846dd053f847cfc318ff493326aea0b5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13

Specification and Verification of Trustworthy Component-Based Real-Time Reactive Systems Authors: Vasu Alagar and Mubarak Mohammad Concordia University Montréal, Canada Presented by: Mubarak Dubrovnik, Croatia, SAVCBS @ Mohammad 2007

Agenda w Context w Motivation w Contributions: – A formal methodology for developing trustworthy RTRS – Automatic generation of component behavior w Modeling Checking w Example w Conclusion SAVCBS @ Dubrovnik, Croatia, 2007 2
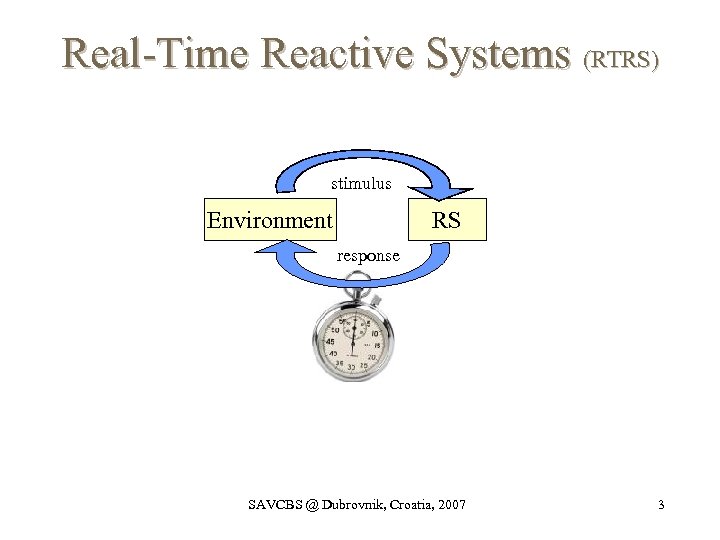
Real-Time Reactive Systems (RTRS) stimulus Environment RS response SAVCBS @ Dubrovnik, Croatia, 2007 3

Trustworthiness w A trustworthy system is a system that can be depended upon for quality of service. w RTRS are required to be trustworthy due to: – Their non-terminating behavior – The critical contexts it operate in w In order to trust, the credentials of trust should be defined and examined: – Safety – Security SAVCBS @ Dubrovnik, Croatia, 2007 4
![Component-Based Development (CBD) w Advantages [1]: – – Reusability Managing design complexity Reducing time Component-Based Development (CBD) w Advantages [1]: – – Reusability Managing design complexity Reducing time](https://present5.com/presentation/846dd053f847cfc318ff493326aea0b5/image-5.jpg)
Component-Based Development (CBD) w Advantages [1]: – – Reusability Managing design complexity Reducing time and effort Increasing productivity w Trustworthy component: a component that guarantees safe and secure interactions. [1] Ivica Crnkovic and Magnus Larsson, editors. building reliable component-based Software Systems. Artech House Publishers, 2002. SAVCBS @ Dubrovnik, Croatia, 2007 5

Motivation w The design of RTRS should rely on rigorous formal model to be formally verifiable. w Provide a formal approach for the development of trustworthy component-based RTRS. SAVCBS @ Dubrovnik, Croatia, 2007 6
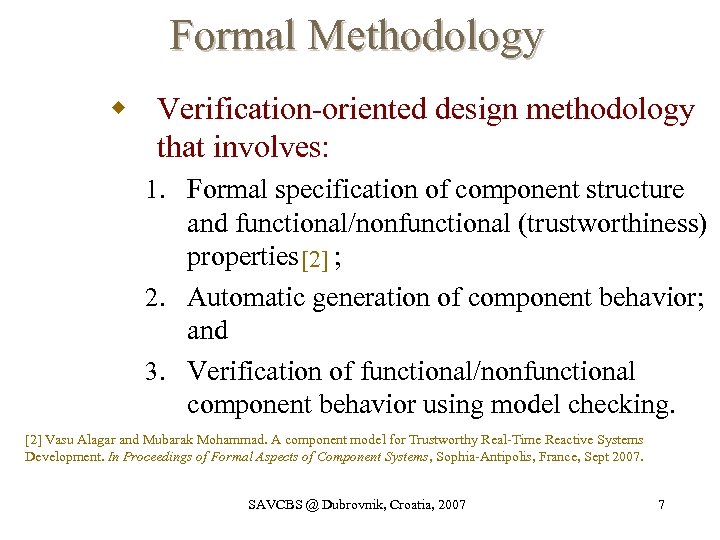
Formal Methodology w Verification-oriented design methodology that involves: 1. Formal specification of component structure and functional/nonfunctional (trustworthiness) properties [2] ; 2. Automatic generation of component behavior; and 3. Verification of functional/nonfunctional component behavior using model checking. [2] Vasu Alagar and Mubarak Mohammad. A component model for Trustworthy Real-Time Reactive Systems Development. In Proceedings of Formal Aspects of Component Systems, Sophia-Antipolis, France, Sept 2007. SAVCBS @ Dubrovnik, Croatia, 2007 7
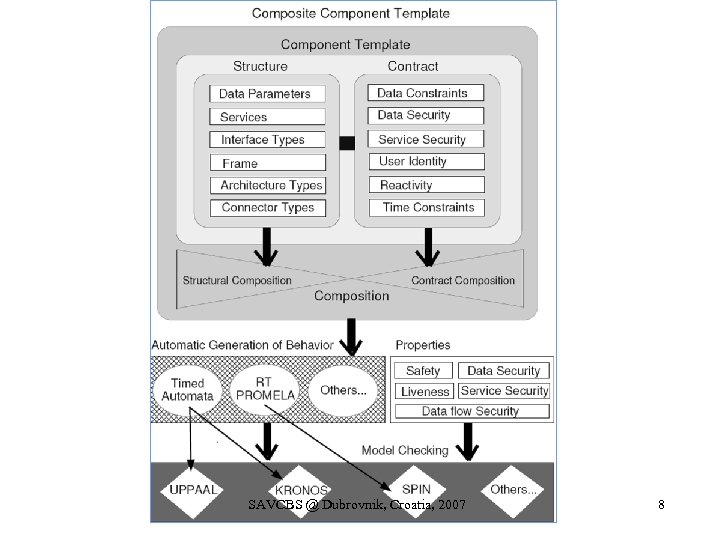
SAVCBS @ Dubrovnik, Croatia, 2007 8
![UPPAAL Modeling Language [3] w. Time Automata (L, l 0, K, A, E, I) UPPAAL Modeling Language [3] w. Time Automata (L, l 0, K, A, E, I)](https://present5.com/presentation/846dd053f847cfc318ff493326aea0b5/image-9.jpg)
UPPAAL Modeling Language [3] w. Time Automata (L, l 0, K, A, E, I) – L is a set of locations denoting states; – l 0 is the initial location; – K is a set of clocks; – A is a set of actions, events causing transitions; – E is a set of edges, transition specifications; and – I is a function assigning clock constraints to locations as invariants. [3] Gerd Behrmann, Alexandre David, and Kim G Larsen. A tutorial on UPPAAL. In Proceedings of SFM-RT’ 04, 2004. SAVCBS @ Dubrovnik, Croatia, 2007 9
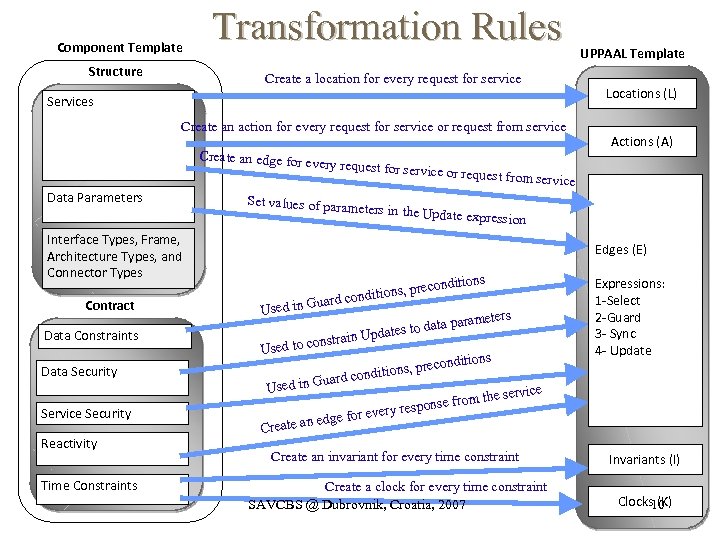
Component Template Structure Transformation Rules Create a location for every request for service Locations (L) Services Create an action for every request for service or request from service Create an edge for ev ery request for serv Data Parameters ice or request from Set values of param eters in the Update Interface Types, Frame, Architecture Types, and Connector Types Contract Data Constraints Data Security Service Security Reactivity Time Constraints UPPAAL Template Actions (A) service expression Edges (E) Used in G uard c , precon onditions data para pdates to in U meters onstra Used to c Used in G onditions, prec rd condit ua or every edge f Create an Expressions: 1 -Select 2 -Guard 3 - Sync 4 - Update e service from th response Create an invariant for every time constraint Invariants (I) Create a clock for every time constraint SAVCBS @ Dubrovnik, Croatia, 2007 Clocks 10 (K)
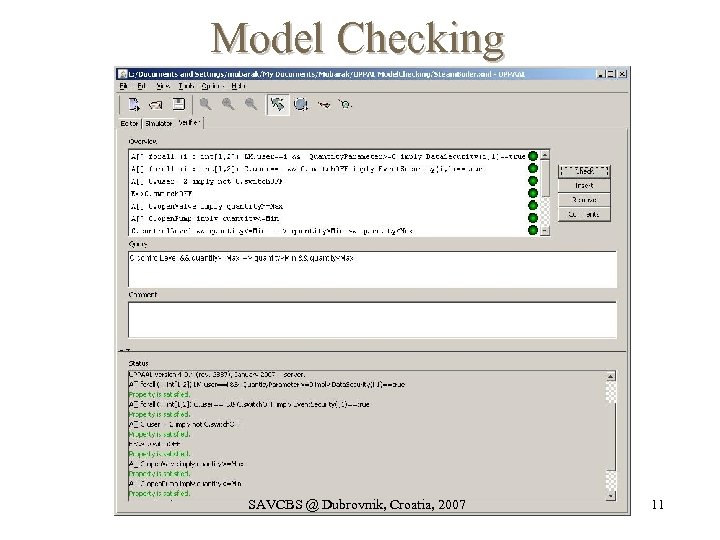
Model Checking SAVCBS @ Dubrovnik, Croatia, 2007 11
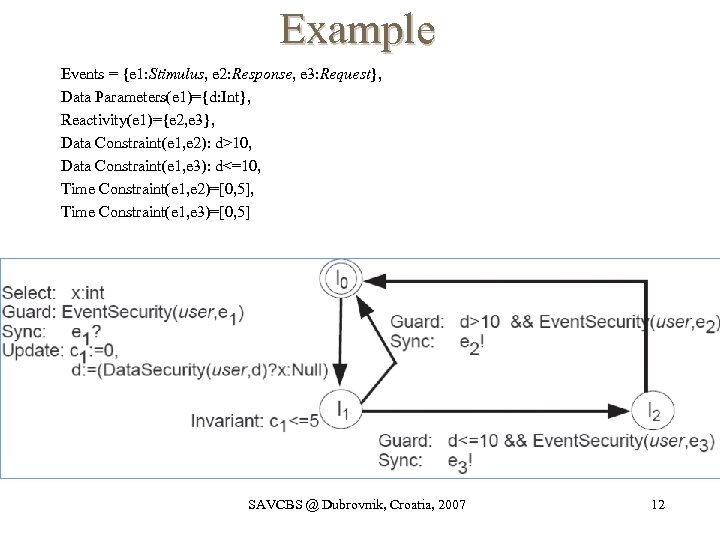
Example Events = {e 1: Stimulus, e 2: Response, e 3: Request}, Data Parameters(e 1)={d: Int}, Reactivity(e 1)={e 2, e 3}, Data Constraint(e 1, e 2): d>10, Data Constraint(e 1, e 3): d<=10, Time Constraint(e 1, e 2)=[0, 5], Time Constraint(e 1, e 3)=[0, 5] SAVCBS @ Dubrovnik, Croatia, 2007 12

Conclusion w We plan to evaluate our method on problems from different domains where safety and security are critical. w We are investigating the requirements of a trustworthy ADL. w We are building a visual interface tool for designing trustworthy RTRS. SAVCBS @ Dubrovnik, Croatia, 2007 13
846dd053f847cfc318ff493326aea0b5.ppt