38bf394d1884cb41d665d334105ec6c1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12
 SPECIES AT THE GENOMIC LEVEL
SPECIES AT THE GENOMIC LEVEL
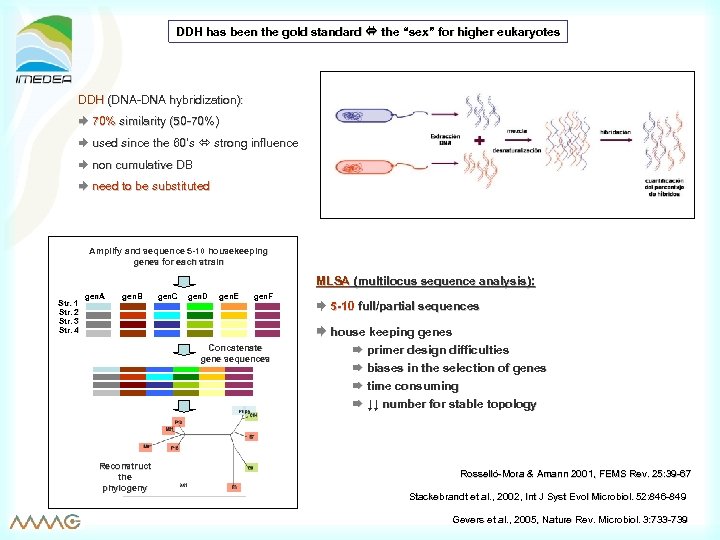 DDH has been the gold standard the “sex” for higher eukaryotes sex” DDH (DNA-DNA hybridization): 70% similarity (50 -70%) used since the 60’s strong influence 60’ non cumulative DB need to be substituted Amplify and sequence 5 -10 housekeeping genes for each strain MLSA (multilocus sequence analysis): Str. 1 Str. 2 Str. 3 Str. 4 gen. A gen. B gen. C gen. D gen. E gen. F Concatenate gene sequences 5 -10 full/partial sequences house keeping genes primer design difficulties biases in the selection of genes time consuming ↓↓ number for stable topology Reconstruct the phylogeny Rosselló-Mora & Amann 2001, FEMS Rev. 25: 39 -67 Stackebrandt et al. , 2002, Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 52: 846 -849 Gevers et al. , 2005, Nature Rev. Microbiol. 3: 733 -739
DDH has been the gold standard the “sex” for higher eukaryotes sex” DDH (DNA-DNA hybridization): 70% similarity (50 -70%) used since the 60’s strong influence 60’ non cumulative DB need to be substituted Amplify and sequence 5 -10 housekeeping genes for each strain MLSA (multilocus sequence analysis): Str. 1 Str. 2 Str. 3 Str. 4 gen. A gen. B gen. C gen. D gen. E gen. F Concatenate gene sequences 5 -10 full/partial sequences house keeping genes primer design difficulties biases in the selection of genes time consuming ↓↓ number for stable topology Reconstruct the phylogeny Rosselló-Mora & Amann 2001, FEMS Rev. 25: 39 -67 Stackebrandt et al. , 2002, Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 52: 846 -849 Gevers et al. , 2005, Nature Rev. Microbiol. 3: 733 -739
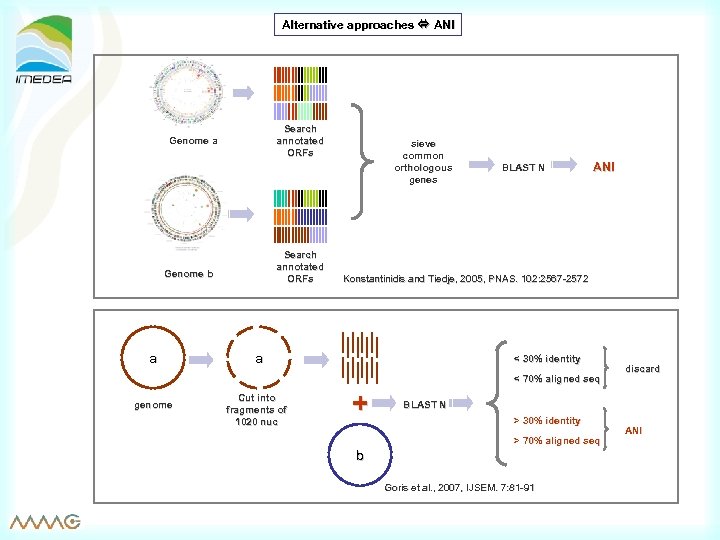 Alternative approaches ANI Search annotated ORFs Genome a Search annotated ORFs Genome b a sieve common orthologous genes BLAST N ANI Konstantinidis and Tiedje, 2005, PNAS. 102: 2567 -2572 a < 30% identity < 70% aligned seq genome Cut into fragments of 1020 nuc + discard BLAST N > 30% identity > 70% aligned seq b Goris et al. , 2007, IJSEM. 7: 81 -91 ANI
Alternative approaches ANI Search annotated ORFs Genome a Search annotated ORFs Genome b a sieve common orthologous genes BLAST N ANI Konstantinidis and Tiedje, 2005, PNAS. 102: 2567 -2572 a < 30% identity < 70% aligned seq genome Cut into fragments of 1020 nuc + discard BLAST N > 30% identity > 70% aligned seq b Goris et al. , 2007, IJSEM. 7: 81 -91 ANI
 JSpecies (www. imedea. uib. es/jspecies) JSpecies Biologist oriented user friendly and usable with multifasta data
JSpecies (www. imedea. uib. es/jspecies) JSpecies Biologist oriented user friendly and usable with multifasta data
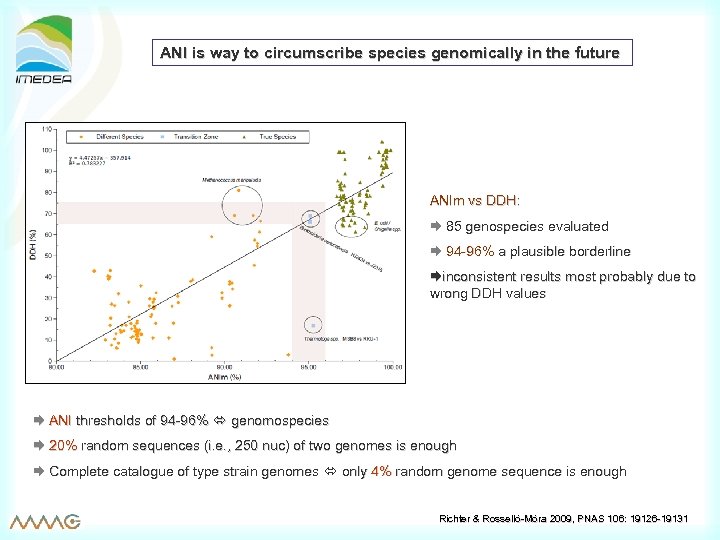 ANI is way to circumscribe species genomically in the future ANIm vs DDH: 85 genospecies evaluated 94 -96% a plausible borderline inconsistent results most probably due to wrong DDH values ANI thresholds of 94 -96% genomospecies 20% random sequences (i. e. , 250 nuc) of two genomes is enough Complete catalogue of type strain genomes only 4% random genome sequence is enough Richter & Rosselló-Móra 2009, PNAS 106: 19126 -19131
ANI is way to circumscribe species genomically in the future ANIm vs DDH: 85 genospecies evaluated 94 -96% a plausible borderline inconsistent results most probably due to wrong DDH values ANI thresholds of 94 -96% genomospecies 20% random sequences (i. e. , 250 nuc) of two genomes is enough Complete catalogue of type strain genomes only 4% random genome sequence is enough Richter & Rosselló-Móra 2009, PNAS 106: 19126 -19131
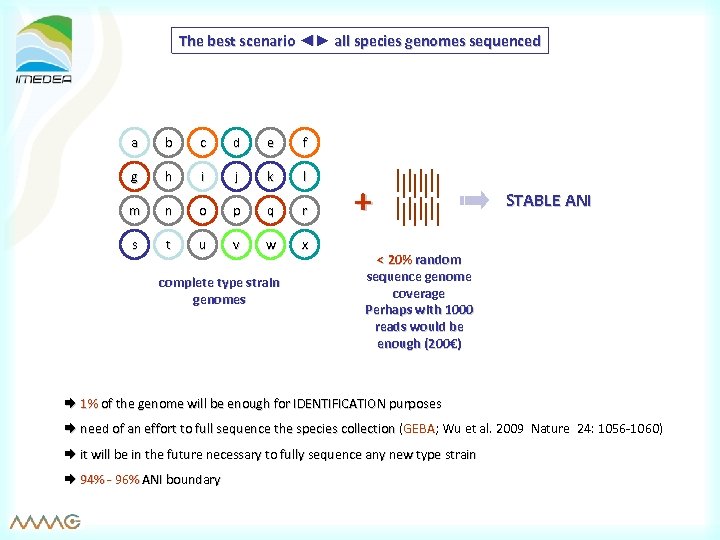 The best scenario ◄► all species genomes sequenced a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x complete type strain genomes + STABLE ANI < 20% random sequence genome coverage Perhaps with 1000 reads would be enough (200€) 1% of the genome will be enough for IDENTIFICATION purposes need of an effort to full sequence the species collection (GEBA; Wu et al. 2009 Nature 24: 1056 -1060) it will be in the future necessary to fully sequence any new type strain 94% - 96% ANI boundary
The best scenario ◄► all species genomes sequenced a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x complete type strain genomes + STABLE ANI < 20% random sequence genome coverage Perhaps with 1000 reads would be enough (200€) 1% of the genome will be enough for IDENTIFICATION purposes need of an effort to full sequence the species collection (GEBA; Wu et al. 2009 Nature 24: 1056 -1060) it will be in the future necessary to fully sequence any new type strain 94% - 96% ANI boundary
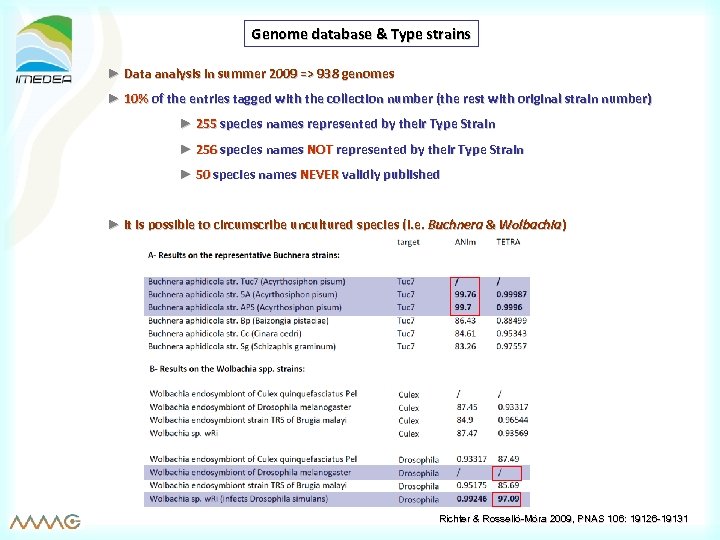 Genome database & Type strains ► Data analysis in summer 2009 => 938 genomes ► 10% of the entries tagged with the collection number (the rest with original strain number) ► 255 species names represented by their Type Strain ► 256 species names NOT represented by their Type Strain ► 50 species names NEVER validly published ► it is possible to circumscribe uncultured species (i. e. Buchnera & Wolbachia) Richter & Rosselló-Móra 2009, PNAS 106: 19126 -19131
Genome database & Type strains ► Data analysis in summer 2009 => 938 genomes ► 10% of the entries tagged with the collection number (the rest with original strain number) ► 255 species names represented by their Type Strain ► 256 species names NOT represented by their Type Strain ► 50 species names NEVER validly published ► it is possible to circumscribe uncultured species (i. e. Buchnera & Wolbachia) Richter & Rosselló-Móra 2009, PNAS 106: 19126 -19131
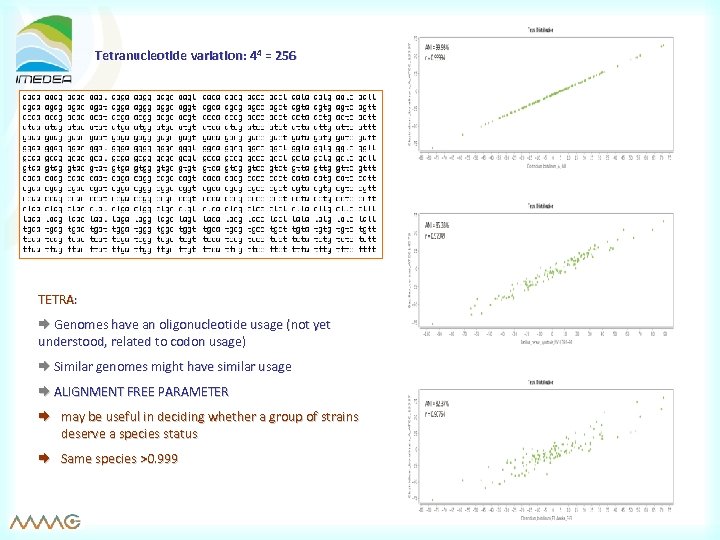 Tetranucleotide variation: 44 = 256 TETRA: Genomes have an oligonucleotide usage (not yet understood, related to codon usage) Similar genomes might have similar usage ALIGNMENT FREE PARAMETER may be useful in deciding whether a group of strains deserve a species status Same species >0. 999
Tetranucleotide variation: 44 = 256 TETRA: Genomes have an oligonucleotide usage (not yet understood, related to codon usage) Similar genomes might have similar usage ALIGNMENT FREE PARAMETER may be useful in deciding whether a group of strains deserve a species status Same species >0. 999
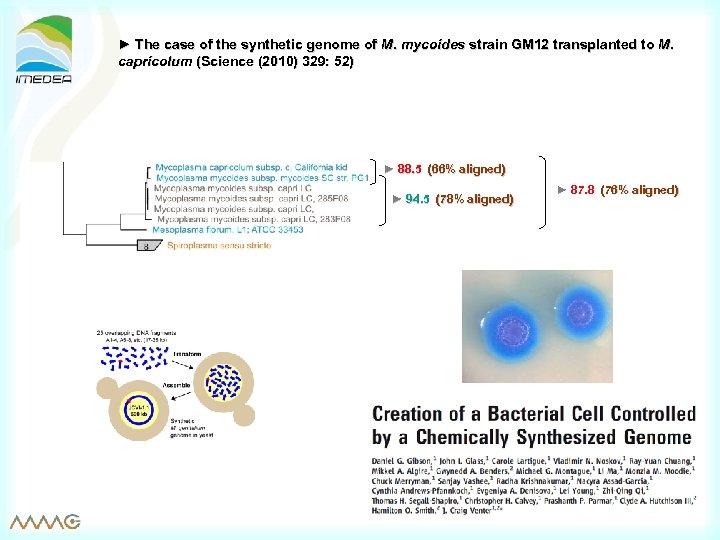 ► The case of the synthetic genome of M. mycoides strain GM 12 transplanted to M. capricolum (Science (2010) 329: 52) ► 88. 5 (66% aligned) ► 94. 5 (78% aligned) ► 87. 8 (76% aligned)
► The case of the synthetic genome of M. mycoides strain GM 12 transplanted to M. capricolum (Science (2010) 329: 52) ► 88. 5 (66% aligned) ► 94. 5 (78% aligned) ► 87. 8 (76% aligned)
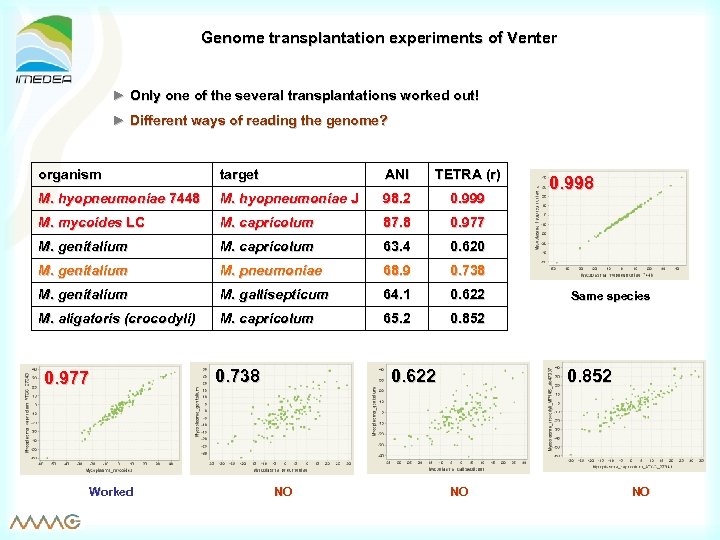 Genome transplantation experiments of Venter ► Only one of the several transplantations worked out! ► Different ways of reading the genome? organism target ANI TETRA (r) M. hyopneumoniae 7448 M. hyopneumoniae J 98. 2 0. 999 M. mycoides LC M. capricolum 87. 8 0. 977 M. genitalium M. capricolum 63. 4 0. 620 M. genitalium M. pneumoniae 68. 9 0. 738 M. genitalium M. gallisepticum 64. 1 0. 622 M. aligatoris (crocodyli) M. capricolum 65. 2 0. 852 0. 977 Worked 0. 622 0. 738 NO 0. 998 Same species 0. 852 NO NO
Genome transplantation experiments of Venter ► Only one of the several transplantations worked out! ► Different ways of reading the genome? organism target ANI TETRA (r) M. hyopneumoniae 7448 M. hyopneumoniae J 98. 2 0. 999 M. mycoides LC M. capricolum 87. 8 0. 977 M. genitalium M. capricolum 63. 4 0. 620 M. genitalium M. pneumoniae 68. 9 0. 738 M. genitalium M. gallisepticum 64. 1 0. 622 M. aligatoris (crocodyli) M. capricolum 65. 2 0. 852 0. 977 Worked 0. 622 0. 738 NO 0. 998 Same species 0. 852 NO NO
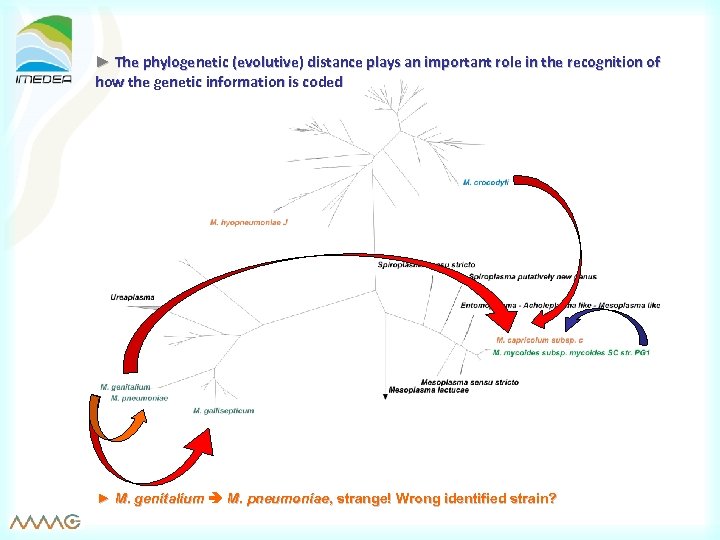 ► The phylogenetic (evolutive) distance plays an important role in the recognition of how the genetic information is coded ► M. genitalium M. pneumoniae, strange! Wrong identified strain?
► The phylogenetic (evolutive) distance plays an important role in the recognition of how the genetic information is coded ► M. genitalium M. pneumoniae, strange! Wrong identified strain?
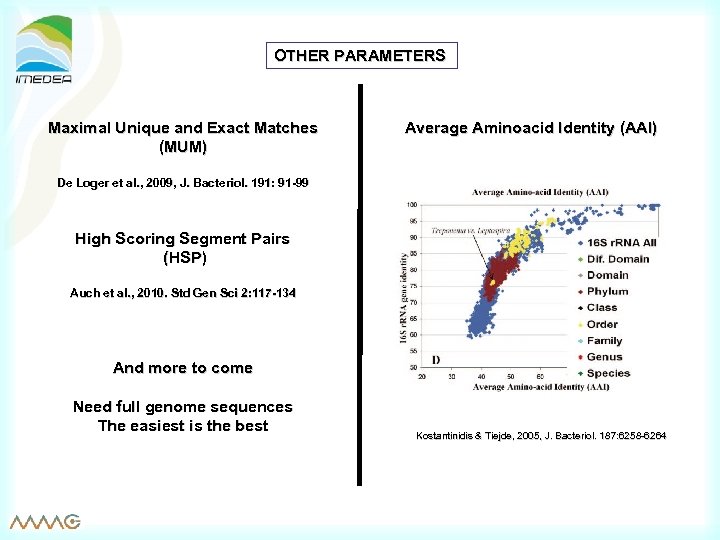 OTHER PARAMETERS Maximal Unique and Exact Matches (MUM) Average Aminoacid Identity (AAI) De Loger et al. , 2009, J. Bacteriol. 191: 91 -99 High Scoring Segment Pairs (HSP) Auch et al. , 2010. Std Gen Sci 2: 117 -134 And more to come Need full genome sequences The easiest is the best Kostantinidis & Tiejde, 2005, J. Bacteriol. 187: 6258 -6264 Tiejde, Bacteriol.
OTHER PARAMETERS Maximal Unique and Exact Matches (MUM) Average Aminoacid Identity (AAI) De Loger et al. , 2009, J. Bacteriol. 191: 91 -99 High Scoring Segment Pairs (HSP) Auch et al. , 2010. Std Gen Sci 2: 117 -134 And more to come Need full genome sequences The easiest is the best Kostantinidis & Tiejde, 2005, J. Bacteriol. 187: 6258 -6264 Tiejde, Bacteriol.


