d8a5b6a577afd54f1986c4c004d39214.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation Michael Elad The CS Department The Technion – Israel Institute of technology Haifa 32000, Israel Statistical Association 2005 Annual Meeting Tel-Aviv University (Dan David bldg. ) May 17 th, 2005 Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation
Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation Michael Elad The CS Department The Technion – Israel Institute of technology Haifa 32000, Israel Statistical Association 2005 Annual Meeting Tel-Aviv University (Dan David bldg. ) May 17 th, 2005 Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation
 Agenda 1. A Visit to Sparseland Motivating Sparsity & Overcompleteness 2. Answering the 4 Questions How & why should this work? Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation Welcome to Sparseland 2
Agenda 1. A Visit to Sparseland Motivating Sparsity & Overcompleteness 2. Answering the 4 Questions How & why should this work? Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation Welcome to Sparseland 2
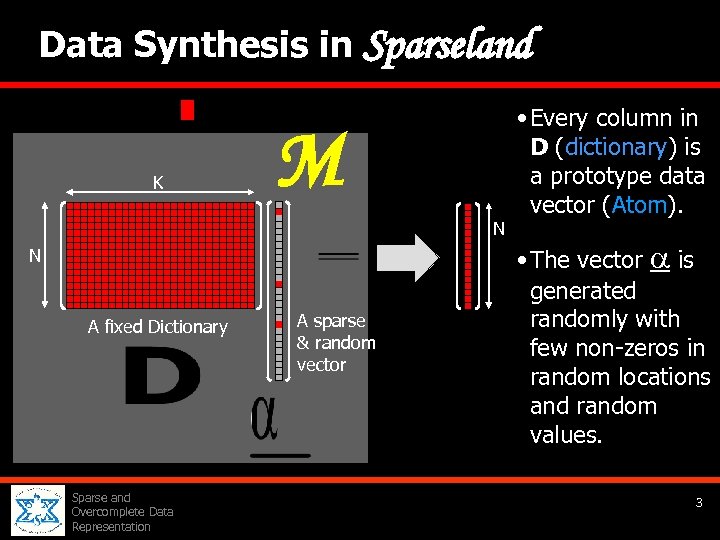 Data Synthesis in K Sparseland M N N A fixed Dictionary Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation A sparse & random vector • Every column in D (dictionary) is a prototype data vector (Atom). • The vector is generated randomly with few non-zeros in random locations and random values. 3
Data Synthesis in K Sparseland M N N A fixed Dictionary Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation A sparse & random vector • Every column in D (dictionary) is a prototype data vector (Atom). • The vector is generated randomly with few non-zeros in random locations and random values. 3
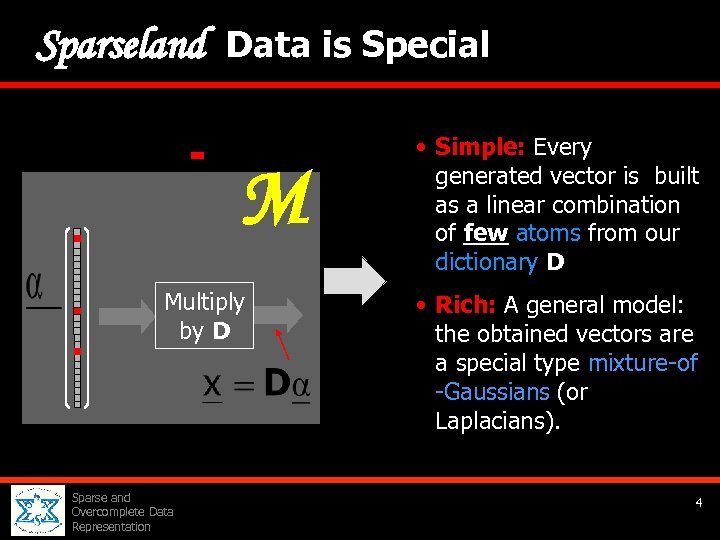 Sparseland Data is Special M Multiply by D Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation • Simple: Every generated vector is built as a linear combination of few atoms from our dictionary D • Rich: A general model: the obtained vectors are a special type mixture-of -Gaussians (or Laplacians). 4
Sparseland Data is Special M Multiply by D Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation • Simple: Every generated vector is built as a linear combination of few atoms from our dictionary D • Rich: A general model: the obtained vectors are a special type mixture-of -Gaussians (or Laplacians). 4
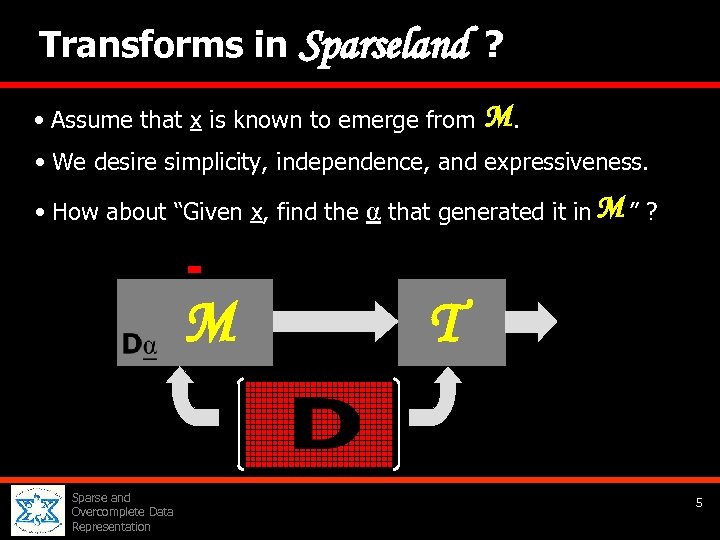 Transforms in Sparseland ? • Assume that x is known to emerge from M . . • We desire simplicity, independence, and expressiveness. • How about “Given x, find the α that generated it in M ” ? M Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation T 5
Transforms in Sparseland ? • Assume that x is known to emerge from M . . • We desire simplicity, independence, and expressiveness. • How about “Given x, find the α that generated it in M ” ? M Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation T 5
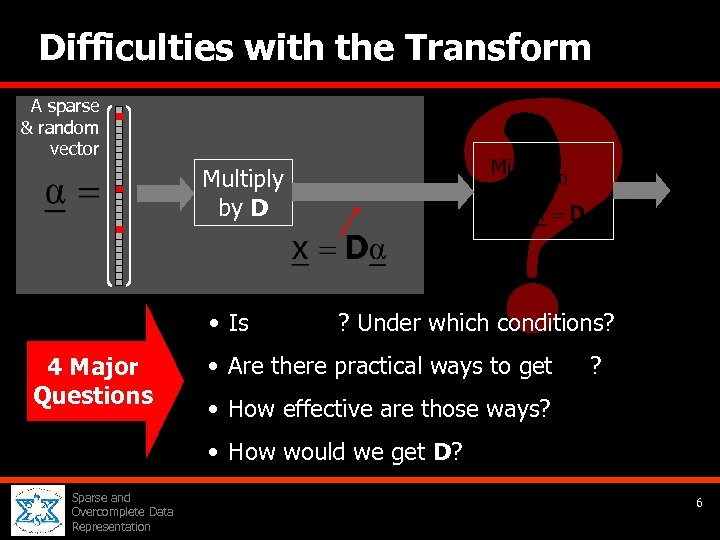 Difficulties with the Transform A sparse & random vector Multiply by D • Is 4 Major Questions ? Under which conditions? • Are there practical ways to get ? • How effective are those ways? • How would we get D? Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation 6
Difficulties with the Transform A sparse & random vector Multiply by D • Is 4 Major Questions ? Under which conditions? • Are there practical ways to get ? • How effective are those ways? • How would we get D? Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation 6
 Why Is It Interesting? Several recent trends from signal/image processing worth looking at: § JPEG to JPEG 2000 - From (L 2 -norm) KLT to wavelet and nonlinear approximation Sparsity. and sel par S RE HE is § From Wiener to robust restoration – From L 2 -norm (Fourier) to L 1. (e. g. , TV, Beltrami, wavelet shrinkage …) Sparsity. § From unitary to richer representations – Frames, shift-invariance, Overcompleteness. bilateral, steerable, curvelet § Approximation theory – Non-linear approximation Sparsity & Overcompleteness. § ICA and related models Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation Independence and Sparsity. 7
Why Is It Interesting? Several recent trends from signal/image processing worth looking at: § JPEG to JPEG 2000 - From (L 2 -norm) KLT to wavelet and nonlinear approximation Sparsity. and sel par S RE HE is § From Wiener to robust restoration – From L 2 -norm (Fourier) to L 1. (e. g. , TV, Beltrami, wavelet shrinkage …) Sparsity. § From unitary to richer representations – Frames, shift-invariance, Overcompleteness. bilateral, steerable, curvelet § Approximation theory – Non-linear approximation Sparsity & Overcompleteness. § ICA and related models Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation Independence and Sparsity. 7
 Agenda 1. A Visit to Sparseland Motivating Sparsity & Overcompleteness 2. Answering the 4 Questions T How & why should this work? Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation 8
Agenda 1. A Visit to Sparseland Motivating Sparsity & Overcompleteness 2. Answering the 4 Questions T How & why should this work? Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation 8
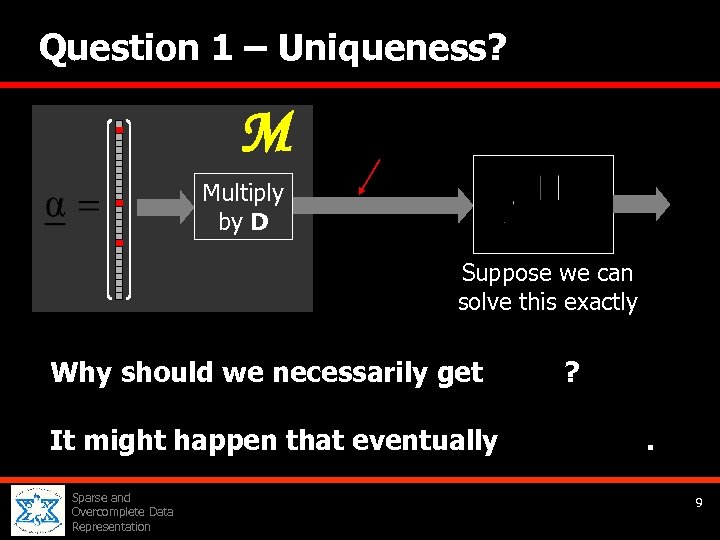 Question 1 – Uniqueness? M Multiply by D Suppose we can solve this exactly Why should we necessarily get It might happen that eventually Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation ? . 9
Question 1 – Uniqueness? M Multiply by D Suppose we can solve this exactly Why should we necessarily get It might happen that eventually Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation ? . 9
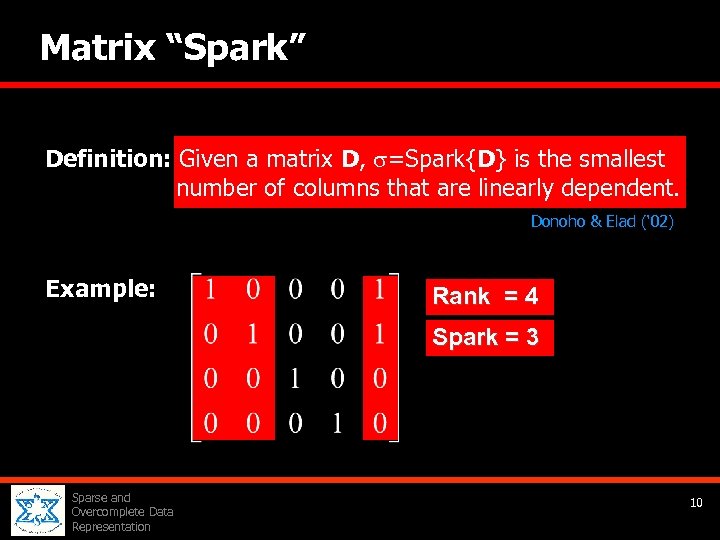 Matrix “Spark” Definition: Given a matrix D, =Spark{D} is the smallest and number of columns that are linearly dependent. Donoho & Elad (‘ 02) Example: Rank = 4 Spark = 3 Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation 10
Matrix “Spark” Definition: Given a matrix D, =Spark{D} is the smallest and number of columns that are linearly dependent. Donoho & Elad (‘ 02) Example: Rank = 4 Spark = 3 Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation 10
 Uniqueness Rule Suppose this problem has been solved somehow Uniqueness If we found a representation that satisfy Donoho & Elad (‘ 02) then necessarily it is unique (the sparsest). M generates vectors using “sparse enough” , the This result implies that if solution of the above will find it exactly. Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation 11
Uniqueness Rule Suppose this problem has been solved somehow Uniqueness If we found a representation that satisfy Donoho & Elad (‘ 02) then necessarily it is unique (the sparsest). M generates vectors using “sparse enough” , the This result implies that if solution of the above will find it exactly. Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation 11
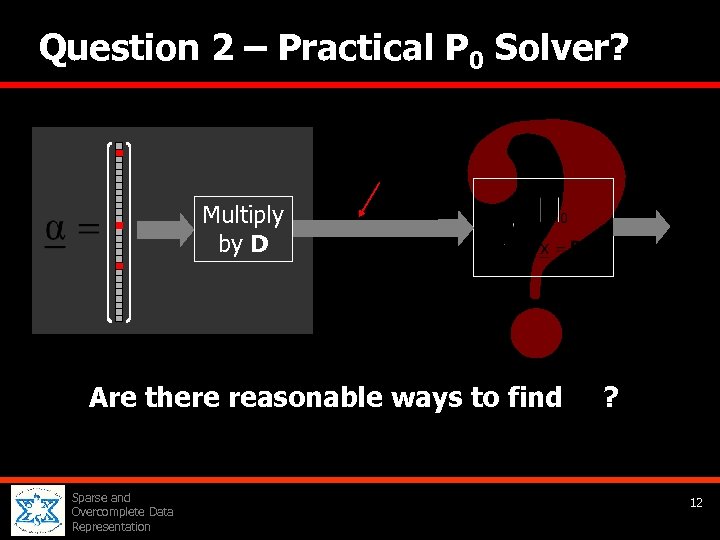 Question 2 – Practical P 0 Solver? M Multiply by D Are there reasonable ways to find Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation ? 12
Question 2 – Practical P 0 Solver? M Multiply by D Are there reasonable ways to find Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation ? 12
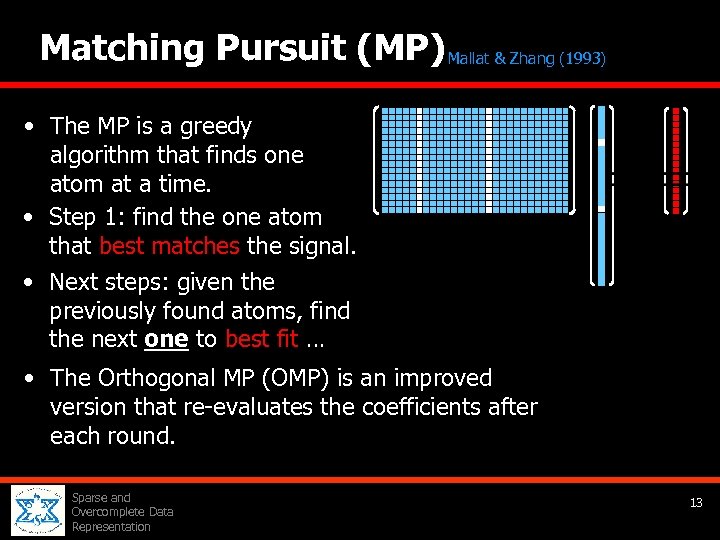 Matching Pursuit (MP) Mallat & Zhang (1993) • The MP is a greedy algorithm that finds one atom at a time. • Step 1: find the one atom that best matches the signal. • Next steps: given the previously found atoms, find the next one to best fit … • The Orthogonal MP (OMP) is an improved version that re-evaluates the coefficients after each round. Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation 13
Matching Pursuit (MP) Mallat & Zhang (1993) • The MP is a greedy algorithm that finds one atom at a time. • Step 1: find the one atom that best matches the signal. • Next steps: given the previously found atoms, find the next one to best fit … • The Orthogonal MP (OMP) is an improved version that re-evaluates the coefficients after each round. Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation 13
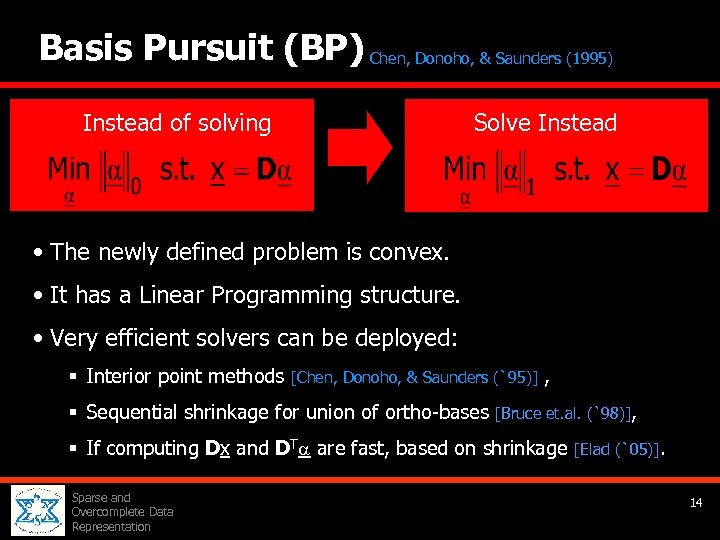 Basis Pursuit (BP) Chen, Donoho, & Saunders (1995) Solve Instead of solving • The newly defined problem is convex. • It has a Linear Programming structure. • Very efficient solvers can be deployed: § Interior point methods [Chen, Donoho, & Saunders (`95)] § Sequential shrinkage for union of ortho-bases , [Bruce et. al. (`98)], § If computing Dx and DT are fast, based on shrinkage Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation [Elad (`05)]. 14
Basis Pursuit (BP) Chen, Donoho, & Saunders (1995) Solve Instead of solving • The newly defined problem is convex. • It has a Linear Programming structure. • Very efficient solvers can be deployed: § Interior point methods [Chen, Donoho, & Saunders (`95)] § Sequential shrinkage for union of ortho-bases , [Bruce et. al. (`98)], § If computing Dx and DT are fast, based on shrinkage Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation [Elad (`05)]. 14
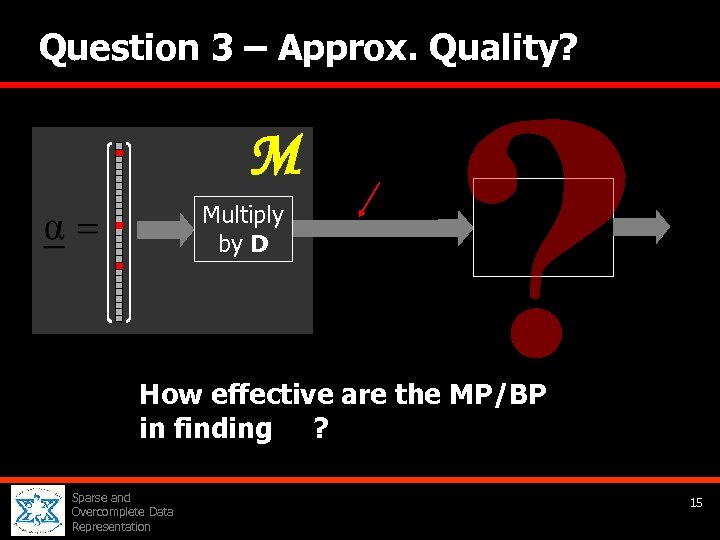 Question 3 – Approx. Quality? M Multiply by D How effective are the MP/BP in finding ? Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation 15
Question 3 – Approx. Quality? M Multiply by D How effective are the MP/BP in finding ? Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation 15
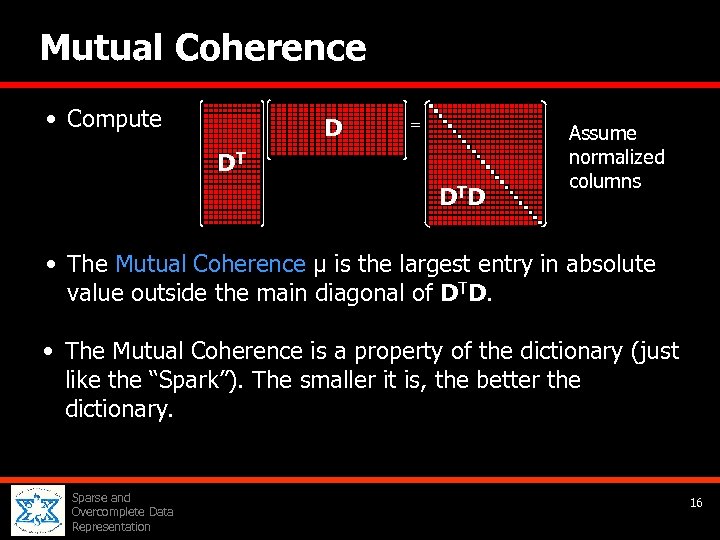 Mutual Coherence • Compute D = DT D TD Assume normalized columns • The Mutual Coherence µ is the largest entry in absolute value outside the main diagonal of DTD. • The Mutual Coherence is a property of the dictionary (just like the “Spark”). The smaller it is, the better the dictionary. Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation 16
Mutual Coherence • Compute D = DT D TD Assume normalized columns • The Mutual Coherence µ is the largest entry in absolute value outside the main diagonal of DTD. • The Mutual Coherence is a property of the dictionary (just like the “Spark”). The smaller it is, the better the dictionary. Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation 16
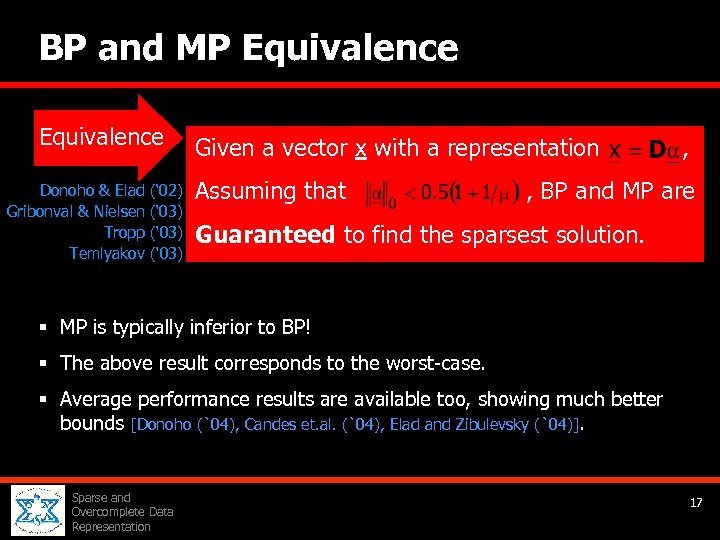 BP and MP Equivalence Donoho & Elad Gribonval & Nielsen Tropp Temlyakov (‘ 02) (‘ 03) Given a vector x with a representation Assuming that , , BP and MP are Guaranteed to find the sparsest solution. § MP is typically inferior to BP! § The above result corresponds to the worst-case. § Average performance results are available too, showing much better bounds [Donoho (`04), Candes et. al. (`04), Elad and Zibulevsky (`04)]. Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation 17
BP and MP Equivalence Donoho & Elad Gribonval & Nielsen Tropp Temlyakov (‘ 02) (‘ 03) Given a vector x with a representation Assuming that , , BP and MP are Guaranteed to find the sparsest solution. § MP is typically inferior to BP! § The above result corresponds to the worst-case. § Average performance results are available too, showing much better bounds [Donoho (`04), Candes et. al. (`04), Elad and Zibulevsky (`04)]. Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation 17
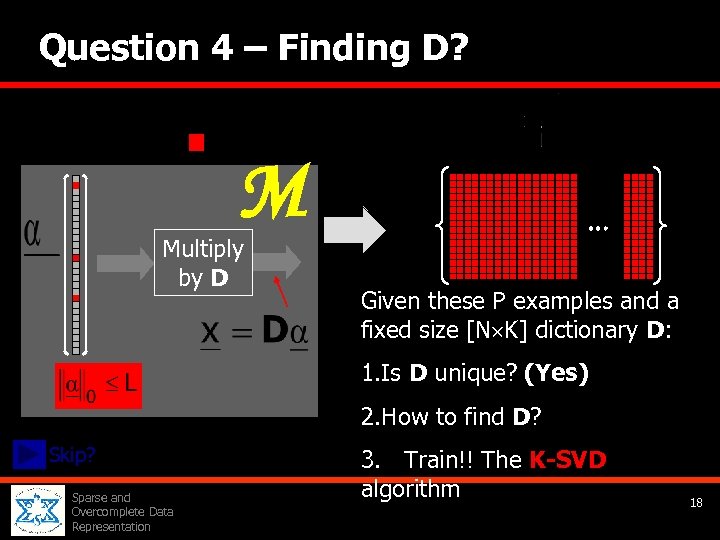 Question 4 – Finding D? M Multiply by D Given these P examples and a fixed size [N K] dictionary D: 1. Is D unique? (Yes) 2. How to find D? Skip? Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation 3. Train!! The K-SVD algorithm 18
Question 4 – Finding D? M Multiply by D Given these P examples and a fixed size [N K] dictionary D: 1. Is D unique? (Yes) 2. How to find D? Skip? Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation 3. Train!! The K-SVD algorithm 18
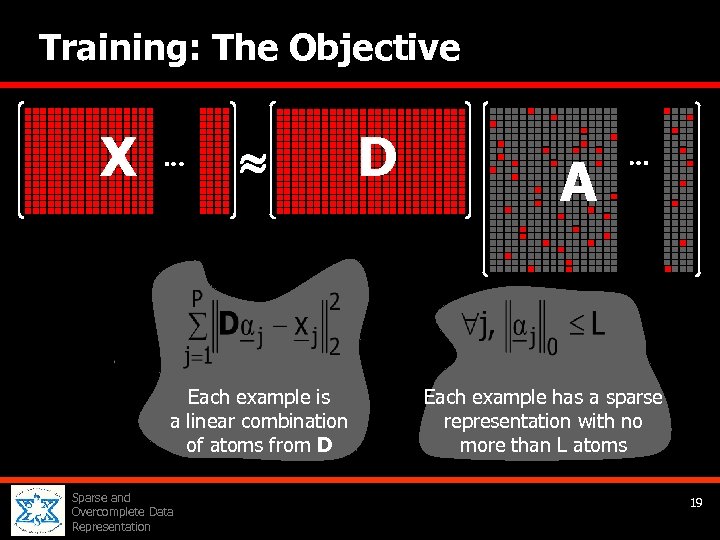 Training: The Objective X Each example is a linear combination of atoms from D Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation D A Each example has a sparse representation with no more than L atoms 19
Training: The Objective X Each example is a linear combination of atoms from D Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation D A Each example has a sparse representation with no more than L atoms 19
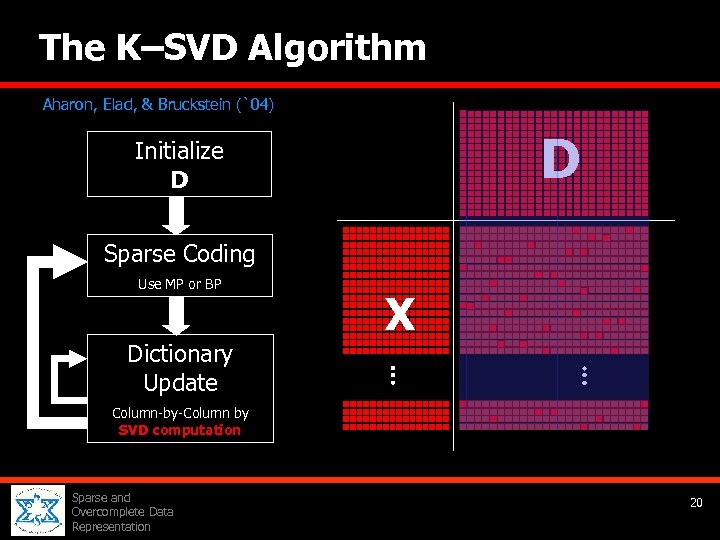 The K–SVD Algorithm Aharon, Elad, & Bruckstein (`04) D Initialize D Sparse Coding Use MP or BP Dictionary Update X Column-by-Column by SVD computation Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation 20
The K–SVD Algorithm Aharon, Elad, & Bruckstein (`04) D Initialize D Sparse Coding Use MP or BP Dictionary Update X Column-by-Column by SVD computation Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation 20
 Today We Discussed 1. A Visit to Sparseland Motivating Sparsity & Overcompleteness 2. Answering the 4 Questions How & why should this work? Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation 21
Today We Discussed 1. A Visit to Sparseland Motivating Sparsity & Overcompleteness 2. Answering the 4 Questions How & why should this work? Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation 21
 Summary Sparsity and Overcompleteness are important There are ideas that can be used in difficulties in designing better tools in using them! data/signal/image processing Future transforms and regularizations will be datadriven, non-linear, overcomplete, and promoting sparsity. Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation We are working on resolving those difficulties: • Performance of pursuit alg. • Speedup of those methods, • Training the dictionary, • Demonstrating applications, • … The dream? 22
Summary Sparsity and Overcompleteness are important There are ideas that can be used in difficulties in designing better tools in using them! data/signal/image processing Future transforms and regularizations will be datadriven, non-linear, overcomplete, and promoting sparsity. Sparse and Overcomplete Data Representation We are working on resolving those difficulties: • Performance of pursuit alg. • Speedup of those methods, • Training the dictionary, • Demonstrating applications, • … The dream? 22


