggs in stools Dwarf tapeworm Autoinfection can occur. Cattle act as intermediate host
Regarding Hymenolepis nana 1. 2. 3. 4. Diagnosed by finding eggs in stools Dwarf tapeworm Autoinfection can occur. Cattle act as intermediate host
 The following parasite is not transmitted by direct contact with infected person autoinfection : 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Enterobius vermicularis. Trichella spiralis. Hymenolepis nana. Giardia lamblia. Entamoeba histolytica. Scabies (sarcoptes scabiei).
The following parasite is not transmitted by direct contact with infected person autoinfection : 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Enterobius vermicularis. Trichella spiralis. Hymenolepis nana. Giardia lamblia. Entamoeba histolytica. Scabies (sarcoptes scabiei).
 Splenomegaly is characteristic feature of one of following parasitic diseases: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Taeniasis malaria Scabies Myiasis Oriental sore.
Splenomegaly is characteristic feature of one of following parasitic diseases: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Taeniasis malaria Scabies Myiasis Oriental sore.
 Laboratory diagnosis of scabies is best done by 1. Serology 2. Blood examination 3. Skin scraping 4. Rectal biopsy 5. Faecal examination.
Laboratory diagnosis of scabies is best done by 1. Serology 2. Blood examination 3. Skin scraping 4. Rectal biopsy 5. Faecal examination.
 Skin myiasis is due to invesion of skin by: 1. 2. 3. 4. Sarcoptes scabiei Trematodes cercaria Lice Fly larvae
Skin myiasis is due to invesion of skin by: 1. 2. 3. 4. Sarcoptes scabiei Trematodes cercaria Lice Fly larvae
 n 1. 2. 3. 4. The following correct regarding scabies Transmitted by direct contact with infected person. Caused by mites Affects skin Diagnosed by stools examination
n 1. 2. 3. 4. The following correct regarding scabies Transmitted by direct contact with infected person. Caused by mites Affects skin Diagnosed by stools examination
 the following parasitic infection are water borne diseases except taenia saginata 2. madina worm 3. Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (Naegleria fowleri) 4. Schistosoma 5. Cryptospordium. 1.
the following parasitic infection are water borne diseases except taenia saginata 2. madina worm 3. Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (Naegleria fowleri) 4. Schistosoma 5. Cryptospordium. 1.
 Acanthamoeba species cause 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Chronic primary meningoencephalitis. Keratitis with blindness. contact lense Granuloma of internal organs and skin. All of above. Non of above.
Acanthamoeba species cause 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Chronic primary meningoencephalitis. Keratitis with blindness. contact lense Granuloma of internal organs and skin. All of above. Non of above.

 Following diseases transmitted by an arthropod vector: 1. 2. 3. 4. malaria Schistosomiasis cystocercosis Hydatid cyst.
Following diseases transmitted by an arthropod vector: 1. 2. 3. 4. malaria Schistosomiasis cystocercosis Hydatid cyst.