77902a0c3ecb6f962c14465c93a4c3cd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 108
 Specific Representation Topics NFFE Forest Service Council
Specific Representation Topics NFFE Forest Service Council
 Position Descriptions n Performance Management n Unacceptable Performance n Discipline and Adverse Actions n Reasonable Accommodation n Hostile Work Environment n Non-selection n Work Schedules n
Position Descriptions n Performance Management n Unacceptable Performance n Discipline and Adverse Actions n Reasonable Accommodation n Hostile Work Environment n Non-selection n Work Schedules n
 Article 14: Position Descriptions (See also Article 16)
Article 14: Position Descriptions (See also Article 16)
 Position Descriptions A great way for the Local to serve employees who are NOT in trouble! n Employees should have accurate PDs n PDs should be well-written to ensure accurate classification n Two parts n
Position Descriptions A great way for the Local to serve employees who are NOT in trouble! n Employees should have accurate PDs n PDs should be well-written to ensure accurate classification n Two parts n
 Position Descriptions n An accurate Position Description involves two parts: ¨ Accurate PD ¨ Accurate Classification
Position Descriptions n An accurate Position Description involves two parts: ¨ Accurate PD ¨ Accurate Classification
 Step 1 – Accurate Position Description n Accurate PD includes ¨ Title, series, and grade ¨ Major duties that are reflected in performance elements. n Must describe ¨ principal duties, ¨ knowledge requirements, and ¨ supervisory relationships are described, and n Must cover 80 percent or more of the work situation.
Step 1 – Accurate Position Description n Accurate PD includes ¨ Title, series, and grade ¨ Major duties that are reflected in performance elements. n Must describe ¨ principal duties, ¨ knowledge requirements, and ¨ supervisory relationships are described, and n Must cover 80 percent or more of the work situation.
 Step 1 – Accurate Position Description Standard PDs n Listings of Standard PDs (and some of the PDs) are on the HCM website: http: //fsweb. hcm. fs. fed. us/classification/ASPD_Lib rary. php ¨ Ones that are not on the website are available in AVUE ¨ To get copies, you can: n n Get AVUE Access Ask HRL to give you the PDs Ask supervisor or admin assistant who has manager access to AVUE to get you a copy. Call the HR Helpdesk and open a case
Step 1 – Accurate Position Description Standard PDs n Listings of Standard PDs (and some of the PDs) are on the HCM website: http: //fsweb. hcm. fs. fed. us/classification/ASPD_Lib rary. php ¨ Ones that are not on the website are available in AVUE ¨ To get copies, you can: n n Get AVUE Access Ask HRL to give you the PDs Ask supervisor or admin assistant who has manager access to AVUE to get you a copy. Call the HR Helpdesk and open a case
 Step 1 – Accurate Position Description Individual PDs n Generally, all PDs are now created in AVUE. Search for relevant duties Select and assign amounts of time that the employee performs duties ¨ Evaluate and answer questions about the position (e. g. is a CDL required, is it in the bargaining unit) ¨ ¨ n OPM Classification Standards – Online at: http: //www. opm. gov/fedclass/index. htm
Step 1 – Accurate Position Description Individual PDs n Generally, all PDs are now created in AVUE. Search for relevant duties Select and assign amounts of time that the employee performs duties ¨ Evaluate and answer questions about the position (e. g. is a CDL required, is it in the bargaining unit) ¨ ¨ n OPM Classification Standards – Online at: http: //www. opm. gov/fedclass/index. htm
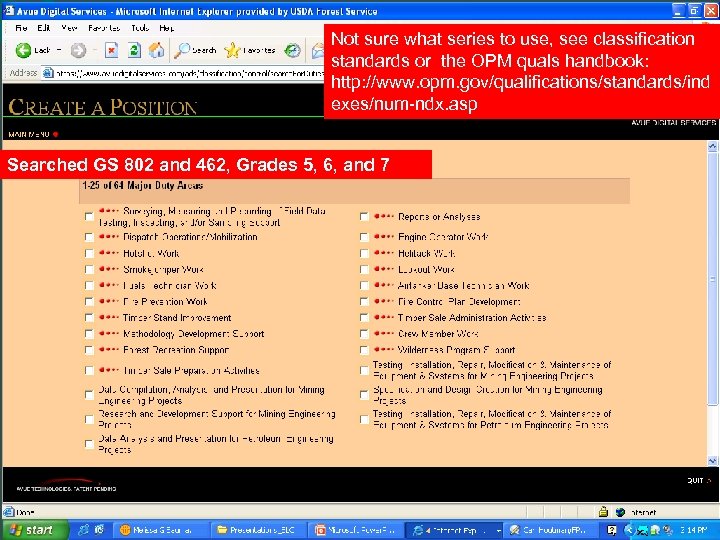 Not sure what series to use, see classification standards or the OPM quals handbook: http: //www. opm. gov/qualifications/standards/ind exes/num-ndx. asp Searched GS 802 and 462, Grades 5, 6, and 7
Not sure what series to use, see classification standards or the OPM quals handbook: http: //www. opm. gov/qualifications/standards/ind exes/num-ndx. asp Searched GS 802 and 462, Grades 5, 6, and 7
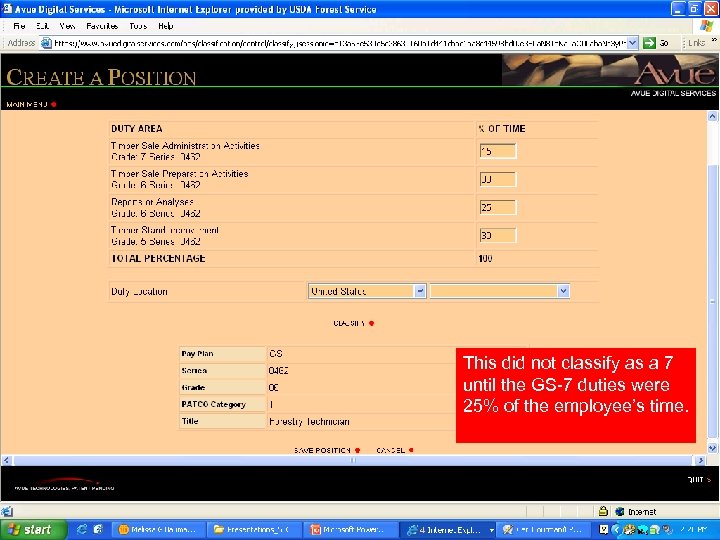 This did not classify as a 7 until the GS-7 duties were 25% of the employee’s time.
This did not classify as a 7 until the GS-7 duties were 25% of the employee’s time.

 Step 1 – Accurate Position Description n The accuracy of a position description is grievable: ¨ Are there duties that the employee is doing that are not in the PD? ¨ Is the supervisory relationship accurately described? ¨ Is the nature and purpose of contacts accurately described? ¨ Etc. ¨ NOT – Is the PD classified correctly?
Step 1 – Accurate Position Description n The accuracy of a position description is grievable: ¨ Are there duties that the employee is doing that are not in the PD? ¨ Is the supervisory relationship accurately described? ¨ Is the nature and purpose of contacts accurately described? ¨ Etc. ¨ NOT – Is the PD classified correctly?
 Article 14. 3 – PD Review Procedure a. Employee may request PD review in writing to immediate supervisor. 45 -day time limit for: n n n Employee to submit inaccuracies/omissions to supervisor Supervisor to prepare the new PD Supervisor to submit PD review package to HRM b. Management may initiate PD changes and will consider feedback from employee prior to submitting PD for classification
Article 14. 3 – PD Review Procedure a. Employee may request PD review in writing to immediate supervisor. 45 -day time limit for: n n n Employee to submit inaccuracies/omissions to supervisor Supervisor to prepare the new PD Supervisor to submit PD review package to HRM b. Management may initiate PD changes and will consider feedback from employee prior to submitting PD for classification
 Classification n After the PD review package is submitted, Human Resources classifies the PD. Classification is the task of assigning a series and grade to the PD. DO NOT submit a poor or inaccurate PD to be classified. ¨ If PD is inaccurate, and management will not change it, file a grievance prior to classification ¨ If PD is poorly written it is harder to classify, and hard to get fixed after a “bad” classification. n Classification may include interviews with the employee.
Classification n After the PD review package is submitted, Human Resources classifies the PD. Classification is the task of assigning a series and grade to the PD. DO NOT submit a poor or inaccurate PD to be classified. ¨ If PD is inaccurate, and management will not change it, file a grievance prior to classification ¨ If PD is poorly written it is harder to classify, and hard to get fixed after a “bad” classification. n Classification may include interviews with the employee.
 Article 14. 3 – PD Review/Class c. PD classification will be communicated to the employee within 45 days of submission d. Employee may have union representation during discussions related to review and classification f. Management will not reassign work during PD review just to avoid reclassification e. Accuracy of the PD is a grievable issue
Article 14. 3 – PD Review/Class c. PD classification will be communicated to the employee within 45 days of submission d. Employee may have union representation during discussions related to review and classification f. Management will not reassign work during PD review just to avoid reclassification e. Accuracy of the PD is a grievable issue
 14. 4 -- Classification Review/Appeal Classification decisions cannot be grieved, only appealed. n Agency appeal n ¨ Higher in FS ¨ USDA n Office of Personnel Management appeal ¨ Generally, not recommended ¨ Decisions by OPM can result in downgrade, and may be applied to other similar PDs in the Forest Service.
14. 4 -- Classification Review/Appeal Classification decisions cannot be grieved, only appealed. n Agency appeal n ¨ Higher in FS ¨ USDA n Office of Personnel Management appeal ¨ Generally, not recommended ¨ Decisions by OPM can result in downgrade, and may be applied to other similar PDs in the Forest Service.
 What may be appealed: grade n series n sometimes the title; and n the pay system of your position (GS or FWS/WG). n
What may be appealed: grade n series n sometimes the title; and n the pay system of your position (GS or FWS/WG). n
 What may not be appealed: n n n the content or accuracy of PD the accuracy of a classification standard an agency's proposed classification decision the classification of a position to which you are not officially assigned; or the classification of a position to which you are detailed or temporarily promoted for a period of less than two years.
What may not be appealed: n n n the content or accuracy of PD the accuracy of a classification standard an agency's proposed classification decision the classification of a position to which you are not officially assigned; or the classification of a position to which you are detailed or temporarily promoted for a period of less than two years.
 14. 5 – Class at higher grade n If PD review and classification results in a higher grade management will either ¨ Decide to redistribute or eliminate the duties within 14 days of the review. ¨ If duties cannot be removed within 14 days, employee will be given a temporary promotion until duties can be removed. ¨ Promote the employee according to Article 16, generally beginning the first pay period after the classification action. ¨ NOTE: Article 16 has
14. 5 – Class at higher grade n If PD review and classification results in a higher grade management will either ¨ Decide to redistribute or eliminate the duties within 14 days of the review. ¨ If duties cannot be removed within 14 days, employee will be given a temporary promotion until duties can be removed. ¨ Promote the employee according to Article 16, generally beginning the first pay period after the classification action. ¨ NOTE: Article 16 has
 Article 16. 6 Do-loop prevention n If, in accordance with Article 14 Section 5, Management elects to remove the higher graded duties rather than promoting the employee and the duties are later reassigned to the employee without an appropriate promotion, the employee is not required to repeat the position description and classification review procedures in Article 14 before moving directly to either the grievance procedures or classification appeal process.
Article 16. 6 Do-loop prevention n If, in accordance with Article 14 Section 5, Management elects to remove the higher graded duties rather than promoting the employee and the duties are later reassigned to the employee without an appropriate promotion, the employee is not required to repeat the position description and classification review procedures in Article 14 before moving directly to either the grievance procedures or classification appeal process.
 16. 6 Accretion of Duties n An accretion occurs when employee has been performing grade-controlling duties classified at a higher grade level for an extended period of time. Criteria are: ¨ Not moving from nonsup/lead to sup or lead; ¨ Old duties are absorbed into the new position; ¨ The expanded duties are within the scope of the work of the organizational unit; and ¨ Other positions within the supervisory unit are not adversely affected. A “supervisory unit” is typically the lowest level of an organizational unit where like work is performed.
16. 6 Accretion of Duties n An accretion occurs when employee has been performing grade-controlling duties classified at a higher grade level for an extended period of time. Criteria are: ¨ Not moving from nonsup/lead to sup or lead; ¨ Old duties are absorbed into the new position; ¨ The expanded duties are within the scope of the work of the organizational unit; and ¨ Other positions within the supervisory unit are not adversely affected. A “supervisory unit” is typically the lowest level of an organizational unit where like work is performed.
 I didn’t get the job! (See Article 16)
I didn’t get the job! (See Article 16)
 Didn’t get a job they applied for n n Non-certification -- Employee didn’t make the certificate of candidates. (Employee was not referred to the hiring official. ) Not qualified: Determination of whether the OPM Qualification Standards were appropriately applied. ¨ http: //www. opm. gov/qualifications/index. asp ¨ n Qualified, but not in the quality group This is a frequent issue with AVUE. ¨ Management can ask for a hand review of applicants if they believe that a quality candidate applied but didn’t make the cert. ¨ The FSPC is working on an appeal process for employees who do not make the “Quality” group. ¨
Didn’t get a job they applied for n n Non-certification -- Employee didn’t make the certificate of candidates. (Employee was not referred to the hiring official. ) Not qualified: Determination of whether the OPM Qualification Standards were appropriately applied. ¨ http: //www. opm. gov/qualifications/index. asp ¨ n Qualified, but not in the quality group This is a frequent issue with AVUE. ¨ Management can ask for a hand review of applicants if they believe that a quality candidate applied but didn’t make the cert. ¨ The FSPC is working on an appeal process for employees who do not make the “Quality” group. ¨
 Didn’t get a job they applied for n Non-selection ¨ Employee made the “cert, ” but was not selected. ¨ Very difficult to win. ¨ Management has the right to hire and it is understood that selection decisions can be very subjective. ¨ Generally the manager can pick from among the “quality” candidates.
Didn’t get a job they applied for n Non-selection ¨ Employee made the “cert, ” but was not selected. ¨ Very difficult to win. ¨ Management has the right to hire and it is understood that selection decisions can be very subjective. ¨ Generally the manager can pick from among the “quality” candidates.
 Non-certification n FS Demo procedure ¨ 1 st level - Request in writing to office which made the decision ¨ 2 nd level – Request in writing to next higher office (RO or WO) ¨ If appeal is successful, candidate is given priority consideration for next position in same location which comes open n Merit Promotion procedure ¨ File Grievance ¨ Appeal to higher level in Agency? ?
Non-certification n FS Demo procedure ¨ 1 st level - Request in writing to office which made the decision ¨ 2 nd level – Request in writing to next higher office (RO or WO) ¨ If appeal is successful, candidate is given priority consideration for next position in same location which comes open n Merit Promotion procedure ¨ File Grievance ¨ Appeal to higher level in Agency? ?
 Non-Selection n Both Demo and Merit Promotion ¨ File a grievance over the issue ¨ EEO if non-selection is based on race, sex, age, etc. n n n Very hard to win, unless there was a “pass-over” of an eligible veteran under demo. May be able to address procedural errors Management does not have to hire the MOST qualified. They select among those who are well -qualified.
Non-Selection n Both Demo and Merit Promotion ¨ File a grievance over the issue ¨ EEO if non-selection is based on race, sex, age, etc. n n n Very hard to win, unless there was a “pass-over” of an eligible veteran under demo. May be able to address procedural errors Management does not have to hire the MOST qualified. They select among those who are well -qualified.
 Article 16. 2. e – Notifications to Applicants n Employees will be informed in writing ¨ whether or not their application has been referred to the selecting official and ¨ whether or not they meet qualifications for the position. n Notification will include who the employee should respond to if requesting a review.
Article 16. 2. e – Notifications to Applicants n Employees will be informed in writing ¨ whether or not their application has been referred to the selecting official and ¨ whether or not they meet qualifications for the position. n Notification will include who the employee should respond to if requesting a review.
 Article 16. 2. e – Review Procedure Within 3 days of receipt, employee may request a review. n Upon such request, Management will perform an independent review of the qualification determination and provide a written explanation within 14 days. n
Article 16. 2. e – Review Procedure Within 3 days of receipt, employee may request a review. n Upon such request, Management will perform an independent review of the qualification determination and provide a written explanation within 14 days. n
 Article 15 Performance Management
Article 15 Performance Management
 Performance Management n Good performance management requires communication about: ¨ Expectations ¨ How employees are meeting expectations Employees should be encouraged to participate in performance discussions, both at the beginning and end of rating period. n The rules are in FSH 6109. 13, 10 n
Performance Management n Good performance management requires communication about: ¨ Expectations ¨ How employees are meeting expectations Employees should be encouraged to participate in performance discussions, both at the beginning and end of rating period. n The rules are in FSH 6109. 13, 10 n
 Performance Management n Each bargaining unit employee should have 3 performance elements ¨ Mission/results (critical) ¨ Managing work assignments (critical) ¨ Teamwork and partnerships (noncritical) Elements are broken down into standards. n Standards are further described by measures. n
Performance Management n Each bargaining unit employee should have 3 performance elements ¨ Mission/results (critical) ¨ Managing work assignments (critical) ¨ Teamwork and partnerships (noncritical) Elements are broken down into standards. n Standards are further described by measures. n
 Performance Standards n n n A Standard is the expression of the performance threshold(s), requirement(s), or expectation(s) that must be met to be appraised at a particular level of performance. The generic standards should be used unless they don’t address a significant component of the employee’s responsibilities. Rating officials are to use an absolute standard (a standard that allows for no margin of error), in only very limited circumstances, such as where failure to perform under a critical element could result in loss of life, injury, breach of national security, or great monetary loss.
Performance Standards n n n A Standard is the expression of the performance threshold(s), requirement(s), or expectation(s) that must be met to be appraised at a particular level of performance. The generic standards should be used unless they don’t address a significant component of the employee’s responsibilities. Rating officials are to use an absolute standard (a standard that allows for no margin of error), in only very limited circumstances, such as where failure to perform under a critical element could result in loss of life, injury, breach of national security, or great monetary loss.
 Performance Measures n n n Measures quantify or qualify the desired result or behavior described in a performance standard. Employee and supervisor develop the measures. Performance measures must be SMART: ¨ ¨ ¨ n n Specific Measurable Attainable Relevant and Reasonable Time-bound Employees must be told what it takes to meet and exceed each element. During the rating period an employee may request a change to performance measures based on mitigating factors.
Performance Measures n n n Measures quantify or qualify the desired result or behavior described in a performance standard. Employee and supervisor develop the measures. Performance measures must be SMART: ¨ ¨ ¨ n n Specific Measurable Attainable Relevant and Reasonable Time-bound Employees must be told what it takes to meet and exceed each element. During the rating period an employee may request a change to performance measures based on mitigating factors.
 Union role in Performance Management n n Ensure that policy is being followed. You may grieve failure to follow the policy. Performance standards and elements generally are not grievable, but application of elements/standards is. Performance discussions are not considered formal meetings. However, if you have a good relationship with management, they may see value in including you in the meetings.
Union role in Performance Management n n Ensure that policy is being followed. You may grieve failure to follow the policy. Performance standards and elements generally are not grievable, but application of elements/standards is. Performance discussions are not considered formal meetings. However, if you have a good relationship with management, they may see value in including you in the meetings.
 Article 15 Provisions n 3. Performance Ratings for Union Officials: ¨ Employees who are Union officials are not rated for their Union duties. ¨ Union Official’s performance expectations will be adjusted for official time used to perform representational work.
Article 15 Provisions n 3. Performance Ratings for Union Officials: ¨ Employees who are Union officials are not rated for their Union duties. ¨ Union Official’s performance expectations will be adjusted for official time used to perform representational work.
 Article 21 Dealing With Unacceptable Performance
Article 21 Dealing With Unacceptable Performance
 Performance-based actions Unacceptable or marginal performance rating n Withholding WGI n Demotion n Removal n
Performance-based actions Unacceptable or marginal performance rating n Withholding WGI n Demotion n Removal n
 Marginal and Unacceptable performance ratings n n Marginal summary rating given when an employee’s performance is unacceptable in a non-critical element Unacceptable summary rating when performance is unacceptable in a critical element. Unacceptable performance rating cannot be given without first placing an employee on a Performance Improvement Plan If an employee is on a PIP at the normal appraisal time, the appraisal will be delayed.
Marginal and Unacceptable performance ratings n n Marginal summary rating given when an employee’s performance is unacceptable in a non-critical element Unacceptable summary rating when performance is unacceptable in a critical element. Unacceptable performance rating cannot be given without first placing an employee on a Performance Improvement Plan If an employee is on a PIP at the normal appraisal time, the appraisal will be delayed.
 Performance-based Actions n (5 CFR 432) Any time an agency becomes aware that an employee’s performance is unacceptable ¨ The n n agency must notify the employee Elements that are unacceptable, and what needs to be done to correct deficiencies Consequences of not improving performance ¨ Agency must provide reasonable opportunity for employee to improve performance ¨ Agency must assist the employee
Performance-based Actions n (5 CFR 432) Any time an agency becomes aware that an employee’s performance is unacceptable ¨ The n n agency must notify the employee Elements that are unacceptable, and what needs to be done to correct deficiencies Consequences of not improving performance ¨ Agency must provide reasonable opportunity for employee to improve performance ¨ Agency must assist the employee
 Article 21 – Unacceptable Performance n Prior to initiating performance-based removal or downgrade, the employee must be notified in writing and be given performance improvement plan. PIP must include: How long the PIP will be in place. ¨ What elements and standards are deficient. ¨ Actions require to improve. ¨ What management will do to assist the employee. ¨ Potential consequences of failure. ¨ Employee Assistance Referral. ¨
Article 21 – Unacceptable Performance n Prior to initiating performance-based removal or downgrade, the employee must be notified in writing and be given performance improvement plan. PIP must include: How long the PIP will be in place. ¨ What elements and standards are deficient. ¨ Actions require to improve. ¨ What management will do to assist the employee. ¨ Potential consequences of failure. ¨ Employee Assistance Referral. ¨
 During and After the PIP n n n Rating Official will meet regularly with the employee, and Union representative may attend PIP meetings. Within 14 days of the end of the opportunity period, employee will be notified in writing whether their performance has improved to the successful level. Employee will be notified within 14 days after end of PIP whether performance is acceptable or not.
During and After the PIP n n n Rating Official will meet regularly with the employee, and Union representative may attend PIP meetings. Within 14 days of the end of the opportunity period, employee will be notified in writing whether their performance has improved to the successful level. Employee will be notified within 14 days after end of PIP whether performance is acceptable or not.
 Article 21 – Unacceptable performance If performance is still unacceptable, management will give the employee at least 30 days notice of their proposed action to demote or remove the employee n Employee will be given an opportunity to reply n Decision to demote or remove must be made by a higher level management official than the proposing official n
Article 21 – Unacceptable performance If performance is still unacceptable, management will give the employee at least 30 days notice of their proposed action to demote or remove the employee n Employee will be given an opportunity to reply n Decision to demote or remove must be made by a higher level management official than the proposing official n
 Article 21 – Unacceptable performance Decision may be grieved or appealed to MSPB n If unacceptable performance is related to a disability, FS will delay action to allow determination to be made concerning the disability retirement n Performance removals and demotions will be stayed 5 days from date of decision n
Article 21 – Unacceptable performance Decision may be grieved or appealed to MSPB n If unacceptable performance is related to a disability, FS will delay action to allow determination to be made concerning the disability retirement n Performance removals and demotions will be stayed 5 days from date of decision n
 Article 22 Discipline and Adverse Actions
Article 22 Discipline and Adverse Actions
 Article 22 – Discipline and Adverse Actions n General ¨ Purpose of discipline is to correct behavior and prevent future occurrences ¨ Concerns will be addressed early, and employees will be instructed to discontinue any misconduct ¨ Misconduct will not be allowed to continue just to increase the penalty ¨ Discipline will be within a reasonable amount of time after the incident
Article 22 – Discipline and Adverse Actions n General ¨ Purpose of discipline is to correct behavior and prevent future occurrences ¨ Concerns will be addressed early, and employees will be instructed to discontinue any misconduct ¨ Misconduct will not be allowed to continue just to increase the penalty ¨ Discipline will be within a reasonable amount of time after the incident
 22. 2 – Letters of Warning n n Letters of warning include any letter that addresses a performance or conduct problem with the exception of Letters of Reprimand. Letters of warning will state ¨ specific reasons that gave rise to the letter ¨ employee’s grievance rights. n n The original shall be given to the employee Letter will remain in effect no longer than 1 year, but may be withdrawn earlier
22. 2 – Letters of Warning n n Letters of warning include any letter that addresses a performance or conduct problem with the exception of Letters of Reprimand. Letters of warning will state ¨ specific reasons that gave rise to the letter ¨ employee’s grievance rights. n n The original shall be given to the employee Letter will remain in effect no longer than 1 year, but may be withdrawn earlier
 Article 22. 2 – Alternative Discipline Use Alternative Discipline whenever appropriate n Alternative Discipline is voluntary n Alternative Discipline may not be used when the final decision is removal n n Encourage that you include the failure to try alternative discipline in your grievance.
Article 22. 2 – Alternative Discipline Use Alternative Discipline whenever appropriate n Alternative Discipline is voluntary n Alternative Discipline may not be used when the final decision is removal n n Encourage that you include the failure to try alternative discipline in your grievance.
 22. 4 Traditional Discipline n Discipline is defined as ¨ ¨ Reprimands Removal Suspension without pay Reduction in pay or grade Disciplinary actions against employees must be based on just cause. . n Before deciding on a particular penalty, agency officials should consider all the pertinent factors as described in USDA Department Personnel Manual 751, Appendix A, May 1994. n
22. 4 Traditional Discipline n Discipline is defined as ¨ ¨ Reprimands Removal Suspension without pay Reduction in pay or grade Disciplinary actions against employees must be based on just cause. . n Before deciding on a particular penalty, agency officials should consider all the pertinent factors as described in USDA Department Personnel Manual 751, Appendix A, May 1994. n
 A note about forums n Adverse Actions are Suspensions of more than 14 days ¨ Reduction in pay or grade ¨ Removal ¨ n n n Disciplinary actions can be addressed through EEO, OSC, or FLRA when appropriate All disciplinary actions can be addressed through a grievance Only adverse actions can be appealed to MSPB
A note about forums n Adverse Actions are Suspensions of more than 14 days ¨ Reduction in pay or grade ¨ Removal ¨ n n n Disciplinary actions can be addressed through EEO, OSC, or FLRA when appropriate All disciplinary actions can be addressed through a grievance Only adverse actions can be appealed to MSPB
 22. 5 Inquiries n n n Prior to issuing discipline an inquiry shall be undertaken. The “inquiry” is the initial phase of an investigation to determination whether further investigation or discipline is warranted Investigations, if warranted, will be in accordance with the standards set forth in USDA Department Manual Chapter 751, Subchapter 3.
22. 5 Inquiries n n n Prior to issuing discipline an inquiry shall be undertaken. The “inquiry” is the initial phase of an investigation to determination whether further investigation or discipline is warranted Investigations, if warranted, will be in accordance with the standards set forth in USDA Department Manual Chapter 751, Subchapter 3.
 22. 5 Inquiries Employee may be represented by the Union (Weingarten). n Once management has been notified that Union is representing an employee, management will notify union of any subsequent meetings and copies of correspondence will be sent to union. n DOES NOT apply to criminal investigations. n
22. 5 Inquiries Employee may be represented by the Union (Weingarten). n Once management has been notified that Union is representing an employee, management will notify union of any subsequent meetings and copies of correspondence will be sent to union. n DOES NOT apply to criminal investigations. n
 Article 22. 5 – Procedures Disciplinary actions will be retained in Agency files in accordance with Records Management Handbook. n Letters of Reprimand n ¨ Clearly titled ¨ Why the letter is being issued ¨ Include grievance rights ¨ Retain in the OPF for one year
Article 22. 5 – Procedures Disciplinary actions will be retained in Agency files in accordance with Records Management Handbook. n Letters of Reprimand n ¨ Clearly titled ¨ Why the letter is being issued ¨ Include grievance rights ¨ Retain in the OPF for one year
 22. 6 – Procedures n Discipline greater that Reprimand ¨ Upon request, Management will provide copies of all evidence supporting proposed discipline. ¨ Employee and/or representative will be permitted reasonable time to provide response to proposal. ¨ Time limits may be extended upon written request.
22. 6 – Procedures n Discipline greater that Reprimand ¨ Upon request, Management will provide copies of all evidence supporting proposed discipline. ¨ Employee and/or representative will be permitted reasonable time to provide response to proposal. ¨ Time limits may be extended upon written request.
 A note about proposals Generally, you do not file a grievance over a proposal. n MSPB will NOT accept a case for a proposal (arguing mgmt has not taken an action yet). n May file grievance or ULP complaint, if you can make a case that the proposal itself is intended to inimidate or retaliate for protected activity. n
A note about proposals Generally, you do not file a grievance over a proposal. n MSPB will NOT accept a case for a proposal (arguing mgmt has not taken an action yet). n May file grievance or ULP complaint, if you can make a case that the proposal itself is intended to inimidate or retaliate for protected activity. n
 22. 6 Procedures n Suspension of 14 days or less. Employee is entitled to: ¨ At least 7 day advance notice ¨ Reasonable time to respond to proposal ¨ Union or other representation ¨ A timely written decision with specific reasons ¨ Grieve the decision
22. 6 Procedures n Suspension of 14 days or less. Employee is entitled to: ¨ At least 7 day advance notice ¨ Reasonable time to respond to proposal ¨ Union or other representation ¨ A timely written decision with specific reasons ¨ Grieve the decision
 22. 6 - Procedures n Adverse Actions (Removal, Suspension for more than 14 days, Furlough for less than 30 days, Reduction in pay or grade). Employee is entitled to: ¨ 30 day advance notice (except in certain criminal cases) ¨ Reasonable time to respond ¨ Be represented by Union or other representative ¨ A timely written decision stating reasons ¨ Grieve the action or appeal to MSPB
22. 6 - Procedures n Adverse Actions (Removal, Suspension for more than 14 days, Furlough for less than 30 days, Reduction in pay or grade). Employee is entitled to: ¨ 30 day advance notice (except in certain criminal cases) ¨ Reasonable time to respond ¨ Be represented by Union or other representative ¨ A timely written decision stating reasons ¨ Grieve the action or appeal to MSPB
 Representation for discipline n Investigation ¨ Participate in Weingarten meetings ¨ Request information about status of investigation n After Proposal ¨ Assist employee with written and/or oral response n Brief history of employee’s employment, including awards n Address the charges, including written statements from witnesses. n Address the severity of the penalty through “just cause” and “Douglas” factors”, but focus primarily on those factors which work in favor of the employee n Raise any affirmative defenses (discrimination, reprisal, etc. )
Representation for discipline n Investigation ¨ Participate in Weingarten meetings ¨ Request information about status of investigation n After Proposal ¨ Assist employee with written and/or oral response n Brief history of employee’s employment, including awards n Address the charges, including written statements from witnesses. n Address the severity of the penalty through “just cause” and “Douglas” factors”, but focus primarily on those factors which work in favor of the employee n Raise any affirmative defenses (discrimination, reprisal, etc. )
 Just Cause
Just Cause
 “Douglas factors” (USDA DPM 751, Appendix A) n n n The nature and seriousness of the offense, and its relation to the employee's position and responsibilities, including whether the offense was intentional or technical or inadvertent, or was committed maliciously or for gain, or was frequently repeated. The employee's job level and type of equipment, including fiduciary role, contacts with the public and prominence of the position. The employee's past disciplinary record. The employee's past work record, including length of service, performance on the job, ability to get along with Federal workers, and dependability. The effect of the offense upon the employee's ability to perform at a satisfactory level and its effect upon supervisors' confidence in the employee's ability to perform assigned duties.
“Douglas factors” (USDA DPM 751, Appendix A) n n n The nature and seriousness of the offense, and its relation to the employee's position and responsibilities, including whether the offense was intentional or technical or inadvertent, or was committed maliciously or for gain, or was frequently repeated. The employee's job level and type of equipment, including fiduciary role, contacts with the public and prominence of the position. The employee's past disciplinary record. The employee's past work record, including length of service, performance on the job, ability to get along with Federal workers, and dependability. The effect of the offense upon the employee's ability to perform at a satisfactory level and its effect upon supervisors' confidence in the employee's ability to perform assigned duties.
 Douglas factors n n n n The consistency of the penalty with others The consistency of the penalty with the Penalty Guide. The notoriety of the offense or its impact upon the reputation of the agency The clarity with which the employee was put on notice of any rules that were violated in the committing of the offense, or had been warned about the conduct in question The potential for the employee's rehabilitation. Any mitigating circumstances surrounding the offense such as unusual job tensions, personality problems, mental impairment, harassment, or bad faith, malice, or provocation on the part of others involved in the matter. The adequacy and effectiveness of alternative sanctions to deter such conduct in the future by the employee or others.
Douglas factors n n n n The consistency of the penalty with others The consistency of the penalty with the Penalty Guide. The notoriety of the offense or its impact upon the reputation of the agency The clarity with which the employee was put on notice of any rules that were violated in the committing of the offense, or had been warned about the conduct in question The potential for the employee's rehabilitation. Any mitigating circumstances surrounding the offense such as unusual job tensions, personality problems, mental impairment, harassment, or bad faith, malice, or provocation on the part of others involved in the matter. The adequacy and effectiveness of alternative sanctions to deter such conduct in the future by the employee or others.
 Reasonable Accommodation
Reasonable Accommodation
 Reasonable Accommodation n FS does not have Directive on Reasonable Accommodation (yet). Refer to USDA Department Manual 4300 (DM-4300) Reasonable accommodation of employees and applicants with disabilities Disability is a physical or mental impairment that substantially limits one or more of the major life activities n Reasonable accommodation ¨ Employee must be otherwise qualified to do the job ¨ Cost is generally not a reason for saying the requested accommodation is not “reasonable”
Reasonable Accommodation n FS does not have Directive on Reasonable Accommodation (yet). Refer to USDA Department Manual 4300 (DM-4300) Reasonable accommodation of employees and applicants with disabilities Disability is a physical or mental impairment that substantially limits one or more of the major life activities n Reasonable accommodation ¨ Employee must be otherwise qualified to do the job ¨ Cost is generally not a reason for saying the requested accommodation is not “reasonable”
 BEWARE! n These may require early, frequent, and aggressive Union assistance. Do NOT hesitate to file an EEO complaint early if the process appears bunged up!
BEWARE! n These may require early, frequent, and aggressive Union assistance. Do NOT hesitate to file an EEO complaint early if the process appears bunged up!
 Requests for RA n n n Does not need to be in writing Can be given to any appropriate management official e. g. supervisor, CR director First line supervisor can approve request Denials must be forwarded to the “Mission Area Designee” Only MAD can deny request
Requests for RA n n n Does not need to be in writing Can be given to any appropriate management official e. g. supervisor, CR director First line supervisor can approve request Denials must be forwarded to the “Mission Area Designee” Only MAD can deny request
 Providing the Accommodation Discussion of accommodation should be an interactive process between the supervisor and employee. n If there is an obvious or previously documented disability, and the requested accommodation is clearly related to the known disability, it should normally be provided within 30 work days. n
Providing the Accommodation Discussion of accommodation should be an interactive process between the supervisor and employee. n If there is an obvious or previously documented disability, and the requested accommodation is clearly related to the known disability, it should normally be provided within 30 work days. n
 Medical information n n Agency may request medical information if they are not sure about whether the employee is disabled or what accommodations would be effective. Medical information should: ¨ Document the employee’s medical condition to determine whether they are a person with a disability. ¨ Help explain how the requested accommodation will assist the employee in performing the essential functions of the job.
Medical information n n Agency may request medical information if they are not sure about whether the employee is disabled or what accommodations would be effective. Medical information should: ¨ Document the employee’s medical condition to determine whether they are a person with a disability. ¨ Help explain how the requested accommodation will assist the employee in performing the essential functions of the job.
 Medical Information Medical documentation is submitted to the Mission Area Designee n MAD is responsible for determining if the employee is a “person with a disability” n Information is confidential, unless the employee wishes to share it with his/her supervisor. n
Medical Information Medical documentation is submitted to the Mission Area Designee n MAD is responsible for determining if the employee is a “person with a disability” n Information is confidential, unless the employee wishes to share it with his/her supervisor. n
 Hostile Work Environment
Hostile Work Environment
 Hostile behaviors at work n n n n Verbal abuse Belittling in front of others Territorialism with respect to work Excessive competition Challenges issued over imagined threats to a person's authority Enforcement of ineffective or unreasonable rules as a way to exert power Interfering with a person's ability to be creative and work in a way that is most productive for the individual “Random” changes in work assignments
Hostile behaviors at work n n n n Verbal abuse Belittling in front of others Territorialism with respect to work Excessive competition Challenges issued over imagined threats to a person's authority Enforcement of ineffective or unreasonable rules as a way to exert power Interfering with a person's ability to be creative and work in a way that is most productive for the individual “Random” changes in work assignments
 Behaviors that “feel” hostile…. n Failure of the supervisor to smile, say hello or good morning, chat with employees, etc. does NOT create a hostile work environment by itself.
Behaviors that “feel” hostile…. n Failure of the supervisor to smile, say hello or good morning, chat with employees, etc. does NOT create a hostile work environment by itself.
 Hostile Work Environment There is no law that requires the Agency to provide a courteous or decent work environment. n There are laws that prevent hostile work environment for certain workers: n ¨ Discrimination laws. ¨ Retaliation provisions in other laws that prohibit retaliation for protected activities.
Hostile Work Environment There is no law that requires the Agency to provide a courteous or decent work environment. n There are laws that prevent hostile work environment for certain workers: n ¨ Discrimination laws. ¨ Retaliation provisions in other laws that prohibit retaliation for protected activities.
 Discrimination-based hostile work environment n n n n Race Religion Sex National origin Age Disability Pregnancy Sexual orientation (only through USDA, not EEOC) Hostile work environment because of these reasons can be addressed through an EEO complaint or a grievance.
Discrimination-based hostile work environment n n n n Race Religion Sex National origin Age Disability Pregnancy Sexual orientation (only through USDA, not EEOC) Hostile work environment because of these reasons can be addressed through an EEO complaint or a grievance.
 Examples of retaliation-based hostile work environment Protected Activity Union activity How to file complaint ULP with the FLRA EEO Activity EEO Complaint Whistle blowing OSC and MSPB Safety-related complaints OSHA A grievance can also be filed for each of these. There may be other protected activity that have other possible remedy routes.
Examples of retaliation-based hostile work environment Protected Activity Union activity How to file complaint ULP with the FLRA EEO Activity EEO Complaint Whistle blowing OSC and MSPB Safety-related complaints OSHA A grievance can also be filed for each of these. There may be other protected activity that have other possible remedy routes.
 Requirements for establishing hostile work environment charges n n n He or she suffered intentional inconsiderate treatment because of the EEO basis or protected activity. The harassment was severe or pervasive. The harassment negatively affected the terms, conditions or privileges of his/her work environment. The harassment would detrimentally affect a reasonable person. Management knew about the harassment, or should have known, and did nothing to stop it.
Requirements for establishing hostile work environment charges n n n He or she suffered intentional inconsiderate treatment because of the EEO basis or protected activity. The harassment was severe or pervasive. The harassment negatively affected the terms, conditions or privileges of his/her work environment. The harassment would detrimentally affect a reasonable person. Management knew about the harassment, or should have known, and did nothing to stop it.
 Case example A young, white male employee comes to you as union rep, and says that he wants to file a hostile work environment complaint. His supervisor has been a real jerk at the office, and has been making his life miserable at work. The supervisor tends to make mean jokes about everyone in the office. He hollers things out like, “good of you to come in today” over the tops of the cubicles when employees come in late. He makes disparaging comments about how long it takes people to get work done. From week to week, no one knows if they are on his good side, or his bad side. There is also a black woman in the office who is considering a complaint. How would you recommend that these two employees address their concerns?
Case example A young, white male employee comes to you as union rep, and says that he wants to file a hostile work environment complaint. His supervisor has been a real jerk at the office, and has been making his life miserable at work. The supervisor tends to make mean jokes about everyone in the office. He hollers things out like, “good of you to come in today” over the tops of the cubicles when employees come in late. He makes disparaging comments about how long it takes people to get work done. From week to week, no one knows if they are on his good side, or his bad side. There is also a black woman in the office who is considering a complaint. How would you recommend that these two employees address their concerns?
 Master Agreement protection from hostile work environment For workers not protected by discrimination or retaliation laws, the Master Agreement is the only protection against a hostile work environment. n A key provision: Article 4. 9 - Every individual has the right to be treated with dignity and respect normal in an employeremployee relationship. n
Master Agreement protection from hostile work environment For workers not protected by discrimination or retaliation laws, the Master Agreement is the only protection against a hostile work environment. n A key provision: Article 4. 9 - Every individual has the right to be treated with dignity and respect normal in an employeremployee relationship. n
 Other key Master Agreement provisions n n n Article 4. 8 - Management will not take reprisal actions against employees for the exercise of any appeal right granted by law, rule, regulation, or this Agreement. Article 4. 10 - Management shall inform employees of rules, regulations, and policies under which they are obligated to work. Article 4. 12 - Employees shall not be given warnings or statements of disapproval, counseled on conduct or unacceptable performance, or given verbal warnings except in a setting that protects confidentiality. * * In special job related situations involving safety and/or well being of employees, immediate public admonishment is appropriate, e. g. , co-worker harassment or safety violations.
Other key Master Agreement provisions n n n Article 4. 8 - Management will not take reprisal actions against employees for the exercise of any appeal right granted by law, rule, regulation, or this Agreement. Article 4. 10 - Management shall inform employees of rules, regulations, and policies under which they are obligated to work. Article 4. 12 - Employees shall not be given warnings or statements of disapproval, counseled on conduct or unacceptable performance, or given verbal warnings except in a setting that protects confidentiality. * * In special job related situations involving safety and/or well being of employees, immediate public admonishment is appropriate, e. g. , co-worker harassment or safety violations.
 Routes for resolution n For any hostile work environment issue, you can file a grievance and include contract violations, as well as violations of law. For hostile work environment issues related to statutory protections, employees may also have a statutory route, in addition to the grievance process. Generally, they may use only ONE of the routes for resolution.
Routes for resolution n For any hostile work environment issue, you can file a grievance and include contract violations, as well as violations of law. For hostile work environment issues related to statutory protections, employees may also have a statutory route, in addition to the grievance process. Generally, they may use only ONE of the routes for resolution.
 Remedies? n What would you ask for to resolve a complaint of hostile work environment?
Remedies? n What would you ask for to resolve a complaint of hostile work environment?
 Possible Remedies for Hostile Work Environment n n n n n Monetary damages for health issues caused by stress related to hostile environment Restoration of leave taken due to stress Transfer out of unit Move office away from supervisor or employee who is causing problems Posting of Article 4. 9 on bulletin boards Letter to all employees about the provisions of Article 4. 9 Training for employees/managers about the negative effects hostile workplaces on health and productivity A written apology ADR to resolve smaller communications problems.
Possible Remedies for Hostile Work Environment n n n n n Monetary damages for health issues caused by stress related to hostile environment Restoration of leave taken due to stress Transfer out of unit Move office away from supervisor or employee who is causing problems Posting of Article 4. 9 on bulletin boards Letter to all employees about the provisions of Article 4. 9 Training for employees/managers about the negative effects hostile workplaces on health and productivity A written apology ADR to resolve smaller communications problems.
 Aside: Disparate application of policy n Managing and supervising the workforce in accordance with established policy is NOT a hostile work environment, e. g. Assigning work and monitoring performance ¨ Assuring accurate time and attendance ¨ n However, enforcement of the rules may be disparate. Evaluate: Is the employee breaking the rules? ¨ Does everyone else break the rules? ¨ Will you be stuck arguing that “everyone else breaks the rules, and this employee wants to, too? ” (This is generally what the employee wants…) ¨ n Generally, a resolution to this type of situation will involve equal application of the rules to all.
Aside: Disparate application of policy n Managing and supervising the workforce in accordance with established policy is NOT a hostile work environment, e. g. Assigning work and monitoring performance ¨ Assuring accurate time and attendance ¨ n However, enforcement of the rules may be disparate. Evaluate: Is the employee breaking the rules? ¨ Does everyone else break the rules? ¨ Will you be stuck arguing that “everyone else breaks the rules, and this employee wants to, too? ” (This is generally what the employee wants…) ¨ n Generally, a resolution to this type of situation will involve equal application of the rules to all.
 Work Schedules
Work Schedules
 Sec 2: Standard Work Schedules n Sec 3 & 4: Flexible Work Schedules n Sec 5: Compressed Work Schedules n Sec 7: Administrative procedures n Sec 11: On Call (new section) n
Sec 2: Standard Work Schedules n Sec 3 & 4: Flexible Work Schedules n Sec 5: Compressed Work Schedules n Sec 7: Administrative procedures n Sec 11: On Call (new section) n
 18. 2 Standard Schedule n n n Fixed Schedule Regularly Scheduled Administrative Workweek (RSAW) is the officially prescribed days and hours the employee is regularly scheduled to work, including any regularly scheduled overtime. Tour of duty is the hours and days of an employee’s RSAW. Under a fixed schedule an employee’s tour and RSAW are the same.
18. 2 Standard Schedule n n n Fixed Schedule Regularly Scheduled Administrative Workweek (RSAW) is the officially prescribed days and hours the employee is regularly scheduled to work, including any regularly scheduled overtime. Tour of duty is the hours and days of an employee’s RSAW. Under a fixed schedule an employee’s tour and RSAW are the same.
 Standard Work Schedule n n n Employee works five 8 -hour days each week Set arrival and departure time (normally between 6 am and 6 pm, M-F). No credit hours. Any time over 8 hours per day or 40 hours per week is overtime. For holidays, employee gets 8 hours paid. For night and Sunday pay, any hours scheduled in the night or Sunday period get premium pay.
Standard Work Schedule n n n Employee works five 8 -hour days each week Set arrival and departure time (normally between 6 am and 6 pm, M-F). No credit hours. Any time over 8 hours per day or 40 hours per week is overtime. For holidays, employee gets 8 hours paid. For night and Sunday pay, any hours scheduled in the night or Sunday period get premium pay.
 Flexible Work Schedules Let the fun begin…… n The challenge: n Balancing flexibility with Management’s right to assign work (at a particular time).
Flexible Work Schedules Let the fun begin…… n The challenge: n Balancing flexibility with Management’s right to assign work (at a particular time).
 Flexible work schedules n Flexible work schedule (FWS) means a work schedule established under 5 U. S. C. 6122, that ¨ has an 80 -hour biweekly basic work requirement that ¨ allows an employee to determine his or her own schedule ¨ within the limits set by the agency. (from OPM Handbook on Alternative Work Schedules)
Flexible work schedules n Flexible work schedule (FWS) means a work schedule established under 5 U. S. C. 6122, that ¨ has an 80 -hour biweekly basic work requirement that ¨ allows an employee to determine his or her own schedule ¨ within the limits set by the agency. (from OPM Handbook on Alternative Work Schedules)
 Flexible work schedules (general info) n n n Employee may vary days they work and arrival/departure times. May earn credit hours. Overtime over 8 hours/day or 40/week, but must be approved in advance. For holidays, employee gets 8 hours. For night and Sunday pay, any hours scheduled in the night or Sunday period get premium pay. (Employee cannot elect to work at night and incur night pay. )
Flexible work schedules (general info) n n n Employee may vary days they work and arrival/departure times. May earn credit hours. Overtime over 8 hours/day or 40/week, but must be approved in advance. For holidays, employee gets 8 hours. For night and Sunday pay, any hours scheduled in the night or Sunday period get premium pay. (Employee cannot elect to work at night and incur night pay. )
 18. 3 Flexible Work Schedules n Four FWS will be used Agency-wide ¨ Variable Day – Core hours on 5 days/week. Must work 40 hours/week. ¨ Variable Week – Core hours on 5 days/week. Must work 80 hours/pay period. ¨ Maxiflex – Core hours on less than 5 days/week. Must work 80 hours/pay period. ¨ Gliding – Employee adjusts arrive and start time, but works 8 hours/day, unless earning or using credit hours, leave, etc.
18. 3 Flexible Work Schedules n Four FWS will be used Agency-wide ¨ Variable Day – Core hours on 5 days/week. Must work 40 hours/week. ¨ Variable Week – Core hours on 5 days/week. Must work 80 hours/pay period. ¨ Maxiflex – Core hours on less than 5 days/week. Must work 80 hours/pay period. ¨ Gliding – Employee adjusts arrive and start time, but works 8 hours/day, unless earning or using credit hours, leave, etc.
 18. 3 Flexible Work Schedules In lieu of an RSAW, employees have a “Basic work requirement” which is the number of hours they must work in a biweekly pay period. (FT=80). n All work performed within the basic work requirement is considered regularly scheduled work for the purpose of premium and overtime pay. n
18. 3 Flexible Work Schedules In lieu of an RSAW, employees have a “Basic work requirement” which is the number of hours they must work in a biweekly pay period. (FT=80). n All work performed within the basic work requirement is considered regularly scheduled work for the purpose of premium and overtime pay. n
 Tour of duty (FWS) n Tour of duty is the limits within which employees must complete the basic work ¨ Maxiflex schedule, 5 a. m. and 10 p. m. on Sunday through Saturday. ¨ Variable Day, Variable Week, and Gliding 5 a. m. and 10 p. m. on 5 consecutive days in each week of the pay period. ¨ Changes to the 5 a. m. to 10 p. m. time band (tour of duty) for a flexible schedule may be negotiated at the Local level
Tour of duty (FWS) n Tour of duty is the limits within which employees must complete the basic work ¨ Maxiflex schedule, 5 a. m. and 10 p. m. on Sunday through Saturday. ¨ Variable Day, Variable Week, and Gliding 5 a. m. and 10 p. m. on 5 consecutive days in each week of the pay period. ¨ Changes to the 5 a. m. to 10 p. m. time band (tour of duty) for a flexible schedule may be negotiated at the Local level
 Core Hours (FWS) n Time periods when an employee on a flexible schedule must be present for work or otherwise account for their time. ¨ Maxiflex: 10 am to 2 pm on the 3 middle days of the employee’s tour of duty. ¨ Variable Day and Variable Week: 10 am to 2 pm on each day of the tour of duty. ¨ Employees may request and supervisors may grant deviations from core hours on a case-by -case basis. n Core hours are locally negotiable.
Core Hours (FWS) n Time periods when an employee on a flexible schedule must be present for work or otherwise account for their time. ¨ Maxiflex: 10 am to 2 pm on the 3 middle days of the employee’s tour of duty. ¨ Variable Day and Variable Week: 10 am to 2 pm on each day of the tour of duty. ¨ Employees may request and supervisors may grant deviations from core hours on a case-by -case basis. n Core hours are locally negotiable.
 Credit Hours (FWS) n Credit hours are those hours within a flexible work schedule that an employee elects to work in excess of their basic work requirement so as to vary the length of a workweek or workday. Credit hours are earned at the election of the employee ¨ Employees must inform their supervisor in advance of their intent to earn credit hours, including what work and approximate time. ¨ Supervisors may deny earning credit hours if there is no work for the employee to perform at that time. ¨ Employees cannot be forced to earn credit hours. ¨
Credit Hours (FWS) n Credit hours are those hours within a flexible work schedule that an employee elects to work in excess of their basic work requirement so as to vary the length of a workweek or workday. Credit hours are earned at the election of the employee ¨ Employees must inform their supervisor in advance of their intent to earn credit hours, including what work and approximate time. ¨ Supervisors may deny earning credit hours if there is no work for the employee to perform at that time. ¨ Employees cannot be forced to earn credit hours. ¨
 Credit Hours (FWS) n n n Use of credit hours must be scheduled like any other absence from work. Credit hours may be earned and used within a pay period. Credit hours may be used during core hours. Credit hours may not be earned while an employee is in training. Credit hours for travel governed by existing law and regulation. A maximum of 24 credit hours may be carried over.
Credit Hours (FWS) n n n Use of credit hours must be scheduled like any other absence from work. Credit hours may be earned and used within a pay period. Credit hours may be used during core hours. Credit hours may not be earned while an employee is in training. Credit hours for travel governed by existing law and regulation. A maximum of 24 credit hours may be carried over.
 18. 4 OT and Premium Pay (FWS) n n n Those hours an employee is directed by management to work in excess of 8 hours per day or 40 hours per week are overtime hours. Night pay and night differential premium pay for night work is handled pursuant to 5 USC 6123(c). Management may restrict an employee on a FWS from electing to perform work as part of their basic work requirement on a Sunday in order to avoid the increased operational costs associated with Sunday premium pay; however, such an employee may elect to earn credit hours on a Sunday.
18. 4 OT and Premium Pay (FWS) n n n Those hours an employee is directed by management to work in excess of 8 hours per day or 40 hours per week are overtime hours. Night pay and night differential premium pay for night work is handled pursuant to 5 USC 6123(c). Management may restrict an employee on a FWS from electing to perform work as part of their basic work requirement on a Sunday in order to avoid the increased operational costs associated with Sunday premium pay; however, such an employee may elect to earn credit hours on a Sunday.
 18. 5 Compressed Work Schedules (General Info) n n n n Employee works less than 10 days each pay period. Set arrival and departure time. No credit hours. Hours worked over the scheduled hours for the day are overtime. Any time over 40 hours per week is overtime. For holidays, employee gets the number of regularly scheduled hours for that day paid. For night and Sunday pay, any hours scheduled in the night or Sunday period get premium pay.
18. 5 Compressed Work Schedules (General Info) n n n n Employee works less than 10 days each pay period. Set arrival and departure time. No credit hours. Hours worked over the scheduled hours for the day are overtime. Any time over 40 hours per week is overtime. For holidays, employee gets the number of regularly scheduled hours for that day paid. For night and Sunday pay, any hours scheduled in the night or Sunday period get premium pay.
 18. 5 Compressed Schedules Fixed schedule in which employees complete their basic work requirement in less than 10 days. n Tour of duty is the hours of a day and days of a week that the employee is regularly scheduled to work. Normally scheduled hours will be between 6 am and 6 pm. n
18. 5 Compressed Schedules Fixed schedule in which employees complete their basic work requirement in less than 10 days. n Tour of duty is the hours of a day and days of a week that the employee is regularly scheduled to work. Normally scheduled hours will be between 6 am and 6 pm. n
 18. 5 Compressed Schedules 4 -10 – Four 10 -hour days per week. n 5 -4/9 – Eight 9 -hour days with one 8 -hour day and one day off. n Specific hours are a matter of joint discussion. n Hardship provisions if employee cannot work a compressed schedule. n
18. 5 Compressed Schedules 4 -10 – Four 10 -hour days per week. n 5 -4/9 – Eight 9 -hour days with one 8 -hour day and one day off. n Specific hours are a matter of joint discussion. n Hardship provisions if employee cannot work a compressed schedule. n
 18. 7 Administration of Work Schedules n Tour of duty will be recorded in the paycheck header. ¨ For Standard and Compressed schedule, this is the employee’s regular hours. ¨ For Maxiflex, the Tour of Duty is 5 am – 10 pm, Sunday-Sat. ¨ For Variable Day and Variable Week the Tour is 5 am – 10 pm, on 5 days a week.
18. 7 Administration of Work Schedules n Tour of duty will be recorded in the paycheck header. ¨ For Standard and Compressed schedule, this is the employee’s regular hours. ¨ For Maxiflex, the Tour of Duty is 5 am – 10 pm, Sunday-Sat. ¨ For Variable Day and Variable Week the Tour is 5 am – 10 pm, on 5 days a week.
 18. 7 Administration Default work schedule is the standard schedule. n Employees may apply to any compressed or flexible work schedule. n Employee may NOT be involuntarily assigned to a FWS. n Employee MAY be assigned to a CWS. n
18. 7 Administration Default work schedule is the standard schedule. n Employees may apply to any compressed or flexible work schedule. n Employee may NOT be involuntarily assigned to a FWS. n Employee MAY be assigned to a CWS. n
 18. 7 Administration n Decision to grant or deny an employee’s request to be on a flexible or compressed schedule will be based on: Productivity n Level of service to customers n Cost of operations n n Denials of an employee’s request for AWS will be in writing and provided to the Union
18. 7 Administration n Decision to grant or deny an employee’s request to be on a flexible or compressed schedule will be based on: Productivity n Level of service to customers n Cost of operations n n Denials of an employee’s request for AWS will be in writing and provided to the Union
 18. 7 Administration Management will not change or discontinue an AWS for the purpose of avoiding overtime n AWS may be discontinued based on n ¨ Productivity ¨ Level of service to customers ¨ Cost of operations
18. 7 Administration Management will not change or discontinue an AWS for the purpose of avoiding overtime n AWS may be discontinued based on n ¨ Productivity ¨ Level of service to customers ¨ Cost of operations
 18. 7. h Administration Special Situations n n Short term changes, no more than 1 pay period, may be made. Employees at training for more than 2 days will be switched to a fixed 8 -hour schedule. Field crew supervisors may limit day to 8 hours if weather or work conditions warrant. Schedules for fire and incidents are covered in Article 28.
18. 7. h Administration Special Situations n n Short term changes, no more than 1 pay period, may be made. Employees at training for more than 2 days will be switched to a fixed 8 -hour schedule. Field crew supervisors may limit day to 8 hours if weather or work conditions warrant. Schedules for fire and incidents are covered in Article 28.
 18. 8 and 18. 9 - Breaks n n Rest Breaks: 15 minutes approximately midway through each 4 -hour period of work. Will be arranged by the employees with the work supervisor, so as not to interrupt the work of the organization. Meal Breaks: ¨ Minimum of 30 minute for an unpaid meal break on work days of more than 6 hours. ¨ Employees who are required to work through their meal period shall be compensated. ¨ Supervisors may approve a short-term deviation to meal break requirement on a case-by-case basis
18. 8 and 18. 9 - Breaks n n Rest Breaks: 15 minutes approximately midway through each 4 -hour period of work. Will be arranged by the employees with the work supervisor, so as not to interrupt the work of the organization. Meal Breaks: ¨ Minimum of 30 minute for an unpaid meal break on work days of more than 6 hours. ¨ Employees who are required to work through their meal period shall be compensated. ¨ Supervisors may approve a short-term deviation to meal break requirement on a case-by-case basis
 18. 11 On-Call n n On-call is unpaid time when an employee may be required to leave a number or carry a pager and remain within a reasonable call back radius. General Provisions: ¨ Employee may make arrangements for another to cover their on-call period (mgmt will provide a list). ¨ If employee is sick, Management will make arrangements for covering the on-call period. ¨ Employee will not be required to report to work in less than an hour.
18. 11 On-Call n n On-call is unpaid time when an employee may be required to leave a number or carry a pager and remain within a reasonable call back radius. General Provisions: ¨ Employee may make arrangements for another to cover their on-call period (mgmt will provide a list). ¨ If employee is sick, Management will make arrangements for covering the on-call period. ¨ Employee will not be required to report to work in less than an hour.
 18. 11 On Call B. Scheduling ¨ On-call periods will be reasonable: Normally 2 days per pay period when not on call, at least one of which will be their regular day off. ¨ On call scheduling shall be done by rotation, first among volunteers ¨ Shall not be on-call during scheduled leave periods. ¨ Annotation: Normally, employees will not be assigned to on-call status for more than two pay periods, without a pay period off.
18. 11 On Call B. Scheduling ¨ On-call periods will be reasonable: Normally 2 days per pay period when not on call, at least one of which will be their regular day off. ¨ On call scheduling shall be done by rotation, first among volunteers ¨ Shall not be on-call during scheduled leave periods. ¨ Annotation: Normally, employees will not be assigned to on-call status for more than two pay periods, without a pay period off.
 19. 9 Relationship between Oncall and pay status n Employees will not be required to provide coverage for call back to duty under conditions more restrictive than those provided for in Article 18. 11 unless they are in pay status.
19. 9 Relationship between Oncall and pay status n Employees will not be required to provide coverage for call back to duty under conditions more restrictive than those provided for in Article 18. 11 unless they are in pay status.


