cd12dd7e7b21e2adac67599a12916d3f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
 Space Weather System-Impact Products SSA Environmental Effects Fusion System - (SEEFS) Overview – For NESSC 14 Oct 2009 Stephen Quigley AFRL/RVBX
Space Weather System-Impact Products SSA Environmental Effects Fusion System - (SEEFS) Overview – For NESSC 14 Oct 2009 Stephen Quigley AFRL/RVBX
 Outline • General Overview • FY 04 -06 Products • Future Products • Input Data Requirements • Status
Outline • General Overview • FY 04 -06 Products • Future Products • Input Data Requirements • Status
 SEEFS Overview - General • SEEFS is an AFSPC sponsored program • SEEFS = Products + Architecture + Database • SEEFS combines environmental info with system specs and thresholds to produce system-impact products outputs • SEEFS was designed to provide real-time support • SEEFS is situated as a pseudo stand-alone system with multiple target integrations being pursued – – • Distributed Mission Operations – Space (DMO-S): For training/exercises Air Force Weather Agency (AFWA/SWOC): 3/5 on SMC “ops” Testbed Joint Space Operations Center (JSp. OC): for Do. D asset ops SSA Maui High Performance Computer Center (MHPCC): For distributed processing And others that can be considered – Defense Threat Reduction Agency (DTRA) – NASA • SEEFS is expected to be a net-centric application • SEEFS to be separated into environmental and system-impact pieces
SEEFS Overview - General • SEEFS is an AFSPC sponsored program • SEEFS = Products + Architecture + Database • SEEFS combines environmental info with system specs and thresholds to produce system-impact products outputs • SEEFS was designed to provide real-time support • SEEFS is situated as a pseudo stand-alone system with multiple target integrations being pursued – – • Distributed Mission Operations – Space (DMO-S): For training/exercises Air Force Weather Agency (AFWA/SWOC): 3/5 on SMC “ops” Testbed Joint Space Operations Center (JSp. OC): for Do. D asset ops SSA Maui High Performance Computer Center (MHPCC): For distributed processing And others that can be considered – Defense Threat Reduction Agency (DTRA) – NASA • SEEFS is expected to be a net-centric application • SEEFS to be separated into environmental and system-impact pieces
 SEEFS Overview - Prototypes Completed (FY 04 -05) Products • • • So. RBE RAC II Rad. Scint Sat. Scint Char/D Delivered to SMC from AFRL Solar Radio Burst Effects Radar Auroral Clutter Radar Scintillation Satcom Scintillation Satellite Charge/Discharge – The current version of SEEFS is prototype – An operational version is nearly complete at SMC SYAG – SEEFS output is in graphical and consolidated text formats • Conout. txt allows for machine-to-machine (Mt. M) uses – SEEFS includes nowcast & forecast capabilities – SEEFS includes confidence levels
SEEFS Overview - Prototypes Completed (FY 04 -05) Products • • • So. RBE RAC II Rad. Scint Sat. Scint Char/D Delivered to SMC from AFRL Solar Radio Burst Effects Radar Auroral Clutter Radar Scintillation Satcom Scintillation Satellite Charge/Discharge – The current version of SEEFS is prototype – An operational version is nearly complete at SMC SYAG – SEEFS output is in graphical and consolidated text formats • Conout. txt allows for machine-to-machine (Mt. M) uses – SEEFS includes nowcast & forecast capabilities – SEEFS includes confidence levels
 • Solar Radio Burst Effects (So. RBE) Product • Requires solar radio data – Currently RSTN • Requires radar & SATCOM receiver specs & thresholds
• Solar Radio Burst Effects (So. RBE) Product • Requires solar radio data – Currently RSTN • Requires radar & SATCOM receiver specs & thresholds
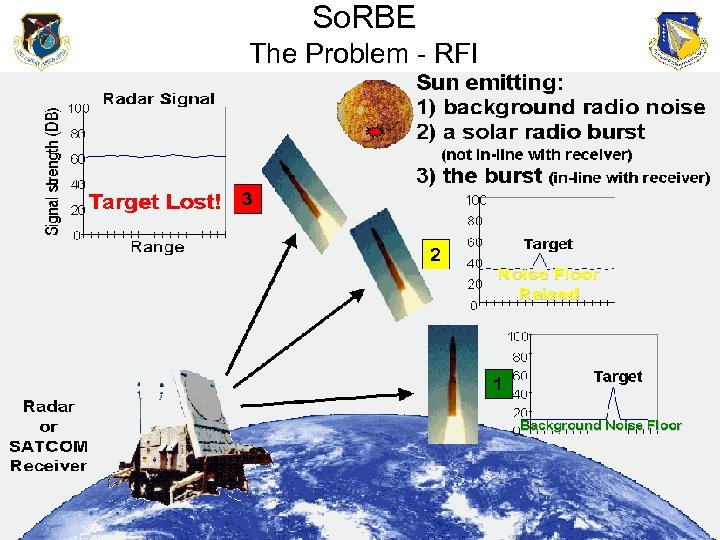 So. RBE The Problem - RFI
So. RBE The Problem - RFI
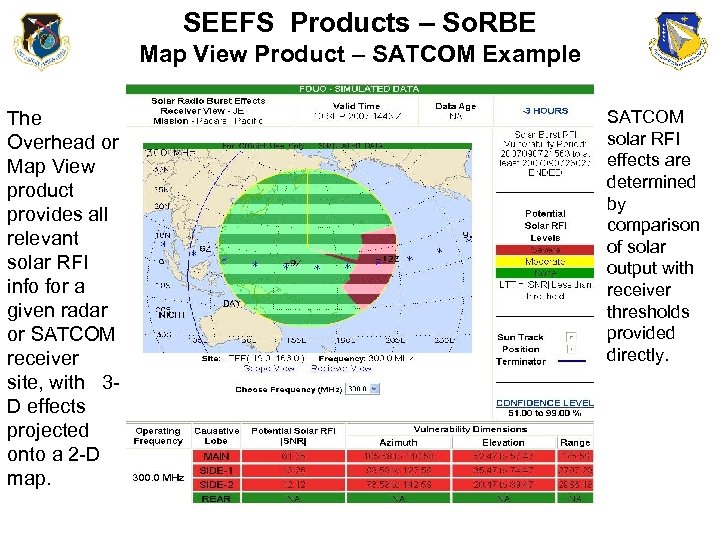 SEEFS Products – So. RBE Map View Product – SATCOM Example The Overhead or Map View product provides all relevant solar RFI info for a given radar or SATCOM receiver site, with 3 D effects projected onto a 2 -D map. Confidence Levels 60 -99% SATCOM solar RFI effects are determined by comparison of solar output with receiver thresholds provided directly.
SEEFS Products – So. RBE Map View Product – SATCOM Example The Overhead or Map View product provides all relevant solar RFI info for a given radar or SATCOM receiver site, with 3 D effects projected onto a 2 -D map. Confidence Levels 60 -99% SATCOM solar RFI effects are determined by comparison of solar output with receiver thresholds provided directly.
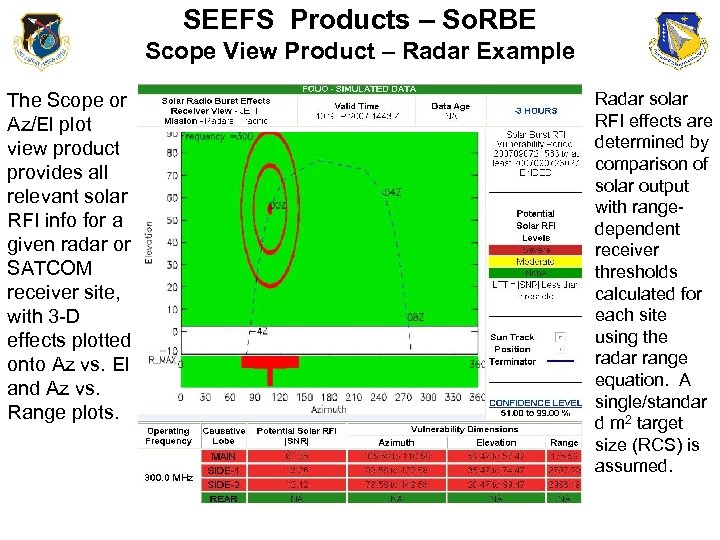 SEEFS Products – So. RBE Scope View Product – Radar Example The Scope or Az/El plot view product provides all relevant solar RFI info for a given radar or SATCOM receiver site, with 3 -D effects plotted onto Az vs. El and Az vs. Range plots. Radar solar RFI effects are determined by comparison of solar output with rangedependent receiver thresholds calculated for each site using the radar range equation. A single/standar d m 2 target size (RCS) is assumed.
SEEFS Products – So. RBE Scope View Product – Radar Example The Scope or Az/El plot view product provides all relevant solar RFI info for a given radar or SATCOM receiver site, with 3 -D effects plotted onto Az vs. El and Az vs. Range plots. Radar solar RFI effects are determined by comparison of solar output with rangedependent receiver thresholds calculated for each site using the radar range equation. A single/standar d m 2 target size (RCS) is assumed.
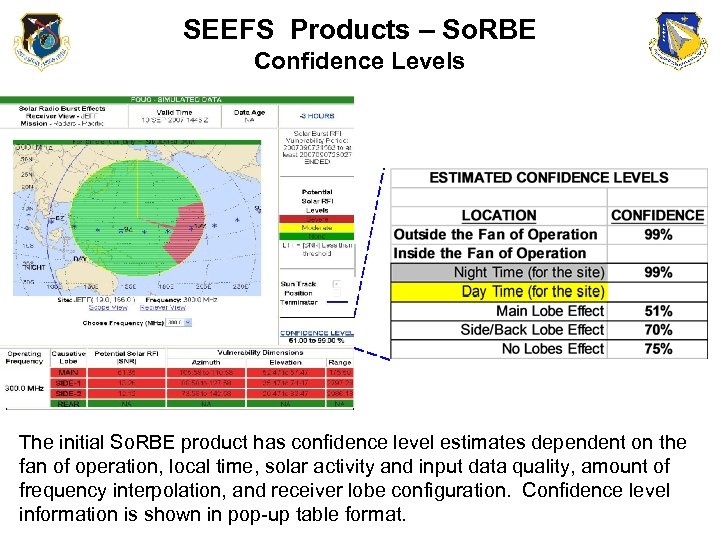 SEEFS Products – So. RBE Confidence Levels 60 -99% The initial So. RBE product has confidence level estimates dependent on the fan of operation, local time, solar activity and input data quality, amount of frequency interpolation, and receiver lobe configuration. Confidence level information is shown in pop-up table format.
SEEFS Products – So. RBE Confidence Levels 60 -99% The initial So. RBE product has confidence level estimates dependent on the fan of operation, local time, solar activity and input data quality, amount of frequency interpolation, and receiver lobe configuration. Confidence level information is shown in pop-up table format.
 • Radar Auroral Clutter (RAC) Product • Requires clutter-effective auroral & SAPS data – Currently via Kp driven boundaries from ground magnetometer or DMSP SSJ/4 data • Requires radar specs • Uses Hardy Auroral Oval and Electron Density models; also uses SAPS model based on John Foster’s SAPS climatology/statistics
• Radar Auroral Clutter (RAC) Product • Requires clutter-effective auroral & SAPS data – Currently via Kp driven boundaries from ground magnetometer or DMSP SSJ/4 data • Requires radar specs • Uses Hardy Auroral Oval and Electron Density models; also uses SAPS model based on John Foster’s SAPS climatology/statistics
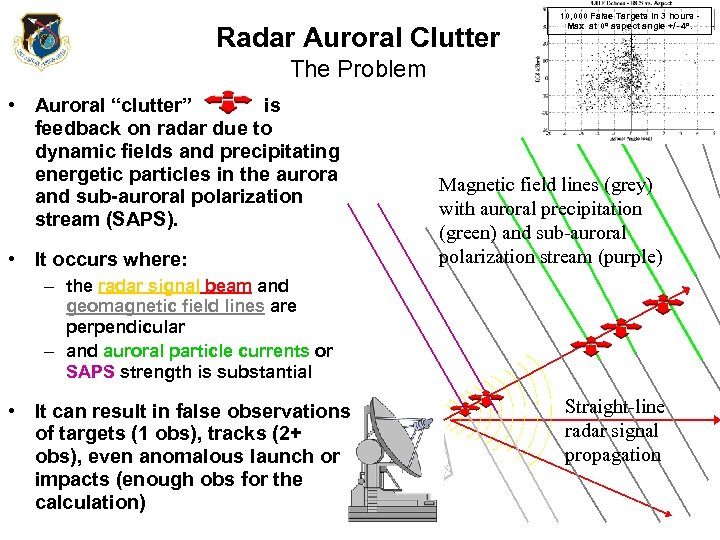 Radar Auroral Clutter 10, 000 False Targets in 3 hours Max at 0 o aspect angle +/- 4 o. The Problem • Auroral “clutter” is feedback on radar due to dynamic fields and precipitating energetic particles in the aurora and sub-auroral polarization stream (SAPS). • It occurs where: Magnetic field lines (grey) with auroral precipitation (green) and sub-auroral polarization stream (purple) – the radar signal beam and geomagnetic field lines are perpendicular – and auroral particle currents or SAPS strength is substantial • It can result in false observations of targets (1 obs), tracks (2+ obs), even anomalous launch or impacts (enough obs for the calculation) Straight-line radar signal propagation
Radar Auroral Clutter 10, 000 False Targets in 3 hours Max at 0 o aspect angle +/- 4 o. The Problem • Auroral “clutter” is feedback on radar due to dynamic fields and precipitating energetic particles in the aurora and sub-auroral polarization stream (SAPS). • It occurs where: Magnetic field lines (grey) with auroral precipitation (green) and sub-auroral polarization stream (purple) – the radar signal beam and geomagnetic field lines are perpendicular – and auroral particle currents or SAPS strength is substantial • It can result in false observations of targets (1 obs), tracks (2+ obs), even anomalous launch or impacts (enough obs for the calculation) Straight-line radar signal propagation
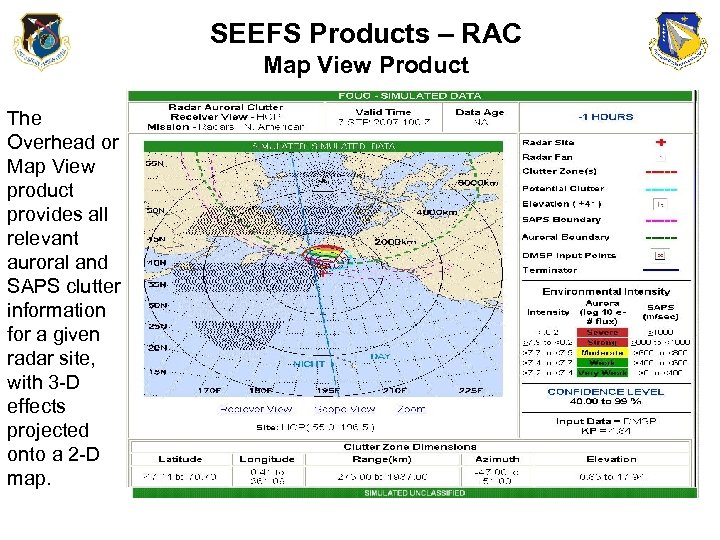 SEEFS Products – RAC Map View Product The Overhead or Map View product provides all relevant auroral and SAPS clutter information for a given radar site, with 3 -D effects projected onto a 2 -D map.
SEEFS Products – RAC Map View Product The Overhead or Map View product provides all relevant auroral and SAPS clutter information for a given radar site, with 3 -D effects projected onto a 2 -D map.
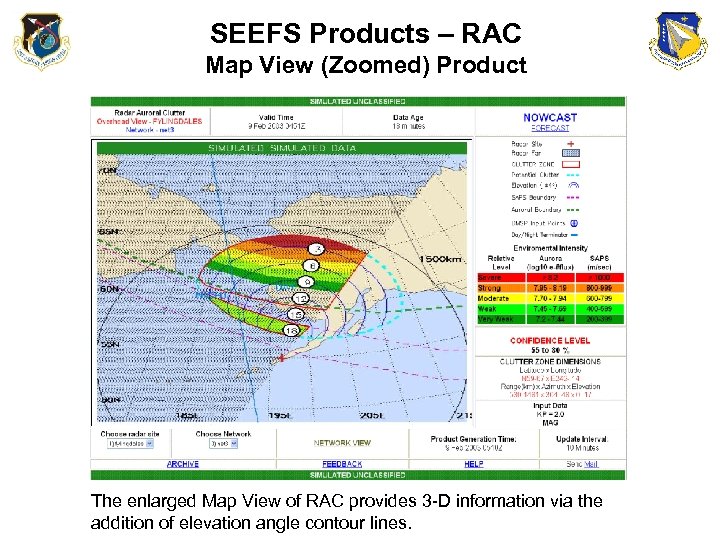 SEEFS Products – RAC Map View (Zoomed) Product The enlarged Map View of RAC provides 3 -D information via the addition of elevation angle contour lines.
SEEFS Products – RAC Map View (Zoomed) Product The enlarged Map View of RAC provides 3 -D information via the addition of elevation angle contour lines.
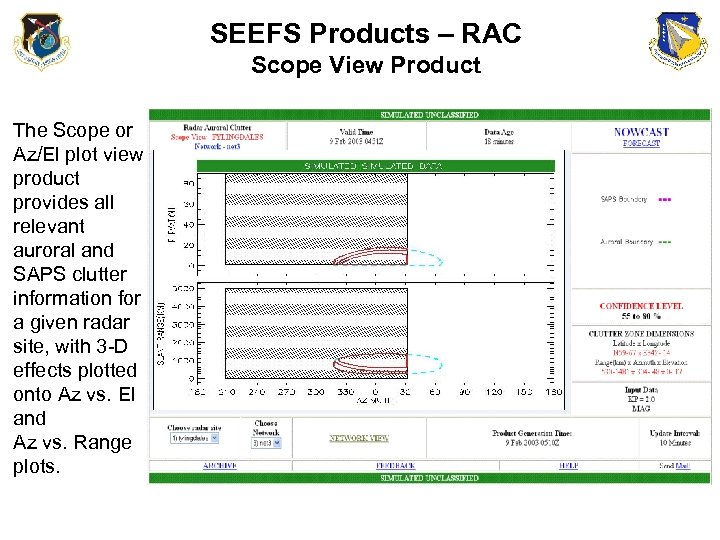 SEEFS Products – RAC Scope View Product The Scope or Az/El plot view product provides all relevant auroral and SAPS clutter information for a given radar site, with 3 -D effects plotted onto Az vs. El and Az vs. Range plots.
SEEFS Products – RAC Scope View Product The Scope or Az/El plot view product provides all relevant auroral and SAPS clutter information for a given radar site, with 3 -D effects plotted onto Az vs. El and Az vs. Range plots.
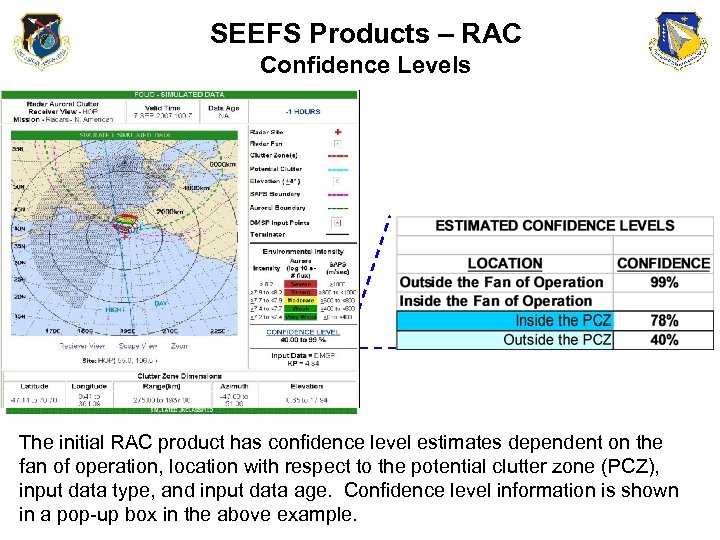 SEEFS Products – RAC Confidence Levels 68 -99% The initial RAC product has confidence level estimates dependent on the fan of operation, location with respect to the potential clutter zone (PCZ), input data type, and input data age. Confidence level information is shown in a pop-up box in the above example.
SEEFS Products – RAC Confidence Levels 68 -99% The initial RAC product has confidence level estimates dependent on the fan of operation, location with respect to the potential clutter zone (PCZ), input data type, and input data age. Confidence level information is shown in a pop-up box in the above example.
 • Satellite & Radar Scintillation (Sat. Scint & Rad. Scint) Products – Requires scintillation & indices (Kp & SSN) data • Currently via SCINDA obs and Kp/SSN – Requires SATCOM & radar receiver specs & thresholds – Uses SCINDA models for real-time obs applications in Sat. Scint; uses WBMOD for climatology applications in Sat. Scint and Rad. Scint
• Satellite & Radar Scintillation (Sat. Scint & Rad. Scint) Products – Requires scintillation & indices (Kp & SSN) data • Currently via SCINDA obs and Kp/SSN – Requires SATCOM & radar receiver specs & thresholds – Uses SCINDA models for real-time obs applications in Sat. Scint; uses WBMOD for climatology applications in Sat. Scint and Rad. Scint
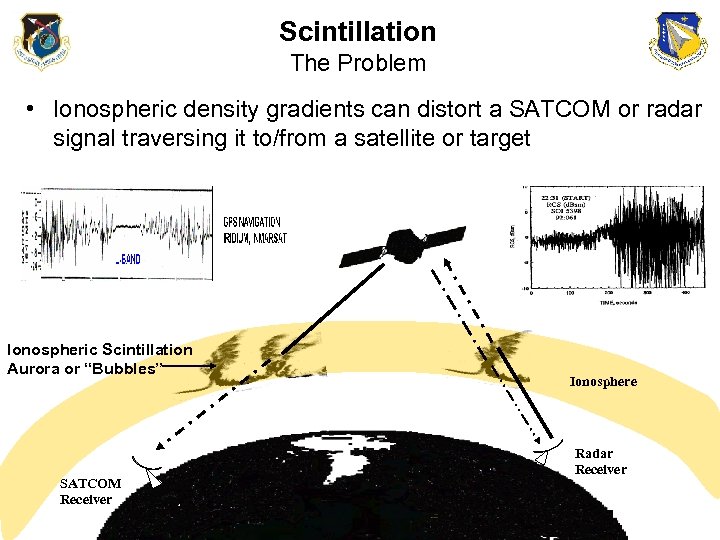 Scintillation The Problem • Ionospheric density gradients can distort a SATCOM or radar signal traversing it to/from a satellite or target Ionospheric Scintillation Aurora or “Bubbles” SATCOM Receiver Ionosphere Radar Receiver
Scintillation The Problem • Ionospheric density gradients can distort a SATCOM or radar signal traversing it to/from a satellite or target Ionospheric Scintillation Aurora or “Bubbles” SATCOM Receiver Ionosphere Radar Receiver
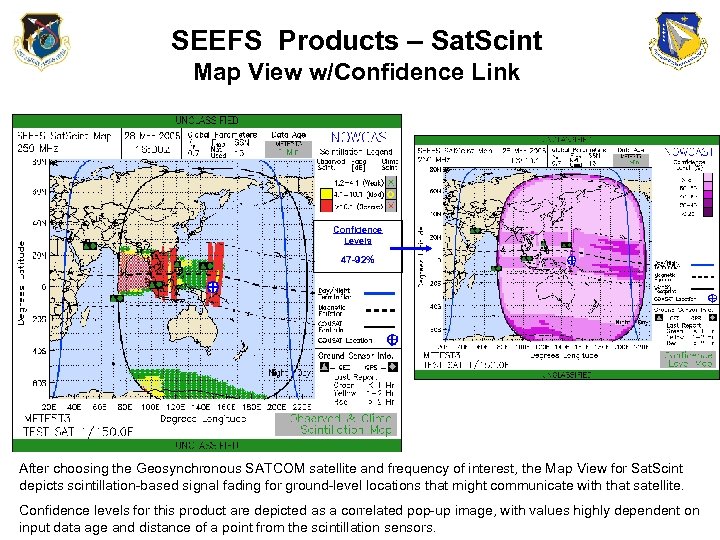 SEEFS Products – Sat. Scint Map View w/Confidence Link Confidence Levels 47 -92% After choosing the Geosynchronous SATCOM satellite and frequency of interest, the Map View for Sat. Scint depicts scintillation-based signal fading for ground-level locations that might communicate with that satellite. Confidence levels for this product are depicted as a correlated pop-up image, with values highly dependent on input data age and distance of a point from the scintillation sensors.
SEEFS Products – Sat. Scint Map View w/Confidence Link Confidence Levels 47 -92% After choosing the Geosynchronous SATCOM satellite and frequency of interest, the Map View for Sat. Scint depicts scintillation-based signal fading for ground-level locations that might communicate with that satellite. Confidence levels for this product are depicted as a correlated pop-up image, with values highly dependent on input data age and distance of a point from the scintillation sensors.
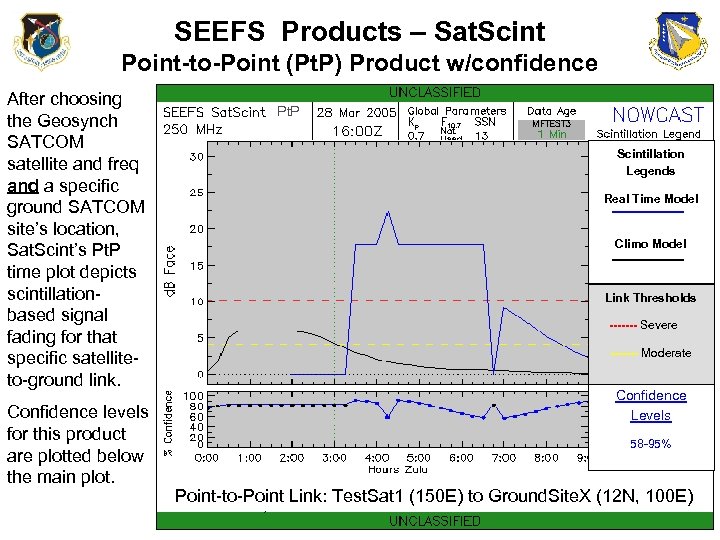 SEEFS Products – Sat. Scint Point-to-Point (Pt. P) Product w/confidence After choosing the Geosynch SATCOM satellite and freq and a specific ground SATCOM site’s location, Sat. Scint’s Pt. P time plot depicts scintillationbased signal fading for that specific satelliteto-ground link. Confidence levels for this product are plotted below the main plot. Pt. P Scintillation Legends Real Time Model Climo Model Link Thresholds ------- Severe ------- Moderate Confidence Levels 58 -95% Point-to-Point Link: Test. Sat 1 (150 E) to Ground. Site. X (12 N, 100 E)
SEEFS Products – Sat. Scint Point-to-Point (Pt. P) Product w/confidence After choosing the Geosynch SATCOM satellite and freq and a specific ground SATCOM site’s location, Sat. Scint’s Pt. P time plot depicts scintillationbased signal fading for that specific satelliteto-ground link. Confidence levels for this product are plotted below the main plot. Pt. P Scintillation Legends Real Time Model Climo Model Link Thresholds ------- Severe ------- Moderate Confidence Levels 58 -95% Point-to-Point Link: Test. Sat 1 (150 E) to Ground. Site. X (12 N, 100 E)
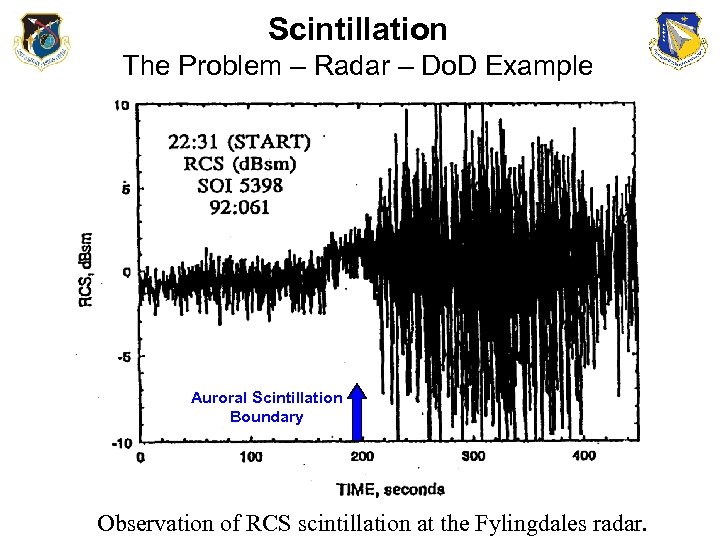 Scintillation The Problem – Radar – Do. D Example Auroral Scintillation Boundary Observation of RCS scintillation at the Fylingdales radar.
Scintillation The Problem – Radar – Do. D Example Auroral Scintillation Boundary Observation of RCS scintillation at the Fylingdales radar.
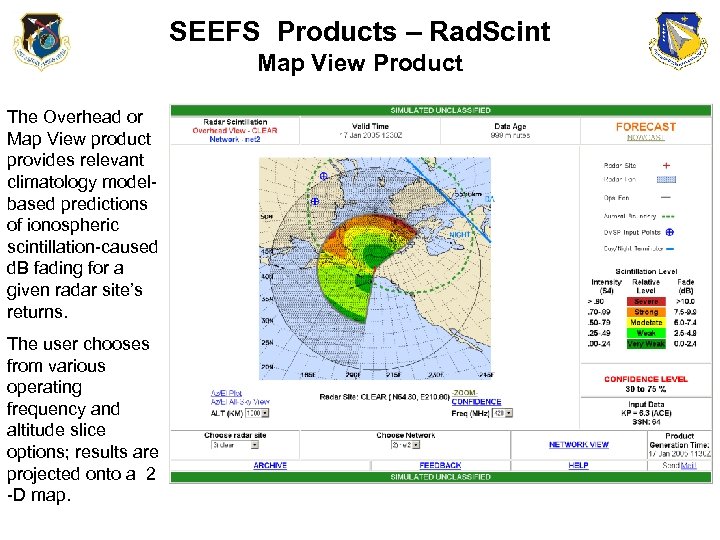 SEEFS Products – Rad. Scint Map View Product The Overhead or Map View product provides relevant climatology modelbased predictions of ionospheric scintillation-caused d. B fading for a given radar site’s returns. The user chooses from various operating frequency and altitude slice options; results are projected onto a 2 -D map.
SEEFS Products – Rad. Scint Map View Product The Overhead or Map View product provides relevant climatology modelbased predictions of ionospheric scintillation-caused d. B fading for a given radar site’s returns. The user chooses from various operating frequency and altitude slice options; results are projected onto a 2 -D map.
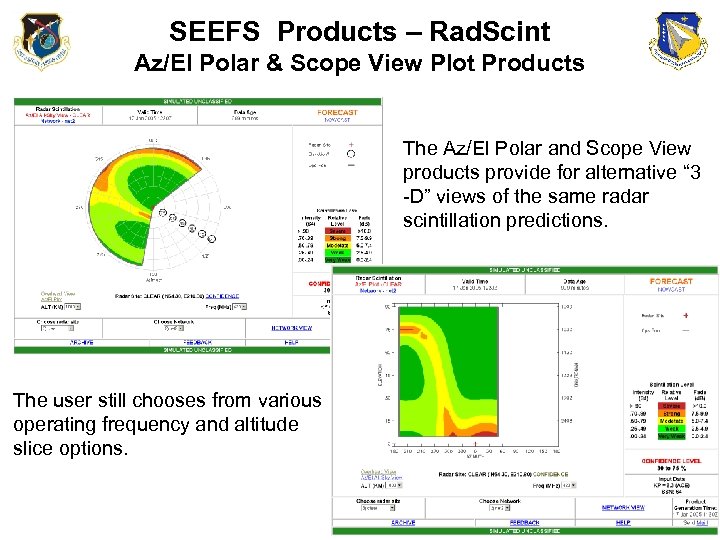 SEEFS Products – Rad. Scint Az/El Polar & Scope View Plot Products The Az/El Polar and Scope View products provide for alternative “ 3 -D” views of the same radar scintillation predictions. The user still chooses from various operating frequency and altitude slice options.
SEEFS Products – Rad. Scint Az/El Polar & Scope View Plot Products The Az/El Polar and Scope View products provide for alternative “ 3 -D” views of the same radar scintillation predictions. The user still chooses from various operating frequency and altitude slice options.
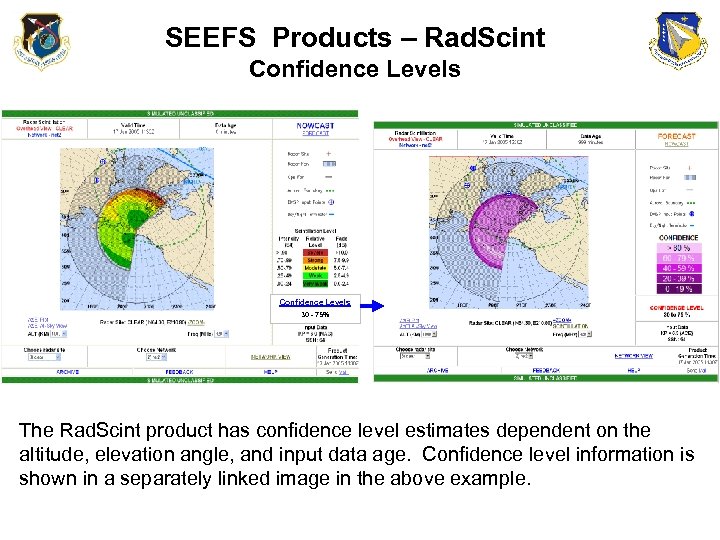 SEEFS Products – Rad. Scint Confidence Levels 30 - 75% The Rad. Scint product has confidence level estimates dependent on the altitude, elevation angle, and input data age. Confidence level information is shown in a separately linked image in the above example.
SEEFS Products – Rad. Scint Confidence Levels 30 - 75% The Rad. Scint product has confidence level estimates dependent on the altitude, elevation angle, and input data age. Confidence level information is shown in a separately linked image in the above example.
 • Satellite Charge/Discharge (Char/D) Products • Requires magnetospheric particle data & indices – Currently via GOES, LANL, ground-based neutron monitor, POES BI and Kp • Requires satellite orbit, specs & thresholds • Uses Magnetopheric Specification Model (MSM), Koons-Gorney Energetic Electron Model, Korth MPA Data Model, CRRES Electron Radiation Belt Model, Hardy Auroral Model, and SOPA/GOES Survey Model, along with NASA’s Spacecraft Charging Analysis Program (NASCAP 2 K)
• Satellite Charge/Discharge (Char/D) Products • Requires magnetospheric particle data & indices – Currently via GOES, LANL, ground-based neutron monitor, POES BI and Kp • Requires satellite orbit, specs & thresholds • Uses Magnetopheric Specification Model (MSM), Koons-Gorney Energetic Electron Model, Korth MPA Data Model, CRRES Electron Radiation Belt Model, Hardy Auroral Model, and SOPA/GOES Survey Model, along with NASA’s Spacecraft Charging Analysis Program (NASCAP 2 K)
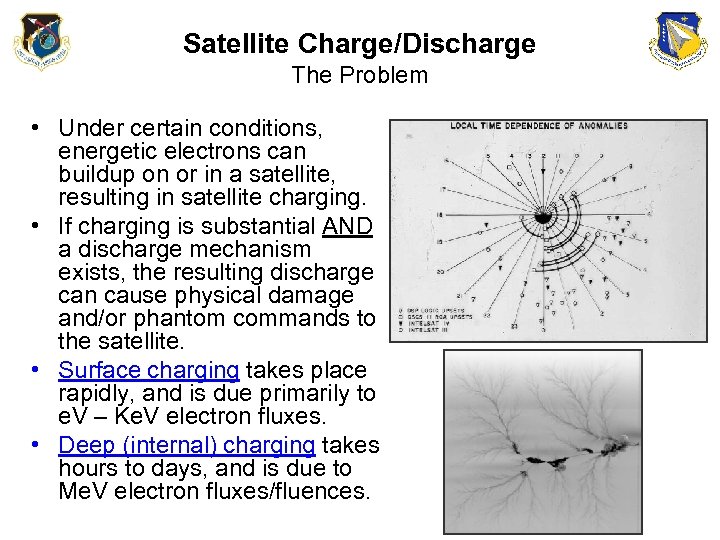 Satellite Charge/Discharge The Problem • Under certain conditions, energetic electrons can buildup on or in a satellite, resulting in satellite charging. • If charging is substantial AND a discharge mechanism exists, the resulting discharge can cause physical damage and/or phantom commands to the satellite. • Surface charging takes place rapidly, and is due primarily to e. V – Ke. V electron fluxes. • Deep (internal) charging takes hours to days, and is due to Me. V electron fluxes/fluences.
Satellite Charge/Discharge The Problem • Under certain conditions, energetic electrons can buildup on or in a satellite, resulting in satellite charging. • If charging is substantial AND a discharge mechanism exists, the resulting discharge can cause physical damage and/or phantom commands to the satellite. • Surface charging takes place rapidly, and is due primarily to e. V – Ke. V electron fluxes. • Deep (internal) charging takes hours to days, and is due to Me. V electron fluxes/fluences.
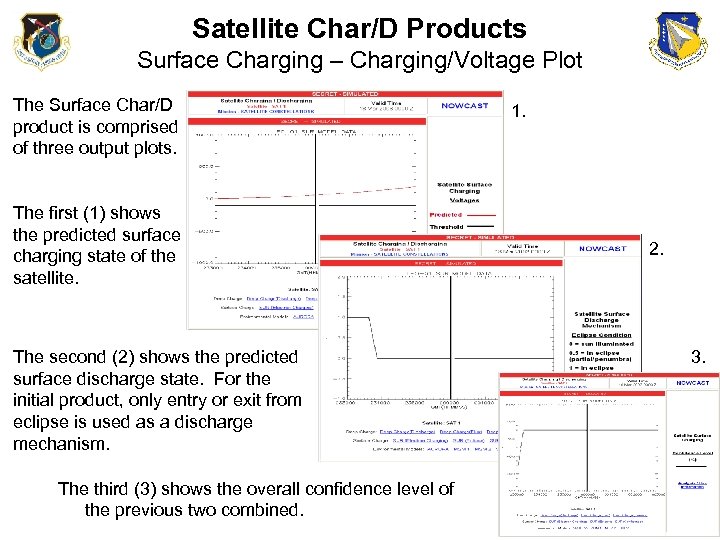 Satellite Char/D Products Surface Charging – Charging/Voltage Plot The Surface Char/D product is comprised of three output plots. The first (1) shows the predicted surface charging state of the satellite. The second (2) shows the predicted surface discharge state. For the initial product, only entry or exit from eclipse is used as a discharge mechanism. The third (3) shows the overall confidence level of the previous two combined. 1. 2. 3.
Satellite Char/D Products Surface Charging – Charging/Voltage Plot The Surface Char/D product is comprised of three output plots. The first (1) shows the predicted surface charging state of the satellite. The second (2) shows the predicted surface discharge state. For the initial product, only entry or exit from eclipse is used as a discharge mechanism. The third (3) shows the overall confidence level of the previous two combined. 1. 2. 3.
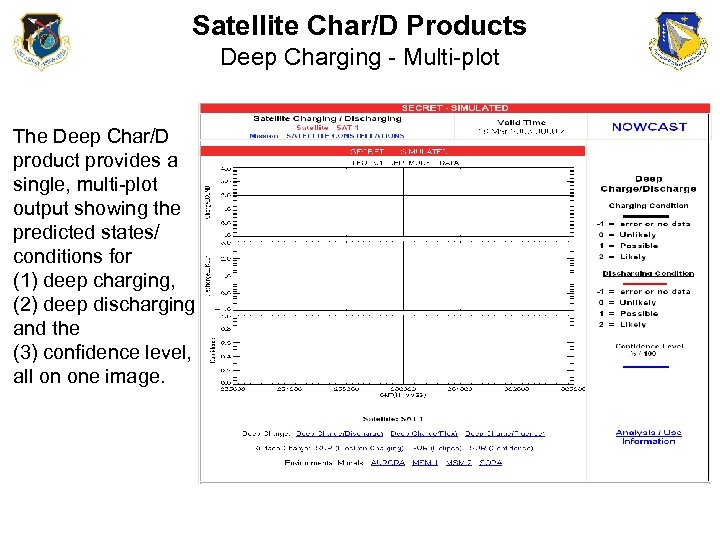 Satellite Char/D Products Deep Charging - Multi-plot The Deep Char/D product provides a single, multi-plot output showing the predicted states/ conditions for (1) deep charging, (2) deep discharging and the (3) confidence level, all on one image.
Satellite Char/D Products Deep Charging - Multi-plot The Deep Char/D product provides a single, multi-plot output showing the predicted states/ conditions for (1) deep charging, (2) deep discharging and the (3) confidence level, all on one image.
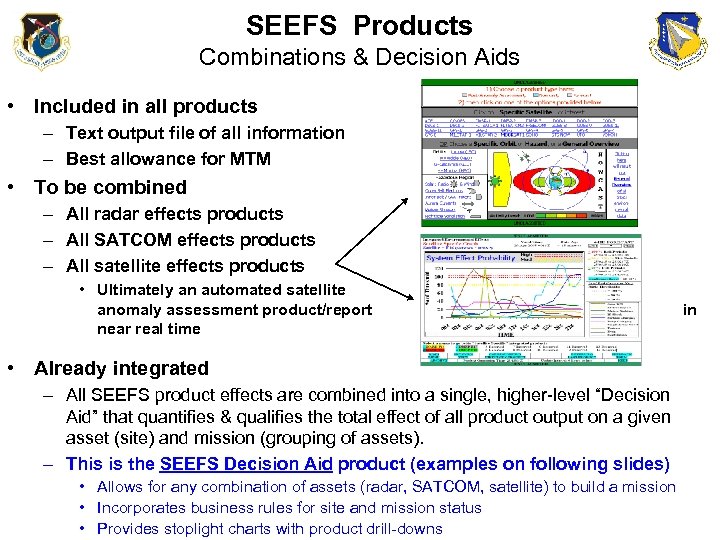 SEEFS Products Combinations & Decision Aids • Included in all products – Text output file of all information – Best allowance for MTM • To be combined – All radar effects products – All SATCOM effects products – All satellite effects products • Ultimately an automated satellite anomaly assessment product/report near real time • Already integrated – All SEEFS product effects are combined into a single, higher-level “Decision Aid” that quantifies & qualifies the total effect of all product output on a given asset (site) and mission (grouping of assets). – This is the SEEFS Decision Aid product (examples on following slides) • Allows for any combination of assets (radar, SATCOM, satellite) to build a mission • Incorporates business rules for site and mission status • Provides stoplight charts with product drill-downs in
SEEFS Products Combinations & Decision Aids • Included in all products – Text output file of all information – Best allowance for MTM • To be combined – All radar effects products – All SATCOM effects products – All satellite effects products • Ultimately an automated satellite anomaly assessment product/report near real time • Already integrated – All SEEFS product effects are combined into a single, higher-level “Decision Aid” that quantifies & qualifies the total effect of all product output on a given asset (site) and mission (grouping of assets). – This is the SEEFS Decision Aid product (examples on following slides) • Allows for any combination of assets (radar, SATCOM, satellite) to build a mission • Incorporates business rules for site and mission status • Provides stoplight charts with product drill-downs in
 SEEFS Products Decision Aid – 1 (Top Menu)
SEEFS Products Decision Aid – 1 (Top Menu)
 SEEFS Products Decision Aid – 2 (Mission Selection)
SEEFS Products Decision Aid – 2 (Mission Selection)
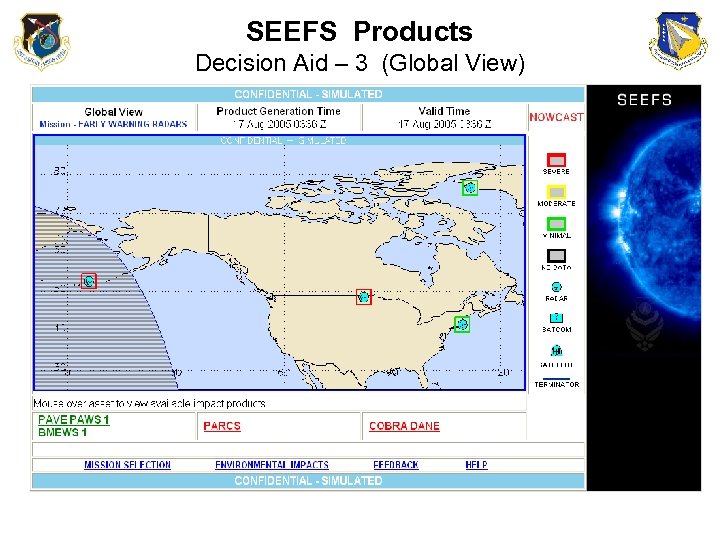 SEEFS Products Decision Aid – 3 (Global View)
SEEFS Products Decision Aid – 3 (Global View)
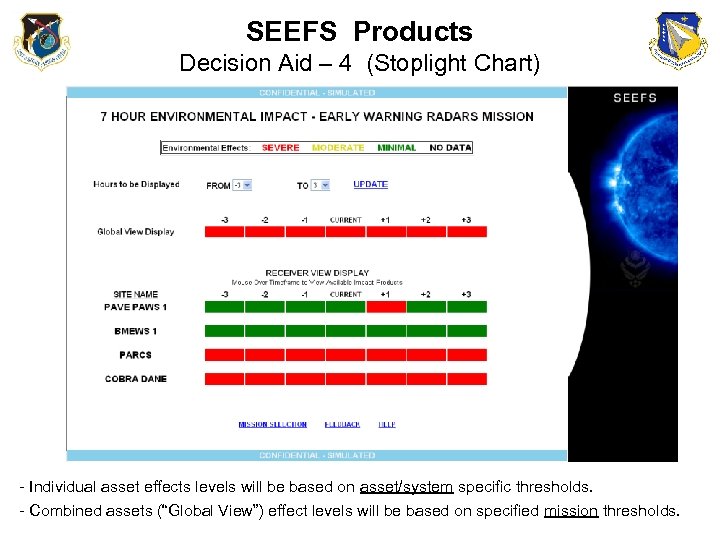 SEEFS Products Decision Aid – 4 (Stoplight Chart) - Individual asset effects levels will be based on asset/system specific thresholds. - Combined assets (“Global View”) effect levels will be based on specified mission thresholds.
SEEFS Products Decision Aid – 4 (Stoplight Chart) - Individual asset effects levels will be based on asset/system specific thresholds. - Combined assets (“Global View”) effect levels will be based on specified mission thresholds.
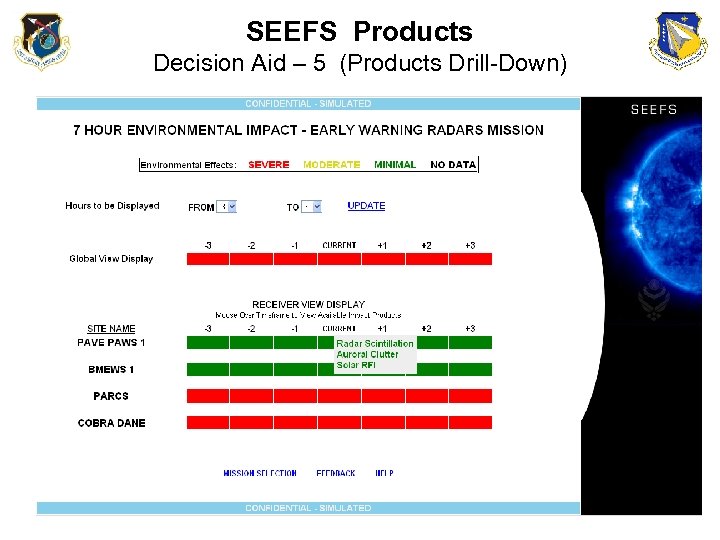 SEEFS Products Decision Aid – 5 (Products Drill-Down)
SEEFS Products Decision Aid – 5 (Products Drill-Down)
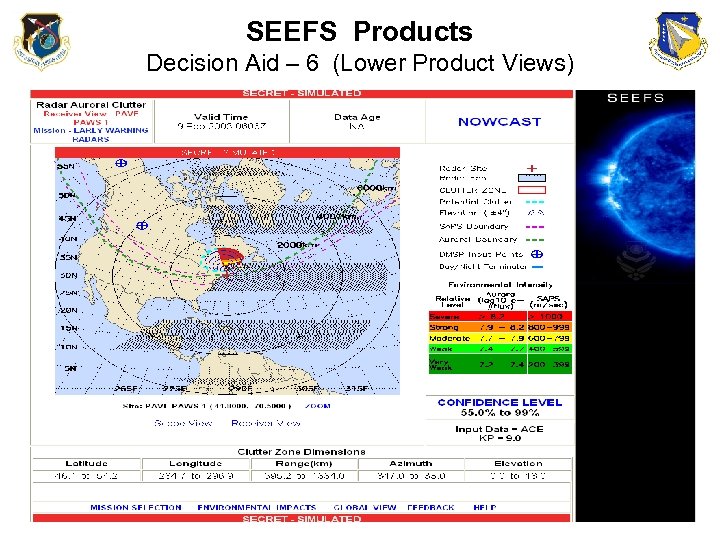 SEEFS Products Decision Aid – 6 (Lower Product Views)
SEEFS Products Decision Aid – 6 (Lower Product Views)
 SEEFS Status - Development & Deliveries • Current SEEFS effort is to operationalize the existing products and link them programmatically • Spiral 1 (prototype So. RBE & Architecture) – Delivered to SSA test bed & Ops Eval done – Mar 2005 • Spiral 2 A (All 5 prototypes & DA & new Architecture/DB) – Delivered and Ops Eval completed – Mar 2006 – Delivered to MHPCC for potential parallelization – Delivered to Portion to DMO-S (Schriever AFB) • Spiral 2 B (operational version of all) – Code rewrites and requirements docs work finishing up NOW – SMC/SYAG ops testbed deliveries to AFWA • Initial radar products (RAC, So. RBE, Rad. Scint) to testbed in Aug 2008 • Second delivery (Sat. Scint & Char/D) to testbed expected in Dec 2009 – Return (re-written “baseline”) delivery to AFRL/RVBX ~ Jan 2010
SEEFS Status - Development & Deliveries • Current SEEFS effort is to operationalize the existing products and link them programmatically • Spiral 1 (prototype So. RBE & Architecture) – Delivered to SSA test bed & Ops Eval done – Mar 2005 • Spiral 2 A (All 5 prototypes & DA & new Architecture/DB) – Delivered and Ops Eval completed – Mar 2006 – Delivered to MHPCC for potential parallelization – Delivered to Portion to DMO-S (Schriever AFB) • Spiral 2 B (operational version of all) – Code rewrites and requirements docs work finishing up NOW – SMC/SYAG ops testbed deliveries to AFWA • Initial radar products (RAC, So. RBE, Rad. Scint) to testbed in Aug 2008 • Second delivery (Sat. Scint & Char/D) to testbed expected in Dec 2009 – Return (re-written “baseline”) delivery to AFRL/RVBX ~ Jan 2010
 SEEFS Operational Evaluation March 2006
SEEFS Operational Evaluation March 2006
 SEEFS Future Work • Depending on requirements and funding, future SEEFS work will focus on one or more of the following: – Validation of current products: note JHU/APL for RAC – Upgrades to current products: So. RBE, RAC, Rad. Scint, Sat. Scint, Char/D, and the Decision Aid – New product development, especially low-hanging fruit… • High-Energy Proton Effects as a Satellite Single Event Upsets and Events (SEUPE) product – Includes existing South Atlantic Anomaly (SAA) maps • • GPS Dual-Frequency Errors (Scintillation) Meteor Effects (ME) - Impact, Sighting, Radar Clutter, Bolides Tropospheric Effects Man-Made Environment Effects (Nukes, engine burns, METOX, etc) – Data Fusion
SEEFS Future Work • Depending on requirements and funding, future SEEFS work will focus on one or more of the following: – Validation of current products: note JHU/APL for RAC – Upgrades to current products: So. RBE, RAC, Rad. Scint, Sat. Scint, Char/D, and the Decision Aid – New product development, especially low-hanging fruit… • High-Energy Proton Effects as a Satellite Single Event Upsets and Events (SEUPE) product – Includes existing South Atlantic Anomaly (SAA) maps • • GPS Dual-Frequency Errors (Scintillation) Meteor Effects (ME) - Impact, Sighting, Radar Clutter, Bolides Tropospheric Effects Man-Made Environment Effects (Nukes, engine burns, METOX, etc) – Data Fusion
 The End
The End


