Special Philology.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 18

Special philology and language families Anna Gubenko УТ-12 -2

Philology is the study of language in written historical sources; it is a combination of literary studies, history and linguistics. It dedicates it’s origin to Alexandria. Later philology was taken up and developed by Greeks and Romans through Roman and Byzantine Empires, and eventually it became a part of Renaissance study. Philology is divided into European (Germanic, Celtic) and non. European (Sanskrit, Persian, Chinese) study.

The meaning of the word The word ”philology” (philologia) comprises 2 words: “affection/love” and “word”, which meant the love of learning. The phrase was changed with the time and entered English language in the 16 th century as “love of literature”. However the 19 th century called it “the study of the historical development of languages”.
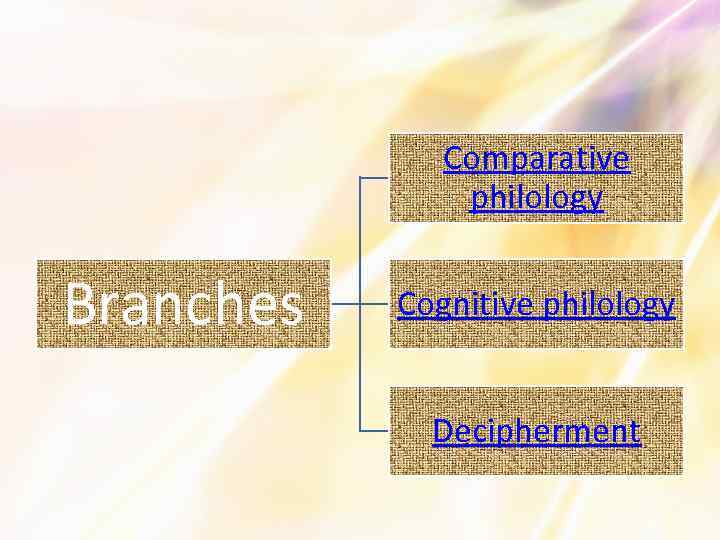
Comparative philology Branches Cognitive philology Decipherment

Comparative philology This branch studies the connections between languages. The idea of a common ancestor of all existing and extinct languages formed a presentation of Proto-Indo-European. It was inspired by 16 th century discovery of common features of European languages and Sanskrit. It also led to study of “exotic” languages (which have not been popular in the West before). Home

Cognitive philology The science which studies written and oral texts as the product of human mental activity. Includes psychology, neuroscience and artificial intelligence. "The point is not the text, but the mind that made it“. … and back

Decipherment A branch of philology which decodes and translates ancient languages and texts. It began with the decipherment of Rosetta Stone by Jean. François Champollion in 1822.

Rosetta Stone is an ancient Egyptian decree issued at Memphis in 196 BC on behalf of the king Ptolemy V. It is written in 3 languages: "language of the gods" (hieroglyphs), the "language of documents" (demotic), and the "language of the Greeks" as used by the Ptolemaic government. The decipherment began in the early 19 th century.

Languages Greek Demotic Hieroglyphs

Language family

Definition A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ancestor, called the proto-language of that family. Right now official sources count 6 909 living languages. However the approximate number varies from 5 000 to 10 000 languages (as it is difficult to distinct dialects from common languages).

Isolates Languages that have no known relatives (or for which family relationships are only tentatively proposed) are called language isolates. An example is Basque. In general, it is assumed that most language isolates have relatives, but at a time depth too great for linguistic comparison to recover them. The most suitable examples are American within Indo. European languages and Basque (Euskara).

Sprachbund A sprachbund is a geographic area having several languages that feature common linguistic structures. The similarities between those languages are caused by language contact, not by chance or common origin, and are not recognized as criteria that define a language family.

Dialects 1) a variety of a language that is a characteristic of a particular group of the language's speakers. 2) A diversity of language of a particular social class.

Examples Peninsular Spanish • • Castilian Andalusian Catalan (Andorra) Portuguese-influenced language of Galicia The Americas Spanish • Latin American Spanish (Mexico, Colombia, Peru, Bolivia) • Rioplatense Spanish (Argentina and Uruguay) • Caribbean Spanish (Cuba, Puerto Rico).

Proof Sweater Spain: jersey Argentina: pulòver Mexico: suèter Peru: chompa
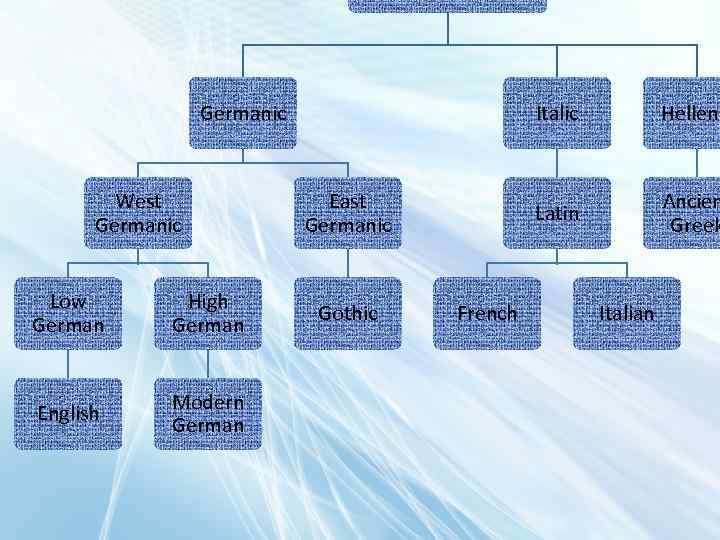
Germanic West Germanic Low German High German English Modern German Italic Latin East Germanic Gothic French Helleni Ancien Greek Italian
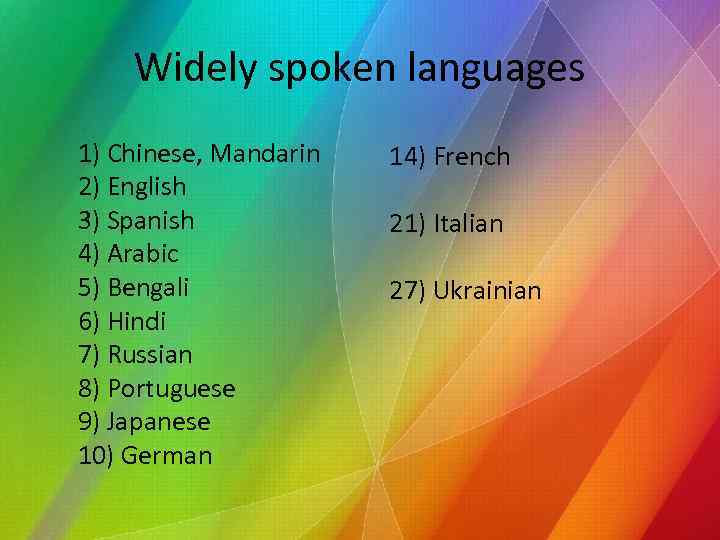
Widely spoken languages 1) Chinese, Mandarin 2) English 3) Spanish 4) Arabic 5) Bengali 6) Hindi 7) Russian 8) Portuguese 9) Japanese 10) German 14) French 21) Italian 27) Ukrainian
Special Philology.pptx