f3139a813f30f42bcf5540b249f912a2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14
 SPANISH EDUCATIONAL SYSTEM
SPANISH EDUCATIONAL SYSTEM
 PRE-SCHOOL EDUCATION • It is a voluntary stage. Its objective is the assistance and education of the early childhood. • It mainly covers the following matters: Ø Body control: knowledge and progressive control of their own bodies. Ø Movement development: games and movement. Ø Early manifestations of language and communication: language development as a learning nucleus. Ø Elementary norms of behaviour and social relationships: living with others. Ø Discovery of immediate surroundings. Ø Balance and development of affectivity. Ø Acquisition of healthy life habits, which will be the base for a proper health education.
PRE-SCHOOL EDUCATION • It is a voluntary stage. Its objective is the assistance and education of the early childhood. • It mainly covers the following matters: Ø Body control: knowledge and progressive control of their own bodies. Ø Movement development: games and movement. Ø Early manifestations of language and communication: language development as a learning nucleus. Ø Elementary norms of behaviour and social relationships: living with others. Ø Discovery of immediate surroundings. Ø Balance and development of affectivity. Ø Acquisition of healthy life habits, which will be the base for a proper health education.
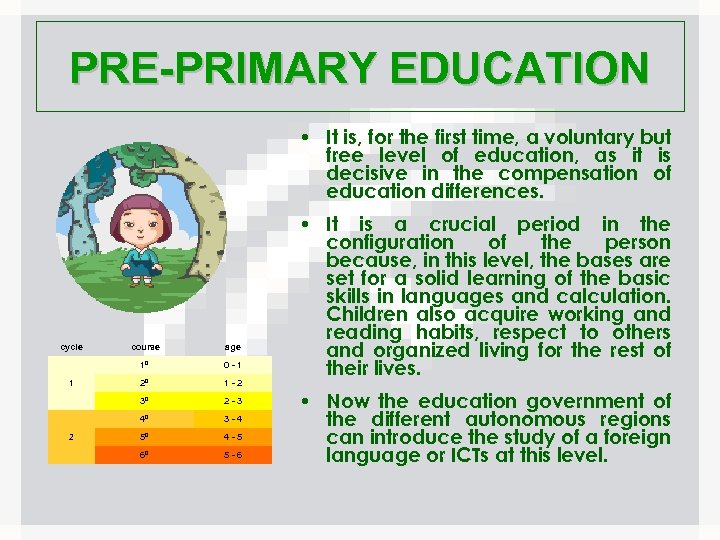 PRE-PRIMARY EDUCATION • It is, for the first time, a voluntary but free level of education, as it is decisive in the compensation of education differences. cycle 0 - 1 2º 1 - 2 3º 2 - 3 4º 2 age 1º 1 course 3 - 4 5º 4 - 5 6º 5 - 6 • It is a crucial period in the configuration of the person because, in this level, the bases are set for a solid learning of the basic skills in languages and calculation. Children also acquire working and reading habits, respect to others and organized living for the rest of their lives. • Now the education government of the different autonomous regions can introduce the study of a foreign language or ICTs at this level.
PRE-PRIMARY EDUCATION • It is, for the first time, a voluntary but free level of education, as it is decisive in the compensation of education differences. cycle 0 - 1 2º 1 - 2 3º 2 - 3 4º 2 age 1º 1 course 3 - 4 5º 4 - 5 6º 5 - 6 • It is a crucial period in the configuration of the person because, in this level, the bases are set for a solid learning of the basic skills in languages and calculation. Children also acquire working and reading habits, respect to others and organized living for the rest of their lives. • Now the education government of the different autonomous regions can introduce the study of a foreign language or ICTs at this level.
 PRIMARY EDUCATION • The name of the different knowledge areas is modified. Objectives are also modified in order to better adequate to their aims. • This period is also decisive for children. At this stage the basis for a solid learning of the basic skills in languages and calculation are set. This is the age when children acquire working and reading habits, respect to others and organized living for the rest of their lives. • It is organized in three cycles of two years each, which makes a total of 6 years. The promotion or repetition (maximum once every stage) will be decided at the end of each cycle. • The learning of a foreign language will begin in the first year of Primary. (It begins in the third year nowadays) • Primary curricula are organized paying special attention to the instrumental areas: language and mathematics. cycle 1 2 3 course age 1º 6 - 7 2º 7 - 8 3º 8 - 9 4º 9 - 10 5º 10 - 11 6º 11 - 12
PRIMARY EDUCATION • The name of the different knowledge areas is modified. Objectives are also modified in order to better adequate to their aims. • This period is also decisive for children. At this stage the basis for a solid learning of the basic skills in languages and calculation are set. This is the age when children acquire working and reading habits, respect to others and organized living for the rest of their lives. • It is organized in three cycles of two years each, which makes a total of 6 years. The promotion or repetition (maximum once every stage) will be decided at the end of each cycle. • The learning of a foreign language will begin in the first year of Primary. (It begins in the third year nowadays) • Primary curricula are organized paying special attention to the instrumental areas: language and mathematics. cycle 1 2 3 course age 1º 6 - 7 2º 7 - 8 3º 8 - 9 4º 9 - 10 5º 10 - 11 6º 11 - 12
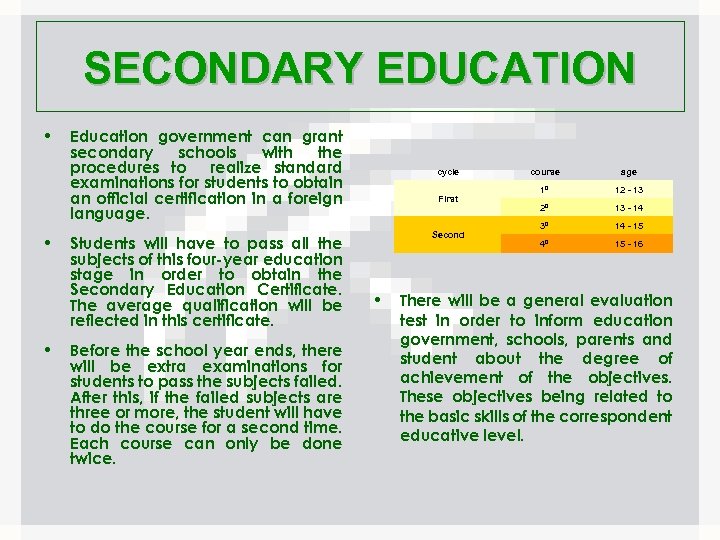 SECONDARY EDUCATION • • • Education government can grant secondary schools with the procedures to realize standard examinations for students to obtain an official certification in a foreign language. Students will have to pass all the subjects of this four-year education stage in order to obtain the Secondary Education Certificate. The average qualification will be reflected in this certificate. Before the school year ends, there will be extra examinations for students to pass the subjects failed. After this, if the failed subjects are three or more, the student will have to do the course for a second time. Each course can only be done twice. cycle First Second • course age 1º 12 - 13 2º 13 - 14 3º 14 - 15 4º 15 - 16 There will be a general evaluation test in order to inform education government, schools, parents and student about the degree of achievement of the objectives. These objectives being related to the basic skills of the correspondent educative level.
SECONDARY EDUCATION • • • Education government can grant secondary schools with the procedures to realize standard examinations for students to obtain an official certification in a foreign language. Students will have to pass all the subjects of this four-year education stage in order to obtain the Secondary Education Certificate. The average qualification will be reflected in this certificate. Before the school year ends, there will be extra examinations for students to pass the subjects failed. After this, if the failed subjects are three or more, the student will have to do the course for a second time. Each course can only be done twice. cycle First Second • course age 1º 12 - 13 2º 13 - 14 3º 14 - 15 4º 15 - 16 There will be a general evaluation test in order to inform education government, schools, parents and student about the degree of achievement of the objectives. These objectives being related to the basic skills of the correspondent educative level.
 SECONDARY EDUCATION • Educative itineraries are offered for the student to profit the most form the educative system, according to their interests, abilities and attitudes. • In 3 rd ESO (14), students can choose between two itineraries: the Technological one and the Scientific-Humanistic one. • In 4 th ESO (15), the choice is between three: Technological, Scientific and Humanistic. • If a student wants none of the itineraries and wants to join the working world, there are Professional Introduction Programmes for them (PGS). • Decisions are taken by the students themselves and their families. • Schools will facilitate the necessary orientation for this decision: at the end of 2º students will obtain a School Orientation Report. The itinerary is voluntary. • The different itineraries lead to the same certification: the Secondary Education Graduate. In this way, whatever the itinerary selected, the student can choose between Bachillerato or Professional Education.
SECONDARY EDUCATION • Educative itineraries are offered for the student to profit the most form the educative system, according to their interests, abilities and attitudes. • In 3 rd ESO (14), students can choose between two itineraries: the Technological one and the Scientific-Humanistic one. • In 4 th ESO (15), the choice is between three: Technological, Scientific and Humanistic. • If a student wants none of the itineraries and wants to join the working world, there are Professional Introduction Programmes for them (PGS). • Decisions are taken by the students themselves and their families. • Schools will facilitate the necessary orientation for this decision: at the end of 2º students will obtain a School Orientation Report. The itinerary is voluntary. • The different itineraries lead to the same certification: the Secondary Education Graduate. In this way, whatever the itinerary selected, the student can choose between Bachillerato or Professional Education.
 PROGRAMAS DE CUALIFICACIÓN PROFESIONAL INICIAL. PCPI • • They are destined to students that didn’t reach the objectives of the ESO, so that they can be given basic and professional education in order to join the working world or go on with their studies. They are originally thought for students of: - • 16 who have no academic certificate, after the adequate educative orientation. 15 (exceptionally) who are in 2º ESO, won’t promote to 3º and have repeated an ESO course. Their parents have to agree and the student enrols in the voluntary modules in order to get ESO graduate The length of a PCPI is two school years. Its contents are organized into two areas or modules: – Obligatory modules • Basic training (14 h. a week) • Health and safety at work • Incorporation to labour force • Professional modules (including training in working places) – Voluntary modules • Communication area • Social area • Scientific and technologic area
PROGRAMAS DE CUALIFICACIÓN PROFESIONAL INICIAL. PCPI • • They are destined to students that didn’t reach the objectives of the ESO, so that they can be given basic and professional education in order to join the working world or go on with their studies. They are originally thought for students of: - • 16 who have no academic certificate, after the adequate educative orientation. 15 (exceptionally) who are in 2º ESO, won’t promote to 3º and have repeated an ESO course. Their parents have to agree and the student enrols in the voluntary modules in order to get ESO graduate The length of a PCPI is two school years. Its contents are organized into two areas or modules: – Obligatory modules • Basic training (14 h. a week) • Health and safety at work • Incorporation to labour force • Professional modules (including training in working places) – Voluntary modules • Communication area • Social area • Scientific and technologic area
 BACHILLERATO • The different types of Bachillerato are called modalities. The established modalities respond better to the objectives of this level of post-obligatory education. These modalities are: Arts, Nature and Health Sciences, Humanities and Social Sciences, and Technology. • The differences in capacities, motivations and interests are well defined at this level. Students in Bachillerato adapt their studies to their preferences thanks to the choice of modality and certain optional subjects. Therefore it is possible to define educative itineraries diverse and personalized, suited to their attitudes, motivation and interests. • A the end of the two years of this level, students can either: – Take the Selectividad examination. Passing it is necessary for the access to university studies. – Join a Ciclo Formativo de Grado Superior
BACHILLERATO • The different types of Bachillerato are called modalities. The established modalities respond better to the objectives of this level of post-obligatory education. These modalities are: Arts, Nature and Health Sciences, Humanities and Social Sciences, and Technology. • The differences in capacities, motivations and interests are well defined at this level. Students in Bachillerato adapt their studies to their preferences thanks to the choice of modality and certain optional subjects. Therefore it is possible to define educative itineraries diverse and personalized, suited to their attitudes, motivation and interests. • A the end of the two years of this level, students can either: – Take the Selectividad examination. Passing it is necessary for the access to university studies. – Join a Ciclo Formativo de Grado Superior
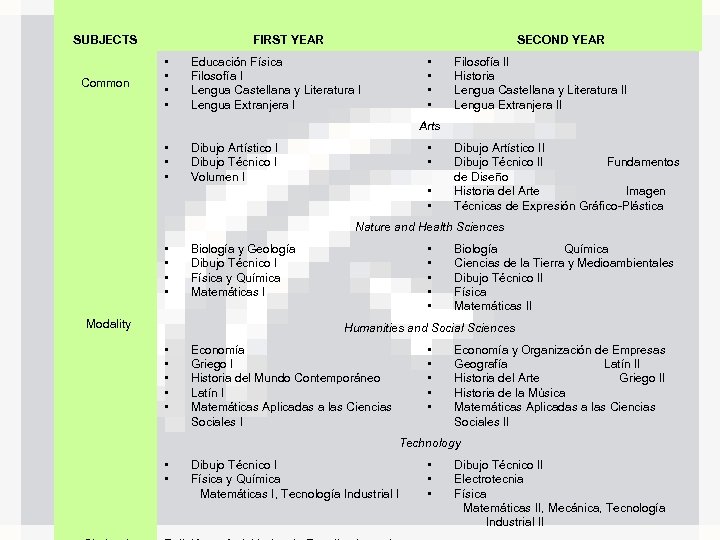 SUBJECTS Common FIRST YEAR • • SECOND YEAR • • Educación Física Filosofía I Lengua Castellana y Literatura I Lengua Extranjera I Filosofía II Historia Lengua Castellana y Literatura II Lengua Extranjera II Arts • • • Dibujo Artístico I Dibujo Técnico I Volumen I • • Dibujo Artístico II Dibujo Técnico II Fundamentos de Diseño Historia del Arte Imagen Técnicas de Expresión Gráfico-Plástica Nature and Health Sciences • • Modality • • • Biología y Geología Dibujo Técnico I Física y Química Matemáticas I Biología Química Ciencias de la Tierra y Medioambientales Dibujo Técnico II Física Matemáticas II Humanities and Social Sciences • • • Economía Griego I Historia del Mundo Contemporáneo Latín I Matemáticas Aplicadas a las Ciencias Sociales I Economía y Organización de Empresas Geografía Latín II Historia del Arte Griego II Historia de la Música Matemáticas Aplicadas a las Ciencias Sociales II Technology • • Dibujo Técnico I Física y Química Matemáticas I, Tecnología Industrial I • • • Dibujo Técnico II Electrotecnia Física Matemáticas II, Mecánica, Tecnología Industrial II
SUBJECTS Common FIRST YEAR • • SECOND YEAR • • Educación Física Filosofía I Lengua Castellana y Literatura I Lengua Extranjera I Filosofía II Historia Lengua Castellana y Literatura II Lengua Extranjera II Arts • • • Dibujo Artístico I Dibujo Técnico I Volumen I • • Dibujo Artístico II Dibujo Técnico II Fundamentos de Diseño Historia del Arte Imagen Técnicas de Expresión Gráfico-Plástica Nature and Health Sciences • • Modality • • • Biología y Geología Dibujo Técnico I Física y Química Matemáticas I Biología Química Ciencias de la Tierra y Medioambientales Dibujo Técnico II Física Matemáticas II Humanities and Social Sciences • • • Economía Griego I Historia del Mundo Contemporáneo Latín I Matemáticas Aplicadas a las Ciencias Sociales I Economía y Organización de Empresas Geografía Latín II Historia del Arte Griego II Historia de la Música Matemáticas Aplicadas a las Ciencias Sociales II Technology • • Dibujo Técnico I Física y Química Matemáticas I, Tecnología Industrial I • • • Dibujo Técnico II Electrotecnia Física Matemáticas II, Mecánica, Tecnología Industrial II
 VOCATIONAL TRAINING • The FP is a set of educative actions that allow students to develop different professions, access to jobs and the active participation in social, cultural and economic life. It includes the teaching of initial professional education, introduction and rehabilitation of workers and practical education in companies. The final objective is the acquisition and permanent updating of professional competencies. • The contents are organized in Professional Units of theoretical and practical knowledge according to the different activities developed in a particular job. • There are two levels according the professional qualification obtained at the end of each one: ü Lower cycle ü Upper cycle
VOCATIONAL TRAINING • The FP is a set of educative actions that allow students to develop different professions, access to jobs and the active participation in social, cultural and economic life. It includes the teaching of initial professional education, introduction and rehabilitation of workers and practical education in companies. The final objective is the acquisition and permanent updating of professional competencies. • The contents are organized in Professional Units of theoretical and practical knowledge according to the different activities developed in a particular job. • There are two levels according the professional qualification obtained at the end of each one: ü Lower cycle ü Upper cycle
 ARTS EDUCATION • Arts education aims to provide students with quality training and guarantee the qualifications of future professionals in the fields of music, dance, dramatic art, art and design. • Arts education consists of the following: a) Elementary music and dance education. b) Professional Arts education. This refers to professional training in music and dance and to intermediate and higher level courses in art and design. c) Higher Arts education. This refers to a higher level studies in music and dance, dramatic art, conservation and restoration of cultural goods, higher studies in design and in arts, which includes ceramics and glass work. • The Education Administrations will allow students to study both professional Arts education and secondary education at the same time.
ARTS EDUCATION • Arts education aims to provide students with quality training and guarantee the qualifications of future professionals in the fields of music, dance, dramatic art, art and design. • Arts education consists of the following: a) Elementary music and dance education. b) Professional Arts education. This refers to professional training in music and dance and to intermediate and higher level courses in art and design. c) Higher Arts education. This refers to a higher level studies in music and dance, dramatic art, conservation and restoration of cultural goods, higher studies in design and in arts, which includes ceramics and glass work. • The Education Administrations will allow students to study both professional Arts education and secondary education at the same time.
 LANGUAGE EDUCATION • Language teaching will take place in official language schools, which are outside the compulsory school system. • To access language teaching students must be 16 years of age in the year of commencing their studies. Students over the age of 14 may access language courses in a language which is not taught in compulsory secondary education. • Official language schools will promote the official languages of the European Union, the coofficial languages existing in Spain and Spanish as a foreign language. They will also provide teaching in other languages of special interest for cultural, social or economic reasons. • In accordance with the stipulations of the Education Administrations, official language schools may offer refresher courses in foreign languages and training for language teachers and other professional bodies.
LANGUAGE EDUCATION • Language teaching will take place in official language schools, which are outside the compulsory school system. • To access language teaching students must be 16 years of age in the year of commencing their studies. Students over the age of 14 may access language courses in a language which is not taught in compulsory secondary education. • Official language schools will promote the official languages of the European Union, the coofficial languages existing in Spain and Spanish as a foreign language. They will also provide teaching in other languages of special interest for cultural, social or economic reasons. • In accordance with the stipulations of the Education Administrations, official language schools may offer refresher courses in foreign languages and training for language teachers and other professional bodies.
 SPORTS EDUCATION • • • The aim of sports education is to prepare students for professional activity related to a sports category or speciality and equip them for the working and sporting environment and for active citizenship. Sports education will contribute to developing capacities which will allow students to: a) Develop general competence in their respective studies. b) Guarantee initial professional competence in basic training, technical improvement, team management and training, management of high performance sports men and women in the corresponding category or speciality. c) Understand the characteristics and the organisation of the respective category or speciality and know the rights and obligations relating to their functions. d) Acquire the knowledge and skills necessary to carry out their work under safe conditions. Sports education is structured into intermediate and higher levels and may relate to the National List of Vocational Qualifications. To access the intermediate level, students must hold the Certificate in Compulsory Secondary Education. To access the higher level they will need to have the Bachiller Certificate and the Technical qualification in Sports, in the corresponding category or speciality. Sports education will be organised into blocks and modules, of varying duration, divided into areas of theory and practice appropriate to the different professional fields.
SPORTS EDUCATION • • • The aim of sports education is to prepare students for professional activity related to a sports category or speciality and equip them for the working and sporting environment and for active citizenship. Sports education will contribute to developing capacities which will allow students to: a) Develop general competence in their respective studies. b) Guarantee initial professional competence in basic training, technical improvement, team management and training, management of high performance sports men and women in the corresponding category or speciality. c) Understand the characteristics and the organisation of the respective category or speciality and know the rights and obligations relating to their functions. d) Acquire the knowledge and skills necessary to carry out their work under safe conditions. Sports education is structured into intermediate and higher levels and may relate to the National List of Vocational Qualifications. To access the intermediate level, students must hold the Certificate in Compulsory Secondary Education. To access the higher level they will need to have the Bachiller Certificate and the Technical qualification in Sports, in the corresponding category or speciality. Sports education will be organised into blocks and modules, of varying duration, divided into areas of theory and practice appropriate to the different professional fields.
 ADULT EDUCATION • It gives people over eighteen the possibility to acquire, update, complete or add to their knowledge and skills for professional and personal development. • Adult education will have the following objectives: a) Acquire basic training, continuously add to and refresh knowledge, abilities and skills and facilitate access to different sectors of the educational system. b) Improve professional qualifications or retrain for other professions. c) Develop personal capacities in areas of self-expression, communication, interpersonal relations and knowledge building. d) Develop capacities to participate in social, cultural, political and economic life and put into practice the right to democratic citizenship. e) Develop programmes which overcome the social exclusion of disadvantaged sectors of society. f) Respond adequately to the challenges related to the gradual aging of the population, ensuring that senior citizens have the opportunity to increase and update their abilities. g) Anticipate and resolve personal, family and social conflicts peacefully. Foster real equality of rights and opportunities between men and women as well as critically assess and analyse inequalities between them.
ADULT EDUCATION • It gives people over eighteen the possibility to acquire, update, complete or add to their knowledge and skills for professional and personal development. • Adult education will have the following objectives: a) Acquire basic training, continuously add to and refresh knowledge, abilities and skills and facilitate access to different sectors of the educational system. b) Improve professional qualifications or retrain for other professions. c) Develop personal capacities in areas of self-expression, communication, interpersonal relations and knowledge building. d) Develop capacities to participate in social, cultural, political and economic life and put into practice the right to democratic citizenship. e) Develop programmes which overcome the social exclusion of disadvantaged sectors of society. f) Respond adequately to the challenges related to the gradual aging of the population, ensuring that senior citizens have the opportunity to increase and update their abilities. g) Anticipate and resolve personal, family and social conflicts peacefully. Foster real equality of rights and opportunities between men and women as well as critically assess and analyse inequalities between them.


