de19862f4c10cfdc1207ff2ce5ec8f1b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Earned Value Management: An Introduction and Short Tutorial Wayne Baggett November 21, 2005 1
Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Earned Value Management: An Introduction and Short Tutorial Wayne Baggett November 21, 2005 1
 Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Outline Ø What is Earned Value? Ø Government Requirements Ø Small Project Usage Ø Why Use Earned Value? Ø Earned Value in a Nutshell Ø Conclusions November 21, 2005 2
Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Outline Ø What is Earned Value? Ø Government Requirements Ø Small Project Usage Ø Why Use Earned Value? Ø Earned Value in a Nutshell Ø Conclusions November 21, 2005 2
 Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series What is Earned Value? How does Dilbert know this? November 21, 2005 3
Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series What is Earned Value? How does Dilbert know this? November 21, 2005 3
 Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series What is Earned Value? Ø Project Management Technique • Integrates technical performance requirements, resource planning, and cost accounting with schedule • Provides insight into project status • Provides “early warning signals” for problems Provides a disciplined means of managing the project November 21, 2005 4
Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series What is Earned Value? Ø Project Management Technique • Integrates technical performance requirements, resource planning, and cost accounting with schedule • Provides insight into project status • Provides “early warning signals” for problems Provides a disciplined means of managing the project November 21, 2005 4
 Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Government Requirements Ø OMB Circular A-11, Exhibit 300 (2004) • Requires EVMS for all major acquisitions • Agencies must have ANSI-compliant EVMS in place by December 31, 2005 • EVMS data must be used to identify problems and provide realistic final cost estimates as a part of decision packages Ø Federal Acquisition Regulations (2005) amended to require contractor-maintained EVMS November 21, 2005 5
Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Government Requirements Ø OMB Circular A-11, Exhibit 300 (2004) • Requires EVMS for all major acquisitions • Agencies must have ANSI-compliant EVMS in place by December 31, 2005 • EVMS data must be used to identify problems and provide realistic final cost estimates as a part of decision packages Ø Federal Acquisition Regulations (2005) amended to require contractor-maintained EVMS November 21, 2005 5
 Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Government Requirements Ø These requirements apply to large projects or programs; DOD requires • Contract Value ≥ $50 M: validated ANSI-compliant EVMS, structured reports and reviews, ongoing surveillance • $50 M > Contract Value ≥ $20 M: ANSI-compliant EVMS (validation not required), tailored reports and reviews, ongoing surveillance • Contract Value < $20 M: EVMS optional, ongoing surveillance Ø Very rigid, heavily constrained system at this level November 21, 2005 6
Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Government Requirements Ø These requirements apply to large projects or programs; DOD requires • Contract Value ≥ $50 M: validated ANSI-compliant EVMS, structured reports and reviews, ongoing surveillance • $50 M > Contract Value ≥ $20 M: ANSI-compliant EVMS (validation not required), tailored reports and reviews, ongoing surveillance • Contract Value < $20 M: EVMS optional, ongoing surveillance Ø Very rigid, heavily constrained system at this level November 21, 2005 6
 Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Small Project Usage Ø Small projects provide “the best opportunities for earned-value employment” • Consider its use for “… all in-house funded developmental projects where a firm commitment is made to management. ” • “Software projects can especially benefit from the employment of a simple earned-value approach. ” (Fleming and Koppelman, “Earned Value Project Management: A Powerful Tool for Software Projects, ” Crosstalk, July, 1998, p. 19. ) November 21, 2005 7
Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Small Project Usage Ø Small projects provide “the best opportunities for earned-value employment” • Consider its use for “… all in-house funded developmental projects where a firm commitment is made to management. ” • “Software projects can especially benefit from the employment of a simple earned-value approach. ” (Fleming and Koppelman, “Earned Value Project Management: A Powerful Tool for Software Projects, ” Crosstalk, July, 1998, p. 19. ) November 21, 2005 7
 Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Small Project Usage Ø The Personal Software Process (PSPSM) and Team Software Process (TSPSM) use EVM • PSP has practitioners estimate task efforts and track their actual efforts v Tasks estimated are very small – about 10 hours each v Data are used to improve future estimates • TSP expands the use of EVM to the project level • Use of PSP and TSP helps projects meet their commitments (Tuma, D. and Webb, D. , “Personal Earned Value: Why Projects Using the Team Software Process Consistently Meet Schedule Commitments, ” Crosstalk, March 2005, p. 17. ) PSP and TSP are registered service marks of Carnegie Mellon University November 21, 2005 8
Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Small Project Usage Ø The Personal Software Process (PSPSM) and Team Software Process (TSPSM) use EVM • PSP has practitioners estimate task efforts and track their actual efforts v Tasks estimated are very small – about 10 hours each v Data are used to improve future estimates • TSP expands the use of EVM to the project level • Use of PSP and TSP helps projects meet their commitments (Tuma, D. and Webb, D. , “Personal Earned Value: Why Projects Using the Team Software Process Consistently Meet Schedule Commitments, ” Crosstalk, March 2005, p. 17. ) PSP and TSP are registered service marks of Carnegie Mellon University November 21, 2005 8
 Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Small Project Usage Ø Several projects at STSc. I have used EVM: • Most used a tailored version of EVM • JWST S&OC development v. FOS, PPS, PRDS • JWST FITS Writer development • INS Master Schedule development • DMS Automated Test System development November 21, 2005 9
Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Small Project Usage Ø Several projects at STSc. I have used EVM: • Most used a tailored version of EVM • JWST S&OC development v. FOS, PPS, PRDS • JWST FITS Writer development • INS Master Schedule development • DMS Automated Test System development November 21, 2005 9
 Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Why Use Earned Value? Ø Obligates planning to the level of task management • Less likely to overlook work Ø Provides objective measures of progress Ø Allows early detection of budget and schedule problems Ø Allows an objective projection of eventual project cost and schedule November 21, 2005 10
Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Why Use Earned Value? Ø Obligates planning to the level of task management • Less likely to overlook work Ø Provides objective measures of progress Ø Allows early detection of budget and schedule problems Ø Allows an objective projection of eventual project cost and schedule November 21, 2005 10
 Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Key to Earned Value Determine the value for every task prior to starting work! November 21, 2005 11
Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Key to Earned Value Determine the value for every task prior to starting work! November 21, 2005 11
 Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Guidelines for Setting/Earning Value Ø Use a consistent unit of measurement that makes sense for the project • Dollars – required for large gov’t projects • Hours – useful on small projects; PSPSM • Arbitrary number – not recommended, but still used Ø Consider task duration Ø Select Earned Value Methods that are as objective as possible November 21, 2005 12
Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Guidelines for Setting/Earning Value Ø Use a consistent unit of measurement that makes sense for the project • Dollars – required for large gov’t projects • Hours – useful on small projects; PSPSM • Arbitrary number – not recommended, but still used Ø Consider task duration Ø Select Earned Value Methods that are as objective as possible November 21, 2005 12
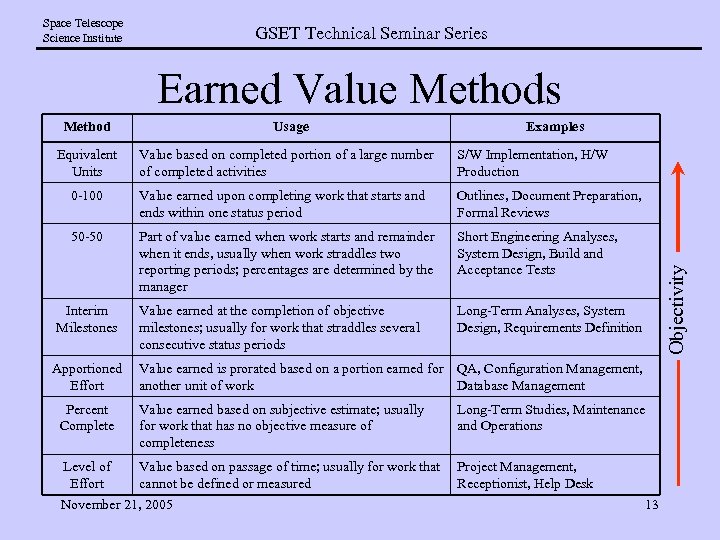 Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Earned Value Methods Method Examples Value based on completed portion of a large number of completed activities S/W Implementation, H/W Production 0 -100 Value earned upon completing work that starts and ends within one status period Outlines, Document Preparation, Formal Reviews 50 -50 Part of value earned when work starts and remainder when it ends, usually when work straddles two reporting periods; percentages are determined by the manager Short Engineering Analyses, System Design, Build and Acceptance Tests Value earned at the completion of objective milestones; usually for work that straddles several consecutive status periods Long-Term Analyses, System Design, Requirements Definition Interim Milestones Apportioned Effort Objectivity Equivalent Units Usage Value earned is prorated based on a portion earned for QA, Configuration Management, another unit of work Database Management Percent Complete Value earned based on subjective estimate; usually for work that has no objective measure of completeness Long-Term Studies, Maintenance and Operations Level of Effort Value based on passage of time; usually for work that cannot be defined or measured Project Management, Receptionist, Help Desk November 21, 2005 13
Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Earned Value Methods Method Examples Value based on completed portion of a large number of completed activities S/W Implementation, H/W Production 0 -100 Value earned upon completing work that starts and ends within one status period Outlines, Document Preparation, Formal Reviews 50 -50 Part of value earned when work starts and remainder when it ends, usually when work straddles two reporting periods; percentages are determined by the manager Short Engineering Analyses, System Design, Build and Acceptance Tests Value earned at the completion of objective milestones; usually for work that straddles several consecutive status periods Long-Term Analyses, System Design, Requirements Definition Interim Milestones Apportioned Effort Objectivity Equivalent Units Usage Value earned is prorated based on a portion earned for QA, Configuration Management, another unit of work Database Management Percent Complete Value earned based on subjective estimate; usually for work that has no objective measure of completeness Long-Term Studies, Maintenance and Operations Level of Effort Value based on passage of time; usually for work that cannot be defined or measured Project Management, Receptionist, Help Desk November 21, 2005 13
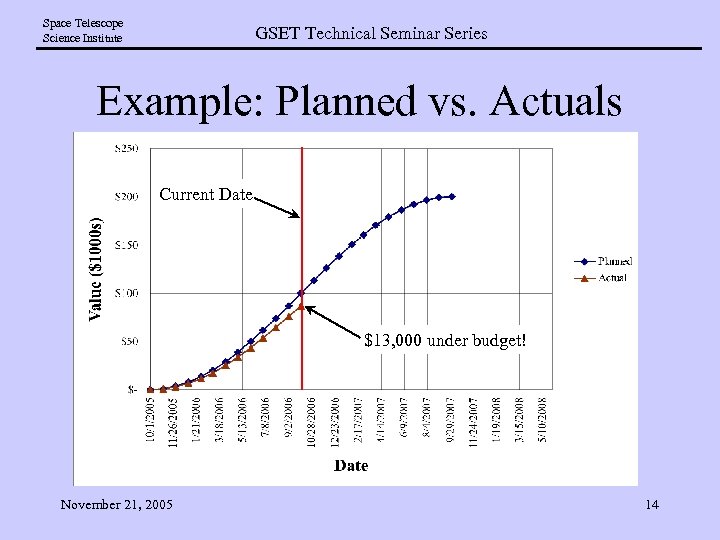 Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Example: Planned vs. Actuals Current Date $13, 000 under budget! November 21, 2005 14
Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Example: Planned vs. Actuals Current Date $13, 000 under budget! November 21, 2005 14
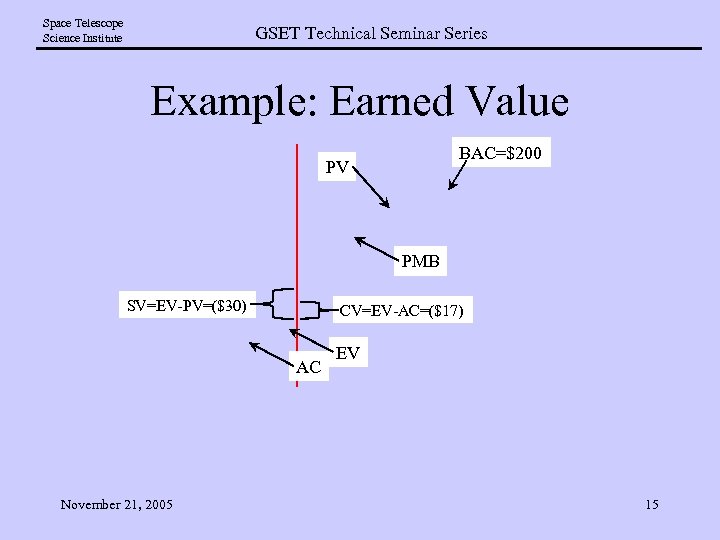 Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Example: Earned Value BAC=$200 PV PMB SV=EV-PV=($30) CV=EV-AC=($17) AC November 21, 2005 EV 15
Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Example: Earned Value BAC=$200 PV PMB SV=EV-PV=($30) CV=EV-AC=($17) AC November 21, 2005 EV 15
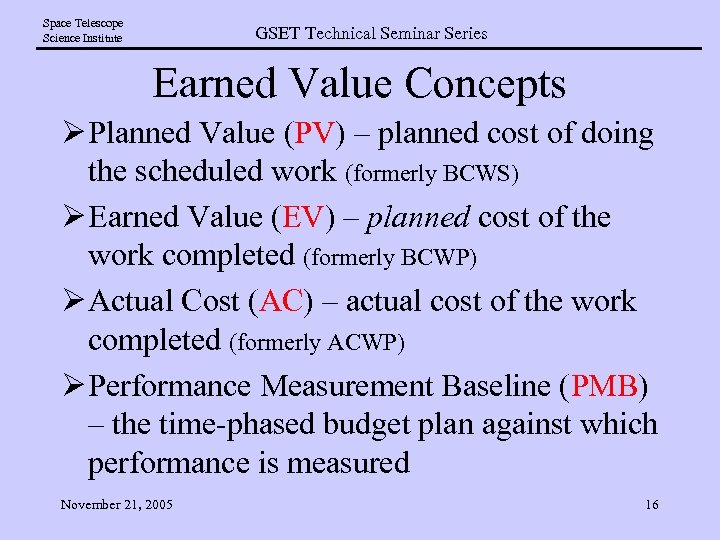 Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Earned Value Concepts Ø Planned Value (PV) – planned cost of doing the scheduled work (formerly BCWS) Ø Earned Value (EV) – planned cost of the work completed (formerly BCWP) Ø Actual Cost (AC) – actual cost of the work completed (formerly ACWP) Ø Performance Measurement Baseline (PMB) – the time-phased budget plan against which performance is measured November 21, 2005 16
Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Earned Value Concepts Ø Planned Value (PV) – planned cost of doing the scheduled work (formerly BCWS) Ø Earned Value (EV) – planned cost of the work completed (formerly BCWP) Ø Actual Cost (AC) – actual cost of the work completed (formerly ACWP) Ø Performance Measurement Baseline (PMB) – the time-phased budget plan against which performance is measured November 21, 2005 16
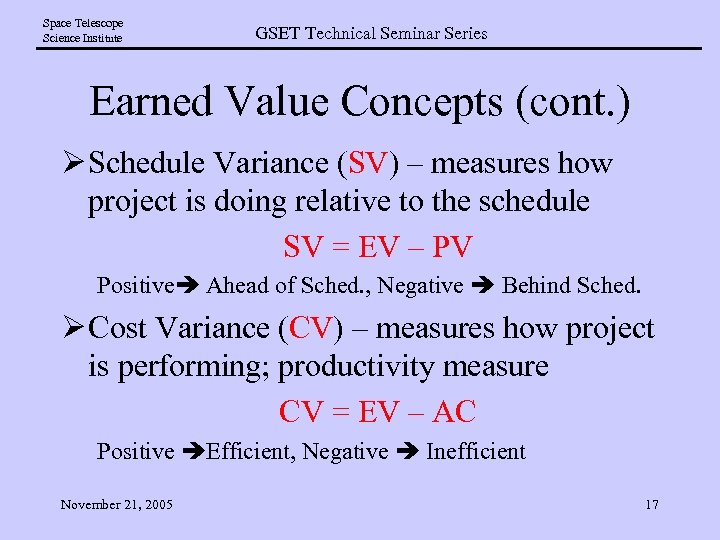 Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Earned Value Concepts (cont. ) Ø Schedule Variance (SV) – measures how project is doing relative to the schedule SV = EV – PV Positive Ahead of Sched. , Negative Behind Sched. Ø Cost Variance (CV) – measures how project is performing; productivity measure CV = EV – AC Positive Efficient, Negative Inefficient November 21, 2005 17
Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Earned Value Concepts (cont. ) Ø Schedule Variance (SV) – measures how project is doing relative to the schedule SV = EV – PV Positive Ahead of Sched. , Negative Behind Sched. Ø Cost Variance (CV) – measures how project is performing; productivity measure CV = EV – AC Positive Efficient, Negative Inefficient November 21, 2005 17
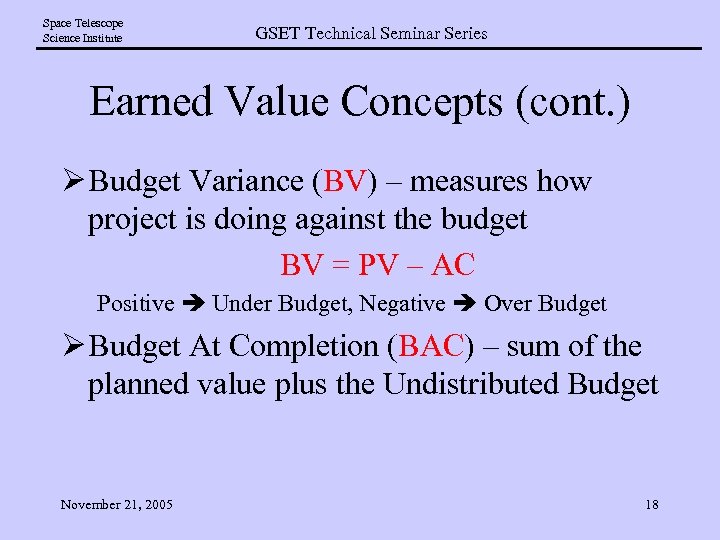 Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Earned Value Concepts (cont. ) Ø Budget Variance (BV) – measures how project is doing against the budget BV = PV – AC Positive Under Budget, Negative Over Budget Ø Budget At Completion (BAC) – sum of the planned value plus the Undistributed Budget November 21, 2005 18
Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Earned Value Concepts (cont. ) Ø Budget Variance (BV) – measures how project is doing against the budget BV = PV – AC Positive Under Budget, Negative Over Budget Ø Budget At Completion (BAC) – sum of the planned value plus the Undistributed Budget November 21, 2005 18
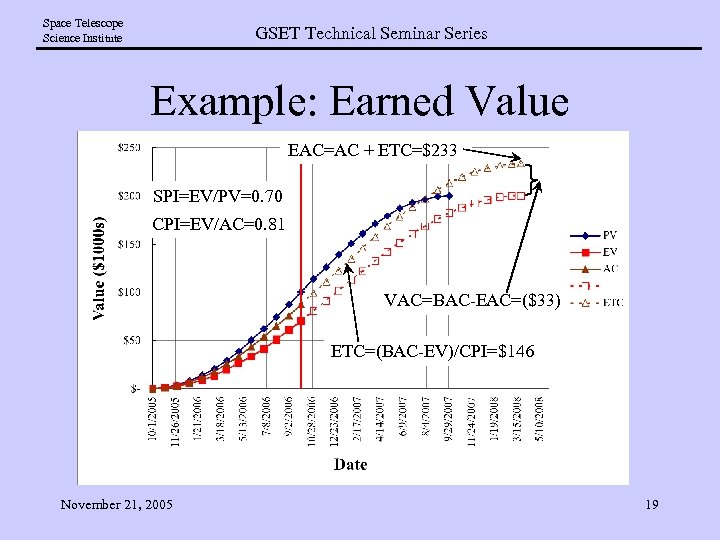 Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Example: Earned Value EAC=AC + ETC=$233 SPI=EV/PV=0. 70 CPI=EV/AC=0. 81 VAC=BAC-EAC=($33) ETC=(BAC-EV)/CPI=$146 November 21, 2005 19
Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Example: Earned Value EAC=AC + ETC=$233 SPI=EV/PV=0. 70 CPI=EV/AC=0. 81 VAC=BAC-EAC=($33) ETC=(BAC-EV)/CPI=$146 November 21, 2005 19
 Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Earned Value Concepts (cont. ) Ø Schedule Performance Index (SPI) – measure of schedule compliance: is work being done at the planned rate? SPI = EV/PV <1 Slower than planned, >1 Faster than planned Ø Cost Performance Index (CPI) – productivity measure: is the work costing what was expected? CPI = EV/AC < 1 Inefficient, > 1 Efficient November 21, 2005 20
Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Earned Value Concepts (cont. ) Ø Schedule Performance Index (SPI) – measure of schedule compliance: is work being done at the planned rate? SPI = EV/PV <1 Slower than planned, >1 Faster than planned Ø Cost Performance Index (CPI) – productivity measure: is the work costing what was expected? CPI = EV/AC < 1 Inefficient, > 1 Efficient November 21, 2005 20
 Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Earned Value Concepts (cont. ) Ø Estimate To Complete (ETC) – estimate of the effort required to complete the project from the current date ETC = (BAC – EV)/CPI Ø Estimate At Completion (EAC) – the estimated total cost of the project EAC = AC + ETC November 21, 2005 21
Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Earned Value Concepts (cont. ) Ø Estimate To Complete (ETC) – estimate of the effort required to complete the project from the current date ETC = (BAC – EV)/CPI Ø Estimate At Completion (EAC) – the estimated total cost of the project EAC = AC + ETC November 21, 2005 21
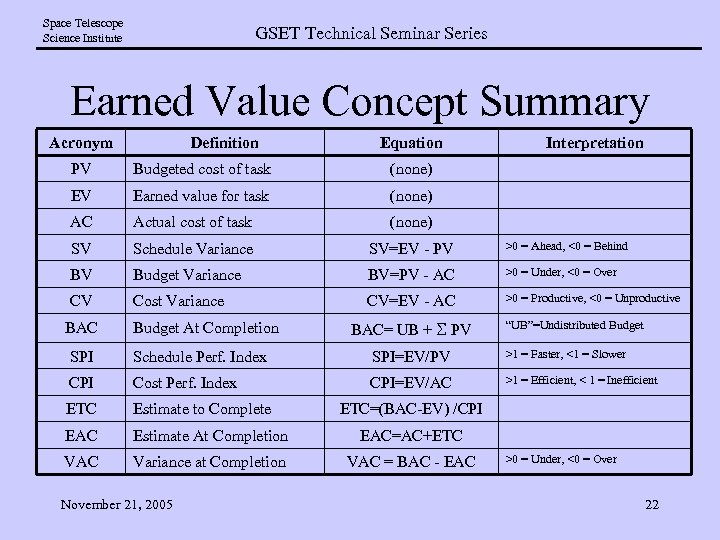 Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Earned Value Concept Summary Acronym Definition Equation Interpretation PV Budgeted cost of task (none) EV Earned value for task (none) AC Actual cost of task (none) SV Schedule Variance SV=EV - PV >0 = Ahead, <0 = Behind BV Budget Variance BV=PV - AC >0 = Under, <0 = Over CV Cost Variance CV=EV - AC >0 = Productive, <0 = Unproductive BAC Budget At Completion BAC= UB + S PV “UB”=Undistributed Budget SPI Schedule Perf. Index SPI=EV/PV >1 = Faster, <1 = Slower CPI Cost Perf. Index CPI=EV/AC >1 = Efficient, < 1 = Inefficient ETC Estimate to Complete EAC Estimate At Completion EAC=AC+ETC VAC Variance at Completion VAC = BAC - EAC November 21, 2005 ETC=(BAC-EV) /CPI >0 = Under, <0 = Over 22
Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Earned Value Concept Summary Acronym Definition Equation Interpretation PV Budgeted cost of task (none) EV Earned value for task (none) AC Actual cost of task (none) SV Schedule Variance SV=EV - PV >0 = Ahead, <0 = Behind BV Budget Variance BV=PV - AC >0 = Under, <0 = Over CV Cost Variance CV=EV - AC >0 = Productive, <0 = Unproductive BAC Budget At Completion BAC= UB + S PV “UB”=Undistributed Budget SPI Schedule Perf. Index SPI=EV/PV >1 = Faster, <1 = Slower CPI Cost Perf. Index CPI=EV/AC >1 = Efficient, < 1 = Inefficient ETC Estimate to Complete EAC Estimate At Completion EAC=AC+ETC VAC Variance at Completion VAC = BAC - EAC November 21, 2005 ETC=(BAC-EV) /CPI >0 = Under, <0 = Over 22
 Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Costs of EVMS Ø Marginal cost of using EVMS is estimated at less than 1% to a few% of total contract cost • Based mainly on large DOD contracts with experienced EVMS users • Some costs are unnecessary according to EVMS criteria, but effort is put into those activities anyway Ø Expect costs to be higher at STSc. I due to inexperience in using EVM and our culture • Mitigated by our implementation Christensen, David S. , “The Costs and Benefits of the Earned Value Management Process, ” Acquisition review Quarterly, Fall, 1998, p. 373. November 21, 2005 23
Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Costs of EVMS Ø Marginal cost of using EVMS is estimated at less than 1% to a few% of total contract cost • Based mainly on large DOD contracts with experienced EVMS users • Some costs are unnecessary according to EVMS criteria, but effort is put into those activities anyway Ø Expect costs to be higher at STSc. I due to inexperience in using EVM and our culture • Mitigated by our implementation Christensen, David S. , “The Costs and Benefits of the Earned Value Management Process, ” Acquisition review Quarterly, Fall, 1998, p. 373. November 21, 2005 23
 Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Benefits of Earned Value Ø It is a single management control system that provides reliable data. Ø It integrates work, schedule, and cost using a work breakdown structure. Ø The associated database of completed projects is useful for comparative analysis. Ø The cumulative cost performance index (CPI) provides an early warning signal. Ø The schedule performance index provides an early warning signal. Christensen, David S. , “The Costs and Benefits of the Earned Value Management Process, ” Acquisition review Quarterly, Fall, 1998, p. 373. November 21, 2005 24
Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Benefits of Earned Value Ø It is a single management control system that provides reliable data. Ø It integrates work, schedule, and cost using a work breakdown structure. Ø The associated database of completed projects is useful for comparative analysis. Ø The cumulative cost performance index (CPI) provides an early warning signal. Ø The schedule performance index provides an early warning signal. Christensen, David S. , “The Costs and Benefits of the Earned Value Management Process, ” Acquisition review Quarterly, Fall, 1998, p. 373. November 21, 2005 24
 Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Benefits of Earned Value Ø The CPI is a predictor for the final cost of the project. Ø It uses an index-based method to forecast the final cost of the project. Ø The “to-complete” performance index allows evaluation of the forecasted final cost. Ø The periodic (e. g. , weekly or monthly) CPI is a benchmark. Ø The management by exception principle can reduce information overload. Christensen, David S. , “The Costs and Benefits of the Earned Value Management Process, ” Acquisition Review Quarterly, Fall, 1998, p. 373. November 21, 2005 25
Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series Benefits of Earned Value Ø The CPI is a predictor for the final cost of the project. Ø It uses an index-based method to forecast the final cost of the project. Ø The “to-complete” performance index allows evaluation of the forecasted final cost. Ø The periodic (e. g. , weekly or monthly) CPI is a benchmark. Ø The management by exception principle can reduce information overload. Christensen, David S. , “The Costs and Benefits of the Earned Value Management Process, ” Acquisition Review Quarterly, Fall, 1998, p. 373. November 21, 2005 25
 Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series “The most common problem product teams face is unreasonable schedule pressure. … When teams are forced to work to unreasonable schedules, they are unable to make useful plans. Every plan they produce misses management’s edicted schedule and is therefore unacceptable. As a result, they must work without the guidance of an orderly plan. Under these conditions, the team will generally take much longer to complete the project than they otherwise would. ” Watts Humphrey, “Pathways to Process Maturity: The Personal Software Process and Team Software Process, ” SEI Interactive, June 1999. November 21, 2005 26
Space Telescope Science Institute GSET Technical Seminar Series “The most common problem product teams face is unreasonable schedule pressure. … When teams are forced to work to unreasonable schedules, they are unable to make useful plans. Every plan they produce misses management’s edicted schedule and is therefore unacceptable. As a result, they must work without the guidance of an orderly plan. Under these conditions, the team will generally take much longer to complete the project than they otherwise would. ” Watts Humphrey, “Pathways to Process Maturity: The Personal Software Process and Team Software Process, ” SEI Interactive, June 1999. November 21, 2005 26


